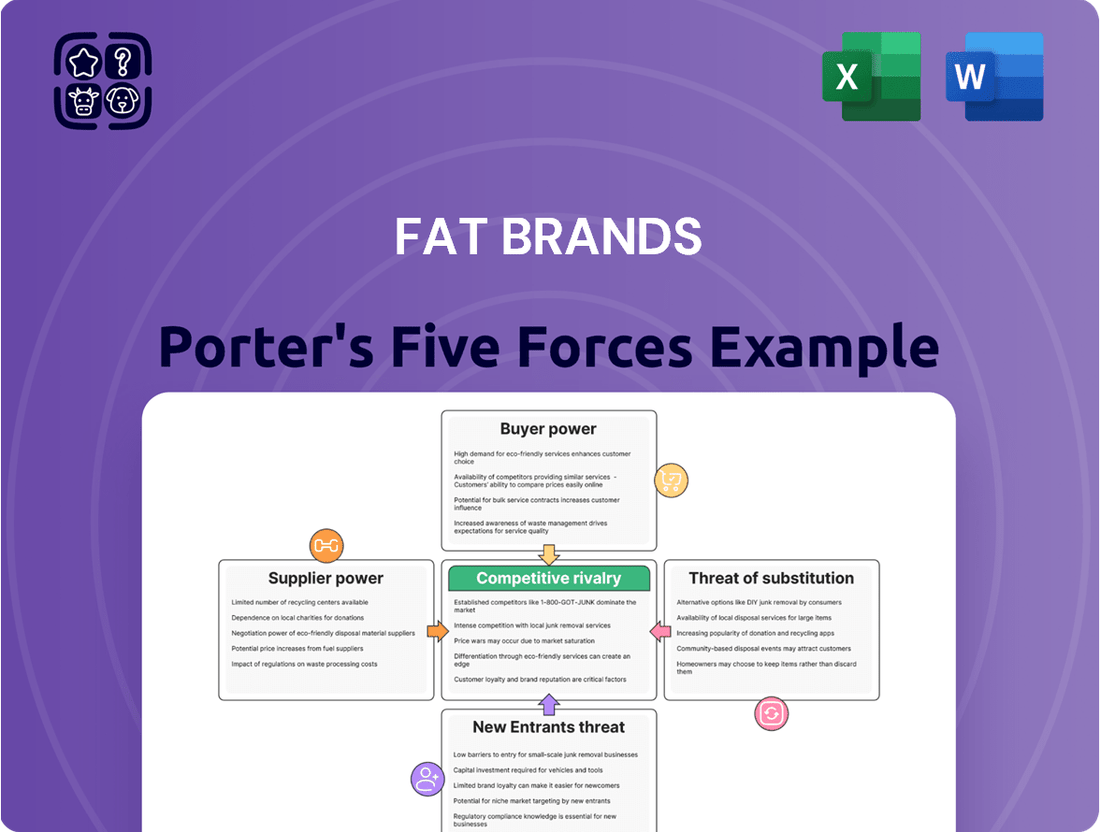
FAT Brands Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
FAT Brands Bundle
FAT Brands faces a dynamic restaurant landscape where buyer bargaining power can shift with consumer trends, and the threat of new entrants is ever-present. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore FAT Brands’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
FAT Brands operates within an industry where a select few suppliers often dominate the market for crucial components. For example, in 2024, the global market for specialized commercial kitchen equipment, essential for restaurant operations, was largely controlled by a handful of manufacturers, estimated to be around 3 to 4 key players. This concentration of suppliers means they hold considerable sway over pricing and contract conditions.
FAT Brands' reliance on a limited number of major food distributors significantly shapes supplier bargaining power. For instance, Sysco Corporation alone fulfills a substantial 65% of the company's ingredient needs.
