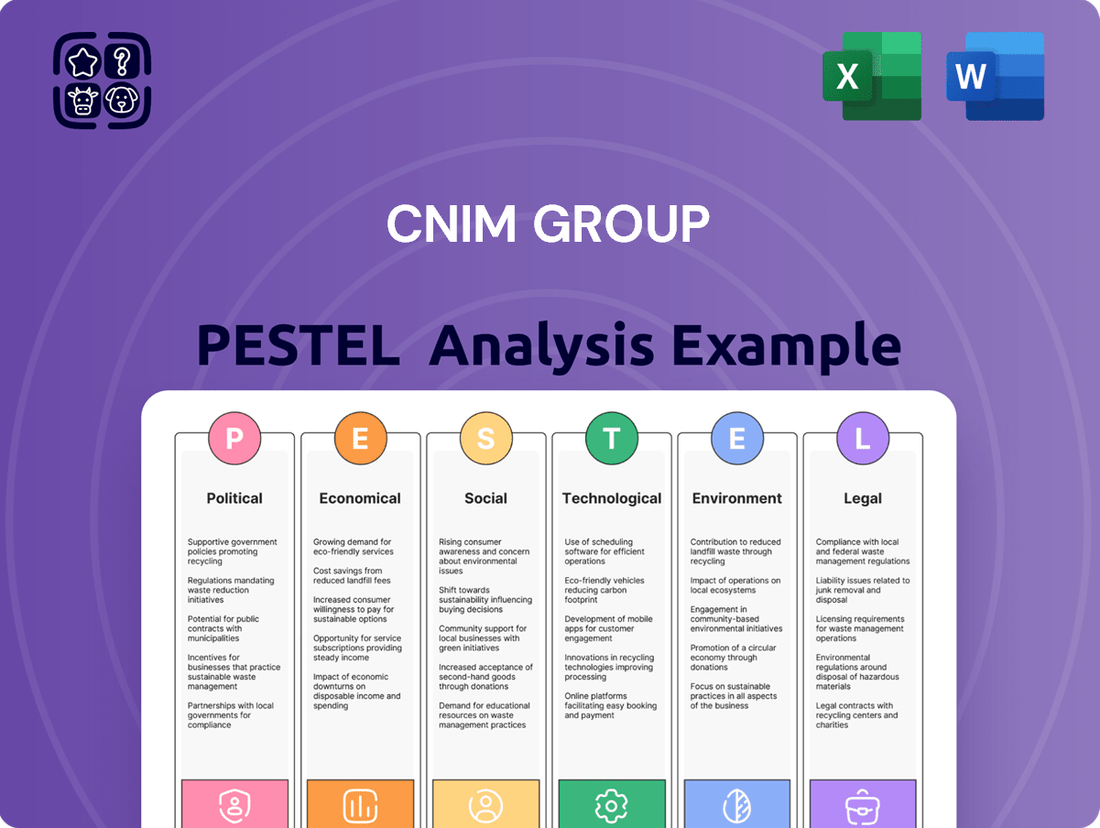
CNIM Group PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CNIM Group Bundle
Navigate the complex external landscape impacting CNIM Group with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand how political shifts, economic volatility, and technological advancements are shaping their operational environment. This expert-crafted report offers actionable intelligence to anticipate challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
Discover the social and environmental trends that could redefine CNIM Group's market position. Our detailed analysis provides a clear view of the forces at play, empowering you to make informed strategic decisions. Gain a competitive advantage by leveraging these critical insights.
Unlock the full potential of your strategic planning with our in-depth PESTLE analysis of CNIM Group. This ready-to-use resource delivers a thorough examination of external factors, perfect for investors, consultants, and business leaders. Download the complete version now to secure your strategic edge.
Political factors
CNIM Group's significant involvement in naval equipment and defense makes it highly sensitive to national and international defense policies and spending. Governments' strategic decisions regarding military modernization directly influence the demand for CNIM's offerings.
The geopolitical landscape in 2024 and continuing into 2025 shows a clear trend of increased defense spending among NATO and EU member states. For instance, Germany's defense budget saw a substantial increase, and many European nations are fulfilling their commitment to allocate 2% of GDP to defense, creating a favorable environment for companies like CNIM.
This heightened investment in military capabilities, particularly in naval modernization and enhancing strategic autonomy, translates into direct opportunities for CNIM. The company's expertise in building advanced naval vessels and providing robust combat engineering solutions aligns perfectly with these governmental priorities.
Government policies championing renewable energy and imposing stricter environmental rules significantly shape CNIM's operational landscape. These directives are particularly impactful in the energy and environmental sectors where CNIM operates.
The updated EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) and the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD), both coming into effect in 2024 and 2025 respectively, will compel industries to adopt cleaner manufacturing processes and enhance energy efficiency. This regulatory push is expected to boost demand for CNIM's specialized waste treatment and thermal power plant technologies.
Furthermore, these evolving regulations are driving innovation and adoption of carbon capture solutions and circular economy principles, areas where CNIM is actively engaged.
CNIM Group, as a global player, is significantly influenced by international trade dynamics and the broader geopolitical landscape. Shifting trade policies and tariffs directly affect its project costs and the reliability of its supply chains, particularly for large-scale industrial and engineering projects. For instance, ongoing trade disputes between major economic blocs can introduce volatility and increase the cost of imported components essential for CNIM's operations.
Geopolitical instability, exemplified by conflicts like the Russia-Ukraine war, highlights both risks and opportunities for CNIM. Such events can disrupt international logistics and increase operational risks. However, they also underscore the critical need for enhanced defense capabilities, potentially boosting demand for CNIM's expertise in military engineering and related infrastructure development.
