CIMB Group Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CIMB Group Holdings Bundle
CIMB Group Holdings navigates a dynamic financial landscape where intense rivalry and the threat of new entrants significantly shape its competitive strategy. Understanding the bargaining power of both customers and suppliers is crucial for maintaining profitability in this sector. The availability of substitute financial products also presents a constant challenge.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping CIMB Group Holdings’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Technology providers hold considerable sway over CIMB Group Holdings, primarily due to the bank's deep reliance on core banking systems, digital platforms, and essential cybersecurity solutions sourced from external vendors. This dependence means that any disruption or pricing change from these tech giants can directly impact CIMB's operations and service delivery.
CIMB's ambitious Forward30 plan, which emphasizes digital transformation and the integration of artificial intelligence, further amplifies the bargaining power of its technology partners. The need for cutting-edge and dependable technology to achieve these strategic goals makes securing and retaining these specialized vendors a critical, and potentially costly, endeavor for CIMB.
CIMB Group Holdings relies heavily on specialized talent in burgeoning fields like digital banking, data analytics, cybersecurity, and Islamic finance. The availability of these highly skilled professionals directly impacts CIMB's ability to innovate and compete. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity experts in the financial sector significantly outstripped supply, driving up salary expectations and making talent acquisition a critical challenge.
CIMB Group Holdings, like many financial institutions, navigates a landscape where its funding sources, primarily depositors and capital markets, hold significant bargaining power. While CIMB actively works to bolster its deposit base to lower funding costs, it remains dependent on a wide array of individual and institutional depositors, as well as its access to capital markets for crucial liquidity and expansion. As of the first quarter of 2024, CIMB reported a total customer deposit growth of 7.4% year-on-year, reaching RM495.5 billion, highlighting the importance of this broad base.
In the competitive financial sector, the influence of large institutional investors and a diverse depositor pool can directly impact funding costs and the terms CIMB secures. A substantial portion of these deposits, particularly from larger clients, can command more favorable interest rates, thus influencing CIMB's overall cost of funds and profitability. This dynamic underscores the necessity for CIMB to maintain strong relationships and offer competitive terms to retain these vital funding providers.
Interbank Market and Central Banks
CIMB Group Holdings, like all financial institutions, is significantly influenced by the interbank market and the actions of central banks across its operating regions. This market is crucial for managing short-term liquidity needs, and central bank policies directly affect borrowing costs and the availability of funds. For instance, changes in policy rates by Bank Negara Malaysia or the Monetary Authority of Singapore can alter CIMB's cost of funding.
Central banks wield substantial power through monetary policy tools. These include setting benchmark interest rates, adjusting reserve requirements for banks, and engaging in open market operations. In 2024, many central banks in ASEAN, including Bank Indonesia and Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, continued to navigate inflationary pressures, which led to adjustments in their policy rates. These adjustments directly impact the cost of funds for banks like CIMB.
- Interbank Market Dependence: CIMB relies on the interbank market for overnight and short-term funding to meet its liquidity requirements, making it sensitive to market interest rate fluctuations.
- Central Bank Influence: Monetary policies enacted by central banks in Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Thailand, and the Philippines directly affect CIMB's cost of funds and operational environment.
- Policy Rate Impact: For example, if Bank Negara Malaysia raises its overnight policy rate, CIMB's borrowing costs in the interbank market will likely increase, impacting its net interest margins.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Changes in reserve requirements or capital adequacy ratios imposed by central banks can also constrain CIMB's lending capacity and profitability.
Key Strategic Partners
CIMB Group Holdings leverages strategic partnerships, notably with fintech innovators and bancassurance providers, to enhance its service offerings. These collaborations are crucial for accessing specialized capabilities and expanding market reach, particularly in dynamic sectors like healthcare technology for SMEs and cross-border payment solutions.
The bargaining power of these suppliers stems from their unique contributions. For instance, a fintech partner providing a cutting-edge digital onboarding solution might command higher fees if CIMB's digital transformation strategy heavily relies on that specific technology. In 2023, CIMB announced a significant collaboration with a leading digital payments provider to bolster its regional payment infrastructure, indicating the strategic importance of such alliances.
- Fintech Partnerships: CIMB collaborates with fintech firms to integrate advanced digital solutions, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Bancassurance Alliances: Strategic ties with insurance companies allow CIMB to offer a broader range of financial products, tapping into new revenue streams.
