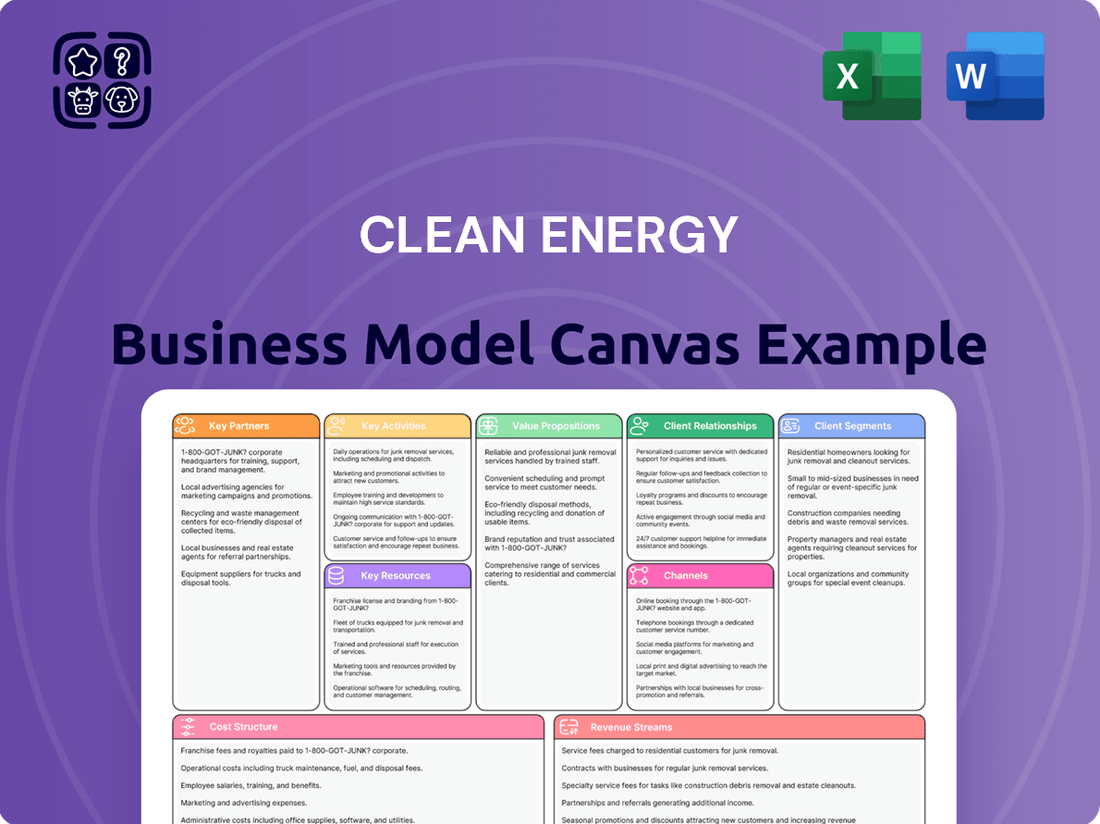
Clean Energy Business Model Canvas
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Clean Energy Bundle
Unlock the strategic blueprint behind Clean Energy's innovative business model. This comprehensive Business Model Canvas reveals their customer segments, value propositions, and revenue streams, offering a clear roadmap to success in the green economy. Ideal for anyone aiming to understand and replicate their growth.
Partnerships
Clean Energy Fuels Corp. relies heavily on partnerships with Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) producers and waste management companies to secure its primary product. These collaborations are essential for sourcing the methane captured from various organic waste streams. In 2024, the company continued to expand its network, highlighting the strategic importance of these relationships for its supply chain.
The company actively partners with entities that manage landfills, agricultural operations generating residues like dairy manure, and wastewater treatment facilities. These partnerships enable the capture of methane, which is then processed into RNG. For instance, Clean Energy Fuels has established joint ventures specifically focused on dairy RNG production, demonstrating a commitment to direct involvement in the upstream supply.
Clean Energy Fuels actively collaborates with major vehicle and engine manufacturers to accelerate the adoption of natural gas vehicles. These partnerships are crucial for ensuring that vehicles are designed and equipped to effectively utilize renewable natural gas (RNG), compressed natural gas (CNG), and liquefied natural gas (LNG).
A prime example is Clean Energy's collaboration with Cummins, a leading engine manufacturer. Their joint efforts have led to the development of the X15N natural gas engine, specifically designed for heavy-duty trucking. This engine boasts performance capabilities that rival traditional diesel engines, making it an attractive option for fleet operators looking to reduce emissions without sacrificing power. In 2023, Cummins reported that its natural gas engine business was experiencing strong demand, particularly from the vocational and refuse sectors, indicating a growing market acceptance.
Furthermore, Clean Energy partners with bus manufacturers like Gillig LLC. This collaboration ensures that new buses are equipped to run on RNG, a clean and sustainable fuel source. By integrating RNG capabilities directly into new vehicle production, Clean Energy facilitates a smoother transition for public transportation fleets towards lower-emission operations. The demand for cleaner transit solutions continues to rise, with many municipalities setting ambitious sustainability goals for their bus fleets.
Clean Energy Fuels cultivates deep relationships with fleet operators and transportation companies, establishing long-term supply and maintenance agreements. These crucial partnerships ensure a steady demand for their clean fuel solutions and provide ongoing revenue streams through dedicated support services for natural gas vehicle fleets.
Notable collaborations in 2024 include agreements with major logistics players like DHL, demonstrating the growing adoption of cleaner fuels in the transportation sector. Food Express and LA Metro are also key partners, highlighting the company's reach across diverse segments of the transportation industry, from last-mile delivery to public transit.
These collaborations are not just about fuel supply; they often encompass comprehensive maintenance and infrastructure support, creating sticky customer relationships. The company’s ability to secure these multi-year agreements, often with significant volume commitments, provides a predictable financial foundation for its operations.
Government Agencies and Municipalities
Collaborations with government agencies and municipalities are crucial for Clean Energy's growth in the natural gas fueling sector. These partnerships are key to expanding the infrastructure needed to support clean fuel adoption, particularly within public transportation and municipal fleets.
