Bilfinger SE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bilfinger SE Bundle
Bilfinger SE operates in a dynamic environment shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power, impacting its pricing and profitability. The threat of substitutes also looms, requiring strategic adaptation to maintain market share.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bilfinger SE’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration can significantly impact Bilfinger SE's operational costs and efficiency. In the industrial services sector, while many general suppliers exist, the need for highly specialized components or advanced engineering software often means dealing with a limited number of providers. This scarcity of options for critical inputs grants these specialized suppliers greater leverage in price negotiations and contract terms.
For instance, if Bilfinger requires unique manufacturing equipment or niche technical consulting, and only a handful of companies offer these services, those suppliers hold considerable bargaining power. This is particularly true as of 2024, where supply chain disruptions and increased demand for specialized skills have amplified the negotiating strength of key suppliers across various industrial segments.
Bilfinger SE faces significant supplier bargaining power when switching costs are high. If Bilfinger has deeply integrated a supplier's specialized technology or operational processes into its complex industrial projects, the effort and expense to transition to a new provider become substantial. This reliance means that changing suppliers could lead to considerable disruptions, impacting project timelines and budgets.
Bilfinger SE's reliance on suppliers with unique or proprietary offerings significantly influences their bargaining power. If suppliers provide highly specialized digital applications for industrial facilities or niche environmental technologies that are difficult for Bilfinger to source elsewhere, these suppliers gain leverage. For instance, a supplier of a patented energy-saving system for chemical plants, for which Bilfinger has no alternative, would command higher prices and more favorable terms.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a potential challenge to Bilfinger SE. If suppliers, particularly those offering specialized technology or components, could realistically enter the industrial services market and compete directly, their leverage over Bilfinger would significantly increase. This scenario is less probable for broad industrial service providers but remains a consideration for niche technology partners who might see value in offering end-to-end solutions.
For instance, imagine a supplier of advanced robotic maintenance systems. If this supplier were to develop the capability to not only provide the robots but also the skilled labor and project management to execute maintenance tasks, they could directly compete with Bilfinger's service offerings. This would shift the power dynamic, allowing the supplier to dictate terms more aggressively.
- Potential for Specialized Suppliers to Enter Industrial Services Market
- Increased Bargaining Power if Suppliers Offer Integrated Solutions
- Less Common for Broad Industrial Service Providers, More Relevant for Niche Technology Firms
Importance of Bilfinger to Supplier's Revenue
The bargaining power of suppliers to Bilfinger SE is significantly influenced by the proportion of revenue Bilfinger generates for them. If Bilfinger constitutes a substantial part of a supplier's income, that supplier's leverage diminishes, as they are heavily reliant on Bilfinger's continued business. For instance, if a specialized component supplier derives over 30% of its annual sales from Bilfinger, its ability to dictate terms or raise prices is constrained.
Conversely, suppliers for whom Bilfinger is a minor client, perhaps representing less than 5% of their total sales, possess considerably more bargaining power. These suppliers, often large entities with diverse customer bases, are less sensitive to losing Bilfinger's business and can therefore command more favorable terms. This dynamic is crucial in understanding the supplier landscape for Bilfinger.
- Supplier Dependence: A supplier heavily reliant on Bilfinger's orders has reduced bargaining power.
- Bilfinger's Client Size: If Bilfinger is a small customer to a large supplier, the supplier's power increases.
- Revenue Contribution: Data from 2024 indicates that for some key raw material suppliers, Bilfinger accounted for less than 10% of their total revenue, strengthening the supplier's position.
- Market Concentration: The bargaining power also shifts based on the concentration of suppliers in a particular market segment relevant to Bilfinger's operations.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Bilfinger SE is a critical factor, particularly when dealing with specialized inputs. In 2024, the market for advanced industrial components and niche engineering services saw a concentration of suppliers, granting them significant leverage in price negotiations. High switching costs, stemming from deep integration of supplier technologies into Bilfinger's complex projects, further amplify this power, making it costly and disruptive to change providers.
