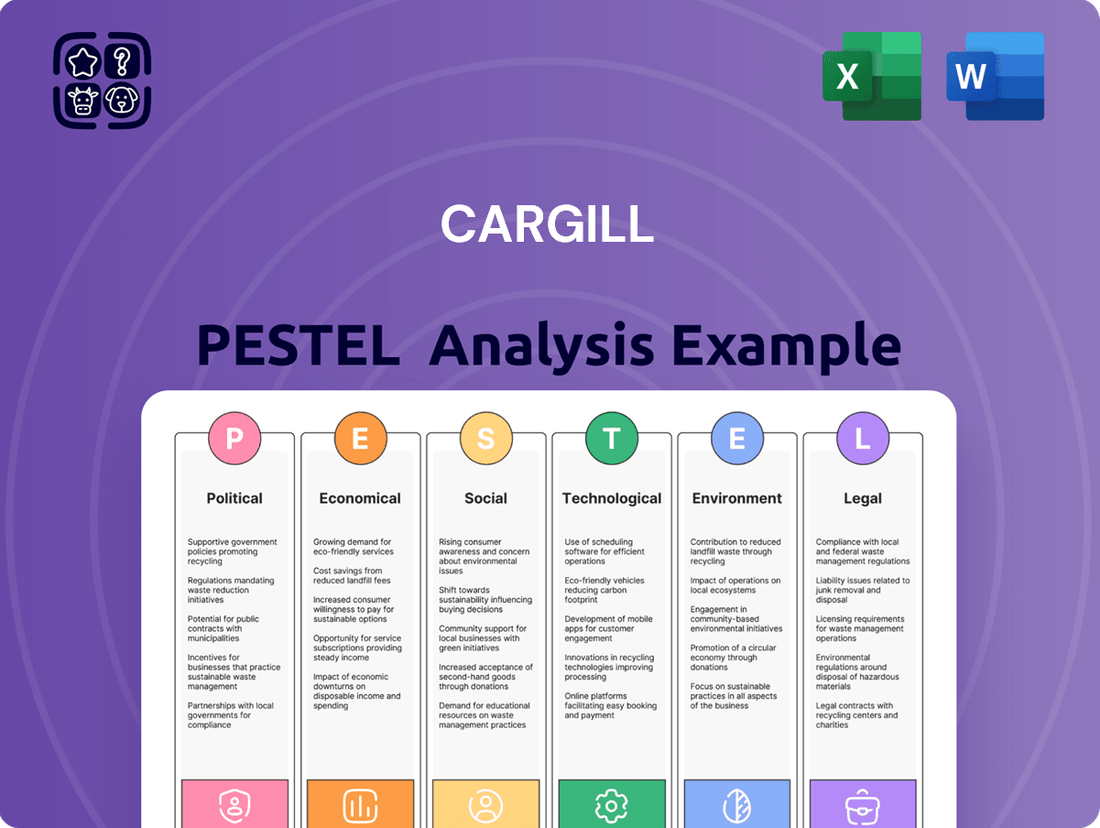
Cargill PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cargill Bundle
Navigate the complex external landscape impacting Cargill's operations with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Uncover critical political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that are shaping the future of this global food giant. Equip yourself with the strategic intelligence needed to anticipate challenges and seize opportunities.
Gain a decisive advantage by understanding the forces at play for Cargill. Our expertly crafted PESTLE analysis provides actionable insights into regulatory shifts, market dynamics, and emerging trends. Download the full report now to unlock a deeper understanding and refine your own strategic approach.
Political factors
Cargill's extensive global operations are directly shaped by international trade policies, tariffs, and agricultural subsidies. Fluctuations in these governmental stances, like the potential impact of new trade agreements or adjustments to existing ones, can significantly alter market dynamics. For instance, changes in import/export regulations can necessitate shifts in Cargill's supply chain strategies and directly affect its profitability. The infrastructure development spurred by expanded trade, such as that seen with the Trump-Australia Beef Trade Deal, can create opportunities for logistics providers within Cargill's network.
