Compagnie Industriali Riunite Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Compagnie Industriali Riunite Bundle
Compagnie Industriali Riunite operates within an industry shaped by moderate buyer power and a significant threat from substitute products, impacting its pricing flexibility and market share. The intensity of rivalry among existing competitors is a key factor, demanding strategic differentiation and operational efficiency. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Compagnie Industriali Riunite’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
In sectors like healthcare, where specialized equipment and pharmaceuticals are key, suppliers of proprietary technologies or unique drugs can wield considerable influence. For Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR), its subsidiary KOS, which manages nursing homes and rehabilitation centers, is particularly susceptible to this. The bargaining power of KOS's suppliers hinges on how concentrated the market for essential medical supplies, equipment, and specialized personnel is, and the distinctiveness of their products.
High switching costs for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) to change suppliers significantly bolster supplier bargaining power. If CIR faces substantial expenses and operational disruptions when switching to a new supplier for critical components or services, it becomes less inclined to do so. This inertia grants existing suppliers leverage, allowing them to potentially dictate terms or prices.
Consider the implications for CIR's subsidiaries. For instance, if CIR's healthcare division, KOS, finds that integrating new medical equipment or changing pharmaceutical providers requires extensive staff retraining, re-certification processes, or risks disrupting patient care, KOS would be hesitant to switch. This reluctance empowers current medical equipment and pharmaceutical suppliers. Similarly, for Sogefi, a CIR automotive components company, the cost of retooling manufacturing lines or re-validating new parts from alternative suppliers can be prohibitively expensive, reinforcing the power of its existing automotive parts vendors.
Suppliers can increase their bargaining power by threatening to integrate forward into the customer's business. For Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR), this could mean a supplier of specialized medical components or a large pharmaceutical firm potentially offering direct healthcare services or acquiring clinics. This threat is more pronounced if suppliers possess significant capital and expertise in the customer's market.
Importance of Supplier's Input to CIR's Business
The criticality of a supplier's input directly correlates with their bargaining power over Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR). For KOS, suppliers providing essential medical devices or specialized pharmaceuticals critical for patient care hold significant leverage. Conversely, suppliers of general office supplies would have considerably less influence.
Similarly, for Sogefi, a subsidiary of CIR, suppliers furnishing key raw materials or complex, engineered sub-components vital for automotive part manufacturing possess substantial bargaining power. These specialized inputs are often difficult to substitute, increasing their importance and, consequently, their negotiating strength.
- KOS: Suppliers of life-saving drugs or advanced medical equipment have higher bargaining power due to the critical nature of their products.
- Sogefi: Suppliers of specialized alloys or precision-engineered automotive components can exert greater influence due to the technical expertise and unique materials involved.
- CIR Overall: The reliance on a limited number of suppliers for proprietary or highly specialized components across its various businesses amplifies supplier bargaining power.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The bargaining power of suppliers for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is significantly influenced by the availability of substitute inputs. If CIR's various subsidiaries, operating in sectors like automotive, healthcare, and media, can readily source comparable materials or services from alternative suppliers without a substantial drop in quality or a significant increase in cost, the leverage of existing suppliers is weakened. For instance, in the automotive sector, the widespread availability of various steel grades or electronic components from multiple manufacturers limits the power of any single supplier. Similarly, in healthcare, the existence of generic drug manufacturers or multiple providers of medical equipment can dilute the influence of original equipment manufacturers.
This ease of substitution directly translates to reduced supplier power. If CIR's operational units can switch suppliers with minimal disruption or added expense, they possess a stronger negotiating position. For example, if a media subsidiary relies on content licensing, the presence of numerous independent content creators or competing distribution platforms diminishes the bargaining strength of any single content provider. This principle holds true across CIR's diverse portfolio, as finding viable alternatives for raw materials, specialized components, or even essential services like logistics can prevent suppliers from dictating terms and prices.
- Automotive Sector: The automotive industry in 2024 saw continued diversification in component sourcing, with many manufacturers actively seeking multiple suppliers for critical parts like semiconductors and battery materials to mitigate single-source dependency.
