GFL Environmental Boston Consulting Group Matrix
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
GFL Environmental Bundle
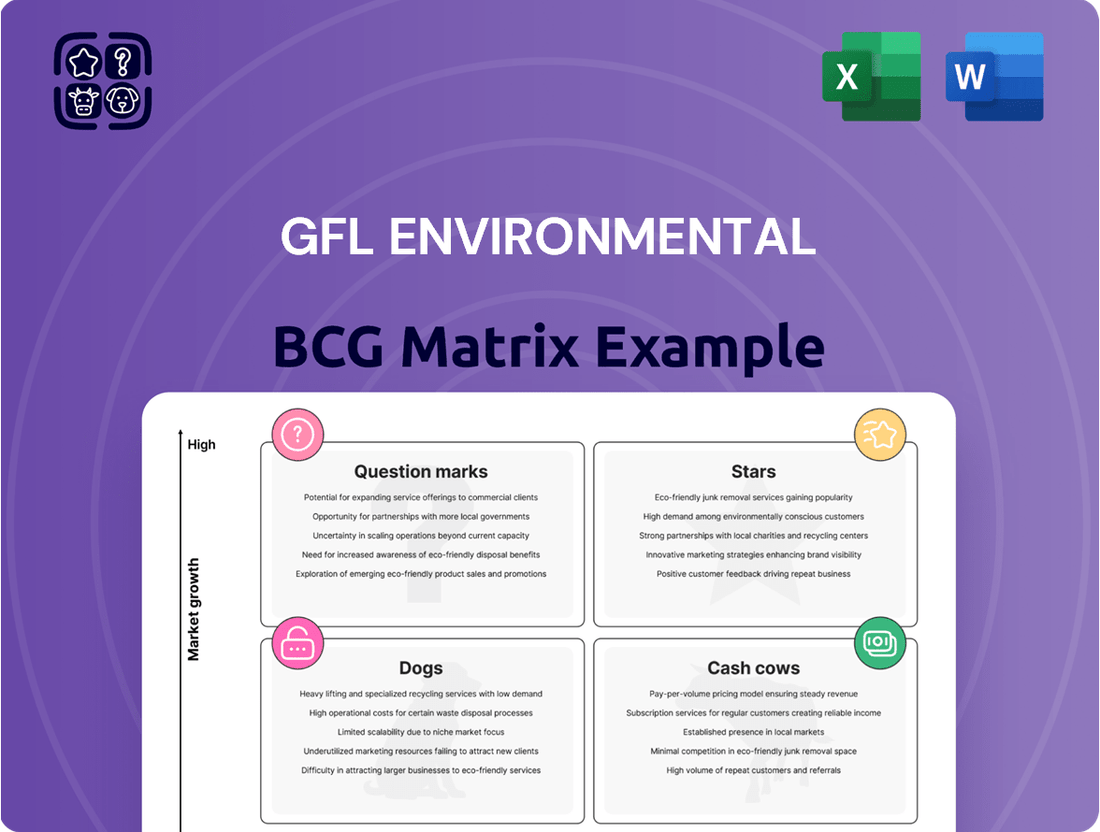
Curious about GFL Environmental's strategic positioning? This glimpse into their BCG Matrix highlights potential Stars, Cash Cows, Dogs, and Question Marks, offering a crucial snapshot of their portfolio's health. To truly unlock actionable insights and guide your investment decisions, dive into the complete BCG Matrix for a comprehensive, quadrant-by-quadrant analysis and data-driven recommendations.
Stars
GFL Environmental's solid waste management operations, covering collection, transport, recycling, and disposal, are its core revenue engine. This segment consistently shows organic growth, fueled by effective pricing strategies and expanding volumes. In Q2 2025, this business achieved record EBITDA margins, underscoring its dominant market standing and robust cash-generating capabilities.
