Everest Re Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Everest Re Group Bundle
Everest Re Group operates in a dynamic insurance landscape, where understanding the forces of competition is paramount. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intense pressures from rivals, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the constant threat of new entrants and substitutes.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Everest Re Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Specialized capital providers, particularly those in the Insurance-Linked Securities (ILS) market, are a significant factor in the bargaining power of suppliers for reinsurers like Everest Re. While traditional capital growth relies on retained earnings, the ILS market saw record highs in 2024, with projections for continued robust growth into 2025.
This growing pool of alternative capital offers reinsurers more funding options, potentially diluting the influence of any single traditional capital source. However, these specialized investors often negotiate specific terms, especially for complex or unique risk exposures, giving them a degree of bargaining power.
The market for highly skilled underwriters and actuaries is exceptionally competitive, particularly as the complexity of risks such as climate change and cyber threats continues to escalate. These professionals are the bedrock of Everest Re's success, directly impacting its ability to underwrite and manage risk effectively.
The scarcity of individuals possessing this specialized knowledge grants them considerable bargaining power. This can translate into higher compensation demands and influence Everest Re's operational costs, as well as its capacity for developing innovative risk solutions.
Insurtech advancements are crucial for efficiency and strategic decisions in reinsurance, with a strong emphasis on data purity, AI/ML for risk assessment, and client-focused digital tools in 2024. Providers of advanced analytics, AI, and data management solutions are gaining significant leverage as reinsurers depend on these technologies for a competitive edge and accurate risk evaluation.
Everest Re's commitment to investing in technology and data is essential to effectively manage the increasing bargaining power of these specialized suppliers. For instance, the global Insurtech market was projected to reach $10.5 billion in 2024, highlighting the significant investment and reliance on these tech providers.
Reinsurance Brokers
Reinsurance brokers, acting as crucial intermediaries between primary insurers (cedents) and reinsurers like Everest Re, can exert significant bargaining power. Their ability to aggregate demand and access a broad spectrum of reinsurers allows them to negotiate favorable terms and pricing for their clients. In the dynamic reinsurance market of 2024-2025, where capacity can fluctuate, brokers are instrumental in matching supply with demand, thereby enhancing their influence.
The bargaining power of reinsurance brokers stems from several factors:
- Market Access and Concentration: Brokers often have established relationships with numerous reinsurers, giving them access to a wider pool of capacity than individual cedents might achieve alone. This concentration of business through a few key brokers can give them leverage.
- Information Asymmetry: Brokers possess valuable market intelligence regarding pricing, terms, and capacity availability, which can be used to their advantage in negotiations.
- Services Offered: Beyond placement, brokers provide value-added services such as claims advocacy, risk management advice, and capital solutions, which can deepen their relationships with cedents and reinsurers alike.
- Competitive Reinsurance Market: With a competitive landscape for reinsurance capacity in 2024, brokers can effectively shop programs, playing reinsurers against each other to secure the best outcomes for their clients.
Catastrophe Modeling Firms and Data Vendors
Catastrophe modeling firms and data vendors hold significant bargaining power over reinsurers like Everest Re Group. Their proprietary models and extensive historical data are crucial for accurately assessing and pricing natural catastrophe risks. This reliance means reinsurers have limited alternatives for obtaining such specialized analytical tools.
The specialized nature of catastrophe modeling means that the costs associated with these services can be substantial. For instance, a single comprehensive catastrophe model from a leading vendor can cost tens of thousands of dollars annually, with more advanced or tailored solutions reaching significantly higher figures. This creates a dependency that strengthens the vendors' negotiating position.
- High Switching Costs: Reinsurers invest heavily in integrating specific modeling platforms into their underwriting and risk management processes, making it costly and time-consuming to switch providers.
- Data Exclusivity: Leading firms often possess unique, proprietary datasets derived from decades of research and analysis, which are not readily available elsewhere.
- Essential for Risk Management: Accurate catastrophe modeling is not optional; it's a fundamental requirement for reinsurers to underwrite portfolios effectively and meet regulatory capital requirements.
