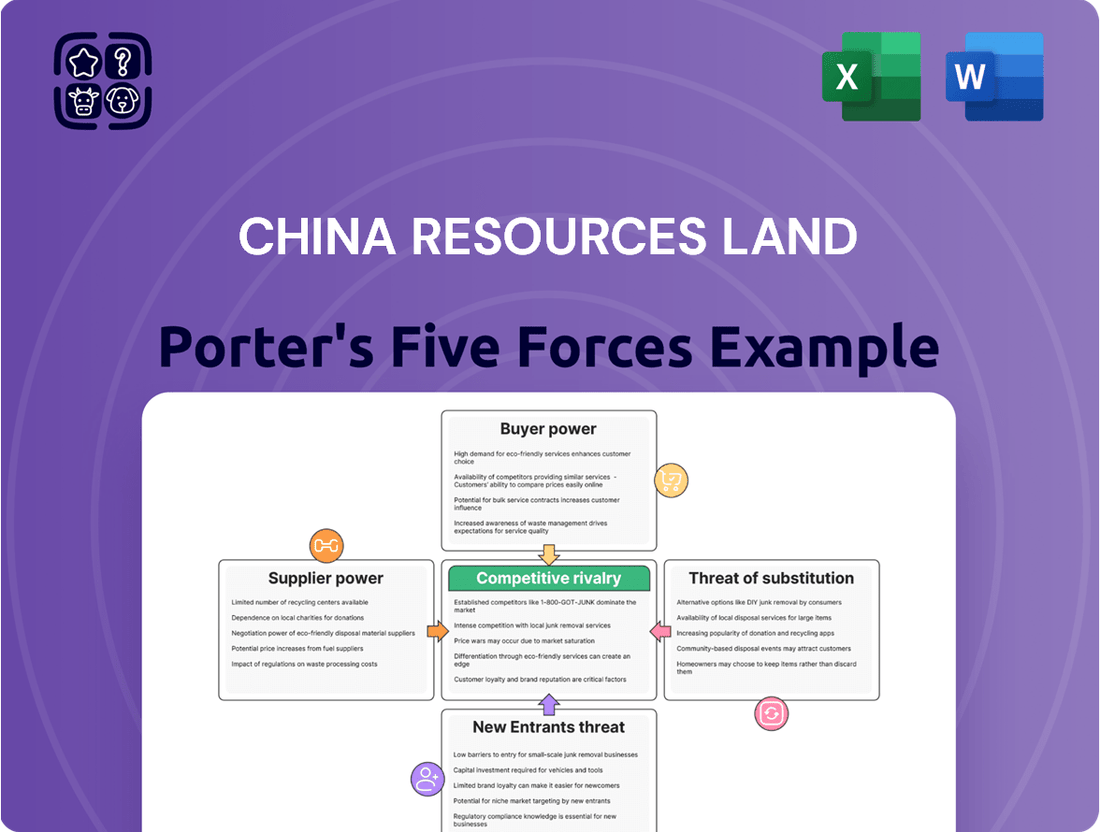
China Resources Land Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China Resources Land Bundle
China Resources Land navigates a dynamic real estate landscape, facing significant buyer power due to market saturation and price sensitivity. The threat of new entrants, while somewhat moderated by high capital requirements, remains a constant pressure. Intense rivalry among established developers also shapes the competitive intensity, forcing strategic differentiation.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore China Resources Land’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The availability and cost of land, a crucial input for property development, directly impact supplier power for China Resources Land. Local governments in China, particularly in sought-after urban areas, hold significant control over land supply. This concentration of power allows them to dictate land prices and terms, even amidst market fluctuations, directly influencing developers' input costs and profitability.
The construction materials sector, encompassing steel, cement, and other essential inputs, presents a moderate level of supplier power for China Resources Land. While China boasts a massive industrial capacity, the availability of specialized or high-grade materials can be limited, potentially driving up acquisition costs. For instance, fluctuations in the price of rebar, a key steel component, can directly impact project budgets. In 2024, steel prices experienced volatility, with benchmarks like the Tangshan rebar futures contract showing periods of significant upward movement, directly challenging developers' cost management strategies.