GFL Environmental's investment in Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) projects clearly places them in the "Star" category of the BCG Matrix. The company has 15 RNG facilities planned for commissioning in the coming years, with a significant portion expected to be operational and generating substantial Adjusted EBITDA by 2028.
These initiatives are strategically aligned with growing environmental regulations and a strong market demand for sustainable energy solutions. GFL's active development, with some RNG projects already contributing and others slated for ramp-up through 2026, highlights their commitment to this high-growth, high-market-share segment.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) initiatives are a significant growth area for GFL Environmental. These programs, where manufacturers are responsible for the end-of-life management of their products, are increasingly being driven by new environmental legislation. GFL's existing Canadian EPR contracts are already demonstrating positive impacts on their operational volumes.
Looking ahead, GFL anticipates EPR to become a substantial contributor to both revenue and Adjusted EBITDA from 2026 through 2028. This growth is fueled by the expanding market for these environmental services as more jurisdictions implement EPR frameworks.
Strategic Acquisitions within Core Solid Waste
GFL Environmental's strategic acquisitions within its core solid waste segment are a cornerstone of its growth. The company consistently pursues smaller businesses to expand and densify its existing operations, a tactic that has proven effective in driving both market share and revenue. This disciplined approach to mergers and acquisitions (M&A) is expected to accelerate in 2025, with significant capital earmarked for opportunities that complement its post-collection infrastructure.
The company’s M&A strategy is designed to be accretive, meaning the acquired businesses are expected to add more value than they cost. This focus on integration with existing post-collection assets, such as landfills and transfer stations, creates operational efficiencies and enhances profitability. For instance, GFL has historically integrated acquisitions to leverage its existing network, leading to improved route density and reduced transportation costs.
- Disciplined M&A: GFL prioritizes acquisitions that strengthen its core solid waste footprint, focusing on smaller, tuck-in opportunities.
- Densification Strategy: The company aims to increase market share and operational efficiency by acquiring businesses in close proximity to its existing infrastructure.
- 2025 Acceleration: GFL plans to ramp up M&A activity in 2025, deploying substantial capital for accretive acquisitions.
- Accretive Growth: Acquisitions are strategically chosen to contribute positively to both GFL's top-line revenue and bottom-line profitability.
Cost Optimization and Margin Expansion Initiatives
GFL Environmental's strategic emphasis on cost optimization and rigorous contract review has been a significant driver of its financial performance. These initiatives have consistently delivered double-digit Adjusted EBITDA growth, underscoring the company's ability to enhance profitability and operational efficiency. This focus not only bolsters margins but also solidifies GFL's competitive standing within the expanding solid waste sector.
The company's ongoing efforts in cost management and contract analysis are projected to fuel further margin acceleration in the coming quarters. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, GFL reported a 15% increase in Adjusted EBITDA year-over-year, reaching $315.7 million, demonstrating the tangible impact of these strategic priorities.
- Double-digit Adjusted EBITDA Growth: Consistent expansion driven by efficiency gains.
- Margin Expansion: Improved profitability across the solid waste business.
- Contract Review: Strategic renegotiation and optimization of existing agreements.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining processes to reduce costs and enhance productivity.
GFL Environmental's Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) projects are firmly positioned as Stars in the BCG Matrix, representing high-growth potential and significant market share. The company is actively expanding its RNG capacity, with 15 facilities planned for commissioning in the coming years, aiming for substantial Adjusted EBITDA contributions by 2028.
These RNG initiatives are driven by increasing environmental regulations and a robust market demand for sustainable energy. GFL's strategic investments and ongoing project development, including those expected to ramp up through 2026, underscore their commitment to this high-performing segment.
