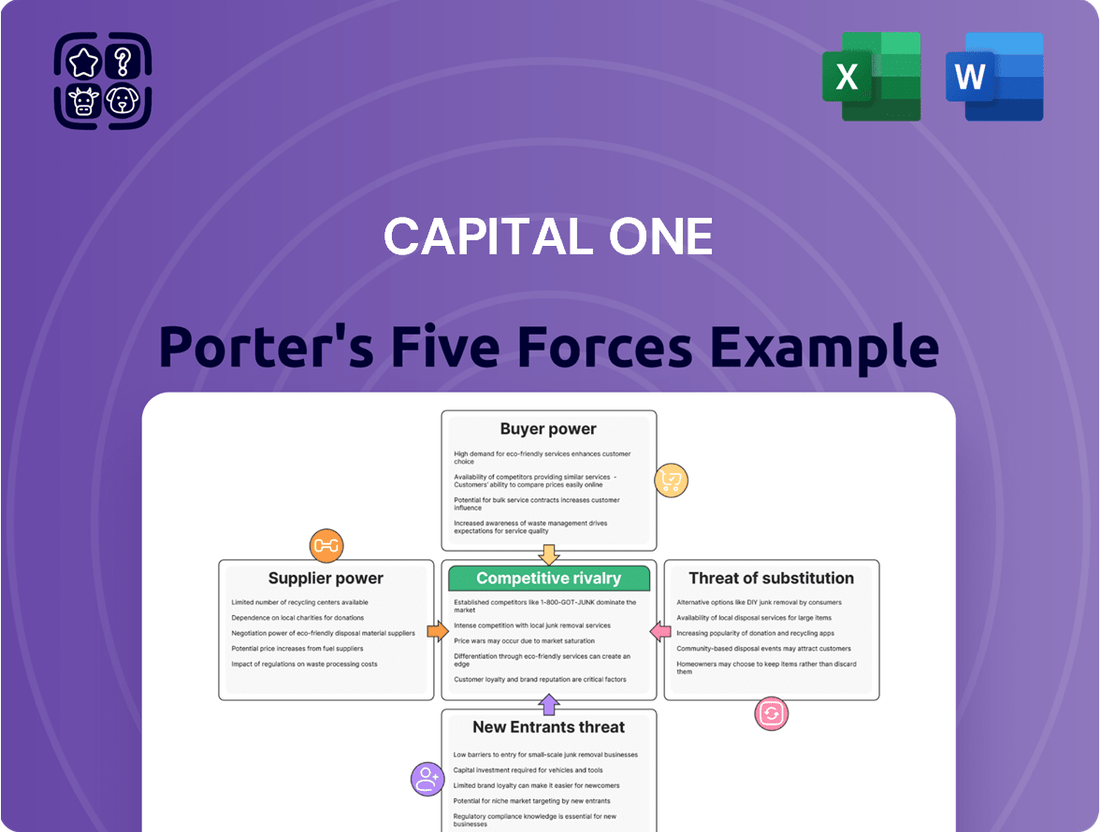
Capital One Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Capital One Bundle
Capital One navigates a dynamic financial landscape, facing intense rivalry and the constant threat of new entrants disrupting established players. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial to their strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Capital One’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Capital One's reliance on specialized technology makes it vulnerable to the concentration of key providers. For instance, major cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform dominate the market, giving them considerable leverage. In 2024, these three companies collectively held over 65% of the global cloud infrastructure market, meaning Capital One has limited alternatives for its critical IT needs.
This limited choice translates to significant bargaining power for these technology firms. They can influence pricing structures, dictate service level agreements, and potentially restrict access to essential updates or innovations. This directly impacts Capital One's operational expenses and its ability to rapidly implement new digital strategies, as seen in the increasing costs associated with advanced data analytics software and robust cybersecurity solutions.
Capital One, as a data-centric financial institution, relies heavily on external data and information services. These critical inputs include credit bureaus, fraud detection platforms, and market intelligence providers. The availability and nature of the data these suppliers offer directly influence their leverage.