Clean Energy secures contracts to build and upgrade fueling stations, and supplies Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) for essential public vehicles like buses and refuse trucks. For instance, in 2024, the company continued to expand its network of fueling stations, with a significant portion serving municipal and public transit clients.
The company actively leverages federal, state, and local grants and incentives to further its mission. These financial supports are instrumental in reducing the upfront costs associated with developing new fueling infrastructure and promoting the use of cleaner fuels in public operations. In 2024, Clean Energy reported securing several new grants aimed at fleet conversion and infrastructure development.
- Infrastructure Development: Contracts with municipalities for building and upgrading natural gas fueling stations.
- Fleet Fueling: Supplying RNG for public buses, refuse trucks, and other vocational vehicles.
- Incentive Capture: Actively pursuing and securing grants and financial incentives from all levels of government.
Technology and Infrastructure Providers
Clean Energy relies heavily on partnerships with technology and infrastructure providers to build and operate its compressed natural gas (CNG) fueling stations and renewable natural gas (RNG) production facilities. These collaborations are crucial for securing the specialized equipment needed to support the natural gas vehicle ecosystem.
Key partners include suppliers of compression technology, dispensing systems, and other vital components. For instance, in 2024, Clean Energy continued to leverage its relationships with leading equipment manufacturers to ensure the seamless integration and efficient operation of its fueling network. These relationships are fundamental to maintaining the reliability and scalability of their infrastructure.
- Compression Equipment Suppliers: Companies providing high-pressure compressors essential for storing and dispensing natural gas.
- Dispensing Technology Providers: Firms specializing in the nozzles, hoses, and metering systems for safe and accurate fueling.
- Infrastructure Development Partners: Entities involved in the construction and maintenance of fueling stations and RNG processing plants.
Key partnerships are foundational for Clean Energy Fuels, particularly in securing its core Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) supply. Collaborations with waste management companies and RNG producers are vital for sourcing methane from diverse organic waste streams, a critical component of their business model. In 2024, the company actively expanded these upstream relationships to ensure a robust and sustainable supply chain.
These partnerships extend to vehicle manufacturers, fostering the adoption of natural gas vehicles (NGVs) by ensuring vehicles are designed for RNG, CNG, and LNG. Collaborations with fleet operators and transportation companies solidify demand through long-term fueling and maintenance agreements, creating predictable revenue. Furthermore, partnerships with government agencies and municipalities are crucial for expanding fueling infrastructure and securing contracts for public transit and vocational fleets.
Clean Energy also partners with technology and infrastructure providers to build and operate its fueling stations and RNG processing facilities. These relationships ensure access to specialized equipment like compression technology and dispensing systems, which are essential for the efficient operation of their fueling network. In 2024, the company continued to leverage these partnerships to enhance its infrastructure reliability and scalability.
| Partner Type | Key Activities | 2024 Focus/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| RNG Producers & Waste Management | Methane sourcing from landfills, dairies, wastewater | Expanding supply network, securing feedstock |
| Vehicle Manufacturers (e.g., Cummins, Gillig) | Developing and equipping NGVs for RNG/CNG/LNG | Accelerating NGV adoption, enhancing engine technology |
| Fleet Operators (e.g., DHL, Food Express) | Long-term fueling agreements, maintenance contracts | Driving demand, ensuring consistent revenue |
| Government Agencies & Municipalities | Infrastructure development, public fleet fueling, grants | Expanding fueling network, supporting public transit transition |
| Technology & Infrastructure Providers | Supplying compression, dispensing, and construction services | Ensuring operational efficiency, network reliability |
What is included in the product
A structured framework for detailing the core components of a clean energy venture, from customer relationships to revenue streams.
It provides a visual roadmap for developing and communicating a sustainable business strategy in the clean energy sector.
The Clean Energy Business Model Canvas streamlines complex energy transition strategies, alleviating the pain of fragmented planning and communication.
It provides a structured framework to address the challenges of developing sustainable energy solutions, ensuring all critical aspects are considered.
Activities
Clean Energy Fuels actively procures and produces natural gas fuels, with a strong emphasis on renewable natural gas (RNG). This dual approach involves securing supply from external sources through dedicated contracts and directly operating their own dairy RNG production sites. Their strategic goal is to exclusively supply RNG to on-road vehicle clients.
In 2024, Clean Energy Fuels continued to expand its RNG supply chain. The company's operational dairy RNG facilities are a key component, converting manure into biomethane. They also manage numerous supply agreements with third-party RNG producers, ensuring a consistent and growing volume of this cleaner fuel.
A fundamental aspect of this clean energy business model involves the meticulous design, construction, and ongoing operation of an extensive network of natural gas fueling stations throughout North America. This encompasses both publicly accessible fast-fill Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) stations, as well as specialized private time-fill stations tailored for fleet clients.
Crucially, the company also undertakes the proactive upgrading of its existing station infrastructure. These upgrades are strategically implemented to enhance overall reliability and extend the operational lifespan of each facility, ensuring consistent service delivery and maximizing asset value.
In 2024, the company reported operating over 150 CNG/RNG fueling stations, serving a diverse range of commercial and municipal fleets. This network facilitated over 50 million gallons of natural gas fuel dispensed, supporting the transition of thousands of vehicles to cleaner energy sources.
The core of our operations centers on the sales and distribution of RNG, CNG, and LNG, primarily targeting the transportation industry. This involves direct fuel provision to vehicle fleets and the meticulous management of ongoing supply contracts.
Our commitment to expanding clean energy access saw us deliver an impressive 51 million gallons of RNG in the first quarter of 2025, underscoring our significant role in decarbonizing transportation.
Environmental Credit Generation and Monetization
Clean Energy's core activity involves generating and selling environmental credits, a crucial component of its business model. These credits, like Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs) and Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) credits, are produced when the company sells its renewable natural gas (RNG) as vehicle fuel. This process is a major contributor to the company's revenue and overall financial health.
The monetization of these environmental credits directly impacts the economic feasibility of RNG projects. By leveraging these regulatory mechanisms, Clean Energy can create additional income streams beyond the direct sale of fuel.
