Cipla Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cipla Bundle
Cipla's competitive landscape is shaped by intense rivalry among established pharmaceutical players and the constant threat of generic drug manufacturers. Understanding the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers is crucial for navigating this dynamic market.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Cipla’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The pharmaceutical sector often depends on a select group of suppliers for crucial Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and other essential raw materials. This limited supplier pool can grant these entities substantial leverage, particularly when dealing with unique or patented components.
For instance, in 2024, the global API market was valued at approximately USD 210 billion, with a significant portion of specialized APIs sourced from a concentrated number of manufacturers in regions like India and China, highlighting the potential for supplier power.
Cipla's strategy to counter this involves broadening its supplier network and, where feasible, developing in-house API manufacturing capabilities. This approach aims to reduce reliance on any single supplier and enhance supply chain resilience.
Cipla's robust in-house API manufacturing capabilities significantly reduce its reliance on external suppliers for key pharmaceutical ingredients. This backward integration grants Cipla greater control over its supply chain and can lead to cost efficiencies, thereby mitigating the bargaining power of suppliers.
Suppliers of pharmaceutical raw materials face rigorous regulatory hurdles, including adherence to current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). These demanding standards, essential for product safety and efficacy, necessitate significant investment in quality control and compliance infrastructure. This complexity naturally restricts the pool of eligible suppliers, thereby bolstering the leverage of those who can consistently meet these stringent benchmarks.
Switching Costs for Cipla
Switching suppliers in the pharmaceutical sector, like for Cipla, often comes with substantial costs. This is primarily due to the rigorous processes of re-validation for raw materials and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), obtaining necessary regulatory approvals, and the potential for significant disruption to ongoing production schedules. These factors collectively increase the bargaining power of existing suppliers, as Cipla faces considerable expense and time delays if it decides to change its supply partners.
Cipla's proactive strategy to diversify its supplier base is therefore a critical move to mitigate these high switching costs. By spreading its sourcing across multiple vendors, Cipla can reduce its reliance on any single supplier, thereby lessening their individual bargaining power and improving its own negotiating position. This diversification is key to maintaining operational stability and cost-effectiveness in its supply chain.
For instance, in 2023, the global pharmaceutical supply chain experienced disruptions, highlighting the importance of robust supplier relationships and contingency planning. Companies like Cipla have been investing in strengthening these ties and exploring alternative sourcing to ensure uninterrupted production of essential medicines. The average cost for regulatory re-approval of a new API supplier can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, not including the potential loss of revenue due to production halts.
- High Re-validation Costs: Pharmaceutical suppliers demand rigorous testing and validation of their products before they can be used in Cipla's manufacturing processes, a process that can be lengthy and expensive.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining approvals from health authorities like the FDA or EMA for new suppliers or materials adds significant time and compliance costs, strengthening the position of established, approved vendors.
- Production Disruption Risk: Changing suppliers can lead to temporary halts in manufacturing, resulting in lost sales and impacting Cipla's ability to meet market demand, a risk that suppliers can leverage.
- Supplier Diversification Strategy: Cipla's efforts to broaden its supplier network are essential to counterbalance the inherent switching costs and enhance its overall supply chain resilience and negotiation leverage.
Supplier's Product Differentiation
When suppliers provide highly differentiated or proprietary raw materials, their leverage over Cipla grows substantially. This is especially evident with novel active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or specialized excipients that are essential for Cipla's unique product formulations, making it difficult to find readily available substitutes. For instance, if a supplier holds patents for a crucial API used in a blockbuster drug, Cipla's dependence on that supplier intensifies.
Cipla might find itself needing to enter into long-term supply agreements or forge strategic alliances to guarantee access to these critical, specialized inputs. This can involve commitments to purchase volumes, joint research and development, or even equity stakes, all aimed at securing supply chains for their innovative products. Such relationships can lock Cipla into specific suppliers, thereby increasing the supplier's bargaining power.
- Supplier Differentiation: Suppliers offering unique APIs or specialized excipients that are critical to Cipla's patented or proprietary formulations possess high bargaining power.
