Comer Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Comer Industries Bundle
Comer Industries faces moderate bargaining power from its buyers, as the market offers some alternatives, but also benefits from a relatively consolidated supplier base. The threat of substitutes is also present, though not overwhelmingly high, as specialized equipment often requires specific components. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Comer Industries’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Comer Industries operates in specialized sectors like agriculture, industrial, and renewable energy, demanding highly engineered components such as gearboxes and transmissions. If a limited number of suppliers can provide these critical, specialized parts, their bargaining power increases significantly because Comer has few alternative sources.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for heavy-duty transmissions, a key area for Comer, is characterized by a few dominant players. This concentration means these suppliers can dictate terms, potentially impacting Comer's costs and supply chain stability.
Switching suppliers for Comer Industries' highly integrated power transmission systems presents significant hurdles. The costs associated with redesigning components, retooling manufacturing processes, and conducting rigorous testing can be substantial, potentially running into millions of dollars. For instance, a major automotive supplier reported that the average cost to qualify a new component supplier can exceed $100,000, not including the product redesign and validation phases.
These extensive switching costs directly bolster the bargaining power of existing suppliers. Comer Industries would face considerable financial outlays and potential production disruptions if they decided to change their current supply chain partners. This situation was highlighted in 2023 when supply chain disruptions led some manufacturers to face extended lead times and price increases from their established component providers, underscoring the difficulty and expense of finding and integrating new sources.
Comer Industries' reliance on highly specialized or proprietary inputs significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. For instance, if a key supplier provides a patented gear system essential for Comer's advanced hydraulic pumps, that supplier holds considerable leverage. This uniqueness means Comer has fewer alternatives, driving up costs and potentially impacting production timelines.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration by suppliers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. If suppliers can begin manufacturing the very products Comer Industries currently produces, they gain a direct competitive edge. This scenario is particularly potent when suppliers possess robust customer relationships or a strong brand presence, allowing them to leverage these assets in a new market. For instance, a key component manufacturer for agricultural equipment, if capable and motivated, could potentially enter the finished tractor market, directly challenging Comer Industries.
Consider a hypothetical scenario: a major supplier of specialized hydraulic systems, which Comer Industries relies on, also possesses advanced manufacturing capabilities and a recognized brand in the industrial machinery sector. If this supplier decides to integrate forward, they could start producing complete hydraulic power units, directly competing with Comer Industries' offerings. This move would not only disrupt Comer's supply chain but also introduce a formidable competitor that understands Comer's product intricacies. In 2024, the increasing consolidation within the industrial component supply chain suggests a growing potential for such integration strategies among key suppliers, as they seek to capture more value.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers with advanced manufacturing technology and R&D can more easily integrate forward.
- Market Incentives: High profit margins in Comer Industries' end markets incentivize suppliers to consider forward integration.
- Brand Strength: A supplier with a strong existing brand can more effectively launch its own end products.
- Customer Relationships: Suppliers with deep ties to Comer's customers can leverage these relationships to gain market share.
Importance of Supplier's Input to Comer Industries' Cost Structure
The proportion of a supplier's input cost relative to Comer Industries' overall product cost significantly influences supplier power. When supplied components represent a substantial percentage of Comer Industries' total expenses, suppliers gain considerable leverage to negotiate higher prices, directly impacting the company's profit margins.
For instance, if a critical raw material accounts for 40% of Comer Industries' cost of goods sold, the supplier of that material holds substantial bargaining power. This leverage allows them to dictate terms and pricing more effectively, potentially squeezing Comer Industries' profitability.
- High Input Cost Proportion: If a supplier's product constitutes a large share of Comer Industries' total production cost, the supplier's bargaining power increases.
- Impact on Profitability: Increased supplier leverage can lead to higher input costs, directly reducing Comer Industries' profit margins.