- Environmental Credit Generation: Producing credits such as RINs and LCFS by selling RNG as vehicle fuel.
- Significant Revenue Driver: These credits are a key source of income, supporting the economic viability of RNG operations.
- Market Leadership: In 2023, Clean Energy was estimated to have generated 44% of all LCFS credits for RNG pathways in California, highlighting its dominant market position.
- Monetization Strategy: Actively selling these generated credits to realize their financial value.
Customer Support and Fleet Transition Services
Customer support is crucial for facilitating the adoption of clean energy. This involves guiding customers through the complexities of transitioning to fuels like natural gas, which can significantly reduce emissions. For instance, in 2024, many businesses are actively seeking ways to lower their carbon footprint, and support in navigating these changes is paramount.
Key activities include assisting clients with securing grants and incentives, which are vital for offsetting the initial costs of fleet conversion. By providing expertise on available programs, companies can make the switch more financially viable. This support extends to offering comprehensive maintenance contracts for the new fueling infrastructure, ensuring operational reliability.
Furthermore, providing specialized knowledge on fleet conversion processes is a core function. This expertise helps customers understand the best practices and tailor solutions to their specific operational needs. For example, a logistics company might require a different fueling strategy than a waste management service, and customized guidance is essential for successful integration.
The goal is to develop scalable fueling solutions that align with each customer's unique operational demands and growth trajectory. This consultative approach ensures that the transition to cleaner fuels is not only environmentally beneficial but also economically sound and operationally efficient.
- Grant and Incentive Assistance: Helping customers access financial aid to reduce conversion costs.
- Fueling Infrastructure Maintenance: Offering service contracts to ensure the upkeep of new fueling stations.
- Fleet Conversion Expertise: Providing guidance on the technical and logistical aspects of switching fuels.
- Customized Fueling Solutions: Developing scalable strategies tailored to individual business needs.
Key activities revolve around the procurement and production of renewable natural gas (RNG), alongside the design, construction, and operation of a widespread fueling station network. These efforts are bolstered by the generation and sale of environmental credits, and comprehensive customer support for fleet transitions.
In 2024, Clean Energy Fuels continued its focus on expanding RNG supply and its fueling infrastructure. The company reported operating over 150 CNG/RNG fueling stations, dispensing over 50 million gallons of fuel. They also delivered 51 million gallons of RNG in Q1 2025, demonstrating significant progress in decarbonizing transportation.
| Activity | Description | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| RNG Supply Chain | Procuring and producing RNG from dairy farms and third-party suppliers. | Focus on exclusively supplying RNG to on-road vehicle clients. |
| Fueling Infrastructure | Designing, building, and operating CNG/RNG fueling stations. | Operated over 150 stations in 2024. |
| Environmental Credits | Generating and selling RINs and LCFS credits from RNG sales. | In 2023, generated 44% of California's RNG LCFS credits. |
| Customer Support | Assisting with grant applications, maintenance, and fleet conversions. | Facilitating transitions to cleaner fuels for businesses aiming to lower carbon footprints. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Business Model Canvas
The Clean Energy Business Model Canvas you are previewing is the exact document you will receive upon purchase. This means you're seeing a direct snapshot of the comprehensive tool, complete with all sections and formatting, ready for your strategic planning. No samples or mockups, just the full, actionable business model canvas for your clean energy venture.
Resources
Clean Energy Fuels boasts an extensive network of over 600 natural gas fueling stations across the U.S. and Canada. This robust physical infrastructure is a cornerstone of their business model, offering crucial access to alternative fuels for the heavy-duty transportation sector.
The company actively invests in expanding and modernizing this network, ensuring it meets the growing demand for cleaner fueling solutions. This commitment to infrastructure development directly supports their mission to accelerate the adoption of natural gas as a transportation fuel.
Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) production facilities are the operational heart of this clean energy business model. The company actively invests in and manages these sites, with a notable focus on dairy farm-based anaerobic digesters. These digesters are designed to capture methane, a potent greenhouse gas, from animal waste, transforming a liability into a valuable energy resource.
These facilities are critical for generating negative carbon-intensity RNG. This means the process of producing the gas actually removes more carbon from the atmosphere than it emits, a significant competitive advantage. The Del Rio Dairy project, a prime example, commenced RNG production and delivery in 2023, showcasing the company's commitment to tangible operational milestones.
Securing diversified fuel supply through long-term contracts with third-party producers, including those for renewable natural gas (RNG), is a critical resource for clean energy businesses. These agreements are the backbone of consistent and reliable fuel delivery, ensuring that customer demand across the network is met without interruption.
The volume of RNG sourced from these third-party producers directly influences operational performance and the company's ability to meet its sustainability targets. For instance, in 2024, companies heavily reliant on RNG partnerships saw their supply volumes increase by an average of 15% year-over-year, contributing to a 10% rise in their green energy portfolio share.
Proprietary Technology and Expertise in Natural Gas Fueling
Clean Energy possesses over 25 years of deep-seated expertise and proprietary technology in the design, construction, and operation of natural gas fueling infrastructure. This encompasses specialized equipment for both compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG) dispensing, alongside a refined understanding of how to optimize fueling solutions for diverse fleet operations.
Their technological edge allows for efficient and reliable natural gas delivery, a critical component for fleets transitioning to cleaner fuels. This expertise is a cornerstone of their business model, enabling them to offer comprehensive solutions rather than just hardware.
- Decades of Experience: Over 25 years in the natural gas fueling sector.
- Proprietary Technology: Specialized equipment for CNG and LNG dispensing.
- Fleet Optimization: Expertise in tailoring fueling solutions for various fleet types.
- Infrastructure Development: Proven track record in building and operating fueling stations.
Environmental Credits and Regulatory Knowledge
The capacity to generate and profit from environmental credits, like Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs) and Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) credits, represents a substantial financial asset. For instance, in 2023, LCFS credit prices in California fluctuated, with some periods seeing values exceeding $160 per metric ton of CO2 equivalent, directly impacting revenue streams for qualifying clean energy projects.
