Cranswick Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cranswick Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any business, and Cranswick is no exception. A Porter's Five Forces analysis helps dissect the underlying forces that shape its industry, revealing the true nature of competition.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cranswick’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for critical inputs like live animals, feed ingredients, and specialized processing equipment can significantly impact Cranswick. If a few large suppliers dominate these markets, they hold greater power to dictate prices and terms. For instance, the global feed grain market, crucial for Cranswick’s pig and poultry operations, saw significant price volatility in 2024 due to geopolitical events and weather patterns, highlighting supplier leverage.
Cranswick's reliance on specific suppliers for key ingredients, such as pork for its bacon products, can create significant switching costs. If a new supplier requires extensive quality assurance re-validation or if the production process needs substantial modification to accommodate different raw material specifications, Cranswick might face elevated costs and potential disruptions. This can grant existing suppliers greater bargaining power.
In 2024, Cranswick's cost of raw materials, including feed for its farms and livestock, represented a substantial portion of its operating expenses. For instance, fluctuations in global grain prices, a primary component of animal feed, directly impact Cranswick's production costs. If specialized feed formulations or particular breeds of livestock are sourced from a limited number of suppliers, the effort and expense involved in transitioning to an alternative could be considerable.
Suppliers providing highly unique or proprietary products, like specialized animal breeds or distinct feed formulations, wield considerable bargaining power. This is particularly true if these offerings are fundamental to Cranswick's strategy of producing premium goods and are difficult for competitors to source elsewhere. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that sourcing ethically raised, traceable pork, a key differentiator for Cranswick, often relies on a limited number of farms with specific welfare certifications, granting those farms greater leverage in price negotiations.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers can significantly bolster their bargaining power against Cranswick. If suppliers possess the capability and credible intent to move into food processing themselves, they could directly compete, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations.
While this threat is less pronounced for typical agricultural raw material providers, it could be a consideration for suppliers of highly specialized ingredients or proprietary processing technologies. The significant capital investment and established market access needed for food processing generally act as a substantial barrier, limiting the likelihood of this occurring for most of Cranswick's suppliers.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers capable of replicating Cranswick's processing and distribution infrastructure pose a greater threat.
- Market Access: Suppliers with existing customer relationships or distribution channels can more easily integrate forward.
- Capital Intensity: High capital requirements for food processing limit the number of suppliers who can credibly threaten forward integration.
- Industry Structure: In sectors with fewer, larger suppliers, the threat of forward integration might be more concentrated.
Supplier's Importance to Cranswick's Cost Structure
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical factor in Cranswick's cost structure. When a significant portion of Cranswick's total expenses is dependent on inputs from a limited number of suppliers, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This leverage allows them to potentially dictate terms and prices, impacting Cranswick's profitability. For instance, if a key ingredient or packaging material is sourced from only a handful of providers, Cranswick's ability to negotiate favorable pricing diminishes.
Managing these cost drivers is paramount for Cranswick's financial health. The company actively works on developing strong supply chain partnerships and implementing efficient sourcing strategies to mitigate the impact of supplier power. This proactive approach aims to secure reliable supply at competitive prices, ensuring that a large chunk of operational costs isn't unduly influenced by external parties.
- Supplier Concentration: Cranswick's reliance on a few key suppliers for essential raw materials or components increases their bargaining power.
- Input Cost Proportion: The greater the percentage of Cranswick's total costs represented by a supplier's product, the stronger that supplier's negotiating position.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Effective management of sourcing and supplier relationships is crucial for controlling costs and reducing vulnerability to supplier power.
