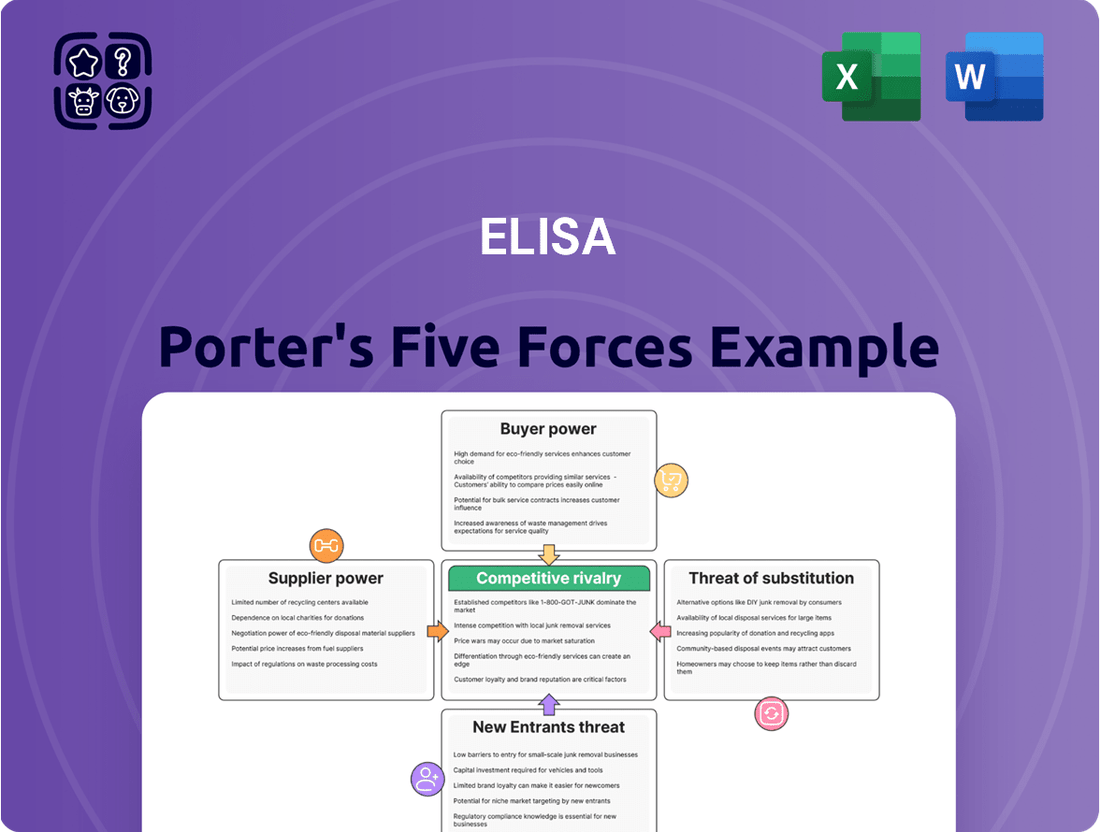
Elisa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Elisa Bundle
Elisa's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intricate web of competitive pressures shaping its market, from the bargaining power of buyers to the looming threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any business aiming to thrive in a dynamic industry.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Elisa’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The telecommunications sector, including companies like Elisa, is heavily dependent on a small group of global providers for crucial network infrastructure. Think of 5G equipment and advanced fiber optic components – these often come from a limited pool of specialized vendors.
This concentration, with companies like Nokia and Ericsson being major players, grants these suppliers considerable influence. For operators such as Elisa, this means less room to negotiate on pricing and contract terms, particularly for essential, cutting-edge technologies where alternative sources are scarce.
Elisa's reliance on core network equipment from a limited number of suppliers creates significant switching costs. These costs encompass the substantial financial outlay for new hardware, intricate software integration, extensive employee training, and the inherent risk of service disruptions during the transition.