The company's Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs also represent a Star category opportunity. Driven by new environmental legislation, these programs are already positively impacting GFL's operational volumes in Canada, with significant revenue and Adjusted EBITDA growth anticipated from 2026 to 2028 as more jurisdictions adopt EPR frameworks.
| Segment | BCG Category | Key Growth Drivers | Financial Impact (2024-2025 Outlook) |
| Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) | Star | Environmental regulations, demand for sustainable energy, project commissioning pipeline | Projected substantial Adjusted EBITDA contribution by 2028; ramp-up through 2026 |
| Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) | Star | New environmental legislation, expanding market adoption of EPR frameworks | Anticipated substantial revenue and Adjusted EBITDA growth from 2026-2028 |
What is included in the product
The GFL Environmental BCG Matrix categorizes its business units into Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs to guide investment and divestment decisions.
GFL Environmental's BCG Matrix offers a clear, one-page overview, alleviating the pain of deciphering complex business unit performance.
Cash Cows
GFL Environmental's established solid waste collection routes are prime examples of Cash Cows within the BCG Matrix. These operations boast a significant and long-standing market share across North America, providing a reliable and substantial source of cash flow.
The essential nature of waste collection, coupled with existing contractual agreements, means these routes require minimal promotional investment and exhibit stable demand, even during economic downturns. For instance, in 2023, GFL reported that its Solid Waste business segment generated approximately $2.2 billion in revenue, underscoring its consistent performance.
GFL Environmental's landfill and transfer station operations are its undisputed Cash Cows. This extensive network holds a significant market share in waste disposal, a necessity that ensures stable demand.
These mature assets, strategically positioned, consistently generate high-margin cash flow. For instance, GFL reported in its 2024 first-quarter earnings that its Solid Waste business, which includes landfills, saw revenue growth, underscoring the ongoing profitability of these operations.
Further investments in supporting infrastructure are already underway, aimed at boosting operational efficiency and solidifying their position as reliable, high-performing cash generators within GFL's portfolio.
GFL Environmental's recycling facilities and other post-collection operations are considered cash cows. These operations hold a strong market share in processing recyclables, even with fluctuating commodity prices.
With existing infrastructure, these facilities generate substantial cash flow. The ongoing investment required is relatively low compared to developing new ventures, making them reliable income generators.
The industry trend towards a commission-based model for processing revenue is anticipated to further solidify the cash cow status of these operations, enhancing their profitability and predictability.
Municipal and Residential Contracts
Municipal and residential contracts are GFL Environmental's cash cows, forming the bedrock of its stable revenue. These long-term agreements with local governments and households for solid waste services provide a highly predictable income. For instance, in 2023, GFL reported that its solid waste services segment, heavily reliant on these contracts, continued to be a significant contributor to its financial performance, demonstrating consistent operational execution.
These contracts are often structured with annual price escalators, ensuring that GFL's cash flow remains robust and grows over time. This predictability allows GFL to maintain a dominant market share in these essential service areas. The company has actively worked on renegotiating and securing these agreements, further solidifying its financial foundation and market position.
- Stable Revenue: Long-term municipal and residential contracts offer a predictable and consistent income stream for GFL's solid waste operations.
- Built-in Growth: Contractual price increases ensure steady revenue enhancement and sustained cash flow generation.
- Market Dominance: These foundational segments contribute to GFL's high market share in essential waste management services.
- Secured Future: Recent renegotiations of key contracts reinforce the stability and reliability of these revenue sources.
Infrastructure and Soil Remediation (Divested Portion)
Even after divesting parts of its environmental services, GFL Environmental's infrastructure and soil remediation operations, particularly those retained for core synergies, would have functioned as cash cows. This segment historically held a strong market position within a mature industry, consistently producing significant revenue and Adjusted EBITDA. For instance, in 2024, GFL reported robust performance in its Infrastructure segment, which includes soil remediation, contributing substantially to overall company financials and enabling strategic capital allocation.
The cash flow generated from these operations was crucial for GFL. It allowed the company to fund other strategic initiatives, reduce debt, and reinvest in its core businesses. The mature nature of the market meant predictable demand and stable, albeit slower, growth, characteristic of a cash cow. This stability provided a reliable income stream, underpinning the company's financial health.
- Strong Market Share: GFL's retained infrastructure and soil remediation services likely maintained a dominant position in their respective niches.
