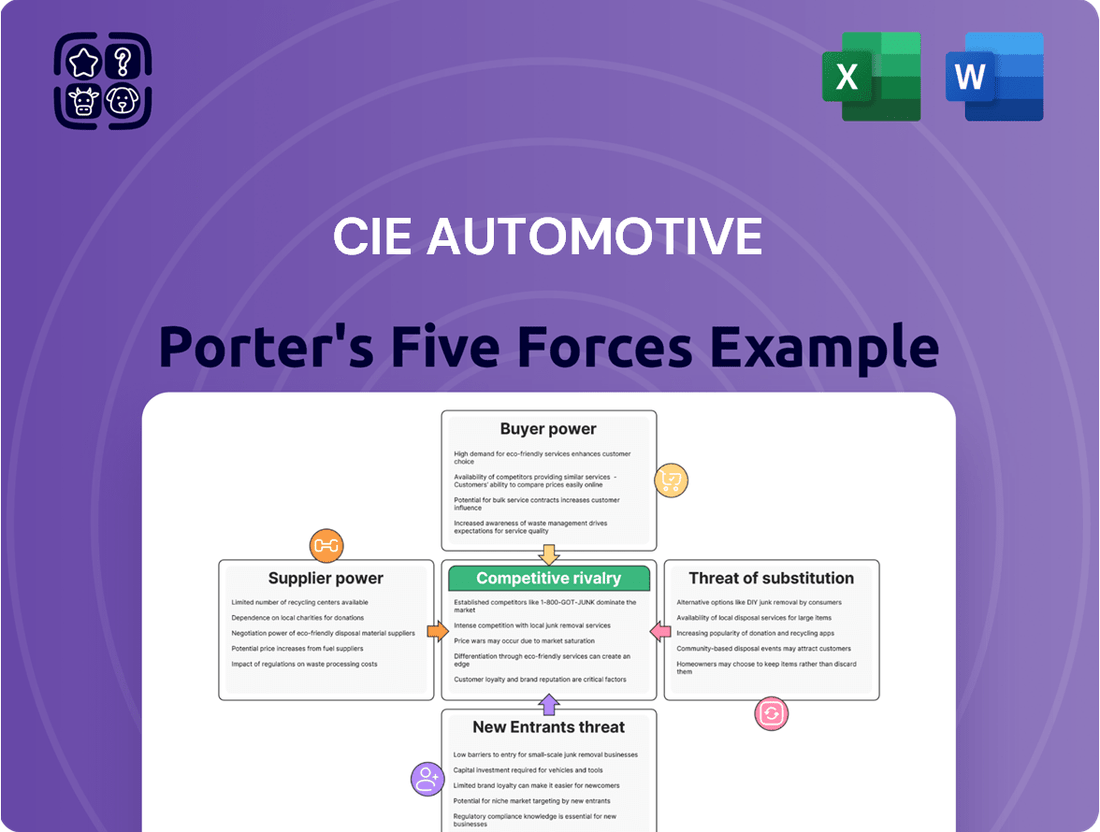
CIE Automotive Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CIE Automotive Bundle
CIE Automotive navigates a complex automotive supply chain where buyer power can be significant due to consolidation among major OEMs. The threat of new entrants is moderate, but existing players face intense rivalry, impacting pricing and innovation. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping CIE Automotive’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration significantly impacts bargaining power. In the automotive components sector, while diverse, certain highly specialized or patented parts may originate from a limited number of suppliers. If CIE Automotive depends heavily on these few providers for essential components, these suppliers gain leverage.
This dependence can translate into higher input costs for CIE Automotive or create vulnerabilities in its supply chain, as seen when a key supplier faces production issues. For instance, in 2023, the semiconductor shortage demonstrated how reliance on a concentrated supplier base for critical electronic components could disrupt global automotive production, affecting companies like CIE Automotive.
Switching suppliers in the automotive sector is a significant undertaking for companies like CIE Automotive. The process often involves substantial costs related to re-tooling manufacturing equipment, obtaining new certifications, and conducting rigorous testing to ensure components meet the extremely strict safety and performance standards demanded by the industry. These high switching costs effectively increase the bargaining power of existing suppliers, as they make it more difficult and expensive for CIE Automotive to change providers.
