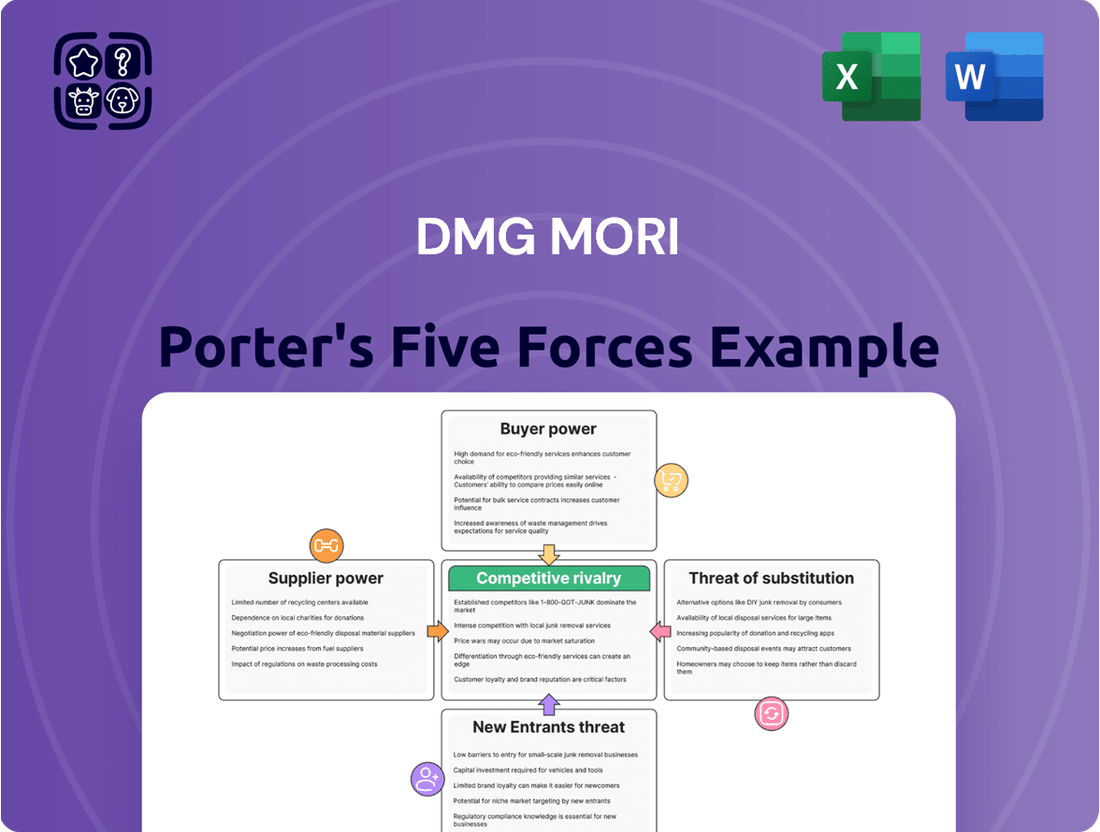
DMG Mori Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
DMG Mori Bundle
DMG Mori, a leader in machine tool manufacturing, faces intense competition and evolving market dynamics. Understanding the forces shaping its industry is crucial for strategic planning. Our analysis delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping DMG Mori’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration significantly impacts the machine tool industry, including DMG Mori. When a limited number of suppliers provide specialized, high-precision components, such as advanced control systems or unique high-grade alloys, their bargaining power escalates. This concentration can translate into higher input costs for DMG Mori, as these suppliers face less competition and can dictate terms. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor shortage, a critical input for advanced control systems, saw prices for certain microcontrollers used in industrial machinery increase by up to 30% for manufacturers relying on a few key chip makers.
Switching suppliers in the machine tool sector, a core area for DMG Mori, is often a significant undertaking. The process can involve substantial costs and complexities, such as redesigning components to fit new specifications, undergoing rigorous re-certification processes for materials, and recalibrating entire manufacturing lines. These high switching costs effectively increase the bargaining power of DMG Mori's suppliers, as they create a strong incentive for DMG Mori to maintain existing relationships even if pricing or terms become less favorable.
