Cooper Companies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cooper Companies Bundle
The Cooper Companies operates in a dynamic healthcare landscape, facing moderate competitive rivalry and significant bargaining power from buyers due to industry consolidation. Understanding these pressures is crucial for strategic planning.
The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles, but the potential for substitutes in certain product lines warrants attention. Supplier power remains a key factor influencing Cooper's cost structure.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Cooper Companies’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The medical device sector, where Cooper Companies operates with its contact lens and women's health divisions, often faces a concentrated supplier base for specialized components. For instance, advanced polymers or unique manufacturing equipment might be sourced from only a handful of global providers.
This limited supplier pool grants them significant leverage. If Cooper Companies relies on a few key suppliers for critical materials, these suppliers can dictate terms, potentially increasing input costs for Cooper. In 2023, the medical device industry saw raw material costs rise, with some specialized polymers experiencing price hikes of 5-10% due to supply chain constraints, directly impacting manufacturers like Cooper.
Suppliers of unique or proprietary inputs, such as advanced silicone hydrogel materials for CooperCompanies' contact lenses or specialized components for their fertility solutions, hold significant bargaining power. The difficulty and cost associated with switching to alternative suppliers for these critical, innovative materials directly empower these suppliers.
For Cooper Companies, the bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by switching costs. These costs can include expenses related to retooling manufacturing processes to accommodate new components, the rigorous process of requalifying new materials to meet stringent quality and safety standards, and navigating complex regulatory approvals for any changes in supplied parts. These hurdles make it expensive and time-consuming for Cooper to change suppliers.
High switching costs directly empower existing suppliers. Cooper Companies would face substantial disruption and considerable expense if they decided to transition to new suppliers, especially for critical components. This financial and operational risk associated with changing suppliers effectively strengthens the leverage of their current supply base.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Cooper Companies' markets, such as manufacturing finished contact lenses or women's health devices, significantly amplifies their bargaining power. This potential competition forces Cooper to negotiate from a weaker position, potentially accepting less favorable terms to mitigate the risk of facing a former supplier as a direct competitor.
For instance, a key raw material supplier for Cooper's contact lens division could, in theory, leverage its manufacturing expertise and existing supply chain to produce its own branded lenses. This would directly challenge Cooper's market share and pricing power. In 2024, the global contact lens market was valued at approximately $11.5 billion, with significant growth potential, making it an attractive area for potential forward integration by suppliers if they possess the necessary capital and technical know-how.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers must possess the financial resources, technical expertise, and market knowledge to successfully enter Cooper's finished product markets.
- Incentive to Integrate: High profit margins or a desire to capture more value in the supply chain can drive suppliers to consider forward integration.
- Market Dynamics: The attractiveness of Cooper's end markets, such as the growing women's health sector which saw global revenues exceed $100 billion in 2023, can increase the incentive for suppliers to integrate forward.
- Competitive Landscape: If Cooper's markets are highly competitive, suppliers might see an opportunity to enter with a differentiated offering or by leveraging cost advantages.
Portion of Supplier's Sales to Cooper Companies
The bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by how much of their sales revenue comes from Cooper Companies. If Cooper represents a small fraction of a supplier's business, that supplier has less incentive to offer favorable terms, as they are not heavily reliant on Cooper's patronage. This independence allows suppliers to exert more influence over pricing and contract conditions.
Conversely, if Cooper Companies is a significant customer for a supplier, the supplier is more likely to be accommodating. A substantial portion of a supplier's revenue tied to Cooper means they have a vested interest in maintaining that relationship. This can lead to suppliers being more willing to negotiate on price, delivery schedules, and other terms to secure Cooper's continued business.
- Supplier Dependence: If Cooper Companies constitutes a minor part of a supplier's overall sales, the supplier holds greater leverage.
- Customer Concentration: Conversely, if Cooper is a primary customer, suppliers are incentivized to offer competitive terms to retain their business.
