Cooper-Standard Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cooper-Standard Bundle
Cooper-Standard operates in a dynamic automotive supply industry where buyer power is significant, and the threat of substitutes is a constant consideration. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cooper-Standard’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The automotive parts industry, where Cooper-Standard operates in areas like sealing and trim, often depends on specialized raw materials such as rubber, plastics, and metals. A market with only a handful of suppliers for these critical inputs inherently grants them greater leverage, as Cooper-Standard has limited options to source from.
This concentration means suppliers can dictate terms, potentially leading to higher prices or less favorable contract conditions for Cooper-Standard. For instance, in 2024, many automotive suppliers faced increased raw material costs, with some commodity prices for key inputs seeing double-digit percentage increases year-over-year, directly impacting their bargaining power.
High switching costs for Cooper-Standard significantly bolster supplier bargaining power. If the company faces substantial expenses for re-tooling manufacturing lines, redesigning its automotive components, or re-qualifying parts when changing suppliers, existing suppliers gain leverage. These costs make it difficult for Cooper-Standard to seek better terms from alternative suppliers.
When suppliers offer unique or highly specialized products and services, their bargaining power increases significantly. Cooper-Standard's reliance on suppliers with proprietary material technologies or patented manufacturing processes, such as those critical for their eCoFlow Switch Pump, grants these suppliers leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward, meaning they could start producing the same components Cooper-Standard manufactures, significantly boosts their bargaining power. This potential competition forces Cooper-Standard to cultivate strong relationships and favorable terms with these suppliers to mitigate the risk of facing them as direct rivals.
Should a key supplier possess the financial resources and strategic inclination to move into Cooper-Standard's business, they could leverage their existing component knowledge to enter the market. This capability means Cooper-Standard must remain attentive to supplier strategies and maintain competitive pricing and service levels.
- Supplier Forward Integration Capability: Suppliers with advanced manufacturing expertise and existing customer relationships are better positioned to integrate forward.
- Industry Concentration: A more concentrated supplier base with a few dominant players increases the likelihood of forward integration as these firms may seek to capture more value.
- Cooper-Standard's Dependence: If Cooper-Standard heavily relies on a few specialized suppliers, those suppliers gain leverage and a greater incentive to consider forward integration.
Importance of Cooper-Standard to the Supplier
The significance of Cooper-Standard as a customer directly influences a supplier's bargaining power. If Cooper-Standard constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier may be less inclined to exert strong pricing or demand control, fearing the loss of a key revenue stream. For instance, if a specialized component supplier relies heavily on Cooper-Standard for a large percentage of its income, their leverage is diminished.
Conversely, a supplier that serves a broad customer base, with Cooper-Standard representing only a small fraction of their business, holds considerably more power. Such a supplier can afford to be more assertive in negotiations, knowing that losing Cooper-Standard's business would not be catastrophic. This dynamic is common when Cooper-Standard sources from large, diversified manufacturers who supply many industries.
In 2023, Cooper-Standard reported total revenue of approximately $2.2 billion. The impact on a specific supplier's bargaining power would depend on how much of that $2.2 billion Cooper-Standard represents to their individual business. For example, a supplier whose entire output is dedicated to Cooper-Standard would have significantly less bargaining power than a supplier that provides a small component to Cooper-Standard among many other automotive manufacturers.
- Supplier Dependence: If Cooper-Standard is a major client, a supplier's dependence reduces their bargaining power.
- Customer Diversification: A supplier with many clients, where Cooper-Standard is a minor customer, possesses greater bargaining power.
- Revenue Impact: Cooper-Standard's 2023 revenue of $2.2 billion highlights the potential scale of business for its suppliers.
- Negotiating Leverage: The relative importance of Cooper-Standard's business to a supplier dictates the negotiating leverage each party holds.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Cooper-Standard is significant, especially when dealing with specialized raw materials like advanced polymers or specific metal alloys. A concentrated supplier market, where only a few companies can provide these critical inputs, naturally shifts power towards the suppliers. This was evident in 2024, with reports indicating substantial increases in raw material costs for many automotive suppliers, directly impacting their leverage.