- Market Dynamics: Fluctuations in commodity prices or availability can significantly influence the bargaining power of suppliers to Cranswick.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Cranswick hinges on factors like supplier concentration and the proportion of input costs. For instance, in 2024, feed ingredients represented a significant portion of Cranswick's operating expenses, granting feed suppliers considerable leverage, especially when specific formulations are sourced from a limited number of providers. This reliance can lead to price dictation and impact profitability.
| Factor | Impact on Cranswick | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier leverage | Key for live animals, feed |
| Input Cost Proportion | Strengthens supplier negotiating position | Feed costs were substantial in 2024 |
| Switching Costs | Can grant existing suppliers greater power | Re-validation for new ingredient sources |
| Unique Inputs | Gives suppliers leverage for premium products | Ethically raised pork sourcing in 2024 |
What is included in the product
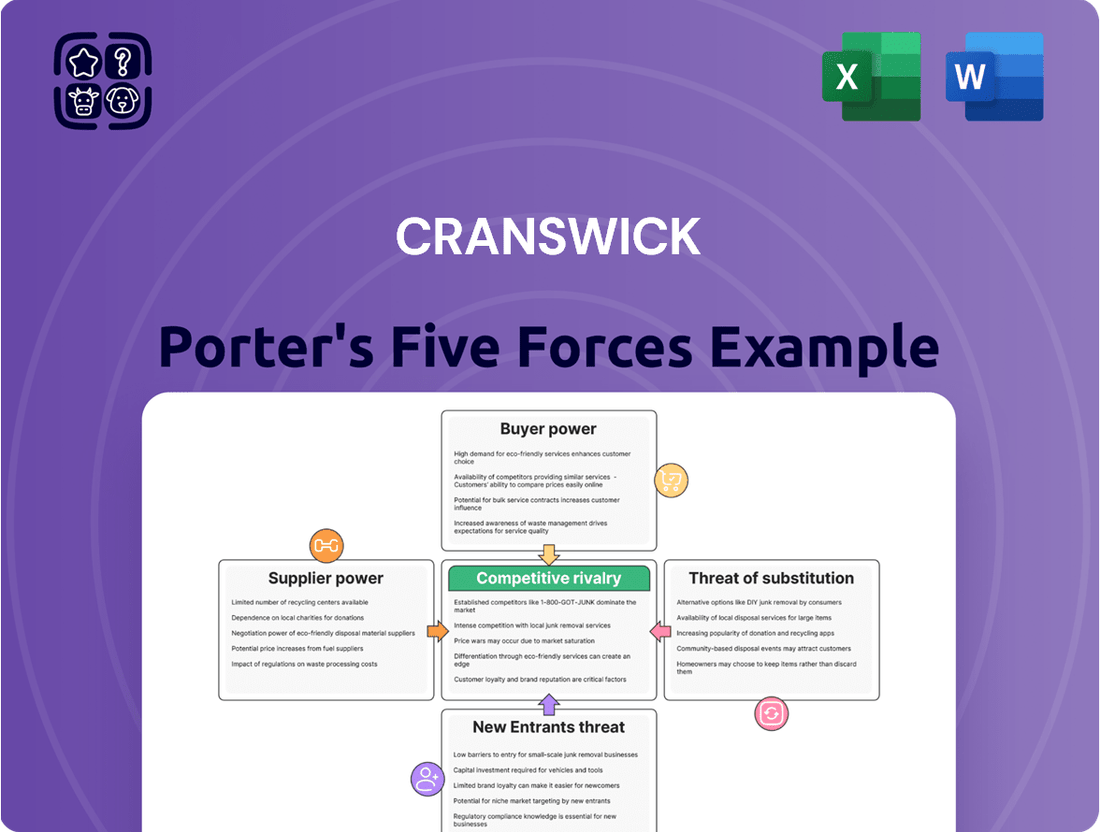
This analysis meticulously examines the five competitive forces impacting Cranswick, revealing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Forces, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cranswick's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by customer concentration and the volume of purchases. The company primarily serves major UK retailers and food service providers, which are often large, consolidated entities themselves.
These key customers purchase in high volumes, granting them substantial leverage. This leverage allows them to negotiate for lower prices, more favorable payment terms, or specific product customizations, directly impacting Cranswick's margins.
For instance, in the fiscal year ending March 2023, Cranswick reported that its top five customers accounted for a significant portion of its revenue, highlighting the concentrated nature of its customer base and the inherent power these entities wield.
The potential loss of a major retail contract, given this concentration, could have a material impact on Cranswick's overall revenues and profitability, underscoring the importance of managing these customer relationships effectively.