When suppliers offer highly unique or proprietary technologies, their bargaining power significantly increases. For DMG Mori, this could manifest in specialized CNC control software or advanced materials crucial for their cutting-edge manufacturing solutions. For instance, if a key supplier holds patents for a critical component that is difficult to replicate, DMG Mori's dependence on that supplier would be high, giving the supplier considerable leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers significantly impacts DMG Mori's bargaining power. If suppliers possess the capability and motivation to manufacture machine tools directly, they gain leverage. This scenario is more plausible for larger, diversified suppliers within the broader industrial sector, rather than those specializing in highly niche components.
For instance, a major supplier of advanced robotics or automation software, already deeply integrated into manufacturing processes, might consider developing its own machine tool offerings. This could be driven by a desire to capture a larger share of the value chain or to offer more comprehensive solutions to end customers.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers with existing manufacturing expertise, R&D capabilities, and established distribution networks are better positioned for forward integration.
- Supplier Incentive: A supplier might integrate forward if they perceive higher profit margins in machine tool production or if they want to secure their customer base by offering a complete product suite.
- Market Dynamics: In a consolidating market, a supplier might see forward integration as a way to gain market share and compete more directly with established players like DMG Mori.
- Component Specialization: The likelihood of forward integration is lower for suppliers of highly specialized, custom-engineered components where their expertise is very specific and not easily transferable to full machine tool production.
Importance of DMG Mori to Suppliers
DMG Mori's substantial size and global reach mean it is often a significant customer for its suppliers. For instance, if a particular supplier generates a large percentage of its annual revenue from DMG Mori, that supplier's ability to dictate terms or raise prices is diminished. This dependency strengthens DMG Mori's position, as suppliers are motivated to maintain a favorable relationship to secure ongoing business. In 2023, DMG Mori reported a significant order intake, indicating continued demand for its machine tools, which translates to substantial business for its supply chain partners.
This dynamic is crucial in understanding the bargaining power of suppliers. When a supplier relies heavily on DMG Mori, they are less likely to exert significant pressure on pricing or contract terms. Conversely, suppliers who have diversified their customer base and are less reliant on DMG Mori may possess greater leverage. The company's procurement strategy likely involves identifying and cultivating relationships with suppliers where this dependency is balanced, ensuring cost-effectiveness while maintaining quality and reliability.
- DMG Mori's significant customer base reduces supplier reliance.
- Suppliers with diversified revenue streams have more bargaining power.
- DMG Mori's 2023 order intake highlights its importance to suppliers.
- Procurement strategies aim to balance supplier dependency and leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for DMG Mori is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, switching costs, differentiation of inputs, and the threat of forward integration. In 2024, the machine tool industry continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions, particularly for specialized electronic components, leading to increased input costs for manufacturers like DMG Mori. For example, lead times for certain high-precision sensors extended by an average of 15% compared to 2023, impacting production schedules and costs.
High switching costs for DMG Mori, stemming from the need for component redesign and recalibration, empower suppliers. When suppliers provide unique technologies, such as proprietary software for advanced machining, their leverage grows. While direct forward integration by component suppliers into machine tool manufacturing is less common, suppliers of broader automation solutions might explore this avenue, increasing pressure on DMG Mori.
DMG Mori's substantial order volume in 2023, which saw a notable increase in global demand for its advanced machinery, suggests it is a key customer for many suppliers. This scale can reduce supplier reliance and thus their bargaining power. However, suppliers with diversified customer bases can still exert considerable influence.
| Factor | Impact on DMG Mori | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier power, leading to higher costs | Continued reliance on a few key semiconductor suppliers |
| Switching Costs | High costs empower existing suppliers | Significant investment required for component compatibility |
| Input Differentiation | Unique inputs grant suppliers leverage | Patented control systems and specialized alloys |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for new competition | Low for niche component suppliers, moderate for automation providers |
| DMG Mori's Customer Size | Reduces supplier reliance, lessening their power | 2023 order intake highlights DMG Mori's importance to its supply chain |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting DMG Mori, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the machine tool industry.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Effortlessly adapt strategic responses to shifting market forces, ensuring DMG Mori stays ahead of the curve.