Suppliers offering unique or proprietary solutions, such as patented energy-saving systems, hold considerable sway, especially when Bilfinger lacks viable alternatives. While the threat of forward integration by suppliers is less common for broad service providers, it remains a consideration for niche technology partners. The proportion of Bilfinger's revenue to a supplier directly impacts this power; for instance, if Bilfinger represents less than 10% of a key supplier's sales in 2024, that supplier's bargaining position is strengthened.
| Factor | Impact on Bilfinger SE | Example Scenario (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High for specialized inputs | Limited providers for advanced robotics software |
| Switching Costs | Significant due to integrated technology | Disruption to project timelines if a core software provider changes |
| Supplier Differentiation | High for unique/proprietary offerings | Patented environmental technology with no direct substitutes |
| Supplier Dependence on Bilfinger | Low for suppliers where Bilfinger is a small client | Supplier representing < 5% of total sales has greater leverage |
| Bilfinger's Dependence on Supplier | Low for suppliers where Bilfinger is a large client | Supplier representing > 30% of sales has reduced leverage |
What is included in the product
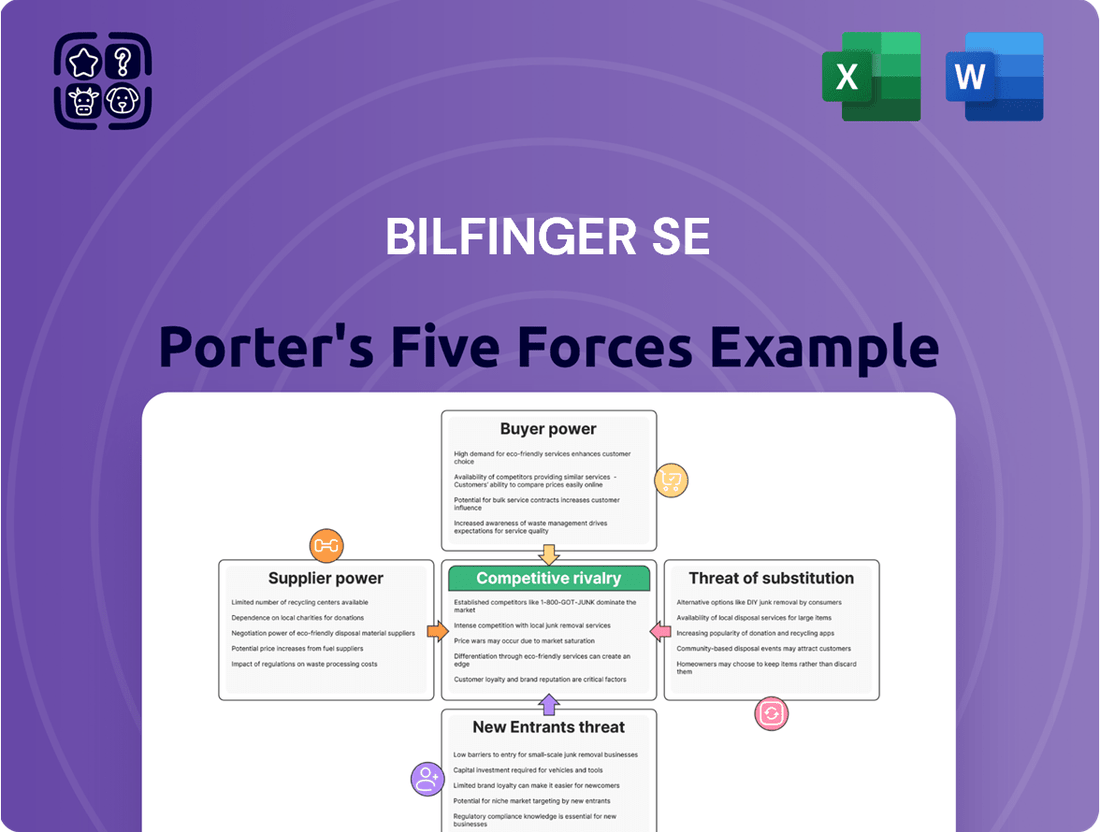
This analysis details Bilfinger SE's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Instantly grasp the competitive landscape of Bilfinger SE with a visual representation of Porter's Five Forces, aiding in strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Bilfinger SE primarily caters to large industrial clients within sectors such as energy, chemicals, petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, biopharmaceuticals, and oil and gas. The concentration of its customer base is a key factor influencing customer bargaining power.
