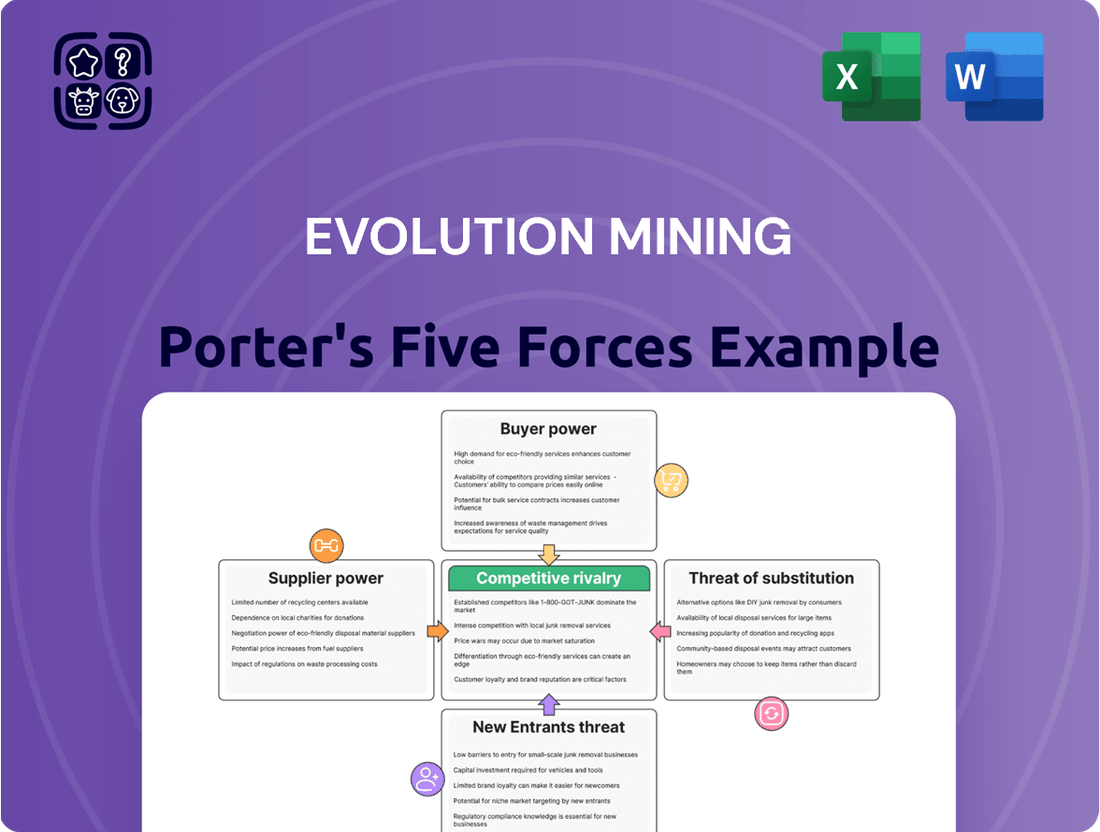
Evolution Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Evolution Mining Bundle
Evolution Mining operates in a dynamic sector where supplier power can significantly impact costs, and the threat of new entrants is ever-present. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Evolution Mining’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The mining sector, including companies like Evolution Mining, is heavily dependent on highly specialized equipment and cutting-edge technology for everything from initial exploration to final processing. This reliance on sophisticated machinery means that the suppliers of these critical tools hold considerable sway.
A key factor is the limited number of global manufacturers capable of producing this specialized mining equipment. This concentration of suppliers means they face fewer direct competitors, allowing them to dictate terms and pricing more effectively to mining operations. For instance, major equipment manufacturers often have long lead times and can command premium prices, impacting a miner's capital expenditure.
In 2024, the global mining equipment market was valued at approximately USD 190 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4.5% through 2030. This robust market size underscores the significant investment miners make in these specialized assets, further amplifying supplier leverage.
