DNOW Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
DNOW Bundle
Discover the core competitive pressures shaping DNOW's market landscape. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of substitutes is crucial for any strategic decision.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for DNOW provides a deep dive into these dynamics, revealing actionable insights into the company's competitive positioning. Unlock the full report to gain a comprehensive strategic advantage.
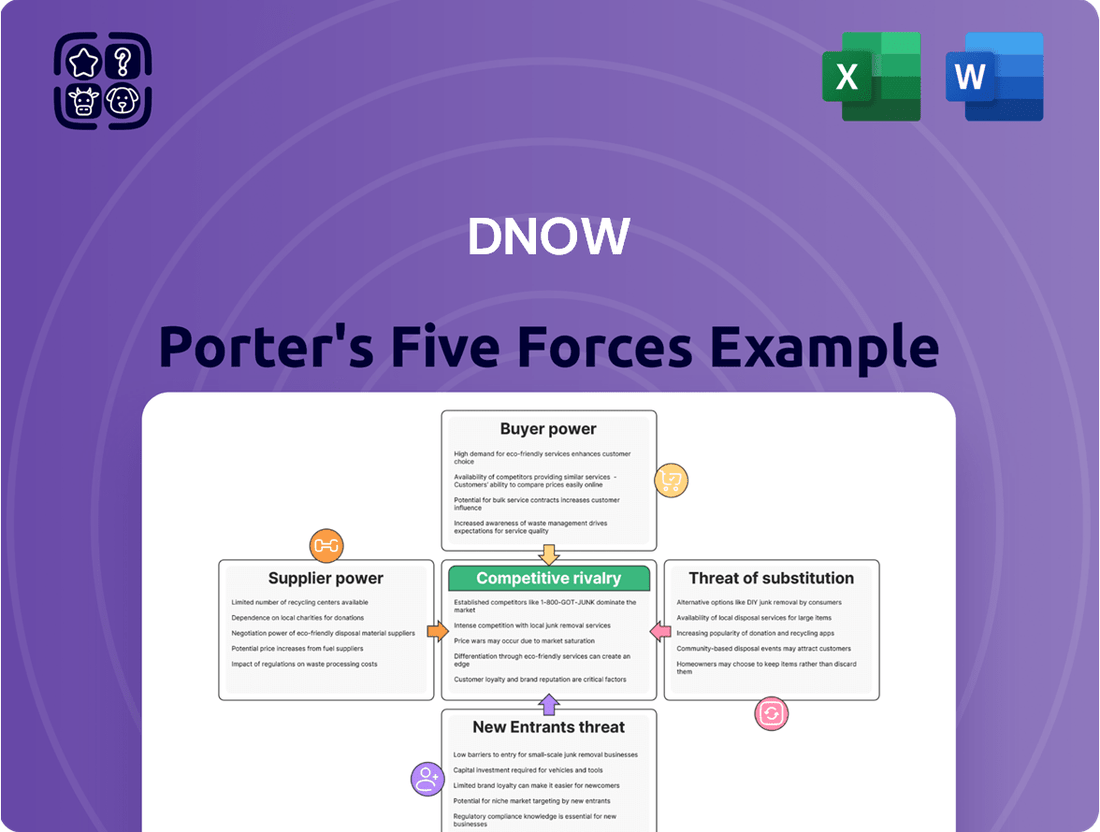
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for DistributionNOW (DNOW) significantly impacts their bargaining power. When a few dominant suppliers provide critical components or products, their ability to dictate terms and raise prices increases, directly affecting DNOW's cost structure.
DNOW actively works to counter this by sourcing from a diverse global network of manufacturers. This broadens their supplier base, reducing reliance on any single entity and thereby mitigating the risk of concentrated supplier power. For instance, in 2024, DNOW’s extensive product catalog includes offerings from thousands of suppliers, ensuring competitive pricing and availability.
