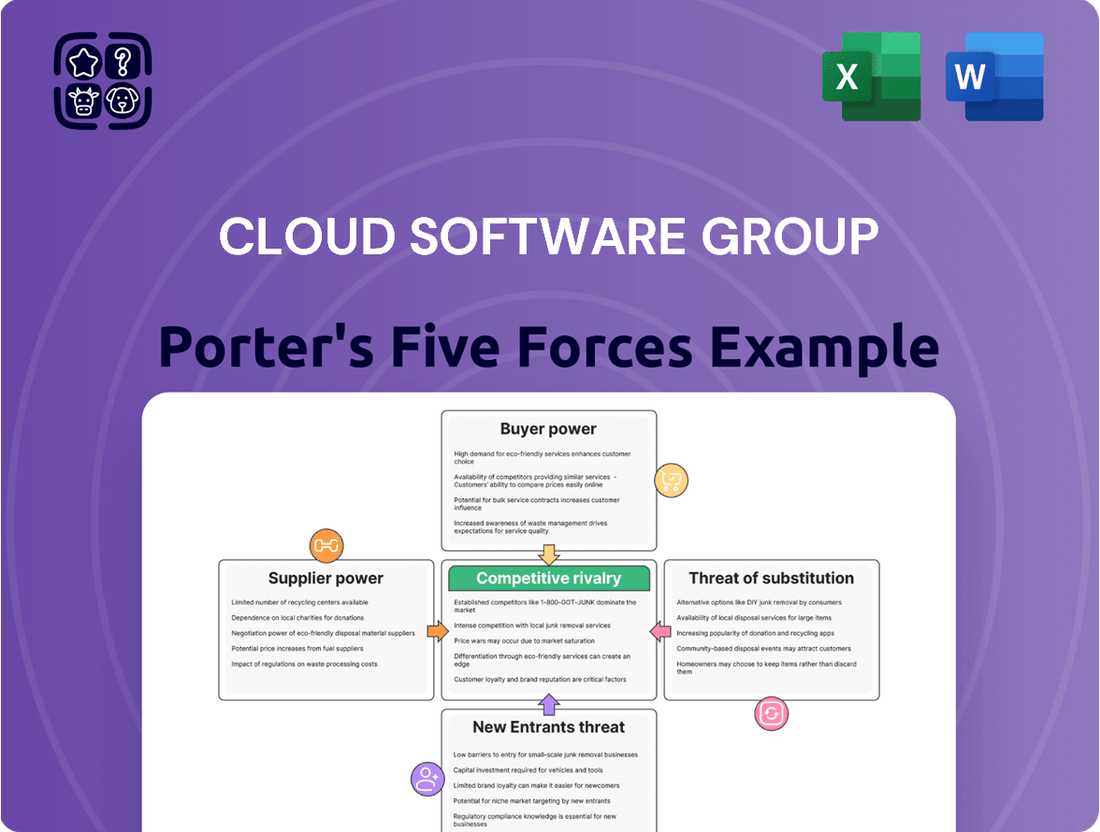
Cloud Software Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cloud Software Group Bundle
Cloud Software Group operates within a dynamic tech landscape, facing significant competitive rivalry and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating this market.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Cloud Software Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Cloud Software Group's reliance on hyperscale cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud is a major factor in supplier bargaining power. These providers dominate the market, offering economies of scale that are difficult for smaller players to match. For instance, in 2024, AWS held approximately 31% of the cloud infrastructure market share, followed by Microsoft Azure at around 24%, and Google Cloud at roughly 11%.
The significant switching costs associated with migrating complex enterprise workloads, which can involve substantial data transfer fees and re-architecting applications, further solidify the bargaining power of these infrastructure giants. This dependence can translate into higher operational expenses for Cloud Software Group if negotiations for favorable terms are unsuccessful, potentially impacting profitability and service pricing.
The specialized nature of enterprise cloud software development, especially in areas like AI, big data, and cybersecurity, means that highly skilled IT professionals are essential suppliers. A scarcity of this talent, or intense competition for their expertise, directly translates to higher labor costs for companies like Cloud Software Group. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cloud computing specialists outstripped supply, leading to average salary increases of 15-20% for senior roles in these fields, significantly impacting operational expenses.