The availability of skilled labor, such as geologists, engineers, and experienced mine operators, is absolutely vital for Evolution Mining's operations. When there's a scarcity of these specialized professionals, it naturally leads to higher wage expectations and increased recruitment expenses, which in turn strengthens the bargaining power of these labor suppliers.
Evolution Mining, like all mining companies, faces significant pressure from volatile energy and input costs. Mining is inherently energy-intensive, meaning swings in the price of electricity, diesel fuel, and processing chemicals directly impact operational expenses. For instance, in 2024, global energy prices saw considerable fluctuations, with oil prices averaging around $80-$90 per barrel for much of the year, impacting fuel costs for heavy machinery and transport.
Suppliers of these critical inputs hold substantial bargaining power, particularly when markets are unstable. If a key supplier of processing reagents or a major energy provider faces its own cost increases or supply chain disruptions, they can pass these onto Evolution Mining, squeezing profit margins. This was evident in early 2024, where some chemical suppliers reported increased costs due to geopolitical events, leading to higher prices for essential mining reagents.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance Services
Evolution Mining's reliance on specialized regulatory and environmental compliance services grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. The company's commitment to sustainable mining necessitates expert assistance in areas like environmental impact assessments, rehabilitation planning, and adherence to evolving environmental regulations. For instance, the Australian government, through bodies like the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water, continuously updates environmental standards, requiring specialized knowledge that only a select few service providers possess.
The specialized nature of environmental management and rehabilitation services means there are fewer alternative suppliers capable of meeting Evolution Mining's stringent requirements. This scarcity, coupled with the critical importance of compliance for operational continuity and social license to operate, allows these providers to command higher prices and favorable contract terms. In 2024, the global market for environmental consulting services was valued at over $40 billion, with a significant portion driven by the mining sector's need for compliance and sustainability solutions.
- Specialized Expertise: Providers offer niche skills in environmental management, rehabilitation, and regulatory adherence, essential for mining operations.
- Regulatory Demands: Increasingly stringent environmental laws and sustainability expectations amplify the need for expert compliance services.
- Limited Alternatives: The specialized nature of these services restricts the number of qualified suppliers, enhancing their leverage.
- Operational Dependence: Evolution Mining's need for uninterrupted operations and social license makes it dependent on reliable compliance partners.
Switching Costs for Critical Inputs
Switching suppliers for highly integrated or specialized mining equipment and services can be incredibly costly for Evolution Mining. These costs aren't just about buying new gear; they include retraining staff on new systems and reconfiguring entire operational processes. For instance, a mine relying on a specific type of automated drilling rig might face millions in costs to switch to a different manufacturer, encompassing everything from operator certification to spare parts inventory adjustments.
These significant switching costs directly empower incumbent suppliers. When it's expensive and disruptive to change providers, Evolution Mining has less leverage. Suppliers of critical inputs, knowing this, can often command higher prices or more favorable terms, as the cost of switching outweighs the potential benefits for the mining company.
Consider the impact on Evolution Mining's operational flexibility. High switching costs tie the company to existing supplier relationships, limiting its ability to seek out better deals or more innovative solutions. This dependency strengthens the bargaining power of suppliers who provide essential, specialized components or services, as their continued provision is vital to ongoing operations.
- High Switching Costs: Retraining, operational reconfiguration, and downtime are major expenses when changing suppliers for specialized mining equipment.
- Supplier Leverage: Incumbent suppliers gain increased bargaining power due to the financial and operational barriers to switching.
- Reduced Flexibility: Evolution Mining’s ability to negotiate favorable terms or adopt new technologies is constrained by these high switching costs.
- Impact on Operations: The reliance on specific suppliers, driven by switching costs, can affect cost management and operational efficiency.
