Bourbon Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bourbon Bundle
Bourbon's competitive landscape is shaped by moderate buyer power and the ever-present threat of substitutes, particularly other premium spirits. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bourbon’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of highly specialized offshore equipment, like dynamic positioning systems and advanced subsea technology, wield considerable influence. Bourbon's reliance on a limited pool of manufacturers for these vital components can result in escalated costs and diminished bargaining power.
Bourbon's strategic investments in fleet modernization and the adoption of fuel-efficient vessels underscore this dependency on cutting-edge technology providers. For instance, the global market for advanced offshore drilling equipment, a segment Bourbon utilizes, saw significant growth leading up to 2024, with demand driven by exploration in deeper waters and a focus on efficiency.
The offshore energy sector, including companies like Bourbon, relies heavily on a specialized and certified workforce. This includes experienced marine crew, subsea engineers, and various technical specialists who possess unique skills crucial for operations. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) reports ongoing efforts to address maritime labor shortages, a trend impacting the availability of qualified personnel globally.
A global scarcity of skilled maritime labor or specific niche expertise significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these suppliers. This can directly translate into increased labor costs for Bourbon, thereby diminishing the company's own leverage in negotiations. Reports from industry bodies like the International Chamber of Shipping in 2024 highlighted persistent challenges in recruiting and retaining qualified seafarers across various segments of the maritime industry.
Bourbon's commitment to safety and operational excellence mandates continuous investment in training and development for its valuable human capital. This focus on maintaining a highly competent workforce is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring efficient project execution in the demanding offshore environment.
The global market for constructing new offshore support vessels (OSVs) and undertaking significant retrofits is dominated by a select group of shipyards. This concentration means these shipyards hold considerable sway over pricing and delivery schedules.
With an aging OSV fleet and a lean orderbook for new vessels, shipyards find their bargaining power amplified. This situation can translate into escalating costs for both new builds and essential repairs for companies like Bourbon.
Bourbon's strategic decision to refresh its passenger transport fleet with modern, adaptable vessels directly involves engaging with these powerful shipyard suppliers. This move highlights the company's need to navigate the current supply landscape.
Fuel and Energy Providers
Fuel and energy providers hold significant bargaining power over Bourbon. Since marine fuel is a substantial operational expense, typically representing 30-50% of a vessel's operating costs, fluctuations in global energy prices directly impact Bourbon's profitability. For instance, the average price of Very Low Sulphur Fuel Oil (VLSFO), a common marine fuel, saw significant volatility in 2023 and early 2024, with prices ranging from approximately $600 to over $900 per metric ton depending on market conditions and location.
The growing emphasis on decarbonization and the push for lower-emission fuels are further amplifying the influence of these suppliers. As Bourbon, like other maritime operators, invests in or transitions to alternative fuels such as LNG, methanol, or biofuels, the suppliers of these specialized energy sources gain leverage. The availability and pricing of these newer fuels are still developing, creating potential dependencies for companies like Bourbon.
- Significant Cost Component: Marine fuel costs can constitute a substantial portion of a company's operating budget, giving fuel suppliers considerable sway.
- Price Volatility Impact: Global energy price swings directly translate to unpredictable operating expenses for Bourbon.
- Emerging Fuel Markets: The rise of alternative fuels empowers new suppliers, potentially shifting the balance of power as demand for cleaner options grows.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification Bodies
Suppliers of regulatory compliance services, such as classification societies and certification bodies, wield significant bargaining power. Their essential role in ensuring safety and environmental adherence makes their services indispensable for companies like Bourbon.
Bourbon must navigate a complex web of international and regional regulations. For instance, adherence to the EU Emissions Trading System and FuelEU Maritime are critical, non-negotiable requirements that directly impact operational costs and necessitate specialized services from these suppliers.
