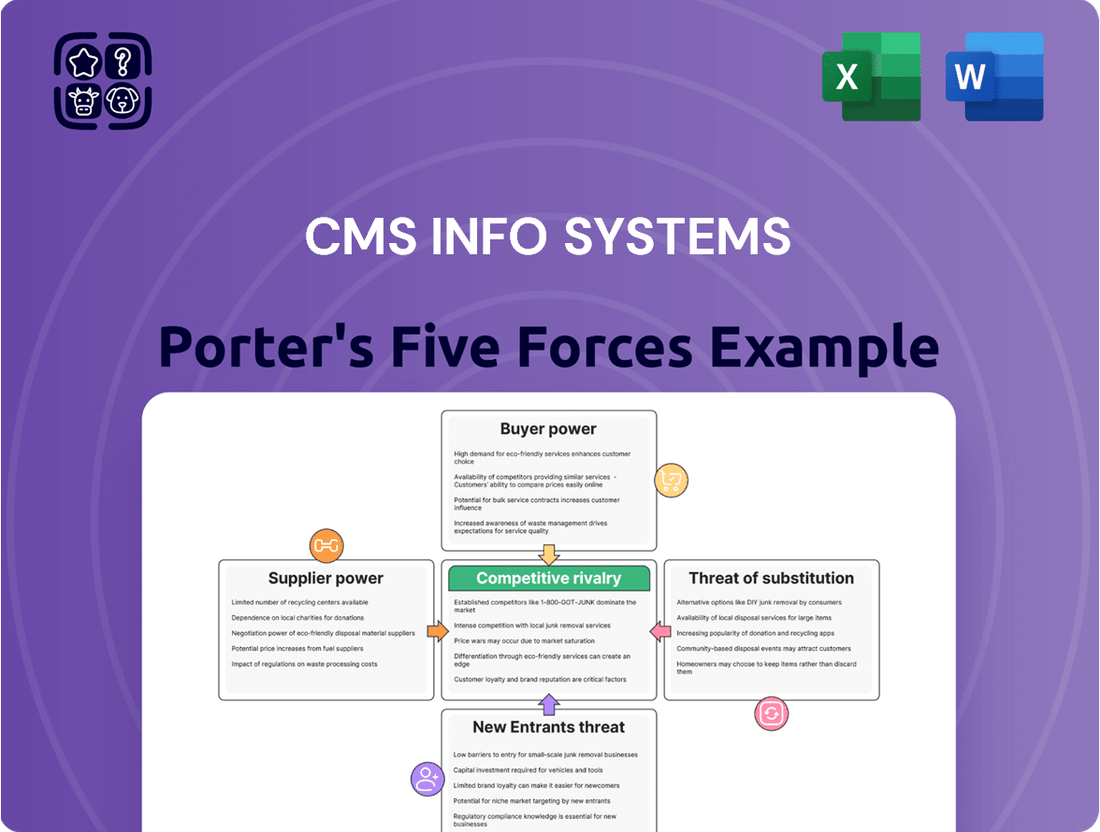
CMS Info Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CMS Info Systems Bundle
CMS Info Systems operates in a dynamic IT services landscape, where understanding the competitive forces is crucial for success. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intricate interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
The complete report unlocks a detailed examination of these forces, providing a data-driven framework to assess CMS Info Systems's competitive intensity and strategic positioning. Gain actionable insights to navigate market challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of CMS Info Systems’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CMS Info Systems' reliance on a mix of generic and specialized components for its cash management and technology solutions means the bargaining power of suppliers varies. For standard IT hardware or basic security equipment, where multiple vendors exist and specifications are uniform, individual supplier power is diminished. This situation allows CMS to secure better pricing and terms, as switching suppliers is a feasible option.
CMS Info Systems' reliance on niche technology providers, especially for specialized areas like banking automation or sophisticated cash optimization analytics, can significantly influence supplier bargaining power. These providers often possess unique, hard-to-replicate solutions.