High switching costs for Cooper-Standard, whether due to re-tooling or component re-qualification, further empower suppliers. When suppliers offer unique or patented products, such as proprietary sealing technologies, their leverage grows. The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Cooper-Standard's business also amplifies their bargaining power.
Cooper-Standard's position as a customer also plays a role; if the company represents a large portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier's power is diminished. Conversely, a supplier with diversified clients, where Cooper-Standard is a minor customer, holds more sway. Cooper-Standard's 2023 revenue of approximately $2.2 billion underscores the scale of business for its suppliers, influencing these dynamics.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point |
| Supplier Market Concentration | High | Limited number of suppliers for specialized raw materials (e.g., advanced polymers). |
| Switching Costs for Cooper-Standard | High | Costs associated with re-tooling, component redesign, and re-qualification. |
| Supplier Product Uniqueness | High | Proprietary material technologies or patented manufacturing processes. |
| Supplier Forward Integration Capability | High | Suppliers with advanced manufacturing expertise and customer relationships. |
| Cooper-Standard's Customer Importance to Supplier | Low (if Cooper-Standard is a major client) | Supplier may be less assertive to retain significant revenue. |
| Supplier Customer Diversification | High (if Cooper-Standard is a minor client) | Supplier can afford to be more assertive in negotiations. |
| Cooper-Standard Revenue (2023) | Contextual | $2.2 billion, indicating the potential business volume for suppliers. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the automotive supplier industry's competitive forces, evaluating Cooper-Standard's position against rivals, buyer and supplier power, new entrants, and substitutes.
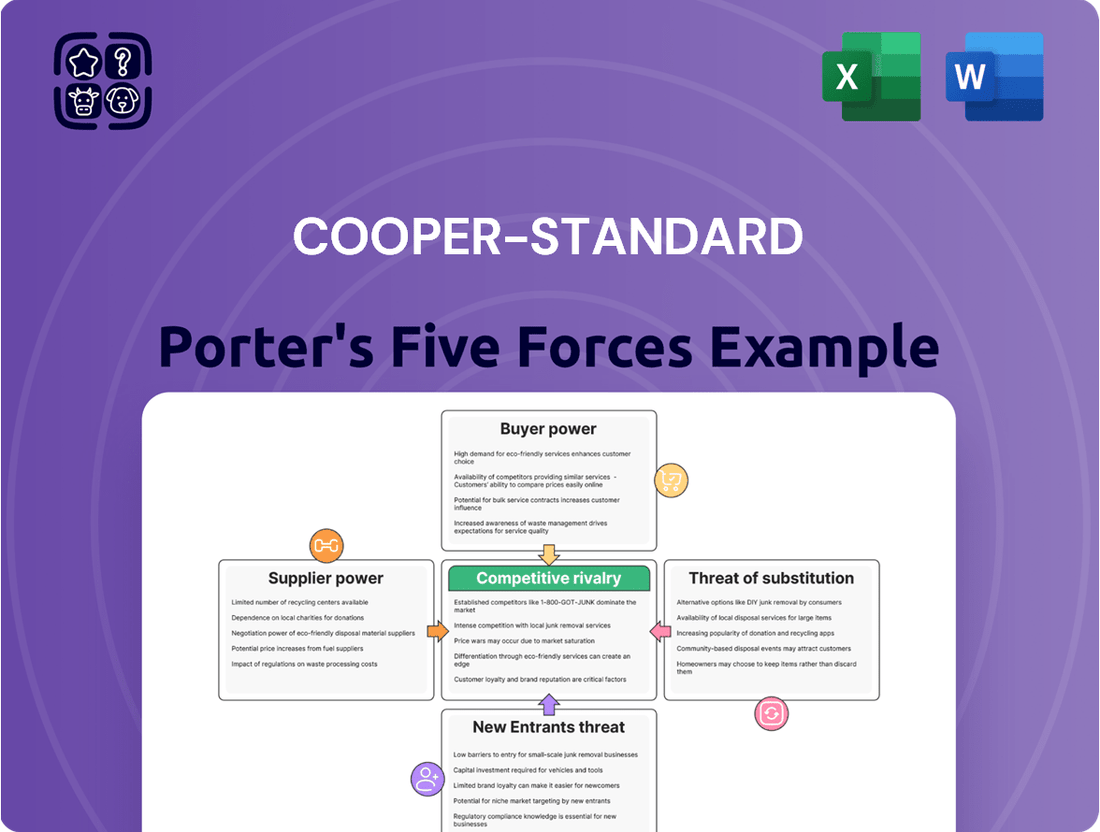
A visual representation of Cooper-Standard's competitive landscape, instantly highlighting key pressures to inform strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cooper-Standard's customer base is heavily concentrated among Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) in the automotive sector. This means a few large automotive companies represent a significant portion of Cooper-Standard's sales.