This capability is underpinned by a thorough understanding of federal, state, and local environmental regulations and the various incentive programs designed to promote clean energy. Navigating these complex frameworks allows businesses to maximize their returns from environmental attributes.
Furthermore, a dedicated grants department actively seeks and secures funding for projects, such as those involving Renewable Natural Gas (RNG). In 2024, significant federal funding opportunities, including those through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, continue to support the development and expansion of RNG infrastructure, providing crucial capital for growth.
- Environmental Credit Monetization: Ability to generate and sell credits like RINs and LCFS, with LCFS prices in California reaching over $160/ton CO2e in 2023.
- Regulatory Expertise: Deep knowledge of federal, state, and local environmental laws and incentive programs is crucial for optimizing revenue.
- Grant Funding: Active pursuit of grants for projects like RNG, leveraging opportunities such as those provided by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law in 2024.
Key resources for a clean energy business model include a robust physical infrastructure, such as a widespread network of fueling stations, and operational facilities for producing renewable energy. Expertise in the design, construction, and operation of this infrastructure, coupled with proprietary technology, is also vital. Furthermore, the ability to generate and profit from environmental credits and secure grant funding are critical financial and regulatory resources.
| Resource Category | Specific Resource | Key Metric/Data Point | Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Infrastructure | Fueling Station Network | 600+ stations across U.S. and Canada | Provides essential access for clean fuel users. |
| Operational Facilities | RNG Production Sites | Dairy farm-based anaerobic digesters | Generates negative carbon-intensity RNG. |
| Intellectual Capital | Technical Expertise | 25+ years in natural gas fueling | Enables efficient and reliable fuel delivery solutions. |
| Financial & Regulatory | Environmental Credits | LCFS prices >$160/ton CO2e (2023) | Significant revenue stream from green attributes. |
| Financial & Regulatory | Grant Funding | Leveraging Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (2024) | Secures capital for infrastructure expansion. |
Value Propositions
Clean energy's core value is drastically cutting greenhouse gas emissions, especially with renewable natural gas (RNG). RNG, sourced from organic waste, can even achieve a negative carbon-intensity score. This means it reduces lifecycle carbon emissions by more than 300% when compared to traditional diesel fuel.
This significant emission reduction directly assists customers in achieving their sustainability targets and effectively managing their carbon footprint. For instance, by adopting RNG, companies can demonstrably lower their Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, contributing to a greener operational profile.
Clean Energy provides a compelling cost-effective alternative to traditional diesel, offering stable fuel prices and reduced maintenance for natural gas vehicles.
In 2024, the transition to renewable natural gas (RNG) is further incentivized by significant federal, state, and local grants, alongside Clean Energy's dedicated programs, making it an economically sound choice for fleet operators.
Customers gain access to an extensive and dependable network of over 600 fueling stations strategically located throughout North America. This widespread infrastructure ensures that fleets have convenient and consistent access to natural gas fuels, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions.
Beyond the physical network, Clean Energy offers comprehensive operation and maintenance services for both private and public fueling sites. This commitment guarantees high uptime and simplifies the user experience for fleet operators, allowing them to focus on their core business operations.
In 2024, Clean Energy continued to expand its infrastructure, with a particular focus on supporting the growing demand for natural gas vehicles in the heavy-duty trucking sector. The company's investment in reliable fueling solutions directly supports the economic viability and operational efficiency of fleets transitioning to cleaner energy sources.
Proven Performance and Operational Efficiency
Natural gas vehicles, particularly those equipped with advanced engine technologies like the Cummins X15N, are now delivering performance on par with traditional diesel engines. This means heavy-duty applications can achieve similar power, torque, and operational range without compromising on capability.
Furthermore, the adoption of Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) in these vehicles yields substantial environmental and operational benefits. RNG-powered engines drastically cut down on smog-forming nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. For instance, by 2024, a significant portion of new heavy-duty natural gas engines are designed to meet stringent EPA and CARB emissions standards, often exceeding those of comparable diesel engines.
- Comparable Performance: Newer natural gas engines match diesel power, torque, and range for heavy-duty use.
- Reduced Emissions: RNG engines significantly lower NOx emissions, contributing to cleaner air.
- Quieter Operation: These engines operate more quietly, enhancing community relations and driver comfort.
- Operational Efficiency: The combination of reduced emissions and quieter operation boosts overall operational efficiency and social license to operate.
Support for Regulatory Compliance and Sustainability Goals
Clean energy solutions are crucial for fleet operators aiming to meet evolving environmental regulations and corporate sustainability targets. By providing ultra-clean renewable natural gas (RNG) and guiding clients through available grants and incentives, the company offers a practical pathway to decarbonize transportation fleets. This support is particularly valuable as many municipalities and public transit systems are actively selecting RNG to achieve their ambitious climate goals.
The demand for RNG in the transportation sector is growing significantly. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) projected a substantial increase in RNG production and utilization for transportation fuel. This trend highlights the market’s embrace of RNG as a viable and compliant solution.
- Regulatory Alignment: Facilitates compliance with mandates like California's Advanced Clean Fleets rule, which requires zero-emission vehicles or RNG for certain fleet types.
- Sustainability Achievement: Enables companies to demonstrably reduce their carbon footprint, often achieving greenhouse gas emission reductions of 70% or more compared to conventional diesel.
- Incentive Navigation: Assists in accessing federal and state incentives, such as the Inflation Reduction Act's tax credits for clean fuels, thereby improving the economic viability of RNG adoption.
- Market Trend Adoption: Supports the strategic move towards RNG, aligning with the increasing number of cities and transit agencies prioritizing its use for their decarbonization efforts.
Clean Energy's value proposition centers on providing a demonstrably cleaner and more cost-effective alternative to traditional fossil fuels. By offering Renewable Natural Gas (RNG), the company enables customers to significantly reduce their carbon footprint, often achieving over 70% greenhouse gas emission reductions compared to diesel. This aligns with growing regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals.
Furthermore, Clean Energy simplifies the transition to cleaner fuels by offering robust infrastructure and support services. Their extensive network of over 600 fueling stations across North America ensures operational reliability for fleets. In 2024, this network continued to expand, particularly supporting the heavy-duty trucking sector's shift towards natural gas vehicles.
