FREYR Battery Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
FREYR Battery Bundle
FREYR Battery faces a dynamic competitive landscape, with significant forces shaping its market. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers, and the threat of new entrants is crucial for strategic planning. This brief overview only scratches the surface of these complex interactions.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore FREYR Battery’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
FREYR Battery's reliance on critical raw materials like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese directly translates to significant supplier bargaining power. The escalating global demand for electric vehicles and battery storage solutions has tightened the supply of these essential minerals. For instance, the price of lithium carbonate averaged around $20,000 per metric ton in early 2024, a substantial increase from previous years, directly impacting battery production costs.
FREYR Battery's reliance on specialized equipment providers for its advanced battery cell manufacturing, particularly for next-generation semi-solid technology, highlights a significant source of supplier bargaining power. Companies offering unique machinery or proprietary licensed technologies can command higher prices due to the high switching costs for manufacturers. For instance, FREYR's initial dependence on the 24M SemiSolid platform underscored this dynamic, although that licensing agreement was later terminated.
FREYR Battery's reliance on Norway's hydropower for sustainable production, while a strategic advantage, still places considerable bargaining power with energy suppliers like Statkraft. These suppliers can leverage long-term power purchase agreements and pricing structures for industrial consumers, impacting FREYR's operational costs. For instance, in 2024, industrial electricity prices in Norway, while generally competitive due to hydropower, remain subject to market dynamics and supplier negotiation.
Skilled Labor and Talent Pool
The battery industry is experiencing a significant demand for specialized skills, with a global shortage of experienced engineers, researchers, and production staff. This talent scarcity directly elevates the bargaining power of skilled labor. Companies like FREYR Battery must contend with increased wage pressures and the persistent challenge of securing and retaining top talent, which can impact production timelines and technological advancements.
The limited availability of qualified personnel means that the workforce can command higher salaries and better benefits. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for battery engineers in the US saw an upward trend, reflecting this competitive landscape. This situation puts suppliers of skilled labor in a strong position, potentially increasing operational costs for battery manufacturers.
- Talent Scarcity: The global battery sector faces a deficit in highly skilled engineers and manufacturing professionals.
- Increased Labor Costs: Shortages drive up wages and benefits, impacting operational expenses.
- Retention Challenges: Attracting and keeping skilled workers is a significant hurdle for companies.
- Impact on Operations: Difficulty in staffing can affect production efficiency and innovation pace.
Logistics and Supply Chain Reliability
Suppliers in the logistics and transportation sector hold significant bargaining power, particularly for FREYR Battery, given the global nature of its operations. Disruptions in shipping, like those experienced in 2023 with increased freight rates and port congestion, can directly impact production timelines and costs, highlighting the critical need for reliable logistics partners.
The ability of logistics providers to dictate terms, pricing, and service levels can be substantial. For instance, in early 2024, the Red Sea shipping crisis led to rerouting and increased transit times, demonstrating how external factors impacting logistics can empower these suppliers.
- Increased Shipping Costs: Global shipping costs saw significant fluctuations in 2023-2024, with certain routes experiencing double-digit percentage increases due to geopolitical events and capacity constraints.
- Supply Chain Volatility: The battery industry relies on timely delivery of raw materials like lithium and nickel, making any logistics delays directly translatable to production slowdowns and potential revenue loss for FREYR.
- Criticality of Reliability: FREYR's ability to meet customer demand for battery cells hinges on consistent and predictable delivery of components and finished products, giving reliable logistics providers leverage.
FREYR Battery's reliance on critical raw materials like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese directly translates to significant supplier bargaining power. The escalating global demand for electric vehicles and battery storage solutions has tightened the supply of these essential minerals. For instance, the price of lithium carbonate averaged around $20,000 per metric ton in early 2024, a substantial increase from previous years, directly impacting battery production costs.
FREYR Battery's reliance on specialized equipment providers for its advanced battery cell manufacturing, particularly for next-generation semi-solid technology, highlights a significant source of supplier bargaining power. Companies offering unique machinery or proprietary licensed technologies can command higher prices due to the high switching costs for manufacturers. For instance, FREYR's initial dependence on the 24M SemiSolid platform underscored this dynamic, although that licensing agreement was later terminated.