China Resources Land's reliance on skilled labor for its high-quality urban developments means that the availability and cost of this workforce significantly influence its operations. As construction projects become more intricate, requiring specialized techniques, the bargaining power of skilled labor can directly affect project schedules and overall expenses. In 2024, the construction industry in China continued to face a tight labor market, particularly for specialized roles, potentially increasing labor costs for developers like China Resources Land.
Supplier Power 4
Financial institutions wield considerable power as suppliers of crucial capital for China Resources Land's land acquisition and project development endeavors. The liquidity challenges that have impacted many Chinese property developers in recent years have tightened access to financing, making it more expensive. For instance, in 2023, the average interest rate on corporate loans in China for real estate companies generally saw an increase compared to previous years, reflecting tighter credit conditions.
While state-owned entities like China Resources Land often possess an advantage in securing financing due to perceived stability, the broader financial market conditions continue to dictate borrowing costs and the terms of credit. This means that even for well-established developers, the bargaining power of banks and other lenders remains substantial, influencing the profitability and feasibility of new projects.
- Financing Costs: The cost of capital directly impacts project margins. Higher interest rates mean higher expenses for land acquisition and construction loans.
- Lender Covenants: Financial institutions can impose strict covenants on borrowers, influencing how China Resources Land manages its finances and operations.
- Access to Capital: In times of market stress, lenders can significantly restrict access to new funding, impacting development pipelines.
- Credit Ratings: A developer's creditworthiness, reflected in its credit rating, directly influences its ability to secure favorable loan terms from financial institutions.
Supplier Power 5
Technology and specialized service providers, particularly those in smart city solutions, green building, and advanced architectural design, wield significant bargaining power due to their unique and often proprietary offerings. China Resources Land's commitment to high-quality, sustainable urban developments means they rely on these suppliers for crucial differentiation, allowing these providers to command premium pricing. For instance, the demand for sophisticated Building Information Modeling (BIM) services, essential for complex urban projects, has seen growth, potentially increasing supplier leverage.
The integration of these advanced technologies is not merely an option but a necessity for maintaining market competitiveness within China's rapidly evolving real estate sector. Suppliers of cutting-edge materials or energy-efficient systems can therefore exert considerable influence over project costs and timelines. By 2024, the global smart building market was projected to reach over $100 billion, indicating a substantial value placed on such specialized services.
- Specialized Technology Providers: Companies offering smart city infrastructure, advanced HVAC systems, or sustainable material sourcing can dictate terms due to limited alternatives for high-performance projects.
- Green Building Expertise: As environmental regulations tighten and consumer demand for eco-friendly housing grows, suppliers with certified green building technologies gain leverage.
- Advanced Architectural Design: Firms providing innovative and complex design solutions that are critical for premium property developments often have strong bargaining power.
- Data Integration Services: The increasing need for seamless data flow in smart buildings positions providers of integrated technology platforms as key influencers in project specifications and costs.
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Resources Land is notably influenced by the concentration of land supply in the hands of local governments, which can dictate prices and terms, impacting developer costs. Furthermore, while China has vast industrial capacity, specialized construction materials and skilled labor can be scarce, increasing their leverage. Financial institutions also hold significant power, as tighter credit conditions in recent years have made capital more expensive and harder to access, directly affecting project feasibility and profitability.
| Supplier Category | Key Influences | Impact on China Resources Land | 2024 Data Points/Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local Governments (Land Supply) | Concentration of land ownership, urban planning policies | High bargaining power, dictates land prices and availability | Continued strong demand for prime urban land, government land sales remain a key revenue source for local authorities. |
| Construction Materials | Availability of specialized inputs, global commodity price fluctuations | Moderate bargaining power, price volatility affects project budgets | Steel prices, particularly rebar, showed fluctuations in 2024, impacting material costs for developers. |
| Skilled Labor | Availability of specialized construction expertise, labor market tightness | Moderate to high bargaining power, impacts project timelines and costs | Tight labor market for specialized roles persisted in China in 2024, potentially increasing labor expenses. |
| Financial Institutions | Liquidity, credit conditions, lender covenants | High bargaining power, influences financing costs and access to capital | Interest rates on corporate loans in China for real estate companies generally remained higher in 2023-2024 compared to prior periods, reflecting tighter credit. |
| Technology & Service Providers | Proprietary offerings, demand for specialized solutions (e.g., smart building tech) | High bargaining power, commands premium pricing for differentiation | Global smart building market projected to exceed $100 billion by 2024, indicating strong demand and supplier leverage for advanced solutions. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for China Resources Land by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the real estate sector.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures on China Resources Land with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic clarity.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of residential homebuyers in China has surged due to an oversupply of properties and falling prices across many urban areas. Buyers are now more discerning, seeking concessions like reduced prices or improved quality, especially given concerns about developer solvency.
