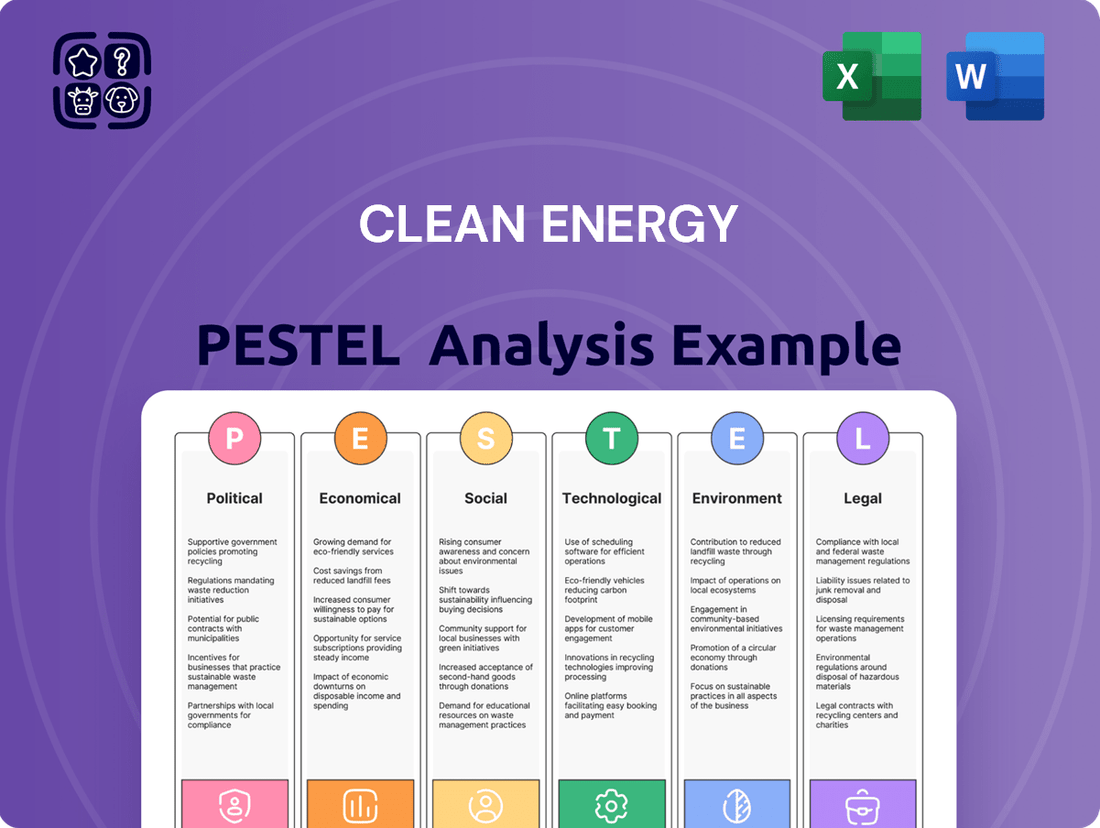
Clean Energy PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Clean Energy Bundle
Navigate the dynamic landscape of the clean energy sector with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the crucial political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors shaping opportunities and challenges. Gain actionable insights to inform your strategy and secure a competitive advantage. Download the full analysis now and unlock your path to success.
Political factors
Government policies and incentives are pivotal drivers for the clean energy sector's growth. These include crucial tax credits for renewable natural gas (RNG) production, grants aimed at developing necessary infrastructure, and specific incentives for vehicles that utilize RNG. For instance, the proposed Renewable Natural Gas Incentive Act of 2025 aims to offer a $1.00 per gallon tax credit for RNG used as transportation fuel. This initiative is expected to substantially reduce operating expenses for fleets, thereby fostering wider adoption of RNG technology.
Stricter environmental regulations are a significant political factor influencing the clean energy sector. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's Greenhouse Gas Emissions Standards for Heavy-Duty Vehicles-Phase 3 rule, implemented in June 2024, directly encourages the adoption of cleaner fuel alternatives such as renewable natural gas (RNG).
These federal mandates, coupled with state-level programs like California's Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS), are creating a powerful regulatory impetus for decarbonization, particularly within the transportation industry. The LCFS, for example, incentivizes the use of low-carbon fuels by assigning credits to fuel producers based on their carbon intensity, driving market demand for RNG and other sustainable options.