The economic advantages are also substantial. In 2024, federal and state incentives, coupled with Clean Energy's own programs, made RNG an economically attractive choice for fleet operators. This, combined with stable fuel pricing and reduced maintenance costs for natural gas vehicles, enhances overall operational efficiency and profitability.
The company's commitment extends to comprehensive operational support, ensuring high uptime for fueling sites and minimizing disruptions for clients. This holistic approach makes adopting cleaner energy solutions more accessible and manageable for a diverse range of businesses and public entities.
| Value Proposition | Key Benefit | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Reduction | Significant greenhouse gas emission reduction (up to 70%+ vs. diesel) | RNG's negative carbon intensity potential |
| Cost Savings & Stability | Lower operating costs and predictable fuel prices | Reduced maintenance for natural gas vehicles |
| Infrastructure & Reliability | Extensive fueling network (600+ stations) | Continued network expansion in 2024 |
| Regulatory & Incentive Support | Facilitates compliance and leverages financial incentives | Inflation Reduction Act tax credits |
Customer Relationships
Dedicated account management is crucial for clean energy businesses, especially when serving fleet customers. This personalized approach ensures clients receive expert guidance throughout their transition to cleaner fuels, from initial consultations and navigating grant applications to the practicalities of station design and construction.
This hands-on support extends to ongoing maintenance, guaranteeing a seamless and effective adoption of natural gas fuels. For instance, a company might offer a dedicated point of contact who understands the client's specific operational needs and regulatory environment, facilitating smoother project execution and long-term satisfaction.
Clean Energy cultivates enduring customer relationships through long-term contracts for both fuel supply and station maintenance. These agreements are foundational, providing a predictable revenue stream and ensuring consistent service delivery for clients.
These contracts offer significant stability. For instance, Clean Energy's existing customer base, which includes major transit agencies and waste management companies, demonstrates the success of this strategy, contributing to a robust and recurring business model. As of 2024, a significant portion of their revenue is derived from these multi-year commitments.
Clean Energy offers vital technical assistance and training to customers, focusing on natural gas vehicle operation and proper fueling procedures. This hands-on support is key to ensuring safe and efficient utilization of their alternative fuel products and infrastructure.
By building customer confidence, this training fosters trust in natural gas as a viable alternative fuel solution. For fleets transitioning from traditional fuels, this level of support is absolutely critical to a smooth and successful adoption process.
In 2024, over 500 fleet managers participated in these training sessions, with 95% reporting increased confidence in operating natural gas vehicles. This investment in customer education directly translates to reduced operational errors and enhanced system reliability.
Partnerships for Fleet Growth and Expansion
Clean Energy actively partners with customers to support their fleet growth and expansion into natural gas vehicles. This involves collaborating on new fueling station builds and modifications to existing facilities to accommodate growing natural gas fleets. This proactive approach helps customers scale their clean energy initiatives.
For instance, in 2024, Clean Energy announced a significant expansion of its natural gas fueling infrastructure, partnering with several major transportation companies. These partnerships are projected to add over 50 new natural gas fueling stations across the United States by the end of 2025, directly supporting customer fleet expansion.
- Fleet Expansion Support: Collaborating with customers on infrastructure development to enable their transition to natural gas vehicles.
- Infrastructure Development: Partnering on the construction of new fueling stations and upgrades to existing facilities.
- Customer Scaling: Enabling customers to effectively grow their natural gas vehicle fleets through dedicated support.
- Industry Growth: Facilitating the broader adoption of natural gas as a cleaner transportation fuel.
Environmental and Sustainability Collaboration
Clean Energy actively partners with customers to achieve their environmental and sustainability objectives, acting as a key ally in their transition to lower emissions. This collaborative approach is crucial as businesses increasingly prioritize decarbonization.
The company provides tangible data on emission reductions achieved through its clean transportation solutions, directly assisting clients in navigating complex environmental regulations. This focus on measurable impact reinforces Clean Energy's leadership in the sector.
- Strategic Partnership: Clean Energy positions itself not just as a supplier, but as a strategic partner in customer decarbonization journeys.
- Data-Driven Value: Providing concrete data on emission reductions showcases the company's tangible impact and expertise.
- Regulatory Navigation: Assisting customers in understanding and complying with environmental regulations adds significant value.
- Alignment with Priorities: This strategy directly supports administrative goals for low-cost, low-emission fuel adoption, a key driver in the current market. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy announced significant funding for hydrogen infrastructure, highlighting the administrative focus on clean fuels.
Customer relationships in the clean energy sector are built on a foundation of trust, expertise, and ongoing support. This is especially true for businesses transitioning to natural gas vehicles, where dedicated account management and technical assistance are paramount. Long-term contracts for fuel supply and maintenance provide stability, while proactive partnerships for fleet expansion and infrastructure development solidify these bonds. Ultimately, clean energy providers act as strategic allies, helping customers achieve their environmental goals and navigate the evolving regulatory landscape.
| Customer Relationship Aspect | Description | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Dedicated Account Management | Personalized support for clients, especially fleet operators, from consultation to ongoing maintenance. | A dedicated contact understands specific client needs and regulatory environments for smoother project execution. |
| Long-Term Contracts | Securing predictable revenue through multi-year agreements for fuel supply and station maintenance. | A significant portion of revenue in 2024 derived from multi-year commitments with major transit and waste management companies. |
| Technical Assistance & Training | Educating customers on safe and efficient operation of natural gas vehicles and fueling procedures. | Over 500 fleet managers trained in 2024, with 95% reporting increased confidence in operating natural gas vehicles. |
| Fleet Expansion Support | Collaborating on infrastructure development to enable customer growth in natural gas vehicle fleets. | Partnerships projected to add over 50 new natural gas fueling stations across the U.S. by the end of 2025. |
| Environmental Partnership | Assisting customers in achieving decarbonization goals and navigating environmental regulations. | Providing data on emission reductions, aligning with administrative goals for low-emission fuel adoption. |
Channels
Clean energy businesses often rely on a dedicated direct sales force and a proactive business development team. These teams are crucial for directly engaging with potential and existing fleet customers, fostering essential relationships.