- Example Scenario: If a key component represents 35% of Comer Industries' manufacturing expenses, the supplier of that component has significant influence over pricing and terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Comer Industries is substantial due to the specialized nature of its components and the limited number of qualified providers. In 2024, the market for critical agricultural and industrial transmissions, essential for Comer's operations, is dominated by a few key manufacturers, granting them significant pricing leverage.
Switching costs for Comer Industries are exceptionally high, often involving millions in redesign, retooling, and testing, which reinforces supplier power. This was evident in 2023 when supply chain disruptions led to price hikes and extended lead times from established component providers, demonstrating the difficulty in finding and integrating new sources.
Comer's reliance on proprietary or highly engineered inputs, such as patented gear systems for advanced hydraulic pumps, further strengthens supplier leverage. The threat of forward integration by these suppliers, who could potentially enter Comer's end markets, also amplifies their power, especially given market consolidation trends observed in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Limited number of dominant players in heavy-duty transmissions market. |
| Switching Costs for Comer | High | Millions in redesign, retooling, and testing; average qualification cost over $100,000. |
| Input Uniqueness/Proprietary Nature | High | Reliance on patented gear systems for specialized hydraulic pumps. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Moderate to High | Increasing consolidation in industrial component supply chain suggests potential. |
| Proportion of Input Cost | Variable (can be high) | If components represent ~35-40% of COGS, supplier influence is significant. |
What is included in the product
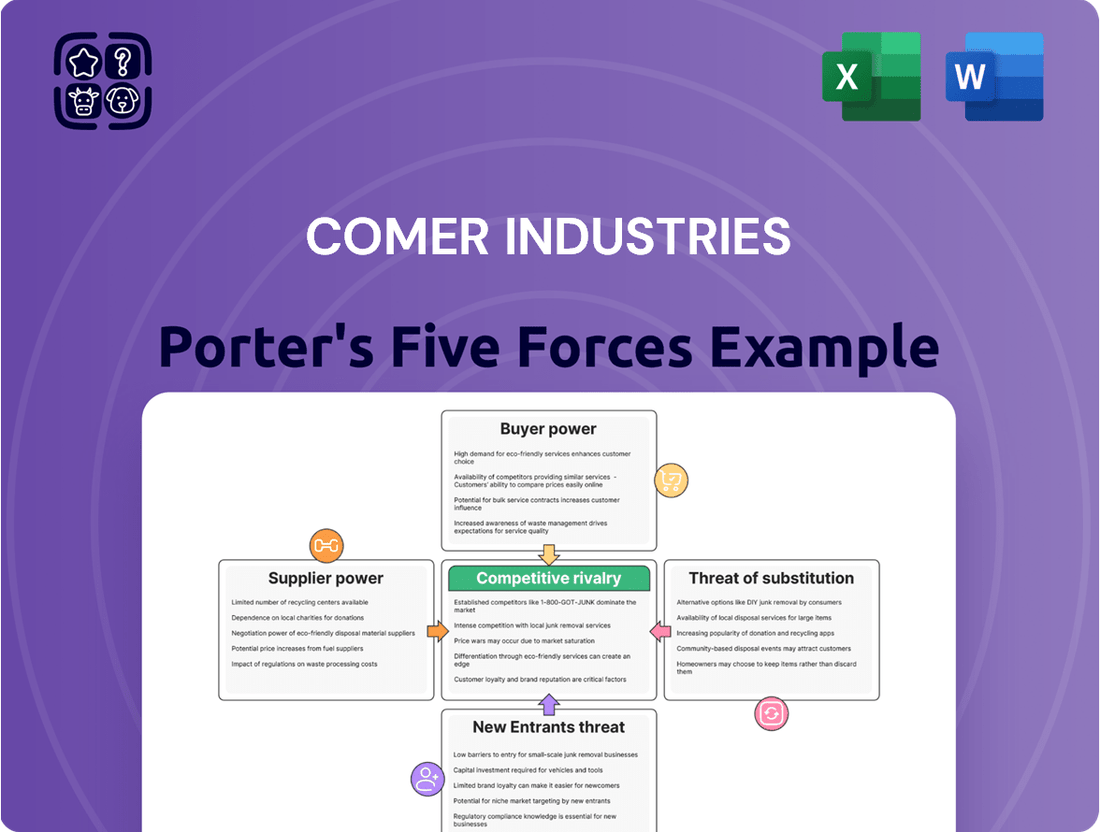
This Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the competitive forces impacting Comer Industries, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces dashboard, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration is a key factor in assessing the bargaining power of customers for Comer Industries. If a few large Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) represent a substantial portion of Comer's revenue, these major clients can leverage their purchasing volume to negotiate lower prices or more favorable contract terms, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
The agricultural sector, a significant market for Comer Industries, making up over 50% of its sales, faced a notable downturn in demand during 2024. This market contraction could amplify the bargaining power of the remaining large customers in this segment, as Comer may be more reliant on securing business from fewer, albeit still substantial, buyers.