Suppliers of specialized mining equipment and critical inputs hold significant bargaining power over Evolution Mining. This leverage stems from the limited number of manufacturers for sophisticated machinery and the essential nature of inputs like energy and processing chemicals, which are subject to market volatility.
The high cost and operational disruption associated with switching suppliers for specialized equipment or services further entrench supplier power. For example, in 2024, the global mining equipment market, valued around USD 190 billion, saw suppliers dictating terms due to these switching costs.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example (2024 Data) |
| Specialized Equipment Suppliers | High leverage due to limited manufacturers and high switching costs for miners. | Global mining equipment market valued at ~USD 190 billion. |
| Energy and Input Suppliers | Strong power, especially during volatile market conditions affecting fuel and chemical prices. | Oil prices averaged $80-$90/barrel; some chemical suppliers increased prices due to geopolitical events. |
| Specialized Service Providers (Environmental) | Considerable power due to niche expertise and stringent regulatory demands. | Global environmental consulting market exceeded $40 billion, with mining as a key driver. |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping Evolution Mining's industry, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Evolution Mining's Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The commodity nature of gold significantly empowers customers in their bargaining. Because gold from different mines is largely indistinguishable, buyers face minimal switching costs when choosing a supplier. This homogeneity means customers can readily shift their purchases to the provider offering the most competitive price or favorable contract terms.
Evolution Mining's gold finds its way into diverse sectors like jewelry, investment vehicles such as ETFs and bullion, central bank reserves, and even industrial uses. This broad customer base means no single group holds significant sway over pricing or terms. For instance, while jewelry demand is a major driver, central bank purchases and investment flows provide alternative outlets, lessening the impact of any one segment's bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers for Evolution Mining is significantly limited because gold prices are set on global commodity markets, not through direct negotiation with individual buyers. Factors like global supply and demand, central bank policies, and investor sentiment dictate the price, making Evolution Mining a price-taker. In 2024, the average gold price hovered around $2,300 per ounce, illustrating this global price-setting mechanism rather than customer-driven negotiations.
Concentration of Refiners and Institutional Buyers
While gold has a broad range of end uses, the immediate purchasers of Evolution Mining's output are typically concentrated. These are often large-scale refiners, major bullion banks, and significant institutional investors who buy gold in bulk. This concentration means these buyers, acting as intermediaries, can exert some influence during negotiations.
However, the bargaining power of these customers is largely tempered by the global, transparent nature of the gold market. The international spot price for gold, which is determined by a multitude of global factors, remains the most significant determinant of the price Evolution Mining receives. In 2024, gold prices have shown volatility, influenced by macroeconomic trends and central bank policies, reinforcing the dominance of the spot market over individual buyer negotiations.
- Concentrated Buyer Base: Refiners, bullion banks, and institutional investors form the primary customer base for raw gold.
- Negotiating Leverage: The concentration of these buyers grants them some ability to negotiate terms with producers like Evolution Mining.
- Spot Price Dominance: The global spot price of gold, influenced by myriad international factors, is the overriding price determinant.
- 2024 Market Influence: Macroeconomic conditions and central bank actions in 2024 continue to shape gold prices, reinforcing the spot market's power.
Copper as a By-product
Evolution Mining's position is influenced by the bargaining power of customers, particularly concerning copper, a significant by-product. In FY24, copper contributed roughly 29% to the company's gross revenue, highlighting its importance.
The demand for copper is closely tied to global industrial activity and economic cycles. This means that fluctuations in these broader markets can empower customers, as they have alternative sources and can exert pressure on pricing.
- Copper Revenue Contribution: Approximately 29% of Evolution Mining's gross revenue in FY24 was derived from copper.
- Market Influences: Industrial demand and global economic cycles significantly impact copper pricing, thereby influencing customer bargaining power.
- Revenue Diversification: While copper adds revenue diversification, its market sensitivities introduce another dimension to customer power dynamics.