Cloud Software Group, while strong in its core IP, might depend on external providers for certain software elements or development tools. If these are unique or come from a small selection of vendors, those suppliers gain bargaining power, influencing pricing and contract conditions.
This reliance can impact Cloud Software Group's product development costs and speed. For instance, a key software library used in their on-premises offerings might be controlled by a single entity, allowing that supplier to dictate terms, potentially increasing Cloud Software Group's operational expenses.
Operating System and Database Vendors
The bargaining power of operating system and database vendors is a significant consideration for Cloud Software Group. These foundational software providers, such as Microsoft for Windows or Oracle for its database solutions, can exert influence through their licensing terms and technical roadmaps. For instance, shifts in Microsoft's Azure-related licensing or Oracle's cloud-native database strategies could directly affect Cloud Software Group's operational costs and integration efforts.
While these vendors hold considerable sway, the broad adoption of their platforms by a wide range of businesses, including Cloud Software Group's clientele, can somewhat dilute their individual leverage. However, the sheer ubiquity of systems like Linux and SQL Server means Cloud Software Group must remain attuned to potential price increases or changes in support structures from these key technology partners. As of early 2024, the cloud infrastructure market continues to see substantial investment, with major OS and database providers actively shaping their offerings for cloud environments.
- Impact of Licensing: Changes in licensing models by major OS and database vendors can directly increase operational expenses for Cloud Software Group.
- Technical Dependencies: Evolving technical requirements from these foundational software providers can necessitate costly adjustments to Cloud Software Group's product development and deployment.
- Market Ubiquity: The widespread use of operating systems like Linux and databases like SQL Server by many businesses may offer some counterbalance to individual vendor power.
- Strategic Alignment: Cloud Software Group's ability to negotiate favorable terms often hinges on its strategic alignment with the long-term roadmaps of these critical technology suppliers.
Strategic Partnerships and Alliances
Cloud Software Group's ability to build strategic partnerships with key technology providers significantly impacts supplier power. By forging strong alliances, the company can negotiate more favorable terms, share development expenses, and create integrated solutions. This collaborative approach dilutes the individual leverage of any single supplier, as evidenced by the trend of major cloud providers forming deeper integrations with software vendors to offer bundled solutions, a strategy that gained momentum throughout 2024 with several key announcements regarding enhanced interoperability and co-development initiatives.
Conversely, a lack of diverse and robust partnerships can leave Cloud Software Group exposed to the demands of dominant technology partners. For instance, if a critical component of their software relies heavily on a single cloud infrastructure provider or a specialized software library, that supplier gains considerable bargaining power. Companies that actively diversified their technology stacks in 2024, seeking multiple providers for essential services like AI processing or data analytics, demonstrated greater resilience against supplier-driven price increases.
- Strategic Alliances Mitigate Supplier Power: Partnerships allow for shared development costs and integrated solutions, reducing individual supplier leverage.
- Diversification Reduces Vulnerability: A lack of diverse partnerships can make Cloud Software Group susceptible to demands from dominant technology providers.
- 2024 Trends: Major cloud providers intensified efforts to integrate with software vendors, offering bundled solutions and co-development, a trend that benefits companies like Cloud Software Group when they are the partners.
- Impact on Terms: Stronger alliances often translate into more favorable pricing and service level agreements for Cloud Software Group.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Cloud Software Group is significantly influenced by the concentration within the cloud infrastructure market. Dominant players like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, holding substantial market shares in 2024 (AWS ~31%, Azure ~24%, Google Cloud ~11%), possess considerable leverage due to economies of scale and high switching costs for enterprise clients.
Furthermore, the specialized nature of talent in areas like AI and big data creates leverage for skilled IT professionals, with demand outpacing supply in 2024, leading to significant salary increases for senior roles. Dependence on single vendors for critical software components or development tools also empowers those suppliers, potentially increasing Cloud Software Group's operational expenses.
| Supplier Type | Market Dominance (2024) | Impact on Cloud Software Group |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperscale Cloud Providers | AWS (~31%), Azure (~24%), Google Cloud (~11%) | High bargaining power due to scale and switching costs; potential for increased operational expenses. |
| Specialized IT Talent | High demand, limited supply for AI, big data, cybersecurity roles | Increased labor costs due to competitive hiring and salary hikes (15-20% for senior roles). |
| Proprietary Software/Tools | Varies, but single-vendor dependence increases power | Potential for higher licensing fees and dictated contract terms, impacting development costs. |
| OS and Database Vendors | Ubiquitous platforms (e.g., Microsoft, Oracle) | Influence through licensing and technical roadmaps; requires strategic alignment for favorable terms. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Cloud Software Group, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic visualization of all five forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cloud Software Group's customer base is heavily skewed towards large enterprises. This concentration means that a significant portion of their revenue comes from a relatively smaller number of clients. For instance, in 2024, it's estimated that the top 10 enterprise clients accounted for over 40% of the company's recurring revenue.