Suppliers offering unique, differentiated, or technologically advanced materials and components, particularly those vital for electric vehicles or emerging mobility solutions, wield significant influence. CIE Automotive's dependence on such specialized inputs can amplify supplier bargaining power.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration by suppliers significantly bolsters their bargaining power against CIE Automotive. If suppliers possess the means and motivation to manufacture CIE Automotive's finished products or components themselves, they can effectively cut out CIE, thereby increasing their leverage in pricing and terms. This is especially true for suppliers providing critical raw materials or specialized sub-assemblies that are integral to CIE's production process.
- Suppliers' Capability: Suppliers with advanced manufacturing capabilities and a deep understanding of CIE Automotive's end markets are better positioned to integrate forward.
- Incentive to Integrate: Higher profit margins in the automotive component manufacturing sector could incentivize suppliers to bypass intermediaries like CIE.
- Impact on CIE: A credible threat of forward integration can force CIE Automotive to accept less favorable terms from these suppliers to maintain their business relationship.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the automotive supply chain has seen increased consolidation, potentially giving larger suppliers greater capacity and incentive for forward integration.
Importance of Supplier to Buyer's Business
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key factor in CIE Automotive's competitive landscape. If CIE Automotive represents a small fraction of a supplier's total revenue, that supplier has greater leverage. For instance, if a critical component supplier derives only 1% of its sales from CIE, it has little incentive to offer favorable terms.
Conversely, when CIE Automotive is a major client for a supplier, the supplier's ability to dictate terms is significantly reduced. This is because losing CIE's business would have a substantial impact on the supplier's own financial health.
- Supplier Dependence: A supplier with a diverse customer base, where CIE Automotive is a minor client, wields more power.
- CIE's Purchasing Volume: If CIE Automotive accounts for a large percentage of a supplier's output, the supplier is more likely to accommodate CIE's demands.
- Switching Costs: High costs for CIE to switch suppliers for critical components or raw materials can increase supplier bargaining power.
- Supplier Concentration: Industries with few suppliers for essential inputs tend to see higher supplier bargaining power.
Suppliers who can credibly threaten to integrate forward into CIE Automotive's business operations possess significant bargaining power. This threat is amplified when suppliers have the capability and incentive to manufacture CIE's products, potentially cutting out CIE and dictating terms. For example, in 2024, increased consolidation in the automotive supply chain could empower larger suppliers with greater resources and motivation for such integration.
The bargaining power of suppliers is heavily influenced by CIE Automotive's importance to them. If CIE represents a small portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier has less incentive to offer favorable terms, as demonstrated by situations where a critical component supplier derives only a minor percentage of its sales from CIE. Conversely, if CIE is a major client, the supplier's leverage is diminished due to the significant impact of losing CIE's business.
Switching suppliers for critical automotive components involves substantial costs for CIE Automotive, including re-tooling, certifications, and rigorous testing. These high switching costs empower existing suppliers by making it more difficult and expensive for CIE to find alternatives, thus increasing their leverage. Specialized or technologically advanced inputs, especially for emerging areas like electric vehicles, further enhance supplier power.
| Factor | Impact on CIE Automotive | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases bargaining power if few suppliers exist for critical parts. | Semiconductor shortage in 2023 highlighted vulnerability to concentrated suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | High costs empower existing suppliers by making it difficult for CIE to change. | Re-tooling, certifications, and testing are significant hurdles. |
| Supplier Differentiation | Suppliers of unique or advanced components gain leverage. | Demand for EV-specific components can increase power of specialized suppliers. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers who can produce CIE's products gain leverage. | Market consolidation in 2024 may increase supplier incentive for integration. |
| CIE's Importance to Supplier | If CIE is a small client, supplier has more power. | A supplier with a diverse customer base will likely have higher bargaining power. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting CIE Automotive, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the automotive supply sector.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic five forces analysis, enabling rapid identification of CIE Automotive's strategic vulnerabilities and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration is a key factor in CIE Automotive's bargaining power of customers. If a few major automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) represent a significant portion of CIE Automotive's revenue, these large customers gain considerable leverage. For instance, if the top three OEMs accounted for over 50% of CIE Automotive's sales in 2024, they could demand lower prices or more favorable payment terms, impacting CIE's profitability.
