Fosun International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fosun International Bundle
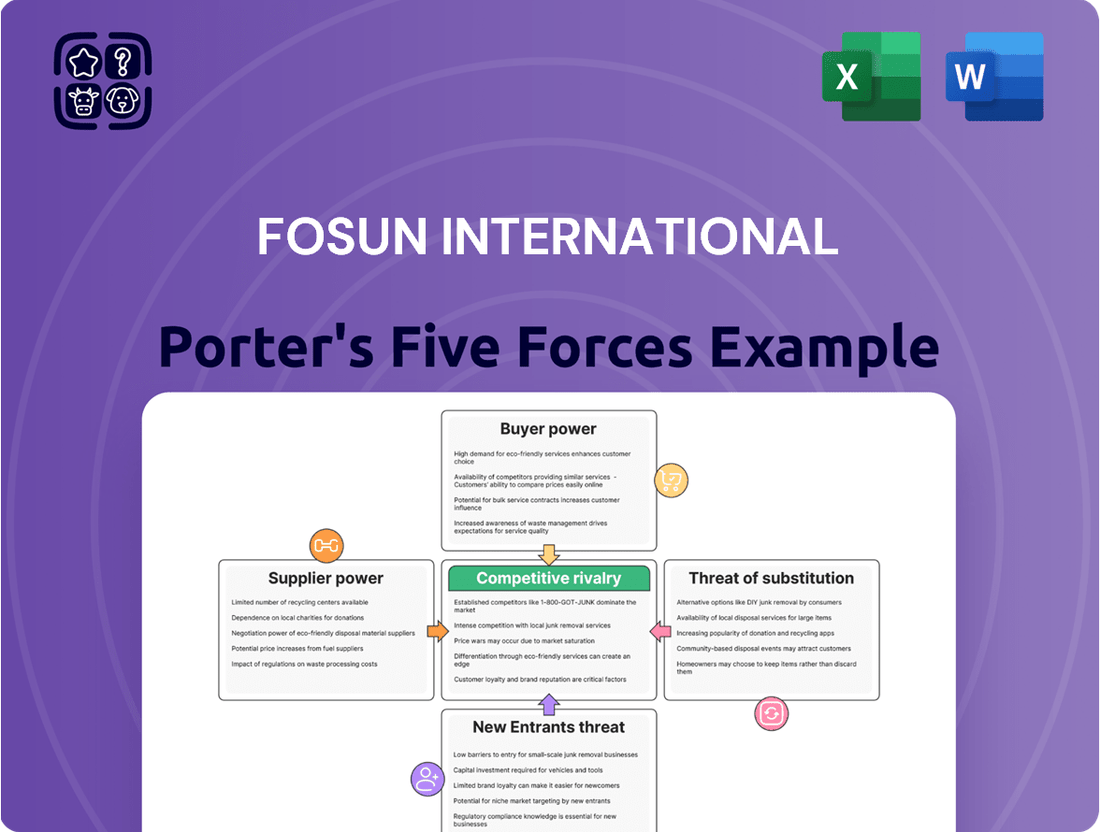
Fosun International navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense industry rivalry and the significant bargaining power of its buyers. The threat of new entrants, while present, is somewhat mitigated by the capital-intensive nature of many of its diverse operations. Understanding the influence of substitute products and the power of its suppliers is crucial for grasping Fosun's strategic positioning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Fosun International’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fosun International’s supplier concentration varies greatly across its diverse business segments. In healthcare, for example, the sourcing of specialized medical equipment or proprietary pharmaceuticals can involve a limited number of global manufacturers, granting these suppliers considerable leverage due to their unique offerings.
Conversely, in sectors like consumer products or general financial services, where inputs are more standardized and readily available from a wider pool of providers, supplier concentration is typically lower. This means Fosun has more options and can negotiate more effectively in these areas.
For instance, in 2024, while Fosun's tourism and leisure segment might face concentrated suppliers for specific resort management technologies or unique destination experiences, its consumer goods divisions likely deal with a broad base of raw material providers and manufacturers, diluting individual supplier power.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a significant factor for Fosun International, particularly when the inputs they provide are critical to the company's core operations and the quality of its final products. For instance, in Fosun Pharma, a key subsidiary, securing proprietary active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or specialized R&D technologies from specific suppliers directly impacts drug efficacy and market competitiveness. This reliance on unique or highly specialized inputs grants those suppliers considerable leverage.