If a few major clients represent a substantial portion of Bilfinger's overall revenue, these significant customers gain considerable leverage. This allows them to negotiate more favorable terms, push for reduced pricing, or demand highly specialized services, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
For Bilfinger's customers, the decision to switch industrial service providers often comes with significant financial and operational hurdles. Consider the complexity involved in long-term maintenance contracts or major plant expansions; these services are deeply integrated into a client's operations, making a change disruptive and costly. For instance, a client undertaking a critical turnaround might face millions in penalties and lost production if a new provider cannot seamlessly take over.
Customers might explore performing certain industrial services internally or opting for alternative, less specialized providers. This is particularly true for more standardized maintenance or basic engineering tasks. For example, if a client can reliably manage routine equipment upkeep themselves, their willingness to pay premium rates to Bilfinger for such services diminishes.
When customers view these alternatives as practical and budget-friendly, their leverage in negotiations with Bilfinger grows. Consider the 2024 market where a surge in skilled trades availability in certain regions could empower clients to bring more maintenance functions in-house, thereby reducing their reliance on external contractors.
However, the feasibility of in-house execution often falters for highly complex, safety-critical, or technically demanding industrial services. Bilfinger's expertise in areas like advanced plant engineering or specialized maintenance for unique industrial equipment presents a significant barrier to direct customer substitution, thus limiting customer bargaining power in these specific niches.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Bilfinger's customers exhibit varying degrees of price sensitivity. In sectors where cost containment is a major driver, such as certain infrastructure projects or industrial maintenance contracts, customers tend to be more sensitive to price fluctuations. This heightened sensitivity directly translates into increased bargaining power for these clients.
Conversely, for specialized services where Bilfinger's technical expertise, project execution reliability, and safety record are critical differentiators, customers may be less inclined to prioritize the lowest price. For example, in complex plant turnarounds or projects requiring highly specialized engineering skills, the risk of disruption or subpar performance often outweighs minor price differences.
- Customer Price Sensitivity: Varies significantly by industry and service criticality.
- Cost-Pressured Industries: Higher price sensitivity, leading to greater customer bargaining power.
- Critical Services: Lower price sensitivity where reliability and expertise are paramount.
- 2024 Data Insight: While specific customer price sensitivity data for Bilfinger in 2024 isn't publicly detailed, general market trends indicate that sectors like renewable energy infrastructure maintenance might see customers more focused on long-term operational cost savings and reliability, potentially moderating pure price sensitivity compared to traditional industrial sectors facing intense competition.
Customer Information and Transparency
Bilfinger SE's customers, particularly large industrial clients, are increasingly well-informed. Access to detailed market pricing, service comparisons, and competitor performance data, often facilitated by digital platforms, significantly strengthens their ability to negotiate terms and pricing. This enhanced transparency in the industrial services sector means customers can more readily identify and leverage alternative providers, putting pressure on Bilfinger to offer competitive value.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by several factors:
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers can readily compare Bilfinger's offerings against those of competitors, understanding pricing structures and service level agreements.
- Digital Platforms: The rise of digital marketplaces and information portals allows customers to aggregate data and identify the most cost-effective or technically superior solutions available.
- Switching Costs: While switching can involve costs, customers often have viable alternatives, limiting Bilfinger's ability to command premium pricing based solely on established relationships.
- Volume Purchasing: Many of Bilfinger's clients are large corporations that purchase services in significant volumes, giving them greater leverage in negotiations.