The bargaining power of customers for Evolution Mining is generally low due to the commodity nature of gold, which is priced on global markets. While a concentrated base of large buyers like refiners and institutional investors exists, their influence is largely overshadowed by the overarching global spot price. For copper, a significant by-product contributing around 29% of FY24 revenue, customer power is more pronounced due to its sensitivity to industrial demand and economic cycles.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024/FY24) |
|---|---|---|
| Gold Homogeneity | Lowers switching costs for buyers, increasing power. | Gold prices averaged ~$2,300/oz globally in 2024. |
| Customer Concentration (Gold) | Limited leverage due to global price-taking. | Primary buyers: Refiners, bullion banks, institutional investors. |
| Copper Revenue | Increases customer power due to market sensitivity. | Contributed ~29% of gross revenue in FY24. |
| Global Market Influence | Dominates pricing, reducing individual customer sway. | 2024 prices influenced by macroeconomics and central bank policies. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Evolution Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Evolution Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape. The document displayed here is the exact, professionally formatted report you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises. You're looking at the actual, ready-to-use analysis, providing comprehensive insights into the industry's dynamics and Evolution Mining's strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The gold mining sector demands substantial upfront investment in exploration, mine construction, and ongoing operational expenses. This creates a significant barrier to entry and necessitates large-scale operations to spread these costs effectively.
To remain profitable, companies like Evolution Mining must maximize their production output and rigorously manage expenses. This competitive pressure intensifies rivalry as firms vie for market share and operational efficiency. For instance, in the 2023 financial year, Evolution Mining reported total gold production of 576,000 ounces, underscoring the volume required to justify their fixed cost base.
The drive for economies of scale and cost optimization often fuels industry consolidation. Evolution Mining has actively participated in this trend, with strategic acquisitions being a key component of its growth strategy, aiming to bolster its production capacity and operational footprint.
The competition for gold reserves and viable mining land is intense, as companies like Evolution Mining pour significant resources into exploration to secure future production. This race is fundamental to long-term survival, directly tied to the quantity and quality of discovered mineral assets.
In 2023, Evolution Mining's total group gold reserves and resources stood at 19.8 million ounces, highlighting the scale of their asset base and the continuous effort required to maintain and grow it. This figure underscores the constant need to find new deposits or extend existing ones to remain competitive in the global gold market.
Evolution Mining faces intense competition from global and regional gold producers. Its operations in Australia and Canada put it head-to-head with industry giants like Northern Star Resources, Mineral Resources, OZ Minerals, and OceanaGold. This rivalry is fierce, not just for mining assets but also for attracting investor interest and securing market share.
Cost Leadership as a Differentiator
In the gold mining sector, where the product itself is a commodity, competitive rivalry often centers on operational efficiency and cost management. Evolution Mining distinguishes itself by aggressively pursuing a low All-in Sustaining Cost (AISC), a key metric in the industry. This focus allows the company to maintain healthier profit margins even when gold prices fluctuate, making it a more resilient player.
Evolution Mining's commitment to cost leadership is evident in its performance. For the fiscal year 2023, the company reported an AISC of A$1,294 per ounce, placing it favorably against many global competitors. This cost advantage is crucial for weathering market downturns and maximizing profitability during favorable periods.
- Cost Efficiency as a Driver: Evolution Mining prioritizes operational excellence to achieve industry-leading low All-in Sustaining Costs (AISC).
- Competitive Advantage: Maintaining a low AISC, reported at A$1,294 per ounce for FY23, provides a significant edge over higher-cost producers.
- Margin Protection: This cost leadership strategy allows Evolution Mining to secure better margins and financial stability, regardless of gold price volatility.
- Market Positioning: By consistently operating at the lower end of the cost curve, Evolution Mining strengthens its competitive position within the global gold mining landscape.
Operational Performance and Project Delivery
Competitive rivalry in the mining sector, particularly concerning operational performance and project delivery, is intense. Companies that excel in these areas, such as Evolution Mining, establish a significant advantage.
