Bendigo & Adelaide Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bendigo & Adelaide Bank Bundle
Bendigo & Adelaide Bank operates within a dynamic financial landscape, facing significant competitive pressures from established banks and emerging fintechs. Understanding the intensity of rivalry and the threat of new entrants is crucial for their strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Bendigo & Adelaide Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's depositor funding strength is a key factor in its bargaining power. With a robust household deposit to loan ratio of 73%, significantly exceeding the major bank average, the bank enjoys a stable and less volatile funding structure. This solid base reduces its dependence on potentially more unpredictable wholesale funding markets.
However, this advantage is tempered by increasing consumer awareness of interest rates. As depositors actively compare offerings, Bendigo and Adelaide Bank faces pressure to maintain competitive rates to secure and retain these essential funds, thus influencing the bargaining power of these depositors.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank, alongside other Australian banks, continues to leverage wholesale funding markets for essential liquidity and capital, even with a strong deposit base. This reliance means these markets exert significant influence on the bank's financial operations and costs.
The phasing out of the Reserve Bank of Australia's Term Funding Facility (TFF) in 2023 and 2024 directly impacted funding costs for the banking sector. For instance, the TFF provided a low-cost funding source, and its absence necessitated a shift to potentially more expensive wholesale alternatives, increasing the bargaining power of wholesale market providers.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's significant investment in its six-year digital transformation, including the Bendigo Lending Platform and new CRM systems, highlights its increasing reliance on technology and software providers. This strategic pivot underscores the growing bargaining power of these specialized suppliers.
The bank's commitment to enhancing digital capabilities means it depends on external vendors for critical IT services and proprietary software solutions. This dependence grants these providers leverage, particularly those offering unique or highly specialized technologies essential for the bank's operational efficiency and competitive edge in the evolving financial landscape.
Skilled Labor Force
The financial services industry, especially banking, relies heavily on a workforce with specialized skills. This includes expertise in crucial areas such as digital innovation, managing financial risks, and analyzing vast amounts of data. Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's reported increase in staff costs for the first half of FY25 highlights the intense competition for this talent.
This competitive environment for skilled professionals means that employees with in-demand capabilities possess significant bargaining power. They can negotiate for higher salaries, better benefits, and more attractive working conditions. For Bendigo and Adelaide Bank, this translates to a direct impact on operating expenses and the need for strategic human resource management to maintain a competitive edge.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: Areas like cybersecurity, AI in finance, and regulatory compliance are critical, driving up demand for qualified professionals.
- Increased Staff Costs: Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's first-half FY25 results showed a rise in staff expenses, reflecting the cost of attracting and retaining this skilled labor.
- Employee Negotiation Power: Skilled employees can leverage their expertise to secure better compensation packages and career development opportunities.
- Impact on Profitability: Higher labor costs can affect the bank's net interest margin and overall profitability if not managed effectively.
Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies, though not direct suppliers of goods or services, wield substantial influence over Bendigo & Adelaide Bank. Agencies like the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) and the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) dictate critical parameters such as capital adequacy ratios and prudential standards. For instance, APRA's ongoing focus on enhancing the resilience of the banking sector means banks must maintain robust capital buffers, directly impacting profitability and strategic choices.
These regulatory mandates significantly shape the bank's operational framework and cost structure. Compliance with evolving prudential standards, such as those related to cybersecurity and data privacy, necessitates ongoing investment in technology and risk management. This power is underscored by the fact that breaches can lead to substantial fines and reputational damage, limiting strategic flexibility.
The bargaining power of these regulatory bodies is high because they control the license to operate. Their decisions on capital requirements, for example, directly influence how much capital Bendigo & Adelaide Bank must hold. In 2024, APRA continued to emphasize strong capital positions, a trend expected to persist, meaning banks must constantly adapt their financial strategies to meet these demands.
- APRA's Capital Requirements: Directly impact Bendigo & Adelaide Bank's ability to lend and invest.
- RBA's Monetary Policy: Influences interest rates and overall economic conditions affecting the bank's balance sheet.