Switching from Comer Industries' power transmission systems to a competitor's offerings can be a complex and costly undertaking for customers. These costs often include significant investments in redesigning existing equipment, re-engineering components for compatibility, and the potential for disruptions in production during the transition. For example, in the heavy equipment sector, integrating a new drivetrain might necessitate changes to the chassis, hydraulic systems, and control software, all adding to the overall expense and time commitment.
The level of these switching costs directly influences the bargaining power of Comer Industries' customers. When switching costs are high, customers are less likely to seek out alternative suppliers, giving Comer Industries more leverage in pricing and contract negotiations. Conversely, if these costs were to decrease, perhaps through standardization of interfaces or more modular product designs, customers would gain greater flexibility to explore and adopt competing solutions, thereby amplifying their bargaining power.
If Comer Industries' key customers, such as agricultural or construction equipment manufacturers, have the necessary technical know-how and financial capacity, they could potentially develop their own power transmission systems. This capability directly increases their leverage in negotiations with Comer.
For instance, if a major OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) for whom Comer supplies a significant portion of its components, were to invest in internal production capabilities, they could reduce their reliance on Comer. This threat is more potent if the switching costs for the customer are high, making it difficult for them to find alternative suppliers quickly.
In 2023, Comer Industries reported that its top ten customers accounted for approximately 60% of its net sales, highlighting the significant concentration of customer power. Should any of these major clients decide to pursue backward integration, it would represent a substantial risk to Comer's market position and pricing power.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers in the agricultural and industrial sectors often exhibit high price sensitivity, especially when market conditions are unfavorable. This was evident in 2024, as the agricultural sector faced challenges with declining commodity prices and rising input costs, leading customers to demand lower prices from suppliers like Comer Industries.
This heightened price sensitivity directly translates into increased bargaining power for customers. When demand weakens or supply is abundant, customers can leverage their purchasing power to negotiate more favorable terms, putting pressure on Comer Industries' profitability.
- 2024 Agricultural Sector Performance: Reports indicated a significant downturn in farm incomes in 2024 due to a confluence of low commodity prices and escalating operational expenses, directly impacting farmers' purchasing power and willingness to pay premium prices.
- Customer Demand for Lower Prices: In response to economic pressures, customers across Comer Industries' key markets actively sought price reductions on equipment and components throughout 2024.
- Impact on Margins: The increased customer bargaining power, driven by price sensitivity, directly threatened Comer Industries' profit margins as the company faced pressure to absorb costs or reduce selling prices.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute power transmission solutions significantly amplifies customer bargaining power for companies like Comer Industries. If customers can readily source comparable products from other manufacturers or adopt entirely different technologies that fulfill the same functional needs, their leverage in negotiations increases. This is particularly relevant in sectors where technological advancements offer diverse approaches to power transmission, such as the growing adoption of electric powertrains in off-highway vehicles as an alternative to traditional hydraulic or mechanical systems.
