Cox Enterprises Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cox Enterprises Bundle
Cox Enterprises operates in dynamic sectors, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, substitute products, and existing rivalry is crucial for strategic planning. This brief overview highlights the core forces, but the full analysis delves into the nuances that truly define Cox's market landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cox Enterprises’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of critical telecommunications infrastructure, such as advanced fiber optic cables and 5G network equipment, hold substantial bargaining power. This is largely due to the highly specialized nature and significant capital investment required for their products. Cox Enterprises, like other major players in the broadband sector, relies heavily on these specialized suppliers for network expansion and upgrades.
The robust demand for high-speed internet fuels this supplier leverage. In 2024 alone, the U.S. saw an impressive 10.3 million new homes passed with fiber broadband. This rapid deployment highlights the essential role of these specific technologies and suggests that Cox Communications may face limited alternatives when sourcing such vital components, thereby strengthening supplier negotiation positions.
Major media conglomerates and independent content creators wield considerable bargaining power over Cox Enterprises' media division. These entities control the popular programming that forms the backbone of cable TV packages, giving them leverage in negotiations.
The cost and availability of licensing agreements for desirable content directly affect Cox Communications' profitability and its ability to compete. For instance, in 2024, the rising costs of sports broadcasting rights continue to pressure cable providers, making these essential licenses a significant expense.
Suppliers of advanced automotive software, such as Dealer Management Systems (DMS) and cloud-based platforms, are gaining significant bargaining power over Cox Enterprises. The market for automotive cloud solutions is expected to expand from $63.94 billion in 2024 to $74.97 billion in 2025, highlighting the increasing reliance on these critical digital infrastructures. Similarly, the DMS market is projected to grow from $4.38 billion to $4.85 billion in the same timeframe, indicating a concentrated demand for specialized software that enhances dealership operations.
Skilled Labor and Technical Talent
The availability of highly skilled labor and specialized technical talent significantly influences supplier bargaining power for Cox Enterprises. Across telecommunications, roles like fiber technicians and network engineers are in high demand. Similarly, the automotive technology sector requires expertise in areas such as AI development and data science.
This demand creates potential labor constraints, directly impacting supplier leverage. For instance, the fiber broadband industry alone is anticipated to require an additional 205,000 workers through 2026 to manage deployment needs, illustrating the competitive landscape for talent.
- High demand for specialized telecommunications roles like fiber technicians and network engineers.
- Need for advanced automotive technology talent, including AI developers and data scientists.
- Projected need for 205,000 additional fiber broadband workers by 2026.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Cox Enterprises' suppliers who possess proprietary technology or hold key patents, especially in areas like advanced broadband network components or sophisticated automotive AI, can exert significant bargaining power. This allows them to dictate terms and command premium pricing. For instance, a supplier holding a patent on a critical fiber optic cable technology essential for Cox Communications' network expansion would have considerable leverage. Similarly, in the automotive sector, a company with exclusive rights to a vital AI algorithm for autonomous driving features used by Cox Automotive could influence contract negotiations.
This technological exclusivity is a major driver of supplier power. As of early 2024, the telecommunications industry continues to see substantial investment in 5G and fiber optic infrastructure, making suppliers of specialized components with unique technological advantages highly influential. In the automotive technology space, the rapid advancement of AI and connectivity means that suppliers of these core technologies are increasingly valuable and can command higher prices due to their innovation. For example, a 2023 report indicated that companies with unique semiconductor designs for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) saw significant revenue growth, reflecting their strong market position.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers with unique, hard-to-replicate technologies in network infrastructure or automotive AI can charge more.
- Patent Protection: Patents grant exclusive rights, limiting competition and increasing supplier leverage over companies like Cox.
- Industry Reliance: Both broadband and automotive sectors depend heavily on continuous innovation, amplifying the power of technology-leading suppliers.
- Market Differentiation: Suppliers offering differentiated, cutting-edge solutions are better positioned to negotiate favorable terms.