Specialized capital providers, particularly in the Insurance-Linked Securities (ILS) market, are a key supplier group for reinsurers like Everest Re. The ILS market saw substantial growth in 2024, with projections indicating continued expansion into 2025, offering reinsurers more funding options. However, these investors often negotiate specific terms for complex risks, thereby holding considerable bargaining power.
The demand for highly skilled underwriters and actuaries remains intense, especially with the increasing complexity of risks like climate change and cyber threats. These professionals are critical for effective risk assessment and management, and their scarcity grants them significant leverage in compensation and influence over operational costs and innovation. The global Insurtech market, projected to reach $10.5 billion in 2024, further highlights the reliance on specialized tech providers, whose advanced analytics and AI solutions are essential for competitive advantage and accurate risk evaluation.
Reinsurance brokers act as vital intermediaries, leveraging market access, information asymmetry, and value-added services to negotiate favorable terms for their clients. In the competitive reinsurance landscape of 2024-2025, their ability to aggregate demand and access diverse capacity enhances their influence. Catastrophe modeling firms also wield significant power due to their proprietary data and models, which are indispensable for accurate risk assessment, leading to high costs and substantial switching barriers for reinsurers.
What is included in the product
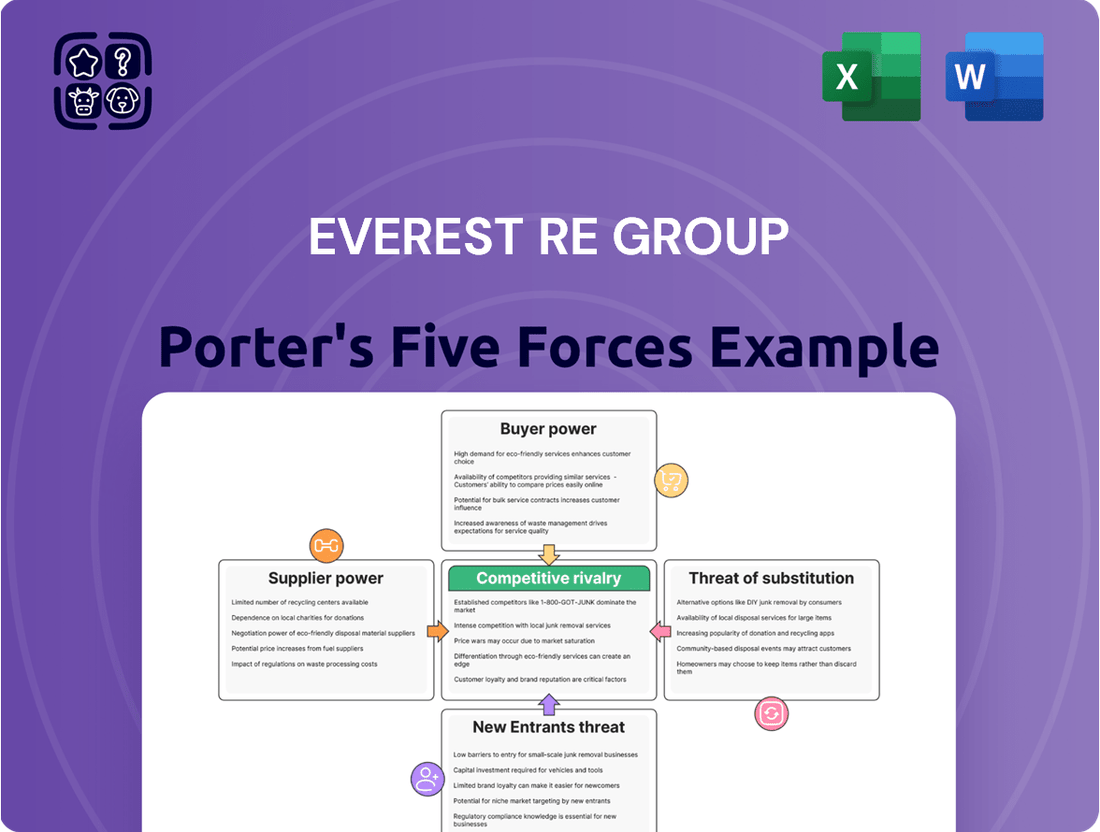
This analysis of Everest Re Group's competitive landscape examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, all within the reinsurance industry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Force, empowering Everest Re Group to proactively address market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers, specifically primary insurers (reinsurance cedents), for Everest Re Group is elevated in mid-2025. The global reinsurance market is characterized by ample capacity, leading to more buyer-friendly conditions, especially in property catastrophe lines. This environment allows primary insurers to negotiate more favorable terms and conditions, putting pressure on reinsurers like Everest Re to remain competitive.