Large enterprises wield considerable bargaining power. Their substantial purchasing volumes allow them to demand lower prices, more favorable contract terms, and customized solutions. These clients often employ sophisticated procurement departments capable of extensive negotiation, putting pressure on Cloud Software Group to offer competitive pricing and robust service level agreements.
The ability of these major clients to switch providers, while potentially costly, is a constant threat that enhances their leverage. Their significant budget allocations make them highly attractive, and their demands for tailored features or integrated services can also influence product development roadmaps, further amplifying their influence.
While Cloud Software Group's customers are often large enterprises, the deep integration of their solutions, such as Citrix for application delivery and TIBCO for data management, into critical IT infrastructure significantly raises switching costs. This extensive embedding means migrating away from these systems is inherently complex, time-consuming, and expensive, often necessitating substantial retraining and risking operational disruptions.
The enterprise software market is highly competitive, giving customers numerous choices for application delivery, virtualization, data management, and analytics. This abundance of alternatives, from established companies to new cloud-focused providers, significantly strengthens customer bargaining power.
With viable alternatives readily available, customers can effectively negotiate for better terms and pricing. They possess the credible threat of switching to a competitor if Cloud Software Group’s offerings are not sufficiently attractive, directly impacting the group's pricing flexibility.
Customer's Demand for Customization and Integration
Large enterprises often demand significant software customization and integration with their existing IT infrastructure. This need can amplify customer bargaining power, as they might seek specific features or integration capabilities from Cloud Software Group. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of enterprise software deals involved custom development, with some studies indicating over 60% of large IT projects requiring bespoke solutions to meet unique business processes.
Cloud Software Group's ability to deliver these tailored solutions is crucial for securing and retaining major client contracts. The capacity to adapt offerings, rather than forcing clients into rigid, off-the-shelf products, directly influences customer loyalty and the potential for lucrative, long-term partnerships. Companies that excel in this area often see higher customer retention rates, with some cloud service providers reporting retention exceeding 90% for clients with customized solutions.
- Customization Demand: Large enterprises frequently require tailored software features to align with their specific operational workflows.
- Integration Needs: Seamless integration with existing IT systems is a critical factor for enterprise adoption of new software.
- Bargaining Power: The demand for customization and integration strengthens customers' ability to negotiate terms and pricing.
- Client Retention: Cloud Software Group's responsiveness to these demands directly impacts its success in securing and retaining large enterprise clients.
Impact of Economic Conditions on IT Budgets
Fluctuations in the global economy significantly impact IT budgets. During economic slowdowns, businesses often scale back software investments, postpone upgrades, or demand steeper price reductions. This dynamic can temporarily amplify customer bargaining power as they prioritize cost optimization.
For instance, in 2024, many companies faced increased pressure to control IT spending due to persistent inflation and geopolitical uncertainties. This led to a more cautious approach to new software acquisitions and a greater emphasis on negotiating favorable terms for existing contracts.
- Reduced Software Spending: Many enterprises adopted a wait-and-see approach, deferring non-essential software purchases.
- Discount Demands: Customers actively sought discounts, sometimes demanding 10-15% off list prices for new deals or renewals.
- Extended Sales Cycles: The approval process for IT investments became lengthier, with more stakeholders involved in budget allocation decisions.
- Focus on ROI: Vendors faced increased scrutiny on the return on investment for their software solutions, pushing for clearer value propositions.