This edge is built on operational excellence and the successful execution of projects, including mine expansions and new developments. Evolution Mining's consistent ability to meet production targets and manage costs effectively is a key factor in its competitive standing. For instance, in FY24, the company reported strong operational results, with gold production meeting guidance and a focus on cost control.
- Operational Excellence: Consistent achievement of production targets and efficient cost management.
- Project Delivery: Successful execution of mine expansions and new development projects.
- FY24 Performance: Evolution Mining demonstrated strong financial and operational results, meeting gold production guidance and maintaining cost discipline.
- FY25 Outlook: Continued focus on operational efficiency and project execution is expected to further solidify competitive positioning.
The gold mining industry is characterized by intense competition, with companies like Evolution Mining vying for market share through operational efficiency and cost management. This rivalry is exacerbated by the commodity nature of gold, where price fluctuations necessitate a relentless focus on minimizing production costs.
Evolution Mining's strategy to maintain a low All-in Sustaining Cost (AISC) is a direct response to this competitive pressure. By achieving an AISC of A$1,294 per ounce in FY23, the company positions itself favorably against higher-cost producers, securing better margins and financial resilience.
This focus on cost leadership is crucial for navigating market volatility and outperforming competitors. The drive for economies of scale through strategic acquisitions further intensifies this rivalry, as companies aim to bolster production capacity and operational footprint.
Evolution Mining's competitive standing is further reinforced by its consistent operational performance and successful project delivery, including mine expansions and new developments. The company's FY24 results, meeting gold production guidance and emphasizing cost control, underscore its ability to execute effectively in a highly competitive environment.
| Metric | FY23 Value | FY24 Guidance/Outlook | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Gold Production (oz) | 576,000 | Meeting Guidance (specific figure not yet released for FY24) | Indicates production scale and operational capability. |
| All-in Sustaining Cost (AISC) (A$/oz) | 1,294 | Focus on Cost Control/Efficiency | Key indicator of cost competitiveness against peers. |
| Total Group Gold Reserves & Resources (Moz) | 19.8 | Continuous Exploration Efforts | Underpins long-term production viability and competitive advantage. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Other precious metals like silver, platinum, and palladium can act as substitutes for gold, especially in industrial applications such as electronics or as alternative investment vehicles. For instance, while gold prices have seen fluctuations, silver's industrial demand remains robust, with global industrial silver demand projected to reach approximately 560 million ounces in 2024.
However, gold's unique properties and its long-standing reputation as a hedge against inflation and a store of value significantly dampen the direct threat from these substitutes. Despite platinum and palladium's critical role in catalytic converters, with the automotive sector driving demand, gold's appeal as a safe-haven asset remains largely distinct.
The threat of substitutes for gold mining companies like Evolution Mining is significant as investors have a vast array of alternative investment vehicles. These include traditional assets such as real estate, equities, and bonds, as well as newer, more volatile options like cryptocurrencies.
While gold's reputation as a safe haven, particularly during times of economic turmoil, can provide a competitive edge, strong returns in other asset classes can easily pull capital away. For instance, in 2023, while gold prices saw fluctuations, major stock indices like the S&P 500 delivered robust returns, potentially diverting investor interest from precious metals.
Technological advancements present a moderate threat to gold's industrial demand. Innovations could lead to the development of new materials that offer similar or superior performance at a lower cost, directly substituting gold in sectors like electronics and dentistry. For instance, research into materials like graphene continues to explore its potential as a more affordable alternative in certain high-tech applications, which could chip away at a portion of gold's market share.
Perceived Value and Cultural Significance
Gold's enduring cultural significance and historical role as a store of value present a formidable barrier to substitutes. Its deep-rooted perception as an intrinsic asset, unlike fiat currencies or even other precious metals, creates a unique demand profile. This inherent desirability is difficult for any alternative to fully replicate, ensuring a resilient baseline demand for gold.