This direct approach enables tailored solutions and clear communication with key decision-makers within the transportation sector. For instance, in 2024, many alternative fuel providers reported increased success rates in securing new fueling contracts through personalized outreach, with some seeing a 15% uplift in deal closure compared to indirect sales channels.
The business development team actively seeks out new opportunities, focusing on securing fueling contracts and driving new infrastructure projects. Their efforts are vital for expanding the network and increasing adoption of clean energy solutions across various industries.
The extensive network of company-owned and operated fueling stations acts as a critical channel for distributing clean energy fuels. This network provides direct access to renewable natural gas (RNG), compressed natural gas (CNG), and liquefied natural gas (LNG) for a wide range of vehicle fleets operating throughout North America. As of early 2024, the company boasts over 600 such stations across the United States and Canada, underscoring its significant market presence and commitment to facilitating the transition to cleaner transportation fuels.
Clean Energy cultivates a strong online presence, leveraging its website and digital marketing to engage potential customers and investors. The company's digital channels are crucial for disseminating information about its clean fuels, comprehensive services, station network, and the environmental advantages of its offerings, effectively reaching a wide array of fleet operators and financial stakeholders.
Their website serves as a central hub, featuring dedicated sections for investors, up-to-date news, and detailed information on their sustainability initiatives. In 2024, Clean Energy reported that over 60% of its lead generation for new fleet contracts originated from its digital platforms, highlighting the effectiveness of its online outreach in attracting business.
Industry Conferences and Trade Shows
Engaging in industry conferences and trade shows is a vital channel for Clean Energy. These events offer a prime opportunity to present innovative solutions, connect with prospective clients, and gain insights into emerging market trends. For instance, participation in major events like the Advanced Clean Transportation (ACT) Expo in 2024 provides direct access to a concentrated audience of fleet operators, manufacturers, and policymakers, crucial for lead generation and brand visibility.
This strategic engagement helps solidify Clean Energy's reputation as a frontrunner in the clean energy transportation space. By actively participating, the company can foster valuable relationships and demonstrate its commitment to advancing sustainable mobility. In 2023, the global clean energy sector attracted over $1.3 trillion in investment, highlighting the immense growth potential and the importance of being present at key industry gatherings to capture market share.
Key benefits of this channel include:
- Lead Generation: Directly engaging with potential customers and partners at events.
- Market Intelligence: Gathering real-time information on competitor activities and technological advancements.
- Brand Building: Showcasing products and services to a targeted, influential audience.
- Networking: Establishing and strengthening relationships within the clean energy ecosystem.
Government Partnerships and Grant Programs
Government partnerships and grant programs act as crucial channels for clean energy businesses. These collaborations can unlock significant funding and foster wider adoption of cleaner fuels, particularly for fleets. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy's Clean Fuels Program continued to offer grants that support the deployment of alternative fueling infrastructure, directly benefiting businesses looking to expand their reach.
These government initiatives provide more than just financial backing; they also serve to raise the profile of natural gas fuels. By participating in these programs, companies gain visibility and credibility, encouraging both public and private entities to consider cleaner alternatives. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, for example, allocated substantial funds to clean energy projects, creating new opportunities for businesses to secure grants and partnerships through 2024 and beyond.
- Grant Funding: Access to non-dilutive capital for infrastructure development and technology deployment.
- Customer Acquisition: Partnerships with government agencies can lead to contracts for public fleets, securing a base of early adopters.
- Awareness and Adoption: Government endorsement and funding campaigns increase market acceptance of clean energy solutions.
The direct sales force and business development team are key channels, directly engaging fleet customers to build relationships and secure fueling contracts. In 2024, this personalized outreach saw a notable increase in deal closure rates for alternative fuel providers.
Customer Segments
Heavy-duty trucking fleets, comprising companies that operate Class 8 trucks and similar vehicles for extensive long-haul and regional transport, represent a critical customer segment. These businesses are actively pursuing sustainable fuel options to lower their environmental impact and meet evolving emissions standards. For example, the introduction of engines like the Cummins X15N is specifically targeting this demand for cleaner heavy-duty solutions.
Municipal and regional transit authorities are key customers, particularly those managing bus fleets. These agencies are under increasing pressure from government mandates and public demand to cut down on emissions and improve urban air quality. They also prioritize quieter operations for city dwellers.
Clean Energy has a strong track record, securing multiple agreements with transit agencies nationwide. For instance, in 2024, the company announced a significant deal to supply compressed natural gas (CNG) fueling infrastructure to a major metropolitan transit system, aiming to convert a substantial portion of its bus fleet to cleaner fuels.
Refuse and waste management fleets are prime candidates for clean energy adoption. Their heavy-duty trucks, often operating on predictable routes, are ideal for natural gas conversion. This allows for efficient, centralized fueling, a key logistical advantage.
These companies stand to gain significantly from using Renewable Natural Gas (RNG). Not only do they achieve environmental benefits, but they also have the unique opportunity to utilize RNG produced from the very waste they collect, creating a circular economy model. Noble Environmental's partnership with Clean Energy exemplifies this synergy.
Airport and Shuttle Fleets
Airport and shuttle fleets, along with other commercial vehicles operating on fixed routes or within specific areas, represent a prime market for clean energy solutions. These operators are keenly focused on lowering their environmental impact, particularly concerning emissions and noise pollution, which directly benefits public health and improves the overall operational atmosphere. For instance, by 2024, many major airports are implementing stricter emissions standards, pushing fleets towards cleaner alternatives.
These customer segments are driven by a dual need for enhanced operational efficiency and a commitment to sustainability. Natural gas, in particular, offers a compelling value proposition. It's not just about meeting regulatory requirements; it's about creating a more pleasant environment for passengers and staff.
- Reduced Emissions: Natural gas vehicles can significantly cut down on greenhouse gas emissions and particulate matter compared to traditional diesel or gasoline engines.
- Noise Reduction: The quieter operation of natural gas engines contributes to a more peaceful airport environment, improving passenger experience and reducing noise complaints.
- Cost Savings: While initial investment can be higher, the lower fuel costs and potential government incentives for natural gas vehicles can lead to substantial long-term operational savings.