Government initiatives and funding are crucial for the expansion of natural gas refueling infrastructure. This support, including investments in new pipelines and refueling stations, directly drives the adoption of natural gas vehicles.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is actively developing a clean energy deployment framework to better coordinate infrastructure development across the nation. This framework aims to streamline processes and encourage private sector investment in vital energy infrastructure.
Trade Policies and International Agreements
International agreements and evolving trade policies significantly shape the clean energy landscape. These frameworks directly influence the demand and supply dynamics of clean energy fuels by setting regulatory standards and market access conditions. For example, the projected increase in U.S. renewable natural gas (RNG) exports to Europe in 2025 is a direct consequence of the European Union's increasingly stringent renewable fuel mandates, highlighting how international policy creates tangible market opportunities.
These trade dynamics can be further understood through key developments:
- Global Climate Accords: Agreements like the Paris Agreement encourage nations to adopt cleaner energy sources, indirectly boosting demand for clean energy technologies and fuels through national commitments and policy adjustments.
- Bilateral Trade Agreements: Specific trade pacts can reduce tariffs and streamline import/export processes for clean energy components and fuels, fostering cross-border investment and market expansion.
- Renewable Fuel Standards: Mandates in regions such as the EU and the U.S. create guaranteed markets for renewable fuels like RNG, driving investment in production and infrastructure. In 2024, the EU’s Renewable Energy Directive (RED III) continues to push for higher renewable energy targets, influencing international trade flows.
Political Stability and Public-Private Partnerships
Political stability is a cornerstone for attracting the substantial, long-term capital required for clean energy infrastructure. Instability can deter investors, leading to project delays and increased financing costs. For instance, the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, a significant piece of legislation, signals a strong political commitment to clean energy, providing a stable policy environment that encourages investment.
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are crucial for de-risking clean energy projects and accelerating their deployment. These collaborations leverage government support, such as tax incentives and loan guarantees, with private sector expertise and capital. By sharing risks and rewards, PPPs can unlock projects that might otherwise be too challenging for either sector to undertake alone, fostering a more dynamic market for companies like Clean Energy Fuels Corp.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Loan Programs Office, for example, has facilitated billions in clean energy financing through various programs, often in partnership with private entities. In 2023, the office continued to support projects ranging from advanced nuclear to renewable energy manufacturing, demonstrating the tangible impact of government-private collaboration on clean energy growth.
- Government Support: Policies like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act provide tax credits and incentives, stabilizing the investment landscape for clean energy.
- Risk Mitigation: Public-private partnerships share project risks, making large-scale clean energy developments more feasible.
- Accelerated Deployment: Collaborative efforts between government and private industry speed up the adoption of clean energy technologies.
- Market Growth: A stable and supportive political environment encourages private investment, driving market expansion for clean energy solutions.
Government policies, including tax credits and grants, are essential for clean energy adoption, exemplified by the proposed Renewable Natural Gas Incentive Act of 2025, which aims to provide a $1.00 per gallon tax credit for RNG as transportation fuel. Stricter environmental regulations, such as the EPA's Greenhouse Gas Emissions Standards for Heavy-Duty Vehicles-Phase 3 rule implemented in June 2024, actively promote cleaner fuels like RNG. Furthermore, international agreements and evolving trade policies, like the EU's renewable fuel mandates driving U.S. RNG exports in 2025, significantly influence global clean energy markets.
Political stability is crucial for attracting the long-term capital needed for clean energy infrastructure, with initiatives like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 fostering a stable investment environment. Public-private partnerships are vital for de-risking projects and accelerating deployment, with the U.S. Department of Energy's Loan Programs Office facilitating billions in clean energy financing through collaborative efforts. These partnerships leverage government support with private sector expertise, making ambitious projects more attainable and driving market growth.
What is included in the product
This Clean Energy PESTLE analysis comprehensively examines the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors influencing the sector, providing a strategic framework for understanding market dynamics.
It delivers actionable insights and forward-looking perspectives, equipping stakeholders with the knowledge to navigate challenges and capitalize on opportunities in the evolving clean energy landscape.
Provides a clear understanding of external factors impacting clean energy, simplifying complex market dynamics to reduce uncertainty and inform strategic decisions.
Economic factors
The predictability of renewable natural gas (RNG) prices offers a distinct economic edge over the often-unpredictable costs of diesel. This stability is crucial for businesses, allowing for more accurate budgeting and financial forecasting.
For commercial fleets, the cost-competitiveness of RNG is further bolstered by potential government incentives. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 extended and enhanced tax credits for clean fuels, making RNG a financially attractive alternative, potentially reducing operational expenses significantly for fleet operators in 2024 and beyond.