Suppliers of critical telecommunications infrastructure and specialized automotive software possess significant bargaining power due to the high capital investment and specialized nature of their offerings. The growing demand for advanced technologies in both sectors, such as fiber broadband and automotive AI, further amplifies this leverage.
The concentration of suppliers in niche markets, coupled with their proprietary technology and patent protection, allows them to dictate terms and command premium pricing. For instance, the increasing reliance on AI in the automotive sector, with its market projected to grow substantially in 2024-2025, highlights the value of technology-leading suppliers.
| Sector | Key Supplier Strength | Impact on Cox |
|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Proprietary fiber optic and 5G network equipment | Limited alternatives for network expansion, potentially higher costs. |
| Media | Exclusive content licensing agreements | Direct impact on programming costs and competitiveness. |
| Automotive Technology | Advanced AI and cloud-based dealership management systems | Increased reliance on specialized software providers, potential price increases. |
What is included in the product
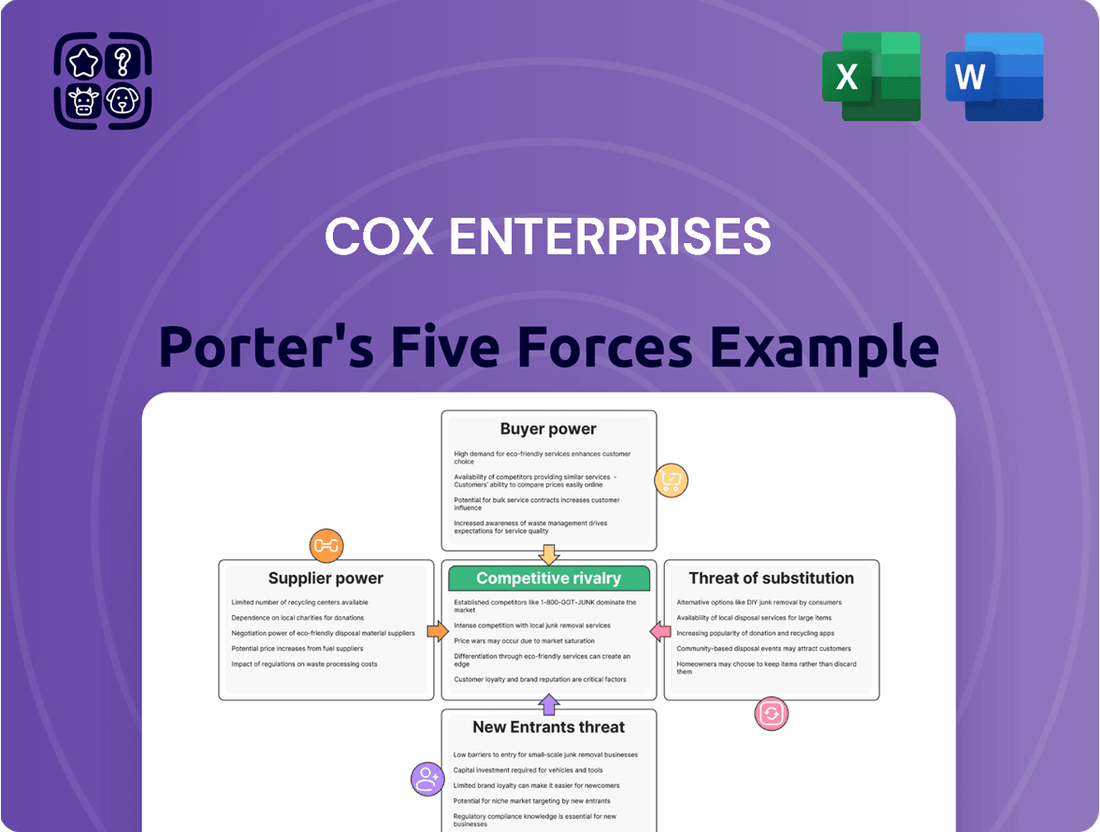
This analysis meticulously examines the competitive forces impacting Cox Enterprises across its diverse media, automotive, and technology sectors, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, allowing Cox Enterprises to proactively address market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Residential consumers of Cox Communications' broadband and cable services generally hold moderate bargaining power. This power stems from the increasing availability of alternative providers, including other cable companies, fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) providers, and fixed wireless access (FWA) services, which offer consumers more choices. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. broadband market saw continued expansion of fiber networks, with estimates suggesting over 70% of U.S. households had access to gigabit speeds, a significant portion of which was via fiber, directly impacting cable providers' competitive landscape.