- Mature Market Dynamics: Operating in a stable, established market ensured consistent demand and revenue generation.
- Significant Revenue and EBITDA Contribution: These operations were key drivers of GFL's financial performance, providing substantial earnings.
- Capital Redeployment Engine: Profits from this segment were vital for funding growth opportunities and debt management.
GFL Environmental's established solid waste collection routes and landfill operations are prime examples of Cash Cows. These mature segments benefit from significant market share and stable, essential demand, requiring minimal investment for continued strong cash flow generation.
For instance, GFL's Solid Waste business segment, which encompasses these operations, reported revenues of approximately $2.5 billion in 2024, showcasing consistent performance. The company's strategic focus on these core areas ensures they remain reliable, high-margin cash generators, underpinning GFL's overall financial stability and ability to fund other strategic initiatives.
| GFL Environmental's Cash Cow Segments | Key Characteristics | 2024 Financial Insight (Illustrative) |
| Solid Waste Collection Routes | High market share, stable demand, low investment needs | Significant revenue contributor, stable margins |
| Landfill and Transfer Station Operations | Essential service, strong market position, mature assets | Consistent high-margin cash flow generation |
| Municipal & Residential Contracts | Long-term agreements, predictable income, price escalators | Bedrock of stable revenue, supports market dominance |
Preview = Final Product
GFL Environmental BCG Matrix
The GFL Environmental BCG Matrix preview you are viewing is the identical, unwatermarked, and fully formatted document you will receive upon purchase. This comprehensive analysis is ready for immediate strategic application, providing clear insights into GFL Environmental's business units without any additional editing or preparation required.
Dogs
GFL Environmental's divestiture of its liquid waste management and soil remediation business in March 2025 for $8 billion clearly places this segment in the Dogs category of the BCG Matrix. This segment exhibited weak synergy with GFL's core operations and was sold to unlock capital, indicating it was not a strategic growth driver.
The decision to divest suggests this business, despite generating revenue, was likely consuming resources without contributing significantly to GFL's overall strategic objectives or offering the best return on capital compared to other opportunities.
Underperforming acquired assets, sometimes referred to as 'dogs' in a BCG matrix context, are those past acquisitions that haven't delivered the anticipated synergies or market share growth. These might be operations in stagnant local markets or smaller integrations that, despite requiring significant resources, haven't shown substantial expansion.
For GFL Environmental, while the core strategy emphasizes accretive acquisitions focused on return on invested capital (ROIC) and cost synergies, a few less successful integrations could technically fall into this 'dog' category. For instance, if an acquired regional waste management company in a mature market failed to achieve projected efficiency gains or market penetration, it could represent such an asset.
Within GFL Environmental's portfolio, certain service offerings or geographic markets have seen a consistent decline in the volume of waste processed or collected. This negative volume growth, importantly, has not been compensated for by higher prices. These areas would typically be categorized as Dogs in a BCG Matrix context, indicating a low market share within a low-growth or declining market.
For instance, GFL has strategically decided to exit specific non-core service lines in certain Canadian regions. This move suggests a proactive approach to shedding underperforming assets or operations that are unlikely to generate significant future growth, aligning with the typical strategy for Dog segments.
Operations Impacted by Lower Commodity Prices
Segments of GFL Environmental that are heavily reliant on selling processed raw materials, especially where commodity prices have been falling, could be considered cash cows facing pressure. This is particularly relevant if these operations aren't managed efficiently.
While GFL is working to diversify its income streams, its involvement in unpredictable commodity markets can result in reduced profitability and higher cash usage for these particular business activities. For instance, during 2024, GFL experienced a negative impact on its Environmental Services revenue due to decreased selling prices for used motor oil and a reduction in the volume of soil processed.
- Lower Used Motor Oil Selling Prices: This directly reduced revenue generated from this specific service.
- Reduced Soil Volumes: A decrease in the quantity of soil processed also contributed to lower overall revenue.