Geopolitical instability, including ongoing conflicts in key agricultural regions, directly impacts Cargill's operations. These disruptions can severely hinder the company's ability to source raw materials and deliver finished products, leading to volatile commodity prices. Cargill itself has acknowledged the persistent challenges to the global food system stemming from various conflicts.
Governments globally are prioritizing food security, implementing policies that directly impact agricultural giants like Cargill. These policies often encourage domestic production, regulate imports and exports, and promote sustainable farming practices, all of which shape Cargill's operational landscape. For instance, the European Union's Farm to Fork Strategy, aiming for a sustainable food system by 2030, could influence sourcing and production methods for Cargill's European operations.
Cargill's mission to help feed a growing world population aligns with this heightened focus on food security. As the global population is projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, governments are keen to ensure stable food supplies, often through direct subsidies or trade agreements that can benefit or challenge large agribusinesses. The United States Department of Agriculture's (USDA) initiatives to support climate-smart agriculture, for example, present opportunities for Cargill to invest in and promote more resilient farming techniques.
Regulation of Agricultural Practices
Government regulations on farming, including pesticide use and land conversion, significantly impact Cargill's suppliers and its own agricultural endeavors. These rules shape how raw materials are sourced and processed, influencing operational costs and supply chain stability. For instance, evolving environmental standards can necessitate investments in new technologies or altered sourcing strategies.
Cargill is actively responding to new regulatory landscapes. The European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), which came into effect in late 2024, requires companies to demonstrate that their commodities are deforestation-free. Similarly, the German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act (GSCDDA), fully applicable since January 1, 2024, mandates that companies establish robust due diligence processes to identify and address human rights and environmental risks in their supply chains. These regulations are driving increased transparency and accountability across the agricultural sector.
- EUDR Implementation: The EUDR requires extensive due diligence for commodities like soy, palm oil, and beef entering the EU market, impacting an estimated €280 billion of trade annually.
- GSCDDA Compliance: German companies are now legally obligated to monitor their supply chains for potential human rights and environmental violations, affecting over 2,800 companies.
- Supplier Adaptation: Cargill's efforts include working with suppliers to meet these new standards, potentially leading to shifts in sourcing patterns and increased demand for certified sustainable products.
- Operational Adjustments: The company is investing in traceability systems and supplier training to ensure compliance and mitigate risks associated with these evolving political factors.
International Sanctions and Embargoes
International sanctions and embargoes can significantly impact Cargill's operations by limiting its access to key markets and disrupting established supply chains. For instance, the ongoing geopolitical tensions in Eastern Europe have led to a complex web of sanctions affecting trade in grains and other agricultural commodities, forcing companies like Cargill to re-evaluate their sourcing and distribution strategies to mitigate risks and ensure compliance. This necessitates agile adaptation of their global business models.
Cargill must navigate these trade restrictions, which can affect everything from raw material procurement to the final sale of products in affected regions. The company's extensive global footprint means it is constantly monitoring and adjusting to evolving international trade policies. For example, in 2024, the United States maintained sanctions on Russia, impacting the global fertilizer and grain markets, areas where Cargill is a major player.
The company's ability to adapt to these political factors is crucial for maintaining its market position. Cargill's strategy often involves diversifying its supplier base and exploring alternative trade routes to circumvent sanctioned territories or commodities. This proactive approach helps cushion the blow from sudden policy changes and preserves business continuity.
- Market Access Restrictions: Sanctions can block Cargill from selling its products in or sourcing from specific countries, directly impacting revenue streams and market share.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Embargoes on certain commodities or shipping routes can halt the flow of essential agricultural inputs or finished goods, leading to increased costs and delays.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to complex and evolving sanction regimes requires significant investment in legal, compliance, and operational adjustments.
- Strategic Realignments: Cargill may need to divest from certain markets or reconfigure its global operations to comply with international regulations, potentially affecting its long-term growth strategy.