When these suppliers hold unique or proprietary datasets, their bargaining power is significantly amplified. For instance, if a credit bureau possesses exceptionally granular or predictive data that is difficult to replicate, Capital One faces increased costs for accessing this vital information. This impacts their ability to accurately assess credit risk and develop innovative financial products, as demonstrated by the ongoing investments in data analytics infrastructure, which reached billions of dollars annually across the financial sector in 2024.
The financial services sector, especially companies like Capital One that lean heavily into technology, has a significant need for specialized expertise. Think about roles in data science, artificial intelligence, and advanced software development – these are the skills in demand. In 2024, the competition for these tech professionals remains incredibly intense, creating a strong bargaining position for the talent itself.
When the labor market is tight for these highly sought-after skills, employees, acting as a collective supplier of their labor, gain considerable leverage. This often translates into upward pressure on wages, salary increases, and enhanced benefits packages. For Capital One, this means potentially higher operational costs as they strive to attract and retain top-tier tech talent in a competitive landscape.
Payment Network Providers
Payment network providers like Visa and Mastercard hold significant bargaining power over Capital One. Their extensive global acceptance and robust transaction processing infrastructure make them indispensable for credit card operations. This dominance allows them to dictate terms, including interchange fees, which directly affect Capital One's profitability.
For instance, interchange fees, a primary revenue stream for card issuers, are largely set by these networks. In 2023, Visa and Mastercard continued to be the primary conduits for a vast majority of card transactions, reinforcing their leverage. Capital One's 2023 financial reports, prior to the full integration of Discover, would have shown substantial expenses related to these network fees.
- High Network Dependence: Capital One's reliance on Visa and Mastercard for transaction processing grants these networks considerable influence.
- Fee Structure Impact: Interchange and network fees paid to these providers directly impact Capital One's cost of revenue and net interest margin.
- Strategic Mitigation: Capital One's acquisition of Discover, a competing payment network, is a strategic move to reduce its dependence on Visa and Mastercard and potentially gain more control over its payment infrastructure and associated costs.
Financial Market Infrastructure Providers
Financial market infrastructure providers, such as those offering interbank clearing, payment gateways, and regulatory compliance software, wield considerable bargaining power over Capital One. The specialized and essential nature of these services means few alternatives exist, and switching costs can be significant, giving these suppliers leverage.
For instance, the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT), a key player in global financial messaging, operates with a network effect that strengthens its position. In 2024, the global market for financial infrastructure services is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the scale and importance of these suppliers.
- High Switching Costs: Implementing new financial infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming, involving significant integration and testing, which discourages Capital One from easily changing providers.
- Limited Number of Providers: The market for highly specialized financial infrastructure often features a concentrated number of players, reducing competition and increasing the bargaining power of existing suppliers.
- Criticality of Services: Disruptions to services like payment processing or regulatory reporting can have severe financial and reputational consequences for Capital One, making them more reliant on their current providers.
- Supplier Concentration: In specific niches, like real-time gross settlement systems or certain types of payment processing, only a handful of vendors may offer the required capabilities, solidifying their bargaining strength.
Capital One's reliance on specialized technology providers, such as cloud services and data analytics platforms, grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. The concentration of major players in the cloud market, with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud holding over 65% of the global market share in 2024, limits Capital One's alternatives and allows these providers to influence pricing and service terms.
Similarly, the need for unique data sets from credit bureaus and fraud detection services amplifies supplier leverage, especially when proprietary information is involved. This dependence can lead to increased costs for essential data, impacting Capital One's risk assessment capabilities and product development.
The intense competition for skilled tech talent in 2024 also empowers employees as suppliers of labor, driving up wages and benefits. Furthermore, payment networks like Visa and Mastercard, due to their extensive reach and essential role in transactions, dictate terms including interchange fees, directly affecting Capital One's profitability. The acquisition of Discover in 2023 was a strategic move to mitigate this dependence.
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive landscape of the credit card and financial services industry, specifically examining the five forces impacting Capital One's profitability and strategic positioning.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive model that pinpoints key areas of strategic vulnerability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the financial services sector, particularly for credit cards and everyday banking, face a landscape brimming with choices from a multitude of institutions. This abundance of options means consumers can readily compare offerings and switch providers if they find more attractive rates or superior service.