- Niche Market Access: Partners specializing in high-growth areas like healthcare tech SMEs or cross-border payments provide CIMB with access to lucrative, underserved markets.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which CIMB relies on a partner's unique technology or market access directly influences the supplier's bargaining power.
CIMB Group Holdings faces supplier power from technology providers, especially those offering core banking systems and digital platforms. The bank's digital transformation initiatives, like its Forward30 plan, increase reliance on these specialized vendors, potentially leading to higher costs. In 2024, the financial sector's demand for cybersecurity talent significantly outpaced supply, impacting acquisition costs for CIMB.
CIMB's funding sources, including depositors and capital markets, wield considerable bargaining power, directly influencing borrowing costs. The bank's customer deposits grew by 7.4% year-on-year to RM495.5 billion in Q1 2024, underscoring the importance of managing these relationships. Institutional investors and large depositors can negotiate more favorable interest rates, affecting CIMB's profitability.
The interbank market and central bank policies significantly impact CIMB's funding costs. Central banks in regions like Malaysia and Singapore adjust policy rates to manage inflation, directly affecting CIMB's borrowing expenses. For example, if Bank Negara Malaysia raises its overnight policy rate, CIMB's interbank borrowing costs will likely rise.
Strategic partnerships with fintech firms and bancassurance providers also represent a source of supplier power for CIMB. Collaborations for digital onboarding or payment solutions can be critical, especially if CIMB heavily depends on a partner's unique technology. CIMB's 2023 collaboration with a digital payments provider highlights the strategic value and potential leverage of such suppliers.
| Supplier Type | Key Dependence Factors | Impact on CIMB | 2024 Data/Trend | Example |
| Technology Providers | Core banking systems, Digital platforms, Cybersecurity | Operational disruption, Increased costs | High demand for cybersecurity talent | Reliance on specialized AI platform for credit scoring |
| Depositors/Capital Markets | Liquidity, Funding costs | Net interest margin, Expansion capability | Customer deposits grew 7.4% YoY in Q1 2024 | Negotiated rates from large corporate depositors |
| Interbank Market/Central Banks | Short-term liquidity, Borrowing costs | Cost of funds, Profitability | ASEAN central banks adjusting policy rates | Impact of Bank Negara Malaysia's policy rate changes |
| Fintech/Strategic Partners | Service enhancement, Market access | Revenue streams, Competitive advantage | Increased fintech collaborations | Partnerships for cross-border payment solutions |
What is included in the product
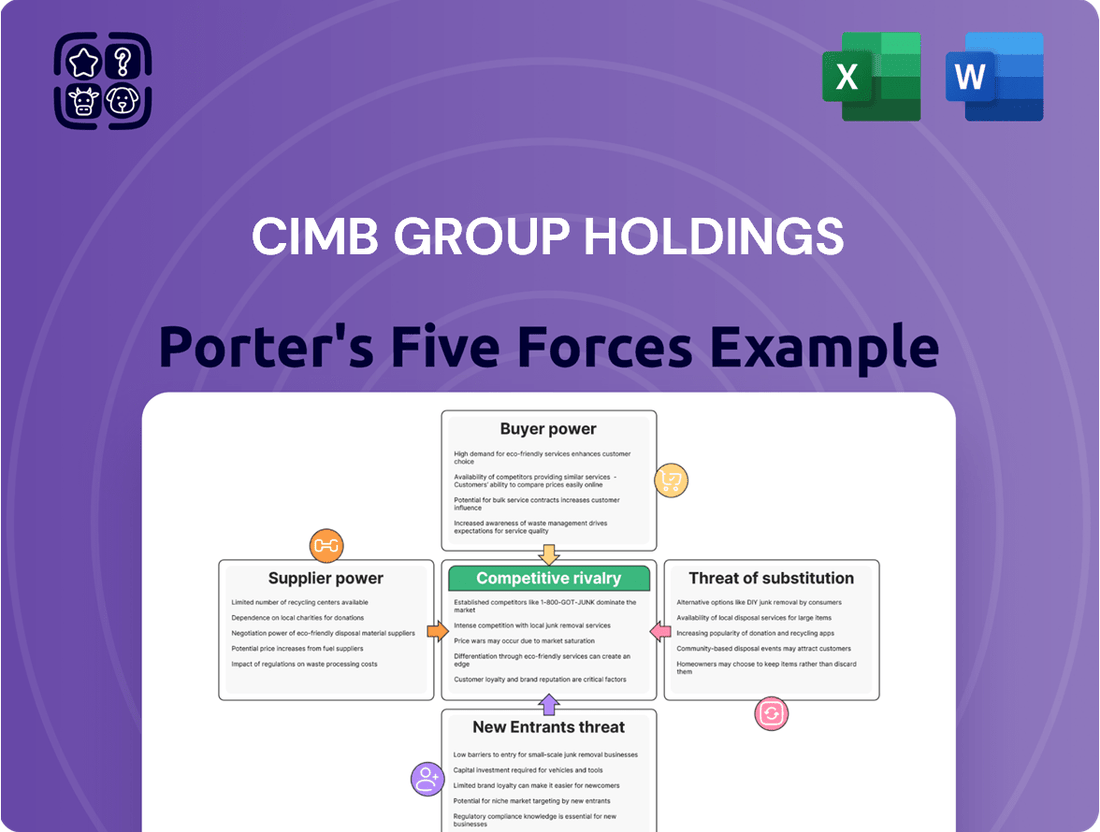
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping CIMB Group Holdings' market, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
A dynamic, interactive dashboard that allows CIMB Group Holdings to visualize and quantify the impact of each Porter's Five Force on their profitability, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual retail customers in the ASEAN region possess significant bargaining power, amplified by the proliferation of digital banking solutions and fintech innovations. With numerous banks and alternative financial service providers offering competitive products, customers can easily switch providers to secure better rates or services. For instance, the digital banking landscape in Southeast Asia is rapidly evolving, with many new players entering the market, increasing customer options.