Large enterprise telecommunications clients wield considerable bargaining power over providers like Cox Communications. Their substantial contract volumes allow them to negotiate favorable pricing, service level agreements, and customized solutions. For instance, in 2024, major corporations often secure discounts of 15-20% on bulk internet and voice services due to their significant spend.
These sophisticated clients typically have dedicated procurement departments focused on optimizing telecommunications costs and performance. Their ability to easily switch providers, often with minimal disruption thanks to industry-standard equipment, further strengthens their negotiating position. A single large enterprise client can represent millions in annual revenue, making retention and satisfaction paramount for Cox.
Automotive dealerships, as major clients for Cox Automotive's diverse services like digital marketing and software, hold considerable sway. Their increasing reliance on advanced technologies, such as AI and omnichannel strategies, means they seek integrated, high-value solutions and have the flexibility to select from various providers, amplifying their bargaining power.
Individual Car Buyers and Sellers
Individual car buyers and sellers wield significant bargaining power when engaging with platforms like Cox Automotive's Autotrader and Kelley Blue Book. This is largely due to the vast number of alternatives available, both online and offline, for researching, pricing, and transacting vehicles.
The car purchasing process has become increasingly omnichannel. In fact, a substantial 43% of recent car buyers utilized a blended approach, combining online research with in-person dealership visits. This flexibility empowers consumers, giving them greater control over their decisions and allowing them to negotiate more effectively.
- High Availability of Alternatives: Consumers can easily compare prices and options across multiple websites and dealerships.
- Information Transparency: Tools like Kelley Blue Book provide detailed pricing information, leveling the playing field for buyers.
- Omnichannel Purchasing Behavior: The 43% of buyers using a blended approach demonstrate a willingness to shop around, increasing their leverage.
Automotive Manufacturers (OEMs)
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are a significant customer group for Cox Automotive's offerings, particularly in areas like vehicle remarketing and digital advertising solutions. Their substantial purchasing power enables them to secure advantageous terms and exert influence over the services provided. For instance, in 2024, major automotive OEMs continued to leverage their scale to negotiate pricing and service level agreements, impacting Cox Automotive's revenue streams from wholesale auctions and digital marketing platforms.
The bargaining power of OEMs is amplified by the availability of alternative service providers in the automotive ecosystem. OEMs can choose from various remarketing channels and digital marketing agencies, creating competitive pressure on Cox Automotive to maintain attractive pricing and innovative solutions. This dynamic was evident in 2024 as OEMs explored partnerships with emerging technology firms offering data-driven insights and direct-to-consumer sales platforms.
- OEMs represent a substantial customer base for Cox Automotive's wholesale and digital services.
- Their large order volumes and strategic importance grant OEMs significant negotiation leverage.
- In 2024, OEMs actively sought competitive pricing and tailored service packages from Cox Automotive.
- The presence of alternative service providers further enhances OEM bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers for Cox Enterprises is multifaceted, influenced by the specific industry segment and the nature of the customer. For Cox Communications, residential customers possess moderate power due to the growing availability of competitive broadband and cable alternatives, a trend amplified in 2024 with significant fiber network expansion. Conversely, large enterprise clients wield substantial power, leveraging their high volume of business to negotiate favorable terms and service level agreements, often securing discounts of 15-20% in 2024.