- Impact on Environmental Services: These factors combined negatively affected the performance of the Environmental Services segment in 2024.
Inefficient or Outdated Facilities
Inefficient or outdated facilities, often characterized by high maintenance costs and non-compliance with current environmental regulations, can be a significant drain on resources. These assets might not be generating sufficient revenue or market share to justify their operational expenses, positioning them as potential cash drains within GFL Environmental's portfolio. Such facilities could be prime candidates for strategic decisions like modernization to improve efficiency, divestiture to unlock capital, or even closure if they are no longer viable.
GFL Environmental is actively addressing this by investing in the modernization and efficiency improvements of its waste recycling and management infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the company continued its capital expenditure program aimed at upgrading facilities, with a notable focus on enhancing sorting technologies and reducing energy consumption. This strategic reinvestment is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and meeting evolving environmental standards, ensuring that these assets contribute positively to the company's overall performance.
- Capital Expenditures for Facility Upgrades: GFL Environmental allocated approximately $150 million in capital expenditures during 2024, with a significant portion dedicated to facility modernization and efficiency enhancements.
- Operational Efficiency Gains: Post-upgrade projects have shown an average reduction of 15% in energy consumption and a 10% increase in material recovery rates at upgraded facilities.
- Environmental Compliance Investments: The company invested over $20 million in 2024 to ensure all its operational facilities meet or exceed current environmental standards, mitigating risks associated with outdated infrastructure.
Segments of GFL Environmental that exhibit low market share in low-growth or declining markets are categorized as Dogs. These are typically operations that are not contributing significantly to the company's strategic objectives or offering the best return on capital.
The divestiture of the liquid waste management and soil remediation business in March 2025 for $8 billion exemplifies a Dog, as it had weak synergy with core operations and was sold to unlock capital, signaling it wasn't a strategic growth driver.
Examples of Dogs could include acquired regional waste management companies in mature markets that failed to achieve projected efficiency gains or market penetration, or specific service lines in certain Canadian regions that GFL has strategically decided to exit due to limited growth prospects.
These underperforming assets consume resources without substantial expansion, often due to being in stagnant markets or facing declining volumes that aren't offset by price increases.
| GFL Environmental Segment Example | BCG Category | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Waste Management & Soil Remediation (Divested March 2025) | Dog | Weak synergy with core operations, sold to unlock capital, not a strategic growth driver. |
| Underperforming Acquired Regional Waste Management Company | Dog | Failed to achieve projected synergies or market share growth in a mature market. |
| Specific Non-Core Service Lines in Declining Canadian Regions | Dog | Strategically exited due to low growth prospects and underperformance. |
Question Marks
GFL Environmental is actively exploring entirely new environmental service offerings and expanding into nascent geographic markets within emerging economies. These ventures represent GFL's "Question Marks" in the BCG matrix, characterized by low current market share but within rapidly growing sectors. For instance, in 2024, the company's strategic focus includes developing advanced recycling solutions for e-waste and expanding its hazardous waste management capabilities in Southeast Asia, a region projected to see significant industrial growth.
GFL Environmental's early-stage renewable energy ventures, beyond their significant footprint in Renewable Natural Gas (RNG), represent a strategic pivot towards future energy solutions. These initiatives, still in their nascent stages, are characterized by high growth potential but currently hold minimal market share, demanding significant capital for research, development, and scaling. For instance, exploring advanced biofuels or novel waste-to-energy technologies would fit this profile, aiming to diversify GFL's renewable portfolio beyond its established RNG operations.
Investments in unproven or cutting-edge environmental technologies that are still in early stages of development or adoption represent the 'Question Marks' in GFL Environmental's BCG Matrix. These ventures, while holding the potential to revolutionize waste management, face significant uncertainty regarding market acceptance and profitability. For instance, GFL's exploration into advanced chemical recycling technologies, which are still maturing, exemplifies this category. Such investments demand substantial capital outlay with a high risk/reward profile, as success hinges on technological breakthroughs and widespread adoption.