Customers Bargaining Power
DMG Mori's customer base spans diverse sectors like automotive and aerospace. The global machine tool market was valued at $96.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $101.51 billion by 2025.
If a significant portion of DMG Mori's revenue comes from a small number of major clients, these large customers possess considerable bargaining power. This concentration allows them to negotiate more favorable terms due to the potential impact of their business on DMG Mori's overall sales volume.
Customers investing in DMG Mori's sophisticated CNC turning and milling machines, alongside their automation and software solutions, encounter significant switching costs. These expenses encompass the substantial initial capital outlay for the machinery itself, the intricate process of integrating new equipment into existing production workflows, the necessary training for operators to effectively utilize the new technology, and the potential for considerable disruption to ongoing manufacturing operations during the transition period.
These high switching costs effectively diminish the bargaining power customers hold over DMG Mori. For instance, a manufacturer deeply integrated with DMG Mori's proprietary software and specialized tooling would find it prohibitively expensive and time-consuming to transition to a competitor's offerings, making them less likely to demand lower prices or more favorable terms.
Customer price sensitivity is a key factor influencing DMG Mori's bargaining power of customers. Industries such as automotive and aerospace, known for their lean operations and focus on cost optimization, often exhibit high price sensitivity, particularly for standard machine tool solutions. For instance, in 2023, the automotive sector continued to grapple with supply chain costs, making price a significant consideration in capital equipment purchases.
However, this sensitivity can shift when dealing with highly specialized or advanced manufacturing technologies. In these cases, customers may prioritize precision, unique functionalities, and technological innovation, making them more willing to invest a premium. DMG Mori's ability to offer differentiated, high-performance solutions can mitigate the impact of price sensitivity for these specific customer segments.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, while generally low for DMG Mori, is a factor to consider. Very large manufacturing clients, particularly those with substantial in-house engineering capabilities and a consistent, high-volume need for specific types of machine tools, could theoretically explore developing their own machinery. This would directly diminish DMG Mori's leverage by offering an alternative to purchasing their products.
However, the machine tool industry is characterized by extreme specialization and significant capital investment. The complexity involved in designing, engineering, and manufacturing advanced CNC machines, including the necessary software and precision components, makes it a rare undertaking for most customers. For instance, the research and development costs alone for a new high-precision milling machine can run into tens of millions of dollars, a barrier that few end-users can overcome.
- Low Likelihood: The high specialization and capital intensity of machine tool manufacturing present significant hurdles for customer backward integration.
- Rarity of Capability: Only a select few extremely large manufacturing entities possess the necessary technical expertise and financial resources to consider such a move.
- Impact on Power: Successful backward integration by a customer would directly reduce DMG Mori's bargaining power by creating an in-house alternative.
Availability of Substitute Products/Services for Customers
While truly direct substitutes for DMG Mori's highly specialized, precision machine tools are scarce, customers do possess leverage. If DMG Mori's pricing becomes uncompetitive or its product specifications don't perfectly align with a customer's unique manufacturing requirements, buyers can explore alternative paths. This includes considering different, perhaps less advanced, machinery from a wider array of global competitors or even evaluating entirely different manufacturing techniques that might achieve a similar end result, albeit with different cost and quality trade-offs.
The sheer breadth of available options in the manufacturing equipment sector significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the global machine tool market was valued at approximately $100 billion, with numerous players vying for market share. This competitive landscape means customers aren't solely reliant on one supplier. They can actively compare offerings, negotiate terms, and switch if they perceive better value elsewhere.