For instance, in the agricultural equipment sector, a key market for Comer Industries, the increasing availability of electric drive systems for tractors and implements presents a viable substitute to their traditional PTO-driven or hydraulic power transmission components. This forces Comer Industries to remain competitive on price and innovation to retain customers who have these alternative options readily accessible.
- Increased Customer Leverage: The presence of viable substitutes empowers customers to demand better pricing, quality, and service from Comer Industries, as they can switch suppliers if their needs are not met.
- Technological Alternatives: The rise of electric and advanced hybrid power transmission technologies offers customers choices beyond conventional mechanical and hydraulic solutions, directly impacting Comer Industries' market position.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: As substitute products become more prevalent and cost-effective, Comer Industries faces pressure to align its pricing to remain competitive, potentially impacting profit margins.
The bargaining power of customers for Comer Industries is significantly influenced by their concentration and price sensitivity. In 2023, Comer's top ten customers represented about 60% of net sales, indicating a high degree of customer concentration. This concentration, coupled with the price sensitivity observed in sectors like agriculture during 2024 due to market downturns, grants these large customers considerable leverage to negotiate lower prices and more favorable terms, directly impacting Comer's profitability.
| Customer Factor | Impact on Comer Industries | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Increased leverage for large buyers | Top 10 customers accounted for ~60% of net sales in 2023. |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on pricing and margins | Agricultural sector faced reduced purchasing power in 2024 due to low commodity prices. |
| Switching Costs | Reduces customer ability to switch, thus lowering their bargaining power | High costs for OEMs to re-engineer equipment for new suppliers. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Potential loss of business if customers produce in-house | Major OEMs could invest in internal production capabilities. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Empowers customers to demand better terms | Rise of electric drive systems in agricultural equipment as an alternative. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Comer Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Comer Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. It is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use, providing actionable insights into market dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Comer Industries operates in markets that have recently seen a slowdown, especially within the agricultural sector. For instance, the global agricultural machinery market, a key area for Comer, experienced a noticeable deceleration in growth through 2023 and into early 2024. This trend is projected to continue with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3.5% for the next few years, a dip from previous higher growth periods.
A declining or slow-growing market naturally fuels more intense competitive rivalry. When the overall market pie isn't expanding, companies like Comer Industries are compelled to fight harder for market share. This often translates into aggressive pricing strategies, increased promotional activities, and a greater emphasis on product differentiation to capture customer attention and loyalty.
Comer Industries operates in a market with a significant number of competitors, including established players like TEXA, Eldor, Sogefi, and Brembo. This diversity in competitor size and strategic focus intensifies the rivalry as each company vies for market share.
Comer Industries distinguishes itself through advanced engineering systems and mechatronic solutions. This high degree of product differentiation, offering unique features and superior performance, effectively dampens direct price-based competition among rivals.
For instance, in 2024, the company continued to highlight its integrated powertrain systems, which combine hydraulics, electronics, and mechanics. This focus on sophisticated, tailored solutions makes it harder for competitors to offer direct substitutes, thereby lowering the intensity of rivalry.
Exit Barriers
Comer Industries likely faces significant exit barriers, a factor that intensifies competitive rivalry. These barriers can include highly specialized manufacturing equipment and dedicated production lines for its niche agricultural and construction machinery components. The substantial investment in these assets makes it difficult and costly for companies to divest or repurpose them if they decide to leave the market.
Furthermore, long-term supply agreements with major OEMs in the agriculture and construction sectors represent another considerable exit barrier. Breaking these contracts often incurs penalties, locking companies into ongoing operations even when market conditions are unfavorable. For instance, in 2024, the global construction equipment market saw continued demand, but companies with fixed production capacities tied to long-term contracts might struggle to adapt to shifts in demand without incurring significant costs.
- Specialized Assets: Comer Industries' reliance on custom-engineered components and heavy machinery for manufacturing creates high capital costs for exiting.
- Long-Term Contracts: Existing agreements with key clients in the agriculture and construction sectors can impose financial penalties for early termination.