Large corporate clients, particularly those seeking primary insurance from Everest Re's Everest Insurance division, wield considerable bargaining power. These sophisticated entities often possess robust risk management capabilities and the financial wherewithal to consider self-insurance or captive arrangements, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations. For instance, in 2024, the increasing complexity of corporate risk profiles means large clients are more discerning about coverage and pricing, directly influencing the terms Everest Re can offer.
In specialty and niche markets, clients often have reduced bargaining power because the specialized nature of the risks and the need for tailored solutions limit the pool of capable providers. Everest Re Group's strategic focus on these less commoditized segments, where unique expertise is paramount, allows it to negotiate more favorable terms, as evidenced by its strong performance in areas like property catastrophe reinsurance.
Price Sensitivity and Market Transparency
Increased market transparency, driven by readily available data and analytics, empowers customers to compare reinsurance offerings more effectively. This heightened transparency can lead to greater price sensitivity among buyers, forcing reinsurers like Everest Re to carefully consider their pricing strategies.
While the reinsurance market experienced a period of favorable pricing for reinsurers throughout much of 2024, the influx of competitive capacity is anticipated to moderate this pricing power in 2025. This dynamic shift means Everest Re needs to navigate a landscape where customers have more options and are increasingly attuned to price differentials.
Everest Re must strike a delicate balance between offering competitive pricing to attract and retain clients and ensuring its pricing adequately supports its profitability objectives. The ability to demonstrate value beyond price, such as superior risk management expertise or innovative product solutions, becomes crucial in mitigating the bargaining power of customers.
- Increased Market Transparency: Advances in data analytics and information sharing allow customers to benchmark reinsurance prices and terms more efficiently.
- Shifting Pricing Environment: While 2024 saw favorable pricing for reinsurers, an anticipated increase in competitive capacity for 2025 suggests a moderation of this trend.
- Strategic Pricing Imperative: Everest Re must align its pricing with market realities while safeguarding its profitability goals, a challenge amplified by customer price sensitivity.
- Value Proposition Differentiation: Success hinges on Everest Re's ability to differentiate its offerings through superior service, expertise, and tailored solutions, thereby reducing reliance solely on price competition.
Access to Alternative Risk Transfer Mechanisms
Primary insurers and large corporations are increasingly leveraging alternative risk transfer mechanisms, such as insurance-linked securities (ILS) and catastrophe bonds, as viable substitutes for traditional reinsurance. This trend directly impacts the bargaining power of customers, as they gain more options beyond the conventional reinsurance market.
The ILS market experienced significant growth, with record issuance levels observed in 2024 and continuing into early 2025. This surge in capacity provides cedents, or those seeking reinsurance, with a broader array of choices, consequently strengthening their negotiating position against traditional reinsurers like Everest Re Group.
- Increased Availability of ILS: The ILS market's expansion offers more capacity and diverse structures for risk transfer.
- Diversification of Risk Financing: Cedents can now access capital markets for risk mitigation, reducing reliance on traditional reinsurers.
- Enhanced Negotiating Leverage: With more alternatives, customers can demand better terms and pricing from reinsurers.
- Impact on Reinsurer Pricing: The competitive pressure from ILS can lead to more favorable pricing for insurance buyers.