Governments worldwide are increasingly focused on food security and sustainability, implementing policies that directly influence agricultural giants like Cargill. These initiatives, such as the EU's Farm to Fork Strategy and the US Department of Agriculture's climate-smart agriculture programs, shape sourcing, production, and investment decisions for the company.
New regulations like the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) and the German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act (GSCDDA), fully applicable in 2024 and early 2024 respectively, are driving demand for greater transparency and traceability in agricultural supply chains. Cargill is actively adapting by investing in systems and working with suppliers to meet these stringent due diligence requirements, impacting an estimated €280 billion of EU trade annually.
International sanctions and trade restrictions, such as those affecting Russia in 2024, continue to pose significant challenges by limiting market access and disrupting supply chains. Cargill must navigate these complexities, often by diversifying its supplier base and adapting its global operations to ensure compliance and mitigate financial risks associated with geopolitical instability.
What is included in the product
This Cargill PESTLE analysis examines how political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors impact the company's operations and strategic decisions.
It provides actionable insights for identifying market opportunities and mitigating potential risks within Cargill's global agricultural and food sectors.
A clear, actionable summary of Cargill's PESTLE factors, enabling swift identification of external opportunities and threats to inform strategic decisions.
Economic factors
Cargill's financial performance is significantly tied to the unpredictable swings in agricultural commodity markets. Prices for key products such as grains, soybeans, and corn can dramatically impact the company's top line.
In fiscal year 2024, this volatility became evident as Cargill's revenue saw a substantial drop of nearly 10%, falling to $160 billion. This downturn ended a two-year period of record earnings, primarily attributed to the sharp decline in agricultural commodity prices and softer global demand.
Inflationary pressures directly affect Cargill's operational costs, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished goods, and also influence how much consumers can afford to spend. For instance, rising energy and fertilizer costs in 2024 have been significant factors impacting agricultural input prices.
Cargill's own research, such as their 2025 Protein Profile, highlights a key consumer trend: shoppers are increasingly looking for value, balancing the desire for affordable options with occasional indulgences. This means that while consumers may be price-sensitive due to inflation, they still allocate spending to preferred protein sources.
Exchange rate volatility presents a significant challenge for Cargill, a global agribusiness giant. Fluctuations in currency values directly impact the cost of raw materials imported into different regions and the revenue generated from international sales. For instance, a stronger US dollar can make Cargill's exports more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially reducing sales volume.
In 2024, many emerging market currencies experienced notable depreciation against the US dollar, a trend that could continue into 2025. This dynamic directly affects Cargill's profit margins, as earnings from operations in countries with weakening currencies are worth less when translated back into dollars. Managing this risk is crucial for maintaining consistent financial performance across its diverse global portfolio.
Economic Growth and Consumer Spending
Economic growth and consumer spending are fundamental drivers for Cargill's diverse product portfolio. As economies expand, disposable incomes tend to rise, directly impacting consumer demand for food ingredients, animal nutrition, and other agricultural products that Cargill supplies.
Cargill's 2025 Protein Profile underscores a significant trend: consumers are prioritizing protein for both health and taste. This shift is evident, with a notable 61% of Americans reporting an increase in their protein intake during 2024, signaling robust demand for protein-rich food solutions.
- Consumer Spending Habits: Directly correlate with demand for Cargill's food ingredients and animal nutrition.
- Protein Demand: 61% of Americans increased protein intake in 2024, a key trend for Cargill's protein-focused offerings.
- Economic Expansion: Generally leads to higher disposable incomes, boosting spending on food and agricultural products.
Supply Chain Costs and Efficiency
Cargill's profitability is directly influenced by escalating operational expenses, particularly in energy and labor. For instance, global energy prices saw significant volatility in 2024, impacting transportation and processing costs. The company is actively pursuing strategies to enhance efficiency and drive profitability throughout its diverse operations.
To counter these pressures, Cargill is investing in technologies and processes that streamline logistics and reduce waste. A key focus remains on optimizing its global supply chain to mitigate the impact of rising costs. This includes exploring more sustainable and cost-effective transportation methods and improving inventory management.
