Fuyo General Lease Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fuyo General Lease Bundle
Fuyo General Lease navigates a competitive landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Fuyo General Lease’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Financial capital providers, including banks and bondholders, wield moderate to high bargaining power over Fuyo General Lease. The Bank of Japan's interest rate hikes, initiated in 2024 and expected to continue into 2025, have directly increased Fuyo's borrowing costs, giving lenders more leverage.
Despite Fuyo's long-standing relationships with major financial institutions like Mizuho Bank, the prevailing environment of rising interest rates generally bolsters the negotiating position of these essential capital suppliers. This increased cost of capital directly impacts Fuyo's operational expenses and profitability.
The bargaining power of equipment and asset manufacturers for Fuyo General Lease significantly shifts based on the asset's specialization. For highly specialized items like aircraft engines or advanced energy infrastructure components, where Fuyo operates, suppliers often wield considerable influence due to limited alternatives and proprietary technologies. This was evident in 2024 with continued supply chain constraints for certain high-tech manufacturing inputs.
Conversely, for more standardized or commoditized equipment, the bargaining power of individual manufacturers tends to be less pronounced. A competitive landscape with numerous suppliers means Fuyo can often negotiate more favorable terms. Fuyo's strategic approach of diversifying its leasing portfolio across various industries, from IT to industrial machinery, effectively dilutes the impact of any single equipment supplier's leverage.
As Fuyo General Lease invests more in its BPO and ICT services, the companies that provide the necessary technology and software are gaining more influence. These suppliers, offering critical solutions like advanced analytics platforms or robust cloud infrastructure, are essential for Fuyo's operational efficiency and its ability to offer unique services. For example, the global cloud computing market, a key area for Fuyo's digital expansion, was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion in 2024, highlighting the significant value and potential pricing power of cloud providers.
Real Estate Developers and Property Owners
In Japan's dynamic real estate market, particularly in bustling metropolitan centers, developers and property owners wield considerable influence. This is especially true when market demand is high, allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms. For Fuyo General Lease, this translates into potentially higher costs for acquiring or leasing properties, impacting their asset finance and leasing operations.
The upward trend in construction expenses in 2024 further amplifies the bargaining power of these suppliers. For instance, reports from the Japan Federation of Construction Contractors indicated an average increase in construction material costs by approximately 7% year-over-year through early 2024. This surge directly affects the profitability of Fuyo's real estate ventures, as it increases their capital expenditure and operational costs.
- Developer Influence: Developers can dictate terms on land acquisition and project timelines, impacting Fuyo's ability to secure prime assets.
- Property Owner Leverage: Property owners, especially those with highly sought-after locations, can demand higher lease rates or stricter contract conditions.
- Cost Pressures: Rising material and labor costs in the construction sector (estimated 7% increase in early 2024) empower developers to pass these onto leasing companies like Fuyo.
- Strategic Partnerships: Fuyo General Lease must cultivate strong relationships and strategic alliances with key developers and property owners to mitigate this supplier power.
Human Capital
The bargaining power of skilled human capital within specialized sectors like finance, technology, energy, and healthcare is generally moderate to high. Companies heavily rely on this talent to create innovative solutions and ensure high-quality service delivery.
In 2024, competitive wage pressures and ongoing labor shortages, particularly evident in Japan's tech and finance industries, are amplifying the influence of skilled employees. This trend directly impacts operational costs and necessitates robust strategies for talent acquisition and retention.
- Talent Dependency: Companies in knowledge-intensive industries depend on specialized skills, granting employees significant leverage.
- Labor Market Dynamics: Shortages in critical areas like AI development and cybersecurity in 2024 empower workers with higher bargaining power.
- Cost Implications: Increased demand for skilled professionals can lead to wage inflation, impacting profitability and operational budgets.
- Retention Challenges: Attracting and retaining top talent becomes a strategic imperative, influencing compensation and benefits packages.