CIMB Group Holdings acknowledges this dynamic by prioritizing customer-centricity and tracking metrics like the Net Promoter Score (NPS). In 2023, CIMB reported a strong NPS, indicating a positive customer experience, which is crucial for retaining customers in this highly competitive environment. This focus on customer satisfaction directly addresses the bargaining power of individuals by fostering loyalty and reducing churn.
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) wield significant bargaining power due to their diverse financing needs and the wide array of available options. They can select from traditional banks, newer challenger banks, and various alternative lending platforms, forcing financial institutions like CIMB Group Holdings to compete on price, service, and product innovation. For instance, in 2024, the SME lending market saw continued growth with many fintech lenders offering faster approvals and more flexible terms, putting pressure on incumbent banks.
CIMB's strategic focus on SMEs, evidenced by initiatives such as SMEBizReady and collaborations to develop bespoke financial solutions, directly addresses this bargaining power. By understanding and catering to the specific requirements of SMEs, CIMB aims to retain and attract this crucial customer segment, ensuring its offerings remain competitive in a dynamic market. This proactive approach is vital as SMEs represent a substantial portion of the economy; in 2023, SMEs contributed significantly to GDP in many Southeast Asian nations, making their loyalty a key differentiator for financial providers.
Large corporations and institutions often have substantial financial needs and high transaction volumes, giving them considerable leverage to negotiate better terms and pricing with banks like CIMB. For example, in 2024, global investment banking fees from large corporate clients were a significant driver of revenue for many institutions, underscoring the importance of these relationships.
These sophisticated clients expect tailored financial solutions and are less sensitive to price when service quality and relationship management are superior. CIMB's focus on wholesale and investment banking services aims to meet these complex demands, where personalized service and deep understanding of client needs become crucial competitive advantages.
Digital Natives and Tech-Savvy Customers
Digital natives and tech-savvy customers represent a significant force, demanding intuitive and efficient digital banking solutions. Their high expectations for seamless user experiences and innovative digital features mean that banks like CIMB must prioritize continuous technological advancement to retain this crucial demographic. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of banking transactions globally occurred through digital channels, underscoring this trend.
This segment's propensity to switch providers based on superior digital offerings directly impacts customer loyalty and market share. Banks that fail to keep pace with evolving digital expectations risk losing these valuable customers.
- Digital Engagement: In 2024, mobile banking app usage among millennials and Gen Z continued to surge, with many preferring these platforms for daily transactions and inquiries.
- Customer Expectations: This demographic expects instant service, personalized digital interactions, and a wide array of self-service options.
- Switching Behavior: Poor digital user experience is a primary driver for customer churn in this segment, leading to increased competition for CIMB.
Islamic Banking Customers
CIMB's Islamic banking customers represent a distinct segment with specific needs for Sharia-compliant financial products. The increasing availability of Islamic financial solutions from various providers means these customers have choices, which can amplify their bargaining power. They can leverage competition to seek better rates, fees, and service quality.