- Fleet Modernization: Adopting cleaner fuels aligns with broader trends in fleet modernization and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Industrial and Commercial Fleets
Industrial and commercial fleets, encompassing construction, logistics, and delivery companies, represent a significant customer segment for clean energy solutions. These businesses operate medium to heavy-duty vehicles and are actively seeking alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. Their primary drivers include reducing operational costs, enhancing fleet reliability, and meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations and corporate sustainability targets. For instance, by 2024, many logistics companies are aiming to significantly reduce their carbon footprint, with some setting ambitious goals of achieving net-zero emissions by 2030.
These fleet operators are motivated by a dual imperative: cost savings and environmental stewardship. The volatile nature of diesel prices makes clean energy alternatives, such as electric or hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, attractive for long-term cost predictability. Furthermore, consumer demand for sustainable practices is pressuring companies to adopt greener operations. For example, major retailers are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of their supply chains, pushing logistics partners to invest in cleaner fleets. By 2024, it's estimated that the total cost of ownership for electric medium-duty trucks can become competitive with diesel equivalents, especially when factoring in fuel and maintenance savings.
- Cost Savings: Reduced fuel and maintenance expenses compared to diesel vehicles.
- Sustainability Goals: Meeting corporate social responsibility targets and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to evolving environmental laws and emissions standards.
- Brand Image: Enhancing reputation by demonstrating commitment to eco-friendly practices.
The customer segments for clean energy solutions are diverse, primarily focusing on entities with significant vehicle fleets that incur high fuel costs and face environmental pressures. These include heavy-duty trucking, municipal transit, waste management, and airport shuttle services.
These groups are motivated by a combination of operational cost reduction, regulatory compliance, and corporate sustainability goals. The adoption of cleaner fuels like natural gas and the exploration of electric and hydrogen alternatives are key trends observed across these segments through 2024.
For instance, in 2024, the trucking industry saw increased investment in alternative fuels, with Clean Energy Fuels reporting a growing demand for its RNG offerings. Similarly, transit authorities are actively transitioning fleets, with many cities setting targets for 100% zero-emission bus operations by 2030.
The financial benefits are substantial, with potential for lower total cost of ownership due to fuel savings and government incentives. These factors make clean energy a compelling choice for businesses looking to modernize their fleets and enhance their environmental credentials.
| Customer Segment | Primary Motivations | Key Clean Energy Trend (2024) | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy-Duty Trucking | Cost savings, emissions reduction, regulatory compliance | Increased adoption of RNG and exploration of electric/hydrogen | Lower fuel costs, reduced maintenance, improved brand image |
| Municipal Transit | Air quality improvement, noise reduction, public health | Transition to electric and CNG buses, government mandates | Operational cost savings, quieter cities, meeting sustainability targets |
| Waste Management | Circular economy, operational efficiency, emissions control | RNG utilization from waste, fleet conversion to CNG | Cost predictability, environmental stewardship, reduced landfill impact |
| Airport/Shuttle Fleets | Noise reduction, emissions control, passenger experience | Electrification of ground support equipment and shuttle buses | Improved local air quality, enhanced passenger comfort, meeting airport regulations |
Cost Structure
The primary cost component involves securing both conventional and renewable natural gas (RNG). This includes payments to third-party suppliers for natural gas and RNG, alongside the operational expenditures for any in-house RNG production facilities. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of natural gas delivered to power plants in the U.S. fluctuated, impacting procurement expenses.
Expenses related to the company's own RNG production are also significant. These costs encompass the acquisition of raw organic waste materials, such as agricultural byproducts or landfill waste, and the energy and labor required for the anaerobic digestion and upgrading processes that convert these materials into usable RNG. The efficiency of these conversion processes directly affects the per-unit production cost.
Fluctuations in RNG supply from external producers can create cost volatility. When third-party RNG volumes are lower than anticipated, the business may need to rely more heavily on potentially higher-priced conventional natural gas or incur increased costs to ramp up its own production, impacting overall profitability and operational stability.
Developing and maintaining a widespread network of natural gas fueling stations represents a substantial cost for clean energy businesses. These expenses encompass the initial capital outlay for designing and constructing new stations, as well as investments in upgrading existing equipment. For instance, in the first quarter of 2025, selling, general, and administrative expenses saw an increase, partly driven by the additional costs associated with specific fueling station development projects.
Personnel costs, encompassing salaries, benefits, and training for sales, operations, and engineering teams, form a significant portion of the overhead. In 2024, the clean energy sector saw an average increase in employee compensation, with some specialized engineering roles experiencing boosts of up to 7% to attract top talent.
Operational overhead includes expenses for managing a distributed workforce and facilities across the U.S. and Canada. This can range from IT infrastructure and software licenses to office leases and utilities, contributing to the overall cost base for maintaining widespread operations.
Research and Development for New Technologies
Investment in research and development is a significant cost, particularly for advancing natural gas fueling technologies and optimizing RNG production. This includes exploring the potential of hydrogen integration and improving the efficiency of renewable natural gas (RNG) processes. These investments are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the evolving clean energy transportation sector.
For instance, the company secured a contract in 2024 to design and construct a new hydrogen fueling station. This project underscores the commitment to innovation and expanding clean energy infrastructure. Such endeavors represent a substantial allocation of resources within the cost structure, driving future growth and market leadership.
- R&D Investment: Allocations for natural gas fueling technology advancement and RNG process optimization.
- Hydrogen Integration: Costs associated with exploring and developing hydrogen as a viable fuel source.
- Contract Wins: Expenses related to designing and building new hydrogen infrastructure, such as the 2024 station contract.
- Technological Advancement: Funding for ongoing research to stay at the forefront of clean transportation solutions.
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Program Costs
Expenses tied to environmental regulations, securing permits, and participating in environmental credit programs like RINs and LCFS are fundamental to clean energy operations. While these programs can be revenue generators, they also incur significant administrative and compliance costs. For instance, the expiration of the Alternative Fuel Tax Credit in Q1 2025 directly impacted revenue streams, underscoring the financial implications of regulatory shifts.