- Proprietary Inputs: If a key ingredient is only available from a single source or a very limited number of sources due to intellectual property or complex manufacturing processes, Cipla's reliance increases.
- Strategic Sourcing: To mitigate this, Cipla may need to engage in long-term contracts or strategic partnerships, potentially agreeing to higher prices or specific volume commitments to secure these vital components.
Suppliers of specialized pharmaceutical ingredients and raw materials hold significant bargaining power, especially when they control patented or proprietary components essential for Cipla's unique drug formulations. This limited availability of substitutes, coupled with the high costs and regulatory complexities associated with switching suppliers, strengthens their negotiating position.
In 2024, the global Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) market, valued at over USD 210 billion, saw a concentration of specialized API manufacturers, particularly in Asia, which can amplify supplier leverage. Cipla's strategy to counter this involves diversifying its supplier base and investing in in-house API manufacturing to reduce dependency and enhance supply chain resilience.
The rigorous validation and regulatory approval processes for new pharmaceutical suppliers, which can cost tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars per supplier, further entrench existing suppliers. These substantial switching costs mean Cipla faces significant financial and operational risks when changing partners, giving current suppliers an advantage.
| Factor | Impact on Cipla | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Specialized APIs) | High leverage for a few key suppliers. | Diversify supplier base, explore in-house manufacturing. |
| High Switching Costs (Re-validation, Regulatory Approvals) | Increases reliance on existing suppliers; costly to change. | Long-term supplier relationships, robust internal quality assurance. |
| Proprietary/Patented Inputs | Limited substitutes, strong supplier control. | Strategic partnerships, long-term supply agreements, R&D collaboration. |
| Regulatory Compliance Demands (cGMP) | Restricts eligible suppliers, bolsters compliant vendors. | Maintain strong supplier audit programs, build relationships with compliant manufacturers. |
What is included in the product
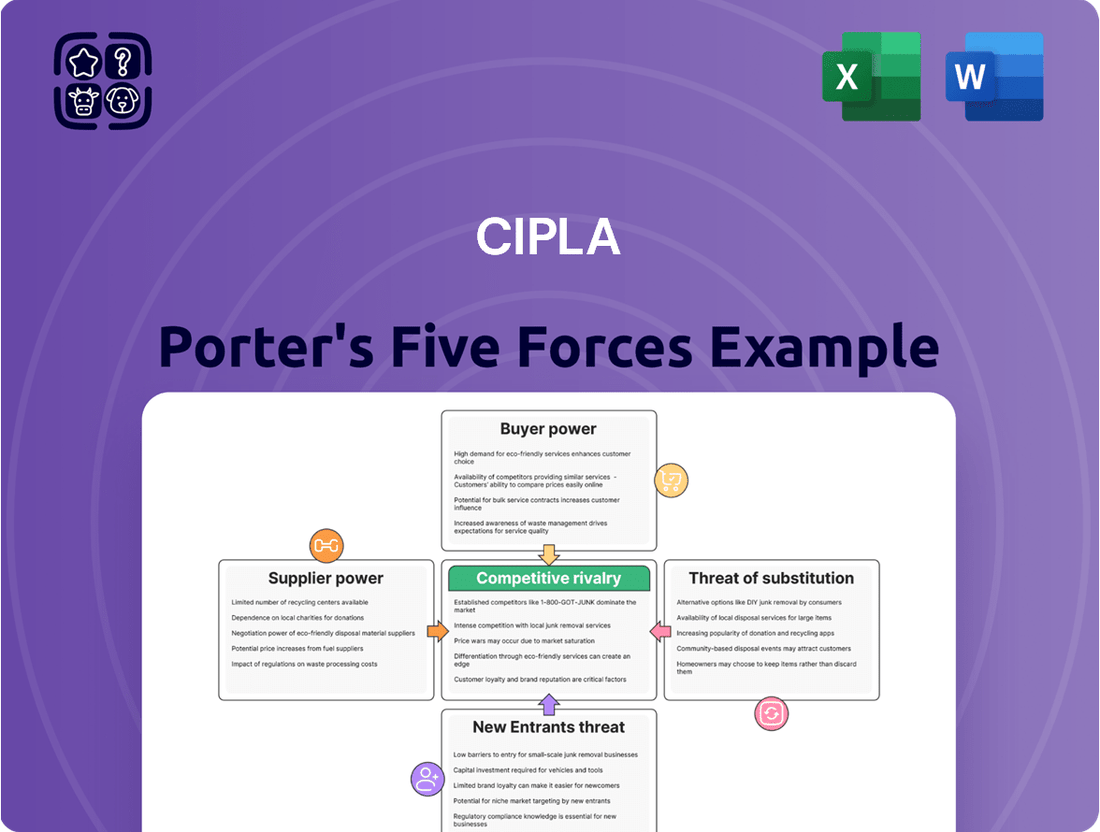
Tailored exclusively for Cipla, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape by examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visually intuitive breakdown of Cipla's Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
In the generic pharmaceutical market, a core segment for Cipla, buyers like pharmacies, hospitals, and government tenders exhibit extreme price sensitivity. This means they actively seek the lowest cost options, directly impacting Cipla's pricing strategies and profitability in this segment.