The bargaining power of CIMB's Islamic banking customers is influenced by several factors:
- Customer Concentration: If a few large customers account for a significant portion of CIMB's Islamic banking revenue, their individual bargaining power increases.
- Switching Costs: The ease or difficulty for customers to move their Islamic banking business to another institution impacts their leverage. Lower switching costs empower customers.
- Availability of Substitutes: The presence of numerous other Islamic banks and conventional banks offering Sharia-compliant products means customers have alternatives, thereby strengthening their position.
- Information Availability: As customers become more informed about available Sharia-compliant products and market rates, their ability to negotiate favorable terms grows.
Individual retail customers hold significant sway due to the ease of switching between financial providers in the digital age. With numerous banking and fintech options available, customers can readily compare and move to secure more favorable terms. This heightened competition compels banks like CIMB to focus on retaining clients through superior service and competitive pricing.
SMEs also wield considerable bargaining power, as their financing needs are diverse and met by a wide array of institutions. They can negotiate based on volume and loyalty, pushing banks to offer specialized products and attractive rates. For example, in 2024, the demand for flexible SME financing solutions continued to rise, emphasizing the need for banks to adapt their offerings.
Large corporate clients possess substantial leverage, often negotiating pricing and services based on the volume and complexity of their transactions. Their ability to switch providers for better deals means banks must offer premium, tailored solutions and strong relationship management to maintain these valuable accounts. In 2023, large-scale corporate banking deals represented a significant portion of revenue for many financial institutions, highlighting the importance of this segment.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | CIMB's Response/Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Customers | Ease of switching, digital alternatives, price sensitivity | Customer-centricity, NPS focus, digital innovation |
| SMEs | Diverse financing needs, multiple provider options, volume | Tailored solutions (SMEBizReady), competitive pricing |
| Large Corporations | High transaction volumes, sophisticated needs, relationship value | Wholesale & investment banking focus, personalized service |
Same Document Delivered
CIMB Group Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the actual Porter's Five Forces Analysis for CIMB Group Holdings, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the banking sector. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive instantly after completing your purchase, offering a comprehensive evaluation of industry rivalry, new entrant threats, buyer and supplier power, and the impact of substitutes. This ensures transparency and immediate access to the full, professionally formatted analysis without any alterations.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The ASEAN banking sector is a crowded arena, with CIMB Group Holdings facing formidable competition from established local and regional banks. This intense rivalry spans consumer, commercial, and wholesale banking operations in vital markets such as Malaysia, Indonesia, and Singapore, where players like Maybank, Bank Mandiri, and DBS Bank are significant forces.
The banking sector is experiencing a dramatic shift with the rise of digital-only banks and agile fintech firms. These new entrants are not just nibbling at the edges; they are directly challenging established players like CIMB Group Holdings in core areas such as payments, lending, and international money transfers. For instance, by mid-2024, many fintech platforms were boasting significantly lower transaction fees for cross-border payments compared to traditional banks, sometimes by as much as 50%.
These digital disruptors often provide a streamlined, user-friendly experience that resonates with a growing segment of consumers. Their ability to offer faster approvals for loans and more personalized digital interfaces, often built on advanced data analytics, puts pressure on incumbent banks to innovate rapidly. By the end of 2023, several leading fintech lenders reported processing times for personal loans that were days, not weeks, shorter than those of many traditional institutions.
Banks vigorously compete by offering a wide array of financial products and services, with key battlegrounds including interest rates on deposits and loans, the breadth of loan products, the sophistication of digital banking features, and the overall quality of customer service. This intense rivalry means that differentiation is crucial for attracting and retaining customers.
CIMB Group Holdings, through its Forward30 strategy, is actively focusing on enhancing its competitive edge by emphasizing cross-selling opportunities across its diverse product portfolio. The aim is to deliver best-in-class services that not only set CIMB apart but also serve as a significant driver for generating new income streams.
In 2023, CIMB reported a notable increase in its digital transaction volume, with over 70% of its customer transactions conducted digitally, highlighting the success of its digital transformation efforts. This focus on digital innovation and customer-centric service quality is central to its strategy for standing out in a crowded market.
