First Watch Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
First Watch Bundle
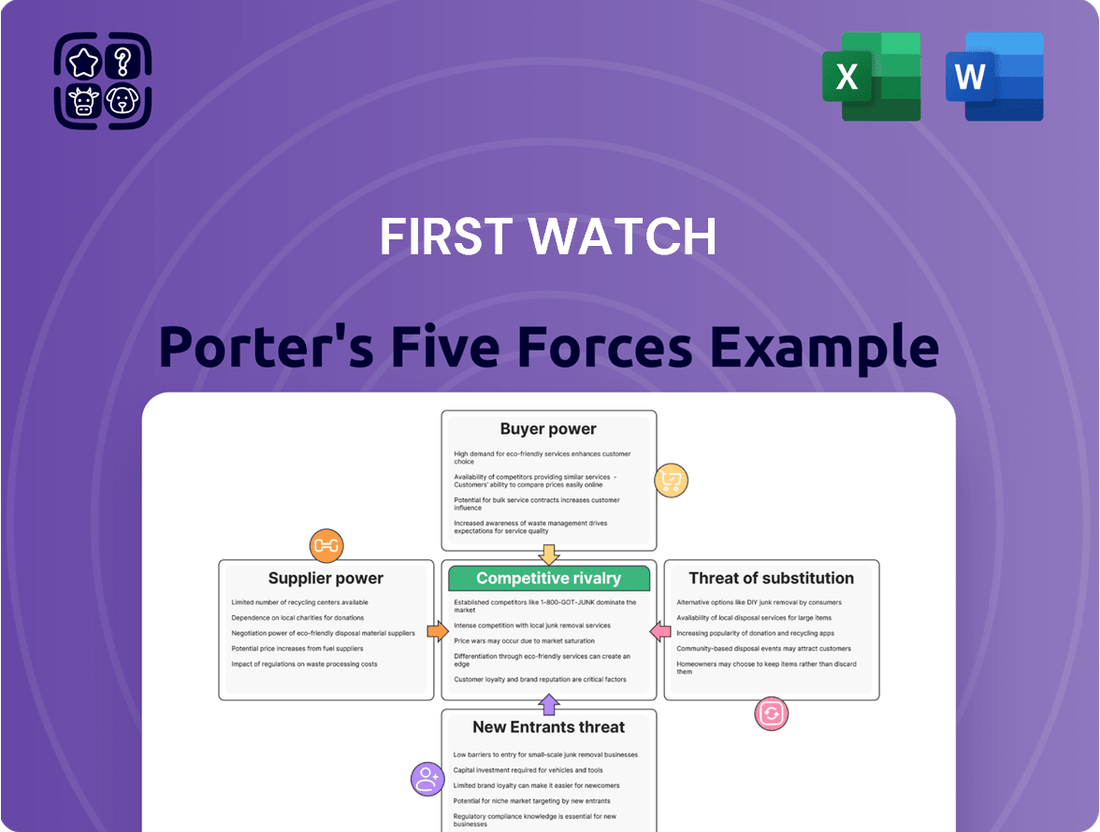
First Watch operates in a competitive restaurant landscape, where understanding the five key forces is crucial for sustained success. This analysis reveals the delicate balance of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the ever-present threat of new entrants and substitutes.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping First Watch’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
First Watch's reliance on a concentrated group of suppliers for key fresh ingredients and specialty items significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. This dependence means that any supply chain hiccups or delivery delays from these few providers can directly disrupt First Watch's operations and menu consistency, a critical factor for its brand promise.
For instance, in the competitive restaurant industry, a single supplier of a unique coffee bean or a specific type of produce might hold considerable sway. If this supplier decides to increase prices or alter terms, First Watch has limited alternatives, potentially impacting its cost of goods sold and profitability. This situation was evident in 2024, where rising agricultural commodity prices, such as coffee beans and certain vegetables, put pressure on restaurant chains to either absorb costs or pass them on to consumers.
The restaurant industry, including players like First Watch, is feeling the heat from increasing input costs. This directly boosts the bargaining power of suppliers. For instance, the Producer Price Index for food away from home saw a significant uptick, contributing to higher costs for restaurants.