The difficulty and expense Fosun International faces when changing suppliers significantly influences supplier leverage. If Fosun must invest heavily in reconfiguring production for new raw materials, as seen in their consumer goods segment, or recertifying critical components within their healthcare operations, suppliers gain considerable power. For instance, a substantial investment in new machinery for a specialized chemical input could lock Fosun into a supplier relationship for an extended period, increasing costs and reducing flexibility.
Conversely, when switching suppliers involves minimal cost or effort, such as sourcing standard office supplies or generic software licenses, supplier bargaining power is inherently weaker. This is particularly relevant for Fosun's diverse portfolio, where many operational needs might be met by readily available, interchangeable goods and services. In 2024, many businesses experienced supply chain disruptions; however, for commodities with numerous providers, the impact of switching costs on supplier power remained relatively low, allowing Fosun to negotiate more favorable terms.
Supplier Differentiation
Supplier differentiation significantly impacts Fosun International's bargaining power. When suppliers offer unique or proprietary products and services, they gain leverage because Fosun has fewer viable alternatives. For instance, if a key supplier provides specialized components essential for Fosun’s manufacturing processes, and these components are not easily sourced elsewhere, that supplier can command higher prices or more favorable terms.
Consider Fosun Pharma's investments in advanced therapies. Suppliers of highly specialized equipment or intellectual property for novel drug development, such as those involved in CAR-T cell therapy through collaborations like Fosun Kairos, hold considerable power. Their unique technological contributions limit Fosun's ability to switch suppliers without substantial disruption or cost, thereby strengthening the supplier's position.
- Supplier differentiation: When suppliers offer unique or proprietary products/services, their bargaining power increases.
- Fosun Kairos example: Suppliers of specialized technology for CAR-T cell therapy enhance their leverage.
- Limited alternatives: The scarcity of comparable offerings reduces Fosun's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
- Impact on costs: Differentiated suppliers can often charge premium prices, affecting Fosun's profitability.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Fosun International's business lines can significantly bolster their bargaining power. This means a supplier could start offering the same products or services that Fosun currently provides, directly competing with them. For a conglomerate like Fosun, with diverse holdings, this threat might be less prevalent across the board but remains a concern for specific, specialized segments.
Consider a scenario where a key technology provider, crucial for Fosun's digital operations, decides to develop and market their own end-user applications. This would shift their role from a component supplier to a direct competitor, giving them considerable leverage in negotiations with Fosun. Similarly, a major content supplier for Fosun's tourism sector could launch their own branded leisure experiences, bypassing Fosun's platforms and services.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers may move into Fosun's markets, increasing their leverage.
- Specialized Segments: While less common for conglomerates, specialized tech or content providers pose a risk.
- Impact on Leverage: Suppliers developing their own end-products or services gain significant power.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: This move directly alters the competitive dynamics, often to Fosun's disadvantage.
Fosun International faces varying supplier bargaining power across its diverse business segments. In specialized areas like advanced pharmaceuticals or unique resort technologies, where a limited number of providers exist, suppliers can exert significant influence. This is particularly true when switching costs are high, as seen in Fosun Pharma's reliance on proprietary drug ingredients or advanced medical equipment.
For instance, in 2024, the sourcing of critical components for Fosun Pharma's innovative therapies, such as those in CAR-T cell development, highlights suppliers with substantial leverage due to their unique technological contributions and limited alternatives. Conversely, in more commoditized sectors like consumer goods, Fosun benefits from a broader supplier base, which dilutes individual supplier power.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, where they might offer competing services or products, also plays a role. A technology provider for Fosun's digital operations, for example, could become a direct competitor, thereby increasing their negotiation power.
| Factor | Impact on Fosun International | Example Segment |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High in specialized sectors, Low in commoditized sectors | Healthcare (High), Consumer Goods (Low) |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs increase supplier power | Fosun Pharma (High), General Services (Low) |
| Differentiation | Unique offerings grant suppliers leverage | Fosun Kairos (High), Standard Office Supplies (Low) |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for suppliers to become competitors | Technology Providers (Potential), Raw Material Providers (Less Likely) |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Fosun International's diverse portfolio of businesses across various industries.