Geographical Market Specifics
Competitive rivalry for CIMB Group Holdings significantly differs across the ASEAN region, reflecting diverse economic landscapes and regulatory environments. For instance, CIMB encounters intense competition in Indonesia, a market characterized by a large, growing population and numerous local and international banking players. In contrast, Thailand presents more challenging market conditions, partly due to slower economic growth observed in recent periods, which can dampen demand for financial services and increase competitive pressures as firms vie for a smaller pool of opportunities.
Success in this fragmented market hinges on a deep understanding of local nuances. CIMB’s strategy must adapt to country-specific dynamics, from consumer preferences to regulatory frameworks. This adaptability is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape effectively. For example, digital banking adoption rates and preferred transaction methods can vary widely, requiring tailored product offerings and marketing approaches.
Key competitive factors and their impact in 2024 include:
- Indonesia: High competition from large state-owned banks and agile digital banks, with a focus on retail and SME lending.
- Thailand: Slower economic growth impacting loan demand, leading to heightened competition for market share among established players and a greater emphasis on cost efficiency.
- Malaysia: Mature market with established domestic and international banks, where differentiation often comes through specialized services and digital innovation.
- Philippines: Rapidly growing market with increasing digital adoption, attracting new entrants and intensifying competition in areas like mobile payments and consumer finance.
Focus on Niche Markets and Strategic Partnerships
Banks are sharpening their competitive edge by zeroing in on specialized niche markets, like small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or high-net-worth individuals. They are also forging strategic alliances to broaden their customer base and enhance their service portfolios.
CIMB Group Holdings exemplifies this strategy through its involvement in areas like healthcare technology and cross-border payment solutions. These collaborations allow CIMB to tap into specific growth segments and offer integrated services.
- Niche Market Focus: Banks are increasingly targeting underserved or high-growth segments, such as digital banking for millennials or specialized financing for green projects.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with fintech firms, for instance, can enable banks to offer innovative digital services more rapidly. In 2023, CIMB announced a partnership with digital health platform DoctorOnCall to provide integrated financial solutions for healthcare providers and patients.
- Cross-Border Expansion: Focusing on cross-border payments, CIMB aims to facilitate easier transactions for businesses and individuals operating internationally, a growing demand in the globalized economy.
Competitive rivalry for CIMB Group Holdings is intense across ASEAN, driven by both traditional banks and digital disruptors. In 2024, the sector sees ongoing pressure from fintechs offering lower fees, with some cross-border payment platforms reporting up to 50% cost savings compared to traditional banks by mid-2024. CIMB's strategy, including its Forward30 initiative and a 70% digital transaction volume in 2023, aims to differentiate through digital innovation and customer service to counter this pressure.
The competitive landscape varies significantly by country; for instance, Indonesia presents high competition from large state-owned banks and digital players, while Thailand's slower economic growth in recent periods intensifies competition for market share. CIMB is adapting by focusing on niche markets and strategic partnerships, such as its 2023 collaboration with DoctorOnCall, to enhance its service offerings and customer reach.
| Market | Key Competitors | Competitive Focus | CIMB's Strategy Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesia | Bank Mandiri, BCA, Digital Banks | Retail & SME Lending, Digital Services | Expanding digital offerings, leveraging partnerships |
| Malaysia | Maybank, RHB Bank | Digital Innovation, Specialized Services | Cross-selling, enhancing digital banking features |
| Thailand | SCB, KBank | Cost Efficiency, Market Share Grab | Focus on digital transformation, operational efficiency |
| Philippines | BDO, BPI, Digital Lenders | Mobile Payments, Consumer Finance | Targeting growing digital adoption, product diversification |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The burgeoning fintech sector, encompassing everything from mobile wallets to peer-to-peer lending, presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services. These digital platforms often provide more streamlined and cost-effective transaction and credit solutions, directly challenging CIMB Group Holdings' core offerings.
For instance, the global digital payments market was valued at approximately $2.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. This rapid expansion means more consumers are opting for convenient digital alternatives over traditional bank transfers or card payments, directly impacting transaction fee revenue for established institutions like CIMB.
Cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, though still developing, represent potential long-term substitutes for traditional banking services. These blockchain-based systems offer alternatives for remittances and asset management, potentially impacting traditional revenue streams. For instance, in 2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization fluctuated significantly, demonstrating investor interest in these alternative assets.