For instance, a major network upgrade could easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of euros, making frequent vendor changes impractical. This financial and operational barrier effectively locks Elisa into existing relationships, thereby bolstering the bargaining power of its current core infrastructure suppliers.
Suppliers of advanced telecom equipment and software often possess proprietary technology and patents. This intellectual property acts as a significant barrier, making it difficult for new suppliers to enter the market and limiting Elisa's options for finding less specialized, cheaper alternatives. For instance, companies holding patents on 5G network infrastructure components can command higher prices due to the exclusivity and advanced capabilities of their products.
Importance of Software and IT Service Providers
Elisa's expanding reliance on IT services, cloud solutions, and cybersecurity elevates the importance of specialized software and IT service providers. This shift means Elisa is increasingly dependent on vendors for critical operational components.
While the software and IT service provider market can be fragmented, certain specialized vendors, especially those offering niche or mission-critical solutions, can wield significant bargaining power. This is particularly true when Elisa requires highly specific platforms or applications essential for its operations.
- Increasing IT Spend: Elisa's investment in digital transformation and cloud services, a trend observed across the telecom industry, likely means a growing proportion of its operational expenditure is directed towards software and IT service providers. For instance, global IT spending was projected to reach $5 trillion in 2024, with cloud services accounting for a substantial portion.
- Vendor Lock-in Potential: For highly integrated or proprietary software solutions that are crucial for Elisa's network management or customer service platforms, switching costs can be substantial. This can give dominant software vendors leverage in negotiations for renewals or upgrades.
- Cybersecurity Dependence: The critical nature of cybersecurity solutions means Elisa has limited flexibility in choosing providers for these essential services. A strong reputation and proven efficacy in cybersecurity can grant these vendors considerable bargaining power.
Global Supply Chain Dependencies
Elisa, like many telecommunications firms, faces significant exposure to global supply chain disruptions. These challenges directly influence the availability and cost of essential components, such as semiconductors and network equipment. For instance, the ongoing global chip shortage, which intensified in 2021 and continued through 2024, has led to increased lead times and price hikes for critical electronic parts used in Elisa's infrastructure and devices.
Geopolitical tensions and economic volatility further exacerbate these supply chain vulnerabilities. Events like trade disputes or regional conflicts can disrupt the flow of goods, impacting lead times and component prices. This uncertainty amplifies the bargaining power of suppliers, as they can leverage limited availability and increased demand to negotiate more favorable terms. In 2024, the ongoing semiconductor supply constraints, coupled with rising energy costs, have put upward pressure on the prices of electronic components, directly affecting Elisa's procurement costs.
- Semiconductor Shortage Impact: Extended lead times for critical components like 5G modems and processors, with some lead times exceeding 52 weeks in early 2024.
- Geopolitical Risk Premium: Increased component costs due to trade tariffs and regional instability, adding an estimated 5-10% to procurement expenses for some electronic goods.
- Supplier Concentration: Reliance on a few key manufacturers for specialized network hardware, granting these suppliers significant leverage in pricing and allocation decisions.
Suppliers of critical network infrastructure, like those providing 5G equipment, hold significant power over telecommunications companies such as Elisa. This is due to the limited number of global vendors, proprietary technologies, and high switching costs for Elisa, which can include substantial financial outlays and operational risks.
The dependence on specialized software and IT services also grants certain vendors leverage, especially for niche or mission-critical solutions essential for Elisa's operations. Global IT spending projected to reach $5 trillion in 2024 highlights this increasing reliance.
Supply chain disruptions, such as the ongoing semiconductor shortage impacting 2024, further empower suppliers by limiting availability and increasing costs. This concentration and reliance give suppliers considerable leverage in pricing and allocation decisions.
| Factor | Impact on Elisa | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Infrastructure) | Limited negotiation power for Elisa | Reliance on a few key manufacturers for 5G core network components. |
| Proprietary Technology | High switching costs, limited alternatives | Patents on advanced network technologies restrict access to cheaper options. |
| IT Service Dependence | Potential vendor lock-in for critical software | Global IT spending projected at $5 trillion, with cloud services a major component. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Increased component costs and lead times | Semiconductor lead times exceeding 52 weeks for some parts; 5-10% cost increase due to geopolitical risks. |
What is included in the product
Elisa Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive framework to understand the competitive intensity and attractiveness of Elisa's operating environment, identifying key factors that shape profitability.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
In the competitive Finnish and Estonian mobile markets, customers possess significant bargaining power due to low switching costs. This ease of transition between operators means customers can readily seek out better deals or improved services, directly influencing pricing and service offerings.