Cloud Software Group's customers, particularly large enterprises, possess significant bargaining power due to their substantial purchase volumes and the availability of numerous alternative solutions in the competitive software market. This leverage allows them to negotiate for lower prices, customized terms, and specific features, directly influencing the company's pricing strategies and product development. The deep integration of Cloud Software Group's solutions into critical IT infrastructure, however, raises switching costs, somewhat mitigating this power.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024 Estimates) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High | Top 10 enterprise clients accounted for over 40% of recurring revenue. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Numerous competitors offer similar application delivery, virtualization, and data management solutions. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to High | Deep integration into critical IT infrastructure increases complexity, time, and cost of migration. |
| Demand for Customization | High | Over 60% of large IT projects in 2024 required bespoke solutions. |
| Economic Conditions | Variable (Increased during slowdowns) | Enterprises focused on IT budget control, seeking 10-15% discounts. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Cloud Software Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview offers a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of the Cloud Software Group, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You can expect to gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the cloud software industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The enterprise software sector is a battleground dominated by tech titans like Microsoft, VMware, Oracle, IBM, and Google Cloud. These established players wield immense resources and broad product offerings, allowing them to challenge Cloud Software Group across its various service areas.
For instance, Microsoft's Azure Virtual Desktop and Power BI, alongside VMware's robust virtualization solutions, directly compete with Cloud Software Group's offerings. Oracle's strength in databases and analytics, and Google Cloud's expanding infrastructure services, further intensify this rivalry.
This intense competition from deeply entrenched giants means Cloud Software Group constantly faces pressure on market share and the cost of acquiring new customers. In 2024, the cloud infrastructure market alone saw significant investment, with hyperscalers like Microsoft, Amazon, and Google continuing to expand their capabilities, underscoring the scale of resources these competitors deploy.
Beyond the major tech players, Cloud Software Group contends with a vibrant ecosystem of specialized competitors. These vendors excel in specific areas like data analytics, with Tableau, acquired by Salesforce in 2019 for $15.7 billion, and Qlik offering robust visualization tools. Databricks, a significant force in data engineering and AI, also presents a formidable challenge with its unified data analytics platform.
This diverse competitive set extends to niche markets such as virtualization and cybersecurity. Companies focusing on specific application delivery needs or advanced data management solutions often provide deep expertise that can challenge broader offerings. For instance, VMware, a leader in virtualization, competes directly in areas of cloud infrastructure management.
The sheer number of these specialized vendors means Cloud Software Group must constantly innovate and clearly define its unique value proposition. Staying ahead requires a commitment to targeted development and a keen understanding of evolving customer needs within these distinct market segments. This dynamic landscape underscores the importance of differentiation to maintain market share and relevance.
The enterprise software landscape is a whirlwind of technological progress, with cloud-native architectures, AI, and machine learning becoming standard. Cybersecurity threats also constantly shift, demanding continuous adaptation. Competitors are always rolling out new features and optimizing performance, making it crucial for companies like Cloud Software Group to stay ahead.
To remain competitive, Cloud Software Group needs to invest significantly in research and development. For instance, in 2024, the global AI market reached an estimated $200 billion, highlighting the immense opportunity and pressure to integrate advanced AI capabilities into software offerings. This investment is vital for enhancing existing products and developing new solutions that address evolving customer needs and emerging technological trends.
Pricing Pressure and Licensing Models
Intense competition within the cloud software sector frequently results in significant pricing pressure. Vendors are constantly battling for market share, particularly in established market segments. Cloud Software Group must navigate the complexities of optimizing its pricing and licensing structures, such as subscription versus consumption-based models, to stay competitive and maintain profitability. Aggressive pricing from competitors can directly impact profit margins, necessitating a close examination of internal cost structures.
The pressure to offer competitive pricing can lead to a reduction in average revenue per user (ARPU). For instance, in 2024, the Software as a Service (SaaS) market saw continued competition, with many providers offering tiered pricing and discounts to attract and retain customers. This environment forces companies like Cloud Software Group to carefully balance aggressive pricing strategies with the need to cover development, support, and operational costs. The effectiveness of their licensing models, whether perpetual, subscription, or usage-based, becomes a critical determinant of their ability to capture and retain customers while ensuring financial health.
- Pricing Pressure: Cloud software vendors often engage in price wars, especially in mature markets, to gain or maintain market share.
- Licensing Model Optimization: Cloud Software Group must adapt its licensing, like subscription or consumption-based, to remain competitive and profitable.
- Margin Erosion: Aggressive competitor pricing can directly reduce profit margins, forcing internal cost-structure reviews.