- Licensing and Prudential Standards: Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, limiting operational freedom.
- Ongoing Regulatory Evolution: Forces continuous adaptation and investment in compliance measures.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's reliance on technology providers for its digital transformation, including its new lending platform and CRM systems, grants these specialized suppliers significant bargaining power. This is particularly true for vendors offering unique or highly specialized technologies crucial for the bank's operational efficiency and competitive edge.
The intense competition for skilled financial professionals, evident in Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's increased staff costs in the first half of FY25, empowers employees with in-demand capabilities. These individuals can negotiate for higher salaries and better benefits, directly impacting the bank's operating expenses.
Regulatory bodies like APRA and the RBA hold substantial power over Bendigo and Adelaide Bank by dictating capital adequacy ratios and prudential standards. For instance, APRA's continued emphasis on strong capital positions in 2024 forces the bank to constantly adapt its financial strategies to meet these demands, limiting strategic flexibility.
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Bendigo & Adelaide Bank's position in the Australian banking sector.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, allowing Bendigo & Adelaide Bank to proactively address threats and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Historically, customers faced significant perceived effort when switching banks, which fostered strong loyalty. However, the advent of initiatives like the Consumer Data Right (CDR) is designed to lower these switching barriers.
By enabling easier data sharing, CDR empowers customers to explore and compare offers from different financial institutions, potentially increasing their propensity to switch for more advantageous terms.
Customers today are incredibly well-informed and actively monitor financial products. They readily compare interest rates for savings accounts and loans across various banks, thanks to readily available online tools and comparison websites. This heightened transparency significantly boosts their ability to negotiate for better pricing and terms, directly impacting Bendigo & Adelaide Bank.
The increasing availability of digital channels and services significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Customers can now easily compare offerings and switch providers with minimal friction, thanks to the proliferation of online platforms and mobile banking apps. This accessibility empowers them to seek the best rates and services across the market.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's strategic focus on digital innovation, exemplified by its growth in digital mortgages and the success of its 'Up' neobank brand, directly addresses this shift. These initiatives provide customers with more convenient and diverse ways to manage their finances, thereby increasing their options and bargaining leverage.
Sensitivity to Pricing and Service Quality
Customers in the banking sector are highly attuned to pricing, such as interest rates on loans and savings accounts, as well as account fees. Service quality also plays a crucial role in their decisions. For Bendigo and Adelaide Bank, maintaining high customer satisfaction, particularly among home loan customers, is vital for retaining market share and attracting new business.
In 2024, the Australian banking landscape remains competitive, with customers having numerous choices. This situation amplifies their bargaining power. For instance, a slight difference in home loan interest rates can sway a customer to switch banks. Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's commitment to customer trust and satisfaction is a strategic response to this dynamic, aiming to mitigate price sensitivity through superior service and relationship building.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers actively compare interest rates on mortgages, personal loans, and deposit accounts across different financial institutions.
- Service Quality Impact: Positive experiences with customer service, digital banking platforms, and branch interactions significantly influence customer loyalty and retention.
- Switching Costs: While switching banks can involve some effort, the potential for better rates or service often outweighs these costs for many customers.
- Reputation: A bank's reputation for trustworthiness and customer care can reduce price sensitivity, as customers may be willing to pay a slight premium for perceived reliability.
Impact of Financial Stress on Customer Behavior
Persistent inflation and elevated interest rates in 2024 have placed a strain on many households, leading to increased financial stress for some borrowers. This heightened sensitivity to repayment obligations means customers are more actively seeking out better deals and more favorable terms from their financial institutions.
This environment directly amplifies customer bargaining power. As individuals and businesses grapple with tighter budgets, they become more willing to switch providers if they can find lower interest rates, reduced fees, or more flexible repayment options. For instance, in early 2024, reports indicated a noticeable uptick in customers comparing mortgage offers, driven by the desire to lock in lower rates amidst ongoing rate uncertainty.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: Customers facing financial stress are more likely to prioritize lower costs when choosing financial products.
- Demand for Flexible Terms: Borrowers may seek out lenders offering more adaptable repayment schedules or hardship assistance programs.