These stringent compliance mandates fuel demand for specialized services and technologies from approved suppliers. Failure to meet these standards can result in severe penalties, including operational shutdowns, underscoring the suppliers' leverage in pricing and contract terms.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: The maritime industry's increasing focus on environmental regulations, like those from the International Maritime Organization (IMO), drives up the cost of compliance. For example, the IMO's 2023 greenhouse gas strategy aims for net-zero emissions by or around 2050, requiring significant investment in new technologies and retrofits.
- Certification Dependency: Classification societies, such as DNV, Lloyd's Register, and ABS, are crucial for vessel certification, which is a prerequisite for insurance and chartering. Their approval processes and standards dictate the technical specifications and operational capabilities of vessels.
- Market Concentration: The market for specialized maritime compliance services is relatively concentrated, with a few dominant players. This limited competition enhances the bargaining power of these established certification bodies and compliance solution providers.
Suppliers of specialized offshore equipment and skilled maritime labor hold considerable power over Bourbon due to limited alternatives and high demand. For instance, the global shortage of qualified seafarers, highlighted by the International Chamber of Shipping in 2024, directly increases labor costs. Similarly, the concentration of shipyards capable of building or retrofitting vessels amplifies their pricing leverage.
Fuel providers also exert significant influence, as marine fuel can represent 30-50% of operating costs. The volatility of fuels like VLSFO, which ranged from $600 to over $900 per metric ton in early 2024, directly impacts Bourbon's expenses. Furthermore, the growing demand for alternative fuels empowers their suppliers, creating new dependencies.
Regulatory compliance service providers, such as classification societies, are indispensable. Mandatory adherence to regulations like the IMO's 2050 net-zero emissions target necessitates their specialized services. The concentration of these certification bodies, like DNV and Lloyd's Register, further strengthens their bargaining power.
What is included in the product
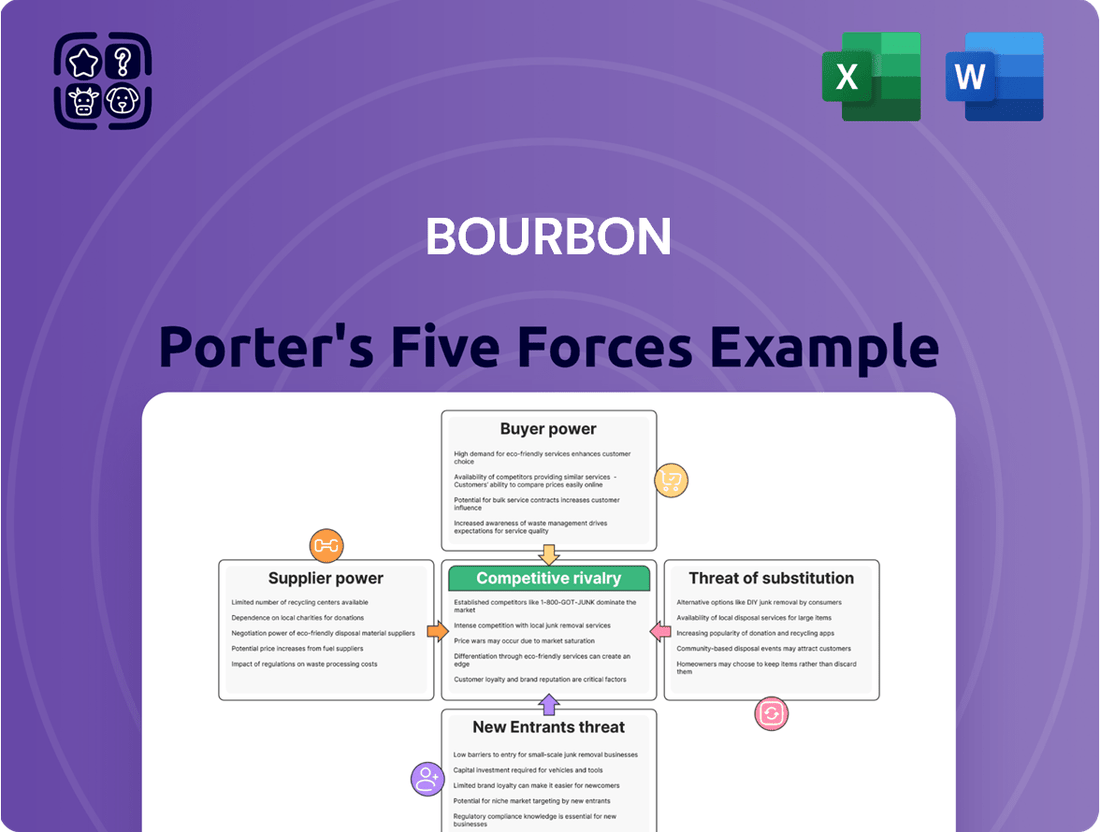
Analyzes the competitive intensity, buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, and substitutes affecting Bourbon's market position.