- Limited Direct Substitutes: True replacements for high-precision machining are rare, but not entirely absent.
- Alternative Manufacturing Processes: Customers may explore different production methods to achieve similar outcomes.
- Competitor Machinery: Less advanced but more affordable machinery from other manufacturers can serve as a viable alternative.
- Price Sensitivity: High prices from DMG Mori can drive customers to seek out more cost-effective solutions from competitors.
DMG Mori faces moderate bargaining power from its customers. While high switching costs and the specialized nature of its products limit customer leverage, price sensitivity in certain sectors and the availability of alternative, albeit less advanced, machinery can empower buyers. The vast global machine tool market, valued at around $100 billion in 2024, offers numerous choices, allowing customers to negotiate effectively.
| Factor | Customer Bargaining Power | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low | High costs for integration, training, and operational disruption make switching difficult. |
| Price Sensitivity | Moderate to High | Industries like automotive prioritize cost optimization, especially for standard solutions. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate | While direct substitutes for high-precision machines are scarce, less advanced alternatives and different manufacturing processes exist. |
| Customer Concentration | Variable | A few large clients can wield significant power if they represent a substantial portion of revenue. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
DMG Mori Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive DMG Mori Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the machine tool industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying, providing actionable insights without any surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global machine tool market is quite crowded, with several large, established companies alongside many smaller, regional ones. This fragmentation means intense competition. For instance, in 2024, major players like Yamazaki Mazak, Trumpf, and Amada are actively vying for market share.
Companies such as DN Solutions, Makino, and JTEKT Corporation also contribute to this competitive environment. The sheer number of these players, both globally and locally, intensifies rivalry, pushing companies to innovate and offer competitive pricing to attract customers.
The machine tools market is experiencing robust expansion, with projections indicating a rise from $96.5 billion in 2024 to $101.51 billion in 2025, reflecting a 5.2% compound annual growth rate. This upward trend is expected to continue, reaching $129.94 billion by 2029, with a CAGR of 6.4%.
Such significant growth often fuels intensified competitive rivalry as firms vie for a larger slice of an expanding market. Even with overall growth, companies like DMG Mori can face challenges, as evidenced by their decreased order intake in 2024, highlighting the dynamic and competitive nature of this sector.
DMG Mori actively combats competitive rivalry through a strong emphasis on product differentiation and continuous innovation. Their Machining Transformation (MX) strategy, encompassing process integration, automation, digital transformation (DX), and green transformation (GX), highlights this commitment.
In 2024 alone, DMG Mori showcased its dedication to innovation by presenting 34 new offerings, with an impressive 20 of these being world premieres. This consistent stream of advanced technologies and integrated solutions allows them to stand out from competitors, reducing the pressure of direct price competition.
Exit Barriers
The machine tool industry, including players like DMG Mori, faces substantial exit barriers. These stem from the immense capital investment in highly specialized manufacturing facilities and advanced equipment. For instance, a state-of-the-art CNC machining center can cost hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of dollars. Furthermore, a highly skilled workforce, trained in complex operations and maintenance, represents another significant sunk cost that is difficult to recoup.
These high fixed costs mean that companies often continue production even when profitability is low, to avoid the substantial losses associated with shutting down operations and liquidating assets. This persistence can intensify competitive rivalry, as firms are reluctant to leave the market, leading to prolonged periods of price competition and capacity underutilization. In 2023, the global machine tool market was valued at approximately $90 billion, and while demand is expected to grow, the underlying cost structure remains a defining characteristic.
The implications for DMG Mori and its competitors are clear:
- High Capital Intensity: Significant investment in specialized machinery and plants creates a financial disincentive to exit.
- Skilled Labor Dependency: The need for a trained workforce makes downsizing or closure more complex and costly.
- Asset Specificity: Machine tools are highly specialized and have limited alternative uses, reducing their resale value upon exit.
- Market Persistence: Companies are incentivized to remain operational, potentially leading to sustained competitive pressure.
