Beazley Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Beazley Bundle
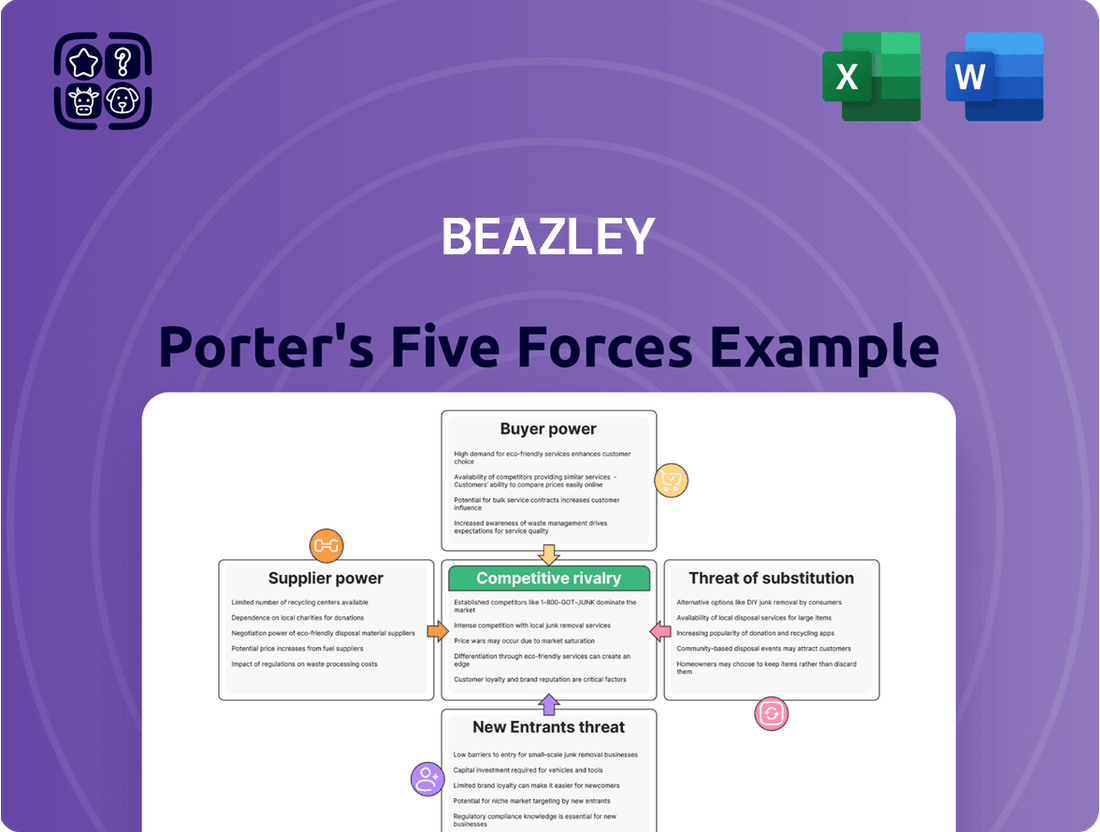
Beazley's competitive landscape is shaped by five key forces: the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate Beazley's market effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Beazley’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Beazley depends on specialist reinsurers to transfer substantial amounts of complex and large risks, which helps them manage capital and lower their exposure. This reliance is a key factor in understanding their operational dynamics.
The market for highly specialized reinsurers, particularly those with deep expertise in areas like cyber risk or political instability, is quite concentrated. This limited pool of providers means they often hold significant bargaining power when dealing with insurers like Beazley, especially when the risks are unusual or new.
In 2023, the global reinsurance market saw premiums grow, with specialty lines like cyber showing particularly strong increases. For instance, cyber insurance premiums continued their upward trend, reflecting the increasing frequency and severity of cyber threats, which in turn can influence the pricing power of reinsurers in this niche.
