Beyond Meat Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Beyond Meat Bundle
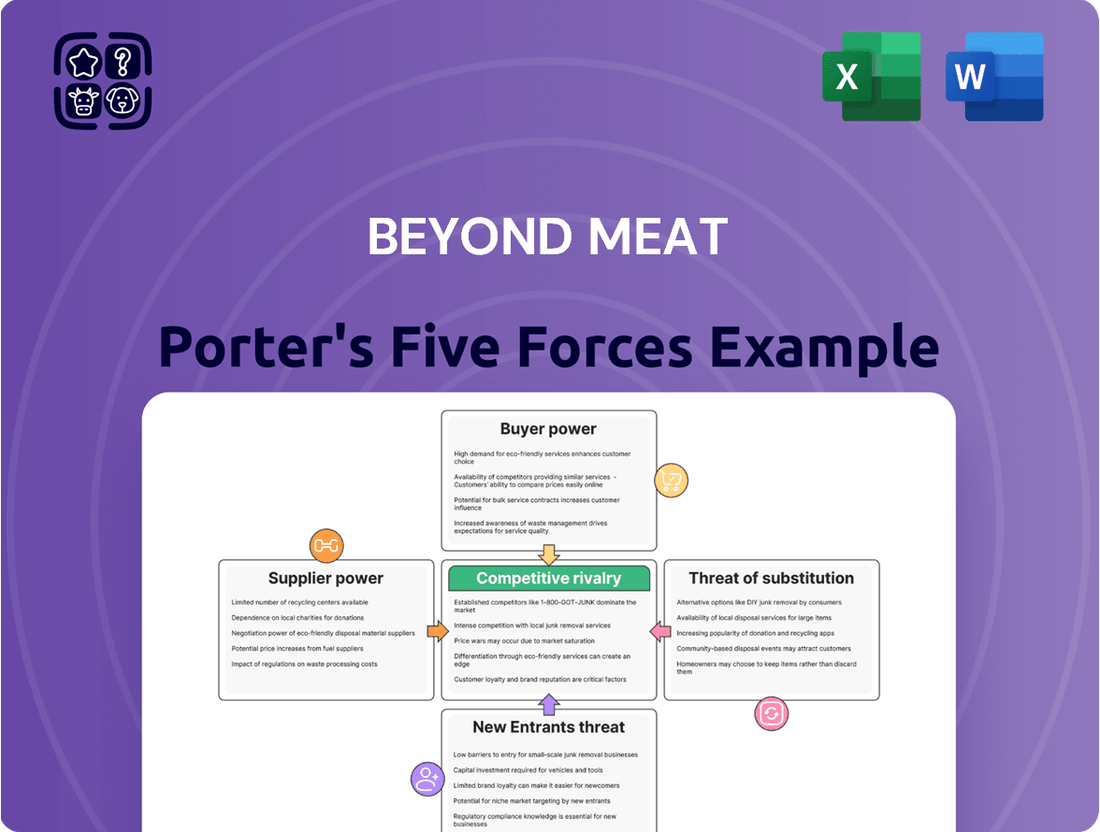
Beyond Meat faces significant competitive rivalry, with established meat producers and emerging plant-based alternatives vying for market share. The threat of new entrants is moderate, as the high capital investment and brand recognition required present barriers, yet the growing demand for plant-based options attracts new players. Buyer power is substantial, as consumers have numerous choices and are price-sensitive.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Beyond Meat’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Beyond Meat's reliance on specific plant-based protein sources, such as peas, brown rice, red lentils, and fava beans, makes it susceptible to the bargaining power of its suppliers. If the market for these specialized ingredients becomes consolidated, with only a few dominant players, these suppliers can exert significant influence over Beyond Meat. This concentration limits Beyond Meat's ability to negotiate favorable terms, potentially leading to increased costs or restricted access to essential raw materials, impacting production and profitability.
Beyond Meat faces significant switching costs when changing ingredient suppliers, a factor that amplifies supplier bargaining power. These costs encompass not only the financial outlay for re-formulating products and conducting rigorous quality and safety re-testing but also the operational complexities of establishing entirely new supply chain logistics. For instance, a shift could require extensive R&D investment, potentially delaying product launches and impacting market responsiveness.