- Impact on Cooper: This dynamic can affect Cooper's input costs and supply chain stability, depending on the concentration of its supplier base.
Suppliers of specialized materials, like advanced polymers for contact lenses, possess significant bargaining power due to limited alternatives and high switching costs for Cooper Companies. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that specialized silicone hydrogel materials, crucial for advanced contact lenses, saw price increases of up to 8% due to production complexities and limited global manufacturers.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, particularly in the lucrative contact lens market valued at approximately $11.5 billion in 2024, also bolsters their negotiating position. This potential competition forces Cooper to accept less favorable terms to maintain supply chain stability.
The bargaining power of suppliers is directly correlated with Cooper Companies' importance to their revenue streams. If Cooper represents a small portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier has less incentive to offer competitive pricing, thereby increasing Cooper's input costs.
| Factor | Impact on Cooper Companies | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for few suppliers | Limited number of global producers for advanced lens polymers |
| Switching Costs | High costs to change suppliers (retooling, requalification) | Regulatory approval timelines can extend up to 12 months for new material suppliers |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers may enter Cooper's markets | Global women's health market exceeded $100 billion in 2023, attracting potential new entrants |
| Customer Dependence | Supplier dependence on Cooper influences negotiation | If Cooper is a minor customer, supplier offers less favorable terms |
What is included in the product
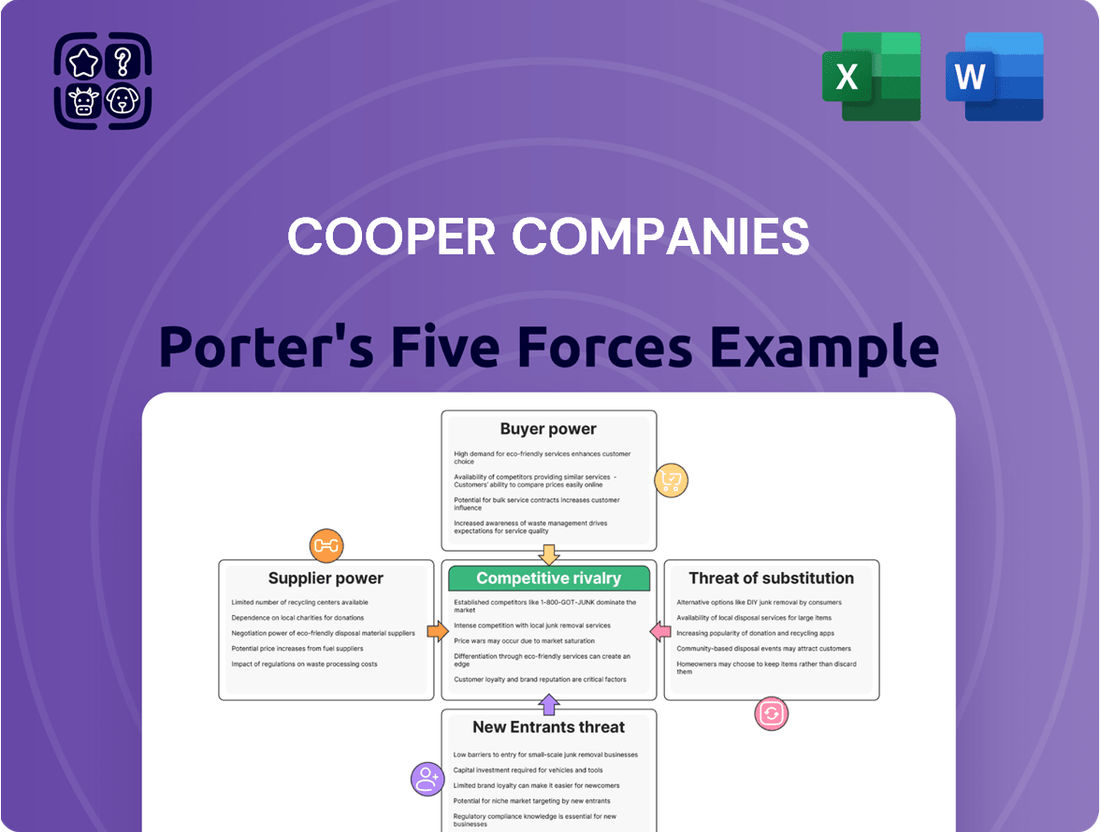
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Cooper Companies, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its markets.