Labor expenses are also on the rise, with many states and cities implementing higher minimum wages. These escalating costs for suppliers mean they can more easily pass those increases along to their customers, like First Watch, squeezing profit margins.
First Watch's dedication to fresh, made-to-order meals and seasonal ingredients means they often rely on suppliers offering specialized or premium products. This reliance can give suppliers more sway, especially if the ingredients are unique and hard to replace. For instance, if a particular farm supplies a key seasonal fruit used in a signature dish, and that fruit isn't readily available elsewhere, that supplier's bargaining power increases significantly.
Switching Costs for First Watch
Switching suppliers for First Watch's core fresh ingredients and proprietary blends could incur significant costs. These include the effort and expense of identifying and vetting new reliable sources, renegotiating contracts, and reconfiguring existing supply chain logistics to accommodate different products or suppliers. These potential hurdles can empower existing suppliers by making it less attractive for First Watch to switch.
However, First Watch's expanding scale as a growing restaurant chain can provide some leverage. The ability to commit to larger purchase volumes often grants more bargaining power, potentially offsetting some of the supplier's advantage. For instance, in 2023, First Watch reported revenue of $1.07 billion, indicating a substantial purchasing volume that could influence supplier terms.
- Potential Switching Costs: Identifying new suppliers, contract negotiation, and supply chain adjustments.
- Supplier Leverage: Higher switching costs can strengthen the bargaining position of existing suppliers.
- First Watch's Counter-Leverage: Growing scale and large purchase volumes offer negotiation power.
- Financial Context: First Watch's 2023 revenue of $1.07 billion underscores its significant purchasing capacity.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers moving into food service themselves, becoming direct competitors, is a theoretical concern for First Watch. While uncommon in the restaurant sector, a supplier controlling unique, high-quality ingredients could consider direct-to-consumer sales or even operating their own eateries to capture more value.
For First Watch, this risk is generally considered low. However, the brand's commitment to fresh, seasonal ingredients means that any supplier offering particularly distinctive or proprietary items could potentially explore such forward integration strategies.
This potential move by suppliers could disrupt First Watch's supply chain and introduce new competitive pressures. For instance, if a major produce supplier began operating cafes, they could leverage their direct ingredient access to undercut First Watch on price or offer a more integrated farm-to-table experience.
While not a primary concern, First Watch must remain aware of its key suppliers' capabilities and market positioning. Monitoring for any signs of diversification into restaurant operations is prudent, especially for those suppliers providing unique or hard-to-source ingredients that form a core part of First Watch's menu appeal.
First Watch's reliance on specialized suppliers for fresh, seasonal ingredients, like unique coffee beans or specific produce, grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. This is amplified when these ingredients are difficult to substitute, leading to potential price increases that impact First Watch's cost of goods sold. For example, in 2024, rising agricultural commodity prices, such as those for coffee and certain vegetables, directly pressured restaurant chains, including First Watch, to manage higher input costs.
The restaurant industry, in general, faced escalating input costs in 2024, with the Producer Price Index for food away from home showing notable increases. This environment inherently strengthens suppliers' ability to pass on higher expenses. Furthermore, rising labor costs for suppliers, driven by increased minimum wages in many regions, contribute to their enhanced bargaining position, allowing them to charge more to businesses like First Watch.
First Watch's commitment to fresh, made-to-order meals and seasonal items means it often depends on suppliers offering premium or specialized products. If a key supplier for a unique seasonal fruit or a proprietary blend holds a near-monopoly on that item, their leverage increases substantially, especially if alternatives are scarce or of lower quality. The potential switching costs for First Watch, including finding, vetting, and integrating new suppliers, further solidify the bargaining power of its current providers.