The bargaining power of customers for Everest Re Group is influenced by several factors, including market transparency and the availability of alternative risk transfer options. In 2024, while reinsurers generally benefited from favorable pricing, the increasing capacity in the market and the growth of insurance-linked securities (ILS) are expected to moderate this advantage into 2025. This means primary insurers and large clients have more leverage to negotiate terms and pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power (Mid-2025 Outlook) | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capacity | Elevated | Ample capacity in property catastrophe lines, leading to buyer-friendly conditions. |
| Alternative Risk Transfer | Increased | Significant ILS market growth in 2024, with record issuance, providing more options beyond traditional reinsurance. |
| Information Transparency | Increased | Greater access to data and analytics empowers customers to benchmark prices and terms effectively. |
| Sophisticated Clients | High | Large corporations with strong risk management can consider self-insurance or captives, enhancing their negotiation leverage. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Everest Re Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis of Everest Re Group you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This document meticulously details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the reinsurance industry, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global reinsurance market exhibits a high degree of concentration, with a few major companies, including Everest Re, holding significant market share. This oligopolistic structure, however, does not diminish the intensity of competition among these established players, as they vie for premium volume and profitable business lines.
The industry's financial health, characterized by strong capitalization and robust operating profits, is expected to continue through 2024 and into 2025. This well-capitalized environment fuels aggressive competition as reinsurers deploy capital to gain or maintain market share, leading to pricing pressures and a constant drive for efficiency.
Global reinsurance dedicated capital hit an all-time high in 2024, with projections for continued expansion into 2025. This surge is fueled by reinsurers retaining more earnings and a robust market for catastrophe bonds.
This significant influx of capital intensifies the competitive landscape, as reinsurers actively seek opportunities to deploy their resources, especially in property and specialty insurance sectors. For instance, in 2024, the abundant capacity contributed to a moderation in pricing for property reinsurance.
Competitive rivalry in the reinsurance sector, particularly concerning underwriting discipline and risk selection, remains intense. Despite ample market capacity, reinsurers like Everest Re are prioritizing disciplined underwriting, especially in casualty lines where historical adverse reserve development continues to be a concern.
Everest Re has demonstrably adjusted its portfolio to navigate this rivalry, strategically reducing its exposure in certain casualty segments. Concurrently, the company has expanded its presence in property and specialty lines, signaling a clear focus on achieving superior risk-adjusted returns. This strategic repositioning is a critical element of its competitive stance.
Investment Income as a Profit Driver
Beyond the core business of underwriting, reinsurers like Everest Re have seen a substantial boost in profitability from investment income. This trend, particularly pronounced in 2024 and projected to continue into 2025, is largely driven by elevated bond yields. This income stream allows companies to achieve robust returns on equity, even when underwriting results experience volatility, directly impacting competitive pressures as firms chase superior overall financial performance.
The impact of investment income on competitive rivalry within the reinsurance sector is significant. Companies demonstrating strong investment management capabilities can offset weaker underwriting periods. For instance, in 2024, higher interest rates provided a tailwind for investment portfolios across the industry, enabling reinsurers to maintain competitive profitability. This dynamic means that the ability to generate substantial investment income is as crucial as underwriting prowess in the ongoing competition for market share and investor capital.
- Higher bond yields in 2024 and expected for 2025 are a key driver of reinsurer profitability.
- Strong investment income enables companies like Everest Re to achieve high returns on equity, irrespective of underwriting fluctuations.
- This financial flexibility influences competitive dynamics, as firms compete on overall return generation.
Product Diversification and Global Reach
Major reinsurers like Everest Re compete fiercely by offering a wide array of property, casualty, and specialty reinsurance and insurance products. This extensive product diversification allows them to tap into various global markets and mitigate risks effectively. In 2024, the reinsurance industry continued to see this trend, with companies expanding their portfolios to capture opportunities across different lines of business and geographic regions, intensifying the competitive landscape.
Everest Re's global reach, serving clients in numerous countries, is a key differentiator in this highly competitive environment. Companies vie for market share not only through product breadth but also by establishing a strong presence in key international markets. This global footprint is crucial for managing exposure to diverse catastrophic events and economic cycles, making geographic expansion a constant strategic focus.
- Product Breadth: Everest Re offers a comprehensive suite of reinsurance solutions, from traditional property and casualty to complex specialty lines.
- Global Footprint: The company operates across North America, Bermuda, Europe, Asia, and other key international hubs, providing broad market access.