The availability of capital is a major driver for clean energy expansion. This includes investments from private equity firms, government grants, and collaborative public-private partnerships, all vital for building out clean energy infrastructure.
For instance, Clean Energy Fuels Corp. demonstrated significant financial readiness, holding $217.5 million in cash, cash equivalents, and short-term investments as of December 31, 2024. This substantial financial position suggests a strong capacity to fund ongoing and future growth initiatives within the clean energy sector.
The global market for natural gas vehicles (NGVs) is experiencing robust expansion, fueled by increasing environmental consciousness and supportive government policies. Estimates place the NGV market at USD 10.37 billion in 2024, with projections indicating a rise to USD 11.16 billion by 2025. This growth trajectory, showing a compound annual growth rate of 7.59% between 2025 and 2034, directly translates to heightened demand for natural gas as a fuel source.
Operational Costs and Efficiency
Technological progress is a major driver in making renewable natural gas (RNG) more economically attractive. As conversion efficiencies improve, the cost of producing RNG from various feedstocks decreases, directly impacting operational expenses. For instance, advancements in anaerobic digestion and gas upgrading technologies are continually pushing down the cost per MMBtu of RNG production.
Furthermore, the operational cost savings extend to end-users, particularly fleets transitioning to natural gas vehicles. These vehicles often boast lower maintenance requirements compared to their diesel counterparts, translating into reduced long-term operating expenses. This is a significant factor for businesses looking to optimize their fleet management budgets.
- Optimized Feedstock Conversion: Technological advancements are increasing the yield of RNG from sources like agricultural waste and landfill gas, lowering the cost of production.
- Reduced Vehicle Maintenance: Natural gas engines typically require less frequent maintenance than diesel engines, leading to lower operating costs for fleets.
- Lower Fuel Costs: In many regions, the price of RNG can be competitive with, or even lower than, traditional diesel fuel, especially when considering incentives and tax credits.
- Efficiency Gains: Improved engine technology for natural gas vehicles also contributes to better fuel efficiency, further reducing operational expenditures.
Carbon Credit Markets and Revenue Streams
The generation and sale of environmental credits, like Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs) under the Renewable Fuel Standard and California's Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) credits, are crucial revenue streams for clean energy companies. These credits directly incentivize the adoption and production of renewable natural gas (RNG), significantly boosting financial performance.
For instance, in 2023, RIN prices for D3 (cellulosic biofuel) saw fluctuations but remained a key component of RNG economics, often trading in the range of $2.00 to $3.00 per gallon, depending on market conditions and RIN vintage. California's LCFS credits, vital for RNG projects in the state, have also demonstrated strong value, with the program's declining carbon intensity targets in 2024 and 2025 expected to maintain or increase credit demand.
- RINs: Renewable Identification Numbers are a primary revenue source for renewable fuel producers, particularly for RNG.
- LCFS: California's Low Carbon Fuel Standard offers substantial financial incentives for low-carbon fuels, including RNG, by rewarding reduced carbon intensity.
- Market Value: In early 2024, D3 RINs were trading around $2.50, while LCFS credits averaged approximately $150-$160 per metric ton of CO2 equivalent, reflecting strong demand.
- Incentive: These credit markets provide a direct financial mechanism that encourages investment and expansion in the clean energy sector, especially for RNG projects.
Economic factors significantly shape the clean energy landscape, with fuel price stability and government incentives playing crucial roles. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, for example, continues to bolster the financial attractiveness of clean fuels like renewable natural gas (RNG) through extended tax credits, impacting operational costs for businesses throughout 2024 and into 2025.
Capital availability, driven by private equity, government grants, and public-private partnerships, is essential for infrastructure development. Companies like Clean Energy Fuels Corp. demonstrate this financial readiness, reporting $217.5 million in cash and equivalents as of December 31, 2024, indicating a strong capacity for growth initiatives.
The growing natural gas vehicle market, projected to reach $11.16 billion by 2025 with a CAGR of 7.59% through 2034, directly fuels demand for natural gas. Technological advancements in RNG production are also reducing costs, making it more economically viable, while lower maintenance needs for natural gas vehicles offer further operational savings for fleets.