The terms and pricing set by these specialist reinsurers directly affect Beazley's ability to underwrite profitably and determine the amount of risk they can retain. This makes the relationship critical for Beazley's financial health and strategic capacity planning.
Capital providers, such as equity investors and debt holders, wield significant influence over Beazley's operations. Their willingness to fund the insurer's underwriting capacity and growth directly impacts Beazley's ability to take on new business. For instance, in early 2024, the insurance sector saw a renewed interest from capital markets, with many insurers successfully raising capital, indicating a generally favorable environment for Beazley to access funding.
The market for highly skilled underwriting talent, actuaries, and claims professionals specializing in niche risks is exceptionally competitive. These experts possess knowledge vital to Beazley's ability to underwrite complex and unusual risks, a core component of their strategy.
The scarcity and specialized nature of these professionals grant them considerable bargaining power. This directly impacts Beazley's recruitment expenses and retention efforts, influencing the overall caliber of their underwriting decisions.
Proprietary Technology and Data Analytics Providers
In the increasingly data-centric insurance landscape, suppliers of proprietary technology and advanced data analytics, including AI tools and specialized underwriting platforms, hold significant bargaining power. Beazley's competitive edge is directly tied to its ability to leverage these innovations for efficient operations and forward-thinking risk assessment.
These technology providers can command higher prices or dictate terms due to the unique value they bring. For instance, companies offering sophisticated AI-driven fraud detection or advanced cyber risk modeling tools are indispensable for insurers aiming to stay ahead of evolving threats.
- Unique Algorithms and Data Sets: Suppliers with exclusive algorithms or comprehensive, proprietary data sets for niche risks, such as climate change impacts or emerging cyber vulnerabilities, can exert considerable influence.
- Cutting-Edge Risk Modeling: Providers of advanced risk modeling software, especially for complex and rapidly changing perils like cyber threats, are critical. Their ability to accurately quantify and predict these risks gives them leverage.
- Operational Efficiency and Innovation: Beazley's reliance on these technological solutions for enhancing underwriting accuracy, streamlining claims processing, and driving innovation means suppliers can impact the insurer's overall performance and market position.
- Market Trends: The global insurtech market is projected to reach $100 billion by 2025, highlighting the growing importance and demand for advanced technological solutions within the insurance sector.
Lloyd's of London Infrastructure
Beazley's reliance on Lloyd's of London infrastructure means the market itself, with its regulatory framework and capital requirements, acts as a significant supplier. This central market dictates operational standards and provides essential access, influencing Beazley's business costs and strategic agility.
Lloyd's, by setting the rules and providing the platform, exerts considerable bargaining power. This is evident in the mandatory adherence to its standards, which directly impacts how Beazley and other syndicates operate and manage their expenses.
- Lloyd's as a Supplier: Lloyd's of London functions as a critical supplier of market access and regulatory oversight for syndicates like Beazley.
- Impact on Costs: Adherence to Lloyd's mandated standards and capital requirements directly influences Beazley's cost of doing business.
- Operational Flexibility: The stringent operational environment set by Lloyd's can limit Beazley's flexibility in certain strategic decisions.
Beazley's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by the concentration of reinsurers, the scarcity of specialized talent, and the critical role of technology providers. The terms offered by these suppliers directly impact Beazley's operational costs and underwriting capabilities.
The concentration in the specialist reinsurance market, particularly for complex risks, grants suppliers significant leverage. Similarly, the demand for niche underwriting expertise means skilled professionals can command higher compensation, increasing Beazley's human capital costs.
Technology suppliers offering advanced analytics and AI tools are essential for Beazley's competitive edge, allowing them to negotiate favorable terms. Lloyd's of London, as a key market infrastructure provider, also exerts influence through its regulatory framework and operational standards.
In 2023, the global reinsurance market experienced a premium growth, with specialty lines like cyber seeing substantial increases, reflecting the pricing power of reinsurers in these areas. The insurtech market is projected to reach $100 billion by 2025, underscoring the value and influence of technology suppliers.