The European Union's strategic push for greater autonomy, especially in defense, is a key trend for CNIM. This initiative aims to localize supply chains and foster intra-European collaboration in defense manufacturing. This could translate into increased opportunities for CNIM within the EU market, as member states prioritize domestic production and regional partnerships, potentially leading to more secured contracts and reduced reliance on external suppliers.
Public Procurement and Industrial Policy
Public procurement policies are absolutely vital for CNIM, especially when it comes to defense contracts and massive infrastructure projects, like the waste-to-energy plants they're involved in. The volume and nature of these government-funded projects directly impact CNIM's order book and revenue streams. For instance, in 2024, many European nations are continuing to ramp up spending on defense modernization and renewable energy infrastructure, areas where CNIM has a strong presence.
Favorable industrial policies can really give CNIM a boost. Think about government support for domestic manufacturing, incentives for research and development, or even specific pushes for green technologies. These kinds of policies can lower operating costs, encourage innovation, and make CNIM's offerings more competitive. The EU's ongoing commitment to the Green Deal, with significant funding allocated for sustainable infrastructure, directly aligns with CNIM's expertise in waste-to-energy solutions.
Government-led infrastructure investment initiatives, even if not directly targeting CNIM's primary markets, can create ripple effects. The US Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), for example, highlights a global shift towards public investment in critical infrastructure. This trend suggests a broader market appetite for large-scale projects, which could translate into indirect opportunities or a more favorable investment climate for companies like CNIM operating in similar sectors worldwide.
- Defense Spending: Several NATO countries have announced significant increases in defense budgets for 2024-2025, potentially leading to more procurement opportunities for CNIM's defense-related divisions.
- Green Investment: The European Union's Green Deal aims to mobilize at least €1 trillion in sustainable investments by 2030, offering substantial potential for CNIM's waste-to-energy and environmental technology projects.
- Infrastructure Focus: Many governments are prioritizing infrastructure upgrades, with a particular emphasis on energy transition and circular economy projects, aligning with CNIM's strategic focus areas.
Political Support for Innovation and Net-Zero Initiatives
The level of government backing for innovation, especially in areas like net-zero technologies and sophisticated scientific equipment, directly impacts CNIM's high-tech divisions. For instance, the European Union's commitment through initiatives like the Net-Zero Industry Act (NZIA) signals a strong regulatory push and potential financial avenues for companies developing green technologies.
These policies, aiming for substantial emissions cuts by 2030 and complete decarbonization by 2050, create a favorable environment for projects that CNIM might undertake in these sectors. Such political endorsement is vital for cultivating a competitive landscape for emerging green technologies and supporting ambitious, large-scale scientific projects.
Specifically, the EU's 2030 climate targets aim for at least a 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to 1990 levels, and the NZIA aims to boost the manufacturing capacity of clean technologies within the EU to at least 40% of the bloc's deployment needs by 2030. This provides a clear market signal and potential for growth in CNIM's relevant business segments.
- EU's Net-Zero Industry Act (NZIA): Aims to increase the EU's manufacturing capacity of net-zero technologies to at least 40% of annual deployment needs by 2030.
- 2030 Climate Targets: Mandate at least a 55% net reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to 1990 levels.
- Green Deal Funding: Significant EU funding is allocated to research, development, and deployment of green technologies, potentially benefiting CNIM's innovation efforts.
Governmental decisions on defense spending and procurement directly shape the demand for CNIM's naval and military engineering solutions. Increased defense budgets among NATO members in 2024-2025, driven by geopolitical shifts, create significant opportunities for CNIM's specialized offerings in naval modernization.
Government policies promoting renewable energy and stricter environmental regulations are crucial for CNIM's environmental and energy divisions. The EU's Green Deal, with its substantial investment targets for sustainable projects through 2030, directly supports CNIM's waste-to-energy technologies and circular economy initiatives.
Public procurement policies, especially for large-scale defense and infrastructure projects, are vital for CNIM's revenue. Many European nations are increasing spending on defense and renewable energy infrastructure in 2024, aligning with CNIM's core business areas.
| Factor | Impact on CNIM | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
| Defense Spending Increases | Boosts demand for naval and military engineering | NATO defense budgets rising; Germany's defense budget increased by €10 billion in 2024. |
| Green Investment Initiatives | Drives opportunities in waste-to-energy and environmental tech | EU Green Deal aims to mobilize €1 trillion in sustainable investments by 2030. |
| Public Procurement Policies | Influences order book for major projects | Continued government focus on energy transition and infrastructure upgrades globally. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis offers a comprehensive examination of the external forces impacting the CNIM Group, detailing how political stability, economic shifts, social trends, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and legal frameworks create both challenges and opportunities for the company.
A clear and concise PESTLE analysis for CNIM Group, presented in an easily digestible format, helps alleviate the pain of complex data interpretation, enabling swift strategic decision-making.
Economic factors
Inflation, especially within the construction and engineering sectors, presents a significant economic challenge for CNIM Group. Projections suggest construction inflation will likely remain elevated from 2026 onward, with difficult market conditions expected to persist until the middle of 2025. This is largely due to ongoing resource limitations and procurement delays impacting the industry.
The volatility in material prices, particularly for key inputs like steel and electrical components, continues to exert pressure on project budgets. For instance, the S&P Global Commodity Insights reported that average steel prices saw fluctuations throughout 2024, impacting the cost of raw materials for infrastructure projects. CNIM's success in navigating these rising input costs and managing supply chain disruptions will be critical for maintaining project profitability.