Suppliers in the logistics and transportation sector hold significant bargaining power, particularly for FREYR Battery, given the global nature of its operations. Disruptions in shipping, like those experienced in 2023 with increased freight rates and port congestion, can directly impact production timelines and costs, highlighting the critical need for reliable logistics partners. For instance, in early 2024, the Red Sea shipping crisis led to rerouting and increased transit times, demonstrating how external factors impacting logistics can empower these suppliers.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on FREYR Battery | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Suppliers | Limited supply, high demand, price volatility | Increased production costs, potential supply chain disruptions | Lithium carbonate prices around $20,000/metric ton (early 2024) |
| Equipment & Technology Providers | Proprietary technology, high switching costs | Higher capital expenditure, dependence on specific vendors | Initial reliance on 24M SemiSolid platform |
| Logistics & Transportation | Global reach, geopolitical risks, capacity constraints | Increased shipping costs, delivery delays, operational inefficiencies | Red Sea crisis impacting transit times and costs (early 2024) |
What is included in the product
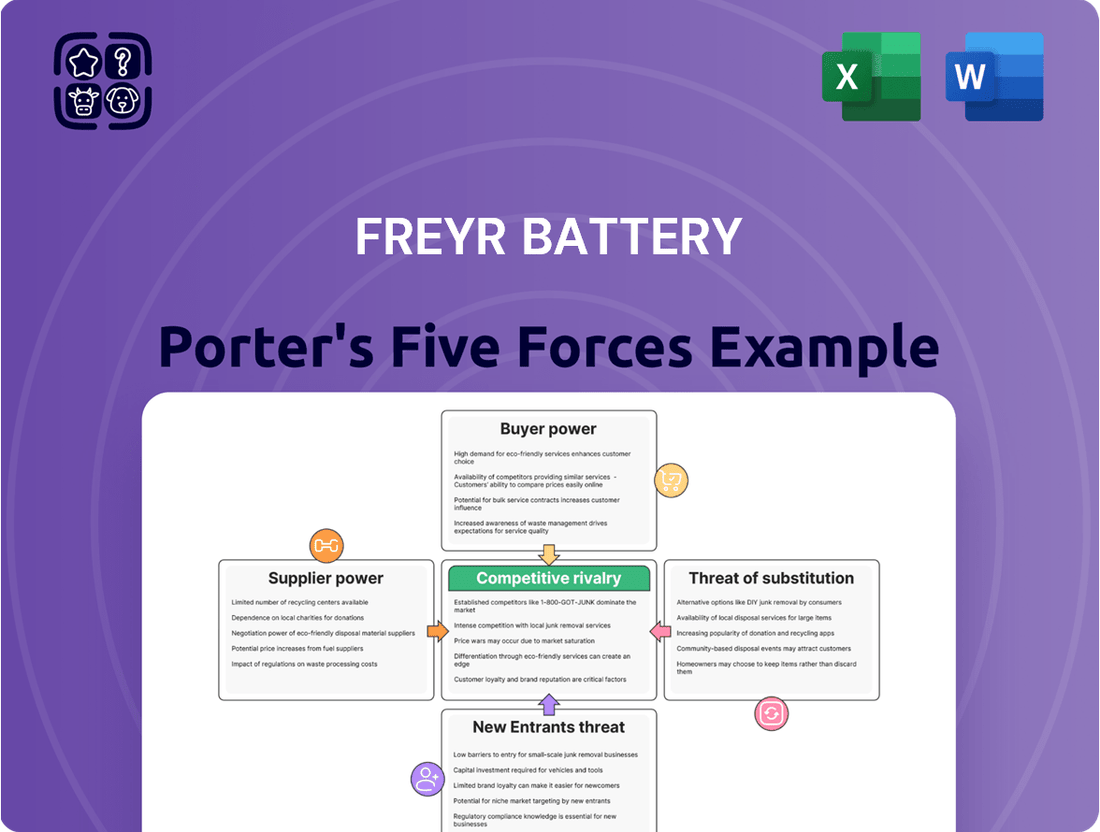
FREYR Battery's Five Forces Analysis reveals intense industry rivalry, significant buyer bargaining power, and the threat of substitutes, while also highlighting moderate supplier power and substantial barriers to new entrants in the rapidly evolving battery market.