The perceived cost and effort involved in switching financial providers for many standard products remain low. For instance, in 2023, the average credit card APR hovered around 20.7%, a figure that can significantly influence a customer's decision to switch if a competitor offers a lower rate. This ease of transition empowers customers, directly impacting Capital One's need to maintain highly competitive pricing and service standards.
The internet and readily available financial comparison tools have significantly boosted information transparency for customers. They can effortlessly compare interest rates, fees, rewards, and loan terms across numerous financial institutions. This empowers consumers to make smarter choices and seek better deals, thereby amplifying their bargaining power.
While switching costs for credit card customers can be relatively low, Capital One actively combats this by implementing robust loyalty programs and tailored retention strategies. These initiatives, like their rewards points systems and personalized offers, aim to increase customer stickiness and reduce the incentive to switch to a competitor. For instance, in 2024, Capital One continued to emphasize its digital platform, which many users find a key differentiator.
Impact of Large Commercial Clients
Capital One's commercial banking segment faces significant bargaining power from large clients. These businesses, often with substantial financial needs and complex requirements, can leverage the volume of their transactions to negotiate better pricing, interest rates, and bespoke service packages.
For instance, in 2024, large corporate clients typically represent a disproportionately large share of a bank's revenue, giving them considerable leverage. This necessitates a highly personalized approach to relationship management, where tailored solutions are paramount to client retention and satisfaction.
- High Transaction Volume: Large commercial clients can dictate terms due to the sheer volume of deposits and loans they bring to Capital One.
- Negotiating Power: Their size allows them to demand lower fees and more competitive interest rates than smaller businesses.
- Customized Services: Sophisticated clients expect and often receive specialized banking solutions, increasing the cost of service but also the potential for deeper relationships.
- Switching Costs: While large clients can switch banks, the complexity of moving significant financial operations can also be a factor in negotiations.
Consumer Demand for Digital-First Experiences
Modern consumers, especially younger generations, are increasingly prioritizing digital-first financial experiences. This includes expecting intuitive mobile apps, effortless online account management, and immediate customer support. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 75% of Gen Z and Millennial consumers prefer to interact with their bank digitally rather than in person.
Capital One's strategic focus on technology and data analytics is designed to cater to these evolving demands. However, if their digital platforms do not consistently meet or exceed these high expectations, customers possess significant leverage. They can readily switch to fintech companies or other financial institutions offering more advanced or user-friendly digital solutions.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by the availability of numerous alternatives in the digital banking space. This competitive landscape means that customer satisfaction with digital offerings is a critical factor in retention and market share. For example, in 2023, digital-only banks saw a 15% increase in customer acquisition, largely driven by superior mobile user experiences.
- Digital Preference: A significant majority of younger consumers favor digital banking channels for their primary interactions.
- Fintech Competition: Agile fintech companies often set the benchmark for digital user experience, pressuring traditional banks.
- Switching Costs: While historically high, digital platforms have lowered switching costs for consumers seeking better digital services.
- Data-Driven Expectations: Customers expect personalized and seamless experiences, informed by data analytics, which Capital One aims to provide.
Customers in the financial services sector, particularly for credit cards and everyday banking, face a landscape brimming with choices from a multitude of institutions. This abundance of options means consumers can readily compare offerings and switch providers if they find more attractive rates or superior service. In 2023, the average credit card APR hovered around 20.7%, a figure that can significantly influence a customer's decision to switch if a competitor offers a lower rate.
The internet and readily available financial comparison tools have significantly boosted information transparency for customers. They can effortlessly compare interest rates, fees, rewards, and loan terms across numerous financial institutions. This empowers consumers to make smarter choices and seek better deals, thereby amplifying their bargaining power.
Modern consumers, especially younger generations, are increasingly prioritizing digital-first financial experiences. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 75% of Gen Z and Millennial consumers prefer to interact with their bank digitally rather than in person. Capital One's strategic focus on technology and data analytics is designed to cater to these evolving demands.
