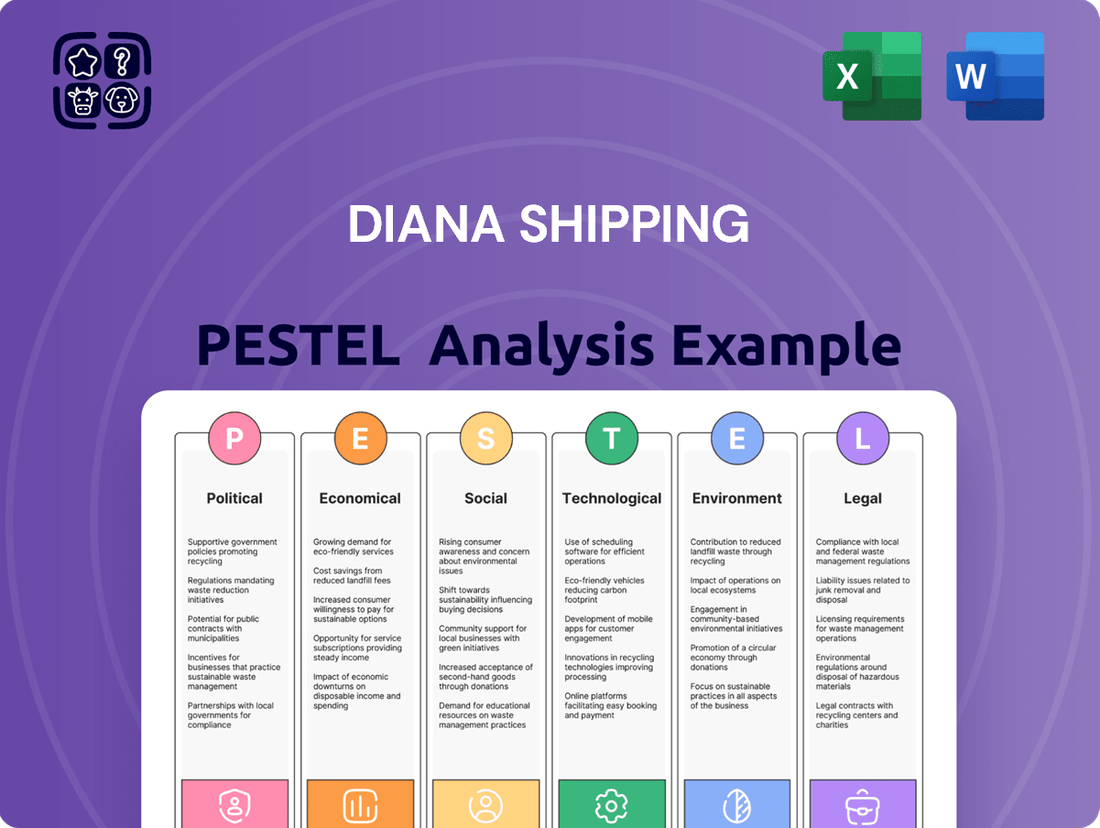
Diana Shipping PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Diana Shipping Bundle
Uncover the critical political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors shaping Diana Shipping's future. Our comprehensive PESTLE analysis provides actionable intelligence to help you anticipate market shifts and capitalize on opportunities. Gain a strategic advantage by understanding the external forces driving this dynamic industry. Download the full version now for a detailed roadmap to success.
Political factors
Geopolitical conflicts, like the ongoing Red Sea security crisis and the war in Ukraine, are significantly impacting shipping operations. These events necessitate rerouting vessels, which in turn extends transit times and escalates operational expenses for companies such as Diana Shipping. For example, rerouting around the Cape of Good Hope instead of the Suez Canal can add 10-14 days to voyages for some routes.
Trade disputes, notably between major economies like the United States and China, continue to create ripples across global commerce. Increased tariffs resulting from these disputes can directly dampen demand for dry bulk cargo, a core segment for Diana Shipping, and instigate shifts in established trade patterns. This dynamic introduces considerable unpredictability and price volatility into the international shipping arena.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the European Union (EU) are significantly tightening emissions standards for the shipping industry. Starting in 2024, the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) now includes maritime transport, with full implementation by 2026. This means companies like Diana Shipping must account for their carbon emissions.
These new regulations translate directly into substantial compliance costs for shipping firms. Diana Shipping, like its peers, will need to invest in more expensive low-sulfur fuels, scrubbers, or alternative technologies to meet these stricter environmental requirements. For instance, the cost of EU ETS allowances for shipping is projected to be significant, potentially impacting operating expenses.