The costs DNOW would face to switch from one supplier to another directly impact how much power those suppliers hold. If changing suppliers means DNOW needs to invest heavily in new equipment, get new certifications, or if it would significantly disrupt their operations, then suppliers gain more bargaining strength. For example, if a supplier provides highly specialized components that require unique manufacturing processes, the cost and time to retool for a new supplier could be substantial.
DNOW actively works to reduce these switching costs through its robust supply chain management. By maintaining a broad network of suppliers and optimizing logistics, DNOW aims to make it easier and less disruptive to transition if necessary. This strategic approach helps to mitigate the leverage suppliers might otherwise have due to high switching costs, ensuring more favorable terms for DNOW.
The uniqueness of products and services from DNOW's suppliers significantly impacts their bargaining power. When suppliers offer highly specialized, proprietary, or critical components with limited substitutes, their leverage increases substantially. DNOW's broad product portfolio likely includes both standardized items and unique, specialized offerings, meaning supplier power can vary greatly depending on the specific product category.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is a key consideration for DNOW. If suppliers were to move into DNOW's distribution space, they could potentially bypass DNOW and directly serve the energy and industrial customers. This would significantly increase their bargaining power.
DNOW's existing infrastructure and customer loyalty are critical defenses against this threat. For instance, DNOW's extensive network of service centers and its relationships built over years provide a competitive advantage that suppliers would find challenging to replicate quickly. In 2023, DNOW reported revenues of $1.7 billion, highlighting the scale of its distribution operations that suppliers would need to match.
- Suppliers' potential to enter DNOW's distribution market directly.
- This would allow them to capture more of the value chain.
- DNOW's established distribution network and customer relationships serve as a deterrent.
Importance of DNOW to Suppliers
The significance of DNOW (DistributionNOW) as a customer directly influences the bargaining power of its suppliers. When DNOW accounts for a substantial percentage of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier is more likely to offer competitive pricing and favorable contract terms to retain this key client. This dynamic is amplified by DNOW's extensive global reach and considerable operational scale, making it an attractive and valuable customer for numerous suppliers within its industry.
For instance, in 2023, DNOW reported total revenue of approximately $1.9 billion. If a particular supplier's business is heavily reliant on DNOW for a significant portion of this revenue, their ability to dictate terms diminishes. Conversely, if DNOW is a small part of a supplier's customer base, the supplier holds greater leverage.
- Revenue Dependence: Suppliers whose revenue streams are significantly dependent on DNOW are likely to have less bargaining power.
- Customer Value: DNOW's large order volumes and consistent demand make it a high-value customer, potentially increasing supplier willingness to negotiate.
- Supplier Concentration: The number of alternative suppliers available for DNOW's needs also plays a role; a fragmented supplier market weakens supplier bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers to DistributionNOW (DNOW) is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, switching costs, product differentiation, and the threat of forward integration. DNOW's strategy of maintaining a broad supplier base and optimizing logistics helps to mitigate these pressures.
In 2024, DNOW's extensive product catalog, featuring offerings from thousands of suppliers, enhances its position by reducing reliance on any single entity. This diversification is key to maintaining competitive pricing and ensuring product availability, thereby limiting individual supplier leverage. The scale of DNOW's operations, evidenced by its 2023 revenue of $1.9 billion, also makes it a valuable customer, potentially increasing supplier willingness to negotiate favorable terms.
| Factor | Impact on DNOW | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier power. | Diversified global sourcing network. |
| Switching Costs | High costs empower suppliers. | Robust supply chain management to ease transitions. |
| Product Differentiation | Unique products give suppliers leverage. | Broad product portfolio with both standard and specialized items. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers entering DNOW's market increases their power. | Established distribution network and customer loyalty. |
What is included in the product
DNOW's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its industry, examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing firms.
DNOW's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making and identifying competitive pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration significantly influences the bargaining power of customers for DistributionNOW (DNOW). When a small number of major clients represent a substantial portion of DNOW's sales, these key customers gain leverage to negotiate more favorable pricing and contract terms, potentially impacting DNOW's profit margins.