Gain clarity on competitive pressures with a visual, easy-to-understand breakdown of each Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Bourbon's primary customers are the major offshore oil and gas companies. These giants possess significant bargaining power due to their immense scale and concentrated demand for offshore support vessels (OSVs). Their ability to negotiate favorable terms, especially on pricing and service conditions, is a key factor in this force.
While Bourbon often secures long-term contracts, these large clients can still exert considerable pressure, particularly when oil and gas prices are volatile. This dynamic means Bourbon must remain agile in its pricing and service offerings to retain these crucial relationships.
However, the global landscape offers some counter-balance. Increased exploration and production activities, especially in burgeoning markets like South America and Africa, are driving higher demand for OSV services. For instance, in 2024, offshore oil and gas investments were projected to rise, potentially creating a more balanced market for service providers like Bourbon.
Offshore wind farm developers represent a significant and growing customer base for companies like Bourbon. The sheer scale of these projects, often involving billions of dollars in investment, means developers can exert considerable influence. For instance, a single offshore wind farm project can require dozens of specialized vessels for installation, operation, and maintenance over its lifespan, giving developers leverage in contract negotiations.
These developers are also increasingly focused on cost efficiency and environmental performance. They seek integrated service solutions rather than just vessel charters, pushing service providers to offer more comprehensive packages. This demand for value-added services and a commitment to sustainability can shift bargaining power towards the customer, particularly for larger, more established developers who can bundle their requirements.
In 2023, global investment in offshore wind reached approximately $77 billion, highlighting the substantial market these developers command. This growth underscores their importance as customers and their capacity to influence pricing and service standards within the offshore support vessel sector.
Bourbon's strategy of forging long-term contracts with its global customer base, like the recent five-year deal with Eni Congo for crewboats, offers significant revenue predictability. However, these extended agreements can constrain Bourbon's ability to pass on increased operational expenses, such as rising fuel prices, directly to clients.
The successful renewal of such substantial contracts underscores the critical importance of sustained high service quality and unwavering operational reliability in retaining major clients. These relationships are the bedrock of Bourbon's stable revenue streams, but they also necessitate a proactive approach to cost management and service excellence to maintain profitability.
Demand for Integrated Services
Customers are increasingly looking for one-stop shops for marine services, wanting everything from subsea work to logistics and vessel support bundled together. This shift towards integrated solutions means companies that can offer this complete package might have an edge. However, it also empowers customers, as their strong preference for these consolidated offerings allows them to negotiate better prices and terms with providers.
This demand for integrated services is pushing marine service providers to innovate and streamline their operations. For instance, in 2024, many offshore service companies were investing in digital platforms to manage and deliver these bundled services more efficiently. The ability to provide a seamless, end-to-end experience is becoming a key differentiator.
- Consolidation of Needs: Clients prefer single vendors for subsea, logistics, and vessel support, simplifying procurement and project management.