Quickly assess competitive intensity with a pre-built Porter's Five Forces model, simplifying strategic planning for The Cooper Companies.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers for Cooper Companies is influenced by customer concentration, especially within its specialized medical device segments. For instance, CooperVision's customer base might include major optical retail chains and large distributors, giving them significant leverage in price negotiations. Similarly, CooperSurgical's key customers, such as large hospital networks and prominent fertility clinics, possess substantial purchasing power that can impact pricing strategies.
Customers wield significant bargaining power when a wide array of substitute products are readily available, offering comparable value. For Cooper Companies, particularly its CooperVision segment, this translates to customers having numerous contact lens brands from competitors, as well as alternatives like eyeglasses and even refractive surgeries such as LASIK. This abundance of choices directly impacts CooperVision's ability to dictate pricing and terms.
Similarly, the CooperSurgical division faces customer bargaining power stemming from the availability of alternative medical devices and fertility treatments from other manufacturers. For instance, if a hospital or clinic can easily source comparable surgical instruments or fertility drugs from a competitor at a lower price or with better service, their leverage over CooperSurgical increases. This competitive landscape, where substitutes are plentiful, forces CooperCompanies to remain competitive on both price and product innovation.
Customer price sensitivity for Cooper Companies can be quite high, especially when their products represent a substantial part of a buyer's budget or when the offerings are largely undifferentiated. For instance, if a particular medical device or diagnostic tool is a significant expense for a hospital, they will naturally scrutinize its price more closely.
In the healthcare sector, the influence of reimbursement policies and insurance coverage significantly shapes the price sensitivity of both individual patients and institutional purchasers like hospitals. These external financial structures can dictate how much end-users or buyers are willing or able to pay for Cooper's medical products and services.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers of Cooper Companies, particularly large healthcare systems or distributors, possess some bargaining power if they consider backward integration. This means they might explore producing their own medical devices or private-label alternatives to Cooper's offerings. While full-scale backward integration into complex areas like contact lens manufacturing is rare due to high R&D and regulatory hurdles, the threat of insourcing or developing private brands can indeed pressure Cooper. For example, a major hospital network might negotiate for lower prices on Cooper's diagnostic products if they perceive a viable alternative through private labeling, thereby increasing their leverage.
The potential for backward integration by customers, while not a dominant threat across all of Cooper Companies' segments, is a factor to monitor. In the contact lens market, for instance, while manufacturing is complex, large optical retailers could potentially invest in private-label production if the economics become compelling enough. Similarly, for fertility solutions, a large fertility clinic network might explore partnerships or in-house development for certain consumables, impacting Cooper's pricing power. The overall healthcare landscape in 2024 saw continued consolidation among providers, potentially amplifying the bargaining power of these larger entities.
- Backward integration by customers is less common in highly specialized and regulated sectors like contact lenses and fertility solutions.
- Large healthcare providers or retail chains may explore private-labeling or insourcing to increase their bargaining power.
- The threat of customers producing their own medical devices can pressure Cooper Companies on pricing and terms.
- Consolidation in the healthcare sector in 2024 may lead to larger customer entities with greater leverage.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers armed with detailed information about pricing, quality, and rival products wield significant influence. This is particularly evident in the medical device sector, where greater transparency, often facilitated by online platforms and comparative analyses, allows customers to secure more favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, the proliferation of health tech platforms offering direct patient-to-provider cost comparisons for common procedures has intensified this trend.