DNOW's strategy of serving a broad range of segments within the energy sector, including upstream, midstream, and downstream operations, helps to mitigate the risk associated with high customer concentration. This diversification spreads revenue across a wider customer base, reducing reliance on any single client and thus tempering individual customer bargaining power.
Customer switching costs are a key factor in how much power buyers have over DNOW. If it's easy and cheap for a customer to switch to a different supplier, they can demand better prices or terms, which weakens DNOW's position.
Conversely, if switching is difficult or expensive, customers have less leverage. DNOW works to make switching costly by offering a wide variety of products, efficient supply chain solutions, and extra services that make it harder for customers to leave. For example, in 2023, DNOW reported that its customer retention rate remained strong, indicating a degree of stickiness due to these integrated offerings.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant lever in the energy sector, particularly in commodity markets where products are often undifferentiated. For instance, in 2024, many upstream oil and gas operators faced pressure to manage costs, making them highly attuned to price fluctuations for essential supplies and services.
This heightened sensitivity directly translates to increased bargaining power for customers. When buyers can easily switch suppliers based on minor price differences, they can exert considerable pressure on distributors like DNOW to lower their margins.
DNOW can mitigate this by focusing on value-added services and engineered solutions. By offering specialized expertise, customized product configurations, or integrated supply chain management, DNOW can move beyond being just a product vendor and reduce direct competition based solely on price.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers integrating backward, essentially performing distribution themselves, directly amplifies their bargaining power against DNOW. If DNOW's clients, particularly large industrial users, possessed the capability and efficiency to source and distribute products directly from manufacturers, it would significantly erode DNOW's value proposition and market position.
However, DNOW's significant investment in an extensive, specialized supply chain network and deep industry expertise acts as a substantial deterrent to such backward integration. For instance, DNOW's robust inventory management and logistics capabilities, which include handling hazardous materials and ensuring timely delivery to remote locations, are complex and costly for individual customers to replicate. In 2023, DNOW reported a gross profit margin of 17.4%, indicating the value and efficiency it brings to the supply chain that would be difficult for customers to match internally.
- Customer Backward Integration Threat: Customers can gain leverage by threatening to perform distribution themselves, potentially bypassing DNOW.
- DNOW's Mitigation: DNOW's specialized logistics, inventory management, and industry knowledge create significant barriers to customers integrating backward.
- Cost of Replication: Establishing a comparable distribution network requires substantial capital investment and operational expertise, making it unattractive for most customers.
- Value Proposition: DNOW's efficient supply chain services allow customers to focus on their core operations, rather than managing complex distribution needs.
Information Availability to Customers
The ease with which customers can access information about pricing and available alternatives significantly impacts their negotiating strength. As market transparency grows, customers can more readily compare DNOW's offerings against competitors, thereby increasing pressure on the company to maintain competitive pricing and service levels. For instance, in 2024, online marketplaces and industry comparison sites continued to proliferate, making it simpler for buyers in the oil and gas distribution sector to identify the best deals.
DNOW's strategic initiative, DigitalNOW®, plays a crucial role in this dynamic. By providing customers with enhanced digital tools and readily accessible product information, DNOW aims to improve the overall customer experience. This focus on information accessibility and convenience can foster stronger customer loyalty, potentially mitigating some of the bargaining power derived from information availability.
- Increased Transparency: Customers' ability to easily compare pricing and product features across various suppliers in 2024 elevated their negotiating leverage.
- DigitalNOW® Impact: DNOW's digital platform aims to counter this by offering superior customer experience and valuable, easily accessible information, fostering loyalty.
- Competitive Pressure: Greater information access directly translates to increased pressure on DNOW to offer competitive pricing and differentiated services.