Non-compliance with these evolving international maritime regulations carries severe consequences. Penalties for exceeding emissions limits can be substantial, and failure to adapt could render vessels less competitive or even non-operational in key markets. This regulatory shift necessitates strategic planning for fleet upgrades and operational adjustments to maintain viability.
US trade policy shifts, including potential tariffs on Chinese-built vessels, are reshaping global shipping. This creates uncertainty in dry bulk routes and elevates operational risks for companies like Diana Shipping, as sourcing patterns change. For instance, the US has historically used tariffs as a tool to address trade imbalances, and any new tariffs on shipbuilding could directly impact the cost and availability of new vessels, influencing fleet expansion or replacement strategies for companies operating globally.
Furthermore, sanctions imposed on nations such as Russia and Iran significantly curtail available cargo routes and introduce complex financial considerations. These restrictions can divert trade flows, potentially increasing voyage distances or forcing companies to navigate more challenging regulatory environments. In 2023, the maritime industry continued to grapple with the fallout from sanctions, leading to rerouting and increased insurance costs for vessels operating in or near sanctioned waters.
Governmental Support and Infrastructure Development
Government infrastructure projects, especially in major economies like China, can provide a degree of support for dry bulk shipping by stimulating demand for key construction materials such as iron ore and cement. For instance, China's commitment to infrastructure spending in 2024, estimated to be around 3.65 trillion yuan (approximately $500 billion USD) for new infrastructure projects, directly influences the volume of these commodities transported.
However, the recovery in material demand from the property sector, a significant consumer of construction materials, may be constrained by evolving urbanization strategies. This can lead to a more moderate impact on overall dry bulk cargo volumes, even with continued infrastructure investment. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected China's GDP growth to be 4.6% in 2024, which influences the pace of both infrastructure and property development.
- Infrastructure Investment: China's infrastructure spending in 2024 is a key driver for iron ore and cement demand, supporting dry bulk shipping.
- Urbanization Shifts: Changes in urbanization policies can moderate the recovery in property sector demand, affecting total dry bulk volumes.
- Economic Context: Global economic growth, as projected by the IMF for 2024, underpins the overall demand for construction materials and shipping services.
Political Stability in Key Regions
Political instability in key maritime regions, particularly the Middle East, remains a significant concern for shipping operations. Disruptions in vital waterways like the Red Sea and Suez Canal, as seen with incidents impacting commercial vessels in early 2024, directly translate to extended voyage times and elevated operational expenses. For instance, rerouting around the Cape of Good Hope can add 10-14 days to journeys, increasing fuel consumption and insurance premiums. This unreliability in transit routes directly impacts supply chain predictability and can lead to increased freight rates, affecting companies like Diana Shipping by potentially delaying cargo delivery and increasing overall shipping costs.
The resilience of passages like the Strait of Hormuz, while generally maintained, is constantly monitored. However, any escalation of regional tensions can quickly affect maritime security. The economic implications are substantial; in 2023, the Suez Canal Authority reported a decrease in transiting ships due to security concerns in the Red Sea, highlighting the direct impact of geopolitical events on shipping volumes and revenue. Such volatility necessitates robust risk management strategies for shipping companies, including contingency planning for alternative routes and insurance coverage for potential security threats.
- Geopolitical Risk Factors: Ongoing conflicts and political tensions in the Middle East and North Africa continue to pose threats to the safety and efficiency of maritime trade routes.
- Impact on Transit: Incidents in the Red Sea and Suez Canal during late 2023 and early 2024 led to significant rerouting of vessels, adding substantial costs and transit times.
- Economic Consequences: Increased fuel consumption, longer insurance periods, and potential cargo delays contribute to higher operational expenses for shipping companies.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Political instability directly impacts the predictability of global supply chains, potentially leading to increased freight rates and inventory management challenges for businesses reliant on maritime transport.
Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes continue to shape global shipping patterns. The ongoing Red Sea crisis, for instance, forces longer routes, adding an estimated 10-14 days to voyages and increasing operational costs for companies like Diana Shipping. Trade friction between major economies can also reduce demand for dry bulk cargo, impacting freight rates and creating market volatility.
Stricter environmental regulations, such as the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) for maritime transport implemented in 2024, impose significant compliance costs. Diana Shipping must now account for carbon emissions, potentially investing in cleaner fuels or technologies to avoid penalties. Non-compliance could lead to substantial fines and reduced competitiveness.
Government infrastructure spending, particularly in China, supports demand for key commodities like iron ore and cement, benefiting dry bulk carriers. China's planned infrastructure investment for 2024, estimated at around 3.65 trillion yuan ($500 billion USD), is a positive factor. However, shifts in urbanization strategies might moderate property sector demand, influencing overall cargo volumes.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal forces impacting Diana Shipping, offering a comprehensive view of its operating landscape.