Within Cox Automotive, individual car buyers and sellers benefit from extensive online and offline options, enhancing their negotiating leverage, further supported by the 43% of buyers in 2024 who used a blended online-offline approach. Automotive dealerships, as key clients for digital marketing and software, also hold considerable sway, seeking integrated solutions and having the flexibility to switch providers. Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) represent a powerful customer segment, negotiating advantageous terms for remarketing and digital advertising services, with their power bolstered by alternative providers in the automotive tech space.
Preview Before You Purchase
Cox Enterprises Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Cox Enterprises, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products within the media and automotive industries where Cox Enterprises operates.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The broadband and cable sector is intensely competitive, with established giants like Cox Communications, Comcast, and Spectrum facing off against each other and newer entrants. The rise of fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) technology is a major disruptor, directly challenging the older hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) networks. In markets where fiber is an option, HFC networks have experienced a significant 33% decline, underscoring the pressure these legacy systems are under.
The automotive services market is a bustling arena, characterized by a wide array of participants. From established giants offering comprehensive solutions to nimble tech startups focusing on niche areas, the competition is intense. This fragmentation means that companies like Cox Enterprises face rivals at every turn, each vying for market share in areas like digital marketing, wholesale auctions, and crucial software systems.
The dynamism within this sector is further underscored by significant growth in key segments. For instance, the automotive cloud-based solutions market is projected to expand at a robust 17.2% compound annual growth rate between 2024 and 2025. Simultaneously, the Dealer Management System market is expected to grow at a healthy 10.22% CAGR during the same period. These figures not only signal opportunity but also highlight the constant innovation and escalating competitive pressures that all players must navigate.
Cox Enterprises' traditional media operations, encompassing newspapers and television stations, contend with intense rivalry from established local and national media conglomerates. This competition is further amplified by the significant migration of advertising budgets towards digital channels and social media platforms, a trend that intensified in 2024 as digital ad spending continued its upward trajectory, capturing an ever-larger share of the market.
The pressure to innovate and adapt is constant, as consumer preferences increasingly lean towards digital content consumption. This necessitates ongoing investment in digital transformation and content diversification to remain relevant and capture audience attention in a fragmented media landscape, a challenge faced by many legacy media companies.
Diversified Conglomerate Rivalry
Cox Enterprises faces significant competitive rivalry as a diversified conglomerate, indirectly contending with major players across its automotive, telecommunications, and media segments. This competition extends beyond direct product or service battles to include fierce contests for essential resources like skilled talent, crucial investment capital, and prime market share within each of its operational arenas.
- Automotive Sector: Cox Automotive, a major player, competes with companies like AutoNation and CarGurus for both consumer attention and dealership partnerships. In 2023, the used car market saw significant activity, with Cox Automotive's Manheim remarketing division playing a crucial role in wholesale vehicle transactions.
- Telecommunications: In its connectivity business, Cox Communications competes with giants such as Comcast and Charter Communications. The broadband market remains highly competitive, with ongoing investments in fiber optic expansion and 5G technology impacting market dynamics.
- Media and Entertainment: Through its media holdings, Cox competes with a broad array of traditional and digital media companies for advertising revenue and audience engagement. The evolving media landscape, driven by streaming services and digital content platforms, intensifies this rivalry.
Innovation and Technology Race
Cox Enterprises faces intense competition driven by a relentless innovation and technology race, especially as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and connected vehicle technologies reshape the telecommunications and automotive industries. This necessitates substantial investment in research and development to stay ahead and satisfy evolving customer expectations.
The imperative to innovate means companies like Cox must allocate significant capital to R&D. For instance, the global telecom market's R&D spending is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars annually, with a substantial portion focused on 5G, AI, and network modernization. Similarly, the automotive sector's investment in connected car technology and autonomous driving is also in the tens of billions, reflecting the high stakes.