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity within Beazley's insurance market by examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of all five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Beazley's strategic focus on underwriting complex and niche risks, such as cyber, marine, and political risks, inherently limits the bargaining power of individual customers. These highly specialized insurance solutions are not readily available from a broad range of providers. This scarcity of comparable expertise and tailored coverage means clients have fewer alternative options, strengthening Beazley's position.
While customers buy insurance, specialist brokers are crucial in the intricate insurance landscape. These intermediaries gather demand and hold substantial market insight, often directing clients to insurers with specific expertise.
For complex or niche risks, brokers actively seek out specialized insurers like Beazley, recognizing their unique underwriting capabilities. This reliance on Beazley's expertise can lessen direct customer price pressure, as the focus shifts to the value and tailored nature of the insurance solution provided.
For large corporations and specialized industries, switching insurance providers for complex coverages is not a simple task. It often requires extensive due diligence, a thorough re-evaluation of intricate risks, and the potential for critical gaps in coverage during the transition period. This complexity inherently limits a customer's ability to easily move to a competitor.
Beazley's established relationships, meticulously tailored policy wordings, and a track record of proven claims service create a significant inertia for its clients. These factors effectively increase the switching costs, thereby diminishing the immediate bargaining power of customers who would face considerable effort and potential disruption to move elsewhere.
Information Asymmetry
In the specialized insurance sectors where Beazley operates, information asymmetry is a key factor influencing customer bargaining power. Beazley's extensive underwriting knowledge and vast data reserves provide a distinct advantage, enabling a more accurate assessment and pricing of risks compared to individual clients.
This knowledge gap empowers Beazley to craft policies and set prices that reflect the true risk profile, effectively reducing the customer's leverage to negotiate solely on price. For instance, in 2024, Beazley reported a combined ratio of 87% for its Specialty lines, indicating strong underwriting performance driven by superior risk selection and pricing, a direct benefit of its information advantage.
- Information Advantage: Beazley's deep expertise in niche insurance markets grants it superior knowledge of risk characteristics and pricing compared to clients.
- Pricing Power: This asymmetry allows Beazley to price policies more accurately, limiting customers' ability to demand lower premiums based on incomplete information.
- Reduced Negotiation Leverage: Customers find it harder to bargain aggressively when Beazley possesses a more comprehensive understanding of the risks involved.
Customized Solutions and Claims Service
Beazley's dedication to crafting customized insurance solutions and delivering expert claims service significantly curtails the bargaining power of its customers. Clients requiring specialized coverage for intricate risks, such as substantial cyberattacks or complex liability issues, place a premium on Beazley's tailored approach and adept claims handling. This focus on specialized value diminishes their inclination to solely negotiate on price, thereby reducing their leverage.
- Customization Reduces Price Sensitivity: By offering bespoke insurance products, Beazley addresses unique client needs, making price a less dominant factor in purchasing decisions.
- Expert Claims Service as a Differentiator: For complex claims, customers prioritize efficient and knowledgeable service over cost savings, strengthening Beazley's position.
- Reduced Bargaining Power: The emphasis on specialized solutions and superior claims handling limits customers' ability to demand lower premiums based on price alone.
The bargaining power of customers for Beazley is generally low, particularly in its specialized insurance segments. This is due to the highly tailored nature of its products and the expertise required to underwrite complex risks, which limits the availability of close substitutes. Customers often rely on Beazley's specialized knowledge, making it difficult to switch providers or negotiate on price alone.
For instance, in 2024, Beazley's focus on underwriting complex risks like cyber and specialty lines meant clients sought out their specific capabilities rather than shopping for the lowest price. This specialization creates a situation where customers are less price-sensitive and more focused on the quality and suitability of the coverage provided.