It provides actionable insights for strategic decision-making by identifying external threats and opportunities relevant to the global shipping industry and Diana Shipping's specific market position.
A concise PESTLE analysis of Diana Shipping that highlights key external factors impacting the dry bulk market, offering clarity for strategic decision-making and risk mitigation.
Economic factors
The global economic outlook is a crucial driver for Diana Shipping, as demand for dry bulk commodities such as iron ore, coal, and grain is directly tied to overall economic activity. A robust global economy typically fuels industrial production and infrastructure development, boosting the need for these raw materials.
For instance, in 2024, projections from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) indicated a global growth rate of 3.2%, a slight uptick from previous years, suggesting a stable, albeit not explosive, demand environment for dry bulk. However, a slowdown in major economies like China, a key importer of iron ore and coal, could significantly dampen freight rates. China's economic performance, particularly its manufacturing output and construction sector activity, remains a primary determinant of dry bulk demand.
Conversely, a downturn in global economic growth, especially if concentrated in large importing nations, directly translates to reduced demand for dry bulk cargo. This scenario would likely lead to lower freight rates for Diana Shipping, impacting its revenue and profitability. For example, if China's GDP growth falters below its projected 5% in 2024, the ripple effect on commodity imports and shipping demand would be substantial.
Freight rates in the dry bulk shipping market are notoriously unpredictable, swinging based on the delicate balance between available ships and the volume of goods needing transport. For 2024, the market has seen stronger demand, but projections for 2025 and 2026 suggest a softening of this balance, which typically translates to reduced shipping prices.
This anticipated downturn in freight rates directly impacts companies like Diana Shipping, as lower rates mean less revenue generated from their fleet. For instance, the Baltic Dry Index, a key benchmark, experienced significant fluctuations throughout 2024, and analysts forecast a potential decline in average daily rates for capesize vessels from approximately $15,000 in late 2024 to closer to $10,000 by mid-2025, a substantial hit to earnings.
Fluctuations in marine heavy fuel oil (HFO) prices are a direct driver of Diana Shipping's operational expenses. For instance, during 2023, the average price of HFO experienced volatility, impacting the company's cost structure. This sensitivity means that even minor shifts in global oil markets can significantly alter profitability.
The ongoing transition to lower-carbon and alternative fuels presents a dual challenge for Diana Shipping. While aiming for environmental compliance and investor appeal, the adoption of new technologies like scrubbers or investments in LNG-powered vessels introduce substantial capital expenditures and ongoing operational costs. These investments are crucial for meeting future regulations, such as those from the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
Supply and Demand Dynamics of Dry Bulk Vessels
The dry bulk shipping market's health hinges on the delicate interplay between vessel supply and demand for shipping services. An oversupply of ships, driven by new builds entering the market, can significantly depress freight rates, impacting companies like Diana Shipping.
For instance, in early 2024, while demand for dry bulk commodities remained relatively stable, the orderbook for new vessels, particularly in the Panamax and Supramax segments, presented a potential oversupply scenario. This influx of new capacity, if not matched by a commensurate rise in global trade volumes, directly pressures charter rates.
Key factors influencing this balance include:
- Fleet Growth: The delivery of new dry bulk vessels, especially in the Panamax and Supramax classes, is a primary driver of supply.
- Demand for Transportation: Global economic activity, commodity prices, and trade policies directly influence the need for dry bulk shipping.
- Scrapping Rates: The rate at which older, less efficient vessels are removed from the fleet also plays a critical role in managing supply.
Access to Capital and Financing
Diana Shipping's access to capital is significantly impacted by the global financial landscape, particularly the availability of funds for fleet expansion and modernization. In 2024, the shipping industry, including dry bulk carriers like Diana Shipping, faced a tightening credit environment as interest rates remained elevated. This makes securing loans for new vessel acquisitions or significant technological upgrades more costly and challenging.
Financiers are increasingly prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. This means companies like Diana Shipping must demonstrate a commitment to cleaner operations to attract favorable financing terms. The demand for green financing is growing, with institutions offering preferential rates for vessels meeting stricter emissions standards. For instance, the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) 2023 greenhouse gas strategy, aiming for net-zero emissions by or around 2050, is driving this trend, requiring substantial investment in newer, more fuel-efficient tonnage or alternative fuels.
The ability to secure financing directly influences Diana Shipping's capacity for fleet renewal and compliance with evolving environmental regulations. As of early 2025, the cost of capital for maritime projects is influenced by geopolitical stability and the overall health of the global economy. Companies that can secure green financing are likely to gain a competitive edge.
- Fleet Renewal Costs: The average price of a secondhand Panamax vessel, a key segment for Diana Shipping, saw fluctuations throughout 2024, impacting the capital required for fleet upgrades.