Capital One's commercial banking segment faces significant bargaining power from large clients. These businesses, often with substantial financial needs and complex requirements, can leverage the volume of their transactions to negotiate better pricing, interest rates, and bespoke service packages. For instance, in 2024, large corporate clients typically represent a disproportionately large share of a bank's revenue, giving them considerable leverage.
| Customer Segment | Key Bargaining Factors | Impact on Capital One |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Credit Card Holders | Lower APRs, better rewards, ease of switching | Pressure on pricing and loyalty programs |
| Large Commercial Clients | High transaction volume, negotiating power, customized services | Need for tailored relationship management and competitive pricing |
| Digital-First Consumers | Superior digital experience, fintech competition | Requirement for advanced, user-friendly digital platforms |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Capital One Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Capital One Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the financial services industry. You're looking at the actual document, providing insights into the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Capital One faces formidable competition from massive, diversified financial giants like JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, and Wells Fargo. These established players boast extensive product portfolios, widespread physical presences, and deeply ingrained brand loyalty, intensifying rivalry across all segments.
The competitive intensity is particularly acute in areas like credit cards, where market share battles are constant, and in consumer and commercial banking services, where scale and customer relationships are paramount. For instance, as of Q1 2024, JPMorgan Chase reported total assets of $3.9 trillion, highlighting the sheer scale of these competitors.
The credit card and banking industries are fiercely competitive, driven by aggressive marketing and a constant stream of new product offerings. Companies like Capital One are continuously innovating, rolling out enhanced rewards programs, novel credit card features, and cutting-edge digital banking solutions to capture and hold onto customers.
In 2024, Capital One's commitment to marketing and product development remains a cornerstone of its strategy. For instance, the company reported significant investments in technology and marketing to enhance its digital platforms and customer experience, aiming to stay ahead in this dynamic market.
Intense competition within the financial services sector frequently translates into significant pricing pressure. For Capital One, this is particularly evident in the interest rates offered on its credit card products and loans, as well as the fees associated with its banking services. Competitors constantly vie for market share, which often forces a reduction in margins to attract and retain customers.
The prevailing interest rate environment presents a dynamic challenge for banks like Capital One. As interest rates fluctuate, maintaining a healthy net interest margin becomes more complex. For instance, if the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, Capital One's cost of funding may increase, but it might not be able to immediately pass on those higher costs to borrowers, squeezing profitability.
In the first quarter of 2024, Capital One reported a net interest margin of 7.05%, a slight decrease from 7.16% in the fourth quarter of 2023, highlighting the sensitivity of this key profitability metric to market conditions and competitive pressures.
Digital Transformation and Fintech Competition
Major banks are pouring billions into digital transformation, aiming to improve customer service and streamline operations. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. banking sector saw significant IT spending, with projections indicating continued growth in digital investments through 2024 and beyond as institutions strive to modernize legacy systems and enhance digital offerings.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by nimble fintech firms that provide specialized, digital-first financial services. These companies often excel in user experience and niche market penetration, challenging traditional banks. For example, the global fintech market size was valued at over $110 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow substantially, demonstrating the increasing influence of these agile players.
- Digital Investment: Major banks are allocating substantial capital to technology upgrades in 2024, focusing on AI, cloud computing, and data analytics to gain a competitive edge.
- Fintech Disruption: Agile fintech companies are capturing market share by offering innovative, user-friendly digital solutions, particularly in payments, lending, and wealth management.
- Capital One's Strategy: Capital One's ongoing commitment to technology, including its acquisition of Discover, aims to bolster its digital capabilities and compete effectively against both traditional banks and fintech challengers.
Mergers and Acquisitions Reshaping the Landscape
The financial services industry is dynamic, with mergers and acquisitions frequently altering the competitive environment. A notable recent event is Capital One's agreement to acquire Discover Financial Services, a move expected to significantly boost Capital One's scale and market influence, especially within the credit card and payments network segments.