Suppliers of specialized equipment, such as advanced manufacturing components or critical IT infrastructure, hold significant bargaining power over Fuyo General Lease. This is due to limited alternative suppliers and proprietary technology, a situation exacerbated by persistent global supply chain challenges observed throughout 2024. For commoditized assets, however, Fuyo benefits from a more competitive supplier landscape, allowing for better negotiation terms.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power | Key Factors | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Equipment Manufacturers | High | Proprietary technology, limited alternatives, supply chain constraints | Continued supply chain issues impacting availability and pricing. |
| Standardized Equipment Manufacturers | Moderate to Low | Competitive market, multiple suppliers | Fuyo can leverage competition for favorable terms. |
| Technology & Software Providers (BPO/ICT) | High | Critical for service delivery, unique solutions, growing market | Global cloud market projected over $1.3 trillion in 2024, increasing provider leverage. |
| Real Estate Developers/Owners | High | Prime locations, high market demand, rising construction costs | Construction material costs up ~7% YoY in early 2024, enabling developers to pass costs. |
What is included in the product
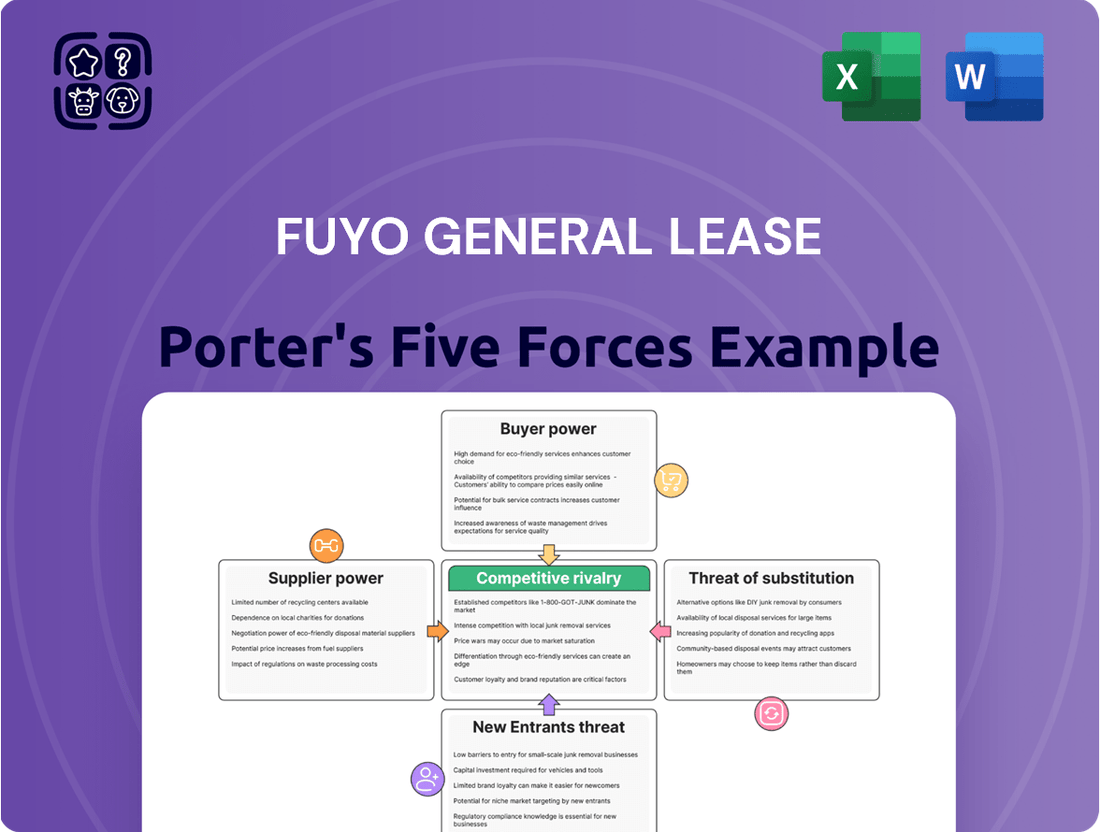
Fuyo General Lease's Porter's Five Forces analysis details the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes within the leasing industry.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces chart, highlighting key pressures on Fuyo General Lease.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats by understanding the interplay of industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fuyo General Lease's broad industry reach, encompassing sectors like manufacturing, IT, and transportation, dilutes the concentrated bargaining power of any single customer segment. For instance, in 2023, its diverse portfolio meant that no single industry accounted for more than 15% of its total leasing revenue, smoothing out demand fluctuations.