- Green Financing Demand: Banks and financial institutions are increasingly offering sustainability-linked loans for shipping, with terms tied to emissions reduction targets.
- Regulatory Compliance Investment: Meeting upcoming emissions standards, such as those related to sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), necessitates significant capital expenditure for retrofitting or purchasing new vessels.
- Interest Rate Environment: Persistent higher interest rates in 2024 and into 2025 have increased the cost of debt financing for shipping companies, potentially limiting investment capacity.
Global economic growth is the primary determinant of dry bulk demand, directly impacting freight rates for companies like Diana Shipping. Projections for 2024 indicated a stable global growth of 3.2%, but potential slowdowns in major economies, particularly China, could significantly reduce demand for commodities like iron ore and coal.
The dry bulk shipping market is sensitive to the balance between vessel supply and cargo demand, with an oversupply of ships potentially depressing freight rates. For instance, analysts forecast a decline in average daily rates for capesize vessels from approximately $15,000 in late 2024 to around $10,000 by mid-2025.
Diana Shipping's operational costs are heavily influenced by fluctuating marine heavy fuel oil (HFO) prices, which saw volatility in 2023 and continue to be a key factor in profitability. The company also faces substantial capital expenditures for adopting cleaner technologies to meet evolving environmental regulations, such as those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
The availability and cost of capital for Diana Shipping are shaped by the global financial landscape, with elevated interest rates in 2024 and 2025 making financing more challenging. Furthermore, increasing demand for green financing means companies must demonstrate ESG commitment to secure favorable terms, impacting fleet renewal and regulatory compliance investments.
| Economic Factor | Impact on Diana Shipping | 2024/2025 Data/Projections |
|---|---|---|
| Global Economic Growth | Drives demand for dry bulk commodities (iron ore, coal, grain). | IMF projected 3.2% global growth in 2024. China's GDP growth below 5% would significantly impact demand. |
| Freight Rate Fluctuations | Directly affects revenue and profitability. | Baltic Dry Index volatility observed. Capesize rates projected to fall from ~$15,000 (late 2024) to ~$10,000 (mid-2025). |
| Fuel Oil Prices (HFO) | Impacts operational expenses and profitability. | Experienced volatility in 2023; continued sensitivity expected. |
| Capital Availability & Cost | Influences fleet expansion, modernization, and regulatory compliance. | Elevated interest rates in 2024-2025 increase borrowing costs. Growing demand for green financing. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Diana Shipping PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis for Diana Shipping covers political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the company. Understand the external forces shaping the maritime industry and Diana Shipping's strategic landscape.
Sociological factors
Crew welfare remains a significant concern in the maritime sector, with issues like workplace harassment and human rights violations impacting seafarer well-being. Ensuring robust health and safety standards is paramount for attracting and retaining talent.
The industry is grappling with potential labor shortages, exacerbated by the need for seafarers to adapt to increasing automation. In 2024, reports indicated a growing deficit in qualified maritime personnel, underscoring the urgency for effective recruitment and retention strategies.
Societal expectations are increasingly shaping the maritime industry, with a growing emphasis on environmental stewardship and ethical operations. Diana Shipping's proactive engagement with ESG principles, including its stated commitment to reducing carbon emissions by 30% by 2030 compared to 2008 levels, directly addresses these evolving public demands.
This focus on sustainability not only bolsters Diana Shipping's corporate image but also aligns with investor preferences; for instance, ESG funds saw significant inflows in 2024, highlighting the market's appetite for responsible companies. Meeting these expectations can translate into stronger client relationships and a more favorable perception among a wider range of stakeholders.
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly underscored the critical role of seafarer welfare and the fragility of global shipping networks. For Diana Shipping, this meant navigating complex crew change restrictions and ensuring the health of its workforce, which directly impacted its ability to operate efficiently. The industry saw an estimated 400,000 seafarers stranded at sea during the peak of the crisis, highlighting the severe logistical and human challenges.
Changing Consumer Demand Patterns
Shifts in consumer preferences, even for industrial clients like Diana Shipping, can ripple through supply chains. For instance, a growing global preference for electric vehicles (EVs) by 2024-2025, driven by environmental concerns and government incentives, directly impacts the demand for materials like lithium and cobalt. This, in turn, influences the need for bulk shipping of these essential components.
Furthermore, the increasing consumer focus on sustainability is reshaping manufacturing processes. As companies pivot to eco-friendly production, the demand for recycled materials and sustainably sourced raw goods rises. This trend could boost the transport of specific commodities, altering the typical dry bulk cargo mix that Diana Shipping handles.
