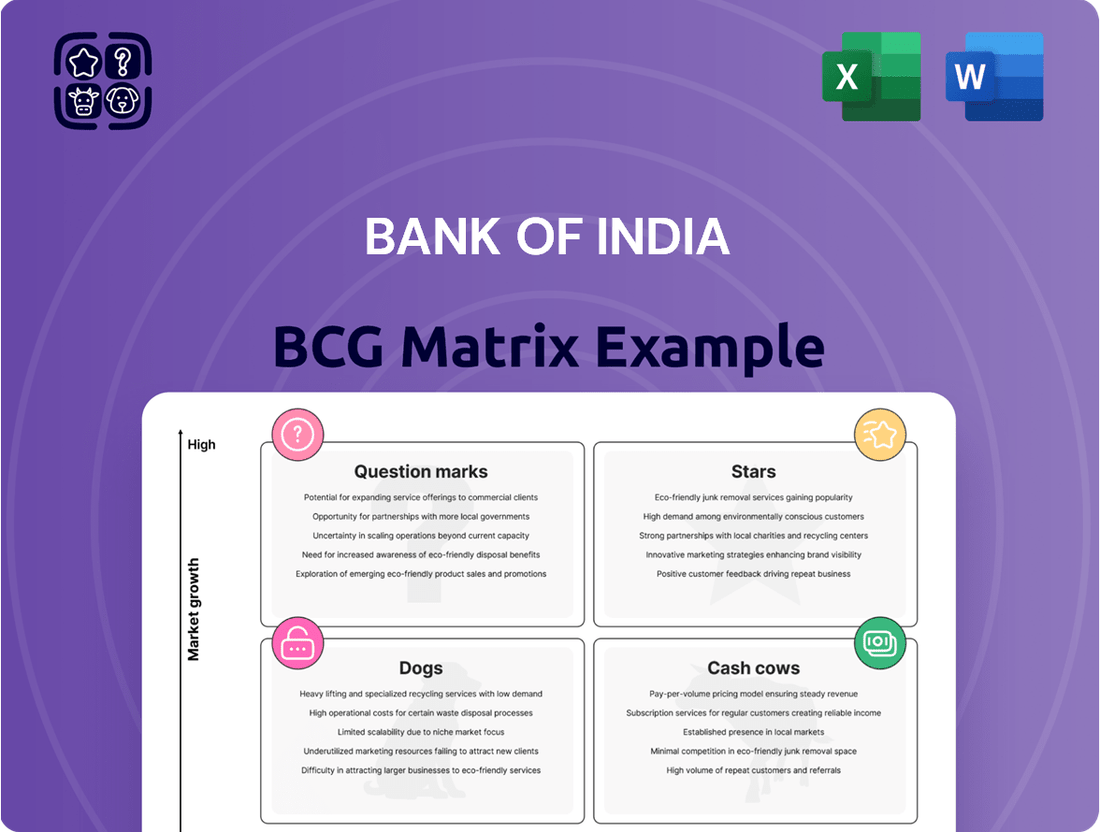
Bank of India Boston Consulting Group Matrix
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bank of India Bundle
Curious about the Bank of India's strategic product portfolio? This glimpse into their BCG Matrix will show you how their offerings stack up as Stars, Cash Cows, Dogs, or Question Marks. Don't settle for just a peek; unlock the full potential of this analysis.
Purchase the complete Bank of India BCG Matrix to gain a comprehensive understanding of their market position and identify key opportunities for growth and resource allocation. This detailed report is your essential tool for informed strategic decision-making.
Stars
Bank of India's retail loan portfolio is experiencing robust expansion, reaching ₹1,33,699 crore by March 31, 2025. This represents a significant year-on-year increase of 19.93%, clearly marking it as a star performer within the bank's business lines.
This impressive growth is distributed across a wide range of retail products, including home loans, vehicle loans, education loans, mortgage loans, and personal loans. Such broad-based expansion suggests a strong market position in a segment that continues to grow.
Bank of India is heavily investing in digital banking, planning to launch 25 new digital customer journeys by March 2025. These initiatives focus on digitizing both retail assets and liabilities, signaling a strong commitment to enhancing its digital presence and customer experience.
The bank's strategic focus on digital footprints, exemplified by Project Aditya, aims to build robust technological platforms and ensure high data quality. This positions digital banking as a high-growth area, with the potential to significantly increase market share in the rapidly evolving digital financial services sector.
Bank of India's profitability has seen a substantial uplift, with its net profit soaring by 82.5% year-on-year to ₹2,625.91 crore in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2025. This robust performance extended throughout the entire fiscal year, culminating in an overall net profit increase of 46% to ₹9,219 crore for FY25.
Concurrently, the bank has made significant strides in improving its asset quality. The gross Non-Performing Assets (NPA) ratio saw a notable reduction, standing at 3.27% by the end of FY25. This dual improvement in profitability and asset quality underscores Bank of India's enhanced financial health and operational efficiency.
Priority Sector Lending
Priority Sector Lending for the Bank of India stands out as a star performer within its business portfolio. The bank has consistently not only met but exceeded the mandated targets for lending to these crucial sectors. This strong showing highlights its strategic focus and commitment to areas that are vital for national development and economic growth.
- Consistent Growth: Bank of India's priority sector advances have demonstrated steady expansion, outperforming regulatory benchmarks.
- Exceeding Targets: As of March 31, 2025, priority sector advances reached 45.44% of Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANBC), well above the 40% requirement.
- Agricultural Focus: Agricultural credit specifically accounted for 21.15% of ANBC, surpassing the 18% target.