Environmental credit markets, such as RINs and California's LCFS, provide vital revenue streams. In early 2024, D3 RINs traded around $2.50, and LCFS credits averaged $150-$160 per metric ton, underscoring the financial incentives driving clean energy investments.
| Metric | 2024 Data | 2025 Projection | Source/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| NGV Market Size | USD 10.37 billion | USD 11.16 billion | Market growth projection |
| Clean Energy Fuels Cash | $217.5 million (as of Dec 31, 2024) | N/A | Financial statement data |
| D3 RIN Price (Early 2024) | ~$2.50 per gallon | N/A | Market trading data |
| California LCFS Credit Avg. | ~$150-$160 per metric ton | N/A | Program credit values |
Full Version Awaits
Clean Energy PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive Clean Energy PESTLE Analysis breaks down the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the sector. You'll gain valuable insights into market trends and strategic considerations.
Sociological factors
Public awareness of climate change is surging, directly influencing consumer choices and pushing for greener alternatives in transportation. This heightened environmental consciousness is a significant driver for the adoption of renewable natural gas (RNG) powered vehicles, as people actively seek ways to reduce their carbon footprint.
The demand for sustainable energy solutions is on the rise, with a clear preference for options that minimize emissions. This societal shift translates into greater acceptance and a willingness to embrace RNG-fueled vehicles, both by individual consumers and commercial entities looking to enhance their environmental credentials.
In 2024, surveys indicated that over 70% of consumers consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions, a figure expected to climb. This growing sentiment directly supports the market expansion for RNG, as its environmental benefits align with public expectations for cleaner transportation.
Corporations are increasingly adopting renewable natural gas (RNG) as a key component of their sustainability strategies, aiming to shrink their carbon emissions and achieve ambitious Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals. This shift reflects a growing awareness of the need for tangible climate action within the business world.
Major players like Amazon, UPS, and WM have already integrated RNG into their transportation fleets, signaling a significant corporate commitment to cleaner fuel alternatives. For instance, in 2023, Amazon announced plans to power its entire delivery fleet with renewable fuels, including RNG, by 2025, underscoring the rapid integration of these solutions.
The successful rollout of clean energy projects hinges on robust community engagement and a commitment to environmental justice. Local communities often bear the direct impacts of new infrastructure, making their input and the equitable distribution of benefits paramount. For instance, the Biden-Harris administration's Justice40 Initiative aims to direct 40% of the overall benefits of federal investments in climate and clean energy to disadvantaged communities, a policy that directly influences project siting and community acceptance in 2024 and beyond.
Job Creation and Economic Impact
The expansion of renewable natural gas (RNG) projects and the necessary infrastructure are significant drivers of local employment. These initiatives create jobs across various sectors, including the initial construction phases, ongoing operations, and essential maintenance activities. This localized job growth directly bolsters community economies.
Investments in the clean energy sector, particularly in areas like low-NOx natural gas trucks, fueling stations, and RNG production facilities, yield substantial employment benefits. Studies suggest a strong correlation between these investments and the generation of both direct and indirect job opportunities, positively impacting local economic development.
- Job Creation: RNG projects create local jobs in construction, operation, and maintenance.
- Economic Impact: Investments in low-NOx trucks, fueling infrastructure, and RNG production generate significant employment.
- Employment Opportunities: These developments foster both direct and indirect job growth, contributing to local economies.
- Sectoral Growth: The clean energy transition is a key enabler of new employment pathways.
Health Benefits from Reduced Emissions
The shift towards cleaner energy sources, like renewable natural gas (RNG), significantly improves public health by reducing harmful air pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter. This is particularly impactful in urban areas and communities that have historically borne the brunt of emissions from transportation and industry, leading to a tangible increase in overall quality of life.
Improved air quality directly translates to fewer respiratory illnesses, such as asthma and bronchitis, and a decrease in cardiovascular problems. For instance, studies indicate that reductions in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) can lead to a measurable decrease in hospital admissions for respiratory and cardiac conditions. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that the health benefits from the Clean Air Act alone have saved billions of dollars annually in healthcare costs and prevented millions of illnesses.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Lower incidence of pollution-related diseases means less strain on healthcare systems and reduced out-of-pocket expenses for individuals.
- Increased Productivity: A healthier population leads to fewer sick days and improved overall productivity in the workforce.
- Enhanced Well-being: Cleaner environments contribute to greater physical and mental well-being for all members of society.
- Environmental Justice: Cleaner energy initiatives often disproportionately benefit disadvantaged communities historically exposed to higher pollution levels.
Public demand for sustainable transportation is a powerful force, with consumers increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly options. This trend is directly fueling the growth of the renewable natural gas (RNG) market, as individuals and businesses alike seek to reduce their environmental impact. By 2024, over 70% of consumers reported considering sustainability in their purchasing decisions, a figure projected to rise further.