- Healthcare Sector: In 2024, the pharmaceutical market continued to experience growth in generic drug approvals, offering patients and healthcare providers more affordable alternatives to branded medications, thereby reducing the bargaining power of original patent holders.
- Media Sector: The media landscape in 2024 was characterized by an abundance of content creators and streaming platforms, providing media companies with a wider array of licensing and distribution options, which inherently limits the pricing power of individual content owners.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is a key factor influencing its profitability across its diverse operations. For its subsidiary KOS in healthcare, suppliers of specialized medical equipment and pharmaceuticals can hold significant sway, especially when these inputs are critical and difficult to substitute. Similarly, Sogefi, in the automotive sector, faces suppliers of specialized alloys or precision-engineered components where technical expertise and unique materials grant them leverage.
In 2024, the automotive sector saw a trend towards diversifying supply chains for critical components like semiconductors, with many manufacturers actively seeking multiple suppliers. This initiative aimed to reduce reliance on single sources, thereby potentially weakening supplier bargaining power. In healthcare, the continued approval of generic drugs in 2024 provided more affordable alternatives, diminishing the leverage of original patent holders.
The media sector in 2024 was marked by a proliferation of content creators and streaming platforms, offering media companies a broader selection of content licensing and distribution avenues. This abundance inherently limits the pricing power of individual content owners, thus reducing supplier bargaining power in that segment.
| CIR Subsidiary | Key Inputs/Services | Supplier Bargaining Power Factors | 2024 Market Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| KOS (Healthcare) | Specialized Medical Equipment, Pharmaceuticals | Criticality of input, Proprietary technology, Concentration of suppliers | Increased generic drug approvals, focus on supply chain resilience |
| Sogefi (Automotive) | Specialized Alloys, Precision Components | Technical expertise, High switching costs, Unique materials | Diversification of semiconductor sourcing, demand for advanced materials |
| Media Operations | Content Licensing, Distribution Platforms | Availability of substitutes, Number of content creators | Abundance of content creators, growth of streaming services |
What is included in the product
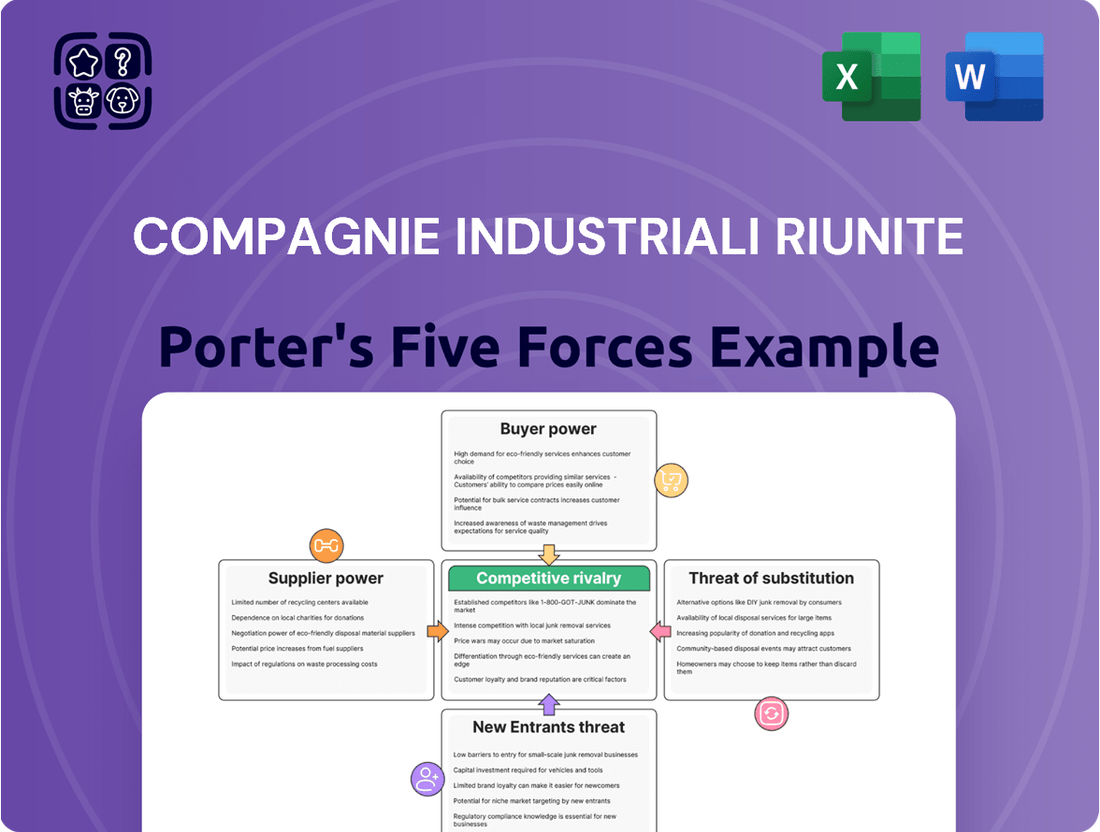
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Compagnie Industriali Riunite, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Porter's Five Forces, empowering strategic responses.