The perceived value of gold is not solely economic; it is intertwined with millennia of human history, art, and tradition. This cultural weight translates into a psychological anchor for investors, making it a preferred safe-haven asset during times of uncertainty. For instance, in 2024, despite fluctuations in other markets, gold prices demonstrated remarkable stability, reflecting this underlying trust.
- Deep Cultural Roots: Gold's association with wealth, power, and divinity across numerous civilizations provides a psychological advantage over potential substitutes.
- Historical Currency Role: For centuries, gold served as a primary medium of exchange, embedding its utility in global economic memory.
- Intrinsic Value Perception: Unlike fiat money, gold is not backed by government decree but by its physical properties and historical acceptance, fostering a sense of inherent worth.
- Resilience in Uncertainty: In 2024, gold's performance as a safe-haven asset highlighted its ability to retain value when other assets falter, a trait difficult for substitutes to match.
Recycled Gold
Recycled gold, sourced from jewelry, industrial waste, and old coins, presents a less direct but significant threat. Increased efficiency and availability in gold recycling can diminish the market's reliance on newly mined gold, effectively substituting for primary production.
The global gold recycling market is substantial. For instance, in 2023, approximately 1,240 tonnes of gold were recycled, contributing significantly to the overall gold supply. This volume highlights the potential impact of recycling on demand for newly extracted gold.
- Recycled Gold Supply: In 2023, global gold recycling reached an estimated 1,240 tonnes.
- Impact on Primary Demand: A more efficient recycling process could decrease the need for newly mined gold by Evolution Mining.
- Price Sensitivity: Higher gold prices often incentivize increased recycling efforts, making recycled gold a more competitive supply source.
- Environmental Considerations: Recycling offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to mining, potentially influencing consumer and investor preferences.
While other precious metals like silver and platinum offer industrial applications, gold's unique position as a perceived inflation hedge and store of value significantly limits their direct substitution. For example, in 2024, gold's stability during market volatility contrasted with other assets, reinforcing its safe-haven appeal.
The threat from alternative investments, including real estate, equities, and even cryptocurrencies, is substantial as investors seek diverse avenues for capital growth. For instance, strong performance in major stock indices like the S&P 500 in 2023 demonstrated how other asset classes can attract investment capital away from gold.
Technological advancements could introduce new materials to substitute gold in specific industrial uses, though gold's intrinsic value perception remains a strong counterforce. The deep cultural significance and historical role of gold as a store of value are difficult for any substitute to fully replicate, ensuring a resilient baseline demand.
| Substitute Category | Examples | 2024 Relevance | Impact on Gold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Other Precious Metals | Silver, Platinum, Palladium | Silver industrial demand projected at ~560 million ounces | Limited due to gold's safe-haven status |
| Alternative Investments | Real Estate, Equities, Bonds, Cryptocurrencies | S&P 500 showed strong returns in 2023 | Significant, capital flow can shift |
| Technological Materials | Graphene, advanced alloys | Ongoing research into alternatives | Moderate, potential for niche industrial substitution |
| Recycled Gold | Scrap jewelry, industrial waste | 1,240 tonnes recycled globally in 2023 | Moderate, affects demand for new production |
Entrants Threaten
The gold mining industry is incredibly capital-intensive, demanding massive upfront investments for exploration, mine development, and specialized machinery. For instance, establishing a new gold mine can easily cost hundreds of millions, and often billions, of dollars. This immense financial hurdle significantly deters potential new entrants from easily joining the market.
New entrants in the mining sector, especially in regions where Evolution Mining operates like Australia, confront a labyrinth of complex and rigorous regulations. These include extensive environmental impact assessments, obtaining specific land use permits, and securing a social license to operate from local communities and Indigenous groups. For instance, the approval process for a new mine in Australia can easily take several years, often exceeding five years, due to these stringent requirements.