The overall health of the global and regional economies significantly influences demand for CNIM Group's industrial facilities and services. While some economic indicators point towards stability, persistent challenges like elevated interest rates and a generally difficult lending environment may lead to delays in new construction and industrial projects. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be 3.2% in 2024, a slight slowdown from 2023, highlighting cautious optimism amidst economic headwinds.
However, anticipated gradual decreases in short-term interest rates throughout 2025 could offer substantial relief and stimulate both public and private sector investments. This potential easing of monetary policy is expected to encourage project initiations, thereby boosting demand in the various sectors CNIM Group operates within, such as energy and defense.
Global defense budgets are on the rise, with European nations significantly boosting their military spending. In 2024, many NATO members are meeting or surpassing the 2% of GDP defense spending benchmark, a trend expected to continue. This increased investment, fueled by ongoing geopolitical uncertainties, directly benefits companies like CNIM involved in defense manufacturing.
CNIM's defense sector is well-positioned to capitalize on this sustained global demand for military equipment and services. The projected growth in defense expenditure, particularly in Europe, translates into a more robust pipeline of opportunities for large-scale contracts. This includes areas where CNIM has established expertise, such as naval systems and combat engineering solutions.
The economic stimulus provided by these heightened defense budgets stimulates broader economic activity. Beyond CNIM's direct revenue, increased defense spending supports supply chains, creates jobs, and drives innovation within the industrial sector. This creates a favorable environment for companies contributing to national security and defense capabilities.
Energy Market Dynamics and Investment in Renewables
Fluctuations in global energy prices, notably the volatility seen in oil and natural gas markets throughout 2024 and projected into 2025, directly influence CNIM's strategic decisions. The increasing global investment in renewable energy sources, which surpassed USD 1.7 trillion in 2023 according to the IEA, presents both challenges and opportunities for CNIM's operations in the energy and environment sectors.
The strong push towards a decarbonized economy, bolstered by ambitious EU energy efficiency targets and directives like the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive, is a significant driver for CNIM. This policy landscape directly increases demand for their waste-to-energy solutions and modern thermal power plants designed to meet stringent sustainability criteria.
Economic incentives are clearly shifting away from traditional energy sources. For instance, the phase-out of financial incentives for fossil fuel boilers by 2025 across several European nations creates a more favorable market for CNIM's renewable and energy-efficient technologies.
- Energy Price Volatility: Global energy prices remain a key factor, impacting project economics for CNIM's clients in the energy sector.
- Renewable Investment Surge: Over USD 1.7 trillion invested globally in renewables in 2023 highlights a major market trend supporting CNIM's green solutions.
- EU Decarbonization Drive: EU energy efficiency targets and sustainability directives are increasing demand for waste-to-energy and modern thermal power solutions.
- Fossil Fuel Incentive Phase-Out: The discontinuation of financial support for fossil fuel boilers by 2025 in key markets enhances the economic viability of CNIM's offerings.
Access to Capital and Project Financing
The ease with which CNIM Group can secure funding for its substantial industrial and infrastructure projects is a critical economic factor. High interest rates have presented a hurdle, but a shift towards more accommodating monetary policies and significant government spending initiatives, such as the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) and the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the United States, are poised to improve financing landscapes. These legislative actions, often mirrored globally, signal a commitment to bolstering infrastructure and green energy sectors, directly benefiting companies like CNIM.
Furthermore, the growing appetite of private equity firms for investment in innovative construction technologies and renewable energy ventures presents promising alternative capital sources. For instance, in 2024, global private equity real estate fundraising reached approximately $200 billion, with a notable portion directed towards infrastructure and sustainability-focused projects, indicating a strong investor interest in CNIM's operational domains.
- Capital Availability: Government stimulus packages and a potential easing of interest rates in 2024-2025 are expected to improve access to capital for large projects.
- Cost of Capital: While rates remain a consideration, the trend suggests a stabilization or potential decrease, making project financing more viable.
- Private Equity Interest: Increased PE investment in renewables and construction tech offers a vital funding avenue for CNIM's strategic growth.
- Government Investment: Acts like the IIJA and IRA demonstrate substantial public investment, creating a more favorable environment for infrastructure development.
Economic factors significantly shape CNIM Group's operational landscape, with inflation and material price volatility presenting ongoing challenges through mid-2025. Despite global growth projections of 3.2% for 2024, elevated interest rates can slow project initiation, though anticipated rate decreases in 2025 may spur investment.
The surge in global defense spending, particularly in Europe, where many NATO members exceed the 2% GDP benchmark in 2024, offers substantial opportunities for CNIM's defense sector. Simultaneously, the strong global push for decarbonization, evidenced by over $1.7 trillion invested in renewables in 2023, aligns with CNIM's focus on waste-to-energy and sustainable solutions, further supported by the 2025 phase-out of fossil fuel boiler incentives in key markets.