- Switching Behavior: A greater willingness to switch banks or financial providers to secure more advantageous terms is evident.
- Focus on Value: Customers are scrutinizing the overall value proposition, including fees and service quality, more closely.
Customers in 2024 possess significant bargaining power due to increased price transparency and readily available comparison tools for financial products like home loans and savings accounts. This heightened awareness means even minor differences in interest rates or fees can drive customers to switch, directly impacting Bendigo & Adelaide Bank's customer retention efforts.
The ongoing digital transformation, including initiatives like the Consumer Data Right (CDR), further erodes switching costs, making it easier for customers to move between institutions. Bendigo & Adelaide Bank's investment in digital offerings, such as its 'Up' neobank, aims to meet this demand for convenience and choice, thereby influencing customer loyalty.
The economic climate of 2024, marked by persistent inflation and elevated interest rates, has amplified customer sensitivity to costs. This financial pressure makes customers more inclined to seek out better deals, increasing their willingness to switch providers for more favorable terms, such as lower mortgage rates or flexible repayment options.
| Factor | Impact on Bendigo & Adelaide Bank | 2024 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High, customers actively compare rates and fees. | Continued focus on mortgage rate competitiveness is crucial. |
| Switching Costs | Lowered by digital channels and CDR. | Digital mortgage applications and online account switching are common. |
| Information Availability | Customers are well-informed via comparison sites. | Online comparison tools for savings accounts and loans are widely used. |
| Service Quality Expectations | Crucial for retention, alongside price. | Customer satisfaction scores remain a key performance indicator. |
What You See Is What You Get
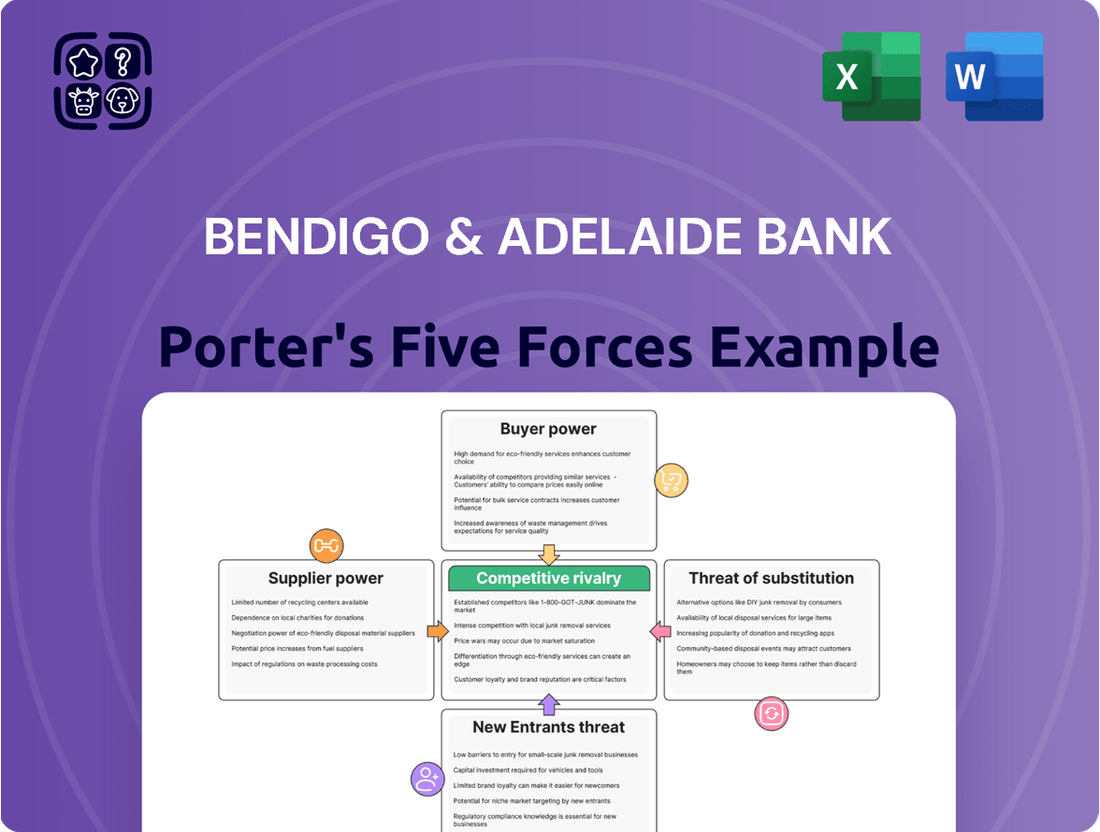
Bendigo & Adelaide Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Bendigo & Adelaide Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces impacting the bank. You'll gain detailed insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, providing a thorough strategic overview without any placeholders or surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Australian banking landscape is notably concentrated, with the four major banks holding a significant majority of the market share. This dominance naturally fuels intense rivalry as institutions like Bendigo and Adelaide Bank strive to capture a larger slice of the pie. For instance, as of late 2023, the "big four" typically controlled over 75% of the total assets in the Australian banking system, underscoring the competitive pressure on smaller players.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank actively positions itself as a strong alternative to these giants, emphasizing its customer-centric approach and regional strengths. This strategy highlights the ongoing challenge of differentiation in a mature market where established players have significant brand recognition and resources, making it a constant battle for market share and customer loyalty.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank faces fierce competition in core lending areas like residential mortgages, which naturally squeezes net interest margins for all players. Despite this, the bank demonstrated its ability to thrive by achieving above-system mortgage growth in 2024, showcasing its effectiveness in a crowded market.