Bilfinger SE's customers, primarily large industrial entities, possess significant bargaining power due to the concentrated nature of their business and the availability of alternatives for certain services. This power is further amplified by increasing market transparency and the potential for customers to bring some services in-house, especially for more standardized maintenance tasks. However, for highly specialized and critical industrial services where Bilfinger offers unique expertise and reliability, customer bargaining power is considerably reduced.
| Factor | Impact on Bilfinger SE | Customer Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High dependence on key clients | High for major clients |
| Switching Costs | High for complex, integrated services | Low for standardized services |
| Availability of Alternatives | Limited for specialized services | High for routine maintenance |
| Customer Information & Digitalization | Increased price and service comparison | Enhanced |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies by service criticality and industry | Higher in cost-sensitive sectors |
Full Version Awaits
Bilfinger SE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the exact Bilfinger SE Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape. You'll gain detailed insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, ensuring no surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial services sector is indeed a crowded space, featuring a broad array of companies. These range from global giants with extensive reach to niche players focusing on specific services or regions. This sheer volume and variety of competitors directly fuels the intensity of rivalry within the market.
Bilfinger SE faces significant competition from well-established firms such as Arcadis, GEA, Wood, Jacobs Solutions, Worley, and Siemens Global. These companies often possess considerable resources, established client relationships, and diverse service portfolios, making them formidable rivals.
For instance, in 2023, Jacobs Solutions reported revenues of approximately $16.6 billion, highlighting the scale of some of Bilfinger's competitors. Similarly, Worley, another key competitor, has a substantial global presence and a broad service offering in the energy and resources sectors.
The industrial services market is poised for robust expansion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) between 5.7% and 7.3% from 2024 to 2029. This strong growth trajectory is a key factor influencing competitive rivalry.
While a growing market can often temper intense competition by providing ample opportunities for all participants, the significant anticipated growth in industrial services may paradoxically intensify rivalry. It could incentivize new entrants to enter the market or encourage existing players, like Bilfinger SE, to aggressively pursue market share gains, thereby sustaining or even escalating competitive pressures.
Bilfinger SE, operating in the industrial services sector, faces significant competitive rivalry stemming from high fixed costs and capacity utilization pressures. Many industrial services require substantial investments in specialized machinery, advanced technology, and a highly skilled workforce, creating a high barrier to entry but also intense competition among established players.
These considerable fixed costs necessitate continuous operation to spread the expense, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies, particularly when demand softens. Companies like Bilfinger must ensure their capacity is efficiently utilized to remain profitable, which can escalate price wars as firms compete for projects to cover overheads.
For instance, in 2024, the industrial services market continues to see companies vying for contracts to maintain operational efficiency. Bilfinger’s focus on sectors like energy and manufacturing means that fluctuations in project pipelines directly impact their ability to leverage their fixed asset base, intensifying the need to secure and execute contracts competitively.
Service Differentiation and Switching Costs
Bilfinger SE differentiates itself by offering highly customized services that span the entire value chain for its clients, with a strong emphasis on operational efficiency and sustainability. This tailored approach, often involving specialized engineering expertise or integrated digital solutions, makes it harder for competitors to directly replicate their offerings.
The company's strategy aims to build strong customer relationships, thereby increasing switching costs. When clients rely on Bilfinger's integrated solutions or specialized knowledge, moving to a competitor can be complex and expensive, involving significant disruption and potential loss of expertise. This differentiation and the associated switching costs serve to lessen the intensity of direct price competition.
- Customized Service Delivery: Bilfinger provides bespoke solutions across the entire asset lifecycle, from planning and engineering to maintenance and upgrades.
- Focus on Efficiency and Sustainability: The company's services are designed to optimize operational performance and promote environmentally responsible practices for its clients.
- Digital Integration: Advanced digital applications and platforms are leveraged to enhance service delivery, data analytics, and client collaboration.
- High Switching Costs: The complexity and integration of Bilfinger's services create barriers for clients looking to change providers, fostering customer loyalty.
Exit Barriers
Bilfinger SE, like many in the industrial services sector, faces significant exit barriers that can prolong competitive intensity. These barriers often include highly specialized assets, such as large-scale fabrication facilities or specialized machinery, which have limited alternative uses and are difficult to sell off without substantial depreciation. For instance, companies heavily invested in specific infrastructure maintenance or construction projects might find their equipment tied to long-term contracts or designed for niche applications, making divestment costly.