Despite these pressures, First Watch's growing scale offers some counter-leverage. With reported revenues of $1.07 billion in 2023, the company possesses significant purchasing volume, which can be used to negotiate more favorable terms with suppliers. This scale can help mitigate some of the impact of increased supplier bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on First Watch | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier bargaining power | Reliance on few suppliers for specialty ingredients |
| Ingredient Specificity | Strengthens supplier leverage | Use of unique seasonal produce and proprietary blends |
| Input Cost Inflation | Empowers suppliers to raise prices | Rising agricultural commodity prices in 2024 |
| Switching Costs | Reduces First Watch's ability to switch | Costs associated with vetting and integrating new suppliers |
| First Watch's Scale | Provides counter-leverage | $1.07 billion in revenue (2023) |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for First Watch, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the breakfast/brunch market.
Instantly identify and prioritize competitive threats with a clear, visual representation of each force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers today are definitely watching their wallets more closely. With inflation impacting household budgets, dining out is often one of the first areas where people look to save money. This means if First Watch's prices feel a bit too steep compared to other options, customers have the leverage to simply go elsewhere.
The fast-casual dining sector, where First Watch competes, has shown resilience, with some reports indicating continued growth in 2024. However, this doesn't mean customers are immune to price concerns. They are actively comparing prices and value propositions across the board, giving them significant bargaining power.
The availability of substitutes significantly boosts customer bargaining power for First Watch. Customers have a wide array of choices for breakfast, brunch, and lunch, ranging from casual dining restaurants and quick-service establishments to coffee shops, grocery store prepared foods, and even home-cooked meals. This abundance of alternatives means customers can easily switch if they perceive better value elsewhere.
For instance, the fast-casual dining segment, a direct competitor, saw continued growth in 2023 and into 2024, with many players offering convenient and often lower-priced options. This ease of switching, often driven by price or convenience, forces First Watch to constantly demonstrate its unique value proposition to retain customers.
First Watch has built a solid brand reputation, earning accolades like a 'Most Loved Workplace' and recognition as a top restaurant brand on Yelp. This strong appeal fosters customer loyalty, making them less likely to switch to competitors. For instance, in 2023, First Watch continued to see positive customer sentiment reflected in its online reviews and brand mentions, a testament to its efforts in creating a desirable dining experience.
Information Availability and Digital Platforms
The pervasive influence of online reviews, social media, and digital ordering platforms significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Customers can readily compare First Watch’s menu offerings, pricing, and user-generated feedback, while also benefiting from convenient takeout and delivery options. This heightened transparency and ease of access empower consumers, enabling them to exert greater influence and demand tailored experiences or superior value.
For instance, in 2024, platforms like Yelp and Google Reviews saw millions of user contributions, allowing potential diners to thoroughly research restaurant options before making a choice. The rise of third-party delivery services, which saw continued growth through 2024, further solidifies customer convenience and, by extension, their leverage. This digital ecosystem means customers can easily switch between dining establishments, putting pressure on First Watch to maintain competitive pricing and high-quality service.
- Information Access: Customers can easily access vast amounts of information about First Watch and its competitors through online reviews, social media, and restaurant aggregator sites.
- Price Comparison: Digital platforms facilitate effortless comparison of prices across different breakfast and brunch establishments.
- Convenience: The availability of online ordering, takeout, and delivery services increases customer convenience and reduces switching costs.
- Brand Perception: Online sentiment and reviews directly impact brand perception, giving customers a collective voice to influence demand.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
For the average diner, the cost and effort involved in choosing a different restaurant for breakfast, brunch, or lunch are relatively low. There are no significant contractual obligations or investments tied to a particular restaurant, making it simple to switch. This low switching cost empowers customers to easily take their business elsewhere if they are dissatisfied with price, quality, or service.
This ease of switching directly impacts First Watch's ability to retain customers. For instance, if a competitor offers a slightly lower price or a more appealing menu item, customers can readily shift their patronage. This dynamic is particularly relevant in the casual dining sector where brand loyalty can be less entrenched compared to industries with higher switching barriers.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers face minimal financial or psychological costs when moving to a competitor.
- Ease of Comparison: Information on pricing and offerings is readily available, facilitating easy comparison between restaurants.
- Customer Choice: In 2024, the casual dining market, especially for breakfast and lunch spots, offers abundant choices, further reducing customer reliance on any single establishment.