Informal lending and alternative financing channels pose a significant threat of substitutes for CIMB Group Holdings in certain ASEAN markets. These channels, often operating outside traditional banking regulations, cater to individuals and small businesses who may struggle to access formal credit. For instance, in countries like the Philippines, informal lenders or peer-to-peer platforms can offer quicker, albeit potentially riskier, access to funds, directly competing with CIMB's loan products.
Direct Investment and Wealth Management Platforms
Customers increasingly have the option to bypass traditional banking channels for investment and wealth management. They can directly invest in assets like stocks and bonds or engage with independent robo-advisors and specialized wealth management platforms. This trend offers alternative avenues for wealth growth, potentially reducing reliance on services offered by entities like CIMB Group.
The proliferation of FinTech has significantly lowered the barriers to entry for substitute services. For instance, the global robo-advisory market was valued at approximately USD 2.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong customer preference for these digital alternatives.
- Direct Investment: Individuals can purchase stocks, bonds, and real estate directly through online brokerages or exchanges, bypassing bank-managed portfolios.
- Robo-Advisors: Automated platforms offer algorithm-driven investment management, often at lower fees than traditional advisors. The global robo-advisory market size was estimated at USD 2.5 billion in 2023.
- Independent Wealth Managers: Specialized firms focus solely on wealth management, providing tailored advice and investment strategies outside of a banking conglomerate.
In-house Corporate Finance Departments
The threat of substitutes for CIMB Group Holdings' corporate finance services is significant, particularly from large corporations with well-established in-house finance departments. These internal teams can effectively manage treasury functions, optimize cash flow, and even secure certain types of financing without external assistance, thereby reducing their need for traditional banking partnerships.
For instance, many multinational corporations maintain sophisticated treasury operations that can handle foreign exchange management and short-term debt issuance. This internal capability directly substitutes for services typically offered by investment banks like CIMB. In 2024, the trend of companies strengthening their internal finance functions continues, driven by a desire for greater control and cost efficiency.
The availability of alternative financing methods also presents a substitute threat. Companies can increasingly turn to capital markets directly through bond issuances or private equity placements, bypassing the need for intermediary banking services. This disintermediation is a growing concern for traditional financial institutions.
- In-house capabilities reduce reliance on external financial institutions for treasury and cash management.
- Direct access to capital markets for debt and equity financing serves as a substitute for bank-led deals.
- The increasing sophistication of corporate finance functions allows for internal handling of complex financial operations.
The threat of substitutes for CIMB Group Holdings is amplified by the rise of fintech, offering digital alternatives for payments, lending, and wealth management. These platforms, like mobile wallets and robo-advisors, are increasingly preferred for their convenience and lower costs. For example, the global robo-advisory market reached approximately USD 2.5 billion in 2023, highlighting a significant shift towards digital financial solutions.
Furthermore, cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) present emerging substitutes, challenging traditional banking models for remittances and asset management. While volatile, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization in 2024 shows sustained interest in these alternative assets. Additionally, informal lending channels in some ASEAN markets provide quicker, albeit riskier, access to funds, directly competing with CIMB's loan products.
Corporations also increasingly leverage in-house finance functions and direct access to capital markets for treasury management and financing, reducing their reliance on traditional banking services. This trend is driven by a desire for greater control and cost efficiency, with companies strengthening their internal finance capabilities throughout 2024.
| Substitute Area | Key Substitutes | Impact on CIMB | Market Data (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payments & Transactions | Fintech Payment Apps, Mobile Wallets | Reduced transaction fee revenue | Global digital payments market: ~$2.5 trillion (2023) |
| Lending & Credit | Peer-to-Peer Lending, Informal Lenders | Competition for loan origination | Varies by region, significant in emerging markets |
| Wealth Management | Robo-Advisors, Direct Investment Platforms | Loss of AUM and advisory fees | Global robo-advisory market: ~$2.5 billion (2023) |
| Corporate Finance | In-house Treasury, Capital Markets Access | Reduced demand for corporate banking services | Growing trend of in-house finance strengthening (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The issuance of digital bank licenses across ASEAN countries presents a significant threat of new entrants for CIMB Group Holdings. These licenses allow nimble, tech-savvy companies to enter the financial services market without the substantial capital investment required for traditional brick-and-mortar operations. For instance, in 2023, the Monetary Authority of Singapore granted digital bank licenses to a consortium including Grab and Singtel, demonstrating a clear pathway for non-traditional players.