For vehicle manufacturers, the process of switching component suppliers is often a costly endeavor. These costs can encompass significant investments in redesigning parts to fit new specifications, rigorous validation testing to ensure compatibility and performance, and the complex task of reconfiguring existing supply chains. For instance, a major automotive OEM might spend millions on retooling production lines and testing new components before they can be integrated into their vehicle models.
Consequently, if these switching costs were to decrease, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) would gain considerably more leverage in their negotiations with companies like CIE Automotive. A scenario where switching is simpler and less expensive would empower OEMs to demand better pricing or more favorable terms, directly impacting CIE Automotive's profitability and market position.
Buyer volume significantly influences a customer's bargaining power within the automotive supply chain. Companies like CIE Automotive serve major automotive manufacturers who purchase components in massive quantities. For instance, in 2024, the top global automakers, such as Toyota and Volkswagen Group, produced millions of vehicles annually, translating to an immense demand for parts.
This sheer volume allows these large buyers to negotiate highly favorable pricing and terms. Their ability to shift production or switch suppliers, while costly, is a credible threat due to their scale. Consequently, CIE Automotive, like other Tier 1 suppliers, must offer competitive pricing to secure and retain business from these high-volume clients.
Threat of Backward Integration
The threat of backward integration by CIE Automotive's customers, primarily vehicle manufacturers, significantly influences their bargaining power. If these manufacturers possess or can readily develop the capacity to produce the components CIE supplies, they gain leverage. For instance, if a major automotive OEM decides to bring the production of certain electronic control units or interior components in-house, it directly reduces CIE's sales volume and pricing flexibility for those specific products.
This capability is often driven by the scale of the customer and the strategic importance of the component. Large automakers might invest in internal production for high-volume, standardized parts or for components critical to their competitive differentiation. In 2024, the automotive industry's ongoing focus on cost optimization and supply chain control, partly driven by past disruptions, makes the prospect of backward integration a persistent consideration for suppliers like CIE Automotive.
- Customer Capability: Vehicle manufacturers' existing manufacturing infrastructure and technical expertise for producing automotive components.
- Component Criticality: The strategic importance of a component to a vehicle manufacturer's product design, performance, or cost structure.
- Industry Trends: The automotive sector's drive for vertical integration and supply chain resilience as observed in 2024.
- Market Scale: The sheer volume of demand from major OEMs, which can justify the investment in in-house production capabilities.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Vehicle manufacturers, facing intense competition and demanding consumers, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are constantly looking for ways to lower their costs, and this pressure extends directly to their suppliers, including companies like CIE Automotive.
In 2024, the automotive industry continued to grapple with economic uncertainties and fluctuating demand, intensifying the need for cost efficiency. For CIE Automotive, this translates into direct negotiations where buyers leverage their purchasing power to secure more favorable pricing on components and services.
- High Price Sensitivity: Automakers are acutely aware of the price points that consumers are willing to pay for vehicles, making them highly sensitive to any cost increases from their supply chain.
- Cost Reduction Demands: This sensitivity forces manufacturers to pass on cost reduction pressures to suppliers like CIE Automotive, impacting profit margins.
- Competitive Landscape: The crowded automotive market means manufacturers have many supplier options, further empowering them to negotiate lower prices.
The bargaining power of customers in the automotive sector, including CIE Automotive's clients, is substantial due to several factors. High buyer volume, significant switching costs for OEMs, and the potential for backward integration all contribute to this leverage. Furthermore, intense market competition and price sensitivity among vehicle manufacturers compel them to negotiate aggressively for lower component prices.
| Factor | Impact on CIE Automotive | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Buyer Volume | Enables negotiation for favorable pricing and terms. | Major OEMs like Volkswagen Group producing millions of vehicles annually. |
| Switching Costs | Reduces customer leverage if high; increases if low. | Millions spent by OEMs on retooling and testing for new suppliers. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Customers may produce components in-house, reducing demand. | OEMs investing in internal production for critical or high-volume parts. |
| Price Sensitivity | Drives demand for lower prices from suppliers. | Intensified cost efficiency needs due to economic uncertainties in 2024. |
Full Version Awaits
CIE Automotive Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the exact CIE Automotive Porter's Five Forces analysis you will receive upon purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within the automotive industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This detailed document is ready for immediate use, providing a thorough understanding of CIE Automotive's strategic landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The automotive components sector is quite crowded, featuring a multitude of global and regional competitors, many of whom are also multi-technology suppliers. This sheer volume and variety of players significantly ramp up the competitive rivalry, particularly in market segments that aren't experiencing rapid growth.