When there are few alternatives for these advanced technologies, suppliers gain leverage. This can translate into higher pricing or less favorable contract terms for CMS, impacting operational costs and flexibility. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that the market for specialized fintech solutions saw price increases averaging 8-12% due to high demand and limited specialized vendors.
The availability of skilled personnel for cash logistics, ATM maintenance, and technology solutions significantly impacts supplier power in the labor market. For instance, a shortage of trained security personnel or specialized IT professionals can elevate the bargaining power of these labor segments.
This increased leverage for workers, or their representative agencies, can translate into higher wage demands or recruitment costs for companies like CMS Info Systems. In 2024, the IT sector in India, a key market for CMS, continued to face a talent crunch, with demand for cybersecurity and cloud computing specialists outstripping supply, potentially driving up labor costs.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Suppliers of cash management equipment and services for companies like CMS Info Systems must adhere to strict regulations from bodies such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). These regulations cover areas like cash handling, security, and data privacy, making compliance a critical factor for suppliers.
Suppliers who possess the necessary certifications and consistently meet these regulatory demands often find themselves in a stronger negotiating position. Their ability to provide compliant and secure solutions is vital for CMS Info Systems to operate legally and maintain the trust of its financial institution clients.
For instance, in 2024, the RBI continued to emphasize enhanced security protocols for cash logistics, meaning suppliers with proven track records in meeting these evolving standards would have greater leverage. This focus on compliance directly impacts the cost and availability of specialized equipment and services, influencing the bargaining power of these key suppliers.
- Regulatory Adherence: Suppliers demonstrating consistent compliance with RBI mandates for cash handling and security gain leverage.
- Certification Value: Holding certifications for security, quality management, and operational standards strengthens a supplier's negotiating position.
- Essential Services: The critical nature of compliant cash management services makes suppliers who meet these requirements indispensable.
- Market Access: Suppliers unable to meet stringent regulatory and certification requirements are effectively excluded from serving the financial sector, reducing competition and empowering compliant suppliers.
Long-term Contracts and Partnerships
CMS Info Systems frequently enters into long-term agreements with its suppliers, particularly for essential technology and infrastructure. These arrangements offer predictable costs and supply continuity, but they can also reduce CMS's agility in seeking alternative vendors during the contract term, thereby enhancing supplier leverage.
For instance, in 2024, the IT hardware sector saw supply chain disruptions impacting lead times and costs for critical components. CMS's long-term contracts in this area would have offered some protection against immediate price hikes, but the commitment limits immediate recourse if a more cost-effective supplier emerges.
- Supplier Leverage: Long-term contracts can solidify supplier relationships but may also reduce a company's ability to quickly adapt to changing market prices or technological advancements from alternative providers.
- Contractual Safeguards: Implementing clauses for performance reviews, price adjustments based on market indices, and competitive re-bidding at renewal can mitigate supplier power.
- Strategic Sourcing: Diversifying the supplier base for non-critical components and maintaining strong relationships with multiple vendors can provide a counterbalance to the bargaining power of any single supplier.
The bargaining power of CMS Info Systems' suppliers is a critical factor, especially when dealing with specialized technology and niche components. In 2024, the market for advanced fintech solutions experienced price increases, with some specialized vendors seeing costs rise by 8-12% due to high demand and a limited number of providers.
Furthermore, the availability of skilled labor, particularly in IT and cash logistics, significantly influences supplier leverage. India's IT sector, a key operational area for CMS, continued to face a talent shortage in 2024, potentially driving up labor costs for specialized roles.
Suppliers who consistently meet stringent regulatory requirements, such as those mandated by the Reserve Bank of India for cash handling and security, hold a stronger negotiating position. The RBI’s continued emphasis on enhanced security protocols in 2024 further empowered compliant suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Technology Availability | High power for unique, hard-to-replicate solutions | 8-12% price increase in specialized fintech solutions |
| Skilled Labor Shortage | Increased power for labor segments in high demand | IT talent crunch in India, impacting specialized roles |
| Regulatory Compliance | Stronger position for compliant and certified suppliers | RBI focus on enhanced security protocols for cash logistics |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping the Information Systems industry, specifically for CMS Info Systems, by examining rivalry among existing firms, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products or services.