Consider the impact on construction materials. A surge in consumer demand for new housing, particularly in developing economies, increases the need for iron ore and cement. By 2025, projections indicate continued urbanization will fuel this demand, directly benefiting dry bulk carriers.
- EV Growth: Global EV sales are projected to exceed 15 million units by 2025, increasing demand for battery metals.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Companies are investing billions in green technologies, creating new supply chains for specialized raw materials.
- Urbanization Trends: By 2025, over 60% of the world's population is expected to live in urban areas, driving construction and related material transport.
Diversity and Inclusion in the Workforce
The shipping industry, historically a male-dominated sector, is under growing pressure to enhance diversity and inclusion. This shift is crucial for attracting a broader talent pool, which is vital as the industry navigates increasing complexity and demands new skills. For instance, a 2023 report by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) highlighted that women still represent a small percentage of the global maritime workforce, often cited around 2% in seafaring roles, underscoring the significant room for improvement.
Embracing diversity is no longer just a social imperative but a strategic necessity for companies like Diana Shipping. By actively recruiting and retaining women and individuals from diverse backgrounds, the industry can unlock fresh perspectives and foster innovation. This is particularly relevant as shipping faces challenges like decarbonization and digitalization, requiring a wider range of expertise and creative problem-solving approaches.
- Industry Shift: The maritime sector is actively working to break down traditional barriers and create a more equitable environment.
- Talent Acquisition: A more inclusive approach is seen as key to attracting skilled professionals needed for future industry growth and technological advancements.
- Innovation Driver: Diverse teams are demonstrably more innovative, bringing varied viewpoints to tackle complex operational and environmental challenges.
- Global Representation: Efforts are underway to increase the representation of women and minority groups across all levels of maritime operations, from shore-based roles to seagoing positions.
Societal expectations are increasingly pushing the maritime industry towards greater inclusivity and diversity, aiming to attract a wider talent pool. Reports from 2023 indicated that women hold only about 2% of seafaring roles globally, highlighting a significant opportunity for growth. Diana Shipping, like its peers, must address these demographic shifts to foster innovation and meet evolving workforce needs.
Technological factors
The shipping industry, including companies like Diana Shipping, is heavily influenced by technological advancements. The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time tracking and the use of AI-driven analytics are revolutionizing fleet management. These technologies enable precise route optimization, reducing fuel consumption and transit times, which is crucial for cost efficiency in the competitive dry bulk market.
Big data analytics provides invaluable insights into operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and market trends. For instance, by analyzing vast datasets on weather patterns, vessel performance, and port congestion, shipping firms can make more informed decisions, leading to significant cost savings. In 2024, the focus on digitalization aims to enhance transparency and reduce operational risks, directly impacting profitability for companies like Diana Shipping.
While fully autonomous ships are still a future vision, automation and semi-autonomous systems are already making waves in the maritime industry. These advancements, including automated navigation and remote monitoring, are becoming increasingly prevalent, signaling a shift towards potentially reduced crew sizes and improved operational safety. For instance, by 2024, several major shipping companies are piloting or have implemented advanced automation features on their vessels, aiming to optimize routes and fuel efficiency.
Maritime companies are actively adopting energy-efficient technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and cut fuel expenses. This trend is driving demand for innovations like electric propulsion, biofuels, and wind-assist systems, impacting new vessel construction and upgrades.
In 2024, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) continues to push for decarbonization, with many shipping firms investing in retrofits and new designs incorporating these cleaner solutions. For instance, by the end of 2024, it's projected that over 500 vessels globally will be equipped with some form of wind-assist technology, a significant jump from previous years.
Advanced Communication Systems
The maritime industry is experiencing a significant upgrade in its communication infrastructure, largely driven by advancements in satellite technology. The expansion of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations, like SpaceX's Starlink, is a prime example. This deployment is transforming how ships connect, offering unprecedented speed and reliability. By mid-2024, Starlink's maritime service had expanded to cover over 70 countries, with a growing number of vessels adopting the technology.
This enhanced connectivity directly impacts operational efficiency and crew well-being. Faster, more stable internet access at sea allows for real-time data transmission, crucial for navigation, logistics, and predictive maintenance. For instance, improved communication facilitates the use of advanced analytics and remote monitoring of vessel performance, potentially reducing downtime and optimizing fuel consumption. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) continues to emphasize the importance of digitalization and connectivity for safety and efficiency.
- LEO Satellite Growth: Continued expansion of LEO constellations like Starlink is increasing global maritime coverage.
- Data-Driven Operations: Enhanced connectivity enables real-time data analysis for improved vessel management and efficiency.
- Crew Welfare: Reliable internet access significantly boosts morale and communication for seafarers.