- Increased Information Access: Digital platforms and online reviews provide customers with unprecedented access to product details and pricing.
- Transparency in Medical Devices: The medical device market is experiencing a rise in transparency, empowering buyers.
- Negotiating Power: Informed customers are better positioned to negotiate prices and terms with suppliers like CooperCompanies.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Customers can easily compare offerings, forcing suppliers to remain competitive on both price and quality.
The bargaining power of customers for Cooper Companies is moderate, influenced by customer concentration and the availability of substitutes. Large hospital networks and distributors, key customers for CooperSurgical and CooperVision respectively, have significant leverage due to substantial purchasing volumes. In 2024, the healthcare sector saw continued consolidation, potentially amplifying the power of these larger entities. For instance, a major hospital group might negotiate harder on pricing for Cooper's diagnostic tools if they can source comparable items elsewhere, or even consider private-labeling.
| Customer Segment | Key Products | Customer Leverage Factors | 2024 Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital Networks | Surgical instruments, diagnostic tools | High volume purchasing, potential for private-labeling | Increased consolidation leading to greater leverage |
| Optical Retail Chains/Distributors | Contact lenses | Brand choice, price sensitivity, potential for private-labeling | Continued competition can empower large buyers |
| Fertility Clinics | Fertility solutions, consumables | Specialized needs, but alternatives exist | Partnership opportunities could shift leverage |
Same Document Delivered
Cooper Companies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of The Cooper Companies, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning. You're looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The contact lens market is dominated by a few major global players, including Johnson & Johnson Vision, Alcon, and Bausch + Lomb, alongside CooperVision. This concentration means CooperVision, despite its significant market share, faces intense rivalry from these well-established giants.
In the women's health and fertility sector, CooperSurgical also encounters established competitors, further intensifying the competitive landscape across Cooper Companies' key business segments.
The Cooper Companies operates in markets with robust growth. Both the contact lens and women's health device sectors are expanding steadily, which can temper intense rivalry. For instance, the global contact lens market is anticipated to see a compound annual growth rate of approximately 5-6% between 2025 and 2035, fueled by rising vision issues and a preference for daily disposable lenses.
Furthermore, the women's health devices market is projected for significant expansion, with an estimated CAGR of 9.8% from 2024 to 2029. While this overall growth is positive, it doesn't eliminate competition; companies still vie fiercely for market share within these expanding segments.
Cooper Companies actively differentiates its offerings, particularly within CooperVision with innovative silicone hydrogel contact lenses like MyDay and clariti, and in CooperSurgical through specialized fertility solutions. This focus on unique features, such as enhanced comfort, extended wear capabilities, and therapeutic benefits like myopia management with MiSight, effectively mitigates direct price-based competition and lowers the intensity of rivalry among market players.
Switching Costs for Customers
For Cooper Companies, switching costs for customers in the contact lens segment are a significant factor. These costs can include the necessity of new eye examinations, obtaining trial lenses to ensure comfort and proper fit, and the adjustment period required to adapt to the feel of a different lens material or design. These hurdles make it less likely for consumers to frequently switch between brands, thereby dampening direct competitive rivalry.
In the women's health devices sector, switching costs can be more substantial. Implementing new equipment often necessitates retraining medical staff, which incurs time and financial investment. Furthermore, integrating new devices into existing clinical workflows and ensuring compatibility with current systems can present considerable challenges for healthcare providers. This complexity further reinforces customer loyalty and reduces the intensity of competitive pressures.
- Contact Lens Switching Costs: Eye exams, trial lenses, adaptation to new lens feel.
- Women's Health Device Switching Costs: Staff retraining, equipment integration, workflow adjustments.
- Impact on Rivalry: Higher switching costs generally decrease competitive rivalry by increasing customer inertia.