Corporate sustainability goals are also a major catalyst, with companies integrating RNG into their fleets to meet ambitious Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) targets. Major logistics companies like Amazon and UPS are actively investing in RNG-powered vehicles, with Amazon aiming for its entire delivery fleet to be powered by renewable fuels by 2025. This corporate adoption signals a significant market shift towards cleaner fuel alternatives.
Community engagement and environmental justice are critical for the successful deployment of clean energy projects. Initiatives like the Biden-Harris administration's Justice40 Initiative, which aims to direct 40% of federal clean energy investment benefits to disadvantaged communities, are shaping project development and acceptance. These efforts ensure that the transition to cleaner energy is equitable and benefits local populations.
The expansion of RNG infrastructure and related clean energy investments are significant job creators. These projects stimulate local economies by generating employment opportunities in construction, operations, and maintenance. Studies consistently show a strong correlation between clean energy investments and the creation of both direct and indirect jobs, bolstering local economic development.
The shift to cleaner energy sources like RNG yields substantial public health benefits by reducing harmful air pollutants. This leads to fewer respiratory and cardiovascular illnesses, particularly in urban areas historically burdened by emissions. The U.S. EPA estimates that clean air initiatives save billions annually in healthcare costs and prevent millions of illnesses.
| Factor | 2024/2025 Trend | Impact on RNG Market |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Awareness | Over 70% consider sustainability in purchases (2024) | Increased demand for RNG vehicles and fuels |
| Corporate ESG Goals | Companies integrating RNG for emission reduction | Growing fleet adoption by major corporations |
| Environmental Justice | Focus on equitable benefit distribution (e.g., Justice40 Initiative) | Influences project siting and community acceptance |
| Job Creation | Clean energy investments drive local employment | Boosts local economies through job growth in RNG sector |
| Public Health | Reduced air pollution leads to fewer illnesses | Enhances societal well-being and reduces healthcare costs |
Technological factors
Innovations in biogas upgrading technologies, like pressure swing adsorption and membrane separation, are boosting methane capture rates and efficiency in renewable natural gas (RNG) production. These advancements are making RNG more scalable and cost-effective, a crucial factor for wider adoption.
Ongoing advancements in natural gas vehicle technology are significantly boosting efficiency and reliability. Innovations like optimized combustion systems and lighter fuel storage solutions are making natural gas a more attractive option for transportation.
The market is seeing the introduction of new, more powerful natural gas engines. For instance, the Cummins X15N engine, slated for release in late 2025, is poised to enhance the performance and adoption of cleaner heavy-duty vehicles, supporting the shift away from traditional fuels.
Technological advancements are significantly improving natural gas refueling infrastructure, making it more efficient and cost-effective. Innovations like high-pressure fueling and fast-fill systems are reducing refueling times, a key factor in wider adoption of natural gas vehicles. For instance, by 2024, the number of public natural gas refueling stations in the US is projected to reach over 1,000, indicating substantial infrastructure growth driven by these technological leaps.
Carbon Capture and Utilization Integration
The integration of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies into natural gas facilities is a key technological advancement, aiming to capture carbon dioxide before it enters the atmosphere. This is crucial for reducing the carbon footprint of traditional energy sources.
Recent developments in carbon capture and utilization (CCU) are also being linked with renewable natural gas (RNG) production. This offers a dual strategy for emission reduction, not only capturing CO2 but also finding ways to reuse it, potentially creating valuable byproducts.
By 2024, the global CCS market is projected to see substantial growth, with investments in new projects accelerating. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in late 2023 that over 30 new CCS facilities were in various stages of development or operation, representing a significant increase in capacity.
The financial viability of these technologies is improving, driven by policy support and technological innovation.
- Technological Focus: Advancements in direct air capture (DAC) and point-source capture are becoming more efficient and cost-effective.
- RNG Synergies: CCU technologies are being explored to capture CO2 from anaerobic digestion processes used in RNG production, creating a circular carbon economy.
- Market Growth: The global CCS market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% through 2030, according to various market research reports.
- Investment Trends: Significant capital is being directed towards research and development, as well as pilot projects, to scale up these capture and utilization solutions.
Smart Methane Detection and Leak Mitigation
Advancements in smart methane detection are rapidly evolving, focusing on swift identification and mitigation of leaks across natural gas infrastructure. These technologies are crucial for a proactive stance on reducing emissions, thereby bolstering safety and minimizing environmental harm.