The sheer volume of generic drug manufacturers creates a highly competitive landscape where numerous alternatives are readily available. This abundance of choice significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers, as they can easily switch to a competitor if Cipla's pricing is not perceived as competitive.
For instance, in many government tenders for essential generic medicines, winning bids are often determined by the absolute lowest price offered. This dynamic means that even slight price differences can lead to substantial market share gains or losses for companies like Cipla, underscoring the immense power of these bulk purchasers.
Large institutional buyers, including national healthcare systems, major pharmacy chains, and group purchasing organizations, are significant players in the pharmaceutical market. Their substantial purchasing volumes give them considerable leverage when negotiating with manufacturers like Cipla.
These entities often secure substantial discounts and more favorable payment terms due to the sheer scale of their orders. For example, in 2024, the top 10 global pharmaceutical distributors accounted for over $600 billion in revenue, highlighting the concentrated purchasing power of a few large entities.
This concentrated demand allows these buyers to exert considerable pressure on pricing and supply agreements, thereby increasing their bargaining power over pharmaceutical companies.
Government regulations and reimbursement policies significantly shape the bargaining power of customers in the pharmaceutical industry. For instance, in 2024, many governments worldwide continued to implement measures to control healthcare expenditure, which can include price negotiations or preferred drug lists. These actions directly empower buyers, such as national health systems or large insurance providers, by limiting the pricing flexibility of companies like Cipla.
These policies often aim to increase drug accessibility and affordability, which can translate into increased pressure on Cipla to lower its prices or offer more competitive terms. For example, the push for generic drug substitution, often mandated or encouraged by regulatory bodies, gives customers more power to choose lower-cost alternatives, thereby reducing Cipla's pricing leverage.
Availability of Information and Comparability
Customers now have unprecedented access to information about drug effectiveness, safety profiles, and pricing. This enhanced transparency, particularly evident in the generic pharmaceuticals market, empowers buyers to readily compare different products and opt for the most economical choices, thereby amplifying their bargaining leverage.
For instance, in 2024, online platforms and government health portals provide detailed comparisons of generic drug prices, often showing significant variations between manufacturers for the same active ingredient. This accessibility means a patient or a healthcare provider can easily identify the most affordable equivalent, putting pressure on Cipla to maintain competitive pricing.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: Widespread availability of pricing data for generic drugs directly impacts customer purchasing decisions.
- Empowered Comparisons: Online resources facilitate easy comparison of drug efficacy and safety, enabling informed consumer choices.
- Shift in Power: Greater information access shifts bargaining power from pharmaceutical companies to customers seeking value.
- Generic Market Impact: The transparency is most pronounced in the generic segment, where product differentiation is minimal, leading to intense price competition.
Shift Towards Value-Based Healthcare
The global healthcare landscape is increasingly focusing on value-based care, meaning customers, including patients and payers, are demanding demonstrable patient outcomes alongside cost-effectiveness. This shift significantly enhances customer bargaining power, compelling pharmaceutical companies like Cipla to prove the real-world efficacy and economic benefits of their products. For instance, by 2024, many healthcare systems are expected to have robust data analytics in place to assess drug value, directly influencing purchasing decisions and contract negotiations.