The threat of new entrants into the gold mining sector, particularly concerning access to quality reserves, is significantly mitigated by the sheer difficulty and cost of identifying and acquiring economically viable gold deposits. This is a substantial barrier for any newcomer looking to establish a foothold.
Established players like Evolution Mining possess a distinct advantage due to their existing portfolios of high-quality, proven gold assets and robust exploration pipelines. These established resources and ongoing exploration efforts make it exceedingly challenging for new companies to compete for the most promising geological targets, which are often already secured by incumbents.
Economies of Scale and Operational Experience
Economies of scale significantly deter new entrants in the mining sector. Established players like Evolution Mining leverage their size to achieve lower per-ounce production costs through bulk purchasing of consumables, efficient processing operations, and optimized logistics. For instance, in the 2023 financial year, Evolution Mining reported an all-in sustaining cost (AISC) of AUD $1,311 per ounce, a figure that is challenging for smaller, less experienced operations to match.
New entrants typically start with smaller operations, lacking the established infrastructure and the deep operational experience that drives cost efficiencies. This initial cost disadvantage makes it difficult for them to compete directly with larger, more established miners on price, acting as a substantial barrier to entry.
- Economies of Scale: Large miners benefit from lower per-unit costs in procurement, processing, and infrastructure.
- Operational Experience: Established firms possess invaluable know-how in efficient mining and cost management.
- Cost Disadvantage for Newcomers: Lacking scale and experience, new entrants face higher initial production costs.
- Competitive Barrier: The cost efficiency of established players like Evolution Mining presents a significant hurdle for new market participants.
Brand Recognition and Market Access
While gold is a commodity, Evolution Mining benefits from established relationships with refiners and financial institutions, coupled with a proven track record of reliable supply. This creates a significant barrier for new entrants. They would need to invest heavily in building these crucial connections and overcoming market perceptions of being unproven suppliers in a well-established sector.
For instance, in 2024, the global gold market continued to see strong demand, with central banks remaining net buyers. New entrants would not only need to secure mining rights but also navigate the complex network of off-take agreements and financing that underpin operations for established players like Evolution Mining. This entrenched network is difficult and time-consuming to replicate.
- Brand Recognition: Established miners like Evolution Mining have built trust and recognition over years of operation.
- Market Access: Existing relationships with downstream partners (refiners, buyers) are critical for smooth sales and operations.
- Supplier Reliability: A history of consistent delivery is a key differentiator in the gold market, making it hard for newcomers to gain immediate traction.
The threat of new entrants in the gold mining sector is generally low due to the substantial capital requirements, complex regulatory landscape, and the difficulty in securing viable gold reserves. Established companies like Evolution Mining benefit from significant economies of scale and deep operational expertise, creating cost advantages that newcomers struggle to overcome.
In 2024, the gold mining industry continued to be characterized by high upfront investment costs, with new mine development often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars. Furthermore, the lengthy and intricate approval processes in key mining jurisdictions, such as Australia, can take several years, adding to the barrier for new players. Evolution Mining's reported all-in sustaining cost of AUD $1,311 per ounce in FY23 highlights the cost efficiencies achieved through scale that new entrants would find challenging to match.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Evolution Mining's Advantage |
| Capital Intensity | Extremely High barrier; requires billions for new mines. | Established access to capital markets and existing infrastructure. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Years-long approval processes for permits and environmental assessments. | Navigated and streamlined compliance due to experience. |
| Access to Reserves | Difficulty in identifying and acquiring economically viable deposits. | Portfolio of proven, high-quality gold assets and exploration pipeline. |
| Economies of Scale | Higher per-ounce production costs due to smaller operations. | Lower costs through bulk purchasing, efficient processing (e.g., FY23 AISC AUD $1,311/oz). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Evolution Mining Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and ASX filings. We also incorporate industry-specific research from reputable sources like S&P Global Market Intelligence and Wood Mackenzie to capture current market dynamics and competitive landscapes.