Customers Bargaining Power
In the healthcare sector, KOS faces significant customer concentration. Large institutional clients, like national health systems and major insurance providers, purchase substantial volumes of services. This concentration means these buyers can wield considerable bargaining power, potentially influencing pricing and contract terms. For instance, a single large health system might account for a significant percentage of KOS's revenue, giving it leverage in negotiations.
Similarly, Sogefi's position in the automotive industry is shaped by its key customers. Major automotive manufacturers, who procure components in bulk, possess substantial leverage due to the sheer volume of their orders. The ability of these manufacturers to switch suppliers or consolidate their purchasing across fewer vendors grants them significant bargaining power, impacting Sogefi's pricing and profitability.
Customer switching costs significantly influence their bargaining power. When it's easy and inexpensive for customers to switch to a competitor, their leverage increases. This is a critical factor for companies like KOS in the healthcare sector, where patients or referring physicians might easily move to another provider if the costs or disruptions associated with changing are minimal.
For instance, if a patient can switch to a different hospital or clinic without incurring substantial financial penalties or facing lengthy administrative hurdles, KOS's ability to dictate terms diminishes. This ease of transition empowers patients and referring bodies, giving them more sway in negotiations over services and pricing.
Similarly, in the automotive components industry, Sogefi's customers, the vehicle manufacturers, benefit from low switching costs if they can readily find alternative suppliers for similar parts. If a carmaker can switch from Sogefi to another manufacturer without significant retooling, supply chain disruption, or increased costs, Sogefi's customers hold greater bargaining power.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Compagnie Industriali Riunite. In sectors like publicly funded healthcare, where cost containment is paramount, customers are highly attuned to pricing, directly impacting KOS's revenue streams.
Similarly, in the automotive industry, manufacturers are perpetually driven to lower their production costs. This intense focus on cost reduction makes Sogefi's clientele exceptionally sensitive to the prices of components, influencing purchasing decisions and supplier relationships.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers can wield significant power if they possess a credible threat of backward integration. This means they could potentially manufacture the products or services they currently buy from CIR's various business units themselves. For example, while individual patients in a healthcare setting would not backward integrate, large automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) might explore insourcing more component production if it becomes economically advantageous.
The feasibility of backward integration for customers depends heavily on the specific industry and the scale of operations. In sectors where component manufacturing is relatively straightforward and cost-effective, customers might find it a viable strategy to gain more control over their supply chain and potentially reduce costs. This pressure can force suppliers like CIR to offer more competitive pricing or improved terms to retain business.
- Automotive OEMs: In 2024, major automotive manufacturers continued to evaluate the cost-benefit of producing certain components in-house, particularly those with high volume and standardized specifications. For instance, some are exploring increased vertical integration in battery production for electric vehicles.
- Healthcare Providers: While less common for direct patient care services, large hospital systems might consider backward integration for specific medical supplies or diagnostic services if procurement costs rise significantly.
- Electronics Manufacturers: Companies in this sector often have the technical expertise and capital to backward integrate into chip manufacturing or component assembly, especially when supply chain disruptions occur.
Availability of Substitute Services/Products for Customers
The availability of substitute services or products significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. When customers have numerous alternatives, they can easily switch to a competitor if prices rise or quality declines. This forces providers to remain competitive.