The bargaining power of customers for DistributionNOW (DNOW) is influenced by several factors, including customer concentration, switching costs, price sensitivity, the threat of backward integration, and information availability. When a few large customers dominate DNOW's sales, they gain significant leverage to negotiate better terms, impacting profitability. DNOW's strategy of serving diverse segments within the energy sector helps to spread risk and reduce reliance on any single client, thereby tempering individual customer bargaining power.
High switching costs for customers strengthen DNOW's position, as it becomes more difficult and expensive for clients to move to a competitor. DNOW actively works to increase these costs by offering a comprehensive product range, efficient supply chain solutions, and value-added services. In 2023, DNOW's strong customer retention rate indicated the effectiveness of these integrated offerings.
Customer price sensitivity is a critical factor, especially in commodity-driven markets like oil and gas, where buyers are highly attuned to price differences. In 2024, many energy operators faced cost pressures, increasing their demand for competitive pricing. DNOW counters this by focusing on value-added services and engineered solutions, differentiating itself beyond mere price competition.
The potential for customers to integrate backward, handling distribution themselves, directly enhances their bargaining power. However, DNOW's substantial investment in a specialized supply chain network and deep industry expertise presents a significant barrier to this integration. The company's robust inventory management and logistics, including handling specialized materials and ensuring delivery to remote sites, are complex and costly for individual customers to replicate. DNOW's 2023 gross profit margin of 17.4% reflects the value and efficiency it brings to the supply chain, which is difficult for customers to match internally.
Increased market transparency, fueled by online marketplaces and industry comparison sites in 2024, empowers customers by making it easier to compare DNOW's offerings with competitors. This heightens pressure on DNOW for competitive pricing and service levels. DNOW's DigitalNOW® initiative aims to mitigate this by enhancing the customer experience with accessible information and digital tools, fostering loyalty and potentially reducing the impact of information availability on bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on DNOW | DNOW's Mitigation Strategy | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High concentration increases buyer power. | Diversification across energy segments. | Ongoing risk management. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs increase buyer power. | Comprehensive product/service offerings, integrated solutions. | Customer retention remains key. |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity increases buyer power. | Focus on value-added services, engineered solutions. | Cost pressures on energy clients are significant. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Threat reduces DNOW's value proposition. | Specialized logistics, inventory management, industry expertise. | High capital and operational barriers for customers. |
| Information Availability | Increased transparency empowers buyers. | DigitalNOW® platform for enhanced customer experience. | Proliferation of online comparison tools. |
Preview Before You Purchase
DNOW Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete DNOW Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the energy industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring there are no surprises or placeholder content. You are looking at the actual document, which is ready for immediate download and use the moment you buy, providing you with actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial distribution market for energy and industrial products is quite crowded, featuring a wide array of companies, from global giants to niche regional specialists. This intense competition means DNOW must constantly adapt and innovate to maintain its market position.
DNOW contends with significant rivals like WESCO International, Genuine Parts Company, Fastenal Company, Motion Industries, and MRC Global. These competitors, many of which are publicly traded, operate with substantial resources and established supply chains, presenting a formidable challenge.
For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, WESCO International reported net sales of approximately $5.7 billion, demonstrating the scale of operations DNOW is up against. Similarly, Fastenal Company, a major player, had a market capitalization in the tens of billions of dollars, indicating its significant market presence and financial clout.
The growth rate of the industrial distribution market directly impacts how intensely companies compete with each other. When the market is expanding quickly, there's more room for everyone to grow, which can lessen the pressure to steal market share. However, if growth slows down, the competition heats up as businesses fight harder for the same pool of customers.
Looking ahead, the global industrial distribution market is expected to see continued growth, which is generally good news for easing competitive pressures. For instance, projections indicate the market could reach approximately $13.8 trillion by 2027, up from around $10.3 trillion in 2022, suggesting an overall expansion. This upward trend could provide a buffer against fierce rivalry.