This concentration means that distributors like Sysco, US Foods (22%), and Performance Food Group (13%) hold considerable sway. Their ability to dictate terms, pricing, and availability is amplified due to FAT Brands' dependence on them for a vast majority of its supply chain requirements.
FAT Brands faces moderate supplier concentration in key areas. For protein ingredients, there are typically 4-5 major suppliers, and for dairy products, it's around 3-4. This concentration can lead to price fluctuations, with protein ingredients seeing annual variations of approximately ±12%.
In contrast, the produce category often features 6-7 regional suppliers, potentially offering FAT Brands more negotiation leverage. However, produce prices can be even more volatile, experiencing annual swings of up to ±15%.
Potential for High Switching Costs
The potential for high switching costs significantly bolsters the bargaining power of suppliers to FAT Brands. For instance, franchise locations can face substantial expenses, estimated between $75,000 and $250,000 per site, when transitioning to new suppliers for essential restaurant equipment and key ingredients.
These considerable financial and operational hurdles make it less appealing for franchisees to frequently change their supply partners. Consequently, suppliers can leverage these high switching costs to command more favorable terms, thereby increasing their influence over FAT Brands.
- High Switching Costs: Franchisees may incur $75,000 to $250,000 per location to switch suppliers for equipment and ingredients.
- Reduced Supplier Turnover: The financial burden discourages frequent supplier changes, reinforcing existing relationships.
- Supplier Leverage: Suppliers can exploit these costs to negotiate better pricing and terms, enhancing their bargaining power.
Impact of Inflation and Supply Chain Challenges
The broader restaurant industry, including brands like FAT Brands, grappled with significant cost increases in recent years. Specifically, food costs surged by approximately 29% over the four years leading up to mid-2024 due to persistent inflation. This inflationary environment directly amplifies the bargaining power of suppliers, as they can command higher prices for their goods and services.
FAT Brands, by utilizing its considerable scale and fostering robust relationships with its partners, aims to mitigate some of these supply chain pressures. However, the widespread inflationary trends and ongoing supply chain disruptions mean that suppliers can still exert considerable influence. This can manifest in less favorable contract terms or the ability to pass on increased input costs more readily.
- Inflationary Impact: Food costs in the restaurant sector rose by 29% over the past four years, increasing supplier leverage.
- FAT Brands' Mitigation: The company uses its scale and partner relationships to manage supply chain challenges.
- Supplier Power: Despite mitigation efforts, overarching inflationary pressures continue to empower suppliers.
FAT Brands faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly in specialized equipment and key food ingredients. The concentration of suppliers in critical areas, such as commercial kitchen equipment with only 3-4 dominant manufacturers in 2024, allows these entities to dictate terms and pricing. This power is further amplified by high switching costs for franchisees, which can range from $75,000 to $250,000 per location, discouraging frequent changes in supply partners and reinforcing supplier leverage.
| Supplier Category | Concentration (Approx. # of Major Suppliers) | Typical Annual Price Volatility | Switching Cost (Est. per Franchise) |
| Commercial Kitchen Equipment | 3-4 | N/A (High upfront cost) | $75,000 - $250,000 |
| Protein Ingredients | 4-5 | ±12% | Included in overall switching cost |
| Dairy Products | 3-4 | N/A (Specific data not provided) | Included in overall switching cost |
| Produce | 6-7 (Regional) | ±15% | Included in overall switching cost |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects FAT Brands' competitive environment, evaluating the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces chart, simplifying complex market dynamics for FAT Brands' strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
FAT Brands manages a broad spectrum of 18 restaurant brands, spanning fast casual to casual dining. This wide variety of choices, both within FAT Brands' own offerings and from competitors, significantly enhances customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the quick-service restaurant market alone saw numerous new entrants and expansions, providing consumers with even more dining alternatives.
In the fast-food and casual dining sectors, where FAT Brands operates, consumers typically face very low switching costs. This means a customer can easily decide to eat at a McDonald's instead of a Fatburger, or opt for a different pizza chain rather than a Great American Pizza, with minimal effort or expense.