Instantly identify and quantify competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive five forces model, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments and pain point relief.
Customers Bargaining Power
CMS Info Systems’ customer base is concentrated among large banks, financial institutions, and major retail chains. These entities represent significant clients, often placing substantial orders for cash management and ATM outsourcing services. For instance, in FY2023, CMS Info Systems reported that its top 10 customers contributed approximately 40% of its revenue, highlighting the concentration and the bargaining power these large clients wield.
The substantial volume of business these customers provide allows them to negotiate favorable terms, including pricing and service level agreements. Their ability to switch providers, while potentially complex due to integration, is a constant consideration for CMS, influencing contract renewals and ongoing service delivery. This dynamic means CMS must continuously demonstrate value and competitive pricing to retain these key accounts.
While CMS Info Systems' customers, particularly large banks and retail chains, hold significant bargaining power due to their volume, the practicalities of switching cash management providers are substantial. These switching costs are a critical factor. For instance, a major bank might face millions in expenses to integrate a new cash handling system, retrain thousands of employees on new procedures, and ensure the new provider meets stringent security and compliance standards, a process that could take over a year to fully implement.
These considerable logistical hurdles and financial outlays mean that the immediate bargaining power of customers is somewhat curtailed. The potential savings or benefits from a new vendor must be weighed against the significant disruption and upfront investment required for a change. This inertia, driven by the complexity of migration, can effectively dampen a customer's ability to exert immediate pressure for lower prices or better terms from CMS Info Systems.
For banks and financial institutions, the reliability and security of cash management services are absolutely critical. Disruptions can result in substantial financial losses and severe reputational damage. This intense need for dependable, secure operations means customers are willing to prioritize proven providers over simply seeking the lowest cost.
CMS Info Systems, as a key player in cash management, understands this. In 2023, the company reported a significant portion of its revenue derived from long-term contracts with major banks, highlighting the sticky nature of these relationships built on trust and consistent service delivery. While customers hold bargaining power, their reliance on secure and efficient cash handling limits their ability to switch providers solely based on price, especially given the high switching costs and inherent risks involved.
Customer's Internal Capabilities
Customers, particularly large banks and financial institutions, may possess or consider developing internal capabilities for cash logistics or technology solutions. This potential for self-sufficiency acts as a significant bargaining chip, enabling them to negotiate more favorable terms with service providers like CMS Info Systems. For instance, a major bank exploring in-house cash management could leverage this threat to secure lower service fees.
The credible threat of developing in-house capabilities, even if not fully implemented, empowers customers. It forces external providers to offer more competitive pricing and enhanced service levels to retain business. This dynamic is crucial in industries where outsourcing is common but the option to insource always looms.
- Customer Capability Development: Large financial institutions often have the resources and expertise to manage certain operational aspects internally, such as cash handling or IT support.
- Negotiation Leverage: The prospect of a customer bringing services in-house provides a strong negotiating position, pushing providers to offer better value.
- Industry Trend: As of early 2024, there's a continued trend of financial institutions evaluating their core competencies and the cost-effectiveness of outsourcing versus insourcing certain functions.
Industry Consolidation Among Customers
Industry consolidation among customers significantly amplifies their bargaining power with CMS Info Systems. As the banking and retail sectors in India consolidate, fewer, larger entities emerge, each representing a more substantial portion of CMS's overall revenue.
This concentration means CMS becomes more reliant on these key clients, making them more vulnerable to demands for lower prices or more favorable terms. For instance, if a major bank that accounts for 10% of CMS's revenue merges with another, the combined entity's share of CMS's business could rise dramatically, increasing its leverage.
- Increased Customer Concentration: Consolidation reduces the number of significant customers.
- Amplified Revenue Dependence: Each remaining large customer represents a greater percentage of CMS's total income.
- Heightened Pricing Pressure: Larger, consolidated customers can more effectively negotiate lower service fees.