The development of sophisticated sensors and integrated monitoring systems promises to revolutionize how methane leaks are managed. This proactive approach is essential for meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations and for improving operational efficiency in the energy sector.
- Technological Advancement: Smart sensors are becoming more sensitive and cost-effective, enabling continuous monitoring of pipelines and facilities.
- Real-time Data: These systems provide real-time data on methane concentrations, allowing for immediate leak detection and response.
- Emission Reduction: By enabling rapid leak repair, these technologies directly contribute to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in 2024 that improved methane detection and mitigation could cut global methane emissions by 75% by 2030.
- Safety and Efficiency: Enhanced detection improves site safety and operational efficiency by preventing product loss and potential hazards.
Technological advancements are making renewable natural gas (RNG) more viable, with innovations in biogas upgrading enhancing methane capture. Simultaneously, natural gas vehicle technology is improving efficiency and reliability, supported by new, powerful engines like the Cummins X15N slated for late 2025. Refueling infrastructure is also seeing upgrades, with the US projected to have over 1,000 public natural gas refueling stations by 2024.
| Technology Area | Key Advancement | Impact | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biogas Upgrading | Pressure Swing Adsorption, Membrane Separation | Increased methane capture rates and efficiency for RNG | Making RNG more scalable and cost-effective |
| Natural Gas Vehicles | Optimized combustion, lighter fuel storage | Enhanced efficiency and reliability | Cummins X15N engine (late 2025) for heavy-duty vehicles |
| Refueling Infrastructure | High-pressure fueling, fast-fill systems | Reduced refueling times, improved cost-effectiveness | Over 1,000 public NG refueling stations in US projected by 2024 |
Legal factors
Federal programs like the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) mandate blending renewable fuels into the transportation fuel supply, directly influencing the demand for biogas-derived renewable natural gas (RNG). In 2023, the RFS program aimed for 20.5 billion gallons of renewable fuels, with a significant portion allocated to advanced biofuels like RNG, driving its market value.
State-level initiatives, particularly California's Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS), further incentivize the production and use of low-carbon transportation fuels, including RNG. The LCFS program, which saw its benchmark carbon intensity target lowered to 18.0% below 2010 levels by 2030, generated substantial credits for RNG projects, with prices for these credits fluctuating, reaching over $200 per metric ton of CO2 equivalent in early 2024, thus bolstering RNG project economics.
Legal mandates like the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Greenhouse Gas Emissions Standards for Heavy-Duty Vehicles-Phase 3, effective June 2024, are reshaping the automotive industry. This rule, for instance, sets specific limits on tailpipe emissions, pushing manufacturers towards cleaner technologies and alternative fuels.
These stringent regulations directly influence vehicle design and production. For example, by 2027, the EPA aims for a significant reduction in nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from heavy-duty trucks, a move that will likely accelerate the adoption of electric and hydrogen fuel cell powertrains, impacting R&D investments and supply chains.
The legal frameworks governing the permitting and siting of new energy infrastructure, such as natural gas fueling stations and renewable natural gas (RNG) production facilities, significantly impact project development timelines and overall costs. These processes can be complex and lengthy, often requiring multiple levels of approval.
In 2024, several states have actively pursued legislative measures aimed at streamlining these regulatory pathways. For instance, some states have introduced expedited permitting for certain clean energy projects, recognizing the need to accelerate deployment to meet renewable energy targets and enhance energy security.
These streamlining efforts are crucial for attracting investment and ensuring that the build-out of essential infrastructure, like RNG facilities which saw a projected 15% increase in operational capacity in the US by the end of 2024, can keep pace with demand and policy goals.
Tax Incentives and Credits Legislation
Legislation that introduces or extends tax incentives and credits plays a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape for clean energy ventures. For instance, the proposed Renewable Natural Gas Incentive Act of 2025, which includes a $1.00 per gallon tax credit for RNG, directly influences the financial feasibility of businesses operating in this sector. The timing of these incentives, whether they are newly enacted or set to expire, significantly sways revenue projections and critical investment decisions for companies in 2024 and 2025.
The impact of these legal frameworks is substantial, affecting everything from project development pipelines to the overall profitability of clean energy operations. As of early 2025, the Inflation Reduction Act continues to provide significant investment tax credits and production tax credits for various clean energy technologies, driving substantial capital deployment. For example, solar and wind projects are seeing increased investment due to these extended credits, bolstering their competitive edge against traditional energy sources.
- Renewable Natural Gas Incentive Act of 2025: Proposed $1.00 per gallon tax credit for RNG.