- Negotiating Leverage: This consolidated demand gives customers greater power to secure competitive pricing and favorable contract conditions.
- Industry Adaptation: Service providers are compelled to expand their capabilities and improve operational synergy to meet this integrated service requirement.
Cost Sensitivity and Project Delays
Customers in the offshore energy sector exhibit significant cost sensitivity, a factor amplified by the massive capital outlays typical of offshore projects. This sensitivity directly impacts their bargaining power, as they actively seek the most economical solutions. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of developing an offshore oil field continued to be a critical consideration for operators, with fluctuations in breakeven prices directly influencing their willingness to commit to new projects or renegotiate existing contracts.
The inherent volatility of global energy prices, coupled with broader economic uncertainties, can trigger project delays or even outright cancellations. This unpredictability grants customers greater leverage, as they can postpone or reduce demand, forcing service providers like Bourbon to offer more favorable terms to secure business. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in early 2024 that ongoing geopolitical tensions and shifting energy transition policies were contributing to increased project planning uncertainty within the sector.
- Cost Sensitivity: Offshore energy clients prioritize cost-effectiveness due to substantial capital expenditures.
- Project Delays: Volatile energy prices and economic uncertainty lead to project delays, increasing customer negotiation power.
- Mitigation Strategy: Bourbon must emphasize cost-efficiency and operational reliability to counter customer leverage.
Major offshore oil and gas companies, Bourbon's primary clients, wield substantial bargaining power due to their concentrated demand and immense scale. This allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and service terms, particularly during periods of oil price volatility. While long-term contracts offer some stability, Bourbon must remain adaptable to retain these key relationships.
The growing offshore wind sector also presents powerful customers. The sheer size of wind farm projects, often requiring numerous specialized vessels, grants developers significant leverage. Their focus on cost efficiency and integrated, sustainable solutions further empowers them to dictate terms, especially for established developers who can bundle their extensive needs.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Bourbon |
|---|---|---|
| Major Oil & Gas Companies | Scale, Concentrated Demand, Price Volatility Sensitivity | Pressure on pricing, need for flexible service offerings |
| Offshore Wind Developers | Project Scale, Demand for Integrated Solutions, Cost Efficiency Focus | Leverage in negotiations for comprehensive service packages |
Full Version Awaits
Bourbon Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Bourbon Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the market. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights without any alterations or missing sections. You can be confident that the preview accurately represents the complete, ready-to-use report that will be instantly available to you, enabling you to leverage its strategic information without delay.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global offshore support vessel (OSV) market, despite its growth, is characterized by intense competition. Numerous regional and international companies actively compete for contracts, creating a dynamic and often challenging environment. This fragmentation means that even as the market expands, the sheer number of participants can put pressure on pricing and profit margins.
Major global players such as Tidewater, Siem Offshore, and Maersk are prominent, but they operate alongside a vast array of smaller, specialized providers. This diverse competitive landscape means that contracts are not solely determined by scale but also by niche capabilities and regional presence. For instance, in 2024, the OSV market continued to see a broad range of companies bidding for projects, from large-scale construction support to smaller, specialized survey vessels.
This high degree of fragmentation often translates into aggressive price competition, especially when the supply of vessels outstrips demand. Periods of reduced offshore activity or an overabundance of available tonnage can force operators to lower rates to secure work. This dynamic directly impacts the profitability of companies operating in this sector, making strategic fleet management and contract negotiation crucial for success.
Bourbon's competitive landscape is heavily influenced by technological advancements, with a significant push towards smart shipping, automation, and environmentally conscious vessel designs. Companies are investing in these areas to secure a market advantage.
Bourbon's strategic focus on fleet modernization, exemplified by their investment in new fuel-efficient crewboats and collaborations for data-driven emission reductions, is vital for staying competitive. For instance, in 2024, Bourbon continued to integrate advanced navigation and operational monitoring systems across its fleet to enhance efficiency.