Should key ingredient suppliers, such as those providing pea protein or specialized flavorings, decide to enter the plant-based meat market directly, they would immediately transform from mere suppliers into direct competitors to Beyond Meat. This capability for forward integration significantly enhances their bargaining power, as they could credibly threaten to withhold essential inputs or, more directly, vie for market share with their own branded plant-based meat products.
While this threat is less pronounced for suppliers of basic, widely available commodities, it becomes a critical strategic consideration when dealing with providers of proprietary or highly specialized ingredients crucial to Beyond Meat's product formulation and differentiation. For instance, a supplier of a unique texturizing agent, if they possess the capital and market insight, could leverage their existing production capabilities to launch a competing line of plant-based burgers.
Uniqueness and Importance of Ingredients
The uniqueness of certain ingredients significantly influences supplier bargaining power. Beyond Meat's advanced formulations, like those in its Beyond IV platform, which incorporate specific ingredients such as avocado oil and a proprietary blend of fava bean and red lentil proteins, may necessitate specialized sourcing or processing from suppliers. This reliance on suppliers capable of meeting these unique specifications can elevate their leverage if these ingredients are difficult for Beyond Meat to replicate elsewhere, directly impacting product consistency and taste.
When a supplier offers a highly distinctive or superior quality ingredient that is challenging to substitute, their bargaining power naturally strengthens. This situation can make companies like Beyond Meat more dependent on these specific suppliers to uphold the desired quality and flavor profiles of their plant-based products. For instance, in 2023, the global plant-based food market was valued at approximately $37.1 billion, highlighting the competitive landscape where ingredient quality is paramount.
- Ingredient Specialization: Suppliers providing unique protein blends or specialized oils for plant-based meat alternatives can command higher prices due to their specialized capabilities.
- Quality Dependence: Beyond Meat's commitment to replicating the taste and texture of traditional meat means a reliance on suppliers who can consistently deliver high-quality, specific ingredients.
- Limited Substitutability: If a supplier's ingredient is proprietary or has undergone significant development for Beyond Meat, finding an alternative supplier with the same quality and consistency can be difficult, increasing the original supplier's power.
Volume of Purchases by Beyond Meat
Beyond Meat's purchasing volume significantly influences its bargaining power with suppliers. If Beyond Meat represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier has a vested interest in maintaining the relationship, potentially leading to more favorable terms for Beyond Meat. Conversely, if Beyond Meat's orders are a small fraction of a supplier's total sales, the supplier may feel less pressure to negotiate on price or other conditions.
The burgeoning plant-based ingredient market, with its increasing number of suppliers, also plays a role. As more suppliers enter the market and diversify their customer base, their reliance on any single buyer, including Beyond Meat, may diminish. This market dynamic could shift the balance of power, potentially reducing Beyond Meat's leverage if suppliers can easily find alternative buyers for their products.
For instance, in 2023, the global plant-based food market was valued at approximately $50 billion, with projections indicating continued strong growth. This expansion means suppliers of key ingredients like pea protein, a staple for Beyond Meat, likely have multiple avenues for sales. Beyond Meat's specific purchasing volume relative to these suppliers' overall capacity and customer portfolio is crucial in determining the extent of their bargaining power.
- Beyond Meat's share of a supplier's revenue: A larger share typically reduces supplier power.
- Supplier's overall customer diversification: More diverse customer bases can decrease reliance on Beyond Meat.
- Growth in the plant-based ingredient market: This expansion offers suppliers alternative sales channels.
- 2023 global plant-based food market valuation: Approximately $50 billion, indicating a competitive supplier landscape.
Suppliers of specialized plant-based ingredients, such as pea protein isolates, can wield significant bargaining power over Beyond Meat. This is particularly true when these ingredients are proprietary or have complex production processes, limiting readily available alternatives. For example, the demand for pea protein, a key component in Beyond Meat's products, has surged, potentially increasing supplier leverage if production capacity is constrained.