Despite this diversification, individual customers within these sectors often possess significant leverage due to the availability of alternative financing and leasing providers. This competitive landscape necessitates Fuyo General Lease's focus on developing highly customized leasing packages that align precisely with client growth objectives and capital expenditure plans.
Customers wield considerable influence when alternative financing, like bank loans or installment plans, is readily available. This gives them choices beyond just leasing, putting pressure on Fuyo General Lease to offer attractive pricing and flexible terms to retain business.
Fuyo General Lease itself provides installment sales, a direct competitor to its leasing services. In 2023, the Japanese banking sector saw continued competition for lending, with interest rates remaining relatively low, further bolstering customer options and their bargaining power.
Large corporate clients, particularly those making significant capital investments or utilizing multiple services from Fuyo General Lease, wield substantial bargaining power. Their sheer volume of business allows them to negotiate more favorable lease terms, preferential interest rates, and customized service packages, directly impacting Fuyo's profitability.
Fuyo's strategic focus on supporting capital expenditures across diverse industries, from manufacturing to IT, means they engage with many of these powerful corporate entities. For instance, in 2023, Fuyo's leasing business saw continued demand from large enterprises seeking to optimize their asset management and financing, underscoring the importance of these client relationships.
Demand for Flexibility and Customization
Customers are increasingly seeking adaptable lease arrangements and versatile commercial spaces. This trend is fueled by changing business operations, such as the widespread adoption of hybrid work models, which necessitate more flexible office solutions. For instance, in 2024, surveys indicated a significant portion of businesses were re-evaluating their office footprints, prioritizing flexibility over long-term commitments.
In the automotive finance sector, a clear shift towards shorter lease terms and customizable payment structures is evident. This preference for flexibility allows customers to better manage their budgets and adapt to changing vehicle needs. By 2024, the average lease term in many developed markets had shortened, reflecting this growing demand for agility.
This heightened demand for customization and flexibility directly amplifies customer bargaining power. Fuyo General Lease, like its competitors, must continually refine its product offerings to meet these evolving expectations. Failure to adapt could result in a loss of market share as customers gravitate towards providers who offer greater choice and responsiveness.
- Demand for adaptable lease terms and multi-purpose spaces is a key driver of customer power.
- Hybrid work models are a significant factor influencing the need for flexible commercial real estate solutions.
- Shorter lease terms and customizable payment plans are increasingly preferred in auto finance.
- Fuyo's ability to offer flexible solutions directly impacts its competitiveness and customer retention.
Information Transparency and Switching Costs
The increasing transparency of financial product information, particularly in leasing, significantly boosts customer bargaining power. With readily available data, customers can easily compare rates, terms, and services across different leasing companies and alternative financing options. For instance, in 2024, online comparison platforms have become ubiquitous, allowing businesses to quickly assess offerings from numerous providers, thereby reducing the perceived uniqueness of any single company's proposition.
Switching costs in the financial services sector, while sometimes present due to specialized solutions or contractual obligations, are generally perceived as decreasing. Customers can more readily move between leasing providers or explore financing alternatives like outright purchase or other forms of credit. This ease of transition means Fuyo General Lease must continuously demonstrate value and superior service to maintain client loyalty, as the financial burden or complexity of switching is often less prohibitive than in the past.
- Information Transparency: Customers can easily access and compare financial product details, including lease rates and terms, from multiple providers.
- Reduced Switching Costs: The effort and expense associated with changing leasing companies or financing methods are often minimal, empowering customers.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of alternative financing solutions and direct comparisons online intensifies pressure on leasing companies to offer competitive pricing and service.
- Customer Retention: Fuyo General Lease must focus on delivering exceptional value and service to mitigate the impact of increased customer bargaining power.