This trend is amplified in smaller cities, but even major metropolitan areas have experienced price stabilization or declines. For instance, in early 2024, the average new home price in 70 major Chinese cities saw a year-on-year decrease, with some cities reporting steeper drops, indicating a clear shift in leverage towards buyers.
Commercial tenants, such as retailers and office space users, wield significant bargaining power. This is particularly evident in major Chinese cities where elevated vacancy rates, dampened consumer confidence, and cautious brand expansion have created a favorable environment for tenants to negotiate more favorable lease terms. For instance, in 2023, retail sales growth in China slowed compared to previous years, impacting the revenue streams of many businesses and increasing their sensitivity to occupancy costs.
China Resources Land, managing a vast array of shopping centers and office complexes, feels this pressure acutely. The need to sustain high occupancy levels and consistent rental income means they must often concede to tenant demands. This can include offering reduced rental rates, extended rent-free periods, or more adaptable lease agreements to secure and retain valuable tenants in a competitive market.
The bargaining power of residential customers in China is increasing, driven by a surge in government-subsidized rental housing and the proliferation of market-oriented rental platforms. These alternatives to traditional homeownership are particularly appealing to younger demographics grappling with job market uncertainties and slower income growth.
In 2024, China's commitment to expanding its rental housing sector is evident. For instance, the government has set targets to significantly increase the supply of affordable rental units in major cities. This growing availability directly translates to more choices for tenants, amplifying their ability to negotiate terms and influencing rental pricing downwards in the broader market.
The rise of digital rental platforms further empowers buyers by providing greater transparency in pricing and a wider selection of properties. This increased accessibility and choice mean that landlords, including major developers like China Resources Land, must be more competitive to attract and retain tenants, directly impacting their pricing strategies and lease agreements.
Buyer Power 4
China Resources Land's customers, particularly homebuyers and commercial tenants, are wielding increasing influence. The proliferation of online real estate portals and property review sites in 2024 has dramatically amplified buyer access to information. This transparency allows for easy comparison of pricing, unit specifications, and developer track records across the market.
This heightened buyer awareness directly pressures China Resources Land to offer competitive pricing and maintain high standards in construction quality and project delivery. For instance, in 2023, the average wait time for new home delivery in many major Chinese cities saw an increase, leading to greater buyer scrutiny of developer timelines and project execution.
- Informed Buyers: Online platforms and media provide extensive data, enabling buyers to compare offerings from various developers, including China Resources Land.
- Price Sensitivity: Increased market transparency means buyers can easily identify and exploit price discrepancies, forcing developers to be more competitive.
- Quality Demands: Buyers are more discerning about construction quality and adherence to project timelines, leading to greater developer accountability.
- Tenant Leverage: In the commercial leasing segment, tenants have more options and information, increasing their bargaining power for rental rates and lease terms.
Buyer Power 5
The bargaining power of customers for China Resources Land is increasing, especially among institutional investors focused on stable income. These investors, prioritizing long-term rental yields over quick sales, are better positioned to negotiate terms. They demand properties with consistent quality and strong operational management, influencing China Resources Land's development and leasing strategies.
This trend is evident as investment properties become a crucial component of portfolios seeking recurring revenue. For instance, in 2023, China Resources Land reported significant recurring income from its investment properties, a key attraction for these sophisticated buyers. The ability to secure favorable long-term leases with creditworthy tenants is paramount for these investors.
- Focus on Yield: Institutional investors are shifting from capital appreciation to rental yield as a primary investment metric.
- Demand for Quality: Higher standards are placed on property quality, location, and tenant mix to ensure stable rental income.
- Negotiating Leverage: A strong pool of institutional buyers grants them greater power to negotiate lease terms and pricing.
- Operational Excellence: Properties with proven, robust operational management are more attractive, allowing investors to secure better returns.