For KOS, a major player in the healthcare sector, the presence of many public hospitals and private clinics directly impacts its customer bargaining power. In 2024, the Italian healthcare market saw continued growth, with a significant number of private facilities operating alongside the national health service, offering patients a wide array of choices for medical treatments and services.
Similarly, for Sogefi, a supplier of automotive components, the bargaining power of its customers, the car manufacturers, is heavily influenced by the availability of alternative suppliers and component designs. In 2024, the automotive industry continued its trend of seeking diverse supply chains to mitigate risks and optimize costs, meaning manufacturers could readily source parts like air and oil filters from multiple global providers.
- Customer Choice: More substitutes mean customers can easily switch providers.
- Price Sensitivity: High availability of alternatives increases customer sensitivity to pricing.
- KOS Impact: Numerous public and private healthcare facilities in Italy enhance patient bargaining power.
- Sogefi Impact: Car manufacturers' ability to select from various component suppliers and designs strengthens their position.
The bargaining power of customers for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is a key factor, influenced by several elements. When customers have many choices or can easily switch to competitors, their ability to negotiate prices and terms increases significantly. This is particularly relevant for CIR's subsidiaries like KOS in healthcare and Sogefi in automotive components, where market dynamics often favor buyers with substantial purchasing volume or access to numerous alternatives.
In 2024, the automotive sector continued to see intense competition among component suppliers, allowing major manufacturers to exert considerable pressure on pricing. Similarly, in Italy's healthcare market, the presence of multiple providers meant that large institutional buyers for KOS could negotiate more favorable contracts. For instance, the average revenue per patient in Italian private healthcare facilities saw moderate growth in 2024, but this was often tempered by strong negotiation from large insurance providers and health systems.
| Factor | Impact on CIR Customers | 2024 Observation (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High concentration grants significant leverage. | Large automotive OEMs purchasing millions of units. |
| Switching Costs | Low costs empower customers to change suppliers easily. | Standardized automotive parts allow quick supplier changes. |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity forces suppliers to be competitive. | Automotive manufacturers constantly seek cost reductions. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Numerous alternatives increase customer bargaining power. | Multiple providers for medical supplies and services in Italy. |
What You See Is What You Get
Compagnie Industriali Riunite Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, ready-to-use Compagnie Industriali Riunite Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. This preview accurately reflects the depth and breadth of the analysis you will receive, providing actionable insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. You're looking at the actual document; once your purchase is complete, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) faces a varied competitive landscape across its diverse business segments. In healthcare, its subsidiary KOS operates within Italy's mixed public-private system, where demand for long-term care is rising, intensifying competition among numerous providers.
Sogefi, CIR's automotive components arm, contends with fierce rivalry in a sector rapidly shifting towards e-mobility. This transition is shrinking revenue from traditional parts, forcing intense competition as companies adapt to new market demands. For instance, the global automotive aftermarket is projected to reach $700 billion by 2025, highlighting the scale of this competitive arena.
The media and publishing sector, where CIR has interests, is also a battleground. Digital platforms and declining print revenues have reshaped the industry, creating a highly dynamic and competitive environment. In 2024, digital advertising spending in Italy is expected to continue its growth, further pressuring traditional media models.
The growth rate of an industry significantly shapes how intensely companies compete. In Italy, the healthcare sector, especially private spending, is experiencing a positive trajectory. This growth, fueled by an aging demographic and perceived limitations within the public healthcare infrastructure, naturally attracts more players and intensifies the battle for market dominance.
Conversely, the automotive component sector in Italy presents a more complex picture. While traditional segments are contracting, the burgeoning e-mobility market offers substantial growth opportunities. This divergence forces companies to pivot and vie fiercely for a stake in these emerging, high-potential areas.
The Italian publishing industry, however, paints a different scenario. With reported declines in sales and overall revenue, it suggests a mature or even shrinking market. In such an environment, competition becomes a zero-sum game, with companies aggressively fighting to capture the attention and spending of a dwindling customer base.