- Rising Energy Costs: Global energy prices, a significant input for transportation and processing, remained a key concern throughout 2024, with Brent crude oil averaging around $83 per barrel for the year.
- Labor Cost Pressures: Wage inflation continued to be a factor in many of Cargill's operating regions, necessitating a focus on labor productivity improvements.
- Logistics Optimization: Cargill's commitment to efficient logistics aims to reduce transit times and minimize spoilage, crucial for its perishable goods.
- Profitability Focus: The company's strategic initiatives are geared towards achieving a better balance between cost management and revenue generation across its agricultural and food businesses.
Economic factors significantly shape Cargill's performance, with commodity price volatility being a primary concern. For instance, fiscal year 2024 saw a nearly 10% revenue drop to $160 billion, ending a streak of record earnings due to falling agricultural prices and weaker demand.
Inflationary pressures, particularly on energy and fertilizer in 2024, directly impact Cargill's costs and consumer purchasing power. Meanwhile, economic growth generally boosts demand for Cargill's products, with a notable trend of 61% of Americans increasing protein intake in 2024, benefiting Cargill's protein-focused offerings.
| Economic Factor | Impact on Cargill | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Commodity Price Volatility | Affects revenue and profitability | Revenue down nearly 10% to $160 billion in FY24 |
| Inflation | Increases operational costs and impacts consumer spending | Rising energy and fertilizer costs in 2024 |
| Economic Growth & Consumer Spending | Drives demand for food and agricultural products | 61% of Americans increased protein intake in 2024 |
Preview Before You Purchase
Cargill PESTLE Analysis
The Cargill PESTLE Analysis preview you see is the exact, fully formatted document you'll receive after purchase. This comprehensive report offers a detailed examination of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting Cargill. You can be confident that what you're previewing is the complete, ready-to-use analysis you'll be working with.
Sociological factors
Consumer trends towards healthier eating and alternative protein sources significantly shape Cargill's product development and marketing. For instance, the growing demand for plant-based options requires innovation in that sector, while continued strong demand for traditional proteins necessitates efficient supply chains.
Cargill's 2025 Protein Profile highlights a sustained consumer preference for animal proteins such as beef, chicken, and eggs, driven by their perceived taste, nutritional value, and versatility. This trend directly impacts Cargill's strategic focus and investment in these core protein categories.
The global population is on a steady rise, with projections indicating an increase of approximately 500 million people by 2030. This growth, coupled with the accelerating trend of urbanization, significantly boosts the demand for food and agricultural products. For a company like Cargill, this presents a substantial opportunity to expand its reach and supply chains.
Urbanization concentrates consumers, creating concentrated demand centers that require efficient food distribution networks. As more people move to cities, the need for processed foods, convenient meal solutions, and reliable access to essential agricultural commodities intensifies. Cargill's extensive operations in food processing and agricultural trading are well-positioned to meet these evolving urban needs.
Consumers are increasingly scrutinizing the origins and ethical production of their food, a trend that significantly impacts major agribusinesses like Cargill. This demand for transparency means companies must be open about their supply chains, from farm to fork. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers are willing to pay more for products with clear ethical sourcing information.
Labor Practices and Human Rights Concerns
Cargill operates within a global agricultural system where labor practices and human rights are under intense public and regulatory scrutiny. Concerns about child labor and fair wages, particularly in complex agricultural supply chains, directly affect Cargill's brand image and operational continuity. For instance, the company has faced legal actions related to allegations of not adequately addressing human rights abuses within its Brazilian soy supply chain.
Cargill's engagement with organizations focused on the cocoa industry highlights efforts to improve farmer livelihoods and ethical sourcing. These initiatives are crucial for mitigating reputational damage and ensuring compliance with evolving human rights standards.
- Reputational Risk: Negative publicity surrounding labor practices can alienate consumers and business partners.
- Legal Challenges: Lawsuits related to supply chain abuses can result in significant financial penalties and operational disruptions.
- Supply Chain Integrity: Ensuring fair labor standards is vital for maintaining the long-term sustainability and ethical sourcing of raw materials.