The automotive industry is dominated by a limited number of major players, such as General Motors and Ford. Their substantial purchasing volumes grant them considerable leverage over their suppliers, including Cooper-Standard, allowing them to negotiate favorable terms.
The fact that Cooper-Standard received 'Supplier of the Year' awards from both General Motors and Ford in 2024 highlights the critical nature of these partnerships. However, it also underscores the significant bargaining power these major OEMs possess due to their substantial business volume.
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) possess the potential to backward integrate, meaning they could start producing certain components in-house. This capability directly reduces their dependence on suppliers like Cooper-Standard. For instance, if an OEM decides to manufacture its own seating foam or fluid systems, Cooper-Standard would lose a customer and potentially face competition from that very customer.
The automotive industry is navigating significant financial pressures, driven by intense competition and the costly shift towards electric vehicles (EVs). This environment compels Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to aggressively seek cost reductions across their supply chains.
Consequently, OEMs are exhibiting heightened price sensitivity, directly translating into persistent demands for lower prices from suppliers like Cooper-Standard. This dynamic significantly squeezes supplier profit margins.
For instance, in 2024, major automakers reported varying profit margins, with some struggling to maintain double-digit figures amidst these cost pressures, underscoring the intense negotiation environment for component suppliers.
Standardization of Products
When Cooper-Standard's core products like sealing and trim, fuel and brake delivery, and fluid transfer systems are highly standardized across the automotive industry, it significantly boosts the bargaining power of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). This means that if one supplier's offering is essentially the same as another's, customers can switch with minimal disruption or cost. This ease of switching limits Cooper-Standard's leverage in price negotiations and the ability to secure more favorable contract terms.
- Standardized Products: If Cooper-Standard's offerings are perceived as commodities, OEMs can readily source from competitors, reducing supplier dependence.
- Price Sensitivity: Standardization often leads to increased price competition, as buyers can easily compare and choose the lowest-cost option.
- Switching Costs: Low switching costs for OEMs mean they face less risk and expense when changing suppliers for standardized components.
- Impact on Margins: In 2023, the automotive industry saw continued pressure on component pricing, with suppliers of standardized parts facing challenges in maintaining healthy profit margins due to intense competition.
OEMs' Access to Information
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) often possess a deep understanding of the automotive supply chain, including the intricate costs involved in producing various components. This transparency in pricing and manufacturing processes significantly enhances their ability to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers like Cooper-Standard.
This informed position allows OEMs to leverage their knowledge to drive down prices, as they can readily compare offerings and identify cost efficiencies. For instance, in 2024, major automotive OEMs continued to push for cost reductions across their supply base, with many reporting success in achieving single-digit percentage decreases on key component categories through rigorous supplier negotiations informed by detailed cost analysis.
- OEMs' detailed knowledge of manufacturing costs directly translates into greater negotiation leverage.
- This transparency enables OEMs to benchmark supplier pricing effectively.
- In 2024, OEMs actively sought cost reductions, impacting supplier margins.