Understand the competitive landscape by visualizing each of Fosun International's five forces with clear, actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fosun International serves a vast global customer base across its health, happiness, and wealth segments, meaning price sensitivity varies significantly. For instance, consumers seeking essential healthcare services are generally less concerned with minor price fluctuations compared to individuals choosing discretionary travel or lifestyle products, impacting how Fosun sets prices across its diverse offerings.
The sheer number of alternative providers and products across Fosun International's diverse business segments directly fuels customer bargaining power. In highly competitive sectors like consumer goods, where Fosun operates with brands such as Fosun Pharma's healthcare products, customers can easily switch to a competitor if prices rise or quality dips. This abundance of choice means customers have significant leverage, demanding better prices and terms.
For instance, in the broader financial services market where Fosun has interests, the availability of numerous banks, investment firms, and fintech solutions means individual and corporate clients can readily compare offerings and negotiate favorable conditions. This competitive landscape puts pressure on Fosun to offer compelling value propositions to retain its customer base.
Conversely, Fosun's more specialized offerings, like premium tourism experiences through Club Med, might present fewer direct substitutes. While other travel providers exist, the unique all-inclusive model and brand reputation of Club Med can reduce customer power, as finding an exact equivalent might be more challenging. Similarly, highly specialized healthcare treatments offered by Fosun Pharma may have limited alternatives, giving Fosun more pricing flexibility in those niche areas.
Fosun International's customer base is largely dispersed, with individual families worldwide forming a significant portion of its clientele. This broad distribution typically means customers have limited individual power to negotiate prices or terms.
However, in certain business-to-business areas, particularly within its financial services and healthcare divisions, Fosun might encounter more concentrated customer groups. For instance, large corporate clients or major government health initiatives could represent a substantial portion of revenue for specific segments.
Such concentrated B2B relationships can increase the bargaining power of these specific customers. They might leverage their significant purchasing volume to demand more favorable pricing or customized service agreements, potentially impacting Fosun's margins in those niche areas.
While specific customer concentration figures for Fosun are not publicly detailed, a general understanding of its diverse operations suggests this dynamic is more pronounced in its B2B segments than its B2C offerings.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for customers significantly influence their bargaining power. When it's easy and inexpensive for customers to switch to a competitor, their power increases. For instance, in the market for basic financial services like savings accounts, customers can often move their funds with minimal hassle and cost, giving them leverage. In 2024, the digital transformation in finance has further lowered these barriers, with many neobanks and fintech platforms offering seamless account switching processes.
However, the degree of switching costs can vary greatly depending on the product or service. While general consumer goods might have negligible switching costs, more complex offerings can present higher barriers. Consider Fosun International's healthcare segment; switching from a comprehensive health insurance plan, especially one with accumulated benefits or specific network providers, can involve significant effort and potential loss of value. Similarly, integrated tourism packages, like those offered by Fosun's travel division, often include loyalty programs and bundled services that make switching less appealing.
- Low Switching Costs: In many consumer markets, customers can switch providers with minimal financial or effort-related barriers, increasing their bargaining power.
- High Switching Costs: Complex products, bundled services, loyalty programs, or specialized features can create higher switching costs, thereby reducing customer bargaining power.
- Digitalization Impact: Technology, particularly in financial services, has generally reduced switching costs, enabling easier comparison and migration between providers.
- Fosun's Diverse Segments: Fosun's varied business portfolio means switching costs differ across segments; for example, healthcare plans may have higher switching costs than basic retail goods.
Customer Information
The bargaining power of customers for Fosun International is significantly influenced by the increasing availability of information. In 2024, consumers across Fosun's diverse sectors, from tourism (like Thomas Cook) to consumer goods and healthcare, have unprecedented access to comparative pricing, detailed product reviews, and service quality assessments online. This makes them more discerning and capable of demanding better value, directly impacting Fosun's pricing strategies and profit margins.
This heightened customer awareness translates into a stronger negotiating position. For instance, in Fosun's healthcare segment, patients can easily research treatment costs and physician credentials, leading them to seek out providers offering superior value or more competitive pricing. Similarly, in the tourism sector, online travel agencies and review platforms empower travelers to compare options extensively, pushing companies like Fosun to offer more attractive packages and customer experiences to retain market share.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers in 2024 leverage digital platforms for price comparisons and reviews across industries like tourism, consumer products, and healthcare.