- AI Integration: Companies are racing to integrate AI for enhanced customer service, network optimization, and data analytics, aiming to personalize experiences and improve operational efficiency.
- IoT Expansion: The growth of IoT devices creates new revenue streams and demands for robust connectivity, pushing providers to expand their network capabilities and develop new service offerings.
- Connected Vehicles: In the automotive sector, the demand for in-car connectivity, infotainment, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication requires continuous technological upgrades, creating a competitive landscape where early adopters gain market share.
- R&D Investment: Leading telecom firms are investing heavily in next-generation network technologies, with some allocating over 15% of their revenue to R&D to maintain a competitive edge.
Cox Enterprises faces intense rivalry across its diverse business segments, from telecommunications and automotive services to media. In the broadband sector, competition is fierce with major players like Comcast and Charter, particularly as fiber optic expansion challenges existing hybrid fiber-coaxial networks. The automotive market sees Cox Automotive competing with numerous digital platforms and physical dealerships, with the used car market remaining a key battleground.
The media landscape is also highly competitive, with traditional outlets like Cox Media Group vying for advertising revenue against digital giants and streaming services. This necessitates continuous adaptation to changing consumer habits and digital migration of ad spend. For example, digital advertising spending continued its strong growth in 2024, increasing pressure on traditional media revenue streams.
| Segment | Key Competitors | Competitive Pressure Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Comcast, Charter Communications | Fiber optic expansion, 5G technology, broadband speed competition |
| Automotive Services | AutoNation, CarGurus, Digital Marketplaces | Online vehicle sales, data analytics, dealership technology adoption |
| Media and Entertainment | Disney, Paramount Global, Digital Ad Platforms | Streaming services, digital content consumption, shifting advertising budgets |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat to Cox Communications' traditional cable TV business comes from streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+. These platforms offer a vast library of on-demand content, often at a lower price point than traditional cable packages, directly appealing to consumers seeking more flexibility and choice.
This shift, often termed cord-cutting, has led to a steady decline in traditional pay-TV subscriptions. For instance, by the end of 2023, it's estimated that over 60 million US households had cut the cord, a number projected to grow. This directly impacts Cox's subscriber revenue and market share in the video entertainment sector.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) and satellite internet, like Starlink, are increasingly becoming viable substitutes for Cox's traditional wireline broadband. These technologies bypass the need for extensive physical cable infrastructure, making them particularly attractive in underserved or rural areas where Cox's network might be less pervasive. The global FWA market is projected for significant expansion, with forecasts suggesting continued robust growth through 2025, indicating a growing competitive threat.
Emerging alternatives like car subscription services and ride-sharing platforms present a growing threat to traditional vehicle ownership models, impacting the broader automotive market that Cox Enterprises operates within. The global car subscription market, valued at an estimated US$7.62 billion in 2024, is on a strong growth trajectory, expected to reach US$34.60 billion by 2030. This significant expansion highlights a clear shift in consumer behavior, with more individuals prioritizing flexible vehicle access over outright ownership.
Direct-to-Consumer Sales by Auto Manufacturers
The rise of direct-to-consumer (DTC) sales by auto manufacturers presents a significant threat. Companies like Tesla have already demonstrated the viability of this model, bypassing traditional franchised dealerships. This trend could directly impact Cox Automotive's core business, which relies heavily on services provided to dealerships.
This shift means manufacturers are taking more control over the customer relationship and sales process, potentially reducing the need for third-party platforms and services that Cox Automotive offers. For example, in 2024, several major automakers continued to experiment with or expand their DTC initiatives, signaling a sustained challenge to the established dealer network.
- Reduced Dealer Dependence: Manufacturers engaging in DTC sales can lessen their reliance on dealerships for customer acquisition and sales, a key revenue stream for Cox Automotive.