Beyond Meat's reliance on a few key suppliers for critical ingredients like pea protein and specialized oils means these suppliers can influence pricing and terms. If these suppliers face production issues or decide to prioritize other customers, Beyond Meat could experience supply disruptions. The global plant-based food market's growth, projected to reach significant figures by 2025, intensifies competition for these vital ingredients.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified by the potential for forward integration, where suppliers could launch their own competing plant-based meat products. This threat is more pronounced for suppliers of unique or proprietary ingredients that are integral to Beyond Meat's product differentiation and quality. For instance, a supplier of a unique texturizing agent could leverage their expertise and production capabilities to enter the market directly.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Relevance to Beyond Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Specialization | High | Beyond Meat relies on specific protein sources and flavorings. |
| Supplier Concentration | Moderate to High | Limited number of large-scale producers for certain ingredients. |
| Switching Costs | High | Reformulation and re-testing are costly and time-consuming. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Moderate | Potential for ingredient suppliers to become competitors. |
| Market Growth | Increasing | Growing demand for plant-based ingredients benefits suppliers. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Beyond Meat dissects the competitive landscape, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the plant-based meat industry.
Navigate the competitive landscape of plant-based meats with a clear, actionable analysis of Beyond Meat's Porter's Five Forces, identifying key pressures and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Consumers, especially those with tighter budgets or feeling the pinch of inflation, are very aware of the cost of plant-based meat. Beyond Meat's products have often been positioned as a premium choice, and any further price hikes, like those potentially seen with their Beyond IV platform, could make budget-minded shoppers look elsewhere.
This price sensitivity gives customers significant leverage. They can readily switch to more affordable plant-based options or simply revert to traditional meat, which can sometimes be cheaper, putting pressure on Beyond Meat to remain competitive on price.
The availability of diverse substitutes significantly empowers customers in the plant-based meat market, directly impacting Beyond Meat. Consumers have a plethora of choices, ranging from direct competitors like Impossible Foods and Gardein to private label store brands and even unprocessed plant-based staples such as tofu and lentils.
This wide array of alternatives means customers are not locked into Beyond Meat. They can easily switch to a different brand or product if they find a better price, taste, or nutritional profile, thereby diminishing Beyond Meat's ability to dictate terms and increasing customer bargaining power.
For the average consumer, the decision to switch from Beyond Meat to another plant-based brand or even back to traditional meat involves very little cost or effort. This ease of transition significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the plant-based meat market continued to see new entrants, offering consumers a wider variety of choices and further reducing any perceived switching costs.
Declining Consumer Demand in Key Markets
Declining consumer demand in key markets significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers for companies like Beyond Meat. The U.S. plant-based meat retail sales saw a downturn in 2024, a trend that continued into 2025. Beyond Meat itself reported weak category demand and a volume decrease in Q1 2025, signaling a market contraction. This reduced enthusiasm means customers hold more sway, pushing brands to improve value, taste, and health propositions.
This shift in market dynamics translates directly into increased customer leverage. With fewer consumers actively seeking plant-based alternatives, brands must work harder to attract and retain them. This necessitates a stronger focus on product quality and competitive pricing, as customers are less likely to tolerate perceived shortcomings when alternatives are readily available and consumer interest is waning.
- U.S. plant-based meat retail sales declined in 2024.
- Beyond Meat reported weak category demand in Q1 2025.
- Volume of Beyond Meat products sold decreased in Q1 2025.
- Market contraction empowers customers to demand better value and product attributes.
Leverage of Retail and Foodservice Channels
Large retail chains and foodservice providers represent critical avenues for Beyond Meat's products. These significant customers, purchasing in substantial quantities, possess considerable leverage. They can heavily influence everything from where Beyond Meat's products appear on shelves to their final pricing and promotional strategies.
This power means that decisions made by these major buyers can directly shape Beyond Meat's sales figures and overall market presence. For instance, if a major supermarket chain decides to reduce shelf space for plant-based alternatives, it could significantly impact Beyond Meat's visibility and revenue.
- Distribution Dependence: Beyond Meat relies heavily on major retailers like Walmart and Kroger, as well as foodservice giants like McDonald's and Burger King, for market access.