- Greater Influence on Terms: Dominant customers can dictate service level agreements and payment cycles.
The bargaining power of CMS Info Systems' customers is significant, primarily due to the concentrated nature of their client base, which includes major banks and retail chains. These large entities account for a substantial portion of CMS's revenue; for example, their top 10 customers contributed around 40% of revenue in FY2023.
While customers possess considerable leverage due to their purchasing volume, the high switching costs and the critical need for reliability in cash management services somewhat mitigate this power. The logistical complexities, potential financial losses, and reputational risks associated with changing providers mean that customers often prioritize dependable service over solely seeking lower prices.
Furthermore, the potential for customers to develop in-house capabilities, coupled with industry consolidation, further strengthens their negotiating position. This forces CMS to continuously offer competitive pricing and robust service levels to retain these vital accounts.
| Customer Segment | Revenue Contribution (FY2023 est.) | Key Bargaining Factors | Mitigating Factors for CMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Banks | Significant portion of top 10 customers | High volume, potential insourcing, switching costs | Need for reliability, security, reputational risk |
| Financial Institutions | Contributes to top 10 customer revenue | Volume, consolidation | Switching complexity, long-term contracts |
| Major Retail Chains | Part of overall customer base | Volume, potential insourcing | Operational reliance, integration costs |
Full Version Awaits
CMS Info Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of CMS Info Systems, detailing competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing information.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian cash management sector is characterized by a moderate level of fragmentation, with CMS Info Systems holding the leading position. However, the competitive landscape is robust, featuring other substantial players such as SIS Prosegur, Brink's Arya, Writer Safeguard, Securevalue, Logicash, and Radiant Cash. This dynamic means there's consistent competition for market share among these established entities.
The cash logistics sector, a cornerstone of CMS Info Systems' operations, frequently experiences significant price sensitivity. Large clients, such as major banks, consistently prioritize cost-efficiency for their high-volume, standardized needs, including ATM cash replenishment and secure cash-in-transit services.
This customer focus on affordability fuels intense price-based competition among cash logistics providers. For instance, in 2023, the average contract value for ATM cash management services saw a slight decrease as companies vied for market share through competitive pricing strategies.
While basic cash handling is becoming a commodity, the real battleground for CMS Info Systems lies in its specialized services. Competitors are increasingly vying for market share through advanced solutions like managed services and integrated technology platforms. This shift means that simply offering cash logistics isn't enough; companies need to provide a more comprehensive package.
CMS is actively carving out its niche by emphasizing value-added services. Their investment in banking automation, for instance, streamlines operations for financial institutions, setting them apart. Furthermore, the integration of AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) for remote monitoring and data analytics offers predictive maintenance and operational insights, a significant differentiator.
This strategic focus on technology and analytics helps CMS move beyond price-based competition. For example, in the fiscal year 2024, CMS reported a significant increase in its managed services revenue, indicating a growing demand for these differentiated offerings. This allows them to command better margins and build stronger, more sticky relationships with clients.
Geographic Reach and Network Density
Competitive rivalry within the cash management sector is intensified by the breadth of geographic reach and the density of service networks. CMS Info Systems, holding the position of India's largest cash management company, leverages its extensive network of ATM points and retail pick-up locations. This vast infrastructure provides a substantial competitive edge against smaller, more localized competitors.
The density of CMS Info Systems' network, encompassing over 120,000 touchpoints as of early 2024, allows for efficient cash handling and faster service delivery across diverse geographies. This extensive presence makes it challenging for new entrants or smaller firms to replicate the same level of accessibility and operational efficiency.
- Extensive Network: CMS Info Systems operates over 120,000 touchpoints across India, facilitating widespread cash collection and distribution.
- Competitive Advantage: This dense network offers a significant barrier to entry and a key differentiator against less established players.