Elisa's mobile post-paid churn in Finland saw a decrease in Q1 2025, a positive sign for customer retention efforts. However, the underlying ability for customers to switch providers easily remains a key factor in their bargaining power.
Consumers for mobile, broadband, and entertainment services often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is particularly true in mature markets like Finland and Estonia, where multiple providers offer comparable basic services. For instance, in 2024, the average monthly mobile subscription cost in Finland remained a key consideration for many users, with intense competition driving down prices for comparable plans.
The ease with which customers can switch providers due to similar service offerings allows them to readily compare prices. This dynamic directly translates into considerable pressure on Elisa's profit margins for these core services. In 2024, promotional offers and bundled discounts were prevalent across the Finnish telecommunications sector, reflecting this customer demand for value.
Elisa's strategy of bundling mobile, fixed, broadband, and entertainment services aims to enhance customer loyalty. However, this can paradoxically strengthen customer bargaining power, as they now expect greater value and potentially lower prices for these integrated solutions. In 2024, the average revenue per user (ARPU) for bundled telecom services often reflects this dynamic, with providers needing to offer competitive pricing to secure and retain subscribers within these comprehensive packages.
Enterprise Customers Seeking Integrated Solutions
Enterprise customers, particularly in the public administration and large business sectors, wield considerable bargaining power when procuring integrated IT solutions from providers like Elisa. These clients often require a broad suite of services, encompassing cloud infrastructure, robust cybersecurity measures, and advanced communication capabilities. Their substantial order volumes and the critical nature of these services mean they can negotiate favorable terms, demanding customized solutions that meet stringent security and performance benchmarks.
The bargaining power of these enterprise clients is amplified by their ability to switch providers, especially if Elisa cannot meet their evolving needs or offer competitive pricing. For instance, in 2024, major telecommunications and IT service providers often saw contract renegotiations driven by clients seeking better integration across their digital infrastructure and demanding greater flexibility in service delivery. The sheer scale of these contracts, often running into millions of euros annually, gives these customers significant leverage.
- High Volume Procurement: Large enterprises purchase substantial quantities of Elisa's IT services, giving them considerable negotiation leverage.
- Demand for Customization: Clients require tailored cloud, cybersecurity, and communication solutions, allowing them to dictate specific features and service levels.
- Switching Costs and Alternatives: While switching can be complex, the potential for cost savings and better-aligned solutions empowers customers to demand better terms.
- Strategic Importance of Services: The critical nature of IT infrastructure for business operations means clients have a strong incentive to secure the best possible offerings.
Regulatory Focus on Consumer Choice
Regulatory focus on consumer choice significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. For instance, Estonia's drive to boost competition in communication services, as seen in their efforts to simplify service provider switching, directly empowers consumers. This regulatory push ensures customers can more easily access and opt for better deals, thereby limiting any single provider's ability to retain them through less competitive pricing or service.
This regulatory environment can lead to tangible benefits for consumers. In 2024, countries with strong consumer protection laws often report higher customer satisfaction rates and more competitive pricing across various sectors. For example, initiatives promoting number portability in telecommunications have historically led to increased switching and, consequently, better offers for consumers.
- Increased Switching Rates: Regulations simplifying provider changes can lead to higher customer churn for incumbent firms.
- Price Competition: Empowered customers are more likely to seek out and switch to providers offering lower prices or better value.
- Service Quality Improvement: To retain customers in a more competitive landscape, businesses are incentivized to improve their service offerings.