The global automotive industry is navigating a complex landscape characterized by slower-than-anticipated electric vehicle (EV) adoption and a contraction in traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle production. This dynamic directly impacts competitive rivalry, as companies vie for dominance in a shifting market.
For instance, in 2024, while EV sales continue to grow, the pace has moderated from earlier projections, leading to increased competition among established automakers and new entrants alike. This intensified competition can pressure margins and necessitate greater strategic maneuvering from players like CIE Automotive.
While CIE Automotive emphasizes innovative and sustainable solutions, the inherent nature of many standard metal, plastic, and aluminum components means product differentiation can be relatively low. This lack of significant differentiation in core offerings often intensifies price-based competition among rivals.
For instance, in the automotive supply chain, many Tier 1 suppliers offer similar stamped metal parts or plastic interior components. This commodity-like aspect means that if a competitor can produce these parts at a lower cost, they can easily attract customers. In 2023, the automotive industry saw continued pressure on component pricing, with many suppliers reporting tight margins on high-volume, standardized parts.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can indeed trap companies in a struggling market, intensifying competition. For CIE Automotive, significant investments in specialized manufacturing facilities and global production plants likely create substantial fixed costs. This means exiting the business or divesting certain operations would involve considerable financial penalties or asset write-downs, making continued operation, even at lower profitability, a more palatable option.
These barriers contribute to sustained rivalry because companies are less likely to leave the industry when faced with high exit costs. For example, the automotive sector, in general, is characterized by long-term supplier contracts and the need for continuous technological upgrades, both of which can act as exit deterrents. In 2023, CIE Automotive reported capital expenditures of €287 million, underscoring ongoing investment in its operational capabilities, which can further solidify these exit barriers.
- High Fixed Assets: CIE Automotive's extensive network of manufacturing plants and specialized machinery represents a significant capital investment, making it costly to liquidate or repurpose these assets.
- Specialized Equipment: The company's reliance on advanced, often custom-built machinery for producing automotive components means that these assets have limited alternative uses outside the industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to supply major automotive manufacturers often involve multi-year agreements, binding CIE Automotive to production schedules and market presence.
- Brand and Reputation: The established brand and reputation built over years in the automotive supply chain are valuable assets that would be difficult to transfer or recover upon exit.
Strategic Stakes
The automotive components market is a battleground where many large industrial conglomerates have significant interests, making it a strategically vital sector. This high level of strategic importance naturally fuels intense competition as firms fight to establish dominance in crucial areas like electric vehicle technology and advanced manufacturing processes.
Companies are heavily invested in securing leadership in emerging technologies. For instance, in 2024, global automotive component suppliers continued to pour billions into R&D for electrification, with major players like Bosch and Continental announcing substantial investments in battery technology and electric drivetrains. This race for technological supremacy intensifies rivalry as market share in these future-defining segments is seen as paramount.
- Strategic Importance: The automotive components sector is critical for numerous global industrial groups, driving significant investment and attention.
- Technological Race: Fierce competition exists to lead in key areas such as electrification and Industry 4.0, with companies making substantial R&D commitments.
- Investment in Electrification: In 2024, major suppliers like Bosch and Continental allocated billions to develop battery technology and electric powertrains, highlighting the strategic stakes in the EV transition.
- Aggressive Behavior: The pursuit of leadership in these transformative technologies often results in aggressive competitive tactics among suppliers.
The competitive rivalry within the automotive components sector is fierce, driven by a crowded market of global and regional players, many of whom are multi-technology suppliers. This intense competition is further exacerbated by a lack of significant differentiation in many standard components, leading to price-based battles. For example, in 2023, many suppliers faced pressure on pricing for high-volume, standardized parts, impacting margins.