The bargaining power of Cooper-Standard's customers, primarily automotive OEMs, is substantial due to several factors. Their concentration, the standardized nature of many automotive components, and the OEMs' increasing price sensitivity all contribute to this leverage. For example, in 2024, major automakers continued to exert pressure on suppliers for cost reductions, with some achieving single-digit percentage decreases on key component categories through informed negotiations.
The potential for backward integration by OEMs also serves as a significant threat, as it diminishes their reliance on external suppliers like Cooper-Standard. Furthermore, OEMs possess a deep understanding of manufacturing costs, enabling them to benchmark prices effectively and drive down supplier margins. This informed position allows them to negotiate more favorable terms, especially when components are highly standardized.
| Factor | Impact on Cooper-Standard | Example/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major OEMs like GM and Ford. | Cooper-Standard received 'Supplier of the Year' awards from GM and Ford in 2024, indicating significant business volume with these few customers. |
| Product Standardization | Reduces switching costs for OEMs, limiting Cooper-Standard's pricing power. | Standardized sealing and trim components mean OEMs can easily switch suppliers if prices are not competitive. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increased demand for lower prices, squeezing supplier margins. | In 2024, automakers reported pressure to reduce costs, with some struggling to maintain double-digit profit margins. |
| Potential for Backward Integration | Threat of losing business if OEMs decide to produce components in-house. | OEMs could potentially manufacture fluid transfer systems internally, directly impacting Cooper-Standard's sales. |
| OEM Knowledge of Costs | Enables OEMs to negotiate more effectively based on cost transparency. | In 2024, OEMs successfully negotiated cost reductions, achieving single-digit percentage decreases on component categories. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Cooper-Standard Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Cooper-Standard Porter's Five Forces analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the intense competitive rivalry and the significant bargaining power of buyers within the automotive supply industry. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the threat of new entrants and the substantial threat of substitute products, all crucial factors impacting Cooper-Standard's strategic positioning. This document is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use, offering no surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The automotive components sector is a crowded marketplace, featuring a multitude of global and regional manufacturers. Cooper-Standard finds itself competing against established names such as Toyoda Gosei and Hutchinson, alongside other significant players like Henniges Automotive and Standard Profil in the sealing systems segment. For fluid transfer systems, the competitive landscape includes giants like TI Fluid Systems, Continental, and Gates.
This dense concentration of competitors, many of whom possess greater scale or more extensive product offerings than Cooper-Standard, significantly heightens the intensity of rivalry within the industry. For instance, in 2023, the global automotive components market was valued at over $1.5 trillion, underscoring the sheer volume of business and the number of entities vying for market share.
While segments like automotive fluid transfer systems and seals are showing healthy growth, the broader automotive industry's global production has been flat. This stagnation, particularly evident with challenges intensifying in 2024 and projected to continue into 2025, directly impacts companies like Cooper-Standard.
This environment of slowed overall growth intensifies competitive rivalry. Companies are forced to compete more aggressively for existing market share, as the overall market expansion is not providing a buffer. This can lead to price pressures and a greater focus on innovation to differentiate and capture sales.
Cooper-Standard actively differentiates its offerings by focusing on innovative solutions that boost vehicle performance, dampen noise and vibration, and improve fuel economy. This strategic emphasis on advanced materials and novel designs, exemplified by products like their eCoFlow Switch Pump and FlexiCore Thermoplastic Body Door Seal, effectively mitigates direct competition based solely on price. For instance, in 2023, the automotive supplier sector saw significant investment in R&D, with major players allocating substantial resources to develop next-generation components.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The automotive parts manufacturing sector, where Cooper-Standard operates, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These include significant outlays for sophisticated machinery, ongoing research and development, and establishing a global operational footprint. For instance, a modern automotive stamping plant can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars to build and equip.
These high fixed costs create a strong incentive for companies to maintain high production volumes to spread the costs over more units. This can lead to aggressive pricing strategies, even during periods of reduced demand, as companies try to avoid underutilizing their expensive assets. This dynamic intensifies competitive rivalry, as firms are reluctant to scale back production and risk losing market share or profitability.