For major retailers, the process of switching meat suppliers can be quite involved. It often means navigating complex logistical adjustments, undertaking new product listing procedures, and potentially facing disruptions to their established supply chains. These factors contribute to the switching costs.
However, the UK market offers a good number of large-scale meat producers. This availability means customers, particularly major retailers, aren't locked into a single supplier. They have the flexibility to explore and secure better deals, which can effectively lower the perceived switching costs and increase their bargaining power.
Cranswick's business model, which is highly integrated, and its consistent product quality play a crucial role in customer retention. By offering reliability and a streamlined supply chain, Cranswick aims to reduce the incentive for customers to incur the costs and risks associated with switching to a competitor.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Cranswick, particularly concerning its staple food products like meat. In the competitive grocery landscape, consumers, and by extension retailers, often scrutinize prices closely. This means Cranswick faces pressure to keep its pricing competitive, even for higher-quality items, as shoppers can readily compare offerings from various brands and supermarkets.
The economic climate plays a crucial role in intensifying this price sensitivity. For instance, during periods of high inflation, such as the elevated rates seen in the UK during 2023 and continuing into early 2024, consumers tend to become even more budget-conscious. This can lead to shifts towards cheaper alternatives or a reduction in overall spending on premium food items, directly impacting Cranswick's sales volumes and profit margins.
Customers' Ability to Backward Integrate
While individual consumers rarely possess the power to backward integrate, large corporate customers, such as major supermarket chains, could theoretically explore entering meat processing. This would allow them to control their supply chain and potentially lower costs. However, the significant capital outlay, the need for specialized operational knowledge, and the sheer complexity of meat processing present substantial barriers to entry.
For a company like Cranswick, the direct threat of a major customer backward integrating is generally low. The operational demands are simply too high for most to consider. Nevertheless, it remains a theoretical consideration for exceptionally large and vertically ambitious buyers in the market.
Consider the scale: a large UK supermarket might process hundreds of thousands of tonnes of meat annually. To replicate Cranswick's capabilities would require billions in investment and years to build expertise. For instance, in 2024, the UK food processing sector saw significant investment, but this was largely by established players, not new entrants from retail.
- Theoretical Threat: Large retailers could, in principle, integrate into meat processing.
- High Barriers: Operational complexity, capital investment, and expertise are significant deterrents.
- Low Direct Impact: Cranswick faces a low direct threat from customer backward integration.
- Market Context: The UK food processing sector's 2024 investment highlights the scale of existing operations.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
Customers have a significant advantage due to the wide availability of substitute protein sources and meat products. This includes offerings from numerous competitors and private label brands, making it simple for consumers to switch if Cranswick's products don't align with their expectations on price, quality, or ethical sourcing. For instance, the UK retail market saw a notable increase in private label penetration, reaching 49.6% in grocery sales by early 2024, indicating a strong customer inclination towards alternatives.
The growing popularity of plant-based alternatives further amplifies customer choice and bargaining power. By mid-2024, the plant-based food market in the UK was valued at over £1 billion, with continuous innovation and a broader product range available to consumers. This trend directly challenges traditional meat producers like Cranswick, as customers can readily opt for these substitutes, putting downward pressure on prices and demanding greater value from meat suppliers.
- Extensive Product Variety: Consumers can choose from a broad spectrum of meat products and alternative proteins.
- Private Label Strength: The significant market share of private label brands provides a readily available, often lower-cost, alternative.
- Plant-Based Growth: The expanding plant-based sector offers a direct substitute, increasing competitive pressure.
- Switching Ease: Customers can easily shift suppliers or product types based on price, quality, or ethical considerations.