Contractual obligations also play a crucial role. Bilfinger often engages in multi-year service agreements and complex project commitments. Exiting these contracts prematurely can incur substantial penalties, legal fees, and reputational damage, effectively locking companies into existing market positions even when they are no longer profitable. Severance costs for a large, skilled workforce, particularly in specialized technical roles, add another layer of financial disincentive to exit.
These high exit barriers mean that even struggling competitors may remain in the market, fighting for survival. This can lead to intensified rivalry, particularly through aggressive pricing strategies as companies try to maintain revenue streams and cover fixed costs. For example, in 2024, the industrial services market saw instances of price erosion in certain segments as companies sought to secure contracts, even at lower margins, to avoid the high costs associated with ceasing operations.
- Specialized Assets: Difficulty in repurposing or selling unique, industry-specific equipment.
- Contractual Commitments: Penalties and reputational risks associated with early termination of long-term service agreements.
- Employee Severance: Significant costs related to laying off a specialized and experienced workforce.
- Market Stalemate: Unprofitable firms remaining active due to exit costs, leading to sustained price competition.
Competitive rivalry within the industrial services sector is intense, driven by a fragmented market with numerous global and niche players. Companies like Arcadis, GEA, Wood, Jacobs Solutions, Worley, and Siemens Global are significant rivals, possessing substantial resources and established client bases.
High fixed costs associated with specialized equipment and skilled labor necessitate high capacity utilization, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies, especially during softer demand periods. For instance, in 2024, the market continues to see companies competing fiercely for contracts to maintain operational efficiency and cover overheads.
Bilfinger SE differentiates itself through customized service delivery, a focus on efficiency and sustainability, and digital integration, which aims to increase switching costs for clients. However, high exit barriers, including specialized assets and contractual obligations, can keep even struggling competitors in the market, prolonging competitive pressures.
| Competitor | Approximate 2023 Revenue (USD Billion) | Key Service Areas |
| Jacobs Solutions | 16.6 | Advanced Facilities, Buildings, Infrastructure, Energy, Water |
| Worley | N/A (Part of Worley Ltd.) | Energy, Chemicals, Resources,ectors |
| Siemens Global | N/A (Part of Siemens AG) | Automation, Digitalization, Electrification, Energy |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers possessing robust in-house resources and skilled personnel might choose to handle specific industrial services internally, bypassing external providers like Bilfinger. This capability acts as a direct substitute, especially for more straightforward maintenance, repair, or less intricate engineering projects.
For instance, a large manufacturing firm with a dedicated engineering department and a history of managing its own plant upkeep can reduce its reliance on third-party service providers. This trend was evident in 2024 as many companies focused on optimizing operational costs, leading some to re-evaluate outsourcing decisions for non-core but essential technical functions.
Emerging technologies like advanced automation, AI-powered predictive maintenance, and digital twins present a significant threat of substitutes for Bilfinger SE's traditional service models. These innovations can potentially reduce the reliance on manual, on-site interventions, thereby offering alternative solutions to clients seeking efficiency and cost savings.
For instance, a client might opt for a predictive maintenance solution that uses IoT sensors and AI algorithms to anticipate equipment failures, thereby reducing the need for Bilfinger's routine inspection and repair services. This shift could impact revenue streams if Bilfinger doesn't adequately adapt its service portfolio to incorporate these advanced technological offerings.
Customers increasingly seek to unbundle services, opting for specialized providers for individual needs rather than Bilfinger's integrated value chain. For instance, a manufacturing plant might contract a separate firm for routine maintenance instead of engaging Bilfinger for a comprehensive asset management solution. This trend suggests a growing threat from less comprehensive, yet potentially cheaper, alternative service packages.
Changes in Regulatory Environment or Industry Standards
Changes in the regulatory landscape or industry standards can significantly impact the threat of substitutes for Bilfinger SE. For instance, stricter environmental regulations or new safety protocols could make existing, less compliant technologies or service providers less attractive, potentially driving demand towards newer, more sustainable alternatives that Bilfinger may not currently specialize in.