The intensity of competition among existing players is significantly shaped by how distinct their offerings are and how difficult it is for customers to switch. For instance, if KOS can offer a specialized medical treatment or a superior patient experience, it reduces the direct competition from other healthcare providers. Similarly, Sogefi’s advantage lies in its proprietary automotive components, making it harder for rivals to directly substitute its products compared to more standardized parts.
In the media sector, unique content and established brand loyalty can create a strong barrier against competitors. However, the digital age often presents challenges, as consumers can easily switch between streaming services or news platforms, thereby lowering switching costs and potentially increasing rivalry.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can indeed trap companies in markets, even when they are not performing well, which naturally fuels competitive rivalry. For Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR), this is particularly relevant across its diverse holdings.
In sectors like healthcare, CIR's subsidiaries often operate facilities that require substantial capital investment. These specialized assets, such as hospitals or advanced medical equipment, are not easily repurposed or sold, creating significant financial hurdles for exiting the market. For instance, the healthcare sector in Italy, where CIR has a notable presence, often involves long-term leases and complex regulatory frameworks that add to these exit barriers.
Similarly, CIR's involvement in manufacturing means dealing with specialized machinery and production lines. The cost and complexity of decommissioning these operations, coupled with potential contractual obligations to suppliers or employees, make exiting these segments a difficult proposition. This can lead to prolonged competition from firms that might otherwise have withdrawn.
In the media sector, the situation is often characterized by established infrastructure and legacy operations. The significant investments in broadcasting rights, distribution networks, and physical studios can represent substantial exit barriers. This means that even if a particular media outlet within CIR is struggling, the sunk costs and operational inertia can keep it competing, thereby intensifying rivalry with more agile players.
- Specialized Assets: Healthcare facilities and manufacturing plants require significant capital and are difficult to repurpose, leading to high exit barriers for CIR's subsidiaries.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term leases, supplier agreements, and employee severance costs in various CIR sectors can make exiting a market financially punitive.
- Legacy Operations: In media, established infrastructure and historical investments create inertia, discouraging divestment and prolonging competition.
- Intensified Rivalry: The presence of these high exit barriers means that even unprofitable competitors may remain in the market, increasing competitive pressure on CIR and its peers.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic importance of the Italian healthcare market fuels intense rivalry among established players and new entrants alike. Companies are driven to maintain and grow their market share, especially as Italy's aging population, projected to reach 26.5% over 65 by 2030, increases demand for healthcare services.
In the automotive component sector, the global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) presents a critical strategic imperative. Manufacturers that fail to adapt their product lines and manufacturing processes risk obsolescence, with EV sales in Europe already surpassing 1 million units in 2023, representing a significant portion of the market.
The media industry faces a constant battle for audience attention and advertising revenue in an increasingly digital landscape. Companies are investing heavily in digital content creation and distribution to stay relevant, as digital advertising spending in Italy was expected to grow by 8.5% in 2024.
- Demographic Trends: Italy's aging population drives demand in healthcare, intensifying competition.
- EV Transition: Automotive component makers must pivot to EV technology to remain competitive.
- Digital Dominance: Media firms compete fiercely for online audiences and advertising revenue.
The competitive rivalry within Compagnie Industriali Riunite's (CIR) operating segments is a significant factor influencing its performance. In healthcare, KOS faces competition from a multitude of Italian providers, with demand for long-term care services steadily increasing due to demographic shifts. Sogefi, in the automotive sector, navigates a highly competitive landscape where the transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping product demand, forcing intense competition among suppliers adapting to new technologies. The media sector, where CIR holds interests, is characterized by intense rivalry driven by digital platforms and evolving consumer habits, with companies vying for attention and advertising revenue.
The intensity of rivalry is amplified by several factors. In healthcare, the growth in private spending, projected to continue, attracts new entrants and intensifies competition among existing players for market share. The automotive sector's shift to EVs creates a high-stakes environment where companies must innovate rapidly to capture growth in this emerging segment; for example, European EV sales exceeded 1 million units in 2023. In media, a mature market with declining print revenues leads to a zero-sum competition for a shrinking customer base, with digital advertising in Italy expected to grow by 8.5% in 2024, further fragmenting revenue streams.