Access to capital is improving, with government initiatives like the US Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and Inflation Reduction Act stimulating infrastructure and green energy projects. Private equity's growing interest in these sectors, with approximately $200 billion in global PE real estate fundraising in 2024, provides additional avenues for financing CNIM's ventures.
| Economic Factor | 2024/2025 Data/Trend | Impact on CNIM Group |
|---|---|---|
| Inflation | Elevated, persistent through mid-2025 | Increased project costs, pressure on margins |
| Material Prices | Volatile (e.g., steel fluctuations in 2024) | Budgetary challenges, supply chain management crucial |
| Global Economic Growth | Projected 3.2% in 2024 (IMF) | Influences demand for industrial facilities and services |
| Interest Rates | High, but potential for gradual decreases in 2025 | Affects project financing viability and investment decisions |
| Defense Spending | Rising globally, many NATO members exceeding 2% GDP in 2024 | Boosts opportunities in defense manufacturing and services |
| Renewable Energy Investment | Over $1.7 trillion globally in 2023 (IEA) | Drives demand for CNIM's green energy solutions |
| Fossil Fuel Incentives | Phasing out by 2025 in certain markets | Enhances competitiveness of CNIM's sustainable technologies |
| Capital Availability | Government stimulus (e.g., US IIJA/IRA), PE interest ($200B 2024 PE RE fundraising) | Improved financing landscape for large projects |
Same Document Delivered
CNIM Group PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of the CNIM Group delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company's operations and strategic direction. You'll gain critical insights into market dynamics, competitive landscapes, and potential growth opportunities. What you see is what you’ll be working with.
Sociological factors
The engineering and construction sectors are grappling with a significant shortage of skilled labor, a trend that intensified through 2024 and is projected to continue into 2025. This isn't just about needing more hands; it's about needing the *right* hands. Companies like CNIM must adapt to a changing landscape where digital proficiency is as crucial as traditional engineering acumen.
Demand is surging for specialized skills in areas like data analytics, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. These digital competencies are becoming essential for optimizing project management, design, and execution within the industry. Simultaneously, foundational engineering expertise remains critical, creating a dual need for both new and updated skill sets across the workforce.
For CNIM, navigating this talent crunch means strategic investment in employee training and development programs to upskill existing staff. Exploring remote work options can also broaden the talent pool beyond geographical limitations. Furthermore, retaining experienced, older workers who possess invaluable institutional knowledge while actively recruiting and nurturing younger talent is key to bridging the generational and skills gap effectively.
Public acceptance is a major hurdle for industrial projects, especially those involving waste-to-energy or defense. CNIM Group needs to carefully manage how communities view these facilities, as negative perceptions can stall or even cancel development. For instance, in France, public consultations for new waste management infrastructure often highlight local concerns about air quality and traffic, demonstrating the direct impact of public opinion on project timelines and budgets.
Transparency is no longer optional; it's a requirement. Companies like CNIM must openly share data on environmental impacts and safety protocols. The European Union's push for greater public access to environmental information, like that facilitated by the Industrial Emissions Portal Regulation (IEPR), means citizens and watchdog groups have more tools to scrutinize operations. CNIM's commitment to clear communication, perhaps through community forums or easily accessible online reports, is vital for building trust and mitigating opposition.
The financial implications of public perception are substantial. Delays caused by community opposition can add millions to project costs, impacting CNIM's profitability. For example, a prolonged public inquiry into a new waste-to-energy plant in the UK in 2023 reportedly added over £5 million to the project's development expenses due to extensive environmental impact assessments and community liaison efforts.
Employee well-being and flexible work are gaining significant traction in the engineering industry. Given the inherent stress of complex projects, companies like CNIM are recognizing the need to invest in mental health resources, adaptable work schedules, and activities that boost team spirit. For instance, reports indicate a 20% increase in employee demand for flexible work options across European engineering firms in 2024, a trend expected to continue into 2025.
CNIM must align its HR practices with these changing employee expectations to remain competitive in talent acquisition and retention. Embracing hybrid work models, for example, could be a key strategy. A 2024 survey of engineering professionals revealed that 65% would prioritize a job offering hybrid flexibility over one that is fully office-based, even if the salary was slightly lower.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and ESG Expectations
Societal expectations around Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) are profoundly shaping business operations, including for entities like CNIM Group. Investors, consumers, and the general public are increasingly scrutinizing companies not just on financial performance but also on their ethical and sustainable practices. This trend means that a company's reputation is directly tied to its ability to demonstrate meaningful commitment to these areas.
The pressure on companies to actively reduce their environmental footprint, enhance energy efficiency, and ensure responsible sourcing throughout their supply chains is intensifying. For CNIM, this translates into a critical need to showcase robust ESG performance. This includes transparent and comprehensive sustainability reporting, aligning with evolving regulatory frameworks such as the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the EU Taxonomy for sustainable activities. Meeting these benchmarks is crucial for building trust, attracting capital from sustainability-focused funds, and maintaining a competitive edge in the 2024-2025 period and beyond.
- Growing Investor Focus: In 2023, ESG funds globally saw significant inflows, with many investors prioritizing companies with strong sustainability credentials. For instance, sustainable investment funds reached an estimated $3.4 trillion in assets under management globally by the end of 2023, a figure expected to continue its upward trajectory into 2025.
- Regulatory Landscape: The implementation of the CSRD in the EU requires extensive ESG disclosures from a growing number of companies, including those in CNIM's operational spheres. Non-compliance can lead to reputational damage and potential financial penalties.
- Consumer Demand: Consumer preference for sustainable products and services continues to rise. A 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for products from environmentally responsible companies.
- Supply Chain Scrutiny: Companies are increasingly expected to ensure ethical labor practices and environmental standards across their entire supply chains, impacting procurement and operational decisions.
Demand for Sustainable and Circular Solutions
Societal expectations are increasingly emphasizing sustainability and circular economy principles, especially in how we manage waste. This is a significant driver for companies like CNIM Group. People are more aware of their environmental footprint, leading to a strong demand for better recycling methods, ways to reduce waste generation, and systems that encourage the reuse of materials.
This growing consciousness translates into market opportunities for CNIM's waste-to-energy and waste treatment divisions. For instance, the European Union has set ambitious recycling targets, with member states aiming to recycle at least 55% of municipal waste by 2025, rising to 60% by 2030 and 65% by 2035. To meet these goals, innovative solutions that support a circular economy are essential, and CNIM is positioned to provide them.