The ability for operators to provide more efficient, safer, and sustainable maritime solutions is a key differentiator. This technological edge directly impacts their appeal to clients seeking to minimize operational costs and environmental impact, a trend that intensified throughout 2024.
Historically, periods of overcapacity in the offshore vessel market have led to significant price erosion, underscoring the critical role of fleet utilization in maintaining profitability. Companies with higher utilization rates are better positioned to absorb fixed costs and achieve better margins.
While the demand for offshore support vessels (OSVs) is showing a positive trend, the global OSV fleet is aging, with new vessel orders remaining relatively subdued. For instance, as of early 2024, the average age of the OSV fleet continues to climb, with limited newbuilds entering the market compared to previous decades.
This aging fleet and low newbuild activity create a competitive advantage for companies possessing modern, efficient vessels. Their ability to command higher day rates and secure long-term contracts is enhanced, directly impacting their pricing power and overall competitive standing.
Geographical Market Focus
Competitive rivalry within Bourbon's operational sectors, particularly offshore exploration & production (E&P) and wind development, can intensify in specific geographical markets. Regions like South America, Africa, and Europe often become hotspots for this activity, drawing in numerous players. This localized competition means that while Bourbon operates globally, its intensity of rivalry can vary significantly depending on the specific region it's active in.
Companies often develop specialized expertise or concentrate their efforts in particular geographic areas. This regional specialization can lead to concentrated competition, where a few key players vie for contracts and market share. For instance, in the offshore E&P sector, companies might focus on the deepwater opportunities in West Africa or the mature fields in the North Sea.
Bourbon's global operational footprint allows it to mitigate risks by diversifying its exposure across different markets. However, this global presence also means it must navigate a spectrum of competitive intensities. In 2024, the offshore support vessel (OSV) market, a key area for Bourbon, saw fluctuating demand influenced by oil prices and new project sanctions, especially in regions with significant offshore activity.
- South America: Increased offshore E&P activity in Brazil and Guyana in 2024 has heightened competition among OSV providers.
- Africa: West Africa remains a crucial market for offshore services, with ongoing projects driving rivalry, particularly for specialized vessels.
- Europe: The North Sea continues to be a competitive arena, with established players and new entrants vying for contracts in both oil and gas and offshore wind projects.
- Bourbon's Global Reach: Operating in over 30 countries, Bourbon encounters diverse competitive landscapes, from highly concentrated regional markets to more fragmented global ones.
Consolidation and Strategic Alliances
The offshore vessel industry is experiencing significant consolidation. For instance, in 2023, Bourbon Offshore, a major player, continued its fleet optimization, a trend seen across the sector. Larger companies are acquiring smaller ones to gain market share and operational efficiencies. This consolidation intensifies competition, particularly for mid-sized operators who may struggle to compete with the expanded resources of larger entities.
Strategic alliances and joint ventures are also becoming more prevalent as a competitive tactic. Bourbon's partnership with Tethys Marine & Logistics in Guyana exemplifies this. These collaborations allow companies to expand their geographical reach and service capabilities, thereby strengthening their competitive position in key markets.
- Fleet Optimization: Bourbon Offshore has actively managed its fleet, a common strategy for enhancing competitiveness and efficiency.
- Market Share Growth: Acquisitions by larger players aim to consolidate market share, increasing pressure on smaller competitors.
- Strategic Partnerships: Alliances, like Bourbon's venture in Guyana, are crucial for expanding service offerings and market presence.
- Economies of Scale: Consolidation drives economies of scale, allowing larger firms to operate more cost-effectively.
Competitive rivalry in the offshore support vessel (OSV) market, a key sector for Bourbon, is intense due to a fragmented industry with numerous global and regional players. Companies like Tidewater and Siem Offshore compete fiercely, alongside many smaller, specialized providers. This dynamic means that pricing is often under pressure, especially when vessel supply exceeds demand, as was evident in various regions throughout 2024.