- Volume Purchases: These large customers buy in massive volumes, giving them substantial negotiating power over pricing and terms.
- Channel Control: Retailers and foodservice companies control shelf space, menu placement, and promotional opportunities, which are vital for Beyond Meat's success.
- Alternative Sourcing: Buyers can easily switch to competing plant-based brands or even conventional meat products if Beyond Meat's terms are not favorable.
Customers wield significant power in the plant-based meat market due to price sensitivity and the abundance of substitutes. Beyond Meat's premium positioning can be a disadvantage, especially with inflation impacting consumer budgets. In 2024, U.S. plant-based meat retail sales saw a decline, a trend that continued into early 2025, with Beyond Meat reporting weak category demand and a volume decrease in Q1 2025. This market contraction further empowers consumers to demand better value and product attributes, as they can easily switch to more affordable options or traditional meat.
| Factor | Impact on Beyond Meat | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High customer leverage due to premium pricing. | Inflationary pressures in 2024-2025 make consumers more cost-conscious. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low switching costs for customers. | Numerous competitors (Impossible Foods, Gardein) and unprocessed options (tofu, lentils) offer easy alternatives. |
| Declining Demand | Increased customer bargaining power. | U.S. plant-based meat retail sales declined in 2024; Beyond Meat saw weak category demand and volume decrease in Q1 2025. |
| Buyer Concentration | Major retailers and foodservice providers have substantial influence. | These large customers control shelf space, pricing, and promotions, impacting Beyond Meat's market access and terms. |
Same Document Delivered
Beyond Meat Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the identical Beyond Meat Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring complete transparency. You're viewing the actual, professionally compiled document, meaning no placeholder content or altered versions will be delivered. Once your transaction is complete, you'll gain instant access to this comprehensive analysis, ready for immediate use and application.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The plant-based meat arena is teeming with competitors, ranging from dedicated startups to massive, established food conglomerates. This crowded field means companies like Beyond Meat are constantly vying for consumer attention and shelf space.
Direct rivals such as Impossible Foods are significant players, but the competition also comes from industry titans like Nestlé, Tyson Foods, Kellogg's, Conagra, and Maple Leaf Foods, all of whom have launched their own plant-based product lines. In 2024, the plant-based meat market continued to see substantial investment and product introductions from these diverse entities, intensifying the battle for market share.
The plant-based meat market, while still showing global growth potential, faced a significant hurdle in the U.S. retail sector during 2024, with sales experiencing a downturn. This contraction in a key market directly fuels competitive rivalry.
Beyond Meat itself felt this pressure, reporting year-over-year revenue declines in its first quarter of 2025. Such a slowdown intensifies competition as companies fight harder for a shrinking or stagnant customer base, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies and increased marketing spend.
Beyond Meat, like many players in the plant-based meat industry, faces intense rivalry stemming from substantial fixed costs. Significant investments in manufacturing plants and ongoing research and development for new products create a high cost base. For instance, the company has invested heavily in scaling its production capabilities, which translates to considerable overheads that need to be covered.
This financial reality pressures companies to maintain high production volumes and achieve economies of scale. To drive sales and cover these fixed costs, there's a constant push for market share, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies and promotional campaigns. This dynamic makes exiting the market difficult, even for underperforming companies, thereby intensifying the competitive landscape.
Continuous Product Innovation and Differentiation
Competitive rivalry in the plant-based meat sector is intense, driven by continuous product innovation and differentiation. Companies are racing to improve taste, texture, and nutritional content, while also introducing novel product formats to capture consumer interest.
Beyond Meat has been a key player in this innovation race, releasing new formulations like Beyond IV and expanding its product line with items such as the Beyond Sun Sausage. This rapid development cycle intensifies competition as firms vie for market share by offering superior or more appealing plant-based alternatives.
- Beyond Meat's Q1 2024 revenue reached $73.7 million, highlighting ongoing sales despite competitive pressures.
- The plant-based meat market is projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated $165.0 billion by 2030, according to various market research reports, fueling further innovation and competition.