Customers at Fuyo General Lease possess considerable bargaining power, largely due to the increasing availability of alternative financing options and the ease with which they can compare leasing deals. This transparency, amplified by online comparison tools, allows clients to readily assess rates and terms across various providers. For instance, by 2024, the proliferation of digital platforms meant that businesses could evaluate multiple leasing and financing offers within minutes, significantly reducing the perceived switching costs and enhancing their negotiating position.
| Factor | Impact on Fuyo General Lease | Customer Leverage |
| Alternative Financing | Reduces reliance on leasing; necessitates competitive pricing. | High, due to options like bank loans and direct purchase. |
| Information Transparency | Increases price sensitivity; demands clear value proposition. | High, with easy access to comparative data and online tools. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers barriers to entry for competitors; requires strong retention strategies. | Moderate to High, depending on contract specifics. |
| Demand for Flexibility | Requires adaptable product offerings and service models. | Increasing, driven by evolving business needs and hybrid work. |
Same Document Delivered
Fuyo General Lease Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Fuyo General Lease Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual document, detailing the competitive landscape for Fuyo General Lease, including threats of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitute products, and intensity of rivalry. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Japanese leasing market, where Fuyo General Lease operates, is highly mature and intensely competitive due to the presence of several large, established domestic players. Companies like JA Mitsui Leasing and Hitachi Capital Corporation offer a broad spectrum of financial services, mirroring Fuyo's own offerings. This similarity in services fuels a fierce rivalry as these firms vie for market share, often leading to price-based competition and a constant need for innovation to differentiate themselves.
Fuyo General Lease contends with intense rivalry from diversified financial institutions that offer leasing as one of many services. Major Japanese banking conglomerates such as Mizuho Financial Group, Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, and Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation possess vast resources and integrated financial offerings, including leasing, which can create significant competitive pressure. These groups leverage their broad customer bases and extensive financial product suites to cross-sell leasing solutions, making it challenging for specialized leasing companies to compete solely on price or service.
Fuyo General Lease's push into growth areas like mobility, energy, and healthcare pits it against highly specialized competitors. For instance, in the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) leasing market, Fuyo might contend with dedicated EV fleet management companies that possess deep sector expertise and established charging infrastructure partnerships. These niche players can offer tailored solutions that intensify rivalry in specific segments Fuyo aims to penetrate.
While Fuyo leverages differentiation, the very attractiveness of these growth fields draws focused competitors. In the energy and environment sector, for example, companies specializing in solar panel leasing or renewable energy project financing present a direct challenge. These specialized firms often have unique technological advantages or regulatory knowledge, intensifying competition in areas where Fuyo seeks to build its market share.
Overheated Real Estate Market
The real estate market, especially in major urban centers, is experiencing an overheated competitive environment. This intense activity means Fuyo General Lease faces significant rivalry for both prime properties and customers in these crucial strategic locations.
This heightened competition can lead to compressed profit margins as companies vie for market share. For instance, in 2024, the average price-to-rent ratio in many global metropolitan areas remained elevated, indicating strong demand and potentially higher acquisition costs for real estate assets.
- Intense Competition: Metropolitan real estate markets are characterized by a high degree of rivalry, impacting Fuyo General Lease's ability to secure favorable terms.
- Margin Pressure: The 'overheated' nature of the market can squeeze profit margins due to increased costs and competition for clients.
- Strategic Importance: Key metropolitan areas are vital for Fuyo General Lease's operations, making the competitive rivalry in these regions particularly impactful.
M&A and Consolidation Trends
The Japanese M&A market is showing robust activity, with a notable rise in unsolicited takeover bids. This trend signals an increasingly competitive environment where companies actively pursue consolidation and strategic partnerships to gain market share and operational efficiencies. For instance, in 2023, the total value of M&A deals in Japan reached approximately $280 billion, a significant increase from previous years.
Fuyo General Lease itself has strategically utilized M&A to expand its service offerings and geographic reach. Recent examples include acquisitions in business process outsourcing (BPO) services and the purchase of a forklift company in Thailand. These moves demonstrate how competitive actions can involve acquiring complementary businesses, thereby intensifying rivalry among leasing and equipment rental providers.
- Increased M&A Activity: Japan's M&A market saw deals worth around $280 billion in 2023, highlighting a dynamic competitive landscape.