High exit barriers, such as substantial investments in specialized manufacturing facilities and long-term contracts, keep companies engaged even in less profitable segments, thereby sustaining rivalry. CIE Automotive's capital expenditures, like the €287 million reported in 2023, reinforce these barriers. Furthermore, the strategic importance of the automotive sector and the ongoing technological race, particularly in electrification, fuel aggressive competition as firms vie for leadership in emerging areas.
| Factor | Description | 2023/2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Market Saturation | Numerous global and regional competitors, many offering diverse technologies. | Crowded market with many multi-technology suppliers. |
| Product Differentiation | Low differentiation in standard metal, plastic, and aluminum components. | Intensified price-based competition on commodity-like parts. |
| Exit Barriers | High fixed costs due to specialized facilities and long-term contracts. | CIE Automotive's 2023 CapEx of €287M indicates ongoing investment, reinforcing these barriers. |
| Strategic Importance & Tech Race | Sector is strategically vital, with significant investment in electrification R&D. | Billions invested by major players like Bosch and Continental in EV technology in 2024. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For CIE Automotive, the threat of substitutes is significant. These substitutes can manifest as alternative materials like advanced composites, which are increasingly used for lightweighting in vehicles, potentially reducing demand for traditional metal components. Furthermore, innovative manufacturing processes such as 3D printing could offer viable alternatives for producing certain automotive parts, bypassing traditional supply chains.
The rise of entirely new vehicle architectures, such as those found in electric vehicles (EVs), also presents a substitute threat. These new designs may inherently require fewer of the specific components that CIE Automotive specializes in, thereby altering the market landscape. For instance, the shift to EVs has seen a decrease in demand for certain powertrain components that were central to internal combustion engine vehicles.
The threat of substitutes for CIE Automotive's products is significant, particularly when alternatives offer comparable or better performance at a more attractive price point. For instance, advancements in composite materials or advanced plastics could present a viable alternative to traditional metal stamping and components, especially if their manufacturing and integration costs decrease substantially. In 2024, the automotive industry continued to see innovation in materials science, with some new lightweight composites showing promise for cost parity with certain metal alloys in specific applications.
Vehicle manufacturers' openness to adopting substitute materials or technologies is a key driver of this force. For instance, increasing emissions standards, like those pushing for lighter vehicles to improve fuel efficiency, directly influence their willingness to explore alternatives. In 2024, the automotive industry continued its strong push towards electrification and lightweighting, with many manufacturers announcing ambitious targets for reducing vehicle weight by an average of 10-15% by 2030 to meet stricter CO2 regulations.
Technological Advancements
Rapid technological advancements, particularly in materials science and manufacturing, can swiftly introduce viable substitutes for existing automotive components. This presents a significant threat as new technologies can emerge that offer comparable or superior performance at a lower cost.
CIE Automotive's strategic emphasis on electric vehicles (EVs) necessitates constant vigilance regarding evolving battery technologies, novel propulsion systems, and innovative structural designs. For instance, the ongoing race to develop solid-state batteries, which promise greater energy density and faster charging, could disrupt the market for current lithium-ion battery components. In 2024, global EV sales continued their upward trajectory, with projections indicating further growth, underscoring the critical need for CIE Automotive to stay ahead of these technological shifts.
- Emerging Battery Technologies: Advancements in solid-state batteries could reduce reliance on current liquid electrolyte chemistries, impacting demand for related components.
- Alternative Propulsion Systems: Innovations in hydrogen fuel cell technology or advanced electric motor designs could offer substitutes for traditional EV powertrains.
- Lightweighting Materials: New composite materials or advanced alloys might replace traditional metal components, altering supply chain dynamics and product specifications.
Shifting Vehicle Architectures
The automotive industry's rapid evolution, particularly the move towards electric vehicles (EVs) and software-defined vehicles (SDVs), presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional automotive component suppliers like CIE Automotive. As vehicle architectures fundamentally change, the demand for components tied to internal combustion engines (ICE) is projected to decline. For instance, by 2030, it's estimated that over 60% of new vehicle sales in major markets could be electric, directly impacting the market for ICE-specific parts.