Customers wield significant bargaining power due to the abundance of dining alternatives, especially in the breakfast and lunch segments. The ease with which consumers can compare prices and offerings online, coupled with low switching costs, means First Watch must continually prove its value to retain patronage. This dynamic is amplified by readily available information and convenient digital platforms, allowing customers to easily shift their spending.
| Factor | Impact on First Watch | Supporting Data (2024 Estimates/Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Fast-casual dining segment growth estimated at 5-7% in 2024, indicating increased competition. |
| Information Availability | High | Over 90% of consumers use online reviews to research restaurants before visiting. |
| Switching Costs | Low | No significant financial penalties or loyalty programs that lock in customers for most casual dining. |
| Price Sensitivity | Moderate to High | Inflationary pressures in 2023-2024 led to a 10% increase in consumer focus on value dining. |
Full Version Awaits
First Watch Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete First Watch Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of industry competitiveness. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing sections. You can confidently acquire this detailed analysis, ready for immediate application to your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The breakfast, brunch, and lunch sector is incredibly crowded, featuring a wide array of businesses from small, local diners to major national brands. This fragmentation means First Watch faces a constant barrage of competition across various restaurant categories, including fast-casual, casual dining, and quick-service establishments that all vie for the same daytime customer. In 2024, the U.S. restaurant industry saw continued growth, with breakfast and brunch concepts specifically demonstrating resilience, further intensifying the competitive landscape for players like First Watch.
The breakfast and fast-casual dining sectors are booming, drawing in both established brands and new entrants. This heightened attractiveness fuels intense competition as companies battle for dominance.
In 2024, the breakfast market has seen a substantial uptick in transactions, demonstrating robust consumer demand and reinforcing the segment's appeal.
This growth, while promising, intensifies rivalry as businesses strive to capture a larger slice of this expanding market, leading to more aggressive strategies.
First Watch carves out its niche by emphasizing fresh, made-to-order meals, a strong selection of healthy choices, and the use of seasonal ingredients, all within a relaxed dining atmosphere. This commitment to quality ingredients and a specific dining experience aims to set it apart.
While First Watch champions freshness, many competitors in the breakfast and brunch segment also highlight similar attributes, such as using fresh ingredients or offering distinctive menu items. This means the competitive landscape is populated by players who can also claim a focus on quality.
The challenge for First Watch, and indeed for many in this sector, lies in its ongoing capacity for innovation. Continuously evolving its menu and enhancing the overall dining experience is paramount for maintaining a competitive edge and attracting customers in a market with numerous appealing options.
Aggressive Expansion by First Watch
First Watch is demonstrating significant ambition in the casual dining space. The company has outlined plans to launch between 59 and 64 new restaurants in 2025, with a much larger long-term objective of establishing 2,200 locations nationwide. This aggressive growth trajectory, which also includes the strategic acquisition of existing franchise-owned sites, directly intensifies competition for other businesses operating within the daytime dining segment.
This expansion directly impacts competitive rivalry by:
- Increasing Market Saturation: First Watch's rapid store rollout means more locations vying for the same customer base, putting pressure on rivals to differentiate or match their growth.
- Driving Innovation and Efficiency: To compete, other players may need to innovate their menus, service models, or operational efficiencies to maintain their market share against First Watch's expanding footprint.
- Potential for Price Wars: As more competitors enter a given market, there's an increased likelihood of promotional activities or price adjustments to attract and retain customers.
High Exit Barriers
First Watch, like many in the casual dining sector, faces high exit barriers. Significant investments in kitchen equipment, dining spaces, and leasehold improvements represent substantial sunk costs. For instance, setting up a new restaurant can easily cost upwards of $500,000 to $1 million, making it difficult for underperforming locations to simply shut down without substantial financial loss.
These high fixed costs mean that even restaurants experiencing declining sales may continue to operate, contributing to market overcapacity. This persistence of struggling players intensifies competitive rivalry, often leading to price wars or aggressive promotional activities as companies fight to maintain market share rather than exit.
- Significant Capital Investment: Opening a casual dining restaurant often requires hundreds of thousands of dollars in initial setup costs.
- Specialized Workforce: Retaining and retraining staff can be costly, further discouraging immediate closure.