- Alternative Sales Channels: DTC models offer consumers an alternative to traditional dealership purchases, directly substituting the services Cox Automotive provides to dealerships.
- Evolving Market Dynamics: The increasing consumer acceptance of online purchasing and manufacturer-controlled sales experiences further strengthens the threat of substitutes in the automotive retail space.
Digital News and Social Media for Traditional Media
The proliferation of digital news and social media poses a significant threat of substitution for Cox Enterprises' traditional media assets, like its newspapers. These digital platforms offer immediate access to information and a vast array of content, often at no direct cost to the consumer. This directly competes with the business model of print publications that rely on subscriptions and advertising.
The shift in consumer behavior towards digital consumption has a direct impact on advertising revenue for traditional media. For instance, by mid-2024, digital advertising spending in the U.S. was projected to exceed $300 billion, a significant portion of which is siphoned away from print and broadcast. This forces companies like Cox to adapt their strategies to capture a share of this digital advertising market.
- Digital platforms offer immediate and often free news delivery, directly challenging traditional media's subscription and advertising models.
- In 2024, digital advertising spending in the U.S. is expected to surpass $300 billion, indicating a substantial shift in advertising budgets away from traditional channels.
- Audience engagement is increasingly fragmented across numerous online sources, making it harder for traditional media to maintain a dominant readership or viewership.
- The need for digital transformation is critical for survival, requiring substantial investment in online content creation, distribution, and monetization strategies.
The threat of substitutes for Cox Enterprises' various business segments is substantial and evolving rapidly. In media, digital platforms and social media provide instant, often free, news and entertainment, directly competing with traditional print and broadcast. By mid-2024, US digital ad spending was projected to exceed $300 billion, a clear indicator of this shift.
In the automotive sector, direct-to-consumer sales models by manufacturers, exemplified by Tesla, challenge Cox Automotive's reliance on dealerships. The car subscription market, valued at an estimated $7.62 billion in 2024, also offers consumers alternatives to traditional ownership, impacting the broader automotive ecosystem.
For Cox Communications, streaming services like Netflix and Hulu are significant substitutes for cable TV, with over 60 million US households having cut the cord by the end of 2023. Furthermore, Fixed Wireless Access and satellite internet are increasingly viable broadband substitutes, especially in less-served areas, with the global FWA market showing strong projected growth through 2025.
| Business Segment | Primary Substitutes | Key Data Point (2023-2025) | Impact on Cox |
|---|---|---|---|
| Media (Newspapers) | Digital News Platforms, Social Media | US Digital Ad Spending > $300 Billion (Mid-2024) | Erodes advertising revenue, challenges subscription models. |
| Automotive (Dealership Services) | Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Sales, Car Subscriptions | Car Subscription Market ~$7.62 Billion (2024) | Reduces manufacturer dependence on dealerships, shifts customer relationships. |
| Telecommunications (Cable TV) | Streaming Services (Netflix, Hulu) | >60 Million US Households Cord-Cutters (End of 2023) | Decreases subscriber numbers and video revenue. |
| Telecommunications (Broadband) | Fixed Wireless Access (FWA), Satellite Internet | FWA Market Projected Strong Growth through 2025 | Offers alternative connectivity, particularly in underserved areas. |
Entrants Threaten
The telecommunications sector demands immense upfront capital, especially for building out advanced infrastructure like fiber optic networks. This high cost of entry acts as a substantial deterrent for new companies looking to challenge established providers such as Cox Communications.
In 2024 alone, the U.S. saw fiber optic networks pass 10.3 million new homes, a testament to the significant investments being made. This expansion, fueled by both private and public funding, underscores the sheer financial commitment required to even begin competing in this space.
The automotive service sector benefits from a deeply entrenched ecosystem, making it challenging for newcomers to break in. Cox Automotive, for instance, has spent years cultivating strong relationships with dealerships and manufacturers, a trust that’s difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate.