- Competitors like Impossible Foods and others are also heavily investing in R&D to enhance their product offerings, creating a dynamic environment where staying ahead requires constant improvement.
Strategic Pricing and Marketing Battles
The plant-based meat sector is characterized by intense strategic pricing and marketing skirmishes. Beyond Meat, for instance, has navigated a complex pricing strategy, sometimes targeting a premium market segment while simultaneously facing significant pressure to match the price points of conventional meat products. This dynamic is further amplified by competitors' substantial investments in broad marketing initiatives.
These marketing efforts are designed to influence consumer perceptions, focusing on key attributes like health benefits, environmental sustainability, and taste profiles. The ongoing battle for consumer mindshare contributes significantly to the overall competitive intensity within the industry. For example, in 2023, Beyond Meat reported net revenues of $343.1 million, and a significant portion of its strategy involves communicating its value proposition through these marketing channels to justify its pricing structure against both established meat producers and emerging plant-based alternatives.
- Pricing Adjustments: Beyond Meat has experimented with pricing, aiming for premium positioning but also working towards price parity with traditional meat.
- Marketing Intensity: Competitors heavily invest in marketing to shape consumer views on health, sustainability, and taste.
- Competitive Pressure: These marketing and pricing battles increase the overall competitive rivalry in the plant-based meat market.
The plant-based meat market is highly competitive, with numerous players ranging from startups to large food corporations. This intense rivalry is fueled by continuous product innovation, aggressive marketing, and strategic pricing as companies battle for market share. For example, Beyond Meat reported net revenues of $343.1 million in 2023, underscoring the significant market presence and competitive efforts within the sector.
The presence of established food giants like Nestlé, Tyson Foods, and Conagra, alongside dedicated plant-based companies such as Impossible Foods, intensifies competition. This crowded landscape means companies must constantly innovate to differentiate their offerings and capture consumer attention. The U.S. retail sector experienced a sales downturn in 2024, further heightening the competitive pressure as companies fight for a potentially shrinking customer base.
Beyond Meat's Q1 2024 revenue of $73.7 million demonstrates the ongoing sales activity despite these competitive pressures. The market's projected growth to an estimated $165.0 billion by 2030 also attracts further investment and innovation, ensuring rivalry remains a defining characteristic of the industry.
| Competitor Type | Examples | 2024 Market Dynamics |
| Dedicated Plant-Based Startups | Impossible Foods | Continued R&D investment, product differentiation |
| Established Food Conglomerates | Nestlé, Tyson Foods, Kellogg's, Conagra, Maple Leaf Foods | Launching new plant-based lines, leveraging existing distribution |
| Beyond Meat's Performance | Q1 2024 Revenue: $73.7 million; 2023 Net Revenue: $343.1 million | Navigating pricing strategies, facing revenue declines |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The enduring strength of traditional animal meat presents a significant threat of substitution for plant-based alternatives like Beyond Meat. Consumers are deeply accustomed to animal meat, with established culinary practices and a strong sense of familiarity acting as powerful deterrents to switching. In 2024, despite the growth in plant-based options, the global meat market, encompassing beef, pork, and poultry, still represents a colossal industry, far outstripping the plant-based meat sector in sheer volume and consumer penetration. This deep-rooted preference, often coupled with price advantages for conventional meat, makes it a formidable substitute.
Consumers increasingly opt for whole, minimally processed plant-based foods like lentils, beans, tofu, and tempeh as protein sources. These are often viewed as healthier and more affordable alternatives to highly processed plant-based meats. For example, the global market for plant-based foods, including whole foods, saw significant growth, with analysts projecting continued expansion through 2025.
The perceived 'cleaner label' of whole plant foods presents a significant threat of substitution for companies like Beyond Meat. Many consumers are actively seeking less processed options, making these readily available staples a direct competitor. Beyond Meat's own product development, such as their 'Beyond Ground' featuring simpler ingredients, reflects an acknowledgment of this consumer preference shift.
The rise of hybrid meat products, which combine plant-based proteins with traditional or cultivated meat, presents a significant threat of substitution for companies like Beyond Meat. These innovations cater to a wider audience, including flexitarians, by offering a less drastic reduction in meat consumption. For instance, in 2024, the plant-based meat market saw continued growth, with hybrid options gaining traction as consumers sought familiar tastes and textures.