This ease of moving between brands, combined with the sheer number of dining choices available, significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. restaurant industry boasted over one million food service locations, offering consumers an abundance of alternatives for nearly every meal occasion.
When switching costs are low, customers can readily shift their spending to competitors if they perceive better value, lower prices, or higher quality. This dynamic forces FAT Brands and its franchisees to remain competitive on price and experience to retain their customer base.
Consumers are increasingly demanding convenience and value, a trend that significantly impacts the restaurant industry. In 2023, the convenience-driven food services sector saw a substantial expansion of 15.7%. Furthermore, a significant 68% of consumers now actively prioritize quick and easy meal solutions.
This shift empowers customers, particularly favoring fast-casual dining options. These establishments offer a compelling blend of affordability and quality, directly appealing to consumers seeking the best value for their money.
Impact of Digital Sales and Loyalty Programs
The increasing prevalence of digital sales channels and robust loyalty programs can, paradoxically, empower customers. For instance, FAT Brands' Great American Cookies saw 25% of its total revenue generated through digital sales and experienced a 40% surge in loyalty-driven sales in 2024. This digital footprint allows customers to easily compare offerings and seek out promotions, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
- Digital Reach: Customers can readily access a wider array of choices and pricing information online.
- Loyalty Program Leverage: Loyalty programs, while fostering retention, also provide customers with tangible benefits that can be weighed against competitors.
- Price Sensitivity: The ease of comparison online can heighten price sensitivity among consumers.
- Information Asymmetry Reduction: Digital platforms diminish the information gap between businesses and consumers, giving customers more leverage.
Price Sensitivity in the Current Economic Climate
Consumers are increasingly scrutinizing their spending due to persistent inflation and economic uncertainty. This heightened price sensitivity means that restaurant chains like those under FAT Brands must tread carefully with their pricing. Customers are actively comparing options and are more inclined to switch to more affordable competitors if value perception diminishes.
- Inflationary Pressures: As of early 2024, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) continued to show elevated levels, impacting household budgets and making consumers more mindful of food expenditures.
- Value-Conscious Consumers: Surveys in late 2023 and early 2024 indicated a significant portion of consumers were actively seeking deals and discounts when dining out.
- Competitive Landscape: The fast-casual and quick-service restaurant sectors are highly competitive, with many brands vying for the price-conscious diner's dollar.
The bargaining power of customers for FAT Brands is substantial, driven by low switching costs and an abundance of dining options. In 2024, the sheer volume of restaurant locations, exceeding one million in the U.S. alone, ensures consumers have ample alternatives. This allows them to easily shift spending based on price, quality, or convenience, forcing FAT Brands to maintain competitive pricing and experiences.
Digital channels further amplify this power. For example, Great American Cookies reported 25% of its 2024 revenue from digital sales, enabling customers to effortlessly compare offerings and promotions. This heightened price sensitivity, exacerbated by persistent inflation in early 2024, means consumers are actively seeking value, making brand loyalty more conditional.
| Factor | Impact on FAT Brands | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs | Customers can easily move between brands. | Minimal financial or effort cost to change dining choices. |
| Numerous Alternatives | Increases customer leverage. | Over 1 million U.S. food service locations in 2024. |
| Digital Information Access | Facilitates price and quality comparisons. | Great American Cookies: 25% of revenue from digital sales (2024). |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers prioritize value due to economic conditions. | Elevated CPI levels in early 2024; consumers seeking deals. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
FAT Brands Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive FAT Brands Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately upon purchase. You are viewing the exact, professionally written document, complete with all insights and formatting, ready for your immediate use. There are no placeholders or samples; what you see is precisely what you get after completing your transaction.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The restaurant industry, especially the fast-food and fast-casual segments where FAT Brands competes, is incredibly fragmented. This means there are a huge number of businesses, from global giants to small local diners, all vying for the same customers. This intense competition naturally leads to fierce rivalry for market share.