- Market Dynamics: The SaaS market in 2024 continued to be characterized by competitive pricing, impacting ARPU for providers.
Customer Retention and Ecosystem Lock-in
Customer retention is paramount in enterprise software, with rivals like Microsoft and Oracle heavily investing in integrating their solutions into client operations, making switching a significant undertaking. This creates a powerful ecosystem lock-in effect, as seen with Microsoft's Azure and Office 365, where the combined utility and data integration discourage customers from migrating to competitors. For Cloud Software Group, maintaining high customer satisfaction and demonstrating ongoing value are critical to stemming churn and fending off aggressive competitive strategies.
The cost of switching for enterprise clients can be substantial, often involving data migration, retraining staff, and reconfiguring business processes. For instance, a study by McKinsey in 2023 indicated that the average cost of switching enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems can range from 10% to 20% of the total system cost, a significant barrier. Cloud Software Group must therefore focus on seamless integration, continuous innovation, and superior customer support to solidify its existing customer relationships and deter potential defections.
- Ecosystem Lock-in: Competitors aim to embed their software deeply into customer workflows, increasing switching costs and fostering loyalty.
- Customer Retention Strategies: Cloud Software Group must prioritize excellent customer support and demonstrate ongoing value to prevent churn.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with data migration and retraining make it difficult for customers to move to alternative solutions.
- Competitive Pressure: Rivals actively seek to attract customers by offering integrated solutions and competitive pricing, intensifying rivalry.
The competitive rivalry within the cloud software sector is fierce, driven by established tech giants like Microsoft, Oracle, and Google Cloud, alongside specialized players. These competitors offer comprehensive solutions and invest heavily in innovation, directly challenging Cloud Software Group's market share and pricing power.
In 2024, the cloud market saw continued dominance by hyperscalers, with significant investments in AI and infrastructure. This intense competition necessitates continuous R&D investment for Cloud Software Group to maintain its edge and address evolving customer demands.
Companies like Tableau and Databricks also pose threats in specific niches, forcing Cloud Software Group to differentiate its offerings and focus on unique value propositions to retain customers amidst aggressive pricing and ecosystem lock-in strategies by rivals.
| Competitor | Key Offerings | Competitive Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft | Azure, Power BI, Microsoft 365 | Broad portfolio, strong ecosystem integration, significant R&D investment |
| Oracle | Cloud Infrastructure, Database Services, Analytics | Established enterprise presence, deep data capabilities |
| Google Cloud | Cloud Infrastructure, AI/ML Services, Data Analytics | Rapidly expanding infrastructure, strong AI focus |
| VMware | Virtualization, Cloud Management | Leader in virtualization, direct competition in infrastructure |
| Databricks | Unified Data Analytics Platform | Strong in data engineering and AI, challenging data-centric offerings |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Public cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud present a significant threat by offering native services that can replace traditional on-premises or managed software. These platforms provide integrated solutions for virtualization, data analytics, and application delivery, often at competitive price points.
The rapid growth of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) further intensifies this threat. In 2024, the global SaaS market was projected to reach over $326 billion, with continued strong growth expected. These readily available SaaS alternatives offer similar functionalities to Cloud Software Group's offerings, but without the burden of extensive on-premises infrastructure or ongoing management for the customer.
Open-source software presents a significant competitive challenge, especially in critical areas like data management and analytics, with tools such as Apache Kafka, Spark, and Hadoop gaining widespread adoption. The increasing prevalence of open-source virtualization (KVM, Xen) and container orchestration (Kubernetes) further intensifies this threat.
These alternatives often boast lower initial costs and robust community-driven development, making them attractive to businesses seeking to minimize licensing expenses and enhance operational flexibility. For instance, the global open-source software market was valued at approximately $21.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong market preference for these solutions.
To counter this, Cloud Software Group needs to clearly articulate the value proposition of its commercial offerings, emphasizing advanced features, dedicated enterprise support, and proven reliability that often surpass what can be found in community-driven projects.
Large enterprises with substantial IT budgets and skilled personnel might opt for in-house development of custom software solutions. This approach directly substitutes for purchasing cloud software, particularly when unique business processes demand tailored functionalities not readily available in commercial offerings. For instance, in 2024, many large corporations continued to invest heavily in their internal IT departments, with global IT spending projected to reach over $5 trillion, indicating a significant capacity for custom development.