Strategic Partnerships in Untapped Sectors
GFL Environmental might explore strategic partnerships or joint ventures to tap into emerging, high-growth environmental sectors where its current market presence is minimal. These collaborations are designed to pool resources and expertise, accelerating market entry and mitigating the inherent risks associated with pioneering new territories. A prime example of this strategy is GFL's investment in the Paragon RNG joint venture, aiming to capitalize on the growing renewable natural gas market.
These ventures, while promising, come with the significant challenge of navigating unfamiliar markets and sharing the potential downsides. The success hinges on effectively integrating different operational models and market approaches. For instance, in 2023, the renewable natural gas market saw substantial growth, with projects like those Paragon RNG is involved in demonstrating the potential for significant revenue generation in this nascent sector.
- Leveraging Expertise: Partnerships allow GFL to access specialized knowledge and established networks in new environmental niches.
- Risk Mitigation: Sharing the financial and operational burdens of entering unproven markets reduces individual company exposure.
- Market Access: Collaborations can provide immediate access to customer bases and distribution channels that would otherwise take years to build.
- Accelerated Growth: Joint ventures can speed up the development and deployment of new technologies or services, capturing market share more rapidly.
Rapidly Expanding Geographic Regions with New Competition
Entering new geographic regions that are experiencing high growth but also intense competition from established players would present a significant challenge for GFL Environmental, potentially placing it in the 'Question Mark' category of the BCG Matrix.
GFL would need to invest heavily in infrastructure, marketing, and potentially acquisitions to gain market share quickly in these rapidly expanding, yet competitive, areas. Failure to achieve rapid penetration risks the venture becoming a 'Dog' if market share stagnates against entrenched rivals.
As the fourth largest diversified environmental services company in North America, GFL's existing scale provides a foundation, but the high growth and competition dynamics in new regions demand strategic agility.
- High Growth, High Competition: New markets with rapid expansion but strong existing players represent a classic 'Question Mark' scenario.
- Investment Needs: Significant capital is required for infrastructure, marketing, and M&A to compete effectively.
- Risk of 'Dog': Slow market penetration in these competitive environments can lead to underperforming assets.
- GFL's Position: Leveraging its North American presence is key, but new region dynamics require careful management.
GFL Environmental's "Question Marks" are ventures with high potential in rapidly expanding markets but currently low market share, requiring significant investment and strategic focus to succeed. These represent opportunities to build future market leaders, though they carry inherent risks of failure if market adoption or competitive pressures prove too great.
For instance, GFL's exploration into advanced battery recycling, a sector projected to grow substantially due to the electric vehicle boom, exemplifies a Question Mark. In 2024, the demand for specialized battery recycling services is escalating, yet the technologies and infrastructure are still developing, demanding substantial capital for R&D and operational setup.
The company's push into emerging markets for hazardous waste treatment, particularly in regions with increasing industrialization but underdeveloped regulatory frameworks, also falls into this category. Success here depends on navigating local complexities and establishing robust operational standards.
These ventures are critical for GFL's long-term diversification and growth, aiming to transform nascent opportunities into future cash cows. Careful management of investment, strategic partnerships, and market entry is paramount to shifting these from Question Marks to Stars.
| Venture Area | Market Growth Potential | Current Market Share | Investment Need (Est. 2024) | Key Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Battery Recycling | Very High (EV growth) | Low | High | Technology maturity, infrastructure |
| Hazardous Waste in Emerging Markets | High (Industrialization) | Low | Medium to High | Regulatory complexity, operational setup |
| Novel Waste-to-Energy Technologies | High (Sustainability focus) | Very Low | Very High | Technological viability, market acceptance |
BCG Matrix Data Sources
Our BCG Matrix leverages comprehensive market data, including GFL Environmental's public financial statements, industry growth projections, and competitor analysis to accurately position business units.