China Resources Land faces amplified customer bargaining power, particularly from residential buyers concerned about developer solvency and falling property prices, a trend clearly seen in the year-on-year price decreases across major Chinese cities in early 2024. Commercial tenants also hold significant sway due to elevated vacancy rates and cautious expansion, compelling developers like China Resources Land to offer concessions such as reduced rents or extended rent-free periods to maintain occupancy, especially as retail sales growth slowed in 2023.
The growing availability of government-backed rental housing and online rental platforms in 2024 provides consumers with more choices, increasing their ability to negotiate favorable terms and driving down rental prices. Furthermore, institutional investors, prioritizing stable rental yields, exert considerable influence by demanding high-quality properties and robust operational management, as evidenced by China Resources Land's reliance on recurring income from investment properties in 2023.
| Customer Segment | Key Drivers of Bargaining Power | Impact on China Resources Land | Supporting Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential Homebuyers | Property oversupply, falling prices, developer solvency concerns | Pressure to lower prices, offer concessions, improve quality | Year-on-year price decreases in 70 major cities (early 2024) |
| Commercial Tenants | High vacancy rates, dampened consumer confidence, cautious expansion | Negotiate favorable lease terms (rent reductions, free periods) | Slower retail sales growth impacting tenant revenue (2023) |
| Rental Market Participants | Increased rental housing supply, online platform transparency | Greater negotiation power for tenants, downward pressure on rents | Government targets for affordable rental units (2024) |
| Institutional Investors | Focus on stable rental yields, demand for quality and management | Influence development and leasing strategies, secure long-term leases | Significant recurring income from investment properties (2023) |
What You See Is What You Get
China Resources Land Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, ready-to-use China Resources Land Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape for this major real estate developer. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying, offering a thorough examination of industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Chinese property development sector is a battlefield, crowded with major state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and numerous private developers. Despite recent industry consolidation and the struggles of some private firms due to financial pressures, the competition for prime land, property sales, and overall market dominance remains exceptionally high.
China Resources Land, as a prominent state-backed entity, has benefited from these shifts, with its market share in sales growing. This trend highlights a significant redistribution of power and influence within the industry, with SOEs increasingly capturing a larger portion of the market.
The current real estate market downturn, characterized by falling sales and thinner profit margins, intensifies rivalry among developers. Companies are compelled to reduce prices, provide incentives, and enhance product offerings to draw in hesitant buyers. For instance, the average net profit margin for major developers saw a substantial contraction in 2024, underscoring the intense price-based competition.
Competitive rivalry within China Resources Land's market is intensifying, particularly in higher-tier cities. Major developers are increasingly focusing their resources on first-tier and strong second-tier urban centers. This strategic shift is driven by more sustained downturns and oversupply issues observed in lower-tier cities.
China Resources Land, along with its peers, is concentrating its development efforts in these prime locations. This heightened focus naturally escalates competition for desirable land parcels and high-value development projects. For instance, in 2023, average land bid premiums in Tier 1 cities remained robust despite broader market cooling, reflecting this intense competition among top developers for premium assets.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Competitive rivalry within China Resources Land's operating landscape is intense, with developers actively differentiating through quality, branding, and integrated services. This focus on premium offerings, including sustainable and smart urban developments, is a common strategy to capture market share. For instance, China Resources Land leverages its prominent MixC shopping mall brand, a cornerstone of its diversified '3+1' business model, to cultivate brand loyalty and offer a holistic customer experience.
The real estate sector in China, particularly in Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities, is characterized by numerous players competing for prime land and discerning customers. China Resources Land's commitment to high-quality construction and innovative design, exemplified by its mixed-use developments that integrate residential, retail, and office spaces, directly addresses this competitive pressure. By offering a comprehensive lifestyle proposition, the company aims to stand out from competitors who may focus on more commoditized offerings.
- Brand Strength: China Resources Land's MixC brand is a significant differentiator, recognized for its premium retail and lifestyle offerings.
- Integrated Business Model: The '3+1' model (residential, commercial, office, plus hotels/property management) creates a synergistic ecosystem that enhances customer stickiness.
- Quality and Sustainability: Investments in high-quality construction and sustainable building practices appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers and investors.
