Bluescope Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bluescope Steel Bundle
Bluescope Steel faces significant competitive pressures from powerful buyers and a moderate threat from new entrants in the steel industry. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its market landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bluescope Steel’s industry—from supplier influence to substitute threats. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BlueScope Steel's reliance on key raw materials like iron ore, coking coal, and energy positions its suppliers with considerable bargaining power. The market for these essential inputs is often dominated by a limited number of large global mining and energy corporations, allowing them to influence pricing and supply terms. For instance, in 2024, iron ore prices saw significant volatility, directly impacting BlueScope's production costs and profitability.
For specialized inputs or high-quality raw materials, the number of qualified suppliers for BlueScope Steel can be quite limited. This scarcity directly impacts BlueScope's bargaining power, as switching suppliers often involves significant costs or a potential dip in product quality. For instance, in 2024, the global supply of certain high-grade iron ore, crucial for premium steel products, remained concentrated among a few major producers, giving them considerable leverage.
The cost and availability of transportation for raw materials like iron ore and coal are critical. For instance, in 2024, global shipping rates, particularly for bulk carriers, experienced volatility due to geopolitical events and supply chain disruptions, directly impacting the landed cost of these essential inputs for Bluescope Steel. Suppliers of logistics services can exert considerable power if they control key shipping routes or if fuel surcharges significantly inflate prices.
Supplier Switching Costs
Supplier switching costs significantly impact BlueScope Steel's bargaining power. If it's costly for BlueScope to switch raw material suppliers or technology providers, perhaps due to the expense of retooling manufacturing equipment or implementing new quality assurance protocols, this can lock the company into existing relationships. For instance, significant upfront investment in specialized machinery for a particular supplier's unique raw material specifications would create a high switching cost.
These elevated switching costs inherently reduce BlueScope's leverage when negotiating with its suppliers. When changing suppliers is a complex and expensive undertaking, BlueScope becomes more reliant on its current partners. This dependency can translate into less favorable pricing or less flexible contract terms, as suppliers recognize the difficulty BlueScope would face in finding and onboarding an alternative.
Consider the automotive industry, a key customer for steel. In 2024, the complexity of integrating new steel grades into existing automotive production lines, which often requires extensive testing and recalibration, highlights these switching costs. For example, a steel supplier providing a highly specialized alloy for a specific vehicle chassis might face minimal competition if the cost for an automaker to qualify a new supplier for that exact alloy is measured in millions of dollars and months of validation.
- High Retooling Expenses: BlueScope might incur substantial costs to adapt its production lines for new raw materials.
- Quality Assurance Investment: Establishing and validating new supplier quality standards demands significant time and resources.
- Contractual Obligations: Existing long-term contracts can impose penalties or significant costs for early termination.
- Supplier Dependence: High switching costs foster a dependence that can weaken BlueScope's negotiating position.
Supplier Integration Threat
The threat of supplier integration poses a significant challenge for BlueScope Steel. If major raw material suppliers, such as iron ore or coking coal producers, were to integrate forward into steel manufacturing, they could become direct competitors. This possibility grants them considerable leverage in price negotiations, as BlueScope would be hesitant to empower a future rival by agreeing to unfavorable terms.
This strategic dynamic can significantly alter the competitive landscape. For instance, a large mining conglomerate with the financial muscle and technical expertise to enter steel production could disrupt existing market structures. Such a move would not only increase competitive intensity but also potentially squeeze profit margins for established steelmakers like BlueScope.
- Supplier Forward Integration: Large raw material suppliers possess the financial capacity and technical know-how to potentially integrate forward into steel production, creating new competitors for BlueScope.
- Increased Bargaining Power: The threat of suppliers becoming direct competitors enhances their bargaining power, allowing them to demand more favorable terms from BlueScope in raw material procurement.
- Market Disruption: A supplier's entry into steel manufacturing could lead to increased competition, potentially impacting pricing, market share, and profitability for existing players like BlueScope.