New regulations or evolving industry standards might favor alternative solutions or technologies that fall outside Bilfinger's current core competencies, thereby increasing the attractiveness of substitute offerings. For example, if new building codes mandate specific energy efficiency standards that are more easily met by prefabricated modular construction rather than traditional on-site building methods, this would elevate the threat of substitutes.
Consider the impact of evolving digital standards in industrial maintenance. If industry-wide adoption of predictive maintenance platforms powered by AI becomes the norm, and Bilfinger's current offerings are less integrated with such advanced digital solutions, companies might opt for specialized digital service providers as substitutes for comprehensive maintenance packages.
In 2024, the European Union's continued focus on sustainability and circular economy principles, as seen in initiatives like the Green Deal, could spur the development and adoption of substitute materials and construction methods. This might affect Bilfinger's traditional engineering and construction services if alternative, more eco-friendly approaches gain significant traction, potentially impacting their market share in specific segments.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The perceived cost-effectiveness of alternative solutions significantly impacts the threat of substitutes for Bilfinger SE. If clients can achieve similar outcomes through in-house capabilities or by adopting different technologies at a lower overall expense, the pressure from substitutes increases.
For instance, if a client can develop a proprietary software solution for asset management that is cheaper than Bilfinger's outsourced services, this represents a direct substitute. The key consideration is whether the substitute offers comparable quality and reliability for the price.
- Cost Comparison: Customers will weigh the total cost of ownership for Bilfinger's services against the cost of implementing and maintaining in-house or alternative solutions.
- Value Proposition: The perceived value of Bilfinger's offerings, including expertise, efficiency, and risk reduction, must be demonstrably superior to justify a higher cost compared to substitutes.
- Technological Advancements: Emerging technologies that simplify complex processes or automate tasks previously handled by service providers like Bilfinger can lower the cost-effectiveness of substitutes.
- Market Trends: A general trend towards digitalization and automation across industries can make alternative, often technology-driven, solutions more appealing and cost-effective for clients.
The threat of substitutes for Bilfinger SE stems from clients' ability to perform services internally or adopt alternative technologies. In 2024, many companies focused on cost optimization, leading some to re-evaluate outsourcing, potentially bringing services in-house. Advanced automation and AI-powered predictive maintenance also offer viable alternatives to traditional on-site services, reducing the need for manual interventions.
Clients increasingly unbundle services, opting for specialized providers for specific needs rather than comprehensive solutions. For example, a manufacturing plant might contract a separate firm for routine maintenance instead of a full asset management package from Bilfinger. This trend highlights the growing appeal of less comprehensive, potentially more affordable, alternative service packages.
The perceived cost-effectiveness of substitutes is a key driver. If clients can achieve similar outcomes through in-house capabilities or alternative technologies at a lower expense, the pressure on Bilfinger increases. For instance, developing proprietary software for asset management could be a cheaper alternative to Bilfinger's outsourced services, provided it offers comparable quality and reliability.
Emerging technologies like AI and IoT are lowering the cost-effectiveness of substitutes. For example, a 2024 report by McKinsey indicated that AI adoption in industrial operations could lead to significant cost savings, making in-house AI solutions more competitive against traditional service providers.
| Substitute Type | Client Action | Impact on Bilfinger | 2024 Trend Indicator | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-house capabilities | Performing services internally | Reduced demand for Bilfinger's core services | Focus on operational cost optimization | Large manufacturing firm managing own plant upkeep |
| Advanced Automation/AI | Implementing predictive maintenance | Decreased need for routine inspections and repairs | Growth in industrial IoT adoption | AI-driven equipment failure prediction |
| Specialized Providers | Unbundling services | Loss of integrated service revenue | Increased outsourcing of niche tasks | Contracting separate firm for routine maintenance |
| Digital Solutions | Developing proprietary software | Competition on cost and customization | Rise of bespoke digital platforms | In-house asset management software |
Entrants Threaten
Entering Bilfinger SE's industrial services sector, particularly for integrated offerings like engineering, maintenance, and large-scale project management, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in specialized machinery, advanced digital technologies, and the recruitment and training of a highly skilled workforce, presenting a formidable barrier for potential newcomers.