- Demand for Value: Easy access to information allows customers to scrutinize offerings, driving demand for better quality and competitive pricing from companies like Fosun International.
- Increased Leverage: Well-informed consumers can more effectively negotiate terms or switch to competitors, thereby increasing their overall bargaining power.
Fosun International faces considerable customer bargaining power due to widespread product availability and low switching costs across many of its segments. In 2024, the ease of comparing prices and services online empowers consumers, particularly in sectors like tourism and consumer goods, to demand better value. While some specialized offerings, such as certain healthcare treatments, might mitigate this power, the overall trend leans towards increased customer leverage.
The bargaining power of customers for Fosun International is amplified by the prevalence of both direct and indirect substitutes. For instance, in 2024, the insurance market, a key area for Fosun, offers numerous providers, allowing customers to easily switch plans if pricing or benefits are more favorable elsewhere. This competitive landscape means Fosun must consistently demonstrate superior value to retain its clientele.
Fosun's diverse customer base, ranging from individual consumers to large corporations, influences their collective bargaining power. While individual consumers typically have limited negotiation strength, concentrated groups of business clients, especially within financial services, can exert significant pressure for better terms. This is a critical consideration for Fosun in its B2B dealings, where large contracts can heavily influence profitability.
The digital landscape in 2024 significantly enhances customer bargaining power by providing easy access to information and comparison tools. For Fosun's health and happiness segments, customers can readily research service providers, compare pricing, and read reviews. This transparency forces companies to be more competitive on both price and quality to maintain customer loyalty.
Full Version Awaits
Fosun International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Fosun International Porter's Five Forces analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase. It details the intensity of rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making. You're looking at the actual document, so rest assured that what you see is precisely what you'll get, fully formatted and ready for your use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Fosun International navigates a landscape of varying industry structures. In sectors like certain consumer goods and local tourism, fragmentation is high, meaning numerous smaller companies vie for attention. This often translates to intense competitive rivalry, where price wars and aggressive marketing are common.
Conversely, Fosun also participates in more concentrated industries, such as specialized pharmaceuticals and large-scale insurance. Here, a smaller number of dominant players typically exist. Competition in these concentrated markets tends to be more strategic, focusing on innovation, market share consolidation, and long-term planning rather than immediate price battles.
For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical market, a sector where Fosun has significant interests, saw major players like Pfizer and Merck continue to dominate with substantial R&D investments, indicating a concentrated competitive environment. In contrast, the broader Chinese consumer electronics market, another area of Fosun’s diverse operations, remained highly fragmented with numerous domestic and international brands competing fiercely on price and features.
The growth rate of the industries Fosun International operates in significantly influences competitive rivalry. For instance, in 2023, while global economic growth moderated, certain sectors like healthcare and wellness within Fosun's portfolio experienced robust expansion. This dynamic can sometimes temper aggressive competition as companies focus on capturing new market share rather than solely fighting over existing customers.
However, when industries mature or exhibit slower growth, the competition for market share intensifies. If Fosun's key markets in 2024 are characterized by saturation, companies are more likely to engage in price wars or intensive marketing campaigns to attract and retain customers. This means that understanding the specific growth trajectory of each segment within Fosun’s diverse business interests is crucial for assessing the level of competitive pressure.
Fosun International leverages product differentiation across its diverse business segments, focusing on its 'health, happiness, and wealth' ecosystem. This strategy aims to create unique value propositions that go beyond mere price competition. For instance, in the happiness segment, Club Med offers distinct vacation experiences, while in health, Fosun Pharma develops innovative treatments like CAR-T cell therapy, setting them apart from competitors.
This high degree of differentiation can significantly weaken competitive rivalry. When customers perceive unique benefits, they are less likely to switch based solely on price. For example, in 2023, Fosun Pharma's pipeline continued to advance, with several innovative drugs progressing through clinical trials, underscoring their commitment to R&D and product uniqueness. This focus on innovation reduces the direct impact of rivals offering similar, albeit less differentiated, products.
Exit Barriers
Fosun International faces heightened competitive rivalry in sectors with substantial exit barriers. For instance, its significant capital commitments in areas like resort development or pharmaceutical manufacturing mean companies are often compelled to remain operational even when facing low profitability. This reluctance to exit intensifies competition as players fight harder for existing market share.