Cranswick's customers, particularly large UK retailers, possess considerable bargaining power. This is driven by their high purchasing volumes and the availability of numerous alternative suppliers and protein sources, including a growing plant-based market. The increasing market share of private label brands further enhances this power, as customers can easily switch to lower-cost options. The threat of customers backward integrating into meat processing, while theoretically present, is mitigated by the substantial capital and expertise required.
| Factor | Impact on Cranswick | Supporting Data/Context (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High | Top five customers accounted for a significant portion of revenue in FY ending March 2023. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate (for customers) | Logistical complexity for retailers, but ample alternative suppliers exist. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Consumers and retailers scrutinize prices, exacerbated by high inflation in 2023-2024. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Low (direct) | Significant capital and expertise barriers prevent most customers from integrating. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Private label penetration reached 49.6% of grocery sales by early 2024; plant-based market valued over £1 billion by mid-2024. |
Full Version Awaits
Cranswick Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis of Cranswick, offering a detailed examination of industry competition, buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis that you will receive immediately after completing your purchase, ensuring no surprises and full immediate utility for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The UK meat processing sector is characterized by a mix of large, established companies and a considerable number of smaller, niche operators. Cranswick, a significant player, contends with other major food manufacturers that also focus on pork and poultry, making market share expansion a challenging endeavor.
In 2024, the competitive landscape remains robust, with key competitors like Tulip Food Company and Vion Food Group actively participating in the market. These companies, along with Cranswick, represent a substantial portion of the UK’s meat processing capacity. For instance, Cranswick reported revenue of £2.3 billion for the fiscal year ending March 2024, highlighting the scale of operations within the industry.
The rivalry is further amplified by the presence of both domestic UK-based businesses and international companies operating within the market. This dual presence ensures a constant drive for efficiency and innovation as firms vie for consumer preference and supply chain dominance.
The growth rate of the UK meat market is a significant factor in competitive rivalry. In 2023, the UK meat market showed signs of maturity, with overall volume growth being relatively modest. This slower growth means that companies like Cranswick are often vying for a larger slice of an existing pie, which can naturally intensify competition as businesses seek to maintain or increase their market share.
When an industry is mature or experiencing slow growth, the battle for customers becomes more pronounced. Competitors may resort to aggressive pricing strategies, frequent promotional offers, and increased investment in product innovation or differentiation to stand out. This dynamic can put considerable pressure on profit margins and necessitates a strong focus on operational efficiency and cost control to remain competitive.
Cranswick plc differentiates itself through a strong focus on premium quality, ethical sourcing, and a fully integrated supply chain, from farm to fork. This approach aims to build brand loyalty and command higher prices, as evidenced by their continued investment in sustainability initiatives and animal welfare standards, which resonate with increasingly conscious consumers. For instance, in their 2024 fiscal year, Cranswick reported a revenue of £2.4 billion, showcasing the market's receptiveness to their value proposition.
However, the meat industry often views many products as commodities, making it difficult to maintain a substantial competitive edge solely through product uniqueness. Competitors can and do attempt to replicate successful product lines and marketing efforts, often through aggressive pricing or by highlighting their own quality claims. This constant imitation pressure means that differentiation requires ongoing innovation and significant marketing investment to stay ahead.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can significantly impact competitive rivalry. For instance, in the food processing industry, which is capital-intensive, companies like Cranswick face substantial costs if they decide to leave the market. These costs can stem from specialized machinery, long-term supply agreements, or substantial employee severance packages. These factors can trap less profitable competitors in the market, leading to prolonged periods of overcapacity and aggressive price competition as they fight to survive.
The persistence of these struggling firms intensifies the pressure on established players. In 2024, the UK food manufacturing sector, a key area for Cranswick, continued to grapple with rising operational costs and fluctuating consumer demand. This environment makes it harder for companies to exit gracefully, meaning weaker competitors might stay in the game longer, potentially driving down prices and margins for everyone, including Cranswick.
- Specialized Assets: Food processing plants often contain highly specific equipment that has limited resale value outside the industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers or large retail customers can create financial penalties for early termination.
- Employee Severance Costs: Significant workforces in large processing facilities mean substantial payouts if operations are wound down.
- Capital Intensity: The high upfront investment in plant and machinery makes exiting a costly affair.
Strategic Stakes and Diversity of Competitors
The competitive landscape for Cranswick is marked by a wide array of players, each with distinct strategic aims. Some competitors prioritize aggressive market share expansion, while others concentrate on specialized, high-margin niches or a cost-leadership approach.