- Risk Mitigation: Diversification across product types and geographies helps Everest Re to balance its risk exposures and capitalize on varied market conditions.
- Competitive Intensity: The industry's high degree of product and geographic diversification means reinsurers must continually innovate and optimize their offerings to stay ahead.
Competitive rivalry in the reinsurance sector is intense, fueled by significant capital inflows and a focus on disciplined underwriting. Despite ample capacity, companies like Everest Re are strategically adjusting portfolios, emphasizing profitable lines and robust investment income to maintain strong returns.
The global reinsurance market saw dedicated capital reach an all-time high in 2024, projected to continue expanding into 2025. This abundant capital intensifies competition, particularly in property reinsurance, leading to pricing moderation. Everest Re's strategic shift towards property and specialty lines, while managing casualty exposures, highlights this competitive dynamic.
Investment income, driven by higher bond yields in 2024 and expected for 2025, provides a crucial competitive advantage. Companies with strong investment management can offset underwriting volatility, enhancing overall profitability and influencing market share battles.
| Metric | 2023 (Actual) | 2024 (Est.) | 2025 (Proj.) |
| Global Reinsurance Dedicated Capital (USD Bn) | ~670 | ~700+ | ~720+ |
| Everest Re Investment Income Growth (%) | +15% | +10-12% | +8-10% |
| Property Reinsurance Pricing Change (%) | -5% to -10% | -2% to -5% | 0% to -2% |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large corporations and primary insurers are increasingly exploring self-insurance and captive insurance arrangements. This allows them to retain more risk internally, thereby reducing their dependence on traditional reinsurers like Everest Re. For instance, the global captive insurance market has seen steady growth, with premiums written by captives reaching an estimated $70 billion in 2023, indicating a significant shift in risk management strategies.
This trend is fueled by a desire for enhanced control over risk management processes and the potential for substantial cost savings. When companies can manage their own risks more efficiently or at a lower cost than through external markets, it directly impacts the demand for traditional reinsurance capacity. This poses a persistent threat to Everest Re's market share as these entities bypass established reinsurance channels.
Insurance-linked securities (ILS), especially catastrophe bonds, represent a potent substitute for traditional property catastrophe reinsurance. In 2024, the market saw record issuance, and this trend is anticipated to continue into 2025, demonstrating their growing appeal as an alternative capital source for peak risk management.
These instruments diversify the risk transfer landscape, often providing more competitive pricing than traditional reinsurance. Everest Re Group, recognizing this shift, actively participates by issuing its own catastrophe bonds, directly engaging with this substitute capital market.
Government-backed insurance programs, particularly for perils like flood or terrorism, can serve as substitutes by offering coverage that private reinsurers might find too risky or costly to provide. These programs, while often utilizing private reinsurers for capacity, can cap the growth potential for traditional reinsurers in specific markets. For instance, the U.S. National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) provides coverage where private insurers might otherwise withdraw, impacting the demand for private flood reinsurance.
Risk Retention Groups and Mutuals
Risk retention groups (RRGs) and mutual insurance companies present a viable substitute for traditional commercial insurance, especially for specialized or hard-to-insure risks. These entities allow groups of similar businesses or professionals to pool resources and self-insure, thereby bypassing the need for external insurance and reinsurance markets.
This self-insurance trend can directly impact the demand for Everest Re Group's services. For instance, in 2024, the RRG market continued to grow, with over 300 RRGs operating in the United States, covering a wide array of industries. These groups collectively wrote billions in premiums, demonstrating a significant alternative to commercial insurers.
The appeal of RRGs and mutuals lies in their potential for cost savings and tailored coverage. By eliminating insurer profit margins and administrative overhead associated with traditional carriers, these alternatives can offer more competitive pricing. This is particularly attractive in sectors facing rising insurance costs or limited capacity from the standard market.
- Niche Market Focus: RRGs often cater to specific industries, offering specialized coverage that might be unavailable or prohibitively expensive through commercial insurers.
- Cost Efficiency: By self-insuring, members can potentially reduce premiums and retain underwriting profits, making them attractive alternatives.