The switching costs for clients needing specialized insurance are also significant. Moving to a new provider for complex coverages involves extensive due diligence and the risk of coverage gaps, which discourages frequent provider changes and thus reduces customer bargaining power.
| Metric | Beazley (2024) | Industry Average (Specialty Lines) |
|---|---|---|
| Combined Ratio | 87% | ~90% (estimated) |
| Customer Retention Rate | High (specific data often proprietary, but indicative of low switching) | Varies by segment |
| Number of Specialized Products Offered | Extensive (e.g., Cyber, Marine, Political Risk) | Limited for non-specialists |
Same Document Delivered
Beazley Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Beazley Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the insurance industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full professional formatting. You're looking at the actual, ready-to-use analysis, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Beazley operates in a fiercely competitive global specialist insurance arena. Rivalry comes from other niche insurers and syndicates within Lloyd's, including prominent players like Hiscox, Lancashire, and Chaucer, all vying for the same complex risk segments. This dynamic environment necessitates constant innovation in product development and service quality to capture market share and secure vital broker relationships.
Beazley faces significant competition from large, diversified global insurers such as Chubb, AIG, and Allianz. These giants operate substantial divisions dedicated to complex commercial risks, directly challenging Beazley's core markets.
These competitors often leverage superior capital strength, expansive distribution channels, and a wider client reach. For instance, in 2023, Chubb reported gross written premiums exceeding $55 billion, highlighting its significant scale and market presence compared to Beazley.
Their ability to offer bundled insurance solutions across various business lines can also present a formidable competitive advantage. This broad offering allows them to potentially capture more of a client's insurance needs, putting pressure on Beazley's specialized approach.
Competitive rivalry in specialist insurance, like Beazley's market, goes beyond just price. It's deeply rooted in specialized knowledge, the creation of novel insurance products, and the quality of claims handling. Competitors are in a perpetual race to design new insurance solutions for emerging risks, such as evolving cyber threats or directors and officers (D&O) liabilities, and to improve existing offerings.
Beazley's continued success hinges on its ongoing investment in skilled underwriters and its capacity to swiftly adapt to changing client demands and the dynamic risk environment. For instance, in 2024, the specialty insurance sector saw significant innovation in areas like parametric insurance for climate-related events, reflecting this drive for new coverages.
Market Cycles and Pricing Discipline
The specialist insurance market, including Beazley's operating environment, experiences distinct underwriting cycles. These cycles swing between hard markets, characterized by elevated premiums and stricter policy terms, and soft markets, which feature reduced pricing and more lenient conditions.
During soft market phases, competitive rivalry intensifies significantly. This heightened competition often translates into considerable pricing pressure, eroding profit margins for all participants in the sector. For instance, in 2023, the global commercial insurance market saw continued competitive pressures, particularly in property lines, as capacity increased and reinsurers sought to deploy capital, leading to rate moderation in many segments.
To effectively navigate these cyclical shifts and maintain profitability, Beazley must exhibit strong pricing discipline and rigorous risk selection. This approach is crucial for differentiating itself and outperforming competitors who may be more susceptible to market downturns.
- Specialist insurance markets are inherently cyclical, alternating between hard and soft pricing environments.
- Intense competition during soft markets leads to significant pricing pressure and reduced profitability.
- Beazley's ability to maintain pricing discipline and rigorous risk selection is key to its success against aggressive competitors.
- In 2023, the commercial insurance market experienced rate moderation in many segments due to increased capacity and competitive pressures.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
The insurance sector, particularly specialist lines, sees intense competition for top-tier underwriting and claims talent. This scarcity of professionals with deep, niche expertise makes talent acquisition a crucial battleground. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cyber underwriters remained exceptionally high, with many firms reporting extended recruitment cycles for these specialized roles.
Competitors frequently engage in aggressive recruitment, often targeting and poaching experienced teams. This practice directly impacts an insurer's ability to maintain its competitive edge and capacity for profitable growth. The retention of these key individuals is therefore paramount, as their departure can significantly disrupt operations and innovation.
- High Demand for Niche Skills: Underwriters and claims specialists with expertise in areas like cyber, professional indemnity, and complex casualty are in short supply.