- Social Costs: Significant workforce reductions and the potential impact on local communities where plants are located can also act as a deterrent to exiting the industry.
- Market Conditions: The cyclical nature of the construction and agriculture industries means that exiting during a downturn can result in selling assets at a substantial loss.
Strategic Stakes
Comer Industries operates in a market where strategic stakes are high, meaning competitors often view the power transmission sector as crucial to their long-term success. This perception fuels intense competition as companies invest significantly to capture or defend market share.
For instance, in 2024, major players in the industrial equipment sector, many of whom are direct or indirect competitors to Comer Industries, continued to prioritize growth in their power transmission segments. This was evident in their capital expenditure plans, with several announcing multi-million dollar investments in R&D and manufacturing capacity for advanced drivetrain solutions.
- High Strategic Importance: Competitors often see the power transmission market as core to their business, driving aggressive strategies.
- Significant Investment: Companies are channeling substantial capital into this sector to enhance their competitive position.
- Market Share Focus: The drive to gain or maintain market share leads to intensified rivalry and innovation efforts.
The competitive rivalry for Comer Industries is shaped by a market with numerous players, a slowdown in key sectors like agriculture, and high exit barriers. While Comer's focus on specialized mechatronic solutions helps differentiate its offerings, the inherent nature of the power transmission market, where strategic stakes are high, fuels persistent competition among established firms and emerging players alike.
| Factor | Impact on Rivalry | Comer Industries' Position |
| Market Growth | Slowdown in agriculture and construction markets intensifies rivalry for market share. | Global agricultural machinery market CAGR projected around 3.5% for the coming years. |
| Number of Competitors | Presence of diverse competitors like TEXA, Eldor, Sogefi, and Brembo increases rivalry. | Significant number of established and niche players. |
| Product Differentiation | High differentiation through advanced engineering dampens price wars. | Focus on integrated powertrain systems and mechatronic solutions. |
| Exit Barriers | High barriers (specialized assets, long-term contracts) keep firms competing. | Significant investment in specialized manufacturing and OEM agreements. |
| Strategic Stakes | Power transmission seen as crucial, leading to aggressive competition. | Competitors continue multi-million dollar investments in drivetrain solutions. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Comer Industries hinges on the price-performance ratio of alternative solutions. For instance, if electric powertrains become significantly more cost-effective and offer comparable or superior performance in off-highway vehicles, they could pose a substantial threat to Comer's traditional drivetrain components. In 2023, the global electric vehicle market saw a significant uptick, with sales of electric cars and trucks reaching new heights, indicating a growing acceptance and potential cost reduction in alternative technologies.
Customers' inclination to switch to alternative solutions for power transmission is a key factor in assessing the threat of substitutes for Comer Industries. This willingness is shaped by several elements, including how aware customers are of other options, their perception of the risks involved in switching, and the strength of their brand loyalty to existing providers. For instance, if customers actively seek out and readily adopt new technologies or are not deeply committed to established power transmission methods, the pressure from substitute products escalates significantly.
Rapid technological advancements present a significant threat of substitutes for Comer Industries. Innovations in areas like electric powertrains and advanced energy storage systems could directly replace traditional mechanical power transmission solutions. For instance, the growing adoption of electric vehicles in off-highway applications could diminish demand for the gearboxes and drivelines Comer Industries specializes in.
Comer Industries itself acknowledges this threat, as evidenced by its strategic investments in e-mobility solutions, aiming to adapt to evolving market demands. This proactive approach is crucial as new technologies can emerge quickly, offering comparable or superior performance at potentially lower costs, thereby eroding the market share of existing products.
Relative Price of Substitutes
A significant drop in the price of substitute products or technologies, especially if they offer comparable performance, can strongly encourage customers to switch away from Comer Industries' offerings. This competitive pressure necessitates that Comer Industries maintain price competitiveness or clearly articulate its unique value proposition to keep its customer base loyal.