These high exit barriers can trap companies in industries, leading to prolonged and often aggressive competition. This situation is particularly relevant for Fosun as it operates across diverse industries, some of which inherently require massive upfront investments and specialized assets. For example, consider the capital intensity of building and maintaining large-scale resort properties, a segment Fosun has been active in. If market conditions sour, divesting such assets is not straightforward or cost-effective, forcing continued operation and competition.
- High Capital Investment: Industries like pharmaceuticals and tourism demand significant upfront and ongoing capital expenditure, creating substantial financial ties that discourage withdrawal.
- Specialized Assets: Many of Fosun's operational assets are highly specialized, making them difficult to redeploy or sell, thus increasing the cost and complexity of exiting.
- Employee and Stakeholder Commitments: Large workforces and long-term contracts with suppliers or customers also act as deterrents to exiting, as companies must consider the impact on stakeholders.
- Regulatory Hurdles: In some regulated sectors where Fosun operates, such as healthcare, there may be regulatory approvals or divestment restrictions that further complicate exiting a market.
Competitor Diversity
Fosun International navigates a highly competitive landscape characterized by significant competitor diversity. Its operations span sectors like insurance, healthcare, and leisure, encountering a broad spectrum of rivals. These range from established global insurance giants with deep pockets and extensive market reach, to nimble, tech-focused startups disrupting traditional models in healthcare. In 2024, the financial services sector alone saw continued consolidation, with major players like Berkshire Hathaway and Ping An Insurance demonstrating strong performance and aggressive expansion strategies, adding to the competitive pressure on Fosun.
This multifaceted competitive environment means Fosun must contend with varying strategic approaches. Some competitors focus on aggressive pricing, while others prioritize innovation or brand loyalty. For instance, in the healthcare segment, companies like UnitedHealth Group continue to invest heavily in digital health solutions, creating a need for Fosun to match technological advancements to remain competitive. The sheer variety of players, each with different cost structures and market objectives, leads to unpredictable competitive dynamics.
- Global Conglomerates: Large, diversified companies often compete across multiple of Fosun's business units.
- Specialized Niche Players: Focused companies excel in specific segments, offering deep expertise.
- Tech-Driven Startups: Emerging companies leverage technology to challenge established players, particularly in digital services.
- Regional Competitors: Local companies with strong brand recognition and understanding of specific markets pose a significant challenge.
Fosun International faces intense competitive rivalry across its diverse portfolio, ranging from fragmented consumer markets to concentrated sectors like pharmaceuticals. In 2024, the global pharmaceutical market, where Fosun is active, saw giants like Pfizer and Merck investing heavily in R&D, intensifying competition. Conversely, the Chinese consumer electronics market remained a battleground of price and features among numerous brands.
Industry growth rates significantly shape this rivalry. While robust expansion in sectors like healthcare in 2023 provided opportunities to gain market share, slower growth in mature markets in 2024 forces companies to engage in aggressive tactics like price wars to retain customers. Fosun's strategy of product differentiation, seen in Club Med’s unique experiences and Fosun Pharma’s innovative treatments, aims to mitigate direct price competition.
High exit barriers, such as substantial capital investments in pharmaceuticals and tourism, trap companies in markets, leading to prolonged and aggressive competition. Fosun must navigate rivals including global conglomerates, specialized niche players, tech-driven startups, and strong regional competitors, each employing distinct strategies from aggressive pricing to technological innovation.
| Industry Segment | Key Competitors (Examples) | Competitive Intensity (2024 Outlook) | Fosun's Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Pfizer, Merck, Novartis | High (driven by R&D and market concentration) | Product differentiation via innovative treatments (e.g., CAR-T) |
| Insurance | Ping An Insurance, Berkshire Hathaway | Moderate to High (consolidation and digital disruption) | Leveraging 'wealth' ecosystem, digital integration |
| Tourism/Leisure | Accor, Marriott International | High (fragmented with global players) | Unique experiences (Club Med), brand loyalty |
| Consumer Goods | Numerous domestic and international brands | Very High (fragmented, price-sensitive) | Brand building, localized offerings |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The attractiveness of substitutes for Fosun International's diverse business segments hinges significantly on the price-performance trade-off they present to consumers. For example, within its pharmaceutical division, Fosun Pharma faces potential substitution from generic drug manufacturers. If these generics offer comparable efficacy at a substantially lower price, they pose a direct threat to Fosun's branded medicines, impacting market share and pricing power. In 2024, the global generic drug market continued its robust growth, estimated to reach over $235 billion, highlighting the persistent competitive pressure from lower-cost alternatives.