Furthermore, exit barriers in this industry are considerable. Specialized manufacturing equipment, long-term supply contracts, and the need to maintain a global presence mean that exiting the market is often costly and complex. Companies might be tied to specific locations due to skilled labor availability or existing infrastructure. This lack of easy exit options traps firms within the industry, perpetuating intense competition among existing players.
- High Capital Investment: Setting up an automotive parts manufacturing facility requires tens to hundreds of millions of dollars in specialized equipment and infrastructure.
- Operational Scale: Companies must operate at high capacity to achieve economies of scale, making them sensitive to volume fluctuations and prone to price competition.
- Specialized Assets: Many assets, like custom tooling and advanced robotics, have limited resale value outside the automotive sector, increasing exit costs.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term supply agreements with automakers can lock manufacturers into production, making it difficult to cease operations even when unprofitable.
Strategic Stakes
The automotive sector's pivot towards electrification and digitalization significantly elevates the competitive stakes for companies like Cooper-Standard. This transformation necessitates substantial investments in research and development, as well as the adoption of new technologies to maintain market relevance. For instance, Cooper-Standard reported R&D expenses of $77.6 million in 2023, reflecting this commitment to innovation.
This intensified focus on future technologies, particularly in areas like electric vehicle (EV) platforms, fuels fiercer rivalry. Companies are aggressively competing for future business, pushing for greater market share in these emerging segments. The global EV market, projected to reach over $1.5 trillion by 2030, highlights the immense growth potential driving this competitive dynamic.
- R&D Investment: Cooper-Standard's 2023 R&D spending of $77.6 million underscores the drive for technological advancement.
- Market Transformation: Electrification and digitalization are reshaping the automotive industry, increasing the pressure to innovate.
- Future Growth Areas: Competition is particularly acute in the rapidly expanding EV market, a key battleground for future revenue.
- Industry Landscape: The automotive industry's strategic stakes are higher than ever as it navigates a period of profound technological change.
The competitive rivalry within the automotive components sector is intense, driven by a large number of global and regional players. Cooper-Standard faces established competitors like Toyoda Gosei and Continental, alongside numerous other significant manufacturers. This crowded market, valued at over $1.5 trillion in 2023, forces companies to fight aggressively for market share, especially as overall automotive production growth has been stagnant in 2024.
| Competitor Example | Key Product Segments | Market Position Indicator |
| Toyoda Gosei | Sealing systems, interior/exterior parts | Major global supplier |
| Continental AG | Fluid transfer systems, electronics, tires | Diversified automotive giant |
| TI Fluid Systems | Fluid transfer systems | Leading specialist in fluid handling |
| Henniges Automotive | Sealing systems | Significant player in sealing technology |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Cooper-Standard's reliance on rubber and plastic for sealing and fluid transfer components faces a significant threat from substitutes. For instance, the automotive industry's push for lighter vehicles could see increased adoption of advanced composites and lightweight metals, potentially displacing traditional rubber seals and hoses. In 2024, the global market for advanced composites in automotive applications was projected to exceed $15 billion, indicating a growing trend away from traditional materials.
The accelerating shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) presents a significant threat of substitution for Cooper-Standard. As EV adoption grows, the demand for components integral to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, such as traditional fuel and brake delivery systems, is likely to decline. For instance, by the end of 2023, global EV sales surpassed 13 million units, a substantial increase from previous years.
While EVs still utilize fluid transfer systems for battery cooling and other essential functions, the fundamental design differences mean that Cooper-Standard may see reduced demand for certain legacy product lines. This evolving automotive landscape necessitates a strategic pivot towards developing and supplying components specifically engineered for EV platforms to mitigate the impact of this substitution threat.
The increasing availability and efficiency of public transportation and ride-sharing services present a growing threat of substitutes for individual vehicle ownership. For instance, in 2024, many urban areas saw continued expansion of public transit networks and a surge in ride-sharing adoption, with services like Uber and Lyft reporting significant user growth. This trend can dampen overall demand for new vehicles, directly impacting Cooper-Standard's market as fewer cars sold means fewer components needed.