However, it's crucial to remember that this overall growth might not be uniform across all segments. Specific energy-related sub-sectors within industrial distribution could experience different growth trajectories. For example, while renewable energy components might see robust demand, traditional oil and gas distribution might face different market dynamics, potentially leading to varied levels of competitive intensity depending on the specific niche.
The degree to which DNOW's competitors can differentiate their offerings significantly influences the intensity of rivalry. When products are similar, price becomes the primary battleground, squeezing profit margins.
DNOW actively works to stand out by providing more than just basic product distribution. Its focus on engineered solutions, comprehensive supply chain management, and specialized valve actuation services creates distinct value propositions that move beyond commoditized offerings.
For instance, in 2023, DNOW reported that its engineered solutions segment, which includes services like valve automation, contributed to its overall revenue growth, demonstrating the market's receptiveness to differentiated services. This strategic differentiation helps DNOW mitigate direct price competition and fosters stronger customer loyalty.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the industrial distribution sector, like those faced by DistributionNOW (DNOW), can intensify competitive rivalry. This is because companies might continue operating even when unprofitable, delaying market consolidation. For DNOW, substantial investments in its extensive network of distribution centers and significant inventory levels act as considerable capital-tied exit barriers.
These investments make it economically challenging for firms to simply cease operations or divest assets without incurring substantial losses. For instance, in 2023, DNOW reported total inventory valued at approximately $1.2 billion, a clear indicator of the capital commitment involved. This high level of investment discourages companies from exiting the market, thereby keeping more competitors in play and sustaining competitive pressure.
- High Capital Investment: DNOW's significant investment in physical infrastructure and inventory creates a substantial hurdle for exiting the market.
- Prolonged Rivalry: The difficulty in exiting means less profitable firms may persist, maintaining a higher level of competition.
- Inventory Value: DNOW's inventory, valued at over $1.2 billion in 2023, exemplifies the capital tied up, increasing exit barriers.
Diversity of Competitors
The competitive landscape for DistributionNOW (DNOW) is characterized by a wide array of players, each with distinct strategic approaches, origins, and objectives. This diversity inherently fuels intense rivalry, as companies compete across various fronts, from pricing and product offerings to service levels and geographic reach. For instance, some competitors might focus on aggressive cost leadership, while others prioritize innovation or specialized service niches. This multifaceted competition makes it challenging for any single player to dominate across all dimensions.
DNOW's strategic actions, such as its acquisition of Trojan Rentals and its combination with MRC Global, underscore the dynamic nature of this rivalry. These moves are designed to bolster DNOW's market position, expand its service capabilities, and potentially achieve greater economies of scale. Such consolidation and strategic realignments are often responses to the pressures exerted by a diverse and active competitive set, aiming to create a more formidable entity capable of navigating the complexities of the market.
The varied strategic priorities among competitors mean that DNOW faces challenges on multiple fronts. A competitor might excel in rapid delivery in one region, while another might offer a broader product catalog or more integrated digital solutions. This necessitates that DNOW continuously adapts its strategies to remain competitive, ensuring it can effectively counter threats and capitalize on opportunities presented by this heterogeneous competitive environment.
- Diverse Competitor Strategies: Competitors employ varied approaches, including cost leadership, product differentiation, and niche market specialization, creating a complex competitive arena.
- Strategic Acquisitions and Combinations: DNOW's moves, like integrating with MRC Global, are strategic responses to intensify rivalry and enhance market standing.
- Impact of Strategic Differences: Divergent strategic objectives among rivals lead to competition on different performance metrics, making market dynamics intricate.
Competitive rivalry within the industrial distribution sector is intense, driven by a crowded market with numerous players ranging from global conglomerates to specialized regional firms. DNOW faces formidable competitors like WESCO International and Fastenal Company, both of which possess substantial financial resources and well-established operational networks. For instance, WESCO International's net sales in Q1 2024 were approximately $5.7 billion, highlighting the scale of DNOW's rivals.