- Talent Poaching: Established insurers and newer market entrants actively recruit experienced teams, leading to significant churn.
- Impact on Profitability: The ability to attract and retain skilled professionals directly influences an insurer's underwriting profitability and innovation capacity.
- Recruitment Challenges in 2024: Many specialist insurers reported average time-to-hire exceeding six months for critical underwriting positions during the year.
Competitive rivalry within Beazley's specialist insurance markets is intense, driven by both niche players and large diversified insurers. This competition extends beyond pricing to encompass innovation in product development, claims handling expertise, and the acquisition of specialized talent. The cyclical nature of the insurance market, particularly the shift between hard and soft markets, significantly amplifies competitive pressures, impacting profitability and strategic decision-making.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitors | Competitive Tactics | Impact on Beazley |
|---|---|---|---|
| Niche Insurers/Syndicates | Hiscox, Lancashire, Chaucer | Specialized product innovation, strong broker relationships | Direct competition in specific risk segments |
| Large Diversified Insurers | Chubb, AIG, Allianz | Capital strength, broad distribution, bundled offerings | Market share erosion, pricing pressure |
| Talent Acquisition | All market participants | Aggressive recruitment of underwriters and claims specialists | Risk to operational capacity and innovation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For large corporations with substantial financial clout and advanced risk management, self-insurance or establishing captive insurance companies presents a viable alternative to traditional specialist insurance. These internal solutions enable companies to manage their own risks, potentially cutting premium expenses and enhancing claims oversight.
In 2024, the global captive insurance market continued its robust growth, with premiums written by captives reaching an estimated $70 billion, according to industry reports. This trend highlights the increasing attractiveness of self-insuring for large enterprises seeking greater control and cost savings.
Beazley must therefore continuously prove its value proposition by offering superior underwriting expertise, tailored coverage, and efficient claims handling that surpasses the benefits of these in-house risk financing mechanisms. Demonstrating strong capital efficiency and a clear return on investment compared to captive structures is paramount for retaining market share.
The increasing prevalence of Alternative Risk Transfer (ART) mechanisms like catastrophe bonds and insurance-linked securities (ILS) offers a significant substitute for conventional insurance products. These capital market tools enable risk to be directly passed on to investors, circumventing traditional insurance carriers. As of early 2024, the ILS market continued its growth trajectory, with total market capacity estimated to be around $100 billion, demonstrating a substantial alternative capacity for specific risks.
Parametric insurance, another ART solution, provides payouts based on predefined triggers rather than actual losses, further diversifying risk management options. While these instruments have historically focused on perils like natural catastrophes, their application is broadening into other specialty lines. This expansion poses a potential challenge to Beazley's property and specialty insurance segments by offering alternative avenues for risk financing.
Technological advancements in risk mitigation and prevention are increasingly diminishing the perceived necessity for traditional insurance products. For instance, sophisticated cybersecurity measures can significantly reduce the probability of breaches, thereby lessening the demand for extensive cyber insurance policies. In 2024, the global cybersecurity market was valued at an estimated $214.1 billion, a figure projected to grow, indicating a strong trend towards proactive risk management.
Beazley, a prominent insurer, faces this threat by needing to evolve beyond mere risk transfer. The company must integrate loss prevention strategies and offer risk advisory services to remain competitive. This shift acknowledges that clients are investing more in preventing losses rather than solely insuring against them, a trend amplified by the increasing availability and effectiveness of preventative technologies.
Government-Backed or Industry-Specific Schemes
Government-backed schemes and industry-specific mutuals can act as significant substitutes for traditional insurance. In areas like terrorism or pandemic risk, where private insurers may find it difficult to price or absorb losses, these alternative structures can offer coverage. For instance, the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act (TRIA) in the US provides a federal backstop for terrorism losses, acting as a substitute for full private market coverage.