- Industry Adoption: An increasing number of shipping companies are investing in advanced communication systems to remain competitive.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection
As the maritime sector embraces greater digitalization, the threat landscape for cyberattacks intensifies. A significant portion of industry professionals, around 70% according to some 2024 surveys, have reported experiencing cyber infiltrations, highlighting the pervasive nature of these risks.
Protecting both operational technology (OT) and sensitive commercial data is no longer optional but a fundamental requirement for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and continuity of maritime operations. This includes safeguarding navigation systems, cargo management platforms, and crew communication networks from malicious actors.
- Increased Digitalization: The maritime industry's growing reliance on digital systems amplifies vulnerability to cyber threats.
- High Incidence of Attacks: Reports indicate a substantial percentage of maritime professionals have faced cyber infiltrations, underscoring the urgency.
- Critical Data Protection: Safeguarding operational technology and sensitive data is essential for uninterrupted and secure shipping activities.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Emerging regulations in 2024 and 2025 are placing greater emphasis on robust cybersecurity measures for vessels and port facilities.
The shipping industry is rapidly adopting advanced technologies to boost efficiency and sustainability. By 2024, the integration of AI and IoT is streamlining fleet management, optimizing routes, and enabling predictive maintenance, with companies like Diana Shipping leveraging these tools for cost reduction. The push for decarbonization is also driving investment in cleaner technologies, with a notable increase in vessels adopting wind-assist systems, projected to exceed 500 globally by the end of 2024.
Enhanced satellite connectivity, particularly through LEO constellations like Starlink, is transforming maritime communications, offering faster and more reliable internet access at sea. This improved connectivity is crucial for real-time data analysis, operational efficiency, and crew welfare, with Starlink's maritime service expanding significantly by mid-2024. However, this increased digitalization also heightens cybersecurity risks, with a substantial percentage of industry professionals reporting cyber infiltrations in 2024, making robust data protection a critical concern.
| Technology Area | Impact on Shipping | Key Developments (2024-2025) | Example Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI & IoT | Fleet management, route optimization, predictive maintenance | Increased adoption for operational efficiency and cost savings | Companies reporting fuel savings of up to 15% through AI-driven route optimization. |
| Decarbonization Tech | Reduced emissions, fuel efficiency | Investment in wind-assist, biofuels, electric propulsion | Projected 500+ vessels globally with wind-assist technology by end of 2024. |
| Satellite Communications | Enhanced connectivity, real-time data transmission | Expansion of LEO constellations (e.g., Starlink) | Starlink maritime service coverage expanded to over 70 countries by mid-2024. |
| Cybersecurity | Protection of operational and commercial data | Increased focus due to digitalization | ~70% of maritime professionals reported cyber infiltrations in 2024 surveys. |
Legal factors
Diana Shipping operates under a stringent framework of international maritime conventions. Key among these are regulations from the International Maritime Organization (IMO), which dictate standards for emissions and safety. For instance, compliance with the IMO 2020 Sulfur Cap, Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI), and Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) is crucial for operational legality and environmental responsibility.
These evolving regulations, such as the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) and the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL), necessitate continuous investment in vessel upgrades and robust compliance programs. Failure to adhere can result in significant penalties and operational disruptions, impacting Diana Shipping's financial performance and market reputation.
The European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) significantly impacts Diana Shipping, requiring them to account for and pay for CO2 emissions on voyages within or entering EU waters. This directly translates to increased compliance costs, estimated to add substantial operational expenses for shipping companies. For instance, under the expanded scope of the EU ETS covering maritime transport from 2024, companies like Diana Shipping must purchase emission allowances, with the price of these allowances fluctuating and directly affecting profitability.
Changes in international trade laws, including those affecting bulk shipping, directly impact Diana Shipping's operational landscape. For instance, the ongoing trade disputes and evolving regulations in major economies can lead to unpredictable shifts in demand for specific commodities, influencing freight rates and vessel utilization.
The imposition of new tariffs by countries, such as those seen in recent years between major trading blocs, can increase the cost of imported goods, potentially dampening trade volumes and affecting the types of cargo Diana Shipping transports. This necessitates agile route planning and a keen awareness of evolving trade policies to mitigate financial impacts.
Economic sanctions imposed by various nations can further complicate international shipping by restricting access to certain ports or prohibiting the transport of specific goods. For example, sanctions targeting particular countries or industries might force Diana Shipping to reroute vessels or seek alternative cargo sources, directly influencing operational efficiency and profitability.
Safety and Security Regulations
Diana Shipping must navigate a complex web of safety and security regulations, particularly those aimed at mitigating piracy and geopolitical risks in critical shipping routes. These regulations necessitate significant investment in robust security protocols and can lead to increased insurance premiums. For instance, in 2024, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) continued to emphasize enhanced security measures following incidents in regions like the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea, impacting operational costs for companies like Diana Shipping.