The intensity of this rivalry is further amplified by high capital investments required for infrastructure and inventory, which act as significant exit barriers. DNOW's own inventory, valued at over $1.2 billion in 2023, exemplifies this commitment, discouraging firms from leaving the market and thus sustaining competitive pressure. This dynamic means that even less profitable companies may remain active, contributing to a persistently competitive environment.
Competitors employ diverse strategies, from aggressive cost leadership to specialized service offerings, forcing DNOW to continuously adapt. DNOW's strategic moves, such as its integration with MRC Global, are responses aimed at strengthening its market position and enhancing its competitive capabilities in this multifaceted landscape.
| Competitor | Approximate Q1 2024 Net Sales (USD Billions) | Market Capitalization (Approximate, USD Billions) | Key Strategic Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| WESCO International | 5.7 | N/A (Publicly Traded) | Broad product and service offerings, supply chain solutions |
| Fastenal Company | N/A | Tens of Billions | Onsite supply, inventory management, industrial and construction supplies |
| Genuine Parts Company | N/A | N/A (Publicly Traded) | Automotive and industrial parts distribution |
| Motion Industries | N/A | N/A (Subsidiary of Genuine Parts Company) | Industrial product and service distribution |
| MRC Global | N/A | N/A (Publicly Traded) | Pipe, valve, and fitting distribution for energy sectors |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for DNOW, a distributor of pipes, valves, and fittings, is a significant concern. Customers can bypass distributors like DNOW by directly sourcing products from manufacturers, potentially cutting out intermediary costs. This direct procurement model is becoming more feasible as supply chains evolve and digital platforms facilitate easier access to producers.
Furthermore, the development of alternative materials and technologies can reduce the demand for DNOW's traditional product lines. For instance, advancements in composite materials or new engineering techniques might offer comparable or superior performance to the metal-based products DNOW typically supplies, thereby diminishing the need for their specific offerings.
The ongoing global transition towards cleaner energy sources also presents a substantial substitution threat. As industries shift away from fossil fuels, the demand for the specialized pipes, valves, and fittings used in oil and gas exploration and transportation may decline. For example, in 2024, renewable energy investments continued to surge, with global renewable energy capacity additions expected to reach record levels, impacting the long-term outlook for traditional energy infrastructure components.
The appeal of substitute products or services hinges significantly on their price-performance ratio. When alternatives provide comparable or superior functionality at a reduced cost, the threat they pose to DNOW intensifies. For instance, if a competitor offers a similar oil and gas supply chain solution for 15% less with only a minor performance difference, customers might be tempted to switch.
DNOW must consistently highlight the superior value and operational efficiency embedded in its supply chain solutions and product offerings. This proactive communication is crucial to validate its pricing structure and retain customer loyalty against potentially cheaper alternatives. For example, demonstrating a 99.8% on-time delivery rate, as DNOW often achieves, can justify a premium over less reliable substitutes.
The likelihood of customers switching from DNOW's offerings to substitutes hinges on how easily they can alter their current operational procedures and established business relationships. If the financial or logistical hurdles involved in adopting an alternative are minimal, customers are more inclined to explore those options.
DNOW actively works to mitigate this threat by emphasizing its integrated solutions, which often involve complex supply chains and specialized services that are difficult for customers to replicate independently. For instance, in 2024, DNOW continued to invest in its digital platforms, aiming to create a more seamless and indispensable experience for its clients, thereby increasing the switching costs.
Technological Advancements Creating Substitutes
Technological advancements are a significant threat, as they can introduce entirely new substitutes that bypass existing industry structures. For instance, breakthroughs in material science might yield advanced composites or polymers, potentially reducing the reliance on traditional metal components that DNOW supplies. This innovation could directly impact demand for DNOW's core product offerings.