- Regulatory Landscape: The Liability Risk Retention Act of 1986 in the U.S. facilitates the formation and operation of RRGs, fostering their growth as a competitive force.
- Growing Premium Volume: The collective premium volume written by RRGs in the U.S. has consistently increased, indicating a growing market share and a direct challenge to traditional insurers.
Advanced Risk Management and Loss Prevention
The increasing sophistication of risk management and loss prevention technologies presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional reinsurance. Businesses are investing in advanced data analytics and AI-driven solutions to identify and mitigate potential risks proactively. For instance, in 2024, the global risk management software market was projected to reach over $40 billion, indicating a strong trend towards in-house risk reduction.
These advancements enable companies to reduce their reliance on external risk transfer mechanisms like reinsurance. By effectively avoiding or minimizing losses, organizations may find they need less coverage, directly impacting the demand for reinsurance services. This shift represents a powerful substitute, as companies can achieve greater financial stability through internal controls rather than external insurance policies.
- Proactive Risk Mitigation: Businesses are enhancing their capacity to manage and prevent losses internally through improved technologies and practices.
- Reduced Reinsurance Need: Effective risk avoidance and reduction directly decrease the demand for reinsurance coverage.
- Market Growth in Risk Management Solutions: The expanding market for risk management software highlights the industry's commitment to in-house risk control.
- Financial Impact: A decrease in the need for reinsurance can lead to lower operational costs for businesses but poses a threat to reinsurers' revenue streams.
The threat of substitutes for Everest Re Group is significant, stemming from alternative risk transfer mechanisms and evolving corporate risk management strategies. Self-insurance, captive arrangements, and government programs offer ways for companies to retain risk internally or access alternative coverage, reducing reliance on traditional reinsurers. For example, the global captive insurance market saw premiums written by captives reach an estimated $70 billion in 2023, highlighting this shift.
Insurance-linked securities (ILS), such as catastrophe bonds, are increasingly competitive substitutes, especially for property catastrophe reinsurance, with strong issuance in 2024 and expectations for continued growth. Furthermore, advancements in risk management technologies and software, with the global market projected to exceed $40 billion in 2024, allow businesses to mitigate risks internally, thereby decreasing their need for external reinsurance capacity.
| Substitute Type | Description | Market Indicator (2023/2024 Data) | Impact on Reinsurers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance/Captives | Corporations retaining risk internally. | Estimated $70 billion in premiums written by captives (2023). | Reduces demand for traditional reinsurance. |
| Insurance-Linked Securities (ILS) | Catastrophe bonds and similar instruments. | Strong issuance in 2024, continuing trend. | Offers competitive pricing for peak risks. |
| Government Programs | State-backed insurance for specific perils. | e.g., U.S. NFIP provides flood coverage. | Limits private reinsurer growth in certain markets. |
| Risk Retention Groups (RRGs) | Industry groups pooling risk. | Over 300 RRGs in the U.S. (2024). | Provides tailored, cost-effective alternatives. |
| Risk Management Technology | AI and data analytics for loss prevention. | Global risk management software market >$40 billion (2024 projection). | Enables proactive internal risk reduction. |
Entrants Threaten
The insurance and reinsurance sectors demand immense capital. Companies need substantial financial reserves to cover potential claims and adhere to strict regulatory solvency rules, creating a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2023, the global insurance market saw premiums exceed $6.5 trillion, underscoring the sheer scale of capital involved.
These high capital requirements mean that aspiring entrants must secure vast sums of money before even beginning operations. This financial hurdle makes it exceedingly difficult for smaller or less-funded entities to challenge established, well-capitalized players like Everest Re, effectively limiting the threat of new competition.
The global insurance and reinsurance markets are characterized by a very strict regulatory landscape. New companies entering this field must navigate intricate licensing, compliance, and solvency requirements that differ significantly across various countries. For instance, in 2024, the Solvency II Directive in Europe continued to impose rigorous capital adequacy and risk management standards on insurers, demanding substantial upfront investment and ongoing compliance efforts.