The bargaining power of BlueScope Steel's suppliers is substantial due to the concentrated nature of raw material markets and high switching costs. For instance, in 2024, the global iron ore market remained dominated by a few major players, allowing them to dictate terms. This dependence is exacerbated by significant investments BlueScope might make in specialized equipment for certain suppliers, making it costly to change. The potential for suppliers to integrate forward into steel production further amplifies their leverage, as they could become direct competitors.
| Factor | Impact on BlueScope Steel | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited suppliers for key inputs (iron ore, coal) give them pricing power. | Iron ore prices showed significant volatility in 2024, directly affecting BlueScope's costs. |
| Switching Costs | High costs to change suppliers (retooling, quality validation) reduce BlueScope's negotiation leverage. | Integrating new steel grades into automotive lines in 2024 required extensive testing, highlighting these costs. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Suppliers becoming competitors increases their power to demand favorable terms. | Large mining firms have the capital to potentially enter steel manufacturing, creating this threat. |
What is included in the product
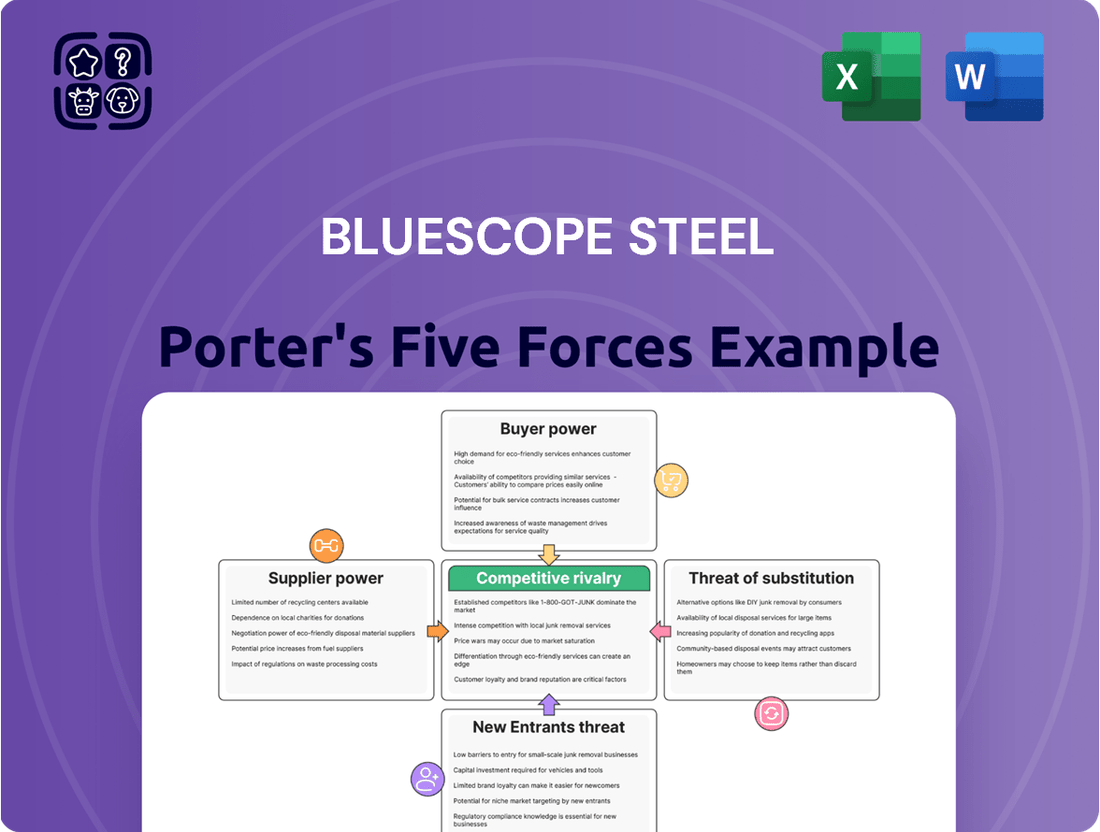
Bluescope Steel's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intense competition, significant buyer power, and moderate threat of new entrants within the steel industry, impacting pricing and profitability.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats and supplier power with a pre-built Bluescope Steel Porter's Five Forces template.