Technological advancements, such as smart shipping and greener vessel designs, are becoming critical differentiators. Bourbon's own investments in fleet modernization and efficiency, including advanced monitoring systems implemented in 2024, highlight the importance of staying ahead technologically. Companies with modern fleets are better positioned to secure contracts and command higher rates, especially given the aging global OSV fleet and limited newbuild orders seen in early 2024.
Consolidation is a growing trend, with larger companies acquiring smaller ones to gain market share and achieve economies of scale. This increases pressure on mid-sized operators. Strategic alliances and joint ventures are also common, as exemplified by Bourbon's partnerships, which help expand service capabilities and market reach in competitive regions like South America and Africa.
| Key Competitor | 2024 Market Focus Areas | Competitive Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Tidewater | Global OSV Operations, Deepwater Support | Largest fleet size, extensive operational experience |
| Siem Offshore | North Sea, Subsea Construction Support | Specialized vessels, strong European presence |
| Maersk Supply Service | Global, Wind Farm Installation Support | Innovative vessel designs, focus on renewables |
| Bourbon Offshore | Global, Oil & Gas and Wind Support | Diversified fleet, strategic partnerships, fleet modernization |
SSubstitutes Threaten
A key substitute for offshore oil and gas production, where Bourbon operates, is onshore extraction. While not a direct replacement for all offshore projects, significant onshore reserves or improved drilling techniques can divert investment and reduce the need for new offshore ventures. For instance, the Permian Basin in the United States has seen substantial growth in oil production from unconventional methods, impacting global supply dynamics.
Despite this, the global energy demand continues to rise, and many established onshore fields are experiencing depletion. This ongoing need for energy, coupled with the limitations of some onshore reserves, still fuels the drive for offshore exploration and development, which offers access to vast, untapped resources. Global oil demand is projected to reach 104.5 million barrels per day in 2024, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
The global energy landscape is rapidly evolving, with a significant push towards alternative energy sources. In 2024, renewable energy, particularly solar and terrestrial wind, continued to gain momentum, representing a growing portion of the global energy mix. This shift away from fossil fuels, including offshore oil and gas, presents an indirect threat of substitution for companies operating in traditional energy sectors.
While the broader trend towards renewables poses a challenge, Bourbon's strategic involvement in the offshore wind sector actually mitigates some of this substitution threat. The offshore wind industry requires specialized marine services, creating a direct demand for Bourbon's expertise and services. This dual role positions Bourbon to benefit from the energy transition rather than being solely threatened by it.
Furthermore, the marine energy market, encompassing wave and tidal power, is also experiencing growth. While these emerging technologies represent potential future competitors or alternative energy focuses, they also present new opportunities for innovation and market expansion for companies like Bourbon that possess marine capabilities.
Innovations in subsea technology, like advanced AUVs and ROVs, are a significant threat to traditional offshore support vessels. These autonomous systems can perform tasks previously requiring human crews and surface support, potentially lowering operational costs for clients. For instance, the global market for underwater robotics, encompassing AUVs and ROVs, was projected to reach $7.5 billion in 2024, indicating substantial investment and development in this area.
Efficiency Improvements and Remote Operations
Advances in digitalization and automation are significantly impacting the marine industry. For instance, remote monitoring and control systems allow for more efficient vessel operations, potentially reducing the need for a large number of vessels or extensive crew deployment. This shift towards smarter shipping, which Bourbon is actively pursuing, aims to streamline operations and cut costs.
The ability to manage marine operations more effectively from onshore can directly influence the demand for certain vessel types or their operational intensity. This technological evolution represents a significant substitute for traditional operational models, forcing companies to adapt or risk becoming less competitive.
- Digitalization in Marine Operations: Companies are investing in technologies like AI-powered predictive maintenance and autonomous vessel navigation to boost efficiency.