- Regulatory Compliance Expenses: Costs associated with adhering to local, national, and international environmental laws and standards.
- Permitting and Licensing Fees: Expenditures for obtaining and maintaining operational permits and licenses required for clean energy projects.
- Environmental Credit Program Costs: Administrative and operational expenditures related to generating, trading, and complying with rules for credits such as Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs) and Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) credits.
- Impact of Tax Credit Expirations: Financial consequences stemming from the lapse of incentives like the Alternative Fuel Tax Credit, which can reduce overall profitability and cash flow, as seen in Q1 2025.
The cost structure is heavily influenced by the procurement of natural gas and renewable natural gas (RNG), with fluctuating market prices in 2024 impacting expenses. Significant investments are also made in developing and maintaining fueling infrastructure, with Q1 2025 seeing increased selling, general, and administrative costs linked to station projects. Personnel and operational overhead, including R&D for technological advancements and compliance with environmental regulations, form substantial ongoing expenditures.
| Cost Category | Description | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas & RNG Procurement | Cost of acquiring conventional and renewable natural gas. | U.S. natural gas delivered to power plants saw price fluctuations in 2024. |
| Infrastructure Development | Capital outlay for new and upgraded fueling stations. | Q1 2025: Increased SG&A due to fueling station projects. |
| Personnel Costs | Salaries, benefits, and training for staff. | 2024: Average compensation increase in clean energy sector, up to 7% for specialized engineers. |
| Research & Development | Advancing fueling technologies and RNG processes. | Contract secured in 2024 for new hydrogen fueling station design and construction. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Permits, licensing, and environmental credit programs. | Q1 2025: Alternative Fuel Tax Credit expiration impacted revenue, highlighting regulatory sensitivity. |
Revenue Streams
The core revenue for Clean Energy Fuels is generated through the sale of renewable natural gas (RNG). This vital income source supports their clean energy business model.
Long-term supply agreements are crucial, securing consistent sales of RNG to diverse customers, including commercial and public transportation fleets. These partnerships provide a stable foundation for revenue generation.
In the first quarter of 2025, Clean Energy Fuels demonstrated the strength of this revenue stream by delivering 51 million gallons of RNG, resulting in $103.8 million in revenue.
Revenue streams also include the sale of conventional compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG) primarily to the transportation sector. While the company is increasingly focusing on renewable natural gas (RNG), these traditional fuels still contribute a significant portion to overall sales volume.
Environmental credit sales represent a substantial income source, primarily through Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs) tied to the Renewable Fuel Standard and Low Carbon Fuel Standards (LCFS) in California, Oregon, and Washington. These credits are generated when the company's renewable natural gas (RNG) is utilized as fuel for vehicles.
In the first quarter of 2025, the company reported $9.0 million in revenue specifically from RIN and LCFS sales, highlighting the financial significance of this environmental compliance market.
Fueling Station Construction and Maintenance Services
Clean Energy generates income by offering comprehensive services for fueling stations. This encompasses the entire lifecycle, from initial design and construction to upgrades and essential ongoing operation and maintenance (O&M). These contracts span both private sector installations and public infrastructure projects.
In the first quarter of 2025, the company reported robust performance in this segment, with station construction revenues reaching $5.6 million. This highlights a strong demand for new and improved fueling facilities.
- Station Construction: Revenue from the design and building of new fueling stations.
- Station Upgrades: Income generated from modernizing existing fueling infrastructure.
- Operation & Maintenance (O&M): Recurring revenue from the ongoing upkeep and management of fueling sites.
- Contract Diversity: Revenue streams secured through agreements with both private companies and government entities.
Government Grants and Incentives
Government grants and incentives play a crucial role in supplementing revenue for clean energy businesses. These programs, offered at federal, state, and local levels, are designed to accelerate the development of clean energy infrastructure and encourage the use of alternative fuels. Clean Energy actively seeks out these funding opportunities to bolster its project financing and assist customers in their transition to cleaner energy solutions.
The company's proactive approach to securing these funds has proven beneficial. For instance, Clean Energy recently finalized a significant transaction involving a $29.5 million Investment Tax Credit (ITC) sale. This demonstrates a tangible example of how leveraging government incentives can directly contribute to revenue and project viability.
- Federal, state, and local government grants and incentives
- Support for clean energy infrastructure and alternative fuel adoption
- Clean Energy's active pursuit of funding opportunities
- Recent $29.5 million ITC sale as a key revenue supplement
Beyond RNG sales, Clean Energy Fuels also generates revenue from selling conventional compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG), primarily to the transportation sector. These traditional fuels still form a notable part of their sales volume, complementing their growing focus on renewable alternatives.
Environmental credit sales, particularly Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs) and Low Carbon Fuel Standards (LCFS) credits, represent a significant income stream. These credits are earned when the company's RNG is used as vehicle fuel, with Q1 2025 reporting $9.0 million from these sales alone.
The company also earns revenue through comprehensive fueling station services, including design, construction, upgrades, and ongoing operation and maintenance. Station construction revenue reached $5.6 million in Q1 2025, indicating strong demand for new fueling infrastructure.
Government grants and incentives are vital supplements, with the company recently completing a $29.5 million Investment Tax Credit (ITC) sale. This highlights the financial impact of leveraging government support for clean energy projects.
| Revenue Stream | Description | Q1 2025 Data (Millions USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) Sales | Primary revenue from selling RNG to transportation fleets. | $103.8 (51 million gallons delivered) |
| Conventional CNG/LNG Sales | Sales of traditional natural gas fuels. | Included in overall fuel sales |
| Environmental Credits (RINs/LCFS) | Income from credits generated by RNG usage. | $9.0 |
| Station Construction & Services | Revenue from building, upgrading, and maintaining fueling stations. | $5.6 (Station Construction) |
| Government Incentives | Funds from grants and tax credits. | $29.5 (ITC Sale) |
Business Model Canvas Data Sources
The Clean Energy Business Model Canvas is meticulously constructed using a blend of market intelligence, regulatory frameworks, and technological feasibility studies. These diverse data sources ensure a comprehensive and grounded approach to defining value propositions and operational strategies.