Exit Barriers
Cooper Companies, like many in the medical device sector, faces substantial exit barriers. These barriers can trap companies in the market, even when profitability is low, thereby intensifying competition. For instance, specialized manufacturing equipment and dedicated research and development facilities represent significant sunk costs that are difficult to recover.
These high exit barriers mean that companies are less likely to simply shut down operations. Instead, they may continue to compete, potentially driving down prices or innovating aggressively to survive. This can lead to prolonged periods of intense rivalry.
- Specialized Assets: Medical device manufacturers often invest in highly specific, often proprietary, machinery and production lines. For example, a facility designed for producing a particular type of implantable device cannot easily be repurposed for other manufacturing.
- Employee Severance and Retraining: The highly skilled workforce in this industry, including engineers and specialized technicians, often comes with significant severance packages or retraining costs if operations are ceased, adding to the financial disincentive to exit.
- Long-Term Contracts: Cooper Companies may be bound by long-term supply agreements with hospitals or distributors, making an abrupt exit financially punitive.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for Cooper Companies, operating in both the contact lens and women's health markets. These sectors are characterized by a few dominant global players, including Johnson & Johnson Vision, Alcon, and Bausch + Lomb, alongside CooperVision, creating an intensely competitive environment. While market growth offers some buffer, companies like Cooper Companies must continuously innovate and differentiate to capture market share, as evidenced by their focus on advanced materials and specialized product lines.
| Market Segment | Key Competitors | Cooper Companies' Strategy | Competitive Intensity Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Lenses | Johnson & Johnson Vision, Alcon, Bausch + Lomb | Product innovation (e.g., silicone hydrogel, myopia management lenses like MiSight) | High, due to established brands and similar product offerings |
| Women's Health Devices | Various specialized medical device companies | Specialized fertility solutions, advanced diagnostic tools | Moderate to High, depending on the niche |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For CooperVision's contact lenses, the primary substitutes are eyeglasses and laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) surgery. Eyeglasses continue to be a widely accessible and cost-effective option, appealing to a broad consumer base. In 2024, the global eyeglasses market was valued at approximately $150 billion, demonstrating their enduring market presence.
LASIK surgery presents a compelling alternative by offering a permanent solution to vision correction, thereby diminishing the ongoing need for contact lenses. Advancements in LASIK technology are enhancing its appeal, with improved precision and faster recovery times making it a more attractive option for consumers seeking long-term vision improvement.
The price-performance trade-off of substitutes is a key factor in assessing their threat to Cooper Companies' contact lens business. While contact lenses provide significant convenience and aesthetic benefits, traditional eyeglasses often present a more budget-friendly option for vision correction. For instance, a year's supply of daily disposable contact lenses can cost upwards of $500, whereas a pair of prescription eyeglasses might range from $100 to $300, offering a clear price advantage.
Furthermore, surgical vision correction procedures like LASIK represent another substitute. Although LASIK involves a substantial upfront investment, potentially ranging from $2,000 to $5,000 per eye, it eliminates the recurring costs associated with contact lens purchases and solutions. This long-term cost-saving potential can make LASIK an attractive alternative for consumers seeking a permanent solution, despite its initial higher price tag.
The perceived value and overall cost-effectiveness of these substitutes directly influence consumer decisions. As of 2024, the global eyeglasses market is projected to reach over $150 billion, underscoring the significant consumer base that prioritizes affordability. Conversely, the contact lens market, while substantial, faces constant pressure from these more economical or permanently cost-saving alternatives.
Customer propensity to substitute for CooperCompanies' contact lens products is shaped by how aware consumers are of alternatives, how easy those alternatives are to access, and what risks they perceive. For instance, some individuals prioritize the convenience of daily disposable lenses, while others might lean towards permanent solutions like LASIK surgery to bypass the daily routine of lens care and the risk of eye infections.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are significantly shaping the threat of substitutes for CooperCompanies' contact lens business. Smart glasses, for instance, are becoming more sophisticated, offering augmented reality features that could reduce the need for vision correction in certain contexts. Similarly, advancements in LASIK surgery, such as the increasing adoption of robotic laser-guided technology, are making vision correction procedures more appealing and effective for consumers seeking a permanent solution to refractive errors.