Customers Bargaining Power
BlueScope Steel caters to a wide array of industries, but within these sectors, a few dominant players often emerge. For instance, major automotive manufacturers or large-scale construction firms represent significant customer segments. These substantial entities, by virtue of their size and consistent demand, wield considerable influence over BlueScope.
The sheer volume of steel these key customers procure directly translates into substantial bargaining power. They can leverage this purchasing volume to negotiate more favorable pricing structures and contractual terms. This concentrated demand from large clients is a critical factor in determining the overall bargaining power of customers in BlueScope's market.
BlueScope Steel faces a challenge with product standardization, particularly in its more basic steel offerings. While they do have specialized, painted products, many core steel items can be viewed as commodities by buyers. This lack of unique differentiation means customers can readily shop around for the best price, significantly boosting their leverage.
In sectors like construction and manufacturing, steel represents a substantial portion of a company's total expenses. This naturally leads to a high degree of price sensitivity among Bluescope's customers, who are actively seeking favorable pricing to manage their own costs.
For instance, in 2024, the construction industry in Australia, a key market for Bluescope, faced rising material costs, including steel. This economic pressure intensified the bargaining power of construction firms, making them more inclined to seek price concessions from their steel suppliers.
Furthermore, periods of economic slowdown or increased competition within these customer industries can significantly amplify their sensitivity to steel prices. When demand for their end products weakens or the competitive landscape intensifies, customers become even more focused on reducing input costs, including the price of steel.
Customer Switching Costs
Customer switching costs for steel suppliers can vary. For many standard steel products, the expense and effort involved in changing suppliers are relatively low, giving customers more leverage. This is particularly true when multiple suppliers offer comparable products, making it easier for buyers to shop around for better prices or terms.
However, switching costs can increase significantly for specialized steel applications. If a customer has integrated a specific supplier's steel into their manufacturing process, requiring unique certifications or extensive retooling, the cost and time to switch can become substantial. For instance, in the automotive sector, specific steel grades used in critical structural components often involve rigorous testing and approval processes that make switching suppliers a complex undertaking.
- Moderate to Low Switching Costs: For many standard steel products, customers face minimal costs when switching suppliers, enhancing their bargaining power.
- Specialized Application Impact: Higher switching costs arise in niche applications where integration, custom specifications, or certifications are involved.
- Supplier Relationship Importance: BlueScope must cultivate strong customer relationships to mitigate the impact of low switching costs and retain market share.
Backward Integration Threat
Large customers, especially in industries like automotive and construction, often have substantial financial clout and the strategic vision to explore backward integration into steel manufacturing. This capability, even if not fully realized, significantly strengthens their negotiating position with steel suppliers like Bluescope Steel.
The sheer possibility of major clients establishing their own steel production facilities acts as a powerful check on Bluescope's ability to raise prices. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer could potentially invest billions in a new steel mill, shifting the power dynamic considerably.
- Customer Leverage: The threat of backward integration by large automotive or construction clients directly increases their bargaining power against steel producers.
- Deterrent to Price Hikes: This potential for self-sufficiency discourages steel companies from implementing significant price increases, as customers could retaliate by developing their own supply.
- Capital Intensity as a Barrier: While backward integration is extremely capital-intensive, the financial capacity of some large customers makes this a credible threat, impacting Bluescope's pricing strategies.
The bargaining power of BlueScope Steel's customers is a significant force, particularly from large industrial clients like automotive manufacturers and construction firms. These buyers often purchase in massive volumes, giving them considerable leverage to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms. For example, in 2024, the automotive sector's demand for specialized steel grades, while critical, also meant that major carmakers could exert pressure on suppliers due to the sheer scale of their orders.
Product standardization, especially for commodity steel, further empowers customers. When steel products are easily substitutable, buyers can readily switch suppliers to secure the best deals, increasing price sensitivity. This was evident in the construction market in 2024, where fluctuating raw material costs made price a primary consideration for many builders.