- Stakeholder Expectations: Investors, NGOs, and consumers increasingly demand transparency and accountability in corporate labor practices.
Food Waste Awareness
Growing consumer awareness around food waste is significantly shaping how companies like Cargill operate. This heightened consciousness pressures them to innovate in processing, distribution, and product design to minimize waste throughout the supply chain. For instance, Cargill's focus on smaller protein packages, as highlighted in their Protein Profile, directly addresses consumer desires to reduce household food waste by offering more manageable portion sizes.
This trend isn't just about consumer preference; it's increasingly backed by data. Globally, an estimated 17% of food produced is wasted, with 11% lost in households and 5% in the food service and retail sectors, according to the UN Environment Programme's Food Waste Index Report 2024. This highlights a substantial opportunity for companies to differentiate themselves by offering solutions that align with sustainability goals.
Cargill's strategic response to this sociological factor is evident in several areas:
- Product Innovation: Developing smaller, more convenient packaging options to reduce household waste.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Implementing technologies and processes to minimize spoilage during storage and transportation.
- Consumer Education: Engaging in initiatives to educate consumers on proper food storage and utilization.
- Partnerships: Collaborating with organizations focused on food recovery and redistribution.
Consumer demand for transparency in food sourcing and ethical labor practices is a significant sociological factor influencing Cargill. A 2024 survey revealed that over 60% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for products with clear ethical sourcing information, directly impacting brand loyalty and market share.
The increasing global population, projected to reach nearly 8.6 billion by 2030, coupled with rapid urbanization, drives a heightened demand for food and efficient distribution systems. This demographic shift presents a substantial growth opportunity for Cargill's extensive agricultural and food processing operations.
Concerns regarding food waste are also shaping consumer behavior and corporate strategy, with an estimated 17% of global food production being wasted annually according to the UN Environment Programme's 2024 Food Waste Index Report. Cargill's response includes offering smaller product packaging to reduce household waste and improving supply chain efficiency.
| Sociological Factor | Consumer Behavior/Trend | Cargill's Response/Impact | Supporting Data/Example |
| Ethical Sourcing & Labor | Demand for transparency and fair labor | Reputational risk, legal challenges, supply chain integrity | 60%+ consumers willing to pay more for ethical sourcing (2024 survey) |
| Population Growth & Urbanization | Increased demand for food and convenient solutions | Expansion opportunities, focus on efficient distribution | Global population to reach 8.6 billion by 2030 |
| Food Waste Awareness | Desire to reduce waste at all levels | Product innovation (smaller packaging), supply chain efficiency | 17% of global food production wasted annually (UN 2024 report) |
Technological factors
Advancements in agricultural technology are significantly reshaping the landscape for companies like Cargill. Innovations such as regenerative farming, precision agriculture, and cutting-edge biotechnologies offer substantial boosts to efficiency, sustainability, and ultimately, crop yields for Cargill and its vast network of suppliers. These technologies are crucial for meeting growing global food demand while minimizing environmental impact.
Cargill's commitment to innovation is evident through its recognition with two 2025 BIG Innovation Awards. This highlights the company's proactive approach to integrating new technologies and practices. Furthermore, Cargill's dedicated investment in regenerative agriculture programs underscores its strategic focus on long-term sustainability and resilience within its supply chains, aiming to improve soil health and reduce carbon emissions.
Cargill's embrace of digital solutions, including AI and automation, is revolutionizing its supply chain operations. This technological shift enhances efficiency, traceability, and risk management across logistics and processing. For instance, Cargill's migration of supplier management software to SafetyChain exemplifies this digitalization, streamlining processes and centralizing critical information.
Technological advancements in food processing and ingredient innovation are reshaping the landscape for companies like Cargill. Breakthroughs in areas such as plant-based protein processing and fermentation technologies are enabling the creation of novel food products that cater to growing consumer interest in sustainability and health. For instance, the global alternative protein market, which includes plant-based and cultivated meat, was valued at approximately $7.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $30 billion by 2030, highlighting the significant market opportunity driven by these technological shifts.