Banks are locked in an aggressive battle for customer deposits, a trend that significantly influences their funding expenses and overall profitability. This intense competition means that even as interest rates climb, the cost of acquiring and retaining customer funds can eat into potential gains, squeezing net interest margins.
In 2024, for instance, major Australian banks reported increased deposit costs as they offered more competitive rates to attract and hold onto customer balances. This proactive stance on deposit gathering is crucial for maintaining liquidity and funding loan growth, but it directly impacts how much profit they can generate from their lending activities.
Digital Innovation and Transformation
The banking sector is experiencing intense rivalry driven by digital innovation. Banks are pouring resources into new technologies to create better customer experiences, boost operational efficiency, and secure a stronger market position. This digital race means that staying ahead requires constant investment and adaptation.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank is actively participating in this digital transformation. Their strategic moves, such as the ongoing development and rollout of their lending platform and the expansion of their digital banking brand, Up, highlight a clear commitment to competing through technological advancement and customer-centric digital solutions.
- Digital Investment: Banks globally are expected to spend billions on digital transformation initiatives. For example, a significant portion of the Australian banking sector's IT budget is allocated to digital upgrades and new platform development.
- Customer Experience Focus: Digital channels are becoming the primary touchpoint for many customers. Banks like Bendigo and Adelaide are leveraging digital tools to streamline processes, offer personalized services, and improve overall satisfaction.
- Competitive Differentiation: Innovation in digital offerings, such as mobile banking apps, AI-powered customer service, and seamless online account opening, serves as a key differentiator in attracting and retaining customers in a crowded market.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Pro-Competition Measures
Regulatory bodies in Australia are stepping up efforts to foster competition in the banking industry. The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) is a key player, actively scrutinizing potential mergers and acquisitions to prevent market concentration. For instance, in 2023, the ACCC continued its focus on ensuring a level playing field for smaller institutions.
These pro-competition measures, including new powers granted to regulators, directly impact competitive rivalry. Banks are incentivized to differentiate themselves through service, innovation, and pricing rather than relying on market dominance. This regulatory push encourages more aggressive, yet fairer, competition among all players, including Bendigo and Adelaide Bank.
The intensity of rivalry is further amplified as regulators aim to support smaller banks and new entrants. This creates a dynamic environment where established banks must constantly adapt and innovate to maintain their market share. For Bendigo and Adelaide Bank, this means a sustained need to outperform competitors on multiple fronts.