These initiatives often emerge when the commercial insurance market is unable or unwilling to provide coverage, or can offer it at more competitive rates due to public backing or collective industry participation. This can directly impact Beazley's market share in specialized lines. For example, some environmental liability pools are formed by industry participants to manage shared risks, potentially offering a more tailored and cost-effective solution than Beazley might provide on its own.
Beazley must remain vigilant in monitoring the growth and scope of these substitute offerings. Areas where systemic risks are high or where regulatory mandates encourage collective risk-sharing are particularly susceptible to this threat. The increasing focus on climate-related liabilities, for example, could spur the development of industry-wide pools or government-supported programs that compete with Beazley's offerings in specialty environmental lines.
- Government Backstops: Programs like the US Terrorism Risk Insurance Act (TRIA) offer a federal backstop, reducing reliance on private insurers for terrorism coverage.
- Industry Mutuals: Sector-specific groups may form mutual insurance companies to cover unique or high-severity risks, potentially at lower costs due to shared risk and reduced administrative overhead.
- Pandemic and Climate Risk: Emerging threats like pandemics and climate change could drive the creation of government-backed or industry-led solutions, particularly for liabilities where private market capacity is limited.
- Competitive Pricing: Subsidies or the absence of profit motives in some public or mutual schemes can lead to more competitive pricing, posing a direct challenge to Beazley's commercial offerings.
Non-Insurance Risk Management Consulting
The threat of substitutes for Beazley's core insurance offerings comes from non-insurance risk management consulting. Companies increasingly invest in robust internal risk management frameworks, potentially reducing their reliance on certain insurance products. For instance, a company that excels at identifying and mitigating operational risks through advanced analytics and process improvements might find less need for specific business interruption insurance.
This trend is supported by a growing market for specialized risk consulting. In 2024, the global risk management consulting market was valued at approximately $40 billion, demonstrating a clear demand for services that help businesses build resilience and proactively manage threats. This focus on internal control and mitigation can diminish the perceived necessity of transferring certain risks externally via insurance.
- Proactive Risk Mitigation: Companies are prioritizing internal strategies to identify, assess, and control risks, reducing the need for insurance as the primary risk transfer mechanism.
- Resilience Building: Investments in operational resilience and business continuity planning by firms can lessen the perceived value of certain insurance policies, particularly those covering predictable or manageable disruptions.
- Consulting Market Growth: The expanding risk management consulting sector, with its focus on internal solutions, presents a viable alternative for businesses seeking to manage their risk profiles without solely relying on insurance.
The threat of substitutes for Beazley's offerings is multifaceted, encompassing self-insurance, alternative risk transfer, technological advancements in risk prevention, government-backed schemes, and non-insurance risk management consulting.
Self-insurance and captive insurance, with the global captive insurance market reaching an estimated $70 billion in premiums written in 2024, represent a direct challenge by allowing large corporations to retain risk internally, potentially reducing costs and increasing control.
Beazley must counter this by demonstrating superior underwriting, tailored coverage, and efficient claims handling that clearly outperforms the benefits of these in-house risk financing mechanisms.
Alternative Risk Transfer (ART) mechanisms like catastrophe bonds and insurance-linked securities (ILS), with an estimated market capacity of around $100 billion in early 2024, offer alternative risk financing avenues, particularly for specialty lines.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the specialist insurance market, especially for complex lines like those Beazley underwrites, demands considerable capital. New entrants must have significant financial backing to satisfy regulatory solvency rules, obtain necessary licenses, and prove their financial stability to policyholders and brokers alike.
For instance, in 2024, regulatory capital requirements for insurers writing cyber insurance, a key area for Beazley, can range from tens of millions to hundreds of millions of dollars depending on the jurisdiction and the volume of business. This substantial financial barrier effectively deters many potential new competitors from entering, particularly when dealing with large, unpredictable risks.
Operating within the Lloyd's of London market, a key arena for Beazley, presents formidable regulatory challenges for newcomers. These include securing intricate licenses and approvals, alongside demonstrating robust compliance with Lloyd's specific market rules and capital requirements.