This empowers customers to scrutinize not only the price of medications but also their impact on patient recovery, reduced hospitalizations, and overall quality of life. Consequently, Cipla must invest in post-market surveillance and real-world evidence generation to support its product value propositions. The increasing availability of comparative effectiveness research further strengthens the customer's ability to compare and choose treatments based on demonstrated value, putting pressure on pricing and market access strategies.
- Value-based purchasing: Customers are increasingly linking payments to health outcomes.
- Real-world evidence: Demand for data proving drug effectiveness in everyday clinical practice is rising.
- Cost containment pressures: Healthcare systems globally are under pressure to reduce expenditure, amplifying customer negotiation leverage.
- Patient empowerment: Informed patients are more likely to question and negotiate treatment costs and options.
Cipla faces significant bargaining power from its customers, particularly in the price-sensitive generic drug market. Large institutional buyers like government tenders and major pharmacy chains leverage their substantial order volumes to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. For example, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical distribution market, dominated by a few key players, demonstrated this concentrated purchasing power.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Cipla |
| Government Tenders | Price sensitivity, bulk purchasing | Intense price competition, lower margins |
| Large Pharmacy Chains | High order volumes, consolidated demand | Negotiation leverage on pricing and payment terms |
| Hospitals & Healthcare Systems | Volume purchasing, value-based care demands | Pressure to demonstrate cost-effectiveness and outcomes |
Same Document Delivered
Cipla Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Cipla's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic decision-making within the pharmaceutical industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global generic pharmaceutical market is a crowded space, featuring a vast number of domestic and international companies. This fragmentation fuels aggressive price competition, a significant factor for Cipla. For instance, in 2024, the generics market continued to see intense bidding for tender business, particularly in emerging markets, directly impacting margins for established players like Cipla.
Cipla encounters substantial competition from other major generic drug manufacturers across its core therapeutic segments and operational regions. This rivalry directly influences Cipla's ability to maintain and grow its market share, as well as its overall profitability. By the end of 2023, several large generic players had expanded their portfolios with biosimilar offerings, adding another layer of competitive pressure in key therapeutic areas where Cipla also has a presence.
Cipla navigates competitive rivalry by focusing on product differentiation, moving beyond basic bioequivalence. While generic competitors often engage in price wars, Cipla's strategy involves developing branded generics and more complex formulations that offer distinct advantages.
This commitment to innovation is evident in Cipla's significant investment in research and development. For instance, their focus on launching complex generics and biosimilars directly addresses the need to carve out unique market positions and mitigate intense price-based competition, a key challenge in the pharmaceutical sector.
The pharmaceutical market's robust growth, especially in emerging economies and key areas such as respiratory and oncology, is a double-edged sword. While it signals significant opportunity, this expansion also intensifies competitive rivalry as more players are drawn to these lucrative segments. For instance, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at approximately $1.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $2 trillion by 2028, indicating a strong growth trajectory that naturally attracts new entrants and existing competitors looking to capture market share.
Cipla's proactive strategy to tap into new growth avenues, such as its expansion into the weight management segment, directly addresses this heightened competition. By diversifying its portfolio and entering promising new therapeutic areas, Cipla aims to solidify its market position and mitigate the impact of increased rivalry from both established pharmaceutical giants and agile biotech firms vying for the same burgeoning markets.
Regulatory Landscape and Approvals
The regulatory environment, particularly the speed of drug approvals and patent expirations, is a critical factor shaping competitive rivalry for pharmaceutical companies like Cipla. Delays in Cipla's pipeline product approvals or the earlier-than-expected market entry of generic competitors can significantly intensify competition and alter market share dynamics.
For instance, the Indian pharmaceutical market, a key region for Cipla, saw its regulatory framework evolve. The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, and its subsequent amendments, along with guidelines from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), dictate the pace of approvals. As of early 2024, the timeline for new drug approvals in India can vary, impacting the first-mover advantage for innovative products.