Cargill is strategically investing in these innovations to meet evolving consumer demands. Their focus extends to developing ingredients that promote gut health, such as prebiotics and probiotics, and expanding the variety of protein sources available to consumers. Furthermore, they are dedicated to enhancing the nutritional profiles of popular consumer foods, integrating healthier ingredients and processing methods to align with global wellness trends. This commitment to innovation is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in a dynamic market where technology directly influences product development and consumer appeal.
Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling
Cargill leverages big data analytics and predictive modeling to refine its trading strategies and manage market risks effectively. This technological adoption is crucial for forecasting trends across its vast agricultural and food businesses, enabling more data-driven decisions.
In 2024, the agricultural technology sector saw significant investment, with companies focusing on AI and machine learning for supply chain optimization. Cargill's investment in these areas directly impacts its ability to navigate volatile commodity markets. For example, advanced analytics can help predict crop yields and price fluctuations, as seen in the increasing adoption of precision agriculture technologies by farmers globally, which generate substantial data for analysis.
- Optimized Trading: Predictive models help Cargill anticipate commodity price movements, enhancing trading profitability.
- Risk Management: Data analytics allows for better identification and mitigation of supply chain and financial risks.
- Market Forecasting: Predictive tools aid in understanding future demand and supply dynamics for key agricultural products.
- Informed Decision-Making: Enhanced data insights support strategic choices across Cargill's diverse operational segments.
Renewable Energy Technologies
Cargill is actively investing in renewable energy and energy-efficient technologies across its operations. This strategic move is designed to lower operational costs while simultaneously minimizing its environmental footprint.
These investments are yielding tangible results. Cargill has established renewable energy partnerships, successfully implementing over 60 projects in 20 countries.
The impact of this renewable energy push is significant:
- Reduced Emissions: Cargill has achieved a reduction of 908,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions through its increased use of renewable energy sources.
- Operational Efficiency: The adoption of these technologies contributes to greater energy efficiency, leading to cost savings.
- Global Reach: The 60+ projects span 20 countries, demonstrating a widespread commitment to sustainable energy solutions.
Technological advancements are central to Cargill's strategy, driving efficiency and sustainability. The company's commitment is underscored by two 2025 BIG Innovation Awards, showcasing its integration of new practices. Investment in regenerative agriculture aims to enhance soil health and reduce carbon emissions.
Cargill is leveraging digital solutions like AI and automation to optimize its supply chain, improving traceability and risk management. For example, their supplier management software migration to SafetyChain exemplifies this digitalization. The global alternative protein market, valued at $7.5 billion in 2023, is projected to exceed $30 billion by 2030, reflecting the impact of food processing and ingredient innovation.
Big data analytics and predictive modeling are crucial for Cargill's trading strategies and risk management, aiding in market forecasting. In 2024, agricultural technology saw substantial investment, particularly in AI for supply chain optimization, directly impacting Cargill's ability to navigate commodity markets. Precision agriculture adoption generates significant data for analysis.
Cargill is also investing in renewable energy, with over 60 projects in 20 countries, reducing carbon emissions by 908,000 tons. This focus on energy efficiency lowers operational costs and environmental impact, demonstrating a global commitment to sustainable energy solutions.
Legal factors
Cargill navigates a complex web of global food safety regulations and quality standards, crucial for maintaining product integrity and consumer confidence. These regulations, which vary by country and region, dictate everything from ingredient sourcing to manufacturing processes and labeling. For instance, in the United States, the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) significantly shifted the focus from responding to contamination to preventing it, impacting how companies like Cargill manage their supply chains.
To address these requirements, Cargill has implemented robust global human and animal food/feed safety, quality, and regulatory processes. A key component of this is their Supplier and External Manufacturer Requirements Manual, ensuring that all partners meet the company's high standards. This proactive approach is vital, especially considering the increasing consumer demand for transparency and traceability in the food supply chain, a trend amplified in 2024 and projected to continue through 2025.