- Increased Regulatory Oversight: Regulators are actively monitoring the Australian banking sector for anti-competitive practices.
- New Powers to Address Mergers: Authorities have been granted enhanced powers to block mergers that could stifle competition.
- Support for Smaller Banks: Initiatives are in place to encourage and support the growth of smaller banking institutions.
- Impact on Rivalry: These measures are driving more intense and transparent competition among all banks operating in Australia.
Competitive rivalry within the Australian banking sector remains exceptionally high, driven by the dominance of the "big four" banks and the strategic efforts of institutions like Bendigo and Adelaide Bank to carve out market share. This intense competition is evident in key areas such as mortgage lending and customer deposits, where banks are actively vying for customers through competitive pricing and enhanced digital offerings.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's strategy to differentiate itself through customer focus and digital innovation is crucial in this environment. The bank’s performance, including achieving above-system mortgage growth in 2024, demonstrates its ability to compete effectively despite the concentrated market structure.
The ongoing digital transformation across the sector, with significant investment in technology for improved customer experience and operational efficiency, further intensifies rivalry. Regulatory efforts by bodies like the ACCC to foster competition by scrutinizing mergers and supporting smaller institutions also contribute to a dynamic and challenging competitive landscape.
| Metric | 2023 (Approx.) | 2024 (Projected/Early Data) | Key Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Four Market Share (Assets) | > 75% | Stable/Slightly Declining | Continued dominance, but with efforts to challenge |
| Deposit Growth Competition | Intense | Very Intense | Banks actively raising deposit rates |
| Digital Banking Investment | High | Increasing | Focus on customer experience and efficiency |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The Australian financial services sector is experiencing a surge in fintech firms and neo-banks. These companies are introducing specialized, digital-first offerings that directly compete with traditional banking products, acting as significant substitutes. For instance, by mid-2024, the Australian fintech sector was projected to reach a valuation of over AUD 18 billion, demonstrating its substantial market presence and capacity to draw customers away from established institutions with their innovative payment, lending, and wealth management solutions.
Alternative lending platforms, such as peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding, present a significant threat to Bendigo & Adelaide Bank. These platforms offer accessible credit to individuals and businesses, often with quicker approval processes and potentially more competitive rates than traditional banks. For instance, the Australian P2P lending market continued its growth trajectory through 2024, with platforms facilitating billions in new loans, directly competing for market share in consumer and business finance.
The rise of digital payment solutions, often from non-bank entities like tech giants, poses a substantial threat of substitution to Bendigo & Adelaide Bank's traditional payment services. These platforms, including mobile wallets and online payment gateways, offer convenience and often lower transaction costs, directly competing with the bank's established offerings.
In 2024, digital payments are projected to continue their rapid growth in Australia, with estimates suggesting that transaction volumes will significantly outpace traditional methods. This shift directly erodes banks' revenue streams from transaction fees, a key income source that is becoming increasingly vulnerable to these substitute technologies.
Direct Investment and Wealth Management Platforms
The threat of substitutes for Bendigo & Adelaide Bank's traditional deposit products is significant and growing. Customers increasingly have access to a wide range of platforms for wealth management and investment, moving funds away from simple bank savings accounts. These alternatives, such as online brokerage platforms, robo-advisors, and superannuation funds, offer competitive returns and specialized services that can be more attractive than standard bank offerings.
For instance, the Australian superannuation industry alone managed over $3.5 trillion in assets as of December 2023, demonstrating a massive pool of capital that could be diverted from traditional bank deposits. Similarly, the rise of fintech solutions has made it easier for individuals to access investment opportunities directly, bypassing traditional banking channels.
- Online Brokerages: Platforms like CommSec, SelfWealth, and Superhero offer low-cost trading and access to a broad range of investments, attracting customers seeking higher potential returns than bank savings accounts.
- Robo-Advisors: Services such as Six Park and Stockspot provide automated, algorithm-driven investment management, appealing to investors looking for a hands-off approach and potentially better diversification.