- Operational Efficiency: The broad geographic reach and network density contribute to economies of scale and improved operational cost-effectiveness.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Technological advancements are significantly reshaping the competitive arena for companies like CMS Info Systems. Those that prioritize and successfully implement innovative solutions, such as AI-driven cash optimization and integrated payment systems, are better positioned to capture market share. For instance, CMS's strategic investments in technology, including its ALGO AIoT Remote Monitoring solutions, are vital for sustaining its competitive advantage in this dynamic environment.
The drive for innovation is a key differentiator. Companies are increasingly leveraging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) to enhance their service offerings and operational efficiency. This focus on cutting-edge solutions allows them to offer more sophisticated and value-added services to their clients, thereby strengthening their market position.
- AI/ML for Cash Optimization: Technologies that predict cash demand and optimize ATM replenishment routes can lead to significant cost savings and improved service availability.
- Remote Monitoring: Advanced remote monitoring systems, often leveraging AIoT, enable proactive issue detection and resolution, minimizing downtime and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Integrated Payment Platforms: The convergence of cash management with digital payment solutions creates seamless customer experiences and opens new revenue streams.
- CMS's Technology Focus: CMS's commitment to developing and deploying these advanced technologies is crucial for its ongoing competitiveness and market leadership.
The competitive rivalry in India's cash management sector is intense, with CMS Info Systems leading a market that includes significant players like SIS Prosegur and Brink's Arya. This rivalry is driven by price sensitivity, especially for high-volume services like ATM replenishment, leading to a constant battle for market share through competitive pricing. However, differentiation is increasingly found in specialized, technology-driven services, where CMS is investing heavily.
CMS Info Systems' extensive network, boasting over 120,000 touchpoints as of early 2024, provides a substantial competitive advantage, making it difficult for smaller rivals to match its reach and operational efficiency. This dense infrastructure allows for economies of scale and improved cost-effectiveness, a key factor in a price-sensitive market.
Technological innovation is a critical battleground, with companies like CMS leveraging AI and IoT for optimized cash management and remote monitoring. CMS's strategic investments in solutions like its ALGO AIoT Remote Monitoring are vital for maintaining its edge. For example, in FY2024, CMS saw a notable increase in managed services revenue, highlighting the growing demand for these advanced, value-added offerings that move beyond basic cash handling.
The sector is characterized by a moderate level of fragmentation, but CMS Info Systems holds the dominant position. The company's focus on value-added services, such as banking automation and AIoT integration, helps it move beyond pure price competition and command better margins. This strategic differentiation is crucial for sustained market leadership in a dynamic environment.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for cash management services like those offered by CMS Info Systems stems from the explosive growth of digital payment platforms, especially India's Unified Payments Interface (UPI). UPI transactions have seen a dramatic increase, with their proportion of all transactions doubling to reach 70% by March 2024. This rapid adoption and continued projected growth directly challenge the need for traditional cash handling, potentially diminishing the demand for physical cash management.
The increasing adoption of digital payment platforms, particularly Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in India, is significantly diminishing the reliance on cash for small transactions. This shift directly impacts businesses like CMS Info Systems, which are involved in cash handling and logistics.
In 2023, UPI transactions in India crossed the 100 billion mark, a substantial increase from previous years, highlighting the rapid move away from cash for everyday purchases. This trend reduces the overall volume of physical currency needed for circulation, potentially lowering demand for cash collection and replenishment services.
The threat of substitutes for CMS Info Systems in banking automation is present, particularly from larger financial institutions developing their own in-house cash management solutions. These banks might invest in advanced technologies like automated cash recycling machines or internal cash processing units, aiming to reduce their dependence on external service providers for certain cash handling operations.
Alternative Financial Technologies (FinTech)
Emerging FinTech solutions, even if not directly replacing cash, can indirectly reduce the reliance on traditional cash management services. For instance, innovations in digital lending and online payment gateways streamline financial processes, potentially diminishing the volume of physical cash transactions that CMS Info Systems handles.
These FinTech advancements, by offering more convenient and efficient alternatives for various financial needs, could shift overall transaction patterns. This shift may move away from cash-centric models towards digital-first approaches, impacting the demand for cash handling and ATM services. For example, the global FinTech market size was valued at approximately $2.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong trend towards digital financial solutions.