- Inflation Reduction Act (IRA): Continues to offer substantial investment and production tax credits for clean energy through 2025.
- Impact on Investment: Tax credits directly influence capital allocation and project viability in the clean energy sector.
- Revenue Projections: The presence or absence of tax incentives significantly alters financial forecasts for clean energy businesses.
Environmental Protection Laws and Enforcement
Environmental protection laws are increasingly stringent, compelling businesses to adopt cleaner energy solutions. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the U.S. offers significant tax credits for clean energy investments, driving adoption. These regulations create a clear legal pathway and financial incentive for decarbonization, shaping corporate strategies and compliance needs for the foreseeable future.
The enforcement of these environmental mandates plays a crucial role. Penalties for non-compliance can be substantial, encouraging proactive measures. Businesses are increasingly factoring these legal requirements into their long-term planning, recognizing that adherence to environmental standards is not just a regulatory burden but a strategic imperative for sustainable growth.
- Stricter Emission Standards: Many jurisdictions are implementing or tightening limits on greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants from industrial and energy sectors.
- Renewable Energy Mandates: Policies like Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) require utilities to source a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources, boosting demand for clean energy.
- Carbon Pricing Mechanisms: The introduction or expansion of carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems makes polluting activities more expensive, incentivizing a shift to cleaner alternatives.
- International Agreements: Commitments under agreements like the Paris Agreement translate into national legislation and corporate responsibility to reduce carbon footprints.
Legal frameworks significantly shape the clean energy sector by mandating renewable fuel blending, like the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) which targeted 20.5 billion gallons of renewable fuels in 2023, and incentivizing low-carbon fuels through programs such as California's Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS). These policies, alongside evolving emissions standards for vehicles, like the EPA's Phase 3 for heavy-duty trucks effective June 2024, directly influence technology adoption and market demand for cleaner alternatives.
Permitting processes for clean energy infrastructure are also under legal scrutiny, with states actively working to streamline approvals in 2024 to accelerate project development, aiming to boost operational capacity for facilities like RNG production by a projected 15% in the US by year-end 2024.
Tax incentives, such as the continued benefits from the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) through 2025 and proposed legislation like the Renewable Natural Gas Incentive Act of 2025 offering a $1.00 per gallon tax credit, are critical financial drivers for clean energy investments, directly impacting revenue projections and investment decisions.
| Legal Factor | Description | 2024/2025 Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Fuel Standards | Mandates for blending renewable fuels into transportation fuel. | RFS target: 20.5 billion gallons (2023). Drives demand for RNG. |
| Low Carbon Fuel Standards | Incentivizes low-carbon transportation fuels. | California LCFS benchmark: 18.0% reduction by 2030. Credit prices exceeded $200/ton CO2e in early 2024. |
| Emissions Standards | Regulations on pollutants from vehicles and industry. | EPA Heavy-Duty Vehicle Emissions Standards Phase 3 (June 2024) aims for reduced NOx by 2027. |
| Permitting Streamlining | Efforts to expedite approval for clean energy projects. | Some states introduced expedited permitting in 2024. RNG capacity projected to increase 15% in US by end of 2024. |
| Tax Incentives | Financial credits supporting clean energy development. | IRA tax credits continue through 2025. Proposed RNG Incentive Act of 2025: $1.00/gallon credit. |
Environmental factors
Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) offers a powerful pathway to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Sources like RNG derived from animal waste can even achieve carbon-negative impacts, directly contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
The transportation sector, being the largest emitter of GHGs in the U.S., stands to benefit significantly from RNG adoption. For instance, in 2022, transportation accounted for 29% of total U.S. GHG emissions, highlighting the critical role RNG can play in decarbonizing this sector.
Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) production is a prime example of effective waste diversion and resource utilization. It transforms organic waste streams, such as those from landfills, farms, and wastewater plants, into a valuable clean energy source. This approach tackles waste management issues head-on while simultaneously creating a usable fuel.
By capturing methane, a potent greenhouse gas, from decomposing organic matter, RNG production significantly reduces emissions. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. RNG market was valued at approximately $5.8 billion, with projections showing substantial growth driven by environmental regulations and the demand for cleaner fuels. This growth directly reflects the increasing recognition of waste as a resource.
The increasing adoption of renewable natural gas (RNG) in transportation is a game-changer for air quality. For instance, a study by the California Air Resources Board indicated that RNG vehicles can reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by up to 90% and particulate matter (PM) by over 95% compared to conventional diesel engines. This translates to cleaner air, especially in densely populated cities, directly benefiting public health by lowering rates of respiratory illnesses.