This consolidation is poised to change the competitive dynamics for all participants in the sector. For instance, the combined entity will possess a larger customer base and a more extensive payment network, potentially intensifying rivalry for other major credit card issuers and payment processors.
The deal, valued at approximately $35 billion as of early 2024, highlights a trend of larger institutions seeking to gain a competitive edge through strategic combinations. Such M&A activity can lead to:
- Increased market concentration: Fewer, larger players can emerge, altering pricing power and service offerings.
- Enhanced competitive capabilities: Acquirers often aim to leverage target companies' technologies, customer bases, or network effects.
- Shifting industry structure: The competitive landscape for rivals like Visa, Mastercard, and other large banks will undoubtedly be impacted.
Capital One operates in a highly competitive arena dominated by large, established financial institutions. These rivals, including giants like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America, possess vast resources, extensive product lines, and strong brand recognition, creating significant pressure on Capital One to innovate and differentiate.
The intense rivalry is evident in aggressive marketing campaigns and continuous product development, particularly in credit cards and banking services. For instance, in Q1 2024, Capital One reported a net interest margin of 7.05%, reflecting the constant need to manage pricing and fees amidst competitive pressures.
Furthermore, the rise of agile fintech companies offering specialized digital solutions adds another layer of competition, forcing traditional players like Capital One to invest heavily in technology. The company's strategic acquisition of Discover, valued around $35 billion in early 2024, underscores the drive to enhance digital capabilities and scale in this dynamic market.
| Competitor | Total Assets (Q1 2024) | Key Competitive Area |
|---|---|---|
| JPMorgan Chase | $3.9 trillion | Broad financial services, credit cards |
| Bank of America | $3.2 trillion | Consumer banking, wealth management |
| Wells Fargo | $1.9 trillion | Commercial banking, mortgages |
| Fintech Sector (General) | N/A (Market size > $110 billion in 2023) | Digital payments, lending, user experience |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The burgeoning landscape of alternative lending platforms, including peer-to-peer (P2P) lenders and a multitude of fintech innovators, presents a substantial threat of substitution for Capital One's traditional banking and lending services. These platforms frequently provide more efficient application processes, reduced overhead costs translating to lower fees, and highly specialized loan products that sidestep the established infrastructure of conventional banks. For instance, the P2P lending market, which saw significant growth leading up to 2024, offers direct connections between borrowers and investors, often at competitive rates.
Fintech companies are increasingly leveraging data analytics and AI to offer personalized financial solutions, from small business loans to consumer credit, directly challenging Capital One's market share. This competitive pressure is a primary driver behind Capital One's strategic investments in technology and digital transformation, aiming to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency to better compete with these agile disruptors. The ability of these substitutes to innovate rapidly and cater to niche markets with tailored offerings underscores the ongoing need for Capital One to adapt its product suite and service delivery models.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services are increasingly becoming a significant substitute for traditional credit cards, especially in the retail sector. These services offer consumers the ability to spread out payments, often interest-free, which directly challenges Capital One's core credit card offerings by providing an alternative for financing purchases.
For instance, the BNPL market saw substantial growth, with global transaction values projected to reach over $3.6 trillion by 2030, up from an estimated $1.5 trillion in 2023. This trend indicates a clear shift in consumer preference towards flexible, installment-based payment solutions, directly impacting Capital One's market share and revenue from credit card interest and fees.
The growing popularity of digital wallets and mobile payment systems presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional credit and debit card services. These solutions, often built into popular retail apps or smartphone operating systems, allow consumers to bypass the need for physical cards, potentially weakening the direct link between cardholders and issuers like Capital One.
While Capital One cards can be integrated into these digital wallets, the user experience and primary payment interface shift towards the wallet provider. This could diminish the brand visibility and direct customer relationship Capital One currently enjoys, impacting loyalty and future product adoption as consumers become accustomed to a single payment hub.
For instance, by mid-2024, global mobile payment transaction volume was projected to exceed $14 trillion, underscoring the rapid shift in consumer behavior. This trend highlights how easily consumers can substitute a digital wallet for direct card usage, thereby increasing the threat of substitutes for traditional card issuers.