Fintech startups are increasingly entering the financial services landscape by focusing on niche markets or specialized services. For instance, companies offering micro-lending platforms or tailored payment solutions can attract customers without needing to replicate the extensive product portfolios of established institutions like CIMB. This targeted approach allows them to build a customer base and gain traction efficiently.
Tech giants like Apple, Google, and Amazon are increasingly embedding financial services into their ecosystems, leveraging vast customer bases and sophisticated data analytics. For instance, Apple Pay processed an estimated $6 trillion in transactions globally in 2023, demonstrating its significant reach. Their ability to offer integrated, user-friendly financial products, often at lower costs due to scale and technological advantage, presents a formidable competitive challenge to traditional players like CIMB Group Holdings.
Cross-Border Expansion of Existing Banks
Established banks from outside CIMB's core ASEAN markets, or even from other global regions, possess the potential to enter CIMB's operating territories. These institutions often bring substantial capital reserves, deep industry expertise, and advanced digital technologies, allowing them to compete effectively. For instance, in 2024, several major European banks continued to explore digital-first expansion strategies into emerging Asian markets, signaling a growing trend of cross-border digital banking initiatives.
The threat is amplified by the increasing ease of digital cross-border financial services. Banks with strong digital platforms can bypass traditional brick-and-mortar expansion hurdles. This means a bank in, say, Europe could offer competitive digital banking services in Malaysia without needing a physical presence initially. By mid-2024, regulatory frameworks in several ASEAN nations were also evolving to accommodate greater foreign digital financial service providers, potentially lowering barriers to entry.
- Capital Strength: International banks often boast significantly larger asset bases, enabling aggressive pricing and investment in technology.
- Digital Prowess: Leading global banks are investing billions in AI, cloud computing, and mobile banking platforms, creating highly competitive digital offerings.
- Regulatory Shifts: Evolving regulations in ASEAN countries are increasingly open to digital-first foreign entrants, reducing traditional entry barriers.
- Market Opportunity: The growing digital economy in ASEAN presents an attractive target for global financial institutions seeking new growth avenues.
Lower Regulatory Barriers in Specific Financial Segments
While established banking faces stringent regulations, the financial technology, or fintech, sector often experiences less oversight in specific niches. This allows new digital lenders or payment providers to enter the market with greater ease, potentially disrupting traditional models.
For instance, the rise of peer-to-peer lending platforms and digital wallets, often operating under lighter regulatory frameworks than full-service banks, demonstrates this trend. In 2024, the global fintech market was valued at over $2.5 trillion, with significant growth driven by these less regulated segments.
- Lower Regulatory Hurdles: Certain financial services, especially those leveraging technology like specific lending or payment solutions, can have less demanding regulatory entry points compared to traditional banking.
- Fintech Disruption: This facilitates the emergence of new players, particularly in the fintech space, who can challenge incumbent institutions by operating with fewer compliance burdens.
- Market Growth: The global fintech market's substantial growth, exceeding $2.5 trillion in 2024, underscores the impact of these lower barriers to entry in specific financial segments.
The threat of new entrants for CIMB Group Holdings remains a significant concern, particularly with the ongoing issuance of digital bank licenses across ASEAN. These licenses enable technology-focused companies to enter the financial services market with lower overheads than traditional banks. For example, by mid-2024, regulatory shifts in several ASEAN nations were making it easier for foreign digital financial service providers to enter, potentially lowering traditional barriers.
Fintech startups are adept at targeting niche markets, offering specialized services that attract customers without needing the broad product range of incumbents like CIMB. This focused approach allows them to build a customer base efficiently. Furthermore, tech giants are increasingly integrating financial services into their ecosystems, leveraging vast customer bases and data analytics. Apple Pay, for instance, processed an estimated $6 trillion globally in 2023, highlighting the scale of these new entrants.
| Type of New Entrant | Key Advantage | Example/Data Point (as of 2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Banks | Lower capital requirements, tech-centric operations | Monetary Authority of Singapore granted licenses to consortia including Grab and Singtel (2023) |
| Fintech Startups | Niche focus, agility | Global fintech market valued over $2.5 trillion (2024) |
| Tech Giants | Vast customer base, data analytics, ecosystem integration | Apple Pay processed ~$6 trillion in transactions globally (2023) |
| International Banks | Capital strength, digital expertise, global reach | European banks exploring digital expansion into emerging Asian markets (2024) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for CIMB Group Holdings is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, including annual and quarterly statements, alongside industry-specific research from reputable financial data providers and market intelligence firms.