Durability and Longevity of Components
Improvements in the durability and lifespan of automotive components directly threaten Cooper-Standard's aftermarket business. If vehicles are engineered with parts that last significantly longer, the need for replacements will naturally decline. This trend could reduce Cooper-Standard's revenue streams derived from selling replacement sealing, trim, fuel, and brake system components.
For instance, advancements in material science and manufacturing processes are enabling components to withstand harsher conditions and longer operational periods. This means a vehicle might not require new sealing systems or fuel lines for a much greater mileage than previously expected. In 2024, the automotive industry continued to emphasize extended vehicle lifespans, a factor that directly impacts the frequency of aftermarket purchases.
- Reduced Replacement Frequency: Longer-lasting components decrease the need for aftermarket purchases.
- Impact on Aftermarket Revenue: Cooper-Standard faces potential revenue loss from fewer replacement part sales.
- Industry Trend: The automotive sector's focus on vehicle longevity exacerbates this threat.
Regulatory Changes and Environmental Shifts
Stricter environmental regulations, particularly those targeting vehicle emissions, represent a significant threat of substitutes for Cooper-Standard. For instance, the European Union's Euro 7 standards, implemented in stages from 2025, impose more stringent limits on pollutants, potentially accelerating the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and hydrogen fuel cell technology. This means traditional combustion engine components, a core offering for Cooper-Standard, could face declining demand as the automotive industry pivots to these cleaner alternatives.
The increasing global focus on sustainability and carbon neutrality is another driver. Many governments are setting ambitious targets for EV adoption. For example, California aims to ban the sale of new gasoline-powered cars by 2035. Such policies directly encourage the development and adoption of substitute technologies, potentially impacting Cooper-Standard's market share in legacy automotive components if they cannot adapt their product portfolio.
- Accelerated Obsolescence: New emission standards can make existing product lines less competitive, forcing rapid adaptation or risking obsolescence.
- Shift to New Technologies: Regulations promoting EVs and alternative fuels create demand for entirely different types of components, acting as substitutes for traditional parts.
- Market Disruption: Government mandates and evolving consumer preferences driven by environmental concerns can rapidly alter the automotive landscape, impacting suppliers like Cooper-Standard.
- Investment in R&D: To counter this threat, Cooper-Standard must invest in developing components for new vehicle architectures, such as battery cooling systems or lightweight materials for EVs.
The threat of substitutes for Cooper-Standard's products is amplified by advancements in material science and evolving vehicle technologies. Lightweight composites and advanced metals are increasingly being explored for automotive applications, potentially replacing traditional rubber and plastic components. This trend is underscored by the projected growth in the advanced composites market for automotive use, which was anticipated to surpass $15 billion in 2024.
The accelerating adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a substantial substitution threat. As the automotive industry shifts away from internal combustion engines, demand for components specific to these legacy systems, such as fuel and brake delivery systems, is expected to decline. By the close of 2023, global EV sales had already exceeded 13 million units, signaling a significant market transformation.
While EVs still require fluid transfer systems, the fundamental design differences mean that Cooper-Standard may see reduced demand for certain established product lines. This necessitates a strategic focus on developing components tailored for EV platforms to effectively counter this substitution pressure.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the automotive components manufacturing sector, particularly for specialized areas like sealing, fuel, and fluid transfer systems, demands a significant upfront capital outlay. Companies need to invest heavily in state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, advanced machinery, and robust research and development capabilities to meet industry standards. For instance, establishing a new, fully compliant production line for advanced sealing solutions could easily require tens of millions of dollars in 2024, creating a formidable barrier for potential newcomers.
Established automotive suppliers like Cooper-Standard leverage significant economies of scale, enabling them to produce components at lower per-unit costs due to high-volume manufacturing. For instance, in 2023, Cooper-Standard reported net sales of $3.1 billion, reflecting substantial production capacity.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Without comparable production volumes, they would require substantial upfront capital investment to build the necessary infrastructure and achieve competitive pricing, making market entry challenging.