In 2024, the U.S. restaurant industry is projected to reach over $1.1 trillion in sales, according to the National Restaurant Association. This massive market size, combined with the sheer volume of establishments, fuels aggressive competition. FAT Brands, with its portfolio of brands like Fatburger and Johnny Rockets, must constantly innovate and differentiate to capture consumer attention.
The restaurant industry is characterized by intense competition as numerous chains, including FAT Brands, aggressively pursue expansion. FAT Brands, for instance, has set a target of over 100 new restaurant openings for 2025, supported by a development pipeline of roughly 1,000 signed agreements.
This widespread ambition for growth among competitors significantly heightens the rivalry. Each new opening by a competitor directly competes for market share, prime locations, and customer attention, making it crucial for FAT Brands to differentiate and execute its expansion effectively.
The restaurant industry, including the quick-service segment where FAT Brands operates, is experiencing a significant wave of consolidation. This trend sees multi-unit conglomerates increasingly dominating the landscape, driven by the pursuit of economies of scale and operational synergies. FAT Brands has been a prime example of this, actively growing its portfolio through strategic acquisitions of various brands.
This aggressive acquisition strategy by larger entities intensifies competition for smaller, independent restaurant concepts. For instance, FAT Brands' acquisition of Great American Cookies, Pretzelmaker, and Hot Dog on a Stick in 2021 for $300 million demonstrates this commitment to expansion through acquiring established brands. Such moves create a more challenging environment for standalone brands seeking to compete effectively in terms of market share and resources.
Impact of Digital Integration and Delivery Services
The competitive rivalry within the restaurant sector, particularly for brands like FAT Brands, is intensified by the pervasive influence of digital integration and delivery services. Consumers now expect seamless online ordering and rapid delivery, pushing restaurants to optimize their digital presence and operational efficiency. This shift means that even traditional brick-and-mortar establishments face pressure from digitally native concepts.
The dominance of third-party delivery platforms continues to shape consumer behavior, with many patrons prioritizing convenience and speed above all else. This reliance on platforms can impact profit margins due to commission fees, but it also provides access to a broader customer base. In 2024, the food delivery market is projected to continue its robust growth, with estimates suggesting it will reach over $300 billion globally, underscoring the critical importance of a strong digital strategy.
- Delivery Platform Dominance: Platforms like DoorDash, Uber Eats, and Grubhub are central to how many consumers order food, creating a significant channel but also adding costs.
- Consumer Demand for Convenience: The expectation for quick, hassle-free delivery is a primary driver of competition, forcing brands to streamline their online and in-house operations.
- Rise of Ghost Kitchens and Virtual Brands: These digitally-focused entities, operating without a traditional storefront, directly compete with established brands by leveraging lower overhead and agile menu development.
- Digital Integration Necessity: Brands must invest in user-friendly websites, mobile apps, and efficient order management systems to remain competitive in this evolving landscape.
Price and Value Competition
FAT Brands operates in a highly competitive landscape where price and value are critical differentiators. With food costs and labor expenses on the rise, many restaurants are focusing on delivering strong value propositions to attract and retain customers. This often means employing strategic pricing and optimizing operational efficiencies to manage costs effectively.
In 2024, consumer price sensitivity remains a significant factor. Restaurants that successfully integrate digital ordering, control labor expenses, and implement smart pricing strategies while ensuring customers perceive good value are likely to gain a competitive advantage. For instance, the National Restaurant Association reported that in early 2024, a significant portion of consumers were actively seeking deals and promotions.
- Price Wars: Intense competition often leads to price wars, particularly among fast-casual and quick-service brands.
- Value Perception: Brands must carefully manage their pricing to align with the perceived value of their offerings.
- Operational Efficiency: Controlling costs through efficient operations is crucial for maintaining competitive pricing.