- Remote Operations: The trend towards onshore control centers for fleet management can reduce the need for extensive onboard personnel and specialized vessels for certain tasks.
- Bourbon's Investment in Smart Shipping: Bourbon is actively implementing digital solutions, aiming to enhance operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in line with industry trends.
- Impact on Vessel Demand: Increased operational efficiency through technology could lead to a reduced requirement for the sheer volume of vessels or their operational hours in the future.
Pipeline Infrastructure for Transport
Pipelines represent a significant substitute for shuttle tankers and other marine transport in moving hydrocarbons from offshore fields. The presence of extensive pipeline networks, particularly in established offshore production areas, can diminish the reliance on ships for transporting crude oil and natural gas to land-based facilities. For instance, as of early 2024, Europe's reliance on pipeline gas imports, primarily from Russia, though shifting, still highlights the scale of this infrastructure's role.
Despite the availability of pipelines, subsea flowlines remain indispensable for offshore operations. These lines are crucial for connecting wells to processing platforms and are vital for efficient production, especially in deepwater environments. The ongoing investment in subsea infrastructure underscores its continued importance, with global subsea equipment market projected to reach over $40 billion by 2027, indicating sustained demand for these specialized pipeline systems.
- Primary Substitute: Pipelines offer a direct alternative to marine transport for offshore hydrocarbon movement.
- Network Impact: Mature pipeline networks reduce the need for vessel-based logistics in oil and gas transport.
- Subsea Necessity: Subsea flowlines are critical components of offshore infrastructure, indispensable for production.
- Market Growth: Continued investment in subsea technology, with market growth projections, reinforces the importance of pipeline infrastructure.
The threat of substitutes for offshore oil and gas services is multifaceted, encompassing both direct energy alternatives and technological advancements that alter operational needs. While onshore extraction and renewable energy sources present broader substitution pressures, innovations in subsea technology and digitalization offer more immediate threats to traditional offshore vessel operations.
Autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) are increasingly capable of performing tasks historically done by manned vessels, potentially reducing demand for Bourbon's core services. The global market for underwater robotics was projected to reach $7.5 billion in 2024, highlighting significant investment in these substitute technologies.
Digitalization and remote operations also act as substitutes by increasing efficiency and potentially reducing the number of vessels or crew required for certain offshore activities. Bourbon's own investments in smart shipping aim to leverage these trends, but they also reflect the underlying shift in what clients may demand from marine support providers.
| Substitute Category | Specific Substitute | Impact on Bourbon | Market Data (2024 Estimates) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Alternatives | Onshore Oil & Gas Production | Diversion of investment, reduced need for new offshore ventures | Permian Basin production growth |
| Energy Alternatives | Renewable Energy (Solar, Wind) | Indirect threat to fossil fuel demand | Growing share of global energy mix |
| Technological Advancements | Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) & Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) | Potential reduction in demand for traditional support vessels | Underwater robotics market: $7.5 billion |
| Technological Advancements | Digitalization & Remote Operations | Increased efficiency, potential reduction in vessel/crew needs | Smart shipping initiatives |
Entrants Threaten
The offshore marine services sector, particularly for companies operating a diverse fleet like Bourbon, presents a formidable threat of new entrants due to extremely high capital investment requirements. Acquiring or constructing specialized vessels, such as offshore support vessels (OSVs), subsea construction ships, and crew transfer boats, along with the necessary advanced technology, can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, a new, state-of-the-art OSV can cost upwards of $50 million, and a complex subsea vessel can exceed $200 million.
The offshore energy sector is a minefield of regulations. New companies entering this space must navigate a complex web of safety, environmental, and operational standards. Think about the costs involved in getting all the right certifications and understanding international maritime laws. For instance, compliance with evolving environmental rules, such as the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS), adds significant financial and operational hurdles. Bourbon's existing, robust compliance framework is a definite plus, giving it an edge over newcomers who are just starting to build theirs.