Switching costs also play a role. While specialized offerings in healthcare or proprietary automotive components can create customer loyalty and reduce direct rivalry, the digital media landscape often features low switching costs for consumers, increasing competitive pressure. High exit barriers, such as significant capital investments in healthcare facilities or specialized manufacturing equipment, can keep even struggling firms competing, thus prolonging rivalry across CIR's diverse business units.
| CIR Segment | Key Competitive Dynamics | Relevant Market Data (2023-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare (KOS) | Intense rivalry due to rising demand for long-term care and a mixed public-private system. | Italy's aging population (over 65 projected at 26.5% by 2030) fuels demand. |
| Automotive Components (Sogefi) | Fierce competition driven by the EV transition, impacting traditional parts revenue. | European EV sales surpassed 1 million units in 2023. |
| Media & Publishing | Dynamic competition from digital platforms and declining print revenues. | Italian digital advertising spending projected to grow 8.5% in 2024. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Compagnie Industriali Riunite's products, particularly in the automotive sector, is influenced by the price-performance trade-off. If alternative components or even entirely different vehicle technologies offer comparable or better performance at a lower cost, this poses a significant threat. For instance, the increasing efficiency and decreasing cost of electric vehicle components could substitute for traditional internal combustion engine parts, impacting demand for Sogefi's offerings.
Customer propensity to substitute hinges on awareness, perceived benefits, and ease of switching. For instance, in the automotive industry, the shift towards electric vehicles is a prime example, with the market for traditional internal combustion engine components projected to shrink by half by 2030, directly illustrating a significant substitution trend.
In publishing, the proliferation of free online content has dramatically altered consumer willingness to pay for news. This accessibility directly impacts the threat of substitutes, as readily available digital alternatives diminish the perceived value of paid subscriptions.
Similarly, within healthcare, patients increasingly favor personalized care and digital health solutions. This growing preference can drive them towards alternative care models, posing a threat to traditional healthcare providers if they fail to adapt.
The threat of substitutes is heightened when alternatives are easily accessible and offer comparable value. For instance, in the automotive sector, Sogefi faces competition from numerous global suppliers of components, and the rapid evolution of automotive technology means that entirely new solutions could emerge, displacing existing offerings. In 2024, the automotive aftermarket saw continued growth, with a significant portion of sales coming from independent repair shops that can source parts from a variety of manufacturers, underscoring the availability of substitutes.
Switching Costs for Customers to Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is influenced by how easily customers can switch to alternative solutions. If the financial, psychological, or logistical costs associated with changing are low, this threat intensifies.
In sectors like automotive components, where CIR operates, the ease with which new vehicle designs or manufacturing methods allow for the integration of alternative parts directly impacts CIR's competitive landscape. For instance, a shift towards modular vehicle architectures could lower the barriers for customers to adopt components from different suppliers, increasing the threat of substitution.
Consider the automotive industry's ongoing evolution. By 2024, the drive towards electrification and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) necessitates new types of components. If suppliers of these new-generation parts can offer them with minimal integration effort for automakers, CIR may face a heightened threat from these substitutes. This is particularly true if the perceived performance or cost benefits of these new components are significant.
The low switching costs in many consumer-facing industries, such as media where free online content readily replaces paid subscriptions, highlight the general principle. For CIR, this translates to needing to continually demonstrate superior value and integration ease to retain its customer base against potential substitute offerings.
Industry Profitability and Aggressiveness of Substitute Producers
The profitability of industries providing substitutes is a key factor. If companies offering alternative solutions are highly profitable, they have more resources to invest in marketing and innovation, thereby intensifying the threat. For instance, if home healthcare providers are experiencing strong profit margins, they are more likely to aggressively market their services and develop advanced technologies that could draw customers away from traditional healthcare models.
Aggressiveness in marketing and innovation by substitute producers directly impacts the competitive landscape. Companies that are actively developing superior alternatives or promoting their offerings more effectively can significantly erode the market share of existing players. Consider the automotive sector; the rapid innovation in electric vehicle technology and aggressive marketing campaigns by new entrants put considerable pressure on established manufacturers of internal combustion engine vehicles.