This strategic divergence means Cranswick needs to be highly attuned to the varied motivations of its rivals. Understanding whether a competitor is aiming for volume, premium positioning, or cost efficiency is crucial for anticipating their next moves and formulating Cranswick's own defensive and offensive strategies.
- Diverse Strategic Objectives: Competitors in the meat sector pursue varied goals, from market share dominance to niche specialization and cost leadership.
- Unpredictable Rival Behavior: The mix of strategies can lead to unpredictable actions from competitors as they chase different objectives.
- Strategic Positioning: Cranswick must decipher these rival strategies to effectively position itself and anticipate market shifts.
Competitive rivalry in the UK meat processing sector is intense, driven by a mature market with modest growth. Companies like Cranswick face pressure from established players such as Tulip Food Company and Vion Food Group, alongside international competitors. This dynamic forces a constant focus on efficiency, innovation, and cost control to maintain market share.
The fight for customers intensifies in slower-growth environments, leading to aggressive pricing and promotions. Cranswick's strategy of focusing on premium quality and ethical sourcing helps differentiate it, as seen in its £2.4 billion revenue for the fiscal year ending March 2024. However, the commodity nature of many meat products means rivals can easily imitate successful offerings, necessitating continuous innovation and marketing investment.
High exit barriers, including specialized assets and long-term contracts, can keep less profitable competitors in the market, prolonging overcapacity and price competition. This situation, prevalent in the UK food manufacturing sector in 2024, creates sustained pressure on margins for all players.
| Competitor | 2024 Revenue (approx.) | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Cranswick plc | £2.4 billion | Premium Quality, Integrated Supply Chain |
| Tulip Food Company | (Undisclosed, significant UK presence) | Pork & Poultry Processing |
| Vion Food Group | (Undisclosed, significant UK presence) | Pork & Poultry Processing |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitution for traditional meat products, like those produced by Cranswick, stems from the rapidly expanding plant-based alternatives market. Consumers are increasingly seeking out healthier, more sustainable, or ethically produced food options, driving demand for products from companies such as Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods. These alternatives are not only gaining traction but are also improving significantly in taste and texture, making them more appealing to a wider consumer base.
For instance, the global plant-based meat market was valued at approximately $6.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $30 billion by 2030, indicating substantial growth. This trend directly challenges the market share of conventional meat producers by offering comparable, albeit different, product experiences.
A significant threat to Cranswick comes from the shifting dietary preferences and growing health consciousness among consumers. Concerns about red meat consumption, its environmental footprint, and general health benefits are increasingly influencing food choices, potentially leading consumers away from traditional meat products.
Public health campaigns and widespread media coverage promoting plant-based diets or reduced meat intake can accelerate this trend. For instance, by mid-2024, the global plant-based food market was projected to reach substantial figures, indicating a growing consumer appetite for alternatives. This societal shift directly impacts demand for Cranswick's core offerings, necessitating a proactive response.
Beyond plant-based alternatives, traditional protein sources like fish, eggs, and dairy remain significant substitutes for meat. For instance, global fish consumption was estimated to be around 160 million tonnes in 2023, providing a readily available protein alternative.
Emerging technologies such as lab-grown or cultured meat present a potential future threat. While still in early stages, advancements in this sector could offer consumers a novel, ethically sourced protein option, potentially impacting demand for conventional meat products in the long term.
Price-Performance Trade-off of Substitutes
The willingness of consumers to switch to substitutes, such as plant-based proteins or alternative meat sources, hinges on their perceived value. This often involves a careful balancing act between price, taste, convenience, and nutritional benefits. If these substitutes can deliver a comparable or even superior experience at a lower cost, or boast enhanced health credentials, the threat to Cranswick's market position significantly increases.
For instance, the plant-based meat market saw substantial growth, with global sales reaching an estimated $7 billion in 2023, indicating a growing consumer appetite for alternatives. This trend underscores the need for Cranswick to continually reinforce the premium quality and unique consumer appeal of its meat products to justify their price points and retain customer loyalty.