These innovations directly challenge the market share of contact lenses by offering alternative ways to achieve clear vision. For example, the global refractive surgery market was valued at approximately $4.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a rising consumer interest in alternatives to traditional vision correction methods like contact lenses and eyeglasses.
- Smart Glasses: Evolving capabilities could offer integrated vision correction and digital information, presenting a novel substitute.
- LASIK and PRK: Continued improvements in laser technology and surgical outcomes make these permanent vision correction options increasingly attractive.
- Eyeglass Technology: Innovations in lens materials and frame design offer enhanced comfort and functionality, appealing to a segment of the vision correction market.
Regulation and Reimbursement of Substitutes
Changes in healthcare regulations and reimbursement policies significantly influence the appeal of substitute products for Cooper Companies' offerings, particularly in the vision care segment. For instance, shifts in insurance coverage or government-sponsored healthcare programs can make procedures like LASIK surgery more financially accessible, thereby increasing its attractiveness as an alternative to contact lenses.
In 2024, the landscape of medical device reimbursement continues to evolve. For CooperCompanies, a key consideration is how changes in Medicare and private payer policies might affect the adoption rates of vision correction alternatives. For example, if reimbursement for refractive surgeries improves, it could draw more patients away from traditional contact lens wear. Conversely, tighter controls on reimbursement for certain procedures could bolster the demand for contact lenses.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Increased regulatory oversight on vision correction procedures can either elevate or diminish their standing as substitutes.
- Reimbursement Trends: Favorable reimbursement for surgical alternatives directly competes with the recurring revenue from contact lens sales.
- Policy Impact: For example, a hypothetical increase in insurance coverage for LASIK by 10% in 2024 could shift a noticeable percentage of the contact lens market.
The threat of substitutes for CooperCompanies' contact lens business is moderate, primarily stemming from eyeglasses and refractive surgery like LASIK. Eyeglasses remain a strong competitor due to their affordability and accessibility, with the global market valued at approximately $150 billion in 2024. While contact lenses offer convenience, the upfront cost of eyeglasses, typically $100-$300, presents a significant price advantage over a year's supply of daily disposables which can exceed $500.
Refractive surgeries, though carrying a higher initial cost ($2,000-$5,000 per eye for LASIK), eliminate recurring expenses associated with contact lenses. This long-term cost-saving potential, coupled with technological advancements improving surgical outcomes and recovery times, makes them an increasingly appealing alternative. The global refractive surgery market, valued at around $4.5 billion in 2023, signals growing consumer interest in these permanent solutions.
| Substitute Type | Estimated Cost (Annual) | Key Advantage | Market Data (2024) |
| Daily Disposable Contact Lenses | $500+ | Convenience, Discretion | Significant portion of vision correction market |
| Prescription Eyeglasses | $100 - $300 | Affordability, Accessibility | Global market valued at ~$150 billion |
| LASIK Surgery | $4,000 - $10,000 (one-time) | Permanent Correction, No recurring costs | Global market valued at ~$4.5 billion (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The medical device sector, where CooperCompanies operates with contact lenses and women's health products, presents a formidable barrier to entry due to exceptionally high capital requirements. Companies looking to establish a foothold need to allocate significant funds towards cutting-edge research and development, building state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, and navigating the complex and costly regulatory approval processes mandated by bodies like the FDA. For instance, the development and launch of a new medical device can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars, making it a daunting prospect for smaller players or those without substantial backing.
The medical device sector, where Cooper Companies operates, faces formidable barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory oversight. Navigating complex approval pathways like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) demands substantial investment in time and resources.