Operating in the demanding offshore sector necessitates significant specialized expertise and extensive experience, particularly in areas like vessel operation and maintenance in challenging marine conditions. Newcomers face a steep learning curve in acquiring the deep technical knowledge and operational know-how that established companies like Bourbon have cultivated over years of service. This accumulated institutional knowledge, coupled with a demonstrated history of safety and reliability, forms a substantial barrier to entry.
Established Customer Relationships and Contracts
Major offshore energy companies often prioritize established service providers with a proven track record and existing relationships. New entrants face a significant hurdle in building the trust necessary to secure long-term contracts with global clients, a process that can take years and substantial investment.
Bourbon's existing global client base and a portfolio of ongoing contracts represent a formidable barrier to entry. For instance, as of early 2024, Bourbon maintained strong partnerships with key players in the energy sector, evidenced by their continued contract wins and renewals, demonstrating a deep level of client loyalty and operational reliability.
- Established Trust: Energy majors favor vendors with a history of successful project delivery, reducing perceived risk.
- Contractual Lock-in: Long-term agreements with existing clients make it difficult for new companies to gain initial traction.
- Bourbon's Advantage: Existing global client relationships and ongoing contracts provide a significant competitive moat.
- High Switching Costs: The effort and potential disruption involved in switching service providers deter clients from onboarding new entrants.
Access to Advanced Technology and Infrastructure
The offshore vessel industry's increasing reliance on advanced technologies like dynamic positioning and integrated subsea systems presents a significant barrier to new entrants. These technologies demand substantial capital investment for acquisition or development, alongside the necessary supporting infrastructure. For instance, Bourbon has strategically invested in upgrading its fleet and digital capabilities, a move that requires considerable financial commitment.
New players would face the challenge of matching the technological sophistication and operational efficiency already established by incumbents. The cost associated with implementing and maintaining cutting-edge systems, such as advanced navigation and real-time data analytics for fleet management, can be prohibitive. This technological gap requires not only financial resources but also specialized expertise.
Bourbon's proactive approach to technological advancement means new entrants must contend with an already established level of operational excellence. This includes investments in:
- Digital fleet management platforms
- Advanced subsea intervention capabilities
- Environmentally conscious propulsion systems
The high upfront costs for technology and infrastructure mean that only well-capitalized companies can realistically enter this market, thereby limiting the threat of new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the offshore marine services sector is significantly mitigated by the immense capital required to acquire specialized vessels and advanced technology, often costing hundreds of millions of dollars per unit. For example, as of 2024, a cutting-edge offshore support vessel can easily exceed $50 million, presenting a substantial financial barrier. Furthermore, stringent regulatory compliance and the need for extensive operational experience in challenging marine environments demand considerable investment and time, which new companies often lack.
Established players like Bourbon benefit from strong client relationships and long-term contracts, creating high switching costs for energy majors and deterring new entrants. The sector’s increasing reliance on sophisticated technologies, such as digital fleet management and advanced subsea systems, further elevates entry barriers, requiring significant upfront investment and specialized expertise that newcomers struggle to match.
| Barrier to Entry | Estimated Cost/Requirement (as of 2024) | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Vessel Acquisition/Construction | $50M - $200M+ per specialized vessel | Extremely High Capital Requirement |
| Regulatory Compliance & Certifications | Significant ongoing investment in safety & environmental standards | Complex and Costly Navigation |
| Specialized Expertise & Experience | Years of operational know-how in demanding conditions | Steep Learning Curve & High Training Costs |
| Client Relationships & Contracts | Long-term agreements, high switching costs | Difficulty in Securing Initial Business |
| Technological Sophistication | Investment in advanced navigation, subsea systems, digital platforms | Prohibitive Cost and Expertise Gap |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of robust data, including industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from key players, and government economic indicators. We also leverage insights from trade associations and expert interviews to capture the nuances of competitive dynamics.