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers may switch to cheaper meat alternatives if the price gap widens significantly.
- Taste and Texture Parity: As plant-based and other meat substitutes improve in taste and texture, they become more viable alternatives.
- Health and Ethical Concerns: Growing consumer awareness around health and ethical considerations can drive demand for substitutes perceived as healthier or more sustainable.
- Innovation in Alternatives: Continuous innovation in the alternative protein sector can introduce new products that directly challenge traditional meat offerings.
Convenience and Accessibility of Substitutes
The growing convenience and accessibility of plant-based and other alternative proteins significantly heighten the threat of substitutes for traditional meat products. As these alternatives become readily available in supermarkets and restaurants, and preparation becomes simpler, consumers are more likely to switch. For instance, the UK plant-based market saw continued growth in 2024, with sales of meat-free products reaching an estimated £1.7 billion by the end of the year.
Cranswick must closely monitor evolving distribution channels and shifting consumer habits. The expansion of ready-to-eat plant-based meals and the increasing presence of these options in quick-service restaurants, for example, reduce the effort required for consumers to choose alternatives. This trend is supported by data showing that in 2024, over 60% of UK consumers reported trying plant-based alternatives, with convenience being a key driver for repeat purchases.
- Increased Availability: Plant-based options are now commonplace in major UK supermarkets, with dedicated aisles and a wider product selection than ever before.
- Simplified Preparation: Many substitute products, like pre-marinated tofu or plant-based burgers, require minimal cooking time, directly competing with the convenience of processed meat products.
- Growing Market Share: The meat-free category in the UK continued its upward trajectory in 2024, capturing an ever-larger share of the overall protein market.
The threat of substitutes for traditional meat products, like those from Cranswick, is significant and multifaceted. The burgeoning plant-based sector, driven by health, ethical, and environmental concerns, offers increasingly palatable and convenient alternatives. For instance, the global plant-based meat market was valued at approximately $6.4 billion in 2023 and is projected for substantial growth. This trend, coupled with established protein sources like fish and emerging technologies such as cultured meat, presents a clear challenge to conventional meat producers by offering consumers a wider array of choices that can directly compete on taste, price, and perceived benefits.
| Substitute Category | Key Drivers | 2023 Market Value (Est.) | Projected Growth Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Meat | Health, Ethics, Sustainability | $6.4 billion (Global) | ~5x by 2030 |
| Fish | Established Protein Source, Health Perceptions | ~160 million tonnes (Global Consumption) | Stable to Moderate |
| Cultured Meat | Ethical Sourcing, Novelty | Nascent (Early Stage Development) | High Potential, Uncertain Timeline |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a presence in the meat processing sector demands significant capital. Think about the cost of building modern abattoirs, sophisticated processing plants, and the entire cold chain infrastructure needed to maintain product integrity from farm to table. These aren't small investments; they represent substantial upfront outlays.
For instance, setting up a new, fully compliant meat processing facility in 2024 could easily run into tens of millions of pounds, depending on scale and automation levels. This high barrier to entry naturally discourages many potential new players, leaving the field more open to established companies.
Companies like Cranswick, with their extensive and already operational network of facilities and advanced technology, possess a considerable advantage. This existing infrastructure means they can operate more efficiently and at a lower cost per unit compared to a newcomer needing to finance every aspect from scratch.
The food industry, particularly meat processing, faces significant regulatory burdens. New businesses must navigate complex rules for food safety, hygiene, animal welfare, and environmental impact. For instance, in 2024, the UK Food Standards Agency continued to enforce rigorous standards, requiring substantial investment in compliance infrastructure for any new player entering the market.
Obtaining the necessary licenses and maintaining ongoing adherence to these regulations presents a considerable barrier for potential entrants. This adds significant cost and extends the time it takes to bring products to market. Cranswick, with its established history, has developed deep expertise in managing these regulatory landscapes, a significant advantage over newcomers.
Securing shelf space in major UK retail chains and food service outlets is a significant hurdle for newcomers aiming to compete with established players like Cranswick. These established channels often have deep-rooted relationships with existing suppliers, making it challenging for new entrants to break in.