Hardware-Based Solutions and Appliances
Hardware-based solutions, particularly in application delivery and network security, present a viable substitute threat to software-centric offerings like those from Cloud Software Group. These dedicated appliances are often engineered for specialized performance and robust security, appealing to enterprises with specific, high-demand use cases.
Despite the strong industry shift towards software-defined architectures, these hardware alternatives persist. For instance, in 2024, the global network security appliance market was projected to reach over $25 billion, indicating continued demand for specialized hardware. This segment of the market could divert potential customers who prioritize the perceived stability and dedicated functionality of hardware over pure software solutions.
- Specialized Performance: Hardware appliances are built for singular, optimized functions, offering raw speed and efficiency that software may struggle to replicate in certain scenarios.
- Security Focus: Many hardware security appliances provide dedicated, purpose-built security features, which some organizations may still prefer for critical infrastructure.
- Market Persistence: The continued significant market size for network security appliances in 2024 demonstrates that hardware remains a relevant and chosen option for a substantial portion of the enterprise market.
Manual Processes or Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)
Manual processes or Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) can serve as substitutes for Cloud Software Group's offerings. For certain analytical or operational tasks, companies might choose to handle them manually or delegate them to BPO providers to avoid the costs and complexities associated with enterprise software. This is particularly true for smaller businesses or during periods of tight budgets, where the perceived value of automation might not outweigh the immediate expense.
While less efficient and scalable than software solutions, these manual or outsourced alternatives represent a fundamental substitution. For instance, a company might opt for manual data entry and analysis instead of implementing a cloud-based CRM or ERP system. This can be a viable, albeit rudimentary, approach for organizations with simpler operational needs or limited financial resources.
- Manual Processes: Businesses might continue using spreadsheets or internal manual workflows for tasks like customer management or financial reporting, particularly if the scale of operations is small.
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO): Companies could outsource specific functions, such as customer support or back-office processing, to third-party BPO providers rather than investing in specialized cloud software.
- Cost Avoidance: The primary driver for these substitutes is often the desire to avoid upfront software licensing, implementation, and ongoing subscription fees, especially for smaller enterprises or during economic downturns.
- Scalability Limitations: While manual or BPO solutions can address immediate needs, they typically lack the scalability and advanced analytics that cloud software provides, limiting long-term growth and efficiency gains.
The threat of substitutes for Cloud Software Group's offerings is substantial, encompassing public cloud providers, SaaS alternatives, open-source solutions, in-house development, hardware appliances, and even manual or outsourced processes.
Public cloud providers offer integrated services that can replace traditional software, while the booming SaaS market in 2024, projected to exceed $326 billion, provides readily available functional alternatives. Open-source software, valued at approximately $21.7 billion in 2023, also presents a cost-effective and flexible substitute, particularly in data management and analytics.
Large enterprises may opt for custom in-house development, leveraging significant IT budgets, with global IT spending projected over $5 trillion in 2024. Hardware-based solutions, especially in network security where the market was projected over $25 billion in 2024, offer specialized performance and security that can appeal to specific enterprise needs.
Finally, manual processes or Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) serve as basic substitutes, particularly for smaller businesses or those with budget constraints, representing a fundamental alternative to investing in enterprise cloud software.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Market Relevance (2023-2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud Providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) | Integrated services, virtualization, data analytics, application delivery | Dominant market share, competitive pricing |
| SaaS Alternatives | Off-the-shelf functionality, reduced infrastructure burden | Global market projected over $326 billion in 2024 |
| Open-Source Software | Lower initial costs, community-driven development, flexibility | Market valued at ~$21.7 billion in 2023, strong growth |
| In-house Development | Customization for unique business processes | Large enterprises invest heavily; global IT spending >$5 trillion in 2024 |
| Hardware Appliances | Specialized performance, dedicated security features | Network security appliance market projected >$25 billion in 2024 |
| Manual Processes / BPO | Cost avoidance, simpler operational needs | Viable for smaller businesses or during budget constraints |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the enterprise cloud software arena demands a massive upfront investment. Companies like Cloud Software Group pour billions into research and development, robust infrastructure, and extensive sales and marketing efforts. For instance, in 2024, major cloud providers continued to report substantial capital expenditures, with some allocating over $50 billion annually for data center expansion and technology upgrades, a figure that new entrants would need to match or exceed to even begin competing.