- Brand Equity and Leases: Existing brand recognition and long-term lease agreements create obligations that make exiting complex and expensive.
- Market Saturation: The reluctance to exit due to these barriers can exacerbate overcapacity, intensifying competition for all players.
The breakfast and brunch market is intensely competitive, with numerous established brands and emerging players all vying for consumer attention. This crowded field means First Watch constantly faces rivals who also emphasize fresh ingredients and unique menu offerings, making differentiation a continuous challenge.
First Watch’s aggressive expansion plans, aiming for 2,200 locations nationwide, directly heighten rivalry by increasing market saturation and pushing competitors to innovate or adjust pricing. The casual dining sector, including breakfast and brunch, also presents high exit barriers due to substantial upfront investments, meaning even struggling businesses tend to persist, further intensifying competition.
| Competitor Type | Key Differentiators | 2024 Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| National Chains (e.g., IHOP, Denny's) | Brand recognition, extensive menus, broad accessibility | Continue to hold significant market share, but face pressure from fast-casual concepts. |
| Fast-Casual (e.g., Panera Bread, Snooze, an A.M. Eatery) | Freshness, speed of service, healthier options, unique atmospheres | Gained significant traction, directly competing with First Watch for the daytime diner. |
| Independent Cafes/Diners | Local appeal, unique community focus, often lower price points | Provide localized competition, especially in markets where First Watch is expanding. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most direct substitute for dining out at First Watch is preparing meals at home. This trend is amplified by the growing popularity of breakfast meal kits, which provide convenience and restaurant-quality ingredients delivered right to consumers' doors.
Consumers are increasingly embracing at-home meal preparation, particularly for breakfast, a meal often perceived as quicker to make. In 2024, the meal kit market continued its robust growth, with many services offering specialized breakfast options, making home cooking a more appealing and accessible alternative to casual dining establishments like First Watch.
The threat of substitutes for First Watch is significant, primarily from grocery and convenience stores. Consumers can easily find breakfast, brunch, and lunch options at these locations, often at a more budget-friendly price point compared to a sit-down restaurant experience. For instance, the U.S. grocery industry generated over $1.1 trillion in sales in 2023, indicating a vast market readily offering convenient food solutions.
These establishments provide a wide array of grab-and-go items, pre-prepared meals, and even ingredients for quick assembly at home, catering to the demand for speed and affordability. This accessibility and cost-effectiveness make them a compelling alternative for consumers seeking a meal without the full restaurant service.
While First Watch focuses on daytime fast-casual dining, consumers have a wide array of substitutes. These include quick-service restaurants (QSRs) like McDonald's and Starbucks, which are increasingly competitive in the breakfast and brunch space, offering speed and lower price points. In 2023, the QSR segment continued its strong growth, with breakfast sales remaining a significant driver, indicating a direct competitive pressure on First Watch's core offerings.
Shift in Consumer Habits
Evolving consumer behaviors significantly impact the threat of substitutes for businesses like First Watch. The widespread adoption of remote work and a heightened preference for convenience have driven demand for alternative dining options. For instance, the rise of meal kit delivery services and the increasing availability of high-quality ready-to-eat meals from grocery stores offer convenient substitutes for sit-down restaurant experiences.
The "all-day breakfast" trend, while a core offering for First Watch, also broadens the competitive landscape. This means consumers can access breakfast-style foods at various times and from a wider range of establishments, not just dedicated breakfast and brunch spots. This increased accessibility to breakfast items from casual dining chains, fast-food restaurants, and even cafes can dilute the unique appeal of a specialized brunch destination.
In 2024, the food delivery market continued its robust growth, with platforms like DoorDash and Uber Eats reporting significant increases in order volumes. This trend directly correlates with the threat of substitutes, as consumers increasingly opt for the ease of having meals delivered to their homes or offices. For example, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of consumers use food delivery services at least once a month, highlighting a substantial shift in how people access food.
- Increased reliance on food delivery services: Consumers are more frequently choosing delivery for meals, including breakfast and brunch items, directly substituting visits to restaurants.