Furthermore, evolving international codes, such as the International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes (IMSBC) Code, directly influence how Diana Shipping handles and documents cargo. Amendments to these codes, often updated to reflect new safety concerns or technological advancements, require continuous adaptation in operational procedures and information management systems. These changes ensure compliance with updated safety standards for various bulk cargoes, potentially affecting loading procedures and required documentation for shipments in 2024 and beyond.
The company's adherence to these safety and security mandates is crucial for maintaining operational integrity and mitigating potential liabilities. For example, the cost of war risk insurance, a component influenced by geopolitical stability in shipping lanes, can fluctuate significantly. In 2024, increased tensions in certain maritime areas saw a rise in these insurance costs for many shipping operators, directly impacting profitability.
- Maritime Safety Regulations: Compliance with IMO standards for vessel construction, equipment, and crew training remains paramount.
- Security Measures: Implementation of best management practices to counter piracy and enhance vessel security in high-risk areas.
- Geopolitical Risk Impact: Increased insurance costs and potential rerouting of vessels due to regional instability.
- Cargo Handling Standards: Adherence to updated codes like the IMSBC Code for safe and compliant transport of bulk cargoes.
Contractual and Charter Party Law
Diana Shipping's operational success hinges on robust contractual and charter party agreements. These contracts, governing time charters and spot market voyages, are the backbone of their revenue generation. For instance, in 2023, the company reported that a significant portion of its fleet operated under time charters, providing a more predictable income stream compared to the volatile spot market.
The legal intricacies of these contracts, particularly clauses addressing fuel efficiency, environmental regulations like IMO 2020 sulfur limits, and force majeure events, directly influence Diana Shipping's financial performance and risk exposure. Failure to adhere to or enforce these terms can lead to substantial financial penalties or disputes.
- Charter Party Clauses: Specific terms regarding vessel performance, hire rates, and off-hire periods are legally binding and impact profitability.
- Dispute Resolution: The legal framework for resolving charter party disputes, often through arbitration, can be costly and time-consuming.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to international maritime laws and conventions, embedded within charter party terms, is critical.
- Contractual Flexibility: The ability to negotiate favorable terms in charter parties provides a competitive advantage in a fluctuating market.
Diana Shipping is deeply affected by international maritime laws, including the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) regulations on emissions and safety. Compliance with standards like the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) and Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI) is essential, with evolving rules potentially increasing operational costs and requiring vessel upgrades.
The European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) mandates that Diana Shipping purchase allowances for CO2 emissions from voyages within EU waters, impacting profitability. For 2024, the cost of these allowances directly influences operational expenses, with prices fluctuating based on market demand.
Trade laws and sanctions significantly shape Diana Shipping's operations. Changes in tariffs or import/export restrictions can alter cargo demand and necessitate route adjustments, as seen with geopolitical tensions impacting shipping lanes in 2024.
Safety and security regulations, including those addressing piracy and geopolitical risks, require ongoing investment. For instance, increased maritime security measures in 2024 led to higher insurance premiums for companies operating in certain regions.
Environmental factors
The global push to address climate change is significantly pressuring the shipping sector to reduce its carbon footprint. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has set ambitious goals, aiming for at least a 20% reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2030, with a long-term vision of net-zero emissions by or around 2050. This regulatory environment directly impacts Diana Shipping's fleet modernization and investment decisions, pushing towards vessels capable of utilizing lower-emission fuels.
This decarbonization trend is fueling a growing demand for alternative fuels like LNG, methanol, and ammonia, alongside the development of wind-assisted propulsion systems. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in its 2024 Oil Market Report that while conventional fuels still dominate, investments in low-carbon shipping technologies are accelerating, indicating a shift in market expectations that Diana Shipping must navigate.
Diana Shipping must navigate increasingly stringent environmental regulations, like the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) EEXI and CII, which mandate improvements in fleet emission efficiency. These rules directly impact operational costs and require proactive management of the company's environmental footprint.
Failure to meet these emission standards can result in substantial penalties and operational limitations, compelling Diana Shipping to invest in fleet modernization and explore cleaner fuel alternatives. For instance, the ongoing transition to lower-sulfur fuels and the development of technologies for carbon capture are key considerations for compliance and future competitiveness.
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events poses a significant challenge for maritime transport. For instance, droughts impacting crucial waterways like the Panama Canal can cause significant delays and rerouting, extending shipping distances and increasing fuel costs. In 2023, the Panama Canal experienced severe drought, leading to restrictions on vessel transits and causing substantial disruptions to global supply chains.