- Promotional Activity: Frequent promotions and loyalty programs are common tactics to attract price-sensitive consumers.
Competitive rivalry within the restaurant sector, particularly for brands like FAT Brands, is intensified by the pervasive influence of digital integration and delivery services. Consumers now expect seamless online ordering and rapid delivery, pushing restaurants to optimize their digital presence and operational efficiency. This shift means that even traditional brick-and-mortar establishments face pressure from digitally native concepts.
The dominance of third-party delivery platforms continues to shape consumer behavior, with many patrons prioritizing convenience and speed above all else. This reliance on platforms can impact profit margins due to commission fees, but it also provides access to a broader customer base. In 2024, the food delivery market is projected to continue its robust growth, with estimates suggesting it will reach over $300 billion globally, underscoring the critical importance of a strong digital strategy.
FAT Brands operates in a highly competitive landscape where price and value are critical differentiators. With food costs and labor expenses on the rise, many restaurants are focusing on delivering strong value propositions to attract and retain customers. This often means employing strategic pricing and optimizing operational efficiencies to manage costs effectively.
In 2024, consumer price sensitivity remains a significant factor. Restaurants that successfully integrate digital ordering, control labor expenses, and implement smart pricing strategies while ensuring customers perceive good value are likely to gain a competitive advantage. For instance, the National Restaurant Association reported that in early 2024, a significant portion of consumers were actively seeking deals and promotions.
| Key Competitive Factors | Impact on FAT Brands | 2024 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Market Saturation & Fragmentation | High rivalry for market share and prime locations. | U.S. restaurant industry sales projected over $1.1 trillion. |
| Aggressive Expansion Strategies | Increased competition from both established chains and new entrants. | FAT Brands targeting over 100 new openings in 2025. |
| Digital & Delivery Integration | Need for efficient online platforms and delivery partnerships. | Global food delivery market projected to exceed $300 billion. |
| Price Sensitivity & Value Perception | Pressure to offer competitive pricing and promotions. | Consumers actively seeking deals and promotions. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for FAT Brands' restaurant concepts is significant, primarily driven by the sheer abundance and variety of food choices available to consumers. In 2024, the quick-service restaurant sector, where FAT Brands primarily operates, faces intense competition not just from direct competitors but also from alternative dining and food preparation methods.
Consumers can easily opt for home-cooked meals, which have seen continued popularity, or choose from the growing market of grocery store prepared foods and meal kits. For instance, the meal kit delivery service market was projected to reach over $20 billion globally by 2024, illustrating a substantial substitute for dining out.
Furthermore, the landscape is crowded with independent restaurants offering unique culinary experiences and other established fast-casual and fast-food chains. This wide array of readily accessible and often more affordable options means consumers can readily switch away from FAT Brands' offerings if perceived value or convenience diminishes.
Customers can easily switch from FAT Brands' offerings to alternatives, as the costs associated with changing their dining choices are very low. This minimal friction means a customer might opt for a different fast-casual or quick-service restaurant without incurring significant financial or time penalties.
The threat of substitutes is amplified because patrons can readily explore other dining options, whether it's another burger chain, a pizza place, or even a home-cooked meal. For instance, in 2024, the fast-casual dining sector, which includes many FAT Brands concepts, saw continued competition from meal kit services and grocery store prepared foods, offering consumers even more convenient alternatives.
The rising popularity of meal delivery services and meal kits presents a significant threat of substitutes for FAT Brands. This market is booming, with projections indicating it could reach approximately $34.35 billion by 2027. Consumers increasingly value the convenience and at-home preparation options these services offer, diverting spending that might otherwise go to traditional restaurant dining.
Rise of Fast-Casual and Quick-Service Alternatives
The growing popularity of fast-casual and quick-service alternatives presents a significant threat to FAT Brands. This segment offers consumers a compelling blend of affordability and quality, directly challenging many of FAT Brands' existing restaurant concepts. For instance, the fast-casual market, projected for substantial growth, appeals to diners seeking convenient, value-driven meals.