DNOW's strategic focus on energy evolution and renewable markets, as evidenced by their participation in projects like the development of hydrogen infrastructure, demonstrates an understanding of and adaptation to these shifting technological landscapes. This proactive approach is crucial for mitigating the threat of substitutes by exploring new avenues for growth and relevance.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by the rapid pace of technological change. Consider how advancements in 3D printing for specialized components could offer an alternative to traditional manufacturing and supply chains. While specific data on the direct impact of these nascent technologies on DNOW's market share in late 2024 or early 2025 is still emerging, the potential for disruption is clear.
- Emerging Materials: Innovations in composites and advanced alloys could offer lighter, more durable, or cost-effective alternatives to steel and iron pipes used in oil and gas infrastructure.
- Digitalization & Automation: Increased use of digital twins and predictive maintenance might reduce the need for physical spare parts and on-site equipment replacements, impacting service revenue streams.
- Alternative Energy Infrastructure: The build-out of renewable energy sources like solar and wind requires different types of specialized components and materials, potentially diverting investment and demand away from traditional energy sector supplies.
- 3D Printing Applications: The growing capability of 3D printing for creating complex metal parts on-demand could disrupt traditional inventory and supply models for specialized equipment.
Regulatory or Environmental Shifts
Changes in regulations or growing environmental concerns can significantly boost the appeal of substitute products and services. For example, if new environmental mandates are introduced, they might push industries towards solutions that DNOW doesn't currently dominate, or accelerate the shift to alternative energy sources that rely on entirely different infrastructure and supply networks.
DNOW's proactive stance on sustainability, including its EcoVapor product line, is a direct response to these evolving market dynamics. These initiatives aim to mitigate the threat by offering solutions that align with increasing environmental scrutiny.
For instance, in 2024, the global investment in clean energy technologies reached an estimated $2 trillion, a substantial increase driven by policy support and environmental awareness. This trend underscores the growing demand for alternatives that DNOW must address.
- Regulatory Pressure: Stricter emissions standards or waste disposal regulations can make existing DNOW offerings less competitive against greener alternatives.
- Environmental Mandates: Government-imposed targets for carbon reduction or renewable energy adoption can spur the market for substitute technologies.
- Consumer and Investor Demand: A growing preference for environmentally responsible products and services influences corporate purchasing decisions, favoring substitutes.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in alternative energy or resource efficiency can create viable substitutes that bypass traditional supply chains.
The threat of substitutes for DNOW is significant, driven by customers' ability to bypass distributors by sourcing directly from manufacturers, a trend facilitated by evolving supply chains and digital platforms. This direct procurement can reduce costs for buyers.
Advancements in materials and technologies also pose a threat, as new solutions may offer comparable or superior performance to DNOW's traditional product lines, diminishing demand for their specific offerings.
The global shift towards cleaner energy sources further amplifies this threat, potentially reducing demand for components used in traditional energy infrastructure. For example, in 2024, renewable energy investments continued to grow, impacting the long-term outlook for oil and gas sector supplies.
The price-performance ratio of substitutes is a key driver of customer switching. If alternatives offer similar functionality at a lower cost, the threat to DNOW increases. For instance, a 15% cost reduction with minimal performance compromise could sway customers.
DNOW mitigates this by emphasizing its value proposition, including operational efficiency and reliability, like its frequent 99.8% on-time delivery rates, to justify its pricing against less reliable substitutes.
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to enter the industrial distribution market presents a substantial hurdle for potential new competitors. Establishing a widespread network of distribution centers, maintaining significant inventory levels, and developing advanced supply chain operations, much like those of DNOW, necessitate considerable upfront investment. For instance, companies in this sector often need millions to set up even a regional presence.
Existing players like DNOW benefit from significant economies of scale in procurement, logistics, and operations. For instance, in 2023, DNOW reported total revenue of $1.7 billion, indicating a substantial operational footprint that allows for bulk purchasing discounts and optimized distribution networks. These cost advantages make it exceedingly difficult for new entrants to initially compete on price against established companies.