Direct-to-Consumer Financial Products
The rise of direct-to-consumer (DTC) financial products presents a significant threat of substitutes for Capital One. These platforms, like investment apps Robinhood and betterment, and neo-banks such as Chime, offer specialized, often lower-cost, alternatives for specific financial needs. For instance, a customer might use a budgeting app and a separate investment platform instead of a full-service bank for all their financial management. This fragmentation of services allows consumers to pick and choose best-in-class solutions for individual needs, bypassing traditional, more comprehensive offerings.
These DTC players often excel in user experience and cater to specific customer segments, drawing away potential business from established institutions like Capital One. For example, Chime reported over 15 million customers as of late 2023, demonstrating the significant adoption of these alternative financial service providers. Similarly, platforms like Robinhood have democratized investing, attracting millions of users who might have previously relied on traditional brokerage services.
- Specialized Offerings: DTC platforms focus on specific financial needs, like investing or budgeting, offering tailored solutions.
- User Experience: Many DTC services prioritize intuitive design and ease of use, appealing to a broad customer base.
- Cost Competitiveness: Often, these alternatives provide services at a lower cost than traditional banks, attracting price-sensitive consumers.
- Market Penetration: Companies like Chime, with over 15 million customers, show the substantial market share these substitutes can capture.
Cryptocurrencies and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) are emerging as potential substitutes for traditional financial services, though mainstream adoption is still developing. These technologies offer alternative avenues for lending, borrowing, investing, and transacting, which could bypass established institutions like Capital One.
As of mid-2024, the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies hovered around $2.5 trillion, indicating significant, albeit volatile, growth. DeFi protocols collectively manage billions in assets, showcasing a tangible shift in financial activity away from traditional intermediaries.
- Nascent Technology: While still in early stages for broad consumer use, cryptocurrencies and DeFi offer a glimpse into future financial ecosystems.
- Disintermediation Potential: DeFi platforms aim to remove the need for traditional banks in many financial transactions, potentially impacting revenue streams for companies like Capital One.
- Growing Asset Management: The total value locked in DeFi protocols reached over $100 billion in early 2024, demonstrating increasing investor confidence and activity in these alternative systems.
Alternative lending platforms, including P2P lenders and fintech innovators, offer more streamlined processes and specialized loan products, directly competing with Capital One's traditional offerings. These substitutes often leverage advanced data analytics and AI to provide personalized financial solutions, challenging Capital One's market share and driving its investment in digital transformation.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services are increasingly replacing traditional credit cards for consumer financing, especially in retail. With global BNPL transaction values projected to exceed $3.6 trillion by 2030, this trend directly impacts Capital One's revenue from credit card interest and fees.
Digital wallets and mobile payment systems are becoming substitutes for physical cards, shifting the primary payment interface away from issuers like Capital One. By mid-2024, global mobile payment transaction volume was projected to surpass $14 trillion, indicating a significant consumer shift that could diminish brand visibility and customer relationships.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) financial products, such as neo-banks and investment apps, offer specialized, lower-cost alternatives that fragment financial management. Companies like Chime, with over 15 million customers by late 2023, demonstrate the substantial market capture by these agile disruptors.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristic | Impact on Capital One | Supporting Data (as of mid-2024 or latest available) |
| Fintech/P2P Lenders | Streamlined processes, specialized products | Direct competition for loans and credit | Market growth indicates increasing consumer adoption |
| BNPL Services | Interest-free installment payments | Threat to credit card revenue | Global transaction value projected to reach $3.6T by 2030 |
| Digital Wallets | Bypass physical cards, integrated experience | Reduced brand visibility, customer relationship shift | Global mobile payment volume projected over $14T |
| DTC Platforms (Neo-banks, Apps) | Specialized, lower-cost, user-friendly | Customer acquisition and service fragmentation | Chime: 15M+ customers (late 2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including institutions like Capital One, faces formidable regulatory hurdles. For instance, in 2024, the Dodd-Frank Act and subsequent regulations continue to mandate substantial capital reserves and stringent compliance protocols. These requirements, often running into billions of dollars, alongside the need for specialized licenses and robust anti-money laundering systems, create a significant barrier to entry for potential new competitors.