Customers in Elisa's markets hold substantial bargaining power, driven by low switching costs and price sensitivity, especially for bundled services. This leverage compels Elisa to offer competitive pricing and value, impacting profit margins. Enterprise clients, due to high volume and customization demands, also negotiate favorable terms, further influencing Elisa's strategic service delivery and pricing models.
| Factor | Impact on Elisa | Supporting Data (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs (Mobile) | Increases customer power, pressure on pricing | Mobile post-paid churn in Finland decreased in Q1 2025, but underlying switching ease persists. |
| Price Sensitivity (Bundled Services) | Demands for value, limits ARPU growth | Promotional offers and discounts were prevalent in the Finnish telecom sector in 2024. |
| Enterprise Procurement Volume | Significant leverage for large clients | Major IT contracts can be worth millions annually, enabling strong negotiation. |
| Regulatory Environment | Amplifies consumer choice and competition | Estonia's focus on simplifying service provider switching empowers consumers. |
Full Version Awaits
Elisa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Elisa Porter's Five Forces Analysis, ensuring the document you receive after purchase is precisely this professionally formatted and ready-to-use report. You are not looking at a sample or placeholder; the material presented here is the exact file you will gain immediate access to upon completing your transaction. This ensures transparency and allows you to confidently acquire a valuable strategic tool for understanding competitive forces within an industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Finnish telecommunications landscape is characterized by significant consolidation, with Elisa, Telia Finland, and DNA dominating market share. This oligopolistic structure, however, does not diminish the intensity of competition. In 2023, Elisa reported revenue of €2.3 billion, Telia Finland also saw strong performance, and DNA, now part of Telenor, continues to be a formidable competitor, all vying for customer loyalty.
Estonia's mobile market is a battleground, primarily contested by three major players: Telia Eesti, Elisa Eesti, and Tele2. This dynamic means that customer acquisition and retention are paramount, driving aggressive strategies.
In 2024, these operators are locked in a constant struggle for market share, which translates into fierce price competition and a relentless pursuit of service innovation. For instance, operators are heavily investing in 5G network expansion and offering bundled services to attract and keep subscribers.
The emphasis on network quality is also a significant differentiator, as customers increasingly expect seamless connectivity and high speeds. This competitive pressure ensures that consumers benefit from a wide range of choices and attractive offers.
Major telecom operators, including Elisa, are locked in a fierce battle, pouring billions into expanding their 5G and fiber optic networks. In 2024, for example, the Finnish telecommunications market saw continued aggressive investment in 5G rollout, with companies like Elisa, Telia, and DNA all reporting substantial capital expenditures aimed at capturing market share and enhancing service quality.
This relentless infrastructure expansion creates a highly competitive environment. Companies are vying to offer the fastest speeds and most reliable connections, driving up operational costs and intensifying rivalry. Elisa's commitment to this network race is a key factor in its competitive positioning, as superior connectivity directly translates to customer acquisition and retention in an increasingly data-centric world.
Differentiation through Digital and IT Services
Competitive rivalry in the telecommunications sector is increasingly defined by differentiation through digital and IT services, moving beyond traditional connectivity. Elisa is actively pursuing this strategy, particularly by expanding its international software services under the Elisa Industriq brand. This focus on areas like cloud solutions and cybersecurity signifies a key battleground where companies aim to capture higher-margin revenue streams and distinguish themselves from competitors.
Elisa's strategic push into international software services is a direct response to evolving market demands and a method to enhance its competitive standing. This diversification allows Elisa to offer more comprehensive solutions to its business clients, thereby fostering deeper relationships and creating new avenues for profitable growth. The company's investment in these advanced digital capabilities underscores a broader industry trend where telecom providers are transforming into integrated digital service enablers.
- Elisa Industriq's international expansion targets profitable growth in digital services.
- Competition now encompasses cloud solutions and cybersecurity, not just core connectivity.
- Differentiation through advanced IT services is a key strategy for telecom providers.