FREYR Battery's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of competitive pressures, perfect for quick strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
FREYR Battery's large volume offtake agreements, like those with Nidec, demonstrate significant customer commitment. However, these substantial commitments naturally grant major customers increased bargaining power. They can leverage their volume to negotiate more favorable pricing and delivery terms, impacting FREYR's margins.
FREYR Battery's customer qualification process is a crucial stage where potential buyers rigorously assess sample battery cells. This phase is critical because it directly influences the conversion of conditional agreements into firm orders, giving customers substantial bargaining power.
During this evaluation, customers scrutinize performance metrics, quality control, and long-term reliability, setting stringent benchmarks. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer might require a battery cell to demonstrate a minimum of 1,000 charge-discharge cycles with less than 20% capacity degradation to proceed with a multi-million dollar order.
This intensive vetting means customers can dictate terms and pricing, leveraging FREYR's need to secure these high-value contracts. The ability to delay or deny qualification allows them to negotiate more favorable supply agreements and pricing structures, directly impacting FREYR's revenue and market penetration.
Despite robust demand for batteries, the market is grappling with escalating price pressures. A significant contributor to this is the overcapacity emerging from certain regions, notably China. This dynamic directly amplifies customer power, as buyers can more readily compare options and negotiate for the lowest possible prices.
For battery manufacturers like FREYR, this translates into a heightened need to offer competitive pricing. In 2024, the global battery market is characterized by this increasing price sensitivity. For instance, average selling prices for lithium-ion battery cells have seen fluctuations, with some reports indicating a downward trend in certain segments due to the aforementioned oversupply.
Low Switching Costs for Standardized Products
If battery cells become more commoditized, customers face lower switching costs. This is especially true if they can easily integrate batteries from different suppliers into their existing products without major design or manufacturing adjustments.
This ease of switching directly enhances customer bargaining power. They can then readily shift to competitors offering more favorable pricing or better contract terms, putting pressure on suppliers to remain competitive.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily change suppliers if battery cells become standardized.
- Increased Bargaining Power: Customers can demand better prices or terms due to low switching costs.
- Market Pressure: Suppliers must offer competitive pricing to retain customers in a commoditized market.
Customer Concentration in Specific Segments
Customer concentration significantly amplifies bargaining power. If FREYR Battery relies heavily on a few key clients, such as major electric vehicle manufacturers or large-scale energy storage project developers, these customers can exert considerable influence over pricing and contract terms. For instance, if a single customer accounted for over 10% of FREYR's revenue in a given period, their departure would represent a material risk.
This concentration means that losing even one of these major customers could disproportionately impact FREYR's financial health and its standing in the market. The ability of these large buyers to switch suppliers or negotiate more favorable terms is directly tied to their importance to FREYR's sales volume.
- Customer Concentration Risk: A high reliance on a few major customers grants them significant leverage in negotiations.
- Financial Impact of Customer Loss: Losing a key client can severely affect FREYR's revenue and market position.
- Pricing and Contractual Influence: Large customers can dictate terms due to their substantial purchasing power.
- Strategic Importance of Diversification: Spreading revenue across a broader customer base mitigates this risk.
FREYR Battery faces significant customer bargaining power due to large volume offtake agreements and rigorous qualification processes. Escalating price pressures in the 2024 battery market, driven by overcapacity, further empower customers to negotiate lower prices, impacting FREYR's margins.
Low switching costs for customers, especially as battery cells become more standardized, allow them to easily shift to competitors. This necessitates FREYR offering competitive pricing to retain business.