Similarly, Fosun Tourism Group might encounter substitutes in the form of independent travel planning services or alternative leisure activities. If consumers perceive that they can achieve a similar or superior travel experience by booking flights and accommodations separately or by choosing different forms of recreation, this erodes the appeal of Fosun's packaged tours. The rise of online travel agencies and personalized itinerary builders, offering greater flexibility and often lower costs, exemplifies this threat, with the online travel market projected to exceed $1.7 trillion by 2027.
Fosun International faces a heightened threat from substitutes when customer switching costs are low. For instance, in the leisure and tourism sector, where Fosun has significant interests, consumers can easily shift between different holiday destinations or entertainment options without incurring substantial financial penalties or needing to learn new skills. This ease of switching directly amplifies the competitive pressure from alternative offerings.
Consider the healthcare segment. If patients can readily switch to other clinics or hospitals offering similar services without significant upfront investment or disruption to their treatment, the appeal of Fosun's healthcare providers is diminished by substitutes. In 2024, the global healthcare market saw continued innovation, with telehealth and specialized clinics emerging as increasingly accessible alternatives, making customer loyalty more challenging to maintain based purely on service provision.
The threat of substitutes is a considerable challenge for Fosun International. Many of Fosun's diverse businesses, from financial services to tourism and healthcare, face competition from alternative offerings that can satisfy similar customer needs. For instance, the traditional banking and insurance sectors, where Fosun has a significant presence, are increasingly challenged by agile fintech companies providing digital-first solutions.
In the tourism sector, the rise of digital platforms offering virtual experiences or alternative leisure activities can siphon demand away from traditional physical travel. Fosun's health and wellness segment also contends with a growing array of preventative health solutions and digital wellness platforms that may substitute for more conventional healthcare services.
Consider the financial services landscape: in 2023, fintech investment globally reached over $140 billion, indicating the rapid innovation and adoption of alternative financial solutions. This constant influx of new technologies and business models creates a dynamic environment where substitute threats can emerge quickly, requiring Fosun to remain adaptable and forward-thinking across its portfolio.
Perceived Value of Substitutes
The perceived value of substitutes significantly impacts Fosun International's competitive landscape. If customers view alternative offerings as providing comparable or even better benefits, the threat posed by these substitutes intensifies. This perception can stem from enhanced convenience, lower costs, or an improved overall customer experience. For instance, the rise of telemedicine platforms offers a compelling substitute for traditional in-person healthcare consultations, a sector where Fosun has significant interests.
For example, in the healthcare sector, the growing adoption of virtual consultations has provided a viable alternative to in-person visits. By early 2024, many healthcare systems reported a substantial increase in telemedicine utilization, with some seeing patient adoption rates climb by over 100% compared to pre-pandemic levels. This shift suggests that for certain medical needs, the convenience and accessibility of remote consultations are now highly valued, potentially reducing the need for Fosun's physical healthcare facilities or services if they don't adapt.
The threat of substitutes is further amplified when these alternatives become more accessible or offer a more streamlined user journey. Consider the financial services industry, where digital-only banks and fintech companies are increasingly challenging traditional banking models. These entities often provide lower fees, faster transaction times, and more intuitive mobile interfaces. Fosun's diverse financial holdings, including its banking and insurance segments, must contend with this evolving customer preference for digital-first solutions.
Key factors contributing to the perceived value of substitutes include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Substitutes that offer lower prices without a significant compromise on quality.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Alternatives that are easier to obtain or use, such as online services versus physical locations.
- Performance and Quality Improvements: Substitutes that offer superior features, technology, or user experience.
- Brand Reputation of Substitutes: Established or rapidly growing brands in substitute industries can sway customer perception.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are a significant driver of substitute threats for Fosun International. Rapid innovations can quickly render existing products and services less appealing or even obsolete, forcing companies to adapt or risk losing market share. For instance, consider the burgeoning field of AI-driven health diagnostics. These systems, by offering faster, more accurate, and potentially more accessible diagnoses, could emerge as potent substitutes for traditional medical services offered by Fosun’s healthcare subsidiaries.