The sheer time and financial investment required to navigate these regulatory processes act as a significant deterrent, effectively raising the barrier to entry for potential competitors seeking to join Beazley in this specialized insurance sector.
The threat of new entrants in specialized insurance, like those offered by Beazley, is significantly mitigated by the critical need for deep underwriting expertise. Building this knowledge, particularly in complex areas such as cyber or political risk, takes years of dedicated experience.
New companies struggle to attract or cultivate teams possessing the specialized skills required to underwrite these niche markets effectively. This talent scarcity presents a substantial barrier, making it costly and time-consuming for newcomers to establish a competitive underwriting foundation against established players.
Brand Reputation and Broker Relationships
In the specialist insurance sector, Beazley's formidable brand reputation and deep-rooted broker relationships act as significant barriers to new entrants. Trust and a proven track record are non-negotiable, and these are cultivated over many years, not months.
Established insurers like Beazley have invested heavily in building strong brands and nurturing extensive networks of brokers. This makes it incredibly difficult for newcomers to gain immediate credibility and access to distribution channels. Brokers, who are crucial gatekeepers for placing complex risks, naturally gravitate towards insurers they know and trust to handle claims effectively and reliably.
- Established Brand Equity: Beazley's long-standing presence has fostered significant brand recognition and trust within the insurance industry.
- Broker Network Dominance: Decades of relationship building provide Beazley with preferential access to brokers, who are essential for distributing specialized insurance products.
- Credibility Gap: New entrants face a substantial challenge in replicating the trust and proven claims handling capabilities that underpin Beazley's market position.
Access to Proprietary Data and Risk Models
Beazley and other established specialist insurers possess extensive proprietary data concerning intricate risks. This data fuels the development of advanced pricing models and underwriting algorithms, a significant advantage. For instance, in 2024, the insurance industry continued to emphasize data analytics, with major players investing heavily in AI-driven risk assessment tools.
New entrants typically lack this deep historical data and the sophisticated analytical infrastructure built upon it. This data deficit hinders their ability to accurately price complex risks and develop competitive underwriting strategies. Without a comparable data advantage, newcomers face a substantial hurdle in matching the efficiency and profitability of incumbents.
- Proprietary Data Accumulation: Incumbents have years of data on niche risks.
- Advanced Analytical Capabilities: Sophisticated pricing and underwriting models are derived from this data.
- Data Deficit for New Entrants: Startups lack the historical datasets and analytical tools.
- Competitive Pricing Barrier: Established players can price risks more accurately, creating a barrier.
The threat of new entrants for Beazley is significantly limited by the substantial capital requirements and stringent regulatory landscape inherent in specialist insurance markets. For example, in 2024, insurers operating in the cyber insurance sector, a core area for Beazley, faced capital requirements that could easily reach tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, depending on the specific jurisdiction and business volume.
Furthermore, gaining entry into established markets like Lloyd's of London involves navigating complex licensing and compliance procedures, a process that demands considerable time and financial resources, effectively deterring many potential newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Significant financial backing needed for solvency and licensing. | High barrier, especially for complex risks. | Cyber insurance capital needs: $10M - $100M+ |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating licenses and compliance in markets like Lloyd's. | Time-consuming and costly entry process. | Multiple approvals required for Lloyd's syndicates. |
| Underwriting Expertise | Deep knowledge in niche areas like cyber or political risk. | Talent scarcity makes it hard to build competitive teams. | Years of experience needed for specialized underwriting. |
| Brand & Broker Relations | Established trust and extensive broker networks. | Difficult for newcomers to gain credibility and distribution. | Brokers prioritize proven claims handling and reliability. |
| Proprietary Data & Analytics | Access to historical data for advanced pricing models. | New entrants lack data for accurate risk assessment. | AI-driven risk tools are a key investment for incumbents. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Beazley Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, drawing from Beazley's annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and data from leading insurance analytics firms to provide a robust competitive landscape.