- Digital Payment Growth: The increasing adoption of digital payment methods, such as mobile wallets and online transfers, directly reduces the need for physical cash handling.
- FinTech Lending Platforms: Innovations in peer-to-peer lending and digital credit scoring offer alternatives to traditional cash-based loan disbursements.
- Wealth Management Tools: Robo-advisors and digital investment platforms are making wealth management more accessible, potentially reducing reliance on cash for investment purposes.
- Cross-Border Payment Solutions: FinTech companies are providing faster and cheaper ways to send money internationally, bypassing traditional cash remittance channels.
Government Initiatives for a Less-Cash Economy
The Indian government and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) have been actively pushing for a less-cash economy. Initiatives like the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) have seen massive adoption, with UPI transactions in India reaching an average of 12.04 billion in the first half of 2024, according to NPCI data. This shift represents a gradual substitution threat to traditional cash management services, as digital payments become more prevalent.
While cash remains significant, these long-term policy directions aim to reduce reliance on physical currency. The continued growth of digital payment infrastructure and evolving consumer behavior in India, supported by government mandates, suggests a persistent, albeit slow, substitution pressure on cash-centric business models.
- Digital Payment Growth: India's digital payments market is projected to reach $1 trillion by 2026, indicating a strong trend away from cash.
- UPI Dominance: UPI has become a primary payment method, handling over 12 billion transactions in early 2024, directly impacting cash volumes.
- Government Push: Policies encouraging financial inclusion and digitization indirectly reduce the demand for cash handling services.
The growing preference for digital transactions, particularly in India with UPI, presents a significant substitute threat to cash management services. UPI transactions in India averaged 12.04 billion in the first half of 2024, a clear indicator of reduced reliance on physical cash for everyday payments.
This digital shift, supported by government initiatives aiming for a less-cash economy, directly impacts the volume of cash requiring handling, collection, and replenishment by companies like CMS Info Systems.
Furthermore, FinTech innovations in lending and payments streamline financial processes, indirectly lessening the demand for traditional cash-centric operations.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Cash Management | Key Data/Trend |
| Digital Payment Platforms (e.g., UPI) | Reduces demand for physical cash handling and logistics. | UPI transactions averaged 12.04 billion in H1 2024 in India. |
| FinTech Lending & Payment Solutions | Streamlines financial processes, potentially lowering cash transaction volumes. | Global FinTech market valued at ~$2.5 trillion in 2023, showing strong digital adoption. |
| In-house Bank Solutions | Large banks may develop proprietary cash automation to reduce outsourcing. | Investment in advanced cash recycling machines by financial institutions. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the cash management sector, particularly to rival CMS Info Systems' established presence, demands immense capital. Think significant investments in secure transportation fleets, advanced vault facilities, and cutting-edge tracking technology. For instance, establishing a nationwide network requires billions of rupees in initial outlay, a daunting prospect for newcomers.
The sheer scale of operations CMS maintains, serving a vast array of banks and retail clients across India, presents another formidable hurdle. Replicating this extensive reach and logistical efficiency demands years of development and substantial ongoing operational expenditure, acting as a strong deterrent to potential entrants.
The cash management and logistics sector in India operates under a strict regulatory framework, primarily overseen by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and various other governmental bodies. This robust oversight creates significant barriers for potential new entrants.
Aspiring companies must navigate complex and costly licensing procedures, adhere to stringent compliance mandates, and implement rigorous security protocols. For instance, obtaining the necessary licenses can involve substantial capital investment and lengthy approval processes, making it difficult for smaller or less capitalized firms to enter the market.
These substantial entry barriers, characterized by significant upfront investment and ongoing compliance costs, effectively deter many potential competitors from challenging established players like CMS Info Systems.
CMS Info Systems benefits significantly from deeply entrenched customer relationships, particularly with major banks and financial institutions. These partnerships, forged over years of reliable and secure service delivery, represent a formidable barrier to entry for potential new competitors. Financial institutions, inherently cautious with their critical operations like cash management, are unlikely to switch from proven, trusted providers to unproven newcomers.