- Availability of "grab-and-go" options: Grocery stores and convenience stores are expanding their prepared food sections, offering quick alternatives to sit-down meals.
- Diversification of dining choices: The "all-day breakfast" trend means competitors beyond traditional brunch spots now offer similar menu items, increasing substitution possibilities.
- Growth in meal kit and home-cooking solutions: Services providing pre-portioned ingredients or fully prepared meals for home consumption present a significant substitute for restaurant dining.
Value Proposition of Substitutes
The perceived value of substitutes, whether in terms of cost, convenience, or speed, poses a significant threat to First Watch. If consumers feel they can obtain a comparable or sufficiently satisfactory meal for less money or with less effort elsewhere, they are likely to switch. For instance, fast-casual chains offering quick breakfast and lunch options can siphon off customers seeking expediency. In 2024, the average check size at fast-casual restaurants hovered around $15-$20, potentially undercutting First Watch's pricing for a similar perceived meal value.
First Watch's core challenge lies in consistently demonstrating that its commitment to quality, fresh, and often locally-sourced ingredients, coupled with a unique dining experience, justifies its price point over these readily available alternatives. The threat intensifies when substitutes can mimic aspects of First Watch's offering without incurring the same overheads for freshness and service. For example, a local diner might offer breakfast at a lower price, appealing to budget-conscious consumers, even if the ingredient quality differs.
- Cost Advantage of Substitutes: Many quick-service restaurants (QSRs) and even some casual dining establishments can offer breakfast and lunch items at a lower price point, directly competing on cost.
- Convenience and Speed: Drive-thru options and grab-and-go services from competitors provide a significant convenience factor for consumers with limited time.
- Perceived Quality Parity: As the fast-casual market matures, some competitors are enhancing their ingredient sourcing and menu innovation, potentially blurring the lines of perceived quality difference.
- Market Saturation: The sheer number of dining options, from independent cafes to large chains, means consumers have a vast array of substitutes to choose from for their breakfast and lunch needs.
The threat of substitutes for First Watch is substantial, stemming from a variety of readily available and often more affordable alternatives. Consumers can easily opt for preparing meals at home, a trend bolstered by the growth of breakfast meal kits. Furthermore, grocery and convenience stores offer convenient grab-and-go options and pre-prepared meals, frequently at lower price points than a sit-down restaurant. The expansion of quick-service restaurants (QSRs) into the breakfast and brunch market also presents a direct competitive challenge.
The rise of food delivery services in 2024, with significant order volume increases reported by platforms like DoorDash and Uber Eats, further amplifies the threat of substitutes. Over 60% of consumers now use food delivery services monthly, indicating a strong preference for at-home dining. This convenience, coupled with the increasing availability of diverse dining choices, including QSRs and cafes offering breakfast items, means consumers have numerous ways to satisfy their breakfast and lunch needs without visiting a specialized brunch spot.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| Home Meal Preparation | Convenience, Cost Savings, Customization | Meal kit market continued robust growth in 2024. |
| Grocery/Convenience Stores | Speed, Affordability, Variety | U.S. grocery industry sales exceeded $1.1 trillion in 2023. |
| Quick-Service Restaurants (QSRs) | Speed, Lower Price Point, Accessibility | QSR segment saw strong growth, with breakfast sales as a key driver in 2023. |
| Food Delivery Services | Convenience, At-home consumption | Over 60% of consumers use food delivery services monthly (2024). |
Entrants Threaten
Opening new restaurants, particularly multi-unit brands like First Watch, demands significant capital. This includes costs for prime real estate acquisition or leasing, construction and build-out, kitchen equipment, and initial inventory and staffing, often running into millions of dollars per location.
High commercial rent and lease rates in desirable, high-traffic areas present a substantial barrier. For instance, in major metropolitan areas, prime retail space lease costs can easily exceed $50-$100 per square foot annually, making it economically challenging for new, unproven concepts to compete for prime locations.
First Watch benefits from significant brand recognition and deeply ingrained customer loyalty, making it challenging for newcomers to gain traction. The company's consistent recognition, such as being named a 'Most Loved Workplace,' underscores its appeal. High customer satisfaction, often reflected in platforms like Yelp, further solidifies this loyalty.