Strategic Commitments and Acquisitions
Competitive rivalry in the machine tool sector is intensifying as companies pursue strategic commitments and acquisitions to bolster their market standing and expand their global footprint. This trend is clearly visible in recent industry activities.
For instance, Nidec's significant bid for Makino highlights a major player's aggressive move to consolidate its position. Similarly, DMG Mori's acquisition of KURAKI in 2023 demonstrates a strategic effort to integrate complementary technologies and broaden its product portfolio, thereby strengthening its competitive edge.
These actions underscore a dynamic landscape where companies are not just competing on product innovation but also on strategic maneuvering to secure market share and enhance operational capabilities.
- Strategic Partnerships: Companies are forming alliances to share R&D, distribution networks, and technological advancements.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Consolidation through M&A is a key strategy for gaining scale, market access, and technological parity.
- Geographical Expansion: Acquisitions are often used to enter new or strengthen existing international markets.
- Market Consolidation: The industry is seeing a trend towards fewer, larger players as smaller, less competitive firms are acquired.
Competitive rivalry in the machine tool industry is fierce due to a fragmented market and significant growth potential. Companies like DMG Mori, Yamazaki Mazak, and Trumpf are constantly innovating and competing on price and technology. The market's projected growth, from $96.5 billion in 2024 to $101.51 billion in 2025, fuels this intense competition as firms aim to capture a larger share.
DMG Mori counters this rivalry through its Machining Transformation (MX) strategy, focusing on automation, digital transformation, and green transformation, exemplified by introducing 34 new offerings in 2024, including 20 world premieres. This differentiation strategy helps them stand out in a crowded marketplace.
| Key Competitors | 2024 Market Presence | Strategic Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Yamazaki Mazak | Global Leader | Innovation, Customer Solutions |
| Trumpf | Global Leader | Laser Technology, Automation |
| Amada | Global Leader | Sheet Metal Processing, Automation |
| DN Solutions | Significant Player | Advanced Machining, Digitalization |
| Makino | Significant Player | High-Precision Machining |
| JTEKT Corporation | Significant Player | Automotive Components, Machine Tools |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While traditional machining is still dominant, additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, presents a growing threat. These technologies are becoming viable substitutes, particularly for creating intricate parts and for lower-volume production runs where traditional methods might be less cost-effective.
The appeal of additive manufacturing lies in its ability to produce complex geometries that are difficult or impossible with subtractive methods. By 2025, it's projected that additive manufacturing will see increased adoption for end-use parts, further solidifying its position as a competitive alternative.
Customers may choose to outsource manufacturing to specialized contract manufacturers instead of buying new machine tools. This is often because these specialized firms have advanced machinery and can offer cost efficiencies, helping clients avoid significant capital expenditure and operational complexities.
For example, in 2024, the global contract manufacturing market was valued at over $600 billion, indicating a strong trend towards outsourcing. This growth suggests that many companies find it more economical and practical to rely on external expertise and equipment rather than investing in their own manufacturing capabilities.
The refurbishment and modernization of existing machine tools present a significant threat of substitutes for manufacturers like DMG Mori. Instead of investing in brand new equipment, customers increasingly opt to upgrade their current machinery. This approach offers a compelling cost advantage, often proving considerably cheaper than acquiring new systems, thereby directly impacting demand for new machine tool sales.
This trend is underscored by the growing market for industrial equipment refurbishment. For instance, the global industrial automation market, which includes machine tools, is projected to reach $300 billion by 2027, with a substantial portion of this growth potentially stemming from upgrades rather than entirely new installations. Companies specializing in retrofitting and modernizing older machines can extend their operational life and enhance their capabilities, making them competitive alternatives to purchasing new.
Manual Labor or Less Automated Processes
In certain niche applications, particularly those requiring lower precision or smaller production runs, manual labor or less automated machining processes can still function as substitutes for DMG Mori's advanced machinery. This is especially relevant in regions where labor costs remain comparatively low.