For instance, in 2023, the top five UK grocery retailers accounted for over 70% of the market share, indicating a highly concentrated distribution landscape. This concentration means that gaining access requires not only competitive pricing but also demonstrable reliability and brand recognition, which new entrants typically lack.
Building the necessary trust and negotiating supply contracts or securing prime shelf placement demands substantial investment in marketing, sales infrastructure, and potentially product development to meet retailer specifications. This upfront cost acts as a powerful deterrent to potential new competitors.
Brand Loyalty and Established Relationships
Cranswick has cultivated significant brand loyalty and nurtured enduring relationships with key customers, notably major retailers, by consistently delivering quality products and ensuring reliable supply chains. This deep-seated trust is a formidable barrier for any new competitor attempting to enter the market.
New entrants would face a substantial challenge in replicating Cranswick's established reputation and customer allegiance, particularly within the premium food sector where consumer confidence in brand heritage and origin is paramount. Building comparable brand equity requires time and substantial investment.
- Brand Recognition: Cranswick's extensive marketing efforts have cemented its position in consumers' minds.
- Customer Relationships: Long-term partnerships with major supermarkets provide preferential shelf space and consistent demand.
- Premium Segment Challenge: Newcomers must overcome the perception that premium products require established, trusted brands.
- Customer Retention: In 2023, Cranswick reported a high customer retention rate, indicating the strength of these established relationships.
Economies of Scale and Supply Chain Integration
Established players like Cranswick leverage significant economies of scale in their operations. For instance, in 2024, Cranswick's substantial purchasing power for raw materials and efficient production processes likely resulted in lower per-unit costs compared to a new entrant. This cost advantage makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price from the outset.
Cranswick's integrated supply chain, encompassing everything from farming to final processing, presents a formidable barrier. This end-to-end control in 2024 allowed for optimized logistics, consistent quality, and reduced waste, efficiencies that are costly and time-consuming for new entrants to build. Replicating this level of integration requires substantial capital investment and operational expertise.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by the high capital requirements and operational complexities associated with achieving comparable economies of scale and supply chain integration. Newcomers would need to overcome these entrenched advantages to effectively challenge established firms like Cranswick.
- Economies of Scale: Cranswick's large-scale operations in 2024 enable cost efficiencies in purchasing, manufacturing, and distribution.
- Supply Chain Integration: From farm to fork, Cranswick's control over its supply chain offers significant operational advantages and quality assurance.
- Barriers to Entry: The capital expenditure and time needed to replicate Cranswick's integrated model create a substantial hurdle for potential new competitors.
- Cost Advantage: This integration translates into a cost advantage for Cranswick, making it difficult for new entrants to match pricing and profitability.
The threat of new entrants into the meat processing industry, particularly for established players like Cranswick, is significantly mitigated by several key factors. These include the substantial capital investment required for facilities and technology, stringent regulatory compliance, and the difficulty in securing distribution channels and building brand loyalty.
The high upfront costs for modern abattoirs and processing plants, estimated in the tens of millions of pounds for a new facility in 2024, alongside the complex regulatory landscape enforced by bodies like the UK Food Standards Agency, create formidable barriers. Furthermore, gaining access to major retail distribution, which in 2023 saw the top five UK grocers holding over 70% market share, demands significant investment in marketing and sales, alongside established trust and brand recognition that newcomers typically lack.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Cost of building and equipping processing facilities. | High; requires substantial upfront funding. | Estimated £10M+ for a new UK meat processing plant (2024). |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to food safety, hygiene, and welfare standards. | Significant; demands investment in infrastructure and expertise. | UK FSA rigorous standards continue to be enforced (2024). |
| Distribution Access | Securing shelf space in major retailers. | Challenging; requires strong relationships and brand recognition. | Top 5 UK grocers held >70% market share (2023). |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Building consumer trust and retailer partnerships. | Difficult and time-consuming; requires consistent quality and marketing. | Cranswick reported high customer retention (2023). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating information from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and government economic statistics to provide a comprehensive view of competitive pressures.