Price Wars and ARPU Management
The telecommunications sector often experiences intense price competition, particularly for standard mobile and broadband services. This pressure forces companies like Elisa to carefully manage their Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) to ensure profitability in established markets.
Elisa's strategic focus on value-added services and the adoption of 5G technology appears to be yielding positive results. For instance, Elisa's mobile post-paid ARPU in Finland saw an increase in the first quarter of 2025, demonstrating an ability to extract more revenue per customer.
- Price Wars: Intense competition can drive down prices for basic mobile and broadband plans.
- ARPU Management: Operators must balance competitive pricing with maintaining or increasing ARPU.
- Value-Added Services: Upselling services like 5G is crucial for ARPU growth.
- Q1 2025 Performance: Elisa reported an increase in Finnish mobile post-paid ARPU, indicating successful strategy implementation.
The competitive rivalry within the telecommunications industry, particularly in Elisa's operating markets, remains exceptionally high. This intensity is fueled by a limited number of major players, such as Telia and DNA in Finland, and Telia Eesti, Elisa Eesti, and Tele2 in Estonia, all aggressively pursuing market share.
Companies are investing heavily in network infrastructure, notably 5G and fiber optics, with significant capital expenditures reported throughout 2024. This race for superior connectivity drives differentiation and customer acquisition. For example, Elisa's commitment to 5G expansion is a direct response to this competitive pressure, aiming to attract and retain subscribers through enhanced service quality.
Beyond traditional connectivity, competition is increasingly focused on digital and IT services, including cloud solutions and cybersecurity. Elisa's strategic expansion into international software services via Elisa Industriq exemplifies this trend, as operators seek higher-margin revenue streams and deeper customer relationships.
This fierce competition often leads to price wars for basic services, forcing operators to manage Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) strategically. Elisa's Q1 2025 results, showing an increase in Finnish mobile post-paid ARPU, suggest success in upselling value-added services and leveraging 5G adoption.
| Operator | Key Market | 2024 Focus | Competitive Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elisa | Finland, Estonia | 5G Expansion, IT Services | Network Quality, Digital Solutions |
| Telia | Finland, Estonia | 5G Expansion, Digitalization | Market Share, Service Innovation |
| DNA (Telenor) | Finland | Network Investment | Customer Retention, Bundled Offers |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The proliferation of Over-the-Top (OTT) communication services like WhatsApp, Zoom, and Skype presents a substantial threat of substitutes for Elisa's traditional voice and SMS offerings. These platforms utilize internet infrastructure, effectively bypassing Elisa's network for basic communication needs, thereby eroding a significant portion of legacy revenue streams.
In 2024, it's estimated that over 80% of global smartphone users actively use at least one OTT messaging application, a figure that has steadily climbed. This widespread adoption means that consumers increasingly view these services as direct replacements for costly traditional calls and texts, putting pressure on Elisa's core connectivity revenues.
While Elisa heavily invests in fiber optic networks, alternative broadband technologies like fixed wireless access (FWA) and satellite internet pose a significant threat. These substitutes offer competitive speeds, particularly in areas where fiber deployment is still in its early stages or proves too costly. For instance, by the end of 2023, the global FWA market was valued at approximately $30 billion and is projected to grow substantially, indicating increasing consumer adoption of these alternatives.
Businesses might choose to build and manage their IT infrastructure and cybersecurity internally instead of outsourcing. This approach, while demanding substantial investment and expertise from the client, acts as a direct substitute for Elisa's services, especially for large corporations with unique requirements.
For instance, a significant trend observed in 2024 is the increasing capability of mid-sized enterprises to handle complex IT functions in-house, driven by advancements in cloud-native development tools and readily available cybersecurity talent. This internal shift can reduce the reliance on external IT service providers.
Content Streaming Services and Cord-Cutting
Elisa's entertainment services face significant substitution threats from a growing array of independent streaming platforms like Netflix, Disney+, and YouTube. These platforms offer vast content libraries and flexible subscription models, directly competing for consumer attention and spending.