Switching costs for customers are generally low for standard steel products, but can increase for specialized, integrated applications. The threat of backward integration by large customers also acts as a powerful deterrent against price hikes, as these entities possess the financial capacity to consider their own steel production.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on BlueScope | 2024 Market Context Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturers | High volume purchasing, potential for backward integration | Strong price negotiation, demand for customization | Increased demand for lightweight steel alloys, driving supplier competition. |
| Construction Firms | Price sensitivity due to material costs, low switching costs for standard steel | Pressure on pricing for basic steel products | Rising input costs in 2024 intensified focus on cost-effective steel sourcing. |
| Specialized Application Buyers | Higher switching costs due to integration and certifications | Lower bargaining power for specific product lines | Continued reliance on BlueScope for high-strength, coated steel in specific building projects. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Bluescope Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the competitive landscape of Bluescope Steel, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global steel sector features numerous substantial, long-standing companies, such as integrated steel producers and mini-mills, alongside regional contenders. BlueScope navigates a market where both sheer size and unique product capabilities are crucial differentiators, often fueling aggressive competition for market dominance.
In 2024, major steel producers like ArcelorMittal and Nippon Steel continue to hold significant global market shares, indicating a concentrated industry. BlueScope's competitive standing is directly influenced by the scale and strategic positioning of these giants, as well as the agility of more specialized regional players.
Bluescope Steel, like many in the steel sector, operates with substantial fixed costs. Think of the massive investment needed for blast furnaces and rolling mills; these are not small expenditures. This capital intensity means companies must run their facilities at high capacity to spread those costs effectively and remain competitive.
This drive for high capacity utilization can be a double-edged sword. When demand softens, as it did for many industrial sectors in early 2024 due to global economic uncertainties, companies may continue producing to cover their fixed costs. This can lead to an oversupply of steel in the market, forcing prices down and intensifying rivalry as companies fight for market share, directly impacting profitability.
BlueScope Steel stands out by moving beyond basic steel, focusing on coated, painted, and engineered products. This product differentiation, particularly in areas like their COLORBOND® steel, allows them to command premium pricing and reduce reliance on pure price competition. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, BlueScope reported strong performance in its coated products segment, highlighting the market's appetite for value-added steel solutions.
Exit Barriers
The steel industry, including players like BlueScope Steel, faces substantial exit barriers. High capital investment in specialized plant and equipment, often running into billions of dollars, makes it incredibly difficult and costly for companies to simply walk away from their operations. This means that even when market conditions are poor, firms are often compelled to continue production, contributing to ongoing overcapacity.
These high exit barriers directly fuel competitive rivalry. Companies are hesitant to cease operations, leading to a situation where excess capacity persists even during economic downturns. This inflexibility in response to demand shifts intensifies competition as firms fight for market share with existing, often underutilized, production facilities.
For instance, major steel producers globally have historically struggled with profitability during periods of low demand, yet the sunk costs associated with their integrated steel mills prevent widespread closures. This dynamic forces companies to compete aggressively on price and volume, impacting margins across the sector.
- High Capital Intensity: The significant upfront investment required for steel manufacturing facilities creates a substantial financial commitment that is difficult to recoup.
- Specialized Assets: Steel production relies on highly specialized machinery and infrastructure that have limited alternative uses, increasing the cost of exiting the market.
- Operational Inertia: Companies often continue operating at reduced capacity rather than incurring the costs associated with decommissioning plants and managing redundant assets, thereby perpetuating overcapacity.
- Employee and Community Obligations: Layoffs and plant closures can incur significant severance costs and have broader community impacts, adding further reluctance to exit.
Global Market Dynamics and Trade Policies
The global steel market is a dynamic arena, heavily shaped by international trade policies, tariffs, and currency exchange rates. BlueScope Steel, like its peers, navigates this complex landscape where shifts in these external factors can dramatically alter competitive pressures.