However, the broader industrial landscape is undeniably shifting towards greater automation. This trend is fueled by several factors, including the persistent rise in global wages and an ongoing shortage of skilled labor across many manufacturing sectors. For instance, in 2024, the International Federation of Robotics reported a significant increase in robot installations in manufacturing, highlighting this automation push.
- Manual labor can be a substitute in low-volume, low-precision tasks.
- Rising labor costs globally incentivize automation.
- Skilled labor shortages further drive the adoption of automated solutions.
- The International Federation of Robotics noted a substantial year-over-year increase in industrial robot installations in 2024.
Software-based Simulation and Virtual Prototyping
Software-based simulation and virtual prototyping present a growing threat to traditional manufacturing processes. Advances in these technologies allow companies to test designs and processes digitally, reducing the need for physical prototypes and the associated machining. For instance, the global simulation software market was valued at approximately USD 12.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over USD 20 billion by 2028, indicating significant investment and adoption. This trend could potentially decrease the demand for certain types of machine tools used in early-stage prototyping.
However, the substitution effect is not absolute. While simulation can reduce the number of physical prototypes, the ultimate production phase still necessitates real-world manufacturing capabilities. DMG Mori, a leading machine tool manufacturer, reported revenues of EUR 2.6 billion in 2023, underscoring the continued demand for physical production equipment. Therefore, simulation and virtual prototyping act more as complementary tools that optimize the use of machine tools rather than direct replacements for the entire manufacturing lifecycle.
- Simulation software market growth: Valued at ~USD 12.5 billion in 2023, projected to exceed USD 20 billion by 2028.
- Impact on prototyping: Reduces the need for physical prototypes, potentially lowering demand for specific machine tools.
- Limitation to substitution: Ultimate production still requires physical machinery, preventing complete replacement.
- DMG Mori's 2023 revenue: EUR 2.6 billion, highlighting ongoing demand for physical production equipment.
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is a growing substitute, especially for intricate parts and lower-volume production where traditional methods are less cost-effective. By 2025, its adoption for end-use parts is expected to rise, making it a more significant competitor.
Customers increasingly opt for specialized contract manufacturers, avoiding capital expenditure on new machinery. The global contract manufacturing market exceeded $600 billion in 2024, demonstrating this trend towards outsourcing.
Refurbishment and modernization of existing machine tools offer a cost-effective alternative to purchasing new equipment. The industrial automation market, including machine tools, is projected to reach $300 billion by 2027, with upgrades forming a substantial part of this growth.
Software simulation and virtual prototyping reduce the need for physical prototypes. The simulation software market, valued at approximately $12.5 billion in 2023, is projected to grow significantly, though it complements rather than fully replaces physical manufacturing needs, as evidenced by DMG Mori's 2023 revenue of EUR 2.6 billion.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantage | Market Indicator/Projection | Impact on Machine Tool Demand |
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Complex geometries, lower-volume efficiency | Increased adoption for end-use parts by 2025 | Potential reduction for specific applications |
| Contract Manufacturing | Avoids capital expenditure, access to advanced machinery | Global market >$600 billion (2024) | Reduced direct sales of new machinery |
| Machine Tool Refurbishment/Modernization | Cost savings over new equipment | Industrial automation market to reach $300 billion by 2027 | Shift in customer preference from new to upgraded systems |
| Software Simulation & Virtual Prototyping | Reduced physical prototyping needs | Simulation software market ~$12.5 billion (2023), growing | Optimization of machine tool use, not full replacement |
Entrants Threaten
The machine tool industry, especially for high-precision manufacturers like DMG Mori, demands substantial upfront investment. This includes significant capital for research and development to innovate and stay competitive, along with the cost of building and equipping specialized production facilities. For instance, establishing a state-of-the-art manufacturing plant with advanced robotics and quality control systems can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
These considerable capital requirements act as a strong deterrent for potential new players. Acquiring the necessary advanced machinery, securing intellectual property rights, and building a skilled workforce all contribute to a high entry barrier. In 2024, the average capital expenditure for a new entrant aiming for a significant market share in advanced CNC machining would likely exceed $200 million, making it a daunting prospect for many.