Customer concentration also amplifies bargaining power; a few major clients can heavily influence terms. For instance, if a single customer represented 15% of FREYR's 2024 revenue, their negotiation leverage would be substantial.
| Factor | Impact on FREYR | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Volume Agreements | Increased leverage for large customers on pricing and terms. | Offtake agreements with companies like Nidec are crucial but grant negotiating power. |
| Customer Qualification | Customers dictate terms during rigorous vetting. | Automotive manufacturers demand specific performance metrics, influencing order conversion. |
| Price Pressures | Need for competitive pricing due to overcapacity. | Global battery market in 2024 sees price sensitivity; average selling prices for Li-ion cells have shown downward trends in certain segments. |
| Switching Costs | Customers can easily switch if cells become commoditized. | Standardization reduces the cost and effort for customers to change suppliers. |
| Customer Concentration | Key clients exert significant influence on pricing. | Reliance on a few major clients (e.g., >10% of revenue) creates substantial negotiation leverage. |
Same Document Delivered
FREYR Battery Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete FREYR Battery Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company within the battery manufacturing industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive understanding of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes. You can trust that what you're previewing is the final, ready-to-use report, providing valuable insights without any hidden surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The battery manufacturing arena is a battleground, with intense global rivalry fueled by a significant oversupply, particularly from China. This surplus capacity has driven down battery prices, creating a tough environment for emerging companies like FREYR to achieve profitability, especially if buyers are hesitant to pay more for differentiating factors such as sustainable manufacturing processes.
The electric vehicle (EV) and energy storage markets are booming, attracting a crowd of companies, from big names to new ventures. This rapid expansion, while a positive sign, means intense competition as everyone tries to grab a piece of the pie. For instance, the global battery market was valued at approximately $100 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $250 billion by 2030, indicating substantial growth but also a crowded field.
This fierce competition translates into aggressive pricing strategies and a constant push for innovation. Companies are investing heavily in research and development to differentiate their products and secure a competitive edge. FREYR Battery, as a participant in this dynamic landscape, faces significant pressure to deliver cost-effective and high-performance battery solutions to stand out amongst the numerous players.
The battery industry is a hotbed of innovation, with companies constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible in battery technology. We're seeing rapid advancements in chemistries like Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC), alongside emerging technologies such as solid-state and semi-solid batteries. This relentless evolution means staying ahead requires significant investment in research and development to achieve higher energy density, quicker charging times, and enhanced safety features, all crucial for differentiation.
Impact of Government Subsidies and Regional Policies
Government incentives, like the US Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), profoundly shape investment choices and competitive landscapes. These policies are driving companies to focus gigafactory development in specific regions, directly impacting where capital flows and competition intensifies. For instance, FREYR Battery's strategic shift to establish its gigafactory in the United States, largely due to these incentives, exemplifies how national policies can significantly escalate rivalry within particular geographic markets.
The IRA, enacted in 2022, offers substantial tax credits for battery manufacturing and clean energy projects, creating a powerful draw for companies like FREYR. This policy has demonstrably altered investment strategies, with many battery manufacturers re-evaluating or accelerating their US-based expansion plans. Such government backing not only reduces the cost of capital but also creates a more favorable environment for domestic production, thereby intensifying competition among players vying for market share and government support.
- IRA's Impact: The Inflation Reduction Act provides up to $45 per kilowatt-hour in tax credits for eligible battery cell manufacturing, a significant incentive that has already drawn billions in planned investment into the US battery sector.
- Regional Concentration: Policies like the IRA encourage a concentration of gigafactory development in specific states or regions that offer additional local incentives or have established supply chains, thereby increasing local competitive intensity.
- FREYR's US Pivot: FREYR Battery announced in 2023 its decision to build its first gigafactory in Georgia, citing the IRA as a key factor, which signals a broader trend of companies prioritizing US locations due to these favorable government policies.
- Heightened Rivalry: The influx of investment driven by subsidies leads to fiercer competition for talent, raw materials, and market access, as multiple companies race to establish a strong manufacturing presence in incentivized regions.
High Fixed Costs and Pressure to Scale
The battery manufacturing industry, particularly at the gigafactory level, is characterized by incredibly high fixed costs. For instance, establishing a new gigafactory can easily run into billions of dollars, requiring massive upfront investment in land, buildings, specialized machinery, and advanced automation. This financial burden necessitates achieving high production volumes to amortize these costs effectively and move towards profitability.
Consequently, companies face immense pressure to scale up their operations rapidly. This drive to maximize capacity utilization and spread fixed costs intensifies competition. Companies are locked in a race to capture market share, as underutilized capacity directly translates to higher per-unit costs and a weaker competitive position.