- Superannuation Funds: These are mandatory retirement savings vehicles that attract significant customer inflows, often offering a variety of investment options and competitive performance, directly competing for customer funds.
- Digital Wallets and Payment Platforms: While not direct deposit substitutes, these platforms are increasingly offering interest-bearing accounts or investment features, further fragmenting the financial services landscape.
Emergence of Embedded Finance
The rise of embedded finance presents a significant threat of substitutes for Bendigo & Adelaide Bank. Financial services are increasingly integrated into non-financial platforms, like e-commerce sites offering buy-now-pay-later options at checkout. This allows consumers to access financial products seamlessly at their point of need, bypassing traditional banking interactions.
This trend fundamentally alters customer behavior and expectations, as users become accustomed to financial convenience within their existing digital journeys. For instance, in 2024, the global embedded finance market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, demonstrating its rapid adoption and the increasing reliance on non-bank providers for financial transactions.
- Embedded finance allows consumers to access financial products at the point of need, reducing reliance on traditional banks.
- This integration blurs industry lines, creating new competitors from non-financial sectors.
- The convenience of embedded solutions can draw customers away from conventional banking channels.
- By 2027, it's estimated that embedded finance could generate over $2 trillion in revenue globally, highlighting the scale of this disruptive force.
The threat of substitutes for Bendigo & Adelaide Bank is substantial, driven by the proliferation of fintech, neo-banks, alternative lending, and digital payment solutions. These alternatives often offer greater convenience, specialized features, and potentially better returns or rates, directly challenging the bank's traditional product offerings. The continued growth of these substitute providers, especially in areas like digital payments and wealth management, erodes banks' market share and fee income, as seen with the massive scale of the superannuation industry attracting customer funds.
| Substitute Category | Examples for Bendigo & Adelaide Bank | Impact on Bank | Market Trend (2024 Focus) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech & Neo-banks | Revolut, Wise, Up Bank | Loss of transaction fees, deposit base erosion | Australian fintech sector projected over AUD 18 billion valuation |
| Alternative Lending | P2P platforms (e.g., SocietyOne), Crowdfunding | Reduced loan origination market share | Australian P2P market facilitating billions in new loans |
| Digital Payments | PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay | Decline in interchange fees, payment processing revenue | Digital payment transaction volumes rapidly outpacing traditional methods |
| Wealth Management/Investment | Online brokerages, Robo-advisors, Superannuation Funds | Shift of customer deposits to higher-yield investments | Australian superannuation assets over $3.5 trillion (Dec 2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The Australian banking sector faces substantial barriers to entry due to rigorous regulatory oversight and significant capital demands. These stringent requirements, overseen by bodies like APRA, necessitate substantial financial investment and complex compliance processes, effectively deterring potential new competitors. For instance, as of early 2024, the average capital adequacy ratio for major Australian banks remained robust, indicating the high level of financial resilience expected of incumbents and thus, a significant hurdle for newcomers.
Established banks like Bendigo and Adelaide Bank leverage decades of brand recognition and customer loyalty, creating a significant hurdle for newcomers. Building this trust and loyalty requires substantial time and investment, as evidenced by the difficulty new digital banks have faced in capturing market share despite technological advantages. For instance, while challenger banks have launched innovative services, incumbent banks continue to hold a dominant position in customer relationships, a testament to the power of long-standing trust.
Existing banks like Bendigo & Adelaide Bank benefit from substantial economies of scale. This allows them to spread fixed costs like technology and compliance over a larger customer base, leading to lower per-unit operating expenses. For instance, in 2023, major Australian banks reported significant cost-to-income ratios, often below 50%, a level difficult for new entrants to match initially.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating these cost advantages. They must invest heavily in establishing their own infrastructure, marketing, and compliance frameworks. This often means higher initial operating costs, making it challenging to compete on price with established players without accepting substantial initial losses.
Access to Funding and Liquidity
New entrants into the banking sector, like potential competitors to Bendigo & Adelaide Bank, often struggle to establish robust and cost-effective funding streams. Securing a stable base of deposits at rates competitive with incumbents is a significant hurdle. For instance, in early 2024, major Australian banks continued to leverage their extensive branch networks and digital offerings to attract and retain retail deposits, often at lower cost than newer players could initially achieve.