The ongoing trend of cord-cutting, where consumers increasingly abandon traditional pay-TV bundles for online streaming alternatives, exacerbates this threat. In 2024, it's estimated that over 50 million US households are expected to have cut the cord, a figure projected to rise further.
- Rising Subscription Fatigue: Consumers are juggling multiple streaming subscriptions, leading to potential churn and a search for more consolidated or cost-effective entertainment solutions.
- Content Exclusivity Wars: Major streaming players are investing heavily in exclusive content, creating strong brand loyalty and making it harder for Elisa to retain subscribers if its content library isn't competitive.
- Bundling and Aggregation: New services are emerging that bundle multiple streaming platforms, offering convenience and potentially lower costs, thereby increasing the substitution pressure on standalone offerings.
- Free, Ad-Supported Alternatives: The growth of free, ad-supported streaming services (FAST) also presents a substitution threat, especially for price-sensitive consumers.
Public Wi-Fi and Unlicensed Spectrum Solutions
The rise of public Wi-Fi, especially in urban centers, presents a viable substitute for mobile data. By mid-2024, an estimated 60% of global internet traffic was expected to originate from Wi-Fi networks, highlighting its significant role in data consumption.
Furthermore, advancements in unlicensed spectrum technologies, such as Wi-Fi 6E and future iterations, offer enhanced speeds and capacity, directly competing with cellular data services for bandwidth-intensive activities. This trend could potentially curb the demand for higher-tier mobile data plans.
- Public Wi-Fi Availability: Continues to expand, offering free or low-cost data alternatives.
- Unlicensed Spectrum Growth: Technologies like Wi-Fi 6E are becoming more prevalent, improving performance.
- Impact on Mobile Data: Can reduce user reliance on cellular data, particularly for stationary or semi-stationary use.
The threat of substitutes for Elisa's core telecommunication services remains significant. Over-the-top (OTT) communication apps like WhatsApp and Zoom continue to gain traction, with over 80% of global smartphone users employing at least one such service in 2024. This widespread adoption directly erodes demand for traditional voice and SMS, impacting Elisa's legacy revenue. Furthermore, alternative broadband technologies such as fixed wireless access (FWA) are increasingly competitive, with the global FWA market valued at around $30 billion in 2023, indicating a growing preference for non-fiber solutions in certain areas.
| Substitute Category | Key Substitute | 2024 Impact/Trend | Elisa's Response/Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication | OTT Apps (WhatsApp, Zoom) | >80% smartphone users use at least one; eroding voice/SMS revenue. | Focus on value-added services, digital transformation. |
| Broadband | Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) | Growing adoption, competitive speeds in non-fiber areas. | Continued fiber investment, exploring FWA partnerships. |
| Entertainment | Streaming Platforms (Netflix, Disney+) | Cord-cutting trend; >50 million US households expected to cut the cord in 2024. | Developing own content, bundling strategies, enhancing TV services. |
| Data Access | Public Wi-Fi | Expected to account for ~60% of global internet traffic in 2024; Wi-Fi 6E growth. | Optimizing mobile network performance, offering attractive data plans. |
Entrants Threaten
Building a robust telecommunications network, a necessity for any serious contender, demands substantial upfront capital. This includes the cost of mobile towers, laying fiber optic cables, and establishing data centers, all of which represent a significant financial hurdle.
For instance, in 2024, the average cost to deploy a single 5G macro cell site can range from $50,000 to $150,000, excluding spectrum acquisition. This immense financial barrier effectively deters many potential new entrants from challenging established players like Elisa, who have already made these substantial investments.
The telecommunications sector faces significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory requirements and licensing. New companies must contend with complex application processes, costly spectrum auctions, and adherence to numerous technical and consumer protection standards. For instance, in 2024, spectrum auction participation often involves bids in the billions of dollars, a substantial hurdle for smaller or unestablished players.