For instance, if the cost of alternative drivetrain solutions for heavy-duty vehicles, such as electric powertrains or advanced hybrid systems, were to fall substantially relative to Comer Industries' traditional offerings, it would present a direct threat. This could force Comer Industries to re-evaluate its pricing strategies or invest further in differentiating its products through enhanced features or performance metrics. In 2024, the automotive industry saw continued investment in electric vehicle technology, with battery costs projected to decline further, potentially making electric drivetrains more accessible as substitutes in various commercial vehicle segments.
- Price Sensitivity: Comer Industries must monitor the price trends of substitute technologies.
- Value Proposition: Demonstrating superior performance or total cost of ownership is crucial.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in alternative solutions can rapidly alter the competitive landscape.
- Market Dynamics: Shifts in consumer preference or regulatory mandates favoring alternatives can accelerate switching.
Switching Costs for Customers to Substitutes
The ease with which Comer Industries' customers can switch to alternative solutions significantly influences the threat of substitutes. If adopting a substitute product requires minimal investment in new equipment, training, or process changes, the threat is elevated.
Conversely, when switching to a substitute product incurs substantial costs for customers, such as significant retooling, integration challenges, or loss of specialized knowledge, the threat of substitution is diminished. For instance, a customer heavily invested in Comer Industries' hydraulic systems, which are deeply integrated into their manufacturing lines, would face high switching costs if they considered moving to a competitor's entirely different technology. This integration creates a barrier, making substitution less likely.
- High Switching Costs: Comer Industries' specialized components, often requiring significant integration into customer machinery, create high switching costs.
- Low Switching Costs: For less integrated product lines, customers might find it easier and cheaper to adopt alternative solutions.
- Customer Investment: The degree to which customers have invested in Comer's technology (e.g., proprietary interfaces, specialized training) directly impacts their willingness to switch.
The threat of substitutes for Comer Industries is amplified by the increasing viability of electric and hybrid powertrains in off-highway equipment. As these technologies mature, their price-performance ratio improves, making them more attractive alternatives to traditional internal combustion engine components. For example, advancements in battery technology and electric motor efficiency continue to drive down the total cost of ownership for electric drivetrains, a trend expected to accelerate through 2024 and beyond.
Customers' willingness to adopt these substitutes is influenced by factors like brand loyalty, perceived switching costs, and awareness of alternative offerings. If customers find it easy and cost-effective to integrate electric or hybrid systems, the pressure on Comer Industries intensifies. The growing availability of charging infrastructure and government incentives further lowers barriers to adoption for electric alternatives.
| Technology | Potential Impact on Comer Industries | Key Trend (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Powertrains | Direct replacement for internal combustion engine components | Continued cost reduction in batteries and motors, increasing adoption in commercial vehicles. |
| Hybrid Systems | Offers a bridge technology, potentially reducing demand for purely mechanical solutions | Growing interest in hybrid solutions for improved fuel efficiency and emissions reduction. |
| Advanced Hydraulics | Could offer improved efficiency and control over traditional hydraulics | Focus on energy recovery and more efficient hydraulic component design. |
Entrants Threaten
Comer Industries, with its extensive global manufacturing footprint and substantial revenue streams, leverages significant economies of scale. This advantage translates into lower per-unit production costs, reduced research and development expenses spread across a larger output, and more favorable terms with suppliers due to bulk purchasing power. For instance, in 2023, Comer Industries reported net sales of $758.1 million, indicating a scale that new entrants would find challenging to replicate quickly.
Newcomers entering the industrial equipment sector face a substantial hurdle in matching Comer Industries' cost efficiencies. The inability to achieve similar production volumes means higher initial manufacturing costs and less competitive pricing. This cost disadvantage makes it difficult for new entrants to gain market share, especially in price-sensitive segments where established players like Comer can absorb lower margins due to their scale.