- Growing Demand: Consumers and businesses alike are actively seeking eco-friendly waste management solutions.
- Circular Economy Focus: The push is towards reducing waste and maximizing material reuse, aligning with circular economy models.
- EU Targets: The EU aims for 55% municipal waste recycling by 2025, creating a clear market need for advanced solutions.
- CNIM's Opportunity: This trend directly benefits CNIM's waste-to-energy and waste treatment businesses by fostering demand for their expertise.
Societal expectations are increasingly emphasizing sustainability and circular economy principles, especially in how we manage waste. This is a significant driver for companies like CNIM Group, as people are more aware of their environmental footprint, leading to a strong demand for better recycling methods and waste reduction systems.
This growing consciousness translates into market opportunities for CNIM's waste-to-energy and waste treatment divisions. For instance, the European Union has set ambitious recycling targets, with member states aiming to recycle at least 55% of municipal waste by 2025, creating a clear market need for advanced solutions.
| Societal Expectation | Impact on CNIM | Supporting Data (2024-2025) |
| Circular Economy & Waste Reduction | Increased demand for waste-to-energy and waste treatment solutions | EU target: 55% municipal waste recycling by 2025; 60% by 2030. |
| Environmental Consciousness | Preference for eco-friendly and sustainable operations | 60% of consumers willing to pay a premium for products from environmentally responsible companies (2024 survey). |
| Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR/ESG) | Need for transparent sustainability reporting and ethical practices | ESG funds saw significant inflows in 2023, reaching $3.4 trillion in assets under management globally. |
Technological factors
Technological advancements are significantly reshaping the waste management landscape, directly influencing CNIM's environmental sector operations. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is proving crucial for boosting the precision and effectiveness of waste sorting processes. Furthermore, the deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) devices is enabling smarter waste collection by optimizing routes and offering real-time operational data, a key factor for efficient logistics.
Emerging innovations such as plasma gasification and anaerobic digestion are pivotal in transforming waste into valuable resources, thereby fostering a more robust circular economy. These technologies allow for the conversion of materials previously considered refuse into energy or other usable byproducts. CNIM is well-positioned to capitalize on these advancements to enhance the overall efficiency and sustainability of its waste-to-energy facilities, aligning with global environmental goals.
The engineering and construction sectors are heavily embracing digitalization and automation, transforming how projects are managed. Tools like Building Information Modeling (BIM) software are now standard for creating digital representations of physical assets, facilitating better planning and execution. Cloud-based collaboration platforms and virtual reality (VR) systems are crucial for enabling seamless project oversight, especially for globally dispersed teams. CNIM can leverage these technologies to streamline operations and improve project delivery across its varied industrial activities.
AI-powered automation and advanced digital tools hold significant potential to boost workforce productivity within CNIM. These technologies can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up engineers and technicians for more complex problem-solving. Furthermore, by adopting cutting-edge digital solutions, CNIM can enhance its appeal to younger generations entering the workforce, who are often drawn to technologically advanced environments. This also directly contributes to improved safety protocols by minimizing human exposure to hazardous situations through robotic assistance and remote monitoring.
The global market for construction technology, including BIM and automation, is projected for substantial growth. For instance, the global construction technology market was estimated to be around $3 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% through 2030. This indicates a strong industry trend towards digital integration that CNIM can capitalize on to maintain its competitive edge.
Technological advancements are paramount in the defense industry, and CNIM Systèmes Industriels is actively demonstrating this with its latest innovations. They are presenting next-generation Motorized Floating Bridges designed to handle the weight of contemporary heavy tanks, a significant upgrade for military logistics. Furthermore, their unmanned systems, such as ROCUS for route clearance, highlight a move towards greater automation and reduced risk for personnel.
The increasing incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into defense systems is a transformative trend. This necessitates ongoing research and development for companies like CNIM to adapt to evolving military technologies and operational demands, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly modernizing landscape.
High-Precision Manufacturing and Scientific Instruments
CNIM's high-technology sector, particularly its work with large scientific instruments, is significantly influenced by ongoing progress in precision manufacturing and laboratory technologies. These advancements are crucial for developing and maintaining the sophisticated equipment that forms a core part of CNIM's offerings in fields like nuclear energy and space exploration. For instance, the global market for scientific instruments was projected to reach over $70 billion in 2024, highlighting the scale of this technologically driven sector.
Key innovations directly impacting CNIM include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies are being used to automate complex data analysis, a vital component in scientific research, and to enable predictive maintenance for sensitive instruments, reducing downtime and ensuring operational continuity. The market for AI in scientific instruments is expected to see substantial growth, potentially reaching tens of billions by the late 2020s.
Furthermore, the trend towards miniaturization and portability in scientific instruments is opening new avenues for application and deployment. This allows for more flexible and on-site data collection, which is beneficial for field research and complex industrial monitoring. Simultaneously, advancements in advanced imaging technologies, such as high-resolution microscopy and spectral analysis, are enhancing the accuracy and depth of scientific discovery, directly supporting CNIM's role in cutting-edge research infrastructure.
These technological shifts collectively contribute to more efficient and accurate scientific research and instrument development, which are fundamental to CNIM's strategic positioning. The company's ability to leverage these advancements ensures its continued relevance and competitiveness in sectors demanding unparalleled precision and technological sophistication.
- Market Growth: The global scientific instruments market is a robust and expanding sector, with significant investment in R&D underpinning its growth trajectory.
- AI Integration: AI and ML are transforming data analysis and operational efficiency for scientific equipment, a trend that CNIM can capitalize on.