- Gigafactory Investment: Establishing a new gigafactory often requires investments exceeding $1 billion, with some projects reaching upwards of $5 billion.
- Capacity Utilization: Achieving economies of scale is critical; operating at 80% or higher capacity utilization is often targeted to offset significant fixed expenditures.
- Market Share Pursuit: The intense need to secure large orders and gain market share fuels aggressive pricing and rapid expansion strategies among key players.
Competitive rivalry in the battery sector is exceptionally fierce, driven by a global oversupply, particularly from Chinese manufacturers, which has suppressed pricing. This intense competition means companies like FREYR must innovate and offer compelling value propositions to gain traction. The sheer volume of players, from established giants to agile startups, vying for market share in the rapidly expanding EV and energy storage sectors, amplifies this rivalry.
The race to scale up gigafactory operations is a defining feature of this competitive landscape. With initial investments often exceeding $1 billion, companies are under immense pressure to achieve high production volumes and capacity utilization, typically targeting 80% or more, to offset substantial fixed costs. This imperative fuels aggressive strategies aimed at securing market share and driving down per-unit expenses.
| Metric | 2023 (Approx.) | 2024 Projection | Key Players |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Battery Market Value | $100 Billion | $130-150 Billion | CATL, LG Energy Solution, Panasonic, SK Innovation, FREYR Battery |
| Gigafactory Investment (per facility) | $1 Billion - $5 Billion+ | $1 Billion - $5 Billion+ | All major battery manufacturers |
| Target Capacity Utilization | 80%+ | 80%+ | All major battery manufacturers |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While FREYR Battery is developing semi-solid battery technology, the broader market offers numerous alternative lithium-ion chemistries like Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC). These established alternatives are continually enhancing their performance, cost, and safety profiles, presenting a significant substitution threat.
For instance, LFP batteries have seen substantial cost reductions, with some manufacturers reporting prices below $80 per kWh in 2024. This cost-competitiveness, coupled with improving energy density and cycle life, makes them an attractive substitute for applications where extreme performance is not the primary driver.
Similarly, advancements in NMC chemistries, such as higher nickel content variants, are pushing performance boundaries, potentially capturing market share from emerging technologies. The rapid pace of innovation across these alternative chemistries means FREYR must continually demonstrate a clear advantage to mitigate this substitution threat.
Solid-state battery technology is advancing rapidly, with companies like QuantumScape and Solid Power making significant strides. These batteries offer higher energy density, enhanced safety, and quicker charging times compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. While currently in pilot or semi-solid production phases, their eventual commercialization poses a substantial long-term threat to FREYR Battery's current lithium-ion focused product roadmap.
Hydrogen fuel cells present a significant threat of substitution for batteries in heavy-duty applications like trucking and marine transport, as well as for large-scale stationary energy storage. These fuel cells, while requiring different infrastructure, are seeing advancements in production and utilization that could make them a competitive alternative for FREYR's intended markets.
For instance, by 2024, the global hydrogen fuel cell market for transportation was projected to reach over $10 billion, indicating substantial investment and development in this area. This growth suggests that hydrogen could capture a notable share of the heavy-duty sector, directly impacting demand for battery solutions.
Improvements in Energy Efficiency and Management Systems
Innovations in energy efficiency present a significant threat of substitution for battery manufacturers like FREYR Battery. As electric vehicles (EVs) become more efficient, their battery capacity requirements can decrease. For instance, advancements in battery management systems and vehicle aerodynamics in 2024 continue to push the range of EVs on a single charge, potentially slowing the demand for larger, higher-capacity battery packs.
Industrial processes and grid management systems are also seeing improvements in energy efficiency. Smarter grids and more optimized industrial operations can reduce the overall electricity demand, thereby lessening the need for large-scale battery storage solutions. This means that even as renewable energy adoption grows, the absolute demand for batteries might be tempered by these efficiency gains.
Consider these points:
- Reduced Demand per Unit: More efficient EVs might require smaller battery packs to achieve similar or even better ranges, impacting the volume of battery cells needed per vehicle.