New entrants face the substantial hurdle of replicating this brand equity. They would need considerable investment in marketing and advertising to even approach First Watch's established presence. Overcoming the existing customer preference for First Watch requires more than just offering similar menu items; it demands building trust and a compelling brand narrative.
Running a restaurant chain like First Watch is operationally intricate. This involves sourcing fresh ingredients daily, ensuring consistent food preparation, training staff effectively, and maintaining high customer service standards across numerous sites. For instance, First Watch emphasizes its commitment to fresh, never-frozen ingredients, which necessitates robust and reliable supplier relationships.
Newcomers face significant hurdles in replicating this complex operational framework. Building efficient supply chains and achieving operational excellence at scale is a substantial barrier. In 2023, the restaurant industry, as a whole, saw average food costs rise, highlighting the ongoing challenge of managing supply chain costs and reliability for all players, including new entrants.
Regulatory Hurdles and Labor Market
New ventures in the restaurant sector confront significant regulatory obstacles. Navigating health codes, obtaining necessary licenses, and complying with zoning regulations can be a protracted and expensive undertaking, often requiring substantial upfront investment and expertise.
The labor market presents another formidable challenge for potential entrants. Ongoing labor shortages, exacerbated by factors like increased demand and a tight job market, coupled with rising minimum wages, make it difficult for new establishments to attract and retain qualified employees. For instance, in 2024, many regions continued to experience elevated wage pressures within the hospitality sector, with some states seeing minimum wage increases taking effect.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Businesses must invest in understanding and adhering to a complex web of local, state, and federal regulations.
- Labor Shortages Impact: Difficulty in staffing can lead to reduced operating hours, decreased service quality, and increased training expenses.
- Wage Inflation: Rising labor costs directly impact profitability, requiring careful menu pricing and operational efficiency.
Rise of Niche and Delivery-Focused Models
The traditional high costs associated with establishing a physical restaurant can be a significant deterrent for new entrants. However, the burgeoning ghost kitchen and delivery-only model landscape is actively reshaping this dynamic. These streamlined operations bypass the need for costly dining room build-outs and prime real estate, effectively lowering the capital required to launch a food service business.
This shift is particularly evident in the food delivery sector. For instance, in 2024, the global food delivery market was projected to reach over $300 billion, signaling substantial consumer adoption and a ripe environment for new, digitally-native concepts. These new entrants can concentrate their resources on developing unique culinary offerings and optimizing their delivery logistics, rather than on the overhead of traditional brick-and-mortar establishments.
- Lowered Capital Investment: Ghost kitchens eliminate the need for expensive dining spaces, reducing upfront costs for new food businesses.
- Focus on Niche Markets: This model allows new entrants to target specific cuisines or dietary preferences with greater agility.
- Delivery Optimization: Businesses can prioritize efficient delivery networks and customer experience without the constraints of dine-in operations.
- Market Growth: The expanding food delivery market provides fertile ground for these agile, delivery-focused new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for a brand like First Watch is moderate. While established players benefit from brand loyalty and operational efficiencies, the rise of ghost kitchens and delivery-only models has lowered the capital barrier to entry, allowing agile newcomers to target niche markets with reduced overhead.
However, significant capital is still required for prime real estate, construction, and initial inventory, alongside the challenge of building brand equity and navigating complex regulations. Labor shortages and wage inflation in 2024 also present ongoing operational hurdles for any new restaurant business.
| Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High (Real Estate, Build-out) | Prime retail lease costs can exceed $50-$100/sq ft annually. |
| Brand Loyalty | Significant Challenge | First Watch's consistent high customer satisfaction scores. |
| Operational Complexity | Substantial Hurdle | Managing fresh ingredient supply chains amidst rising food costs. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Costly and Time-Consuming | Navigating health codes and licensing requirements. |
| Labor Market | Difficult to Staff | Elevated wage pressures and labor shortages in the hospitality sector. |
| Ghost Kitchens/Delivery | Lowered Barrier | Global food delivery market projected over $300 billion in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our First Watch Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and publicly available competitor information to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