Entering the advanced engineering systems and mechatronic solutions market, where Comer Industries operates, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in research and development, state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, and highly specialized equipment crucial for producing complex components.
These high capital requirements act as a formidable barrier to entry, deterring many potential competitors from even attempting to enter the market. For instance, Comer Industries' recent capital expenditure on a new US plant, reported to be a multi-million dollar project, underscores the scale of investment needed to establish and maintain a competitive presence.
Established players like Comer Industries have secured well-developed distribution networks and forged strong relationships with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) across key sectors such as agriculture, construction, and renewable energy. These existing channels are crucial for reaching end customers efficiently.
New entrants would find it difficult and costly to replicate these established networks. Building trust and securing shelf space or access to these vital distribution channels requires significant time, investment, and a proven track record, which newcomers typically lack.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Comer Industries' dedication to advanced engineering systems and mechatronic solutions indicates a strong reliance on proprietary technology and patents. This intellectual property acts as a significant barrier, requiring potential competitors to undertake substantial research and development to replicate their advanced offerings. For instance, in 2023, Comer Industries reported significant investments in R&D, underscoring their commitment to maintaining a technological edge.
The threat of new entrants is therefore mitigated by the high cost and time associated with developing comparable technological capabilities. Companies looking to enter this space must overcome these hurdles, which often involve securing their own patents and building specialized expertise. This can be seen in the patent filings by Comer Industries, which protect their innovative product designs and manufacturing processes.
- Proprietary Technology: Comer Industries leverages advanced engineering and mechatronics, creating unique solutions.
- Patents and IP: Significant investment in intellectual property, including patents, protects their innovations.
- R&D Investment: In 2023, Comer Industries' R&D spending was a key factor in developing and safeguarding their technological advantage.
- High Entry Costs: New entrants face substantial costs to develop comparable technologies and secure intellectual property rights.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations significantly impact the threat of new entrants for companies like Comer Industries. Strict regulations, industry standards, and certification requirements in its core sectors – agricultural, industrial, and renewable energy – act as substantial barriers. For instance, meeting EPA emissions standards for agricultural equipment or obtaining certifications for industrial components requires significant investment and expertise, deterring many potential new players.
Navigating these complex regulatory landscapes adds considerable cost and time to market for any new entrant. In 2024, the ongoing evolution of environmental regulations, particularly concerning emissions and sustainability in manufacturing, continues to raise the compliance bar. Companies must demonstrate adherence to these evolving standards, a process that can be both costly and time-consuming, thereby limiting the ease with which new competitors can enter the market.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with evolving environmental and safety standards in agricultural and industrial equipment manufacturing presents significant upfront costs for new entrants.
- Certification Requirements: Obtaining necessary certifications for components used in critical sectors like renewable energy can involve lengthy and expensive processes, acting as a barrier.
- Increased Time-to-Market: The need to navigate complex legal and regulatory frameworks delays product launches, increasing the financial risk for new businesses entering the market.
The threat of new entrants for Comer Industries is generally low due to several significant barriers. These include the substantial capital required for advanced manufacturing and R&D, the difficulty in replicating established distribution networks, and the protection afforded by proprietary technology and patents. Furthermore, stringent government regulations and certification requirements in its key sectors add complexity and cost for potential newcomers.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Comer Industries' Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, manufacturing facilities, and specialized equipment. | Deters many potential competitors due to upfront costs. | Leverages economies of scale and past investments. |
| Distribution Networks | Established relationships with OEMs and efficient global channels. | Difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate. | Secured market access and strong OEM partnerships. |
| Proprietary Technology & IP | Unique engineering solutions protected by patents. | Requires significant R&D to match technological capabilities. | Maintains competitive edge through innovation and IP protection. |
| Regulatory Environment | Strict industry standards and certifications in key sectors. | Adds cost, time, and complexity to market entry. | Expertise in navigating and complying with regulations. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Comer Industries is built upon a foundation of robust data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and competitor disclosures. We also incorporate insights from trade publications and economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