This necessitates substantial financial backing for any new player aiming to develop competitive products, attract top engineering talent, and build a recognizable brand. The sheer scale of these requirements acts as a significant deterrent, effectively shielding established entities like Cloud Software Group from smaller, less-funded startups attempting to enter the market directly.
For Cloud Software Group, brand recognition and customer trust are significant barriers to new entrants. It takes considerable time and resources to build a strong reputation, especially with large enterprise clients who prioritize reliability and proven performance.
Companies like Cloud Software Group, with established brands like Citrix and TIBCO, have cultivated deep relationships and a track record that new players simply cannot match immediately. This existing credibility makes it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
New entrants must therefore invest heavily in marketing and sales to even begin proving their worth, a substantial challenge when trying to secure lucrative enterprise contracts. Without this established trust, their path to market entry is significantly more arduous.
The complexity of enterprise sales cycles and integrations presents a significant barrier for new entrants in the cloud software market. These cycles can extend for months, even years, demanding extensive proof-of-concept demonstrations, rigorous security audits, and intricate integration with a client's existing IT infrastructure.
New players often struggle to match the established sales infrastructure, specialized professional services, and deep integration know-how that incumbents possess. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that the average enterprise software sales cycle can last between 6 to 18 months, with integration phases adding several more months. This lengthy and resource-intensive process deters many potential new competitors.
Intellectual Property and Patent Portfolios
Cloud Software Group, by absorbing companies like Citrix and Tibco, has likely amassed a substantial collection of patents and proprietary technology. This intellectual property, covering areas such as virtualization, networking, and data analytics, creates a significant hurdle for potential new competitors. New entrants would either need to invest heavily in developing unique, non-infringing technologies or risk costly legal battles over patent violations, thus safeguarding Cloud Software Group's technological foundation.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the substantial investment required to replicate Cloud Software Group's established intellectual property. For instance, companies in similar software sectors often spend millions annually on research and development to build and protect their patent portfolios. A new player would need to navigate this complex legal and innovation landscape, making market entry particularly challenging.
- High R&D Costs: Developing proprietary technology comparable to Cloud Software Group's existing patents can cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Patent Infringement Risk: New entrants face legal challenges and potential financial penalties if their products infringe upon existing patents.
- Time to Market: Building a competitive technology suite from scratch, without infringing, can add years to a new company's time to market.
- Established Brand and Reputation: Existing players benefit from brand recognition, which new entrants lack, further complicating market penetration.
Regulatory Compliance and Security Requirements
For enterprise cloud software, navigating the labyrinth of regulatory compliance and security is a formidable hurdle for newcomers. Meeting standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and various industry-specific mandates requires substantial upfront investment and ongoing vigilance. For instance, in 2024, the global cybersecurity market was valued at over $230 billion, with a significant portion dedicated to compliance and data protection solutions, indicating the scale of investment needed.
New entrants must build these robust compliance frameworks into their software from inception, a process that demands specialized expertise and considerable financial resources. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, deterring many potential competitors. The continuous evolution of these regulations, such as updates to data privacy laws or emerging cybersecurity threats, further escalates the cost and complexity for any new player aiming to enter the market.
Consider the following:
- High Compliance Costs: Developing software that meets stringent global and industry-specific regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) necessitates significant investment in legal, technical, and auditing resources.
- Evolving Security Standards: The need to constantly adapt to new cybersecurity threats and evolving data protection laws requires continuous R&D and infrastructure upgrades, adding to the barrier.
- Demonstrating Trust: New entrants must prove their commitment to security and compliance to enterprise clients, often requiring extensive certifications and audits, which are time-consuming and expensive.
The threat of new entrants into the enterprise cloud software market, particularly for established players like Cloud Software Group, is largely contained. The immense capital required for R&D, infrastructure, and market penetration, coupled with the need to build brand trust and navigate complex sales cycles, presents formidable challenges. Furthermore, protecting and replicating sophisticated intellectual property and ensuring stringent regulatory compliance add significant layers of difficulty for any aspiring competitor.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Cloud Software Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including comprehensive market research reports, financial filings from public companies, and insights from industry-specific publications. This multi-faceted approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive dynamics.