- Patent Expirations: The expiry of patents on key blockbuster drugs opens the door for generic manufacturers, increasing competitive pressure and potentially leading to price erosion.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Stringent and evolving regulatory requirements for drug approvals, both in India and international markets where Cipla operates, can create barriers to entry but also lead to delays for new product launches, impacting competitive positioning.
- Generic Competition: The presence of numerous domestic and international generic players in Cipla's core markets means that once patents expire, intense price competition is inevitable.
- Biosimilar Approvals: In the biologics space, the regulatory pathway for biosimilar approvals also influences competition, with faster biosimilar entry potentially eroding market share from originator biologics.
Global Presence and Strategic Partnerships
Cipla's extensive global footprint and carefully cultivated strategic partnerships are crucial in mitigating the intense competitive rivalry within the pharmaceutical sector. By establishing operations in numerous countries and forging alliances for research, development, and distribution, Cipla enhances its ability to compete with both established local players and large multinational corporations.
These collaborations are not just about market access; they are instrumental in sharing the significant costs and risks associated with drug development. For instance, in 2024, Cipla continued to invest in its international presence, aiming to strengthen its position in key emerging markets. The company's strategy often involves partnerships that leverage local expertise and distribution networks, allowing for more agile responses to market dynamics and competitive pressures.
- Global Market Penetration: Cipla operates in over 80 countries, providing a broad base to counter rivals.
- R&D Collaborations: Partnerships in 2024 focused on areas like oncology and respiratory diseases, sharing innovation costs.
- Distribution Alliances: Strategic tie-ups ensure efficient product delivery, a key differentiator against competitors.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Global partnerships help streamline manufacturing and logistics, reducing operational costs and improving competitiveness.
The competitive rivalry within the pharmaceutical industry, particularly for a company like Cipla, is exceptionally fierce due to the high number of players and the nature of the market. This intense competition is driven by patent expirations, the rapid entry of generic and biosimilar manufacturers, and the constant pursuit of market share in lucrative therapeutic areas. For example, in 2024, the global generics market continued to be characterized by aggressive price competition, especially in emerging markets, directly impacting the profit margins of established companies like Cipla.
Cipla faces direct competition from numerous global and domestic pharmaceutical firms across its key therapeutic segments. This rivalry necessitates strategic differentiation beyond simple bioequivalence, with companies like Cipla focusing on branded generics and complex formulations. By the end of 2023, the increasing number of biosimilar offerings from major competitors added another layer of pressure in critical therapeutic areas where Cipla also holds a significant presence.
The pharmaceutical market's substantial growth, projected to exceed $2 trillion by 2028 from approximately $1.5 trillion in 2023, naturally attracts more competitors. This expansion, especially in high-growth areas like respiratory and oncology, intensifies rivalry as both existing players and new entrants vie for market share. Cipla's strategic diversification into segments like weight management in 2024 is a direct response to this escalating competition.
| Key Competitor Type | Impact on Cipla | Example Action (2024) |
| Large Generic Manufacturers | Price erosion, market share pressure | Expansion of biosimilar portfolios |
| Branded Generic & Complex Formulation Players | Need for product differentiation | Focus on R&D for niche products |
| Emerging Market Domestic Players | Intense local competition | Aggressive bidding for tender business |
| Biotech Firms (in specialized areas) | Innovation challenges, niche market competition | Development of novel therapies |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Branded drugs with strong patent protection represent a significant threat to Cipla's generic portfolio. These innovative treatments often boast superior efficacy or novel mechanisms, creating a strong pull from healthcare providers and patients, which can erode the market share of even established generics. For instance, the launch of a new patented biologic in a therapeutic area where Cipla has a significant generic presence can rapidly shift prescribing patterns.
The increasing prevalence of biosimilars and innovative biologics poses a significant threat to Cipla's established generic drug portfolio, particularly in specialized therapeutic areas. These complex biological products can directly substitute for traditional chemical-based generics, eroding market share.
While Cipla is actively investing in its own biosimilar development pipeline, the expanding market for these advanced therapies means that patients and healthcare providers have more choices beyond conventional generics. For instance, the global biosimilars market was valued at approximately $20.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift in treatment options.