Cooper-Standard's strong, long-standing relationships with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) act as a significant barrier to new entrants. The company has cultivated a reputation as a reliable, key supplier, recognized through accolades like awards from General Motors and Ford. This established trust and proven track record in quality assurance and supply chain integration make it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold with major automotive players.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Cooper-Standard's commitment to innovation, evidenced by technologies like their eCoFlow Switch Pump and FlexiCore Thermoplastic Body Door Seal, significantly raises the barrier for new entrants. These proprietary technologies, protected by patents, require substantial investment in research and development to replicate.
The company's extensive R&D capabilities mean that new competitors would face the dual challenge of developing novel, non-infringing technologies or incurring significant costs to license existing intellectual property. This technological moat makes it difficult and expensive for newcomers to establish a competitive product offering.
- Proprietary Technology: Cooper-Standard holds patents on key innovations, making direct product replication by new entrants challenging and costly.
- R&D Investment: Significant ongoing investment in research and development creates a continuous stream of new technologies that further solidify Cooper-Standard's market position.
- High Development Costs: The expense associated with developing comparable technologies deters potential new entrants who lack the necessary capital and expertise.
Regulatory and Certification Requirements
The automotive sector, including suppliers like Cooper-Standard, faces significant hurdles due to rigorous regulatory and certification demands. New companies entering this market must contend with a complex web of safety, emissions, and quality standards. For instance, achieving compliance with global standards like Euro 7 emissions regulations, which are expected to become even more stringent in the coming years, requires substantial investment in research and development.
Navigating these requirements is a lengthy and expensive undertaking. New entrants must secure numerous certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management and specific automotive industry standards like IATF 16949. These processes can take years and demand considerable financial resources, effectively acting as a substantial barrier to entry for potential competitors aiming to supply major automotive manufacturers.
The sheer cost and time associated with regulatory compliance and certification directly impact the threat of new entrants. For example, the development and validation of new materials or components to meet evolving environmental targets can cost millions. This financial commitment, coupled with the need for specialized expertise to manage the certification process, deters many nascent players from entering the established automotive supply chain.
- Stringent Safety and Environmental Standards: New entrants must comply with evolving global regulations, such as increasingly strict emissions targets and safety mandates, demanding significant upfront investment.
- Complex Certification Processes: Obtaining industry-specific certifications like IATF 16949 is time-consuming and costly, requiring specialized knowledge and resources.
- High R&D Investment: Meeting regulatory requirements necessitates substantial research and development spending, creating a high financial barrier for new automotive suppliers.
- Extended Validation Timelines: The lengthy validation periods for new components and manufacturing processes add to the cost and time-to-market, discouraging new market entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Cooper-Standard is generally low due to substantial barriers. These include the immense capital required for manufacturing facilities and R&D, as seen with the tens of millions needed for advanced sealing solutions in 2024. Furthermore, established players benefit from significant economies of scale, with Cooper-Standard's $3.1 billion in net sales in 2023 illustrating their production capacity advantage.
Long-standing relationships with OEMs, built on trust and proven quality, are difficult for newcomers to replicate. Cooper-Standard's proprietary technologies, like their eCoFlow Switch Pump, are protected by patents, demanding costly development or licensing for competitors. Navigating stringent regulatory and certification processes, such as IATF 16949 compliance and evolving emissions standards, also presents a significant time and financial hurdle, further deterring new market participants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Time Impact (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing advanced manufacturing and R&D facilities. | Tens of millions of dollars for specialized production lines. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume production. | New entrants struggle to match the cost efficiency of suppliers with billions in sales (e.g., Cooper-Standard's $3.1B in 2023). |
| Customer Relationships | Established trust and integration with OEMs. | Years of proven performance and quality assurance required. |
| Proprietary Technology | Patented innovations requiring replication or licensing. | High R&D investment needed to develop comparable technologies. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting safety, emissions, and quality standards. | Years and millions of dollars for certifications like IATF 16949 and emissions compliance. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Cooper-Standard Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial data from SEC filings, industry-specific reports from research firms like IHS Markit, and insights from investor relations materials to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