Established financial institutions like Capital One have cultivated significant brand recognition over many years, fostering deep customer trust. This is a formidable barrier for newcomers attempting to enter the market.
New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and transparent operations to build a reputable brand and earn consumer confidence, especially in the critical financial services sector where security and reliability are paramount.
Capital One's brand strength, built on consistent service and perceived trustworthiness, acts as a substantial competitive advantage, making it difficult for new players to attract and retain customers.
Economies of scale are a major hurdle for new entrants in the banking sector. Established players like Capital One leverage their vast customer base to spread fixed costs over a larger volume of transactions, leading to lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to invest billions in technology infrastructure and marketing campaigns, costs that are prohibitive for startups.
This cost advantage makes it difficult for new entrants to compete on price. They cannot match the operational efficiencies or the marketing reach of incumbents, forcing them to operate at a higher cost base. This inherent disadvantage in cost structure significantly dampens the threat of new entrants.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Data
Capital One's established distribution network, encompassing digital interfaces, physical branches, and strategic alliances, presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. This network facilitates customer acquisition and service delivery, a capability that newcomers must painstakingly replicate.
The sheer volume of customer data Capital One holds is another formidable barrier. This data is instrumental in refining product offerings and assessing credit risk, giving the company a competitive edge in understanding and serving its market. Newcomers would need considerable time and resources to amass comparable data sets.
For instance, in 2024, Capital One reported a significant digital engagement rate, with a substantial portion of customer interactions occurring through its mobile app and online platforms. This digital-first approach, built on years of data accumulation and analysis, makes it challenging for new players to gain traction without similar technological infrastructure and data insights.
- Established Distribution: Capital One leverages its digital platforms, branches, and partnerships, which are difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate.
- Customer Data Advantage: Access to extensive customer data allows Capital One to refine products and manage risk more effectively than new competitors.
- Digital Engagement: In 2024, Capital One's high digital engagement rates highlight the importance of a robust online presence, a key barrier for new entrants.
- Resource Intensive Entry: Building a comparable customer base and data infrastructure requires substantial investment and time, deterring potential new competitors.
Technological Innovation and Digital Disruption
Technological innovation, especially from nimble fintech startups, poses a significant threat to established players like Capital One. These new entrants are adept at utilizing cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and sophisticated data analytics. This allows them to carve out specific market niches or deliver exceptionally smooth digital customer experiences, potentially disrupting established banking segments.
For instance, in 2023, venture capital funding for fintech companies globally reached over $150 billion, with a substantial portion directed towards companies focused on AI-driven lending and personalized financial management. This influx of capital empowers these startups to challenge traditional banking models with innovative solutions.
- Fintech Funding Surge: Venture capital investment in fintech exceeded $150 billion globally in 2023, fueling innovation.
- AI and Data Analytics: Startups leverage AI and advanced data analytics to offer personalized financial products and services.
- Digital Experience Focus: New entrants prioritize seamless digital interfaces, attracting customers seeking convenience.
- Niche Market Disruption: Agile startups can target specific customer segments with tailored offerings, bypassing broader market challenges.
The threat of new entrants for Capital One is generally considered moderate, primarily due to high barriers to entry in the banking sector. Significant capital requirements, stringent regulatory compliance, and the need for extensive technological infrastructure are substantial deterrents. For example, in 2024, the cost of meeting evolving cybersecurity standards alone represents a considerable investment for any new player.
Established brands and customer loyalty, cultivated over years, also present a formidable challenge. Newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and building trust, a process that can take considerable time and resources. Capital One's strong digital presence and data analytics capabilities, honed over years, further solidify its competitive position against potential disruptors.
While fintech innovation offers avenues for new entrants to challenge incumbents with specialized services, the overall landscape remains challenging. The scale of operations required to compete broadly in retail banking, coupled with the need for a robust distribution network, means that truly disruptive new entrants capable of challenging a player like Capital One are relatively few.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Capital One Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and expert commentary from financial analysts to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