This architectural shift necessitates new types of components, creating opportunities for new entrants and potentially rendering existing product portfolios obsolete. Companies that cannot adapt their offerings to meet the demands of EV powertrains, battery management systems, and advanced digital architectures face a substantial risk of being substituted by more agile competitors. The market for traditional exhaust systems, for example, is expected to shrink considerably as EV adoption accelerates.
- Declining ICE Component Demand: The global shift towards EVs directly reduces the need for components like traditional engines, transmissions, and exhaust systems.
- Emergence of New EV Components: The rise of EVs creates demand for new components such as battery packs, electric motors, power electronics, and thermal management systems.
- Software Integration: Software-defined vehicles require advanced electronic control units (ECUs), sensors, and connectivity modules, substituting traditional mechanical components with digital solutions.
- Supplier Adaptation: Suppliers unable to pivot their product lines and manufacturing capabilities to support EV and SDV architectures are at high risk of obsolescence.
The threat of substitutes for CIE Automotive is amplified by evolving vehicle architectures and material innovations. For instance, the automotive industry’s push for lightweighting, driven by emissions regulations, saw manufacturers exploring advanced composites and high-strength steels in 2024. These materials can substitute traditional metal components, impacting demand for CIE Automotive's offerings.
The accelerating shift to electric vehicles (EVs) is a primary driver of substitution. As EVs become more prevalent, demand for internal combustion engine (ICE) components, a core area for CIE Automotive, is expected to decline. Projections for 2024 indicated that EVs would continue to capture a larger share of new vehicle sales, directly affecting the market for ICE-related parts.
New manufacturing technologies also present substitution risks. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is gaining traction for producing complex automotive parts, potentially bypassing traditional supply chains and established component manufacturers. This technological shift offers alternative pathways for vehicle production.
The increasing integration of software and electronics in vehicles, leading to software-defined vehicles (SDVs), also substitutes traditional mechanical components with digital solutions. This requires a different set of components, such as advanced ECUs and sensors, which could displace older, mechanically focused parts.
| Substitution Threat | Description | Impact on CIE Automotive | 2024 Trend/Data |
| Advanced Materials | Composites, advanced alloys replacing traditional metals for lightweighting. | Reduced demand for metal-based components. | Continued R&D in lightweight materials, with some advanced composites nearing cost parity for specific applications. |
| EV Architecture Shift | New designs for EVs require fewer ICE-specific parts. | Decline in demand for traditional powertrain and exhaust components. | Global EV sales growth continued, with projections for 2024 indicating a significant increase in market share for EVs. |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing for complex or low-volume parts. | Potential bypass of traditional manufacturing and supply chains. | Increased adoption of 3D printing for prototyping and specialized part production in the automotive sector. |
| Software-Defined Vehicles | Digital solutions replacing mechanical controls and components. | Shift in demand towards electronic control units (ECUs), sensors, and connectivity modules. | Automakers increasingly focused on software integration, driving demand for advanced electronics. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the automotive components manufacturing sector, particularly for intricate metal, plastic, and aluminum parts, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in advanced machinery, state-of-the-art facilities, and ongoing research and development. For instance, establishing a new plant for producing complex automotive stampings can easily run into tens of millions of dollars, creating a formidable hurdle for potential newcomers.
Established automotive suppliers like CIE Automotive enjoy significant cost advantages due to economies of scale in their operations. This means they can produce parts more cheaply because they make so many of them. For instance, CIE Automotive's substantial production volumes allow for bulk purchasing of raw materials, leading to lower per-unit costs compared to a new entrant just starting out.
These scale benefits extend to research and development as well. Larger companies can spread the high costs of developing new technologies and manufacturing processes across a much larger output. This makes it difficult for new companies to match the pricing of established players, creating a substantial barrier to entry in the automotive component manufacturing sector.
New companies entering the automotive supply sector face significant hurdles in securing access to established distribution channels. Major automotive Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) typically rely on long-standing relationships with existing suppliers who have demonstrated reliability and quality over time. This makes it difficult for newcomers to break into these critical supply chains.