Beyond traditional pharmaceutical drugs, a growing array of alternative therapies and lifestyle interventions presents a significant threat of substitutes for Cipla. These include practices like yoga, meditation, acupuncture, and dietary changes, particularly in managing chronic conditions where patients increasingly seek holistic approaches. For example, the global wellness market, which encompasses these alternative treatments, was valued at approximately $4.5 trillion in 2022 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong preference shift away from solely medication-based solutions.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications
The availability of over-the-counter (OTC) medications presents a significant threat to Cipla's prescription drug business. When conditions treatable by prescription generics also have accessible OTC alternatives, consumers may switch to these more convenient and often less expensive options. This shift can directly impact Cipla's sales volume for certain prescription products.
For instance, common ailments like mild pain, allergies, or digestive issues often have both prescription and OTC solutions. In 2024, the global OTC market continued to grow, with consumers increasingly seeking self-care options. This trend suggests that Cipla needs to monitor the competitive landscape of OTC alternatives closely.
- Increased accessibility of OTC drugs for common ailments like pain relief and allergies.
- Price sensitivity of consumers favoring cheaper OTC alternatives over prescription generics.
- Potential for reduced prescription volumes for Cipla's products facing direct OTC competition.
- The growing self-medication trend further amplifies the threat of substitution.
Preventive Healthcare and Wellness Trends
The increasing focus on preventive healthcare and wellness, including early disease detection, presents a threat of substitutes for traditional curative medications. This trend could lead to a reduced demand for certain pharmaceutical products as individuals adopt healthier lifestyles and utilize preventative measures.
For instance, the global digital health market, which includes wellness apps and remote monitoring, was valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly. This expansion signifies a shift towards proactive health management, potentially impacting the market share of companies reliant on treating existing conditions.
- Preventive Care Growth: A growing emphasis on wellness and early disease detection can diminish the need for certain curative medications.
- Long-Term Impact: While a gradual shift, this trend represents a potential substitute for pharmaceutical interventions by reducing disease incidence.
- Market Shift: The expanding digital health sector, valued at around $200 billion in 2023, highlights a move towards proactive health management.
The threat of substitutes for Cipla is multifaceted, encompassing both direct pharmaceutical alternatives and broader health management approaches. Branded drugs with strong patent protection, biosimilars, over-the-counter medications, and even lifestyle interventions all represent potential substitutes that can erode Cipla's market share. The expanding global wellness market, valued at approximately $4.5 trillion in 2022, and the growing digital health sector, around $200 billion in 2023, underscore a significant consumer shift towards proactive and alternative health management.
| Substitute Category | Example | Market Value (Approx.) | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Branded Drugs | New patented biologics | N/A (Specific drug dependent) | Ongoing |
| Biosimilars | Generic versions of biologics | $20.4 billion | 2023 |
| OTC Medications | Self-care products for common ailments | Growing market | 2024 |
| Alternative Therapies | Yoga, meditation, acupuncture | $4.5 trillion (Wellness Market) | 2022 |
| Digital Health | Wellness apps, remote monitoring | $200 billion | 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
The pharmaceutical sector, including companies like Cipla, faces a significant threat from new entrants due to exceptionally high capital requirements. Developing new drugs involves massive investments in research and development, clinical trials, and securing regulatory approvals, often running into hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars. For instance, the average cost to bring a new drug to market has been estimated to be over $2 billion, a substantial hurdle for any newcomer.
Furthermore, establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities that meet stringent global quality standards and ongoing R&D for pipeline development demand continuous, large-scale capital allocation. Cipla's existing, robust R&D infrastructure and extensive manufacturing network, built over decades, represent a formidable barrier, making it difficult for new entities to compete on scale and innovation from the outset.
The pharmaceutical industry, where Cipla operates, is characterized by extremely stringent regulatory approvals and compliance requirements. New entrants must navigate a complex and often lengthy process to gain approval for their drugs from bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA). This involves extensive, multi-phase clinical trials and adherence to rigorous Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), creating a significant barrier to entry.