Similarly, the travel and tourism sector, a key area for Fosun, is not immune. Virtual reality (VR) tourism experiences are rapidly improving, offering immersive ways to explore destinations without the cost and time commitment of physical travel. This could present a compelling substitute for traditional holiday packages and resort stays. In 2024, the global VR tourism market was valued at approximately $4.5 billion and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a tangible shift in consumer preferences and potential disruption.
Financial services also face disruption from technology. Blockchain technology and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms are creating new ways to manage and transact assets, potentially substituting traditional banking and investment services provided by Fosun's financial arms. The global DeFi market capitalization, while volatile, has seen substantial growth, with key metrics often surpassing hundreds of billions of dollars in total value locked, underscoring the disruptive potential of these technologies.
- AI in Healthcare: AI diagnostic tools are improving accuracy and speed, challenging traditional medical practices.
- VR Tourism: Immersive virtual experiences offer an alternative to physical travel, impacting the hospitality sector.
- Blockchain & DeFi: These technologies are reshaping financial services, providing potential substitutes for established institutions.
- Market Trends: The growing adoption of these technologies signals a shift in consumer behavior and emerging competitive pressures.
The threat of substitutes for Fosun International is significant across its varied business segments. For instance, in healthcare, the increasing adoption of telemedicine and AI-driven diagnostics provides accessible alternatives to traditional services. In 2024, telemedicine platforms saw continued high patient engagement, with some reporting over a 100% increase in usage compared to pre-pandemic levels. Similarly, the tourism sector faces substitutes like virtual reality experiences, with the VR tourism market valued at approximately $4.5 billion in 2024, offering immersive travel without physical presence.
In financial services, fintech innovations and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms present potent substitutes for conventional banking and insurance. DeFi's market capitalization has frequently reached hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating a substantial shift towards digital-first financial solutions. These alternatives often offer greater cost-effectiveness, convenience, and improved user experiences, intensifying competitive pressure on Fosun’s established offerings.
The ease with which customers can switch to these substitutes, often with low switching costs, amplifies the threat. Whether it's choosing a digital bank over a traditional one or opting for a virtual holiday over a package tour, the low barriers to entry for substitutes mean Fosun must constantly innovate to retain customer loyalty and market share.
Key substitute threats impacting Fosun International by sector include:
| Sector | Primary Substitute Threats | 2024 Market Data/Trends |
| Healthcare | Telemedicine, AI Diagnostics, Wellness Apps | Telemedicine usage remains high; AI in diagnostics shows rapid accuracy improvements. |
| Tourism | VR Tourism, Independent Travel Planning, Alternative Leisure Activities | VR Tourism market valued at ~$4.5 billion; growth in DIY travel planning platforms. |
| Financial Services | Fintech, DeFi Platforms, Digital-Only Banks | DeFi market capitalization in hundreds of billions; Fintech investment remains strong. |
Entrants Threaten
Fosun International operates in sectors like pharmaceuticals and tourism, where the sheer cost of entry is a major deterrent. For instance, setting up a pharmaceutical manufacturing facility demands significant investment in research, development, and regulatory compliance, often running into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. Similarly, developing a large-scale integrated tourism resort requires massive upfront capital for land acquisition, construction, and infrastructure.
Fosun International, a sprawling global investment conglomerate, leverages significant economies of scale. This cost advantage is evident across its diverse business units, from manufacturing and procurement to research and development and marketing efforts. For instance, in 2024, Fosun's consolidated revenue reached approximately $15 billion, allowing for bulk purchasing power and shared operational efficiencies that smaller competitors simply cannot match.
New entrants face a formidable barrier in replicating these scale-driven cost efficiencies. Attempting to enter Fosun's various markets without comparable scale would necessitate higher per-unit costs, making it exceedingly difficult to compete on price with Fosun’s established, cost-optimized operations.
Established brands like Club Med, a significant asset within Fosun Tourism Group, and the strong reputation of Fosun Pharma create substantial barriers for new entrants. These existing brands have cultivated deep customer loyalty and distinct market identities, making it challenging for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, Club Med's decades-long presence and unique all-inclusive vacation model have built a dedicated customer base.