Growth of Private Label Alternatives
The rise of private label plant-based meat products presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like Beyond Meat. Major grocery chains are expanding their own-brand offerings, often at lower price points. For instance, by early 2024, many supermarkets featured their store-brand plant-based burgers and sausages, directly competing with established brands.
These private label options are particularly appealing to budget-conscious consumers. Their competitive pricing, coupled with prominent placement in retail stores, allows them to capture market share swiftly. This trend intensifies the pressure on premium brands to justify their higher costs through innovation and brand loyalty.
- Retailer Private Label Expansion: Many grocery chains are actively developing and promoting their own plant-based meat alternatives.
- Price Competitiveness: Private label products are frequently priced below comparable offerings from national brands, attracting price-sensitive shoppers.
- Market Share Capture: The affordability and accessibility of private label substitutes can lead to rapid gains in market share, impacting established players.
- Consumer Value Perception: Consumers may perceive private label options as offering similar quality at a better value, shifting purchasing habits.
Future Threat from Other Alternative Proteins
The long-term threat from substitute proteins is a significant consideration for Beyond Meat. Emerging technologies such as cultivated (lab-grown) meat and insect-based proteins are on the horizon. As these alternatives progress through regulatory approvals and achieve greater production scale, they could offer consumers new choices for sustainable and ethical protein consumption.
These novel protein sources might eventually compete with plant-based options, potentially even surpassing them in certain consumer-preferred attributes like taste and texture mimicry. For instance, by 2025, the global cultivated meat market is projected to reach billions, indicating a growing investor and consumer interest in these next-generation proteins.
- Cultivated Meat: Aims to replicate the taste and texture of traditional meat without animal slaughter, offering a potential high-fidelity substitute.
- Insect-Based Proteins: Already gaining traction in some markets, insect proteins offer a highly sustainable and nutrient-dense alternative.
- Market Projections: The cultivated meat market is expected to see significant growth, with some forecasts placing its value in the tens of billions by the early 2030s, indicating a substantial future competitive landscape.
- Consumer Acceptance: While still developing, consumer acceptance of these novel proteins will be a key factor in their ability to displace existing plant-based options.
The most significant substitute threat for Beyond Meat stems from traditional animal meat. Consumers' deeply ingrained habits and preferences for familiar tastes and textures make switching a challenge. In 2024, the global meat market remained vastly larger than the plant-based sector, indicating the immense scale of this substitute. Additionally, the availability of whole, minimally processed plant foods like beans and lentils offers a healthier and more economical alternative, appealing to a growing segment of health-conscious consumers.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | 2024 Market Relevance | Threat Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Animal Meat | Familiar taste, texture, established culinary use | Dominant global market share, deeply entrenched consumer habits | High |
| Whole Plant Foods (Legumes, Tofu) | Healthier, unprocessed, cost-effective | Growing consumer preference for 'clean labels', accessible and affordable | Medium-High |
| Hybrid Meat Products | Combines plant and animal/cultivated meat | Appeals to flexitarians, offers familiar attributes | Medium |
| Private Label Plant-Based | Lower price point, retailer-driven | Increasing availability and promotion by major grocers | Medium |
| Cultivated & Insect Proteins | Novel, sustainable, potential for high-fidelity mimicry | Emerging technologies, growing investment and research | Low to Medium (Future) |
Entrants Threaten
Developing and scaling plant-based meat alternatives that closely mimic the taste and texture of traditional meat demands considerable upfront investment. This includes substantial spending on research and development to perfect formulations, building specialized manufacturing plants, and establishing robust supply chains for unique ingredients. For instance, companies entering this space often face millions in capital expenditure just to set up pilot production lines.
Beyond Meat, alongside early movers like Impossible Foods, has poured significant resources into cultivating brand recognition and a loyal customer following since its launch. New companies entering the plant-based meat market must contend with this established presence and the difficulty of winning over consumers who already have preferred brands, though Beyond Meat's recent sales downturn indicates that this loyalty isn't absolute.