- Market Presence: With a strong presence in key economic hubs, China Resources Land benefits from established market knowledge and customer relationships.
Competitive Rivalry 5
The competitive landscape for China Resources Land is characterized by intense rivalry, largely driven by high exit barriers within the Chinese real estate sector. These barriers, including substantial fixed assets, considerable debt burdens, and the social and political ramifications of project abandonment, effectively trap many developers, even those facing financial distress, in the market.
This persistence of struggling entities contributes to an oversupply of properties and fuels aggressive price competition. Consequently, financially sound companies like China Resources Land find it challenging to expand their market share solely through the natural attrition of weaker competitors, as distressed firms continue to operate and compete aggressively.
For instance, by late 2023 and into 2024, the ongoing property market downturn saw several smaller developers defaulting on their obligations, yet many continued to operate under restructuring plans or government oversight, preventing a significant consolidation that would typically reduce competitive pressure.
- High Fixed Assets: Real estate development inherently requires massive capital investment in land acquisition and construction, making it difficult and costly for companies to cease operations.
- Significant Debt Loads: Many developers rely heavily on debt financing, creating substantial obligations that are hard to shed even when facing losses, thus forcing them to remain active.
- Social Implications: The social contract and government policies often discourage outright project cancellations to protect homebuyers and maintain social stability, keeping even struggling developers engaged.
- Persistent Oversupply: The inability of financially weak players to exit the market exacerbates oversupply conditions, leading to downward pressure on prices and rental yields.
Competitive rivalry in China Resources Land's market remains fierce, fueled by a large number of developers vying for market share, especially in prime urban locations. The ongoing property market downturn in 2024 has intensified this competition, forcing companies to engage in aggressive pricing and offer attractive incentives to secure sales.
Developers are increasingly differentiating themselves through product quality, brand reputation, and the provision of integrated services, such as lifestyle-oriented mixed-use developments. China Resources Land’s MixC brand, for example, serves as a significant competitive advantage, fostering customer loyalty and a premium market perception.
High exit barriers within the Chinese real estate sector, including substantial fixed assets and debt, mean that even financially strained developers persist, contributing to oversupply and sustained price pressures. This dynamic limits the ability of financially robust players like China Resources Land to gain market share through the natural exit of weaker competitors.
| Metric | 2023 (Approx.) | 2024 (Projected/Early Data) | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Developer Count (Tier 1/2 Cities) | High (Hundreds) | High (Slight consolidation) | Intense competition for prime land and buyers. |
| Average Net Profit Margin (Major Developers) | Contracted Significantly (e.g., ~5-7%) | Further contraction expected (e.g., ~4-6%) | Aggressive pricing and cost-cutting measures. |
| Land Bid Premiums (Tier 1 Cities) | Robust (e.g., 30-50% premium over base) | Slightly moderated but still competitive | Continued high cost of acquisition for top-tier assets. |
| Sales Volume Growth (Major Developers) | Mixed (some growth, some decline) | Projected modest growth for market leaders | Focus on market share capture by strong players. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Rental housing presents a significant substitute for traditional property ownership for China Resources Land. This trend is fueled by evolving demographics, with younger generations often delaying homeownership due to financial pressures or lifestyle choices. For instance, by the end of 2023, the urbanization rate in China reached 66.16%, meaning a substantial portion of the population resides in urban areas where rental options are more prevalent and often more accessible than outright purchase.
Government initiatives are further bolstering the rental market, introducing a potent threat to developers focused on sales. Policies promoting build-to-rent developments and expanding public rental housing options directly cater to a growing segment of the population. This government support not only increases the supply of rental units but also legitimizes and encourages their use, directly competing with the demand for purchased properties.
Co-living spaces and serviced apartments are emerging as significant substitutes for traditional residential property development, particularly for younger demographics and mobile professionals. These alternatives offer flexibility, often including furnished units and shared amenities, appealing to those who value convenience and community over outright ownership. For instance, in major Chinese cities, the growth of serviced apartments, like those offered by Ascott Residence Trust, provides a compelling alternative, potentially dampening demand for long-term residential purchases. This trend directly impacts developers like China Resources Land by offering renters choices that bypass the conventional buy-to-own model.