Existing operators like Elisa benefit significantly from economies of scale. For instance, Elisa's extensive network infrastructure across Finland, covering 99% of the population with its 5G network as of early 2024, allows for lower per-user operational costs. New entrants would face immense difficulty matching this scale and the associated cost efficiencies without a substantial upfront capital injection, making it challenging to compete on price or service quality.
Strong Brand Loyalty and Established Customer Bases
Elisa boasts a deeply entrenched brand loyalty and a well-established customer base, particularly in its core markets of Finland and Estonia. This strong connection is underscored by its consistently high brand reputation, including a leading sustainability brand ranking in Finland. For any new company looking to enter the telecommunications sector, overcoming Elisa's established trust and customer allegiance presents a formidable barrier.
New entrants face the significant hurdle of replicating Elisa's brand equity, a process that typically requires substantial investment in marketing and customer acquisition. For instance, in 2023, Elisa reported a customer base of over 2.8 million mobile subscriptions in Finland alone, demonstrating the sheer scale of its existing relationships.
- Brand Recognition: Elisa is a household name in Finland, built over decades.
- Customer Loyalty: High customer retention rates, a testament to satisfaction and switching costs.
- Sustainability Leadership: Elisa's commitment to sustainability enhances its brand appeal, making it harder for new entrants to differentiate.
- Market Share: Elisa consistently holds a significant market share in Finland's mobile and fixed broadband segments, indicating strong customer preference.
Limited Available Spectrum
Access to radio spectrum is fundamental for operating a mobile network. These licenses are limited resources, often secured through expensive government auctions. For instance, in 2024, many countries continued to hold spectrum auctions for 5G services, with significant sums changing hands. The scarcity and high cost of acquiring this essential spectrum create a substantial hurdle, effectively limiting the number of new companies that can realistically enter the mobile operator market.
The high barrier to entry posed by spectrum availability directly impacts competition. New entrants must be prepared for substantial upfront investment to even begin operations. This financial commitment, coupled with the technical expertise required to utilize spectrum efficiently, filters out many potential competitors. As of early 2025, the ongoing demand for mobile data and the rollout of advanced technologies like 6G are likely to keep spectrum prices elevated, reinforcing this barrier.
- Spectrum Scarcity: Radio spectrum is a finite resource crucial for mobile communications.
- Auction Costs: Acquiring spectrum licenses often involves significant financial outlay through government auctions.
- High Entry Barrier: The cost and limited availability of spectrum deter new mobile network operators.
- Impact on Competition: This barrier limits the number of players, influencing market dynamics.
The threat of new entrants for Elisa is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements for building and maintaining a telecommunications network. High costs for infrastructure like cell towers and fiber optics, coupled with expensive spectrum auctions, create substantial financial barriers. For example, in 2024, acquiring spectrum for 5G services often involved bids in the billions of dollars, a prohibitive cost for most new players.
Furthermore, stringent regulatory hurdles and licensing processes demand considerable time and financial resources. New companies must navigate complex applications and adhere to technical standards, adding to the difficulty of market entry. Elisa's established economies of scale, with its 5G network covering 99% of Finland's population by early 2024, also provide a cost advantage that new entrants would struggle to match.
Elisa's strong brand loyalty and extensive customer base, evidenced by over 2.8 million mobile subscriptions in Finland as of 2023, represent another significant barrier. Replicating this brand equity requires substantial marketing investment, making it challenging for newcomers to gain traction against a trusted incumbent.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Elisa | 2024/2025 Data Point |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for network infrastructure. | Deters new entrants. | 5G macro cell site deployment: $50,000 - $150,000 per site. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing and spectrum acquisition. | Increases cost and time for new entrants. | Spectrum auction participation often costs billions. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-user costs for established players. | Makes it difficult for new entrants to compete on price. | Elisa's 5G network covers 99% of Finland (early 2024). |
| Brand Loyalty & Customer Base | Established customer relationships and trust. | Creates a significant hurdle for customer acquisition. | Elisa had over 2.8 million mobile subscriptions in Finland (2023). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating information from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and expert interviews. This multi-faceted approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