The threat of substitutes is amplified when these alternatives are not only profitable but also actively pushing boundaries. For example, digital-native media outlets and free content platforms have aggressively expanded their reach and offerings. This has created significant pressure on traditional publishing businesses, which saw a decline in advertising revenue and subscription numbers. In 2024, the global digital advertising market was projected to reach over $600 billion, highlighting the scale of this shift.
- Profitability of Substitutes: Higher profits for substitute providers fuel their ability to invest in competitive strategies.
- Marketing Aggressiveness: Vigorous marketing by substitutes directly challenges incumbent products or services.
- Innovation in Substitutes: Continuous development of better or cheaper alternatives by competitors increases the threat.
- Impact on CIR: For Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR), this means that if sectors offering alternatives to its core businesses (e.g., traditional publishing) become more profitable and innovative, the pressure on CIR's market position will intensify.
The threat of substitutes for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is significant, particularly in sectors like automotive components where alternative materials and technologies are rapidly emerging. For instance, the automotive industry's push towards electrification means that components for internal combustion engines face substitution from parts designed for electric vehicles. This trend is accelerating, with projections indicating that by 2030, the market for traditional engine components could significantly contract.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives is driven by factors like cost, performance, and ease of adoption. In the automotive aftermarket, for example, the availability of a wide range of suppliers in 2024 means that independent repair shops can easily source alternative parts, increasing the threat of substitution for established component manufacturers. If substitute products offer a better price-performance ratio or are easier to integrate into new designs, CIR's market position can be challenged.
The profitability and marketing aggressiveness of companies offering substitutes also amplify this threat. For example, in the digital media space, highly profitable online platforms with aggressive marketing strategies have significantly impacted traditional publishing, a sector where CIR has interests. The global digital advertising market's immense size, projected to exceed $600 billion in 2024, underscores the financial power behind these substitute offerings.
Entrants Threaten
High capital requirements are a major hurdle for new players looking to enter industries where Compagnie Industriali Riunite operates. For instance, establishing a new nursing home or rehabilitation center, similar to KOS, demands millions in upfront investment for buildings, medical equipment, and staffing. In 2024, the average cost to build a new skilled nursing facility in the US could range from $20 million to $50 million, depending on size and location.
Similarly, venturing into automotive component manufacturing, a sector Sogefi is active in, requires substantial capital. Setting up a new plant involves significant spending on advanced machinery, robotics, research and development for new materials, and securing supply chains, often running into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars. The automotive industry's continuous need for technological upgrades means ongoing capital investment is also a factor.
Even in traditional media like publishing, while perhaps less capital-intensive than manufacturing, significant upfront investment is still necessary. This includes costs for printing presses, distribution networks, digital infrastructure, and marketing campaigns to build brand recognition. The sheer scale of operations needed to compete effectively in these sectors creates a formidable barrier for potential new entrants.
Existing players within Compagnie Industriali Riunite's (CIR) sphere, such as its subsidiaries, already leverage significant economies of scale. This inherent advantage makes it incredibly challenging for any new company to enter the market and compete effectively on price. For instance, KOS, operating a wide network of healthcare facilities, realizes substantial cost efficiencies through bulk purchasing of supplies, optimized staffing models, and streamlined administrative processes.
Similarly, Sogefi, a prominent global automotive supplier, benefits immensely from its large-scale manufacturing operations, advanced research and development capabilities, and highly efficient supply chains. These established efficiencies allow them to produce components at a lower per-unit cost than a newcomer could hope to achieve.
New entrants would face a steep uphill battle to replicate these cost advantages. This is particularly true in the Italian automotive market, where vehicle production volumes have seen a downturn. For example, Italian automotive production decreased by approximately 10% in 2023 compared to 2022, creating a more competitive environment where cost is a critical factor.
Newcomers often struggle to secure shelf space or digital placement in crowded markets, a significant barrier to reaching customers. For instance, in the fast-moving consumer goods sector, securing prime placement in major retail chains can be incredibly difficult for emerging brands, often requiring substantial slotting fees or proven sales history. Similarly, in the software industry, gaining visibility on app stores or securing partnerships with enterprise resource planning (ERP) providers necessitates overcoming established players’ deep integration and brand loyalty.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policies and regulations act as a significant barrier to entry for new companies. For instance, in Italy's healthcare sector, stringent licensing, accreditation, and quality standards are mandatory, making it challenging for newcomers to establish a foothold. Similarly, the automotive industry faces rigorous regulations concerning safety, emissions, and component standards, which require substantial investment and compliance efforts.