The threat of substitutes for China Resources Land's commercial properties is a significant consideration, particularly within the office sector. The growing popularity of flexible office spaces, such as co-working environments, offers companies alternatives to traditional long-term leases. This trend, coupled with the increasing acceptance of remote and hybrid work models, allows businesses to reduce their physical office footprint or opt for more adaptable arrangements. For instance, in 2024, the global flexible workspace market was projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift in how companies approach office needs.
4
Government-subsidized housing initiatives can act as a significant substitute, influencing tenant preferences and diverting demand from market-priced properties. These programs, by offering more affordable alternatives, create downward pressure on rents and sales prices for privately developed housing. For instance, in 2024, China continued its focus on affordable housing construction, aiming to deliver millions of new units, which directly competes with the market-rate offerings of companies like China Resources Land. This competition isn't always direct in terms of product, but it fundamentally impacts the overall housing affordability landscape and consumer choices.
The availability of these subsidized units directly impacts the pool of potential renters and buyers for China Resources Land's projects. This can lead to:
- Reduced demand for market-rate housing: As more affordable options become available, fewer consumers will opt for higher-priced private sector housing.
- Downward pressure on pricing: Landlords and developers may need to lower rents or sales prices to remain competitive with subsidized alternatives.
- Shifts in tenant demographics: Certain income segments may be entirely captured by government programs, altering the customer base for private developers.
- Increased competition for prime locations: When government projects are developed in desirable areas, they further limit the availability of land for private developers and influence local market dynamics.
5
The threat of substitutes for China Resources Land (CR Land) is influenced by evolving consumer preferences. A notable shift towards smaller living spaces, pre-fabricated homes, or an increased value placed on public amenities and infrastructure over private property size can create long-term substitution effects. For instance, in 2024, the demand for compact urban living solutions has been growing, particularly in tier-one cities, as affordability and convenience become paramount for a segment of the population.
CR Land proactively addresses this by focusing on integrated urban living and commercial spaces. This strategy aims to offer comprehensive solutions that go beyond just standalone properties. By developing projects that incorporate retail, entertainment, and community facilities, CR Land seeks to enhance the overall value proposition and reduce the attractiveness of alternative housing or lifestyle choices. This approach is crucial as developers worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of creating holistic living environments rather than just selling square footage.
- Evolving Housing Trends: Consumer interest in smaller, more efficient living spaces and modular/pre-fabricated housing options continues to rise, presenting a potential substitute for traditional, larger residential units.
- Infrastructure vs. Private Space: A growing preference for well-developed public amenities, green spaces, and efficient transportation networks could diminish the perceived value of extensive private property.
- Integrated Living Concepts: CR Land's focus on mixed-use developments, combining residential, commercial, and lifestyle components, serves as a strategic countermeasure to attract and retain customers by offering a comprehensive urban living experience.
- Market Adaptability: The company's ability to adapt its product offerings to align with these changing consumer desires will be key in mitigating the threat of substitutes in the dynamic real estate market.
The threat of substitutes for China Resources Land is significant, especially with the rise of rental housing, co-living spaces, and serviced apartments. These alternatives appeal to younger demographics and those prioritizing flexibility over ownership. For instance, by the end of 2023, China's urbanization rate hit 66.16%, meaning a large urban population has access to these rental options.
Government initiatives further bolster these substitutes. Policies promoting build-to-rent and expanding public rental housing directly compete with traditional property sales. This government support increases supply and legitimacy, impacting demand for purchased properties. Additionally, flexible office spaces and hybrid work models present substitutes for commercial property, with the global flexible workspace market projected for substantial growth in 2024.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on CR Land | Relevant Data Point (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rental Housing | Flexibility, lower upfront cost | Reduced demand for ownership | Urbanization rate reached 66.16% (end of 2023) |
| Co-living/Serviced Apartments | Convenience, community, furnished units | Alternative to traditional residential units | Growth in serviced apartments in major Chinese cities |
| Flexible Office Spaces | Adaptability, reduced footprint | Reduced demand for long-term leases | Projected substantial growth in global flexible workspace market (2024) |
| Government-Subsidized Housing | Affordability | Downward pressure on market prices | Continued focus on affordable housing construction (millions of units planned in 2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in China's property development sector remains moderate, primarily due to the substantial capital requirements. Initiating operations necessitates significant investment in land acquisition, construction, and extensive marketing campaigns. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of acquiring prime development land in Tier 1 cities like Beijing and Shanghai often runs into billions of dollars, a formidable hurdle for smaller, less capitalized firms.