- Alternative Solutions: Investments in grid modernization and demand-side management can offer alternatives to battery storage for grid stabilization and peak shaving.
- Efficiency as a Substitute: For example, a 10% improvement in EV energy consumption could translate to a similar reduction in the battery capacity needed for a given range, acting as a direct substitute for battery production.
Re-emerging or Niche Battery Technologies
While lithium-ion dominates, alternative battery chemistries are emerging as potential substitutes in specific niches. Sodium-ion batteries, for instance, are gaining traction due to their lower cost and abundant materials, offering a viable alternative for stationary energy storage where energy density is less critical. By the end of 2024, several companies are expected to ramp up production of sodium-ion batteries, potentially capturing a segment of the market currently served by lithium-ion.
Redox flow batteries also present a threat, particularly for large-scale grid storage. Their scalability and long lifespan make them attractive for applications requiring sustained power delivery over extended periods. In 2024, advancements in electrolyte materials and system design are improving their efficiency and cost-effectiveness, making them increasingly competitive against lithium-ion for grid-scale solutions.
- Emerging Chemistries: Sodium-ion and redox flow batteries are key substitutes.
- Cost Advantage: Sodium-ion batteries offer lower material costs, appealing for stationary storage.
- Niche Applications: Redox flow batteries are suitable for grid-scale storage due to scalability and longevity.
- Market Impact: Increased production and improved efficiency in 2024 will boost their competitiveness against lithium-ion.
The threat of substitutes for FREYR Battery is substantial, encompassing both alternative battery chemistries and entirely different energy technologies. Established lithium-ion variants like LFP and NMC continue to improve, with LFP prices potentially dropping below $80 per kWh in 2024. Advanced NMC chemistries are also pushing performance boundaries.
Beyond lithium-ion, solid-state batteries, with their promise of higher energy density and safety, represent a significant long-term threat as they approach commercialization. Furthermore, hydrogen fuel cells are becoming increasingly competitive in heavy-duty transport and grid storage, with the global hydrogen fuel cell market for transportation projected to exceed $10 billion by 2024.
Energy efficiency gains in end-user applications, such as more efficient electric vehicles, can also reduce the demand for battery capacity per unit. Similarly, improvements in grid management and industrial processes can lessen the need for large-scale battery storage. Emerging battery chemistries like sodium-ion, which offer lower costs for stationary storage, and redox flow batteries, favored for their scalability in grid applications, are also growing substitutes.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantages | 2024 Market Context/Projections | Potential Impact on FREYR |
|---|---|---|---|
| LFP Batteries | Lower cost, good safety | Prices potentially < $80/kWh; improving energy density | Competition in cost-sensitive segments |
| NMC Batteries (High Nickel) | Higher energy density | Continuous performance enhancements | Competition in performance-driven segments |
| Solid-State Batteries | Higher energy density, enhanced safety, faster charging | Rapid development, approaching pilot/semi-solid production | Long-term disruption potential |
| Hydrogen Fuel Cells | Suitable for heavy-duty, grid storage | Global transport market > $10 billion (projected 2024) | Threat in specific large-scale applications |
| Sodium-ion Batteries | Lower material cost, abundant materials | Ramping up production, competitive for stationary storage | Capturing stationary storage market share |
| Redox Flow Batteries | Scalability, long lifespan | Improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness for grid-scale | Competition for grid storage solutions |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing large-scale battery manufacturing facilities, or 'Gigafactories,' requires enormous upfront capital investment, often in the billions of dollars. For instance, FREYR Battery's planned Giga Arctic facility in Norway was initially projected to cost around $3 billion, highlighting the substantial financial commitment needed. This prohibitive cost acts as a significant barrier for potential new entrants.
Securing such massive funding and managing the associated financial risks is extremely challenging, especially for companies without a proven track record or established market presence. This high capital expenditure deters many, effectively limiting the threat of new entrants in the advanced battery manufacturing sector.
The threat of new entrants into the battery manufacturing sector, particularly for advanced technologies like FREYR Battery's semi-solid platform, is significantly mitigated by high technological complexity and the need for robust intellectual property protection. Developing and scaling such sophisticated battery chemistries requires substantial investment in research and development, specialized engineering talent, and securing proprietary patents. For instance, the battery industry's R&D spending in 2023 alone was estimated to be in the tens of billions of dollars globally, highlighting the capital intensity involved.