BlueScope faces intense rivalry not just from domestic competitors but also from imported steel. Countries with lower production costs or government subsidies can introduce steel into markets at prices that challenge established players. For instance, in 2024, the European Union maintained its steel import safeguard measures, impacting trade flows and influencing pricing dynamics for companies like BlueScope operating within or exporting to the region.
- Global Steel Trade Volume: In 2023, global steel trade volumes saw fluctuations influenced by geopolitical events and regional demand, with significant flows originating from Asia.
- Tariff Impacts: The continuation of Section 232 tariffs in the United States, though subject to ongoing review and adjustments, continued to impact steel import costs and domestic pricing strategies for companies like BlueScope in 2024.
- Currency Volatility: Fluctuations in major currencies, such as the Australian Dollar against the US Dollar, directly affect the landed cost of imported steel and the competitiveness of BlueScope's exports.
- Subsidies and Trade Defense: Allegations and investigations into state subsidies for steel production in various countries, as seen in ongoing WTO disputes, highlight the regulatory environment BlueScope must contend with, potentially leading to anti-dumping duties that alter competitive parity.
The competitive rivalry within the steel industry, impacting BlueScope Steel, is fierce due to the presence of large, established global players and agile regional competitors. This dynamic is amplified by the industry's high capital intensity and significant exit barriers, which compel firms to maintain production even during downturns, leading to persistent overcapacity and price pressure. BlueScope differentiates itself through value-added products like COLORBOND steel, aiming to mitigate direct price competition.
In 2024, companies like ArcelorMittal and Nippon Steel continue to be dominant forces, influencing market dynamics. BlueScope's strategy of focusing on coated and engineered steel products, rather than just commodity steel, is crucial. This specialization was evident in fiscal year 2023, where BlueScope saw robust performance in its coated products segment, demonstrating the market's demand for higher-value steel solutions and providing a buffer against the intense rivalry driven by commodity price fluctuations.
SSubstitutes Threaten
In the construction sector, a key market for BlueScope, steel faces significant competition from alternative materials. Concrete, timber, aluminum, and various composite materials each present distinct advantages in terms of cost, performance characteristics, and aesthetic appeal, depending on the specific building application.
For instance, timber offers a renewable and often more aesthetically pleasing option for residential construction, while concrete remains a staple for foundational work due to its compressive strength and cost-effectiveness. Aluminum is frequently chosen for its lightness and corrosion resistance in facade systems.
BlueScope's strategy must emphasize steel's superior strength-to-weight ratio and long-term durability to counter these substitutes. In 2024, the global construction market, valued at over $13 trillion, continues to see diverse material usage, making differentiation crucial.
Customers often weigh the performance of steel against its cost when considering substitutes. For instance, if engineered wood products offer comparable structural integrity for certain building applications at a reduced price, this presents a challenge for BlueScope. In 2024, the global construction market saw continued interest in sustainable and cost-effective materials, with engineered wood gaining traction in residential projects.
The threat intensifies when substitutes provide superior performance in specific niches. For example, advanced composites might offer lighter weight and higher strength-to-weight ratios for specialized automotive or aerospace components, even at a higher initial cost. BlueScope must continually innovate to ensure its steel products deliver an optimal performance-cost balance to remain competitive against these specialized alternatives.
Technological advancements are a significant threat, as ongoing research in materials science continuously introduces and improves substitutes. For example, breakthroughs in lightweight composites and advanced plastics are making these materials increasingly competitive with steel in sectors like automotive and manufacturing, potentially reducing demand for Bluescope's core products.
Environmental and Sustainability Preferences
Growing environmental concerns and sustainability mandates can significantly influence material selection, posing a threat of substitutes for BlueScope Steel. While steel is highly recyclable, other materials might be perceived as more environmentally friendly in specific applications, or emerging regulations could favor alternative building components. For instance, by 2024, the global construction market is increasingly scrutinizing embodied carbon, with some projects actively seeking materials with lower lifecycle emissions. BlueScope's strategy must therefore highlight its commitment to sustainable steel production and the inherent recyclability of its products to counter this pressure.