For instance, the average cost of bringing a new drug to market can exceed $2.6 billion, with many of these costs incurred during the lengthy clinical trial and regulatory submission phases. This substantial financial and time commitment acts as a powerful deterrent for potential new competitors, effectively protecting established companies like Cipla that have already invested heavily in building this expertise and infrastructure.
Existing patents on branded drugs and proprietary manufacturing processes act as significant barriers, deterring new entrants from easily replicating Cipla's offerings. These intellectual property rights prevent the production and marketing of similar pharmaceuticals until patent expiration, a common strategy in the pharmaceutical industry. In 2023, the global pharmaceutical market, valued at approximately $1.5 trillion, heavily relies on patent protection to foster innovation and recoup R&D investments, a landscape Cipla navigates effectively with its extensive patent portfolio.
Brand Loyalty and Established Distribution Channels
Building strong brand loyalty and extensive distribution channels in the pharmaceutical industry is a formidable hurdle for any new entrant. Cipla, with its decades of operation, has cultivated a deep-seated trust among healthcare professionals and consumers alike, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. This established reputation acts as a significant moat, deterring potential competitors from entering the market.
Cipla's robust distribution network, spanning across numerous countries and reaching a vast array of healthcare providers and pharmacies, represents another substantial barrier. For instance, as of the fiscal year ending March 31, 2023, Cipla reported a presence in over 80 countries, showcasing the breadth of its reach. New companies would need to invest heavily and invest considerable time to replicate such an expansive and efficient supply chain, a task that is both capital-intensive and logistically complex.
- Brand Recognition: Cipla's long-standing presence has fostered significant brand recall and trust, a critical factor in pharmaceutical purchasing decisions.
- Distribution Network: An established network of over 80 countries as of FY23 provides Cipla with unparalleled market access, making it challenging for new entrants to compete on reach.
- Healthcare Provider Relationships: Years of consistent supply and product quality have cemented strong relationships with doctors and pharmacists, who often influence prescription choices.
- Customer Loyalty: Proven efficacy and patient satisfaction with Cipla's products contribute to a loyal customer base, reducing churn and new customer acquisition needs.
Economies of Scale in Manufacturing and Procurement
Established pharmaceutical giants, including Cipla, leverage significant economies of scale. This advantage spans manufacturing, where bulk production lowers per-unit costs, and procurement, allowing for more favorable pricing on raw materials and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). For instance, in 2023, Cipla reported a consolidated revenue of approximately INR 27,058 crore, indicating a substantial operational footprint that supports cost efficiencies.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost advantages. Achieving similar economies of scale would necessitate massive upfront investment in manufacturing facilities and supply chain infrastructure. This makes it challenging for newcomers to compete effectively on price, particularly in the highly competitive generic drug market where margins are often tight.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Large-scale production facilities reduce overhead per unit.
- Procurement Power: Bulk purchasing of raw materials leads to lower input costs.
- R&D Investment: Established players can spread high R&D costs over a larger output.
- Price Competition: New entrants struggle to undercut incumbents due to lack of scale.
The threat of new entrants in the pharmaceutical sector, impacting companies like Cipla, is somewhat mitigated by substantial barriers. High capital requirements for R&D, clinical trials, and regulatory approvals, often exceeding $2.6 billion per drug, deter many potential new players. Furthermore, established players like Cipla benefit from extensive patent portfolios and strong brand loyalty, built over decades of operation and consistent product quality.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example (Cipla) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Massive investment needed for R&D, clinical trials, and regulatory approvals. | High barrier, requiring significant funding. | Average cost to bring a drug to market > $2.6 billion. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents on drugs and manufacturing processes protect market exclusivity. | Prevents direct replication of existing products. | Cipla leverages its patent portfolio to maintain market position. |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Established trust with healthcare providers and consumers. | Difficult for new entrants to gain market access and prescriptions. | Cipla's long-standing reputation fosters strong doctor and patient relationships. |
| Distribution Network | Extensive and efficient supply chains are crucial for market reach. | Replicating broad market access is costly and time-consuming. | Cipla's presence in over 80 countries (FY23) highlights its extensive network. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Cipla Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings from Cipla and its key competitors. We also leverage industry-specific market research reports and data from reputable financial databases to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