Securing widespread distribution is a significant hurdle for new entrants in the plant-based meat sector. Beyond Meat, for instance, has cultivated relationships with major grocery chains and fast-food giants over years, creating a formidable barrier. In 2023, the plant-based food market experienced a slowdown, with sales declining by 2.4% according to the Plant Based Foods Association, making it even harder for newcomers to displace established brands from prime shelf space or gain traction with key foodservice partners.
Technological and R&D Expertise
The significant investment in food science and proprietary formulations needed to replicate meat's sensory attributes presents a substantial hurdle for new entrants. Beyond Meat, for instance, has invested heavily in R&D to perfect its plant-based burger, which requires complex ingredient interactions and processing techniques. This technological know-how is difficult and expensive to replicate, acting as a barrier.
New competitors face the challenge of either developing this specialized expertise internally, a process that demands considerable time and financial resources, or acquiring it through costly mergers or acquisitions. For example, the plant-based meat market saw significant venture capital funding in 2023, with companies raising hundreds of millions to bolster their R&D capabilities and market entry strategies.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by the high entry costs associated with developing and maintaining advanced technological and R&D capabilities in the plant-based protein sector. Companies must demonstrate a commitment to innovation, as seen in the ongoing patent filings for novel plant-based ingredients and processing methods, to effectively compete.
- High R&D Investment: Replicating meat's taste and texture demands significant capital expenditure on food science and proprietary formulations.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: Securing specialized food scientists and researchers is competitive and expensive, increasing operational costs for newcomers.
- Proprietary Formulations: Unique ingredient blends and processing methods, often patented, create a competitive advantage that is hard for new entrants to match.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape and Labeling Challenges
The threat of new entrants in the plant-based meat sector is significantly influenced by an evolving regulatory landscape, particularly concerning labeling. As of early 2024, various regions are enacting or considering 'Truth-in-Labeling' laws. These regulations aim to restrict the use of traditional meat terms like 'burger' or 'sausage' for plant-based alternatives, creating compliance challenges.
Navigating these complex and often inconsistent regulations across different markets presents a substantial barrier. New companies must invest in understanding and adhering to these varying rules, which can be costly and time-consuming. For instance, some U.S. states have introduced legislation to define terms like 'meat' and 'plant-based meat,' potentially limiting marketing claims for new entrants.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Ongoing changes in labeling laws create an unpredictable environment for new companies.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to diverse 'Truth-in-Labeling' requirements across jurisdictions adds significant operational expenses.
- Marketing Restrictions: Limitations on using familiar meat-related terminology can hinder brand recognition and consumer appeal for new market entrants.
The threat of new entrants into the plant-based meat market is currently moderate. While the market shows promise, significant capital investment is required for research and development to replicate meat's taste and texture, alongside building specialized manufacturing and supply chains. For instance, pilot production lines alone can cost millions in capital expenditure.
Established brands like Beyond Meat have already invested heavily in brand recognition and distribution networks, making it challenging for newcomers to gain consumer loyalty and secure shelf space. The plant-based food market saw a 2.4% sales decline in 2023, further complicating market entry for new players.
Proprietary formulations and the expertise to create them are difficult and expensive to replicate, acting as a technological barrier. Companies entering this space often need to secure substantial venture capital, as seen with hundreds of millions raised in 2023, to bolster their R&D and market entry strategies.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High | Millions in CAPEX for pilot production; hundreds of millions in VC funding raised in 2023. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Challenging | Established players have strong brand recognition and distribution; 2.4% sales decline in plant-based foods in 2023. |
| Technological Expertise | Significant Barrier | Complex R&D for taste/texture replication; proprietary formulations are hard to match. |
| Regulatory Landscape | Moderate Barrier | Evolving 'Truth-in-Labeling' laws create compliance costs and marketing restrictions. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Beyond Meat leverages a comprehensive dataset including Beyond Meat's SEC filings, investor relations materials, and reports from leading market research firms like Nielsen and Mintel. This approach ensures a robust understanding of the competitive landscape, from supplier power to the threat of new entrants.