Established institutions benefit from deep-seated customer loyalty and diversified funding channels, including access to wholesale markets. This allows them to maintain greater liquidity and manage funding costs more efficiently. By mid-2024, the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) data indicated that the major banks held a substantial portion of the total deposit market share, underscoring their established funding advantage.
- Deposit Acquisition Costs: New banks may need to offer higher interest rates on deposits to attract customers away from established brands, increasing their cost of funds.
- Wholesale Funding Access: Incumbents often have better credit ratings and longer track records, granting them preferential access to wholesale funding markets at lower rates.
- Liquidity Management: Established banks possess sophisticated liquidity management systems and a proven ability to manage funding through various economic cycles, a capability new entrants must build.
- Funding Diversification: A wider range of funding sources, from retail deposits to securitization, provides resilience against market shocks, which is often more readily available to established banks.
Technological Infrastructure and Cybersecurity Demands
Developing and maintaining the sophisticated technological infrastructure required for modern banking presents a substantial hurdle for new entrants. This includes everything from core banking systems to customer-facing digital platforms, all of which demand significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
The escalating demands for cybersecurity and data protection further amplify this barrier. In 2024, the financial sector continues to be a prime target for cyberattacks, necessitating robust defenses that are both complex and costly to implement and manage, even with the advent of cloud technologies.
- High Capital Outlay: New entrants must invest heavily in secure, scalable IT systems, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars, to compete effectively.
- Cybersecurity Investment: In 2024, banks are expected to spend billions globally on cybersecurity to combat sophisticated threats, a cost new entrants must absorb.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stringent data protection regulations, such as those related to privacy and financial crime, add layers of complexity and cost to technological development.
- Talent Acquisition: Securing specialized IT and cybersecurity talent is competitive and expensive, posing a challenge for new players establishing their teams.
The threat of new entrants for Bendigo & Adelaide Bank remains relatively low, largely due to the substantial regulatory hurdles and capital requirements inherent in the Australian banking sector. These barriers, enforced by regulators like APRA, necessitate significant financial investment and complex compliance, making it difficult for new players to establish themselves. For instance, as of early 2024, the average capital adequacy ratios for major Australian banks remained high, a clear indicator of the financial strength expected of any new competitor.
Established brand loyalty and trust also act as significant deterrents. Bendigo & Adelaide Bank, like its larger counterparts, benefits from decades of customer relationships, which are challenging and costly for newcomers to replicate. Even with technological advancements offered by digital banks, incumbent institutions continue to maintain a strong hold on customer relationships, highlighting the enduring value of established trust.
Economies of scale further bolster the position of existing banks. Bendigo & Adelaide Bank can spread its fixed costs across a broader customer base, leading to lower per-unit operating expenses. In 2023, major Australian banks consistently reported cost-to-income ratios below 50%, a benchmark that new entrants would find extremely difficult to match in their initial years of operation.
New entrants face considerable challenges in securing stable and cost-effective funding. Attracting retail deposits at competitive rates is a primary hurdle, as established banks leverage their extensive networks to retain funding. By mid-2024, major Australian banks held a dominant share of the total deposit market, underscoring their established funding advantage and the difficulty new players face in accessing similar resources.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Regulatory Capital Requirements | APRA mandates strict capital adequacy ratios. | Requires substantial upfront investment, limiting the number of potential entrants. |
| Brand Loyalty and Trust | Long-standing customer relationships. | New entrants struggle to attract customers without a proven track record. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for incumbents. | New entrants face higher initial operating costs, making price competition difficult. |
| Funding Access | Established deposit base and wholesale market access. | New entrants must offer higher rates to attract deposits, increasing funding costs. |
| Technological Infrastructure | Need for sophisticated and secure IT systems. | High capital expenditure and ongoing maintenance costs for new players. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bendigo & Adelaide Bank is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the bank's annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry analysis firms and macroeconomic data providers to ensure a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