- Miniaturization: The drive for smaller, more portable instruments expands application possibilities and data acquisition methods.
- Imaging Technology: Enhanced imaging capabilities are critical for pushing the boundaries of scientific understanding and instrument performance.
Energy Efficiency and Decarbonization Technologies
The global drive for decarbonization and energy efficiency is a significant technological catalyst, spurring innovation across the energy sector. This trend directly impacts companies like CNIM, pushing for advancements in areas such as cleaner syngas production through sophisticated gasification technologies. For instance, the market for CCUS technologies, crucial for reducing emissions, is projected to grow substantially, with some estimates placing its value in the hundreds of billions of dollars by the early 2030s.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies is becoming essential for optimizing energy recovery at waste-to-energy (WtE) facilities. CNIM's established expertise in thermal power plants presents a clear avenue for evolution by incorporating these advanced solutions. This strategic integration is key to meeting increasingly stringent emission targets, such as those outlined in the European Union's Green Deal, and for actively contributing to the development of a carbon-neutral economy.
- Advancements in Gasification: Development of next-generation gasification processes to produce cleaner syngas, reducing downstream processing needs.
- CCUS Integration: Implementation of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage solutions to mitigate emissions from thermal processes.
- Smart WtE Optimization: Deployment of IoT and AI for real-time monitoring and control of waste-to-energy plants to maximize efficiency and energy recovery.
- Emission Target Alignment: Focus on technologies that help meet and exceed evolving environmental regulations and carbon neutrality goals.
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping CNIM's operational landscape, driving innovation across its diverse sectors. From AI-powered waste sorting to advanced gasification for cleaner energy, these innovations are critical for efficiency and sustainability. CNIM's engagement with cutting-edge technologies like BIM, IoT, and unmanned systems positions it to enhance project delivery, optimize resource management, and maintain a competitive edge in evolving global markets.
| Technology Area | Impact on CNIM | Market Growth/Data (2024/2025) |
| AI & Machine Learning | Enhanced waste sorting, predictive maintenance for scientific instruments, process optimization | Global AI in scientific instruments market projected to reach tens of billions by late 2020s. |
| IoT & Smart Technologies | Optimized waste collection routes, smart WtE facility management | IoT in waste management market expected to grow significantly, reaching over $10 billion by 2025. |
| Digitalization (BIM, Cloud, VR) | Streamlined construction project management, improved collaboration | Global construction technology market projected for CAGR over 15% through 2030. |
| Advanced Gasification & CCUS | Cleaner syngas production, emissions reduction | CCUS technologies market expected to grow into hundreds of billions by early 2030s. |
| Unmanned Systems & Automation | Route clearance, reduced personnel risk in defense | Global drone market expected to exceed $40 billion by 2025. |
Legal factors
CNIM Group must navigate the evolving landscape of EU environmental regulations, with the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) and the new Industrial Emissions Portal Regulation (IEPR), effective from 2024, imposing stricter emission limits. These directives demand a proactive approach to sustainability and compliance.
The updated IEPR, for instance, mandates electronic permitting processes and requires companies like CNIM to create detailed 'transformation plans' aimed at achieving climate neutrality by 2050. This includes a significant focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving energy efficiency across operations.
Failure to adhere to these increasingly stringent environmental standards can lead to considerable financial penalties, potentially impacting CNIM Group's profitability and operational continuity. Consequently, ongoing investment in cleaner technologies and sustainable operational practices is a critical imperative.
Legal frameworks are significantly shaping the energy landscape for companies like CNIM Group. For instance, the revised Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD), which became effective in May 2024, along with the Energy Efficiency Directive (EED), places new obligations on energy savings and the adoption of renewable energy sources across buildings and industrial sectors.
These directives are designed to bolster energy independence and curb overall energy consumption. This directly influences CNIM's energy solutions by prioritizing projects that meet stringent efficiency and renewable energy targets, while simultaneously leading to a gradual reduction in incentives for fossil fuel-based systems.
In 2023, the European Union continued to advance its energy efficiency goals, with member states reporting progress toward their 2030 targets. For example, national energy efficiency plans submitted in late 2023 indicated a collective effort to reduce final energy consumption by approximately 11.7% below 2020 levels by 2030, a figure that will continue to drive demand for CNIM's expertise in sustainable energy solutions.
CNIM Group's defense operations are heavily shaped by a complex web of national and international procurement laws, stringent export controls, and overarching security agreements. Navigating these regulations is paramount for securing lucrative defense contracts and maintaining access to sensitive military markets.
The growing trend of defense cooperation within the European Union and NATO, including joint procurement initiatives, presents both opportunities and challenges. For instance, the European Defence Fund (EDF) aims to foster collaborative research and development, potentially influencing contract allocation and market entry for companies like CNIM. These collaborative efforts, driven by a desire for greater interoperability and efficiency, could see increased contract values in shared projects, with the EDF allocating €7.03 billion for 2021-2027.
Compliance with these intricate legal frameworks is not merely a procedural step but a critical business imperative. Failure to adhere to export control regulations, for example, can result in significant penalties, reputational damage, and the loss of essential market access. CNIM's ability to effectively manage these legal requirements directly impacts its capacity to compete and succeed in the global defense industry.
Corporate Governance and Reporting Requirements
As a public entity, CNIM Group operates under stringent corporate governance and financial reporting mandates. The European Union's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is a key legal factor, with its application expanding significantly in 2025. This directive necessitates detailed sustainability disclosures, covering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, thereby boosting transparency and accountability for companies like CNIM.