This trend means consumers have more choices that can easily substitute for the dining experiences FAT Brands provides. As these alternatives gain traction, they can siphon off customer traffic and revenue.
- Fast-casual market growth: Expected to see significant expansion, offering a direct alternative to FAT Brands' offerings.
- Consumer preference shift: Consumers increasingly favor affordable yet quality dining options, a sweet spot for fast-casual.
- Competitive pressure: This segment directly competes for customer dollars, potentially impacting FAT Brands' market share.
Health-Conscious and Dietary Trend Shifts
The increasing consumer focus on health and wellness presents a significant threat of substitutes for FAT Brands. As people actively seek out healthier food choices, they are increasingly turning to options like salads, grilled lean proteins, and plant-based meals. This dietary shift means that if FAT Brands' core offerings, often associated with indulgent fast-casual dining, are perceived as less healthy, consumers might easily switch to competitors or alternative dining formats that better align with their wellness goals.
This trend is not just a fleeting fad; it's a fundamental change in consumer behavior. For instance, the global plant-based food market was valued at approximately $30 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer demand for alternatives. Restaurants that fail to adapt by incorporating or highlighting healthier options risk losing market share to establishments that cater to these evolving preferences. FAT Brands' ability to innovate its menu to include or emphasize healthier preparations and ingredients will be crucial in mitigating this threat.
- Health-Conscious Consumerism: Growing awareness of nutrition and wellness drives demand for healthier food options.
- Dietary Diversification: Consumers are exploring and adopting diets rich in salads, lean proteins, and plant-based alternatives.
- Competitive Landscape: Restaurants offering healthier menus or perceived healthier options pose a direct substitute threat.
- Market Value: The plant-based food market alone, a key substitute category, was valued around $30 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of this shift.
The threat of substitutes for FAT Brands is substantial due to the vast array of dining and food preparation alternatives available to consumers. In 2024, the ease with which customers can switch to home-cooked meals, meal kits, or prepared foods from grocery stores significantly impacts the quick-service restaurant sector. The low switching costs mean consumers can readily choose other fast-casual or quick-service options without penalty.
| Substitute Category | 2024 Market Insight/Projection | Impact on FAT Brands |
|---|---|---|
| Meal Kits & Prepared Foods | Global meal kit market projected over $20 billion in 2024. | Offers convenience, diverting spending from restaurants. |
| Home Cooking | Continued popularity, especially with increasing focus on value. | Directly competes for meal occasions, reducing restaurant visits. |
| Plant-Based Alternatives | Global plant-based food market valued around $30 billion in 2023. | Appeals to health-conscious consumers, posing a threat if FAT Brands' offerings are perceived as less healthy. |
| Independent & Other Chains | Highly fragmented market with diverse culinary experiences. | Provides constant competition for customer loyalty and dining dollars. |
Entrants Threaten
While launching a new restaurant generally demands significant investment, FAT Brands' reliance on a franchising model can make it more accessible for individual operators. However, the initial franchise fees can vary, typically falling between $0 and $50,000 per location, and prospective franchisees for FAT Brands are generally required to demonstrate a net worth of at least $1,500,000 with $500,000 in liquid assets.
FAT Brands boasts a portfolio of 18 well-established restaurant brands, a significant advantage that creates a high barrier to entry for newcomers. This established brand recognition, cultivated over years of operation, allows FAT Brands to attract and retain customers more readily than a new, unproven entity. For instance, brands like Fatburger and Johnny Rockets have a loyal following that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly.
Furthermore, FAT Brands' robust development pipeline, with approximately 1,000 signed agreements for new locations, signals substantial future growth and market penetration. This aggressive expansion strategy means new entrants will face an already crowded marketplace with a dominant player actively increasing its footprint, making it harder to secure prime locations and market share.