Even sectors that seem less regulated, like media, can present entry hurdles. Concerns over data protection and content regulation necessitate careful navigation and compliance, adding complexity for potential new entrants. These regulatory landscapes can significantly deter new competition by increasing the cost and difficulty of market entry.
- Healthcare Sector: Italy's healthcare regulations, including licensing and quality standards, can require initial investments of tens of thousands of euros, deterring smaller new entrants.
- Automotive Industry: Compliance with EU emissions standards, like Euro 7, which is being phased in, requires significant R&D and manufacturing adjustments, creating a high barrier for new car manufacturers.
- Media Sector: GDPR compliance in Italy, impacting data handling for media companies, adds operational costs and legal scrutiny for any new digital media platform.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
A strong brand identity and deep-rooted customer loyalty present a formidable barrier to new entrants. For instance, in 2024, companies with a well-established reputation, like those in the healthcare sector, often benefit from patient trust built over years, a difficult asset for newcomers to replicate. This loyalty translates into consistent demand, making it challenging for new players to capture significant market share without substantial investment in marketing and brand building.
Consider Sogefi, a component supplier to the automotive industry. Their long-standing relationships with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and a proven track record of quality serve as a significant deterrent. In 2023, Sogefi reported revenues of €1.7 billion, underscoring its established market position. New entrants would face the hurdle of not only matching this quality but also securing the trust of major automotive brands, a process that typically takes considerable time and proven performance.
Even in sectors like media, where digital disruption is prevalent, established brands often retain loyal audiences. While the media landscape is evolving, legacy news organizations in 2024 continue to leverage their brand recognition and editorial integrity to maintain readership. For a new media outlet, building a comparable level of trust and attracting a dedicated following requires a sustained commitment to quality journalism and effective audience engagement strategies, a steep climb against established names.
- Brand Loyalty as a Moat: Companies with high customer loyalty, like those with strong healthcare reputations, benefit from repeat business and reduced marketing costs, making it harder for new entrants to gain traction.
- OEM Relationships: In industries like automotive parts, established suppliers like Sogefi, which generated €1.7 billion in revenue in 2023, benefit from deep ties with manufacturers that new entrants struggle to penetrate.
- Reputation Capital: A company's established reputation and the trust it has cultivated over time act as a significant barrier, requiring new competitors to invest heavily in building credibility.
The threat of new entrants for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is generally moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and established brand loyalty across its diverse business segments. For example, KOS's healthcare operations demand significant upfront investment, with new facility construction costs in 2024 potentially reaching $20 million to $50 million.
Sogefi's position in the automotive component sector also presents high entry barriers, involving substantial outlays for advanced manufacturing technology and R&D, especially with evolving emissions standards like Euro 7. These capital-intensive industries, coupled with regulatory hurdles and the need to build customer trust, create a significant deterrent for potential new competitors.
Established players benefit from economies of scale, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price. For instance, in 2023, Sogefi's €1.7 billion in revenue reflects its operational efficiencies. New entrants would struggle to match these cost advantages and the deep-rooted OEM relationships that are crucial for market penetration.
| Barrier Type | Example Industry/Company | Impact on New Entrants | Relevant 2023/2024 Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Healthcare (KOS) | High; facility construction costs | $20M - $50M for new skilled nursing facilities (2024) |
| Economies of Scale | Automotive Parts (Sogefi) | Significant cost advantage for incumbents | Sogefi 2023 Revenue: €1.7 Billion |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Healthcare, Automotive | Difficult to replicate trust and relationships | Established trust is a key differentiator |
| Government Regulation | Healthcare, Automotive | Increases cost and complexity of entry | Euro 7 emissions standards require significant R&D |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Compagnie Industriali Riunite is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research, and relevant trade publications to capture the competitive landscape.