Water Quality and Soil Health Benefits
The production of Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) from agricultural waste, like dairy manure, goes beyond just cutting greenhouse gas emissions. It actively contributes to better water quality and healthier soil by managing and repurposing farm byproducts. This dual benefit offers farmers an extra income source while encouraging more sustainable farming methods.
Consider the impact on water: By capturing methane from manure lagoons, RNG projects prevent nutrient runoff that can pollute waterways. For instance, a 2024 report from the American Biogas Council highlighted that active biogas projects in the U.S. are preventing an estimated 1.7 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent from entering the atmosphere annually, with a significant portion of this stemming from improved manure management which directly benefits water quality.
Soil health sees a boost too. The digestate, a byproduct of the anaerobic digestion process used for RNG, is a nutrient-rich fertilizer. Using this instead of synthetic fertilizers can improve soil structure and water retention. Farmers can see reduced reliance on chemical inputs, saving costs and enhancing the long-term viability of their land. In 2023, the U.S. Department of Agriculture noted that farms adopting advanced manure management practices, often linked to biogas production, reported improved soil organic matter content.
- Water Quality Improvement: RNG projects reduce nutrient runoff from farms, preventing contamination of rivers and groundwater.
- Soil Health Enhancement: Digestate from RNG production serves as a natural fertilizer, improving soil structure and reducing the need for synthetic chemicals.
- Farmer Revenue Streams: Farmers gain additional income by selling manure and utilizing digestate, supporting the economic viability of sustainable practices.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Agricultural byproducts are transformed into valuable energy and fertilizer, promoting a circular economy in agriculture.
Biodiversity Protection and Land Use
Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) production significantly aids biodiversity protection by leveraging existing waste streams and infrastructure. This method reduces the demand for new, land-intensive energy projects, preserving natural habitats.
This strategy directly supports sustainable land use, aligning with circular economy principles. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. RNG market saw substantial growth, with production increasing by over 20%, often utilizing agricultural waste and wastewater treatment facilities, thereby minimizing new land acquisition for energy generation.
- Reduced Land Footprint: RNG projects typically require less land compared to solar or wind farms, preserving ecosystems.
- Waste Stream Utilization: By converting waste into energy, it tackles environmental issues associated with landfill expansion and methane emissions.
- Circular Economy Integration: This approach embodies resource efficiency, turning byproducts into valuable energy sources.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Minimizing new land development directly contributes to safeguarding natural habitats and species diversity.
Environmental factors are critical drivers for Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) adoption, particularly its role in mitigating climate change and improving air quality. RNG production directly addresses greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane, a potent warming gas, from organic waste. For example, in 2022, the U.S. transportation sector, a major emitter, accounted for 29% of total GHG emissions, underscoring RNG's potential impact. Furthermore, RNG's ability to reduce nitrogen oxide and particulate matter emissions by significant margins, as seen in California studies, directly benefits public health by improving local air quality.
The environmental benefits extend to resource management and ecosystem health. RNG projects transform waste streams, such as agricultural byproducts and landfill gas, into valuable energy and fertilizer. This process prevents nutrient runoff into waterways, thereby improving water quality. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that U.S. biogas projects prevent millions of metric tons of CO2 equivalent from entering the atmosphere annually, partly through improved manure management. The digestate, a byproduct of RNG production, acts as a nutrient-rich soil amendment, enhancing soil health and reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers, a practice noted by the USDA to improve soil organic matter.
| Environmental Benefit | Description | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| GHG Emission Reduction | Captures methane from organic waste, preventing its release into the atmosphere. | U.S. transportation sector emissions were 29% of total U.S. GHG emissions in 2022. |
| Air Quality Improvement | Reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) emissions in transportation. | RNG vehicles can reduce NOx by up to 90% and PM by over 95% compared to diesel. |
| Water Quality Protection | Prevents nutrient runoff from agricultural waste into water bodies. | Active U.S. biogas projects prevent an estimated 1.7 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent annually through improved manure management. |
| Soil Health Enhancement | Digestate from RNG production improves soil structure and reduces synthetic fertilizer use. | Farms adopting advanced manure management practices reported improved soil organic matter content in 2023. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Clean Energy PESTLE Analysis is built on a robust foundation of data from government energy departments, international climate organizations, and leading market research firms. We incorporate policy documents, economic forecasts, and technological innovation reports to provide comprehensive insights.