The franchise industry is experiencing heightened regulatory uncertainty, especially with the Federal Trade Commission's Franchise Rule undergoing revisions and evolving franchisor-franchisee relationships. New entrants must contend with these intricate compliance requirements, which can significantly deter market entry.
Economies of Scale and Supply Chain Access
Established multi-brand companies like FAT Brands leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in procurement and supply chain management. This allows them to negotiate more favorable pricing with suppliers, a crucial advantage in the food service industry. For instance, in 2023, FAT Brands reported total revenues of $237.8 million, demonstrating the scale of their operations.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Without the same purchasing power, they are likely to incur higher ingredient costs and operational expenses. This disparity can put them at a distinct competitive disadvantage from the outset, making it harder to compete on price or maintain healthy profit margins.
Access to established supply chains is another barrier. FAT Brands has existing relationships and infrastructure that facilitate efficient sourcing and distribution. Newcomers must invest heavily in building these networks, which can be time-consuming and capital-intensive.
- Economies of Scale: FAT Brands’ size allows for bulk purchasing, reducing per-unit costs of ingredients and supplies.
- Supply Chain Integration: Existing robust supply chain networks provide FAT Brands with reliable and cost-effective access to necessary goods.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Start-ups lack the purchasing volume to negotiate similar supplier rates, leading to higher operating costs.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: Higher costs for new entrants limit their ability to offer competitive pricing against established players like FAT Brands.
Intense Competitive Environment
The restaurant industry is already incredibly crowded, meaning new players face a tough climb to even get noticed. Established brands have built significant customer loyalty and recognition, requiring newcomers to pour substantial resources into marketing and developing truly distinctive concepts to carve out a niche. For instance, in 2024, the US restaurant industry saw continued consolidation and aggressive promotional activity from major chains, making it even harder for a new franchise to gain immediate traction.
New entrants must also contend with the high capital requirements for opening and operating a restaurant, including real estate, equipment, and staffing. This financial barrier, coupled with the need for innovative menu items and strong operational efficiency, intensifies the challenge. In 2024, average startup costs for a quick-service restaurant could easily range from $150,000 to $300,000, a significant hurdle for any aspiring business.
- Saturated Market: The sheer number of existing restaurants makes differentiation a significant challenge for new entrants.
- High Capital Investment: Opening a new restaurant requires substantial upfront capital for real estate, equipment, and initial marketing.
- Brand Loyalty: Established brands benefit from existing customer bases, forcing new entrants to invest heavily in customer acquisition.
- Operational Complexity: The restaurant business demands efficient operations, supply chain management, and skilled labor, all of which are challenging to establish quickly.
The threat of new entrants for FAT Brands is relatively moderate, primarily due to the significant capital investment and established brand recognition required in the quick-service restaurant sector. While the franchise model can lower some initial barriers, the overall market saturation and the need for substantial marketing and operational setup make it challenging for newcomers to gain immediate traction.
In 2024, the average startup costs for a quick-service restaurant could range from $150,000 to $300,000, presenting a considerable financial hurdle. New entrants must also overcome the established customer loyalty of brands like Fatburger and Johnny Rockets, which have cultivated strong market presence over years of operation. FAT Brands' aggressive expansion, with approximately 1,000 signed agreements for new locations, further intensifies this challenge by increasing market density.
| Factor | Impact on FAT Brands | New Entrant Challenge |
| Capital Investment | Managed through franchise fees and corporate backing | High, ranging from $150k-$300k for QSRs in 2024 |
| Brand Recognition | Strong, with multiple established brands | Low, requiring significant marketing spend |
| Market Saturation | Well-positioned within a crowded market | High, making differentiation difficult |
| Economies of Scale | Significant, leading to cost advantages | Limited, resulting in higher operating costs |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our FAT Brands Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including publicly available financial statements, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from trade publications and news articles to capture current market dynamics and competitive landscapes.