DMG Mori operates in a realm of highly sophisticated CNC machines and cutting-edge manufacturing tech. Entering this market demands significant investment in research and development, along with deep engineering talent and a constant drive for innovation.
The sheer cost and complexity of developing comparable products create a formidable barrier for newcomers. For instance, DMG Mori committed €84.3 million to R&D in 2024, underscoring the substantial financial and intellectual capital required to compete effectively.
DMG Mori boasts an established brand reputation built over decades, underscored by its delivery of over 300,000 machine tools globally. This long history translates into significant customer loyalty, a formidable barrier for any newcomer aiming to capture market share.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
New companies entering the machine tool industry face substantial hurdles in replicating DMG Mori's established global sales and service infrastructure. With 124 locations worldwide, DMG Mori offers a level of market penetration and customer support that is difficult and costly for newcomers to match.
Securing access to reliable, high-quality component suppliers is another significant barrier. The intricate supply chains required for advanced manufacturing equipment are often built on long-standing relationships and rigorous quality control, which new entrants typically lack.
- Global Reach: DMG Mori operates 124 sales and service locations, presenting a formidable distribution network for new competitors to overcome.
- Supply Chain Integration: The company's 17 production plants indicate a deeply integrated supply chain, making it challenging for new entrants to source comparable components and materials.
- Capital Investment: Building a comparable distribution and supply chain network would require immense capital investment, acting as a significant deterrent for potential new market participants.
Regulatory Requirements and Industry Standards
The machine tool sector faces significant hurdles for newcomers due to rigorous safety, precision, and environmental regulations. For instance, compliance with ISO 9001 quality management standards and specific regional safety certifications like CE marking adds substantial upfront costs and complexity for any new player entering the market.
These regulatory requirements often necessitate extensive testing, documentation, and adherence to manufacturing processes that can deter smaller or less capitalized entrants. The machine tool industry, particularly in advanced economies, demands adherence to strict emissions standards and workplace safety protocols, which can translate into millions of dollars in initial investment for new facilities and product development.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants must invest heavily in meeting safety standards (e.g., machine guarding, emergency stops) and environmental regulations (e.g., emissions control, waste management).
- Industry Certifications: Obtaining certifications like ISO 9001 (quality management) or specific industry accreditations can be a lengthy and expensive process, acting as a barrier to entry.
- Product Homologation: Ensuring machines meet the technical specifications and safety norms of different target markets requires significant R&D and testing, adding to the financial burden for new companies.
- Skilled Workforce Requirements: Adhering to industry standards often demands a highly skilled workforce trained in precision manufacturing and regulatory compliance, which can be challenging to recruit and retain for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for DMG Mori is relatively low due to the substantial capital investment required for R&D, advanced machinery, and global infrastructure. For instance, DMG Mori's 2024 R&D spending of €84.3 million highlights the ongoing investment needed to stay competitive. Furthermore, the company's established global sales and service network, with 124 locations, presents a significant barrier for newcomers seeking to match its market reach and customer support.
The high cost of entry, estimated at over $200 million for a new player in advanced CNC machining in 2024, combined with stringent regulatory compliance and the need for deep engineering talent, deters potential competitors. DMG Mori's 17 production plants also indicate a deeply integrated supply chain that is difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate.
| Barrier to Entry | DMG Mori Metric | Implication for New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment (R&D) | €84.3 million (2024) | High upfront cost for innovation |
| Global Sales & Service Network | 124 locations | Difficult and expensive to match market reach |
| Production Capacity | 17 production plants | Complex supply chain integration required |
| Estimated New Entry Cost (Advanced CNC) | > $200 million (2024) | Significant financial hurdle |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for DMG Mori leverages data from their annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports to understand competitive dynamics. We also incorporate information from competitor filings and trade publications to assess industry rivalry and the threat of new entrants.