- Unsolicited Bids: A growing number of unsolicited takeover attempts indicates aggressive competitive strategies and potential market restructuring.
- Fuyo's Strategic Acquisitions: Fuyo General Lease's expansion through M&A, such as in BPO and the Thai forklift sector, exemplifies how companies leverage acquisitions to strengthen their competitive position.
- Impact on Rivalry: These consolidation trends and strategic acquisitions directly intensify competition, forcing other players to adapt or risk being outmaneuvered.
Fuyo General Lease operates in a highly competitive Japanese leasing market, facing pressure from large, established domestic players like JA Mitsui Leasing and Hitachi Capital Corporation, who offer similar services. Diversified financial institutions, including major banking groups, also intensify rivalry by cross-selling leasing solutions to their extensive customer bases. Furthermore, specialized niche competitors in growth sectors such as EV leasing and renewable energy financing present targeted challenges, forcing Fuyo to innovate and differentiate to maintain its market position.
| Competitor Type | Example Competitors | Competitive Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Large Domestic Leasing Firms | JA Mitsui Leasing, Hitachi Capital Corporation | Direct competition on services and pricing; need for differentiation. |
| Diversified Financial Institutions | Mizuho Financial Group, MUFG, SMBC Group | Leverage broad customer bases and integrated offerings for cross-selling. |
| Niche/Specialized Competitors | EV fleet management firms, renewable energy financiers | Deep sector expertise and tailored solutions in growth areas. |
| Real Estate Market Competitors | Various developers and property investors | Intense rivalry for prime properties and customers in urban centers. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute for leasing is the outright purchase of assets, often funded by traditional bank loans or corporate bonds. Businesses might choose to own assets outright, especially if they have long-term needs or can leverage specific tax benefits associated with ownership. Fuyo General Lease directly addresses this by offering installment sales, which function as a form of direct financing for asset acquisition.
Cloud services and SaaS represent a potent threat to traditional IT leasing by offering flexible, subscription-based alternatives. Instead of leasing physical hardware and perpetual software licenses, businesses can access computing power and applications on demand, often at a lower upfront cost. This shift significantly reduces the need for capital expenditure on IT assets.
For instance, the global cloud computing market was valued at approximately $610 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear preference for these flexible models. Companies like Fuyo General Lease are responding by expanding into Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) services, aiming to integrate these cloud-based offerings into their portfolio and mitigate the impact of this substitute threat.
For shorter-term needs or specific projects, rental services present a viable alternative to long-term leasing, especially for equipment and vehicles. This flexibility caters to fluctuating demands, making it easier for businesses to access necessary assets without the commitment of ownership or extended leases. For instance, the construction equipment rental market, a significant segment for companies like Fuyo General Lease, was projected to reach over $120 billion globally by 2024, highlighting the substantial appeal of rental solutions.
Internal Asset Management and Self-Funding
Large corporations with significant financial clout, in 2024, increasingly opted for internal asset management and self-funding. This approach allows them to bypass leasing agreements by directly acquiring assets using their own substantial capital reserves. For instance, many large industrial companies, flush with retained earnings, can fund major equipment purchases without needing external financing, thereby circumventing the need for a lessor like Fuyo General Lease.
This internal capability serves as a potent substitute for traditional leasing. Companies prioritizing absolute control over their assets and seeking to avoid lease-related covenants or fees find self-funding particularly attractive. The ability to manage depreciation schedules and eventual asset disposal internally also appeals to firms with sophisticated treasury operations.
- Internal Capital Allocation: Companies can deploy cash and equivalents directly for asset acquisition, bypassing lease payments and interest costs.
- Full Ownership and Control: Self-funding ensures complete ownership, allowing for unrestricted asset modification and disposal.
- Reduced Transaction Costs: Eliminates the administrative and legal overhead associated with lease agreements.
- Tax Implications: Direct ownership may offer different tax depreciation benefits compared to lease accounting.
Emerging Technologies and Business Models
Technological innovation continuously introduces novel substitutes that can quickly diminish the relevance of established products and services. For instance, the rise of shared economy platforms and pay-per-use models directly challenges traditional long-term asset leasing by offering more flexible and potentially cost-effective alternatives.