Newcomers face a significant challenge in accessing established distribution channels and securing relationships with key customers. DNOW, with its extensive history, has cultivated a robust network of branches and strong ties with major players in the energy and industrial markets, making it difficult for new entrants to replicate this advantage.
Product and Service Differentiation
DNOW's extensive product catalog, coupled with its value-added services and custom-engineered solutions, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. Replicating this breadth and depth of offering, which includes specialized pipe, valve, and fitting solutions tailored to specific industry needs, would require substantial investment and time. For instance, DNOW's ability to provide integrated supply chain management and technical support alongside its product offerings creates a sticky customer relationship that is difficult for newcomers to disrupt.
New entrants must develop a truly unique value proposition to lure customers away from established players like DNOW. This might involve focusing on niche markets, leveraging disruptive technology, or offering a significantly lower cost structure. However, DNOW's established reputation for reliability and its deep understanding of customer operational requirements, honed over decades, make it a formidable competitor to displace. In 2023, DNOW reported revenue of $2.1 billion, demonstrating its significant market presence.
- Comprehensive Product Range: DNOW offers a vast array of pipe, valve, and fitting products, often customized for specific industrial applications.
- Value-Added Services: Services like inventory management, technical support, and project-specific kitting enhance customer loyalty and create switching costs.
- Engineered Solutions: DNOW's capacity to design and deliver engineered solutions for complex projects is a key differentiator that requires specialized expertise and infrastructure.
- Market Presence: With a strong track record and established customer relationships, DNOW benefits from significant brand recognition and trust, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policies and regulations, especially within the energy sector, significantly shape the threat of new entrants for companies like DNOW. Strict compliance requirements, the need for various permits, and adherence to specific industry standards can create substantial hurdles and increase the initial capital investment required for newcomers. For instance, environmental regulations mandated by bodies such as the EPA can necessitate costly equipment upgrades or operational changes, making market entry more challenging.
DNOW's established track record and deep understanding of these complex regulatory landscapes, including those pertaining to oil and gas exploration and distribution, provide a distinct competitive advantage. This familiarity allows them to navigate the permitting processes and compliance obligations more efficiently than a new entrant might. In 2024, the energy sector continued to see evolving regulations around emissions and safety, further solidifying the importance of regulatory expertise as a barrier.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants face significant upfront costs to meet environmental and safety standards in the energy sector.
- Permitting Processes: Obtaining necessary permits for operations can be time-consuming and complex, acting as a deterrent.
- Industry Standards: Adherence to specific technical and operational standards requires investment in specialized equipment and training.
- DNOW's Advantage: Existing players like DNOW benefit from established relationships with regulatory bodies and a proven ability to comply, reducing this threat.
The threat of new entrants for DNOW is generally considered moderate due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for infrastructure and inventory, coupled with established economies of scale enjoyed by DNOW, make it difficult for newcomers to compete on price. Furthermore, DNOW's extensive distribution networks, strong customer relationships, and comprehensive product and service offerings create substantial switching costs for clients, further deterring new market participants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | Significant investment needed for distribution centers, inventory, and supply chain infrastructure. | High barrier, requiring substantial upfront funding. |
| Economies of Scale | DNOW's large operational footprint (e.g., $2.1 billion revenue in 2023) allows for cost advantages in procurement and logistics. | New entrants struggle to match DNOW's cost efficiency. |
| Distribution Channels & Customer Relationships | DNOW's established branch network and long-standing ties with key industrial clients. | Difficult for new players to gain access and build trust. |
| Product Breadth & Value-Added Services | Extensive product catalog, engineered solutions, and services like inventory management. | Requires significant investment in expertise and offerings to replicate. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex regulations, particularly in the energy sector, demands expertise and investment. | Adds to upfront costs and operational complexity for new entrants. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our DNOW Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive blend of data, including company financial statements, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from trade publications and publicly available competitor data to provide a robust assessment of the competitive landscape.