New players entering the markets where Fosun operates must contend with the considerable effort and capital required to build similar brand recognition and trust. Overcoming established customer preferences and the inherent appeal of well-known brands demands strategic marketing, product innovation, and a significant financial commitment. This process often takes years, if not decades, to achieve a comparable level of market penetration and customer loyalty.
Access to Distribution Channels
Gaining access to established distribution channels represents a significant hurdle for new entrants looking to compete with Fosun International. For instance, within the healthcare sector, securing partnerships with major hospital networks or widespread pharmacy chains is paramount, and these established relationships are difficult for newcomers to replicate.
Similarly, in the tourism industry, reliance on established online booking platforms and experienced travel agencies is critical for reaching a broad customer base. Newcomers often struggle to gain visibility and trust on these platforms, which are dominated by existing players.
Fosun International benefits from its existing, robust networks across various sectors, which directly translates into a competitive advantage. These established channels reduce the friction for bringing new products and services to market and reaching target consumers efficiently.
Consider the healthcare segment: In 2024, securing shelf space in major pharmacy chains, which often have limited capacity and stringent selection processes, posed a significant challenge for emerging pharmaceutical brands. Fosun's established relationships with key distributors and retailers in this area provide a distinct advantage.
- Barrier to Entry: Established distribution channels are a major obstacle for new companies.
- Healthcare Example: Accessing hospital networks and pharmacy chains is crucial for healthcare product distribution.
- Tourism Example: Dominant booking platforms and travel agencies are vital for market penetration in tourism.
- Fosun's Advantage: Fosun's existing networks offer a significant competitive edge against new entrants.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation act as a significant barrier for new entrants looking to compete with established players like Fosun International. Sectors where Fosun operates, such as healthcare and financial services, are often subject to rigorous governmental oversight. For instance, in 2024, China's financial sector continued to emphasize stricter capital requirements and compliance protocols for institutions, making it harder for new companies to gain a foothold without substantial investment in meeting these standards.
Navigating this complex regulatory environment requires new entrants to secure numerous approvals and adhere to stringent operational standards. This process is not only time-consuming but also incurs significant costs, deterring many potential competitors. The ongoing focus on financial stability and consumer protection in major markets where Fosun has a presence means that regulatory hurdles are likely to remain high, if not increase, in the coming years.
The threat of new entrants is therefore mitigated by the substantial resources and expertise required to comply with evolving government policies. This includes:
- Obtaining necessary licenses and permits, which can take months or even years.
- Meeting capital adequacy ratios and solvency requirements, particularly in financial services.
- Complying with data privacy and security regulations, such as those impacting healthcare and fintech.
- Adhering to industry-specific operational and ethical standards set by regulatory bodies.
The threat of new entrants for Fosun International is considerably low due to high capital requirements and established economies of scale. For example, in 2024, the significant investment needed for pharmaceutical R&D and manufacturing, often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars, acts as a substantial barrier. Fosun's consolidated revenue of around $15 billion in 2024 further amplifies its cost advantages, making it difficult for smaller, less capitalized competitors to match its pricing or operational efficiency.
Brand loyalty and established distribution networks also deter new players. Fosun's well-recognized brands, like Club Med, and its strong relationships with healthcare distributors, cultivated over years, present formidable challenges for newcomers seeking market access and customer trust. Navigating complex regulatory environments, particularly in finance and healthcare, adds another layer of difficulty, requiring extensive time and capital for compliance.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example for Fosun (2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment needed for operations. | Pharmaceutical manufacturing: $100M+; Tourism resorts: Significant land and construction costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale operations. | Fosun's ~$15B revenue enables bulk purchasing and shared R&D costs. |
| Brand Loyalty | Established customer preference for existing brands. | Club Med's unique vacation model and Fosun Pharma's reputation. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to established networks for sales and marketing. | Securing shelf space in major pharmacies; visibility on travel booking platforms. |
| Government Regulation | Compliance with industry-specific rules and licenses. | Stricter capital requirements in Chinese finance; healthcare product approvals. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Fosun International is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Fosun's annual reports, filings with regulatory bodies like the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, and insights from reputable financial news outlets and industry-specific publications.