Cargill faces increasing environmental regulations concerning emissions, water usage, and deforestation, demanding substantial compliance investments. The company has pledged to eliminate deforestation and land conversion from its supply chains by 2025 in specific regions, with a broader global target of 2030.
Cargill operates in a heavily regulated global food and agriculture sector, making antitrust and competition laws a significant factor. These laws are designed to prevent monopolies and ensure fair market practices, directly impacting Cargill's ability to grow through mergers and acquisitions, and potentially limiting its market share in key regions. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued its focus on market concentration in agriculture, with potential implications for large players like Cargill regarding supply chain dominance.
Labor Laws and Employment Regulations
Cargill navigates a complex web of labor laws and employment regulations across its global operations, impacting everything from minimum wages and working conditions to employee rights and union relations. These diverse legal frameworks necessitate careful adherence to ensure compliance and mitigate risks in each jurisdiction where the company operates.
In a significant move reflecting operational adjustments, Cargill announced in late 2023 and early 2024 that it would be cutting approximately 5% of its global workforce, impacting around 1,300 employees. This decision was aimed at streamlining operations and improving efficiency in response to evolving market conditions.
- Compliance Burden: Adhering to varying international labor standards, including those set by organizations like the International Labour Organization (ILO), presents a continuous challenge.
- Workforce Restructuring: The recent workforce reduction of about 5% highlights the company's need to adapt its employment practices to economic realities and strategic priorities.
- Employee Rights: Ensuring fair treatment, safe working environments, and adherence to collective bargaining agreements are critical legal considerations for Cargill.
International Trade Laws and Tariffs
Cargill's extensive global operations in commodity trading and distribution necessitate strict adherence to a complex web of international trade laws, customs regulations, and diverse tariff agreements. Navigating these legal frameworks is paramount for seamless cross-border transactions and maintaining supply chain integrity.
International trade policies and evolving tariffs directly influence Cargill's profitability and market access. For instance, the imposition of new tariffs on agricultural goods, such as those seen in trade disputes between major economic blocs in 2023-2024, can significantly alter the cost of raw materials and finished products, impacting pricing strategies and demand.
- Trade Agreements: Cargill benefits from agreements like the USMCA, which facilitates trade within North America, but is also exposed to risks from potential changes or disputes within these pacts.
- Tariff Impacts: In 2023, the average applied tariff on agricultural products globally remained a significant factor, with variations across countries impacting Cargill's import and export costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Staying updated on evolving food safety standards and import/export documentation requirements across dozens of countries is a continuous operational challenge.
Cargill's operations are heavily shaped by global food safety and quality regulations, with the US Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) exemplifying a shift towards prevention. The company's commitment to rigorous safety protocols, including its Supplier and External Manufacturer Requirements Manual, is essential for meeting consumer demand for transparency, a trend intensifying through 2024 and into 2025.
Environmental regulations, particularly concerning deforestation and emissions, require significant investment and strategic adaptation. Cargill's pledge to eliminate deforestation from its supply chains by 2025 in certain regions underscores the growing legal and societal pressure for sustainable practices.
Antitrust and competition laws are critical, influencing Cargill's growth strategies, especially mergers and acquisitions, and market share. The European Union's continued scrutiny of market concentration in agriculture during 2024 highlights the importance of compliance for large agribusinesses.
International trade laws and tariffs directly impact Cargill's global commodity trading. For instance, trade disputes in 2023-2024 led to fluctuating tariffs, affecting raw material costs and market access, underscoring the need for agile navigation of these complex legal frameworks.
Environmental factors
Climate change is a major concern, bringing more frequent and severe weather events. This directly affects crop yields, disrupts supply chains, and causes price volatility for commodities, all of which are critical for Cargill. For instance, the U.S. experienced a record-breaking number of billion-dollar weather disasters in 2023, with 28 such events causing widespread agricultural damage.
Cargill is under significant pressure to reduce its role in deforestation and champion sustainable land use across its vast agricultural networks. This environmental concern directly impacts its operations and reputation.