Existing players like Bilfinger SE leverage significant economies of scale, meaning their large operational footprint allows for lower per-unit costs in areas like procurement and project management. For instance, in 2024, Bilfinger's substantial backlog across diverse sectors provided a stable revenue base to absorb fixed costs more effectively than a new entrant could. This scale translates directly into a competitive pricing advantage.
Furthermore, Bilfinger benefits from economies of scope by offering a broad spectrum of integrated services, from engineering and maintenance to digital solutions, across multiple industries such as energy and infrastructure. This diversification allows for shared resources and expertise, reducing overall operational costs and creating bundled value propositions that are difficult for new, specialized entrants to replicate. A new competitor would face immense challenges in building a similarly comprehensive and cost-efficient service portfolio.
Bilfinger SE benefits from deeply entrenched, long-term relationships with major industrial clients, built on a foundation of proven safety and quality performance. Newcomers struggle to replicate this trust and secure vital contracts in an industry where established connections are paramount.
Gaining access to established distribution channels and the customer loyalty Bilfinger enjoys presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. These established relationships are not easily bypassed, requiring substantial investment and time to cultivate.
Proprietary Technology and Expertise
Bilfinger SE's competitive advantage is significantly bolstered by its proprietary technology and deep industry expertise, particularly in specialized engineering, environmental solutions, and digital applications. For instance, Bilfinger's advanced digital platforms, like its predictive maintenance solutions, require substantial investment in research and development, creating a considerable hurdle for potential new entrants. The company's commitment to innovation is reflected in its 2023 R&D expenditure, which supported the development of these unique offerings.
The high cost and time required to develop comparable proprietary technology, coupled with the necessity of accumulating extensive industry-specific knowledge and a highly skilled workforce, act as significant barriers. Newcomers would face immense challenges in replicating Bilfinger's established technological capabilities and the tacit knowledge embedded within its experienced personnel, thereby limiting the threat of new entrants.
- Proprietary Technology: Bilfinger's specialized engineering, environmental technologies, and digital applications are difficult for new firms to replicate.
- Industry Expertise: The company possesses deep, accumulated knowledge and a skilled workforce that new entrants would struggle to match.
- High Barriers to Entry: Developing comparable technology and expertise requires substantial investment and time, deterring new competition.
- Digitalization Focus: Bilfinger's investment in digital solutions, such as predictive maintenance, further entrenches its market position.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and stringent regulations significantly impact the threat of new entrants for Bilfinger SE. Sectors Bilfinger operates in, such as energy, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals, are heavily regulated, demanding substantial investment in compliance and operational standards. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to enforce rigorous environmental directives like the Industrial Emissions Directive, which requires significant capital expenditure for new facilities to meet emission reduction targets.
These regulatory barriers are not uniform across all markets. While some regions might have established frameworks, others are evolving, presenting both challenges and opportunities for new players. Navigating complex permitting processes, safety certifications, and environmental impact assessments can deter potential entrants due to the time, cost, and expertise required.
Key regulatory aspects that act as barriers include:
- Safety Standards: Adherence to stringent safety protocols, especially in hazardous environments like chemical plants or offshore energy platforms, necessitates specialized training and equipment, increasing initial setup costs.
- Environmental Compliance: Meeting emissions targets, waste management regulations, and sustainability reporting requirements, such as those outlined in the EU's Green Deal initiatives, adds considerable operational complexity and financial burden.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Obtaining necessary licenses and certifications for specialized services, like those in the nuclear or pharmaceutical sectors, can be a lengthy and costly process, limiting the pool of qualified new entrants.
- Local Content Requirements: In certain geographies, governments mandate a certain percentage of local labor or materials, which can complicate supply chains and increase costs for international firms looking to enter the market.
The threat of new entrants for Bilfinger SE is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for specialized equipment and a highly skilled workforce. Economies of scale and scope, coupled with established client relationships and proprietary technology, create significant barriers. Furthermore, stringent government regulations and industry-specific certifications add further complexity and cost for potential newcomers.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bilfinger SE is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Bilfinger's annual reports, investor presentations, and official press releases. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry analysis firms and relevant market research databases to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