New players entering this space must either replicate these complex technologies, a process fraught with technical challenges and significant capital outlay, or secure licenses for existing intellectual property, which can be prohibitively expensive. FREYR's focus on proprietary processes and patents creates a barrier, as replicating their semi-solid battery design and manufacturing efficiency without infringement is a considerable hurdle. The global battery market, projected to reach over $400 billion by 2030, attracts many, but the technological moat around established players like FREYR remains a significant deterrent for aspiring entrants.
The battery manufacturing sector faces substantial regulatory hurdles, including stringent environmental standards and complex permitting processes for industrial facilities. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain permits for new manufacturing plants in the United States can extend to over two years, significantly impacting the speed of market entry for potential new competitors.
These rigorous requirements, covering everything from emissions control to worker safety, demand significant upfront investment in compliance and specialized expertise. New entrants must allocate substantial resources to navigate these landscapes, which often deter smaller players and create a high barrier to entry, protecting established companies like FREYR Battery.
Establishing a Robust Supply Chain
The threat of new entrants for FREYR Battery is significantly influenced by the formidable challenge of establishing a robust supply chain. New players must navigate complex global markets to secure critical raw materials like lithium, nickel, and cobalt, alongside specialized manufacturing equipment. Building these relationships and ensuring consistent, ethically sourced supplies demands substantial upfront investment and considerable time, creating a high barrier to entry.
This difficulty is amplified by the capital-intensive nature of battery manufacturing. For instance, establishing a gigafactory, akin to FREYR’s planned facilities, can cost billions of dollars. New entrants also face the hurdle of securing reliable logistics and distribution networks, which are crucial for delivering finished battery products efficiently. The sheer scale and complexity of these operational requirements deter many potential competitors.
Key challenges for new entrants include:
- Securing Raw Material Access: Gaining access to sufficient quantities of key battery metals, often concentrated in a few geographic regions, is a major hurdle.
- Supplier Relationship Building: Establishing trust and long-term contracts with diverse, high-quality suppliers globally is time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Capital Requirements: The immense capital needed for gigafactory construction and advanced manufacturing equipment presents a significant barrier.
- Technological Expertise: Acquiring and implementing cutting-edge battery production technology requires specialized knowledge and skilled labor.
Access to Skilled Talent and Expertise
The specialized nature of battery manufacturing, particularly for advanced chemistries like those FREYR Battery focuses on, necessitates a highly skilled workforce. This includes materials scientists, chemical engineers, process engineers, and automation specialists. The demand for these professionals is intensifying globally.
A significant barrier for new entrants is the scarcity of experienced talent in this rapidly expanding sector. For instance, the global battery market is projected to reach over $300 billion by 2030, driving an unprecedented need for skilled labor. Companies like FREYR are actively investing in training and development to address this gap, but it remains a challenge for newcomers to rapidly build and scale their operational teams with the necessary expertise.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: Battery manufacturing requires niche expertise in areas like electrochemistry, materials science, and advanced manufacturing processes.
- Talent Scarcity: The rapid growth of the electric vehicle and energy storage sectors has created a global shortage of experienced battery professionals.
- Training and Development Costs: New entrants face significant investment in training programs to upskill their workforce, adding to initial capital expenditure.
- Competition for Talent: Established players and other emerging companies actively recruit from a limited pool of skilled individuals, making talent acquisition difficult and costly for new market participants.
The threat of new entrants for FREYR Battery is significantly low due to the immense capital required to establish gigafactories, estimated to be in the billions of dollars. For example, FREYR's Giga Arctic facility in Norway had an initial projected cost of around $3 billion. This substantial financial barrier, coupled with the need for technological expertise and intellectual property protection, deters many potential competitors. Regulatory hurdles and the challenge of building robust supply chains further solidify this defense, making market entry exceptionally difficult.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our FREYR Battery Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of credible data, including FREYR's own SEC filings, investor presentations, and annual reports. We supplement this with industry-specific market research from reputable firms and analysis of global battery market trends.