Compliance with the CSRD requires CNIM Group to implement and maintain robust internal reporting systems capable of capturing and presenting comprehensive ESG data. This includes reporting on climate-related risks and opportunities, social impacts on employees and communities, and governance structures. For instance, the directive will require reporting on Scope 1, 2, and potentially Scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
CNIM Group's adherence to these regulations impacts its strategic planning and operational execution. Failure to comply can result in penalties and reputational damage. The increasing focus on ESG performance by investors and stakeholders means that strong corporate governance and transparent reporting are no longer just a legal obligation but a competitive advantage.
Key legal factors affecting CNIM Group include:
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD): Mandates extensive ESG disclosures for large EU companies, phased in from 2024 and expanding in 2025.
- Financial Reporting Standards: Adherence to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or equivalent national standards for accurate financial statements.
- Market Abuse Regulations: Compliance with rules preventing insider trading and market manipulation to ensure fair and orderly markets.
- Environmental Regulations: Adherence to EU and national environmental laws concerning emissions, waste management, and pollution control impacting its industrial operations.
Waste Management and Circular Economy Legislation
Legislation focused on advancing the circular economy and implementing more rigorous waste management protocols directly influences CNIM Group's waste-to-energy operations. For instance, new regulations in various jurisdictions, such as the proposed Solid Waste Management Rules 2024, alongside ambitious EU waste management targets aiming for specific recycling rates by 2030, create a dynamic operating environment.
These legal frameworks are designed to boost recycling percentages, minimize landfill dependency, and introduce extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes. This, in turn, fuels market demand for sophisticated waste treatment and recycling technologies, areas where CNIM has significant expertise.
CNIM must navigate these evolving legal requirements to sustain its competitive edge and ensure compliance, thereby avoiding potential financial penalties and maintaining its operational licenses. The group's ability to adapt to these stringent environmental mandates is key to its ongoing success.
- EU targets aim for at least 65% of municipal waste to be recycled by 2035.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes are becoming more widespread, increasing manufacturer accountability for product lifecycles.
- Stricter landfill diversion targets mean less organic waste can be sent to landfills, necessitating advanced treatment methods.
- The global waste management market is projected to reach over $2 trillion by 2030, driven by regulatory pressures and sustainability initiatives.
CNIM Group's operations are significantly influenced by evolving environmental legislation, particularly concerning emissions and energy efficiency. The EU's Industrial Emissions Directive and the new Industrial Emissions Portal Regulation, effective from 2024, impose stricter limits, requiring transformation plans for climate neutrality by 2050. Similarly, the revised Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) and Energy Efficiency Directive (EED), effective May 2024, mandate energy savings and renewable energy adoption. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in substantial financial penalties.
The defense sector faces stringent procurement laws, export controls, and security agreements. Initiatives like the European Defence Fund (EDF), which allocated €7.03 billion for 2021-2027, encourage collaborative R&D and can impact contract allocation. Effective management of these legal requirements is crucial for market access and competitiveness.
Corporate governance and financial reporting are also key legal factors. The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) expands in 2025, requiring detailed ESG disclosures and robust internal reporting systems for greenhouse gas emissions. Compliance with these mandates is essential for transparency and investor confidence.
Circular economy and waste management laws are shaping CNIM's waste-to-energy business. With EU targets aiming for 65% municipal waste recycling by 2035 and growing Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes, CNIM's expertise in advanced waste treatment is increasingly in demand. Navigating these regulations is vital for maintaining operational licenses and avoiding penalties.
| Legal Factor | Description | Impact on CNIM Group | Key Data/Target |
| CSRD | Mandatory ESG disclosures | Requires robust data reporting systems, impacts strategic planning | Phased in from 2024, expanding in 2025 |
| EPBD & EED | Energy efficiency and renewables | Prioritizes sustainable energy solutions, reduces fossil fuel system incentives | Revised directives effective May 2024 |
| EU Waste Targets | Circular economy and recycling | Drives demand for waste treatment tech, requires compliance | 65% municipal waste recycled by 2035 |
| EDF | Defense R&D and procurement | Influences contract allocation and market entry in defense | €7.03 billion allocated for 2021-2027 |
Environmental factors
Global and regional concerns about climate change are significantly intensifying the drive for decarbonization, directly impacting CNIM's operations within the energy and industrial sectors. These environmental pressures are not abstract; they translate into concrete regulatory and market demands.
The European Union's ambitious climate targets, aiming for a 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and achieving net-zero by 2050, mandate substantial investments in cleaner technologies and sustainable practices across all industrial operations. This regulatory landscape directly influences the strategic direction and operational adjustments required for companies like CNIM.
CNIM's core business, including its waste-to-energy solutions and thermal power plants, must actively adapt to these increasingly stringent carbon reduction goals. This adaptation likely involves integrating advanced technologies such as carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) to meet compliance and maintain competitiveness in a low-carbon economy.
Growing global awareness of resource limitations and the push for circular economy models directly impact industrial players like CNIM. This shift prioritizes minimizing waste, boosting recycling, and maximizing material reuse. For instance, the Ellen MacArthur Foundation projects that a fully circular economy for plastics could deliver a net positive environmental impact and significant economic benefits by 2050.
CNIM’s core competencies in waste-to-energy and advanced waste treatment are particularly relevant here. These capabilities offer solutions for recovering valuable resources from waste streams, significantly reducing the burden on landfills. In 2023, the European Environment Agency reported that recycling rates across the EU continued to climb, indicating a strong market for circular economy solutions.