The perception of 'greenness' can be a powerful driver. While steel boasts a high recycling rate, often exceeding 90% for construction scrap, the energy intensity of primary steel production remains a point of discussion. This can lead specifiers to consider alternatives like engineered timber or advanced composites, especially where regulatory frameworks or client preferences prioritize bio-based or lower-energy-intensive materials. BlueScope needs to proactively communicate its decarbonization efforts and the circular economy benefits of steel to maintain its competitive edge against these perceived greener substitutes.
- Steel's recyclability rate is a key advantage, often cited as over 90% for construction scrap.
- Emerging regulations and client demand for lower embodied carbon can favor alternatives like engineered timber.
- BlueScope must actively promote its sustainable manufacturing processes and the circularity of steel.
Shifting Design and Aesthetic Trends
Shifting design and aesthetic trends can indeed act as a threat of substitutes for steel. For instance, if architectural movements increasingly favor natural materials like wood or advanced composites for their unique visual appeal or perceived sustainability, demand for steel in certain construction segments could decline. This was seen in some residential construction trends where timber framing gained popularity for its aesthetic and perceived environmental benefits, though steel's structural advantages often remain dominant in larger projects.
The adaptability of steel manufacturers to evolving design preferences is crucial. If new construction methods or design philosophies emerge that are inherently more compatible with alternative materials, steel could face erosion in market share. For example, the rise of modular construction, while often utilizing steel, also opens doors for prefabricated components made from other substances, potentially reducing the need for traditional on-site steel work.
Consider the impact of sustainability mandates. While steel is highly recyclable, if emerging building codes or consumer preferences heavily favor materials with a lower embodied carbon footprint in their initial production, this could present a challenge. For 2024, the global construction industry is increasingly scrutinizing the life-cycle assessment of materials, and innovations in lower-carbon steel production will be key to mitigating this threat.
- Evolving Design Preferences: Contemporary architectural styles might favor materials other than steel, impacting demand.
- New Construction Methods: Emerging building techniques could be better suited to alternative materials, posing a substitution risk.
- Material Adaptability: Steel producers must adapt to market trends and design shifts to maintain market share.
- Sustainability Focus: Increasing emphasis on embodied carbon in construction materials could favor alternatives if steel production remains carbon-intensive.
The threat of substitutes for BlueScope Steel is significant across its diverse markets, driven by material innovation and evolving customer preferences. In construction, concrete, timber, and aluminum offer competitive advantages in specific applications, while in manufacturing, advanced composites and plastics present alternatives.
For example, while steel boasts a high recycling rate, often exceeding 90% for construction scrap, the perceived lower embodied carbon of materials like engineered timber can influence specifiers, especially with growing sustainability mandates. The global construction market, valued at over $13 trillion in 2024, sees continued demand for cost-effective and environmentally conscious materials, requiring BlueScope to highlight steel's recyclability and decarbonization efforts.
Technological advancements in materials science continuously introduce and improve substitutes, such as lightweight composites in the automotive sector, potentially reducing demand for traditional steel components. BlueScope must therefore focus on delivering a strong performance-cost balance and adapting to shifting design trends to maintain its competitive edge.
| Substitute Material | Key Advantages | Potential Impact on BlueScope |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete | Cost-effectiveness for foundations, high compressive strength | Limits steel usage in structural components, especially for lower building levels |
| Timber (Engineered Wood) | Renewable, aesthetic appeal, potentially lower embodied carbon | Threatens steel in residential construction and specific architectural designs |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion resistance | Competes in facade systems and applications where weight is critical |
| Advanced Composites | High strength-to-weight ratio, specific performance characteristics | Challenges steel in niche sectors like automotive and specialized construction |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a new steel manufacturing plant demands a colossal capital investment, often running into billions of dollars for land acquisition, cutting-edge machinery, essential infrastructure, and advanced technology. This substantial financial hurdle acts as a significant deterrent for aspiring competitors, as only a select few organizations can muster the necessary resources to even consider entering the market.