Economies of Scale and Network Effects
Existing players in the cash management and ATM services sector, like CMS Info Systems, have built substantial economies of scale. This means they can operate more efficiently and at a lower cost per unit due to their large operational size. For instance, in 2023, CMS Info Systems managed over 100,000 ATMs and cash processing points, enabling significant cost advantages in logistics, technology deployment, and bulk purchasing of equipment and supplies.
New entrants would face considerable challenges in matching these cost efficiencies. They would need to invest heavily to build a comparable infrastructure and customer base, making it difficult to compete on price against established players who have already amortized these initial costs. This cost barrier is a significant deterrent.
Furthermore, network effects play a crucial role. A larger network of ATMs and cash processing centers attracts more banks and retailers due to the convenience and reach it offers. This creates a virtuous cycle where more users lead to a more valuable network, making it harder for newcomers to gain traction. As of early 2024, CMS Info Systems' extensive network across India provides a distinct competitive edge that is difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Economies of Scale: CMS Info Systems leverages its large operational footprint to achieve lower per-unit costs in cash handling and ATM management.
- Network Effects: The company's extensive network of ATMs and cash points creates a strong pull for new clients, reinforcing its market position.
- Cost Barriers: New entrants would require substantial upfront investment to achieve comparable operational scale and cost efficiencies, posing a significant threat.
Access to Skilled Manpower and Technology
The cash management services industry demands a highly specialized workforce proficient in security protocols, intricate logistics, and advanced technology integration. New entrants would likely struggle to attract and retain this talent pool, facing significant recruitment costs and potential training investments. For instance, as of early 2024, the demand for cybersecurity professionals, a critical component of cash management technology, continued to outpace supply, with average salaries for experienced professionals in India often exceeding ₹15 lakhs annually, according to industry reports.
Developing or acquiring the proprietary technology necessary for efficient and secure cash handling, such as advanced cash sorting machines, cash-in-transit tracking software, and robust data analytics platforms, presents another substantial barrier. Integrating these systems seamlessly with the complex IT infrastructures of banking clients, which often involve legacy systems, requires considerable technical expertise and capital expenditure. The cost of such technological adoption can easily run into millions of dollars for a new player aiming to compete at scale.
- Specialized Workforce: High demand for security, logistics, and tech-savvy personnel.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: Difficulty in recruiting and retaining skilled staff, driving up labor costs.
- Technology Investment: Significant capital required for proprietary software, hardware, and integration.
- Integration Hurdles: Complexity in connecting new technologies with existing banking IT systems.
The threat of new entrants for CMS Info Systems is generally low due to substantial capital requirements, extensive operational scale, and stringent regulatory hurdles. These factors, combined with established customer loyalty and significant economies of scale achieved by CMS, make it difficult and costly for newcomers to gain a foothold in the cash management sector.
New players must overcome high initial investments in infrastructure, navigate complex licensing, and match the cost efficiencies of established firms. For instance, CMS Info Systems' 2023 operations managing over 100,000 ATMs highlight the scale advantage that deters new entrants.
The need for a specialized workforce and significant investment in proprietary technology further elevates the barriers. The difficulty in recruiting skilled talent, with cybersecurity professionals in India earning upwards of ₹15 lakhs annually in early 2024, adds to the cost burden for potential competitors.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in secure fleets, vaults, and technology. | Significant upfront cost, limiting potential entrants. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex licensing and stringent RBI oversight. | Lengthy approval processes and ongoing compliance costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large operational size. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies. |
| Network Effects | Wider reach attracts more clients, creating a virtuous cycle. | Difficult for newcomers to build comparable reach and value. |
| Talent Acquisition | High demand for specialized security and logistics personnel. | Increased recruitment and training costs for new firms. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CMS Info Systems Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including the company's annual reports, industry-specific market research from reputable firms, and publicly available regulatory filings. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