By providing technologies that enable resource recovery and reduce reliance on virgin materials, CNIM is well-positioned to capitalize on this evolving economic landscape. This strategic alignment creates new avenues for growth and reinforces the company's role in a more sustainable, resource-efficient future.
The global waste generation is a critical environmental concern, with projections indicating a significant increase. In 2023, global waste was estimated at 2.3 billion tonnes, and this figure is expected to reach 3.4 billion tonnes by 2050 if current trends continue. E-waste, in particular, is a rapidly growing segment, with 62 million tonnes generated globally in 2023, a 5.1% increase from 2022. This escalating volume necessitates sophisticated waste management and pollution control strategies.
Public and regulatory bodies are increasingly demanding more effective solutions. For instance, the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan sets ambitious targets for waste reduction and recycling. These pressures drive a need for advanced technologies in waste treatment facilities, such as those operated by CNIM. Companies must invest in innovations like AI-driven sorting to improve material recovery rates and comply with evolving environmental standards.
CNIM's expertise in waste-to-energy and waste treatment plants directly addresses these environmental challenges. The company's solutions aim to convert waste into valuable resources while minimizing environmental impact. In 2024, investments in advanced recycling technologies, including chemical recycling for plastics, are becoming crucial for meeting stringent pollution control requirements and achieving higher material circularity.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Protection
Environmental factors, particularly concerning biodiversity and ecosystem protection, are increasingly shaping industrial operations for companies like CNIM Group. These considerations directly impact the siting, design, construction, and ongoing operation of industrial facilities, demanding a keen awareness of ecological footprints.
Projects must navigate a growing landscape of regulations designed to minimize harm to natural habitats and biodiversity. While specific data for CNIM's direct biodiversity impact isn't publicly detailed, the broader industrial sector, especially in large-scale infrastructure and energy projects, frequently undergoes rigorous environmental impact assessments to evaluate potential effects on local ecosystems. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to strengthen its biodiversity strategy, with initiatives like the Nature Restoration Law aiming for significant ecological improvements by 2030, influencing project approvals across member states.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Industrial projects face heightened scrutiny regarding their impact on sensitive ecosystems and biodiversity, often requiring comprehensive environmental impact assessments.
- Ecological Footprint: Companies must increasingly demonstrate strategies to minimize their ecological footprint, from site selection to operational practices.
- Biodiversity Strategy Alignment: Adherence to evolving biodiversity strategies, such as those promoted by the EU, is becoming critical for project viability and corporate reputation.
- Ecosystem Services Valuation: There's a growing trend in valuing ecosystem services, which can influence project cost-benefit analyses and the adoption of nature-based solutions.
Water Management and Emissions from Operations
CNIM Group's industrial activities are directly impacted by stringent environmental regulations governing water management and emissions. The European Union's revised Industrial Emissions Directive is a significant driver, targeting a substantial reduction in air pollutant emissions. Specifically, the directive aims for up to a 40% decrease in key air pollutants by 2050, using 2020 levels as a baseline. This regulatory push mandates the adoption of sophisticated pollution control technologies and highly efficient water management systems across all CNIM's industrial sites.
Ensuring compliance with these evolving environmental standards is crucial for CNIM to maintain its operational license and minimize its ecological impact. The directive's focus on reducing emissions into both air and water necessitates continuous investment in advanced abatement technologies and water recycling processes.
Key considerations for CNIM include:
- Water Usage Optimization: Implementing closed-loop water systems and advanced filtration to reduce freshwater intake and wastewater discharge.
- Air Emission Control: Investing in state-of-the-art scrubbers, filters, and catalytic converters to meet stringent air quality standards.
- Compliance Monitoring: Establishing robust systems for continuous monitoring and reporting of emissions and water discharge to regulatory bodies.
- Technological Upgrades: Regularly assessing and upgrading industrial processes and equipment to incorporate the latest pollution prevention and control technologies.
Environmental factors like climate change and resource scarcity are driving significant shifts in industrial practices, directly influencing CNIM Group. The push for decarbonization and circular economy principles necessitates innovation in waste management and energy solutions. For instance, global waste generation is projected to reach 3.4 billion tonnes by 2050, highlighting the demand for advanced treatment technologies.
CNIM's expertise in waste-to-energy and resource recovery aligns with these evolving environmental demands, positioning the company to benefit from increased investments in sustainable infrastructure. The EU's commitment to a circular economy, with rising recycling rates, further underscores the market opportunity for CNIM's solutions.
Stringent environmental regulations, such as the EU's Industrial Emissions Directive, mandate significant reductions in air and water pollutants. CNIM must continuously invest in advanced pollution control and water management technologies to ensure compliance and minimize its ecological footprint.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on CNIM Group | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change & Decarbonization | Increased demand for low-carbon technologies, pressure to reduce operational emissions. | EU's net-zero targets by 2050 drive investment in CCUS and efficient energy solutions. |
| Circular Economy & Resource Management | Opportunity for waste-to-resource technologies, focus on recycling and material reuse. | Rising global waste volumes (2.3 billion tonnes in 2023) create demand for advanced waste treatment. |
| Biodiversity & Ecosystem Protection | Need for rigorous environmental impact assessments, focus on minimizing ecological footprint. | EU's biodiversity strategies (e.g., Nature Restoration Law) influence project approvals and site selection. |
| Water & Air Quality Regulations | Mandatory upgrades for pollution control and water management systems. | EU's Industrial Emissions Directive aims for up to 40% reduction in key air pollutants by 2050. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for CNIM Group is meticulously constructed using data from reputable sources, including official government publications, international financial institutions, and leading industry research firms. We ensure every insight, from political stability to technological advancements, is grounded in verifiable and current information.