Existing steel producers like BlueScope leverage substantial economies of scale, enabling them to achieve lower per-unit production costs. For instance, in 2023, BlueScope's total revenue reached AUD 17.1 billion, indicative of their production capacity and associated cost efficiencies.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies without achieving massive initial production volumes. This disparity creates a considerable cost disadvantage for newcomers attempting to enter the market and compete on price against established players.
The steel industry is heavily regulated, with strict environmental standards and safety protocols. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to implement its Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which imposes costs on carbon-intensive imports, directly impacting steel producers.
Newcomers must navigate a complex web of permitting processes and invest significantly in pollution control technologies to meet these requirements. This compliance burden, including obtaining necessary licenses and adhering to evolving safety regulations, represents a substantial financial and temporal barrier to entry, effectively deterring many potential competitors.
Access to Raw Materials and Distribution Channels
Established steel producers like BlueScope often benefit from long-standing relationships that secure preferential pricing and consistent supply of raw materials such as iron ore and coking coal. For instance, in 2024, major integrated steel mills typically have multi-year supply agreements in place, shielding them from short-term price volatility. New entrants would face significant hurdles in negotiating similar terms, potentially paying higher spot prices for essential inputs.
Furthermore, existing players have invested heavily in sophisticated logistics and distribution networks, including dedicated rail lines, port facilities, and warehousing. This infrastructure allows for efficient and cost-effective delivery of finished steel products to a wide customer base. A new competitor would need substantial capital to replicate these established channels, facing higher per-unit distribution costs initially.
- Secured Supply Contracts: Major steel manufacturers often hold long-term contracts for critical raw materials, ensuring stable supply and pricing.
- Developed Distribution Networks: Established players possess extensive logistics infrastructure, including transportation and warehousing, which new entrants would find costly to replicate.
- Economies of Scale in Procurement: Existing companies leverage their size to negotiate better terms for raw materials compared to smaller, new entrants.
- Customer Relationships: Long-standing relationships with distributors and end-users create a barrier for new companies attempting to establish market access.
Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
In mature sectors like steel, established players like BlueScope leverage significant brand recognition and a proven track record. This makes it tough for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in 2024, major steel producers continued to emphasize their long-standing commitment to quality and reliability, a key factor in securing large industrial contracts.
New entrants face the daunting task of building trust and market share. They'd need substantial marketing and sales investments to even begin competing with incumbent loyalty. This investment hurdle is substantial, as building a brand in heavy industry requires years of consistent performance and customer engagement.
- Brand Equity: Companies with decades of operation have built substantial brand equity, a significant barrier to entry.
- Customer Relationships: Existing, long-term relationships with key buyers create inertia, making it difficult for new suppliers to break in.
- Marketing Investment: New entrants must allocate considerable resources to marketing and sales to overcome established brand loyalty.
- Reputation for Quality: A proven history of delivering high-quality products is crucial in industries where material integrity is paramount.
The threat of new entrants for BlueScope Steel is considerably low due to immense capital requirements, estimated in the billions for plant setup. This financial barrier alone prevents most potential competitors from even considering market entry. Furthermore, established players like BlueScope benefit from significant economies of scale, as evidenced by their 2023 revenue of AUD 17.1 billion, which translates to lower per-unit production costs that newcomers struggle to match.
Navigating stringent regulations and environmental standards, such as the EU's 2024 Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, adds another layer of complexity and cost for potential entrants. Securing reliable and cost-effective raw material supplies through long-term contracts, a common practice for major steel producers in 2024, is also a challenge for new players who often face higher spot prices.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example for BlueScope (2023-2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment for plant and machinery. | Billions of dollars required for new steel mill construction. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large production volumes. | BlueScope's AUD 17.1 billion revenue in 2023 indicates significant scale advantages. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance with environmental and safety standards. | Adherence to evolving emissions regulations like the EU's CBAM in 2024. |
| Raw Material Access | Securing stable and cost-effective input supply. | Long-term supply agreements for iron ore and coking coal in 2024. |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Established customer trust and distribution networks. | Years of proven quality and reliability, leading to strong industrial contracts. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Bluescope Steel Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from Bluescope's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld, and global economic indicators to assess competitive intensity.