These rigorous processes, designed to ensure patient safety and product efficacy, represent a significant hurdle for potential new competitors. For instance, the cost of obtaining FDA clearance can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the device's complexity and risk classification.
Furthermore, compliance with evolving global safety standards and the need for extensive clinical data create a high cost of entry. This regulatory landscape effectively deters many smaller or less-capitalized firms from entering the market, thereby protecting established players like Cooper Companies.
Established brand loyalty and extensive distribution channels present a significant barrier for new entrants. Cooper Companies, for instance, has cultivated strong relationships with healthcare professionals and boasts a global reach, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. In 2023, CooperCompanies reported net sales of $3.2 billion, reflecting the scale of their established market presence.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Cooper Companies' strong portfolio of proprietary technology and patents significantly raises the barrier to entry for new competitors in both the contact lens and women's health markets. For instance, their advancements in silicone hydrogel materials and innovative myopia management solutions are protected, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate their product performance and market appeal without substantial R&D investment and legal hurdles. This intellectual property acts as a powerful deterrent, safeguarding their market share and profitability.
- Proprietary Technology: CooperCompanies holds patents on key contact lens materials and designs, including those focused on myopia management.
- Intellectual Property Protection: These patents create a significant barrier, preventing easy replication of their innovative products by potential new entrants.
- Market Deterrent: The cost and time required to develop and legally navigate around CooperCompanies' intellectual property discourage new players from entering these specific market segments.
Economies of Scale in Production and R&D
Cooper Companies, like many established players in the medical device and fertility sectors, leverages significant economies of scale. This advantage translates into lower per-unit production costs due to high-volume manufacturing and bulk purchasing of raw materials. For instance, in 2024, CooperSurgical’s revenue reached $3.7 billion, indicating substantial operational scale that smaller competitors struggle to match.
The ability to spread substantial research and development (R&D) costs across a larger revenue base is another critical barrier. Cooper Companies can invest more heavily in developing new technologies and improving existing products, creating a competitive edge. In 2023, the company reported R&D expenses of $405 million, a testament to their commitment to innovation, which new entrants would find challenging to replicate without significant upfront capital.
- Economies of Scale in Production: Cooper Companies benefits from reduced manufacturing costs per unit due to high-volume output.
- Purchasing Power: Bulk procurement of raw materials and components leads to lower input costs compared to new entrants.
- R&D Investment Capacity: Significant financial resources allow for sustained investment in innovation, creating product differentiation.
- Competitive Cost Structure: The combined effect of production and R&D scale enables Cooper Companies to maintain a competitive pricing strategy.
The threat of new entrants for Cooper Companies is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles in the medical device and women's health sectors. For example, the development of advanced contact lens materials or new surgical instruments requires massive R&D investment, easily reaching hundreds of millions of dollars. Navigating regulatory bodies like the FDA and EU MDR is a lengthy and expensive process, with approval costs potentially running into millions, effectively deterring smaller players.
Cooper Companies also benefits from strong brand loyalty and established distribution networks, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share. Their significant investment in proprietary technology and patents, such as those in myopia management contact lenses, creates a formidable intellectual property barrier. In 2023, CooperCompanies' net sales reached $3.2 billion, underscoring their substantial market presence and the scale of operations that new entrants must contend with.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | CooperCompanies' Position |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High (R&D, Manufacturing, Regulatory) | Well-established infrastructure and funding capacity |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Significant (FDA, MDR compliance costs and time) | Expertise and experience in navigating complex approvals |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Challenging to build | Strong existing relationships with healthcare providers |
| Intellectual Property | Difficult to replicate or circumvent | Extensive patent portfolio protecting key technologies |
| Economies of Scale | Limited for new entrants | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume production (e.g., CooperSurgical 2024 revenue $3.7 billion) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for The Cooper Companies leverages a comprehensive dataset including annual reports, SEC filings, industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld, and financial data from platforms such as S&P Capital IQ.