Established players like China Resources Land benefit immensely from their strong financial backing and extensive land reserves, which are critical competitive advantages. Their ability to secure favorable financing and navigate complex regulatory landscapes further solidifies their position. This financial muscle and existing infrastructure make it incredibly challenging for newcomers to gain a foothold and compete effectively on scale and resources.
The threat of new entrants for China Resources Land is relatively low, primarily due to extensive regulatory hurdles. Navigating land acquisition, zoning, and construction in China involves complex approval processes that demand significant expertise and established relationships.
Furthermore, the Chinese government's ongoing efforts to stabilize the property market, such as the 'Three Red Lines' policy introduced in 2020 and continued in 2024, impose strict financing and sales regulations. These measures disproportionately affect new entrants who may lack the financial stability and track record of established players like China Resources Land.
The threat of new entrants into China's real estate market remains moderate, largely due to the significant capital requirements and established brand loyalty enjoyed by incumbents like China Resources Land.
China Resources Land boasts a strong brand reputation, built over years of delivering high-quality projects. This trust is a substantial barrier for newcomers, especially given recent market challenges that have eroded consumer confidence in developer stability. For instance, in 2023, the total sales value of the top 100 Chinese developers saw a decline, highlighting the importance of a proven track record.
New entrants would face considerable hurdles in replicating China Resources Land's established customer loyalty and brand recognition. The company's consistent focus on quality and customer satisfaction has fostered a loyal customer base, making it difficult for new players to gain traction quickly in a competitive landscape.
4
The threat of new entrants in China's property market, particularly for developers like China Resources Land, is significantly mitigated by the intense competition for prime land. Access to these crucial development sites is often a substantial hurdle, with established players frequently holding an advantage.
New companies entering the market would face considerable difficulty in securing strategically located land parcels at prices that would allow for profitable development. This is especially true in desirable urban centers where land availability is scarce and competition is fierce. By 2024, the Chinese government continued to emphasize land supply reforms, but the competitive landscape for prime urban land remained a key barrier. For instance, in major Tier 1 cities, land auction prices often reached unprecedented levels, requiring substantial upfront capital and deep market knowledge, which new entrants typically lack.
- Limited Land Access: New developers struggle to acquire prime land parcels due to high competition and restrictions.
- Government Relationships: Established developers benefit from strong ties with local governments, influencing land allocation.
- Capital Requirements: The high cost of prime land in urban areas necessitates significant financial resources, deterring new entrants.
- Market Knowledge: Navigating land acquisition processes and understanding local market dynamics requires experience that newcomers lack.
5
The threat of new entrants for China Resources Land remains low, primarily due to the current severe headwinds in the Chinese property market. Challenging market conditions, including significant oversupply in many regions, declining property prices, and a widespread liquidity crisis affecting many existing developers, create a highly unattractive landscape for newcomers. These factors significantly increase the barriers to entry, making it difficult and risky for any new player to gain a foothold.
The high risks associated with the industry, coupled with the persistently low average profit margins seen in recent years, further deter new investment. For instance, in 2023, the average profit margin for listed Chinese property developers hovered around 3-5%, a stark contrast to previous decades. This makes the sector an unappealing environment for those considering new ventures, thereby reducing the incentive for new competitors to emerge and challenge established players like China Resources Land.
- Deterrent Factors: Oversupply, declining prices, and developer liquidity crises discourage new entrants.
- Risk and Profitability: High industry risks and low average profit margins (around 3-5% in 2023) reduce investment attractiveness.
- Barrier to Entry: The current market climate acts as a significant barrier, limiting the emergence of new competitors.
The threat of new entrants for China Resources Land is low. Significant capital requirements, stringent government regulations, and established brand loyalty act as substantial barriers. The current challenging market conditions in China's property sector, characterized by oversupply, price declines, and liquidity issues for existing developers, further deter new investment, making the industry unattractive for newcomers.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for China Resources Land leverages data from official company annual reports, investor presentations, and disclosures from the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. We supplement this with industry-specific reports from reputable real estate research firms and government statistics on the Chinese property market.