These evolving consumption-based models, such as mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) or equipment-sharing networks, present a significant threat by reducing the perceived necessity for outright ownership or long-term commitments to assets. This shift directly impacts leasing companies like Fuyo General Lease.
Fuyo's strategic emphasis on 'Rising Transformation' fields, including mobility and the circular economy, demonstrates a proactive approach to understanding and potentially capitalizing on these disruptive trends. This focus suggests an awareness that traditional leasing may need to adapt to new service-oriented and usage-based paradigms.
- Shared Economy Growth: The global shared economy market was valued at approximately $57.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong consumer shift towards access over ownership.
- Mobility as a Service (MaaS): MaaS adoption is accelerating, with projections suggesting it could become a multi-trillion dollar industry by 2030, offering integrated transportation solutions that reduce reliance on individual vehicle ownership and leasing.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Increasing focus on sustainability and resource efficiency is driving demand for rental, leasing, and refurbishment models, which can be both a threat to traditional ownership and an opportunity for adaptable leasing companies.
The threat of substitutes for leasing is multifaceted, encompassing direct purchase, cloud services, rentals, internal funding, and evolving shared economy models. These alternatives offer varying degrees of flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and control, directly challenging the traditional leasing value proposition.
For instance, the increasing adoption of cloud computing, projected to reach over $1 trillion by 2028, directly reduces the need for IT hardware leasing. Similarly, the construction equipment rental market, estimated to exceed $120 billion globally by 2024, provides a readily available substitute for long-term equipment leases.
Large corporations in 2024, leveraging strong balance sheets, increasingly opted for self-funding asset acquisition, bypassing lease agreements altogether. This trend highlights a preference for complete ownership and avoidance of lease-related administrative costs.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristic | Market Indicator (2023/2024 Data) | Impact on Leasing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outright Purchase/Self-Funding | Full ownership, control, potential tax benefits | Large corporations' increased internal capital allocation | Reduced demand for traditional lease financing |
| Cloud Services/SaaS | Subscription-based, pay-as-you-go, reduced upfront cost | Global cloud market valued at ~$610 billion (2023) | Decreased need for IT hardware leasing |
| Rental Services | Short-term flexibility, project-based access | Construction equipment rental market projected >$120 billion (2024) | Alternative for fluctuating asset needs |
| Shared Economy/MaaS | Access over ownership, usage-based models | Shared economy market valued at ~$57.2 billion (2023) | Challenges long-term asset commitments |
Entrants Threaten
The diversified leasing and financial services industry demands significant upfront capital, particularly for large-scale investments across multiple sectors. Fuyo General Lease's extensive operating asset base underscores the immense financial resources necessary to even consider entering this competitive landscape.
For instance, as of March 31, 2024, Fuyo General Lease reported total assets of ¥8,004.6 billion, a figure that highlights the substantial financial muscle required to compete effectively. This high barrier effectively deters many potential new entrants.
The financial services sector in Japan, overseen by the Financial Services Agency (FSA), imposes stringent regulations that new entrants must meticulously follow. These requirements include obtaining complex licenses, adhering to strict compliance protocols, and fulfilling extensive reporting obligations, all of which demand substantial time and financial investment. For instance, in 2023, the cost of compliance for financial institutions in Japan was estimated to be in the billions of yen, a significant deterrent for potential new players.
Fuyo General Lease, established in 1969 and a key player within the Fuyo Group, leverages decades of experience to foster deep-rooted customer relationships and a robust brand presence in the Japanese market. This established trust presents a significant barrier for any new competitor aiming to penetrate the sector.
New entrants would find it exceptionally challenging to replicate the loyalty and confidence that Fuyo General Lease has cultivated over many years. Customers accustomed to Fuyo's commitment to superior service standards are unlikely to switch easily, creating a substantial hurdle for newcomers seeking to gain market share.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Existing players in the leasing sector, such as Fuyo General Lease, leverage significant economies of scale. This allows them to secure more favorable terms on asset procurement and financing due to their substantial purchasing power and established credit lines. For instance, in 2024, major leasing firms often negotiate bulk discounts that can be several percentage points lower on financing costs compared to a new entrant seeking initial capital.