Storms and hurricanes also directly affect port operations and vessel safety, leading to unpredictable closures and delays. These disruptions can impact Diana Shipping's ability to maintain its schedule and increase operational expenses due to longer transit times and potential rerouting, directly affecting their bottom line.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Protection
Beyond direct emissions, the maritime sector is under increasing pressure to mitigate its impact on marine biodiversity. This includes stringent regulations and evolving best practices for ballast water management, crucial for preventing the spread of invasive species. For instance, the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) Ballast Water Management Convention, fully ratified in 2017, continues to drive significant investments in treatment systems. Diana Shipping, like its peers, must navigate these requirements to avoid penalties and maintain operational continuity.
Noise pollution from vessels is another growing concern, impacting marine life communication and behavior. Efforts to develop quieter propulsion systems and operational strategies are underway. The industry's commitment to sustainability, as evidenced by initiatives like the Poseidon Principles for shipping finance, will likely see increased focus on these ecological aspects in the coming years. By 2024, the global shipping fleet is expected to see continued adoption of technologies aimed at reducing underwater noise, a trend Diana Shipping will need to monitor and integrate.
- Ballast Water Management: Continued compliance with the IMO's Ballast Water Management Convention requires ongoing investment in treatment technologies for Diana Shipping's fleet.
- Noise Pollution Mitigation: The industry is increasingly focused on reducing underwater noise, prompting research and development into quieter ship designs and operational adjustments.
- Ecosystem Protection Initiatives: Growing awareness and regulatory pressure on marine biodiversity will likely lead to stricter guidelines and greater demand for environmentally sound shipping practices.
- Sustainability Frameworks: Adherence to broader sustainability principles, such as the Poseidon Principles, will influence financial and operational decisions concerning ecological impacts.
Transition to Sustainable Fuels and Technologies
The global push for decarbonization is fundamentally reshaping the shipping industry, driving a significant transition towards sustainable fuels and technologies. Diana Shipping must navigate this environmental imperative by adapting its fleet to incorporate alternative fuel capabilities, such as Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) and biofuels. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) 2023 greenhouse gas strategy aims for net-zero emissions by or around 2050, creating a clear regulatory roadmap for this shift.
Embracing these changes isn't just about compliance; it's about future-proofing operations and maintaining a competitive edge. This includes exploring advanced technologies like wind-assisted propulsion systems, which can significantly reduce fuel consumption and emissions. For instance, companies are investing in rotor sails and kites, with some trials showing fuel savings of up to 20%.
- Regulatory Pressure: Increasing global regulations, such as the IMO's GHG strategy and regional emissions trading schemes, necessitate the adoption of cleaner shipping practices.
- Fuel Availability and Cost: The availability and cost-effectiveness of sustainable fuels like LNG, methanol, and biofuels are critical factors in fleet modernization decisions for companies like Diana Shipping.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in engine technology, hull coatings, and energy-saving devices, including wind-assisted propulsion, offer pathways to reduce environmental impact and operational costs.
- Market Demand: Growing customer and investor demand for sustainable supply chains will likely favor shipping companies that proactively adopt greener solutions.
Environmental regulations are a significant driver for Diana Shipping, with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) setting ambitious targets for greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reductions, aiming for net-zero by 2050. This push for decarbonization necessitates investments in cleaner technologies and fuels, impacting operational costs and fleet modernization strategies.
Extreme weather events, such as droughts affecting key waterways like the Panama Canal, can disrupt shipping routes and increase transit times and fuel expenses. For example, the 2023 drought in the Panama Canal led to significant transit restrictions, highlighting the vulnerability of global supply chains to climate-related impacts.
The industry is also facing increased scrutiny regarding marine biodiversity, particularly concerning ballast water management to prevent invasive species. Initiatives like the Poseidon Principles, which guide shipping finance towards sustainability, are likely to intensify focus on ecological impacts and drive demand for environmentally sound practices.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Diana Shipping | Key Data/Initiatives |
| Decarbonization Goals | Fleet modernization, investment in alternative fuels (LNG, methanol), adoption of energy-saving technologies. | IMO's net-zero target by 2050; 20% GHG reduction by 2030. |
| Extreme Weather | Supply chain disruptions, increased transit times, higher fuel costs due to rerouting. | 2023 Panama Canal drought leading to transit restrictions. |
| Marine Biodiversity | Compliance with Ballast Water Management Convention, potential for quieter propulsion systems. | IMO Ballast Water Management Convention (fully ratified 2017). |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for Diana Shipping is meticulously constructed using data from maritime industry reports, financial news outlets, and regulatory bodies. We also incorporate information from economic indicators and geopolitical analyses to provide a comprehensive view.