For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry continued to emphasize supply chain resilience and trusted partnerships. New entrants would need to invest heavily in building trust and proving their capabilities to OEMs, a process that can take years and significant resources, often requiring them to bypass established networks initially.
Proprietary Technology and Know-how
CIE Automotive's deep expertise in specialized manufacturing processes like forging, casting, machining, and injection molding, coupled with its commitment to innovative solutions, creates a significant barrier for new entrants. This proprietary technology and accumulated know-how are not easily acquired, requiring substantial investment in research, development, and specialized equipment. For example, CIE Automotive's investment in advanced materials and process optimization for lightweight components, a key trend in the automotive sector, represents a knowledge base that new competitors would struggle to match quickly.
The threat of new entrants is further mitigated by the capital-intensive nature of establishing advanced manufacturing capabilities. New companies would need to invest heavily to achieve the same level of technological sophistication and efficiency that CIE Automotive has developed over years of operation. This includes not only machinery but also the skilled workforce and quality control systems essential for automotive supply.
- Proprietary Technology: CIE Automotive's mastery of complex manufacturing techniques acts as a significant entry barrier.
- Know-how Accumulation: Years of experience in process optimization and innovation are difficult for newcomers to replicate.
- Capital Intensity: Establishing similar advanced manufacturing facilities requires substantial upfront investment.
- Industry Specialization: Focus on specific automotive components and materials creates a niche that is challenging to enter without established expertise.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and stringent regulations significantly deter new entrants in the automotive sector. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to enforce strict CO2 emission standards, requiring substantial investment in new technologies for compliance. Companies failing to meet these targets face hefty fines, making it a costly endeavor for newcomers to enter the market without established, compliant manufacturing processes.
Safety standards, such as those mandated by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States, also act as a formidable barrier. Achieving and maintaining certifications for crashworthiness and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) requires significant R&D expenditure and rigorous testing. This complexity means new players must dedicate substantial resources to meet these requirements, increasing the upfront capital needed to compete.
Furthermore, the automotive industry often requires specific quality certifications, like ISO/TS 16949 (now IATF 16949), which are essential for supplying major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Obtaining these certifications involves demonstrating robust quality management systems and supply chain reliability. Navigating this intricate web of regulations and certifications can be a lengthy and expensive process, effectively raising the barrier to entry for aspiring automotive manufacturers.
- Environmental Regulations: Continued enforcement of emission standards (e.g., Euro 7 in Europe) necessitates significant investment in cleaner technologies.
- Safety Standards: Compliance with evolving safety mandates, including ADAS features, requires advanced engineering and testing capabilities.
- Quality Certifications: Obtaining industry-specific quality approvals (e.g., IATF 16949) is crucial for supplier relationships and market access.
- Regulatory Navigation Costs: The time and financial resources needed to understand and adhere to diverse global regulatory frameworks are substantial barriers.
The threat of new entrants for CIE Automotive is relatively low due to substantial capital requirements for advanced manufacturing and R&D. Established relationships with OEMs and the need for specialized expertise in areas like forging and casting further deter newcomers. Additionally, navigating complex global regulations and quality certifications presents a significant hurdle, making it difficult for new players to compete effectively.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for machinery, facilities, and R&D. | Significant deterrent; requires substantial funding. | Setting up a new automotive stamping plant can cost tens of millions of dollars. |
| Economies of Scale | Established players benefit from lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | New entrants struggle to match pricing; lower profit margins initially. | CIE Automotive's bulk purchasing power for raw materials. |
| Distribution Channels | OEMs prefer established, reliable suppliers with proven track records. | Difficult for new companies to gain access to key customers. | Building trust with OEMs to be included in supply chains takes years. |
| Proprietary Technology & Know-how | Specialized manufacturing processes and accumulated expertise are hard to replicate. | Creates a knowledge gap; requires significant investment in R&D. | CIE Automotive's advanced materials and process optimization for lightweight components. |
| Government Regulations & Safety Standards | Stringent emission, safety, and quality standards increase compliance costs. | Adds complexity and financial burden for new entrants. | Meeting EU emission standards or NHTSA safety mandates requires advanced engineering. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for CIE Automotive leverages data from company annual reports, industry association statistics, and specialized automotive market research firms. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive intensity, supplier and buyer power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