These scale advantages translate directly into operational efficiencies. Fuyo's ability to spread fixed costs across a vast portfolio of leased assets, from vehicles to specialized machinery, reduces per-unit overhead. New companies entering the market would face higher initial operating costs, making it challenging to match the pricing structures of established, scaled competitors.
- Economies of Scale: Fuyo General Lease benefits from lower per-unit costs in procurement and financing due to its large asset base.
- Financing Costs: Established firms in 2024 likely secure financing at rates 1-3% lower than new entrants.
- Operational Efficiency: Spreading fixed operational costs across a larger portfolio significantly reduces overhead for incumbent lessors.
- Price Competition: New entrants struggle to compete on price without achieving similar scale, creating a barrier to entry.
Specialized Expertise and Niche Markets
Fuyo General Lease's strategic expansion into specialized sectors such as energy, environmental solutions, healthcare, and aviation creates significant barriers to entry. Building the deep expertise, sector-specific knowledge, and robust industry connections required to thrive in these niches is a substantial hurdle for new, less specialized competitors.
While Fuyo General Lease is cultivating these specialized capabilities, the threat from new entrants isn't entirely absent. For instance, agile FinTech startups are increasingly targeting specific digital financial service niches within these broader industries, potentially disrupting traditional leasing models with innovative solutions.
- Specialized Investments: Fuyo General Lease is actively investing in high-growth, specialized sectors like energy and environment, healthcare, and aircraft leasing.
- High Barrier to Entry: Developing the necessary technical expertise, regulatory understanding, and established networks in these niche markets is a significant challenge for generalist new entrants.
- FinTech Disruption: Focused FinTech companies may still pose a threat by offering specialized digital financial services within these sectors, potentially bypassing traditional leasing structures.
The significant capital investment required to establish a substantial asset base, coupled with stringent regulatory compliance in Japan's financial services sector, creates a formidable barrier for new entrants. Fuyo General Lease's total assets of ¥8,004.6 billion as of March 31, 2024, illustrate the immense financial scale needed to compete. Furthermore, the complexity and cost of obtaining licenses and adhering to FSA regulations, which can run into billions of yen annually for compliance in 2023, deter many potential challengers.
Fuyo General Lease's established brand reputation and deep customer loyalty, cultivated over decades since its 1969 founding, present another significant hurdle. Newcomers would struggle to replicate the trust and service standards that Fuyo offers, making customer acquisition a challenging endeavor. This is compounded by the economies of scale enjoyed by established players; in 2024, major leasing firms can secure financing at rates 1-3% lower than new entrants, giving them a distinct pricing advantage.
The company's strategic focus on specialized sectors like energy, healthcare, and aviation also raises entry barriers, as these require niche expertise and industry connections. While FinTech startups may target specific digital niches, the overall threat from broad new entrants remains low due to these combined factors.
| Factor | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Fuyo General Lease's Position | Data Point (2024 unless specified) |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for asset acquisition and operational setup. | Significant barrier. | Substantial asset base (¥8,004.6 billion total assets as of March 31, 2024). | |
| Regulatory Environment | Stringent licensing, compliance, and reporting obligations enforced by the FSA. | Time-consuming and costly to navigate. | Established compliance infrastructure. | Estimated compliance costs in billions of yen annually for financial institutions (2023). |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Long-standing customer relationships and trust. | Difficult for new entrants to penetrate. | Decades of experience and strong market presence. | Founded in 1969. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower procurement and financing costs due to large volume. | Creates pricing disadvantages for new entrants. | Leverages significant purchasing power and credit lines. | Financing rates potentially 1-3% lower than new entrants. |
| Sector Specialization | Deep expertise and networks in niche industries (e.g., aviation, healthcare). | Requires specialized knowledge and investment to replicate. | Strategic expansion into high-growth, specialized sectors. | Investments in energy, environmental solutions, healthcare, aviation. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Fuyo General Lease is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Euromonitor and Nikkei, and relevant government economic indicators.