These complex and often costly regulatory hurdles act as a significant barrier to entry. New entrants must invest heavily in legal expertise, compliance infrastructure, and capital reserves to meet these demands. This financial and operational burden makes it challenging for smaller or less capitalized firms to compete effectively with established players who have already built the necessary systems and relationships.
In the insurance and reinsurance sectors, building a strong brand reputation and fostering trust is absolutely crucial. Clients are entrusting their financial security to these companies, often through long-term agreements, making a company's perceived stability and reliability a primary concern. Newcomers face a significant hurdle in replicating the decades of trust and established client relationships that major players like Everest Re have cultivated.
Access to Distribution Networks and Expertise
Newcomers face substantial hurdles in establishing robust distribution networks, a crucial element for reaching customers in the insurance sector. Building these channels, whether via brokers, agents, or direct sales, demands considerable capital and a lengthy developmental period. For instance, the global insurance distribution market is projected to reach over $2.5 trillion by 2025, highlighting the scale of investment required.
Furthermore, acquiring the necessary underwriting expertise across a wide array of complex risks is a significant barrier. This deep knowledge is not easily replicated and takes years to cultivate. Everest Re Group, with its established broker relationships and a team of seasoned underwriters, possesses a distinct advantage in this regard.
- Distribution Network Investment: Building and maintaining extensive broker and agent networks requires significant upfront and ongoing financial commitment.
- Underwriting Expertise Barrier: Developing specialized knowledge in diverse and complex risk classes is a time-consuming and resource-intensive process.
- Everest Re's Advantage: The company benefits from its pre-existing, well-developed distribution channels and a deep pool of specialized underwriting talent.
Data and Technology Investment
The threat of new entrants in the reinsurance sector, particularly concerning data and technology, is tempered by the immense investment required. While insurtech innovations can lower barriers in certain niches, establishing the sophisticated data analytics, artificial intelligence, and advanced catastrophe modeling capabilities that incumbents like Everest Re possess necessitates significant capital outlay. Newcomers often find it challenging to replicate the extensive historical data infrastructure and analytical depth that established players leverage for precise risk assessment and pricing.
Consider these points:
- High Capital Requirements: The cost of building and maintaining advanced data analytics platforms and AI capabilities can be prohibitive for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, major reinsurers continued to heavily invest in AI, with some allocating upwards of $100 million annually to data science and technology initiatives to enhance underwriting and risk modeling.
- Data Infrastructure Gap: Everest Re and similar established firms benefit from decades of accumulated proprietary data, which is crucial for training sophisticated models. New entrants must either acquire this data, which is difficult and expensive, or build their own data sets, a lengthy and resource-intensive process.
- Talent Acquisition: The demand for skilled data scientists, AI specialists, and catastrophe modelers remains high. New entrants may struggle to attract and retain the necessary talent to compete with the compensation and resources offered by established, well-capitalized companies.
The threat of new entrants for Everest Re Group is generally low due to substantial barriers. The insurance and reinsurance industries require immense capital, with global premiums exceeding $6.5 trillion in 2023, making it difficult for newcomers to match the financial reserves of established players.
Stringent regulatory environments, such as Europe's Solvency II Directive in 2024, demand significant upfront investment in compliance and capital. Furthermore, building trust and a strong brand reputation, alongside developing sophisticated underwriting expertise and extensive distribution networks, takes considerable time and resources, which new entrants often lack.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Need for substantial financial reserves to cover claims and meet solvency rules. | High; limits smaller or less-funded entities. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex licensing, compliance, and solvency rules across jurisdictions. | High; requires significant investment in legal and compliance infrastructure. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Crucial for long-term client relationships and financial security. | High; difficult for newcomers to replicate decades of established trust. |
| Distribution Networks | Establishing broker, agent, or direct sales channels requires capital and time. | High; significant upfront and ongoing financial commitment needed. |
| Underwriting Expertise | Developing specialized knowledge in diverse and complex risk classes. | High; time-consuming and resource-intensive process to cultivate. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Everest Re Group is built upon comprehensive data from their annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We supplement this with industry-specific research from reputable sources like AM Best and S&P Global Ratings, along with macroeconomic data to capture the broader market landscape.