Developing the kind of comprehensive, integrated service offerings that Cox Automotive provides, which span everything from inventory management to vehicle remarketing, demands substantial investment and time. This existing infrastructure and network effect create a significant hurdle for any new player looking to enter the market.
Both the telecommunications and automotive sectors, where Cox Enterprises operates, are burdened by significant regulatory frameworks. These include stringent licensing, evolving compliance standards, and growing data privacy mandates.
These substantial regulatory barriers and the associated compliance expenditures act as a deterrent for potential new entrants. For instance, in 2024 alone, U.S. wireless carriers incurred nearly $200 million in penalties due to data protection lapses, highlighting the financial risks involved.
Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
Cox Enterprises benefits from significant brand recognition and deeply ingrained customer loyalty, particularly in its broadband and automotive sectors. This established trust makes it challenging for new entrants to quickly capture market share, as customers often stick with familiar and reliable providers for essential services.
For instance, in the competitive broadband market, customer retention rates are a critical factor. While specific 2024 data for Cox's loyalty metrics isn't publicly available, industry trends indicate that switching costs and the perceived hassle of changing providers contribute to strong customer stickiness for established players. New entrants must overcome this inertia with compelling offers and superior service.
- Strong Brand Equity: Cox has cultivated a recognizable brand over decades, fostering consumer trust.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Existing loyalty initiatives encourage repeat business and discourage switching.
- High Switching Costs: For broadband, the effort and potential disruption involved in switching providers deter many customers.
- Perceived Reliability: Established providers are often seen as more reliable, a key factor for essential services.
Access to Proprietary Data and Technology
Cox Enterprises, especially via Cox Automotive, possesses a significant advantage with its extensive proprietary data and advanced technological infrastructure. This data, gathered from its vast network of operations, provides deep market insights and powers sophisticated solutions that are difficult for new competitors to replicate. For instance, Cox Automotive's platforms process billions of data points annually, enabling highly targeted marketing and operational efficiencies.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by the substantial investment required to build a comparable data and technology ecosystem. Newcomers would face considerable hurdles in acquiring the volume and quality of data Cox possesses, as well as in developing the analytical capabilities to leverage it effectively. This technological moat acts as a significant barrier, protecting Cox's market position.
- Proprietary Data: Cox Automotive manages vast datasets from its diverse businesses, including dealerships, auctions, and digital platforms.
- Technology Investment: Significant ongoing investment in data analytics, AI, and cloud infrastructure creates a high barrier.
- Market Insights: Proprietary data allows for granular market analysis and prediction, a capability difficult for new entrants to match quickly.
- Competitive Advantage: This data and technology fusion provides Cox with a distinct edge in developing innovative products and services.
The threat of new entrants for Cox Enterprises is generally low due to substantial capital requirements, particularly in telecommunications for infrastructure development. For example, the ongoing build-out of 5G networks demands billions in investment, a significant barrier for smaller players.
Furthermore, established brand loyalty and high customer switching costs, especially in broadband services, make it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. Cox Automotive also benefits from deep industry relationships and data insights that are time-consuming and expensive to replicate.
Regulatory hurdles and compliance costs, such as evolving data privacy laws, also add to the difficulty for new companies entering Cox's operating markets.
| Sector | Barrier Type | Example Data/Fact (2024/Latest Available) |
|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Capital Intensity | US broadband providers invested over $100 billion in network upgrades in 2024. |
| Automotive Services | Economies of Scale & Relationships | Cox Automotive processed over 10 million vehicle transactions in 2024. |
| Telecommunications | Regulatory Compliance | FCC fines for telecom compliance issues averaged $50,000 per violation in 2024. |
| All Sectors | Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | Customer retention in subscription-based services like broadband often exceeds 90% for established providers. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Cox Enterprises is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating insights from the company's annual reports, SEC filings, and investor relations materials. This primary data is supplemented by industry-specific market research reports from reputable firms and analyses from financial news outlets.