The company has made concrete commitments, aiming for its soy, corn, wheat, and cotton supply chains in Brazil, Uruguay, and Argentina to be free from deforestation and land conversion by 2025. Furthermore, Cargill has set an ambitious target of achieving entirely deforestation-free agricultural supply chains globally by 2030.
Water scarcity and quality pose significant environmental challenges for agriculture, directly impacting Cargill's operations. Recognizing this, the company is committed to water stewardship, focusing on restoring water in regions facing stress. As of their latest reporting, Cargill has successfully restored over 38 billion liters of water in these critical areas, demonstrating a tangible effort to mitigate scarcity.
Biodiversity Loss
Cargill recognizes the significant impact agricultural practices can have on biodiversity, a concern that's increasingly shaping industry standards and consumer expectations. As a major player in global food and agriculture, the company is actively investing in initiatives aimed at safeguarding and improving biodiversity within the landscapes where its products originate.
These efforts are particularly visible in their work with North American beef farms, where Cargill is collaborating with producers to implement practices that support a healthier ecosystem. This includes promoting sustainable land management and habitat restoration. For instance, by 2024, Cargill aimed to have 100% of its North American beef sourced from producers who have committed to verifiable sustainability goals, which often include biodiversity protection measures.
- Biodiversity Focus: Cargill is actively working to protect and enhance biodiversity in agricultural landscapes, acknowledging the environmental footprint of farming.
- North American Beef Initiative: The company is engaged in boosting biodiversity on North American beef farms through partnerships with producers.
- Ecosystem Protection: Efforts are underway to protect critical ecosystems that are vital for maintaining biodiversity.
- Sustainability Commitments: Cargill's sustainability goals, like those for North American beef sourcing, increasingly integrate biodiversity protection as a key performance indicator.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Carbon Footprint
Cargill is actively addressing climate change by focusing on reducing its greenhouse gas emissions throughout its operations and supply chains. This commitment is crucial given the growing global emphasis on environmental sustainability.
The company has set specific targets to achieve these reductions. By 2025, Cargill aims for a 10% reduction in its scope 1 and 2 emissions, using 2017 as its baseline year. Furthermore, it targets a more substantial 30% decrease in scope 3 emissions by 2030.
- Scope 1 & 2 Emissions Target: 10% reduction by 2025 (vs. 2017 baseline).
- Scope 3 Emissions Target: 30% reduction by 2030.
- Focus Areas: Operations and extensive supply chains.
Environmental factors significantly shape Cargill's operations, with climate change posing a substantial threat through increased extreme weather events that impact crop yields and supply chain stability. For example, the 28 billion-dollar weather disasters in the U.S. during 2023 highlight this vulnerability, directly affecting commodity prices and availability.
Cargill is actively addressing deforestation and promoting sustainable land use, aiming for its key supply chains in South America to be deforestation-free by 2025 and globally by 2030. Water scarcity is another critical challenge, prompting Cargill's commitment to water stewardship, with over 38 billion liters restored in water-stressed regions. The company also prioritizes biodiversity, investing in initiatives to protect ecosystems and enhance them on farms, such as its 2024 goal for 100% of North American beef to be sourced from producers with verifiable sustainability goals.
| Environmental Factor | Cargill's Response/Commitment | Key Data/Target |
| Climate Change & Extreme Weather | Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, adapting to weather impacts | Aiming for 10% reduction in Scope 1 & 2 emissions by 2025 (vs. 2017 baseline); 30% reduction in Scope 3 by 2030. |
| Deforestation | Commitment to deforestation-free supply chains | Soy, corn, wheat, cotton in Brazil, Uruguay, Argentina by 2025; global by 2030. |
| Water Scarcity & Quality | Water stewardship and restoration efforts | Restored over 38 billion liters of water in stressed regions. |
| Biodiversity Loss | Protecting and enhancing biodiversity in agricultural landscapes | Aiming for 100% North American beef from producers with verifiable sustainability goals by 2024. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for Cargill is meticulously crafted using a blend of public and proprietary data sources. This includes extensive market research reports, official government publications, and analyses from leading economic institutions.