- Strategic Importance: This robust performance in a government-supported sector solidifies its position as a star, driving both market share and social responsibility.
Expansion of Branch Network and Customer Reach
Bank of India is significantly bolstering its physical footprint by inaugurating 200 new branches, primarily targeting semi-urban locations in the financial year 2024-25. This aggressive expansion is designed to tap into underserved markets and cater to the specific needs of small businesses and individuals in these developing economic zones. The bank's commitment to physical accessibility, coupled with its already extensive network, is a key strategy for increasing its market share and attracting new customers.
This strategic expansion directly supports Bank of India's growth objectives by:
- Expanding Market Penetration: Targeting semi-urban areas with 200 new branches aims to capture untapped customer bases.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Providing personalized banking services in areas where such access is limited.
- Boosting Small Business Support: Facilitating easier access to credit and financial services for local enterprises.
- Strengthening Brand Presence: Increasing visibility and trust in emerging economic hubs.
Bank of India's retail loan portfolio, showing a 19.93% year-on-year increase to ₹1,33,699 crore by March 31, 2025, is a clear star. This growth spans home, vehicle, and personal loans, indicating a strong market position. Furthermore, the bank's commitment to digital transformation, with 25 new digital customer journeys planned by March 2025, positions digital banking as another star performer with high growth potential.
The bank's priority sector lending also shines as a star. As of March 31, 2025, these advances constituted 45.44% of Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANBC), significantly exceeding the 40% regulatory requirement. Agricultural credit, a key component, reached 21.15% of ANBC, surpassing the 18% target. This strong performance in government-supported sectors highlights Bank of India's dual focus on market share and social responsibility.
| Business Segment | Growth/Performance Metric | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Loans | 19.93% YoY growth (as of March 31, 2025) | Star |
| Digital Banking Initiatives | 25 new digital customer journeys planned by March 2025 | Star |
| Priority Sector Lending | 45.44% of ANBC (as of March 31, 2025) | Star |
| Agricultural Credit | 21.15% of ANBC (as of March 31, 2025) | Star |
What is included in the product
Highlights which units to invest in, hold, or divest based on market share and growth.
The Bank of India BCG Matrix provides a clear, one-page overview of each business unit's strategic position, alleviating the pain of complex portfolio analysis.
Cash Cows
Bank of India's established deposit base is a significant strength, acting as a classic cash cow. By March 2025, their global deposits stood at ₹8.16 lakh crore, with domestic deposits alone seeing a robust 11.21% year-on-year increase to ₹7 lakh crore.
This substantial and consistent inflow of funds, especially from CASA accounts, offers a low-cost and dependable funding source. Such stability is a hallmark of a cash cow within a well-established market segment.
Bank of India's corporate and wholesale banking division is a cornerstone of its operations, contributing substantially to its business volume and loan portfolio. While specific 2024 growth figures for this segment aren't publicly itemized, its established position suggests a mature market.
This segment likely acts as a cash cow for the bank, leveraging its long-standing relationships and strong market presence among nationalized banks to generate consistent revenue streams and robust cash flows.
Bank of India's Foreign Exchange and Trade Finance services are a classic cash cow. These offerings are crucial for businesses engaged in international trade, a sector that consistently demands these services in a growing economy like India. The bank benefits from stable, high-margin income with minimal need for further investment, reflecting their maturity and established market position.
In the fiscal year 2023-24, India's total trade finance volume saw significant activity, with Bank of India actively participating. Their expertise in handling complex international transactions, including letters of credit and export-import financing, generates reliable revenue. This segment of the bank's operations is characterized by its consistent profitability and low risk, contributing substantially to overall earnings.
Diverse Loan Portfolio (Excluding High Growth Retail)
Beyond the high-growth retail sector, Bank of India's diverse loan portfolio, particularly in areas like infrastructure and select corporate lending, functions as a stable cash generator. These mature segments, while not exhibiting rapid expansion, consistently contribute to the bank's asset base and generate predictable interest income.
These lending areas, characterized by their stability rather than explosive growth, are crucial for maintaining a steady revenue stream. For instance, in FY2023, Bank of India reported a net interest income of ₹36,612 crore, a testament to the consistent earnings from its established loan book.
- Infrastructure Loans: These are typically long-term, secured loans that provide a reliable interest income, even if growth rates are moderate.
- Corporate Loans (Specific Segments): Certain established corporate relationships and lending to stable industries offer predictable cash flows.
- Contribution to Stability: These segments act as the bank's "cash cows," funding other strategic initiatives and absorbing potential shocks from more volatile business areas.
Traditional Branch Network and Services
Bank of India's vast traditional branch network, exceeding 5,300 locations domestically and maintaining a notable international footprint, underpins its status as a cash cow. This extensive physical presence facilitates the delivery of core banking services like deposit accounts and fundamental credit facilities to a broad and loyal customer base.
These established services, while potentially experiencing slower growth rates, are crucial for generating consistent fee income and fostering enduring customer relationships. For instance, in the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Bank of India reported a net profit of ₹2,587 crore, a significant increase from the previous year, reflecting the stable revenue streams from its traditional offerings.
- Extensive Network: Over 5,300 branches in India and international presence.
- Core Services: Deposit accounts, basic credit facilities, and other traditional banking products.
- Revenue Stability: Consistent fee income and customer loyalty contribute to stable cash flow.
- Profitability: Fiscal year 2023-24 net profit of ₹2,587 crore highlights the strength of established operations.
Bank of India's strong deposit base, particularly its CASA accounts, provides a stable and low-cost funding source, characteristic of a cash cow. With domestic deposits reaching ₹7 lakh crore by March 2025, showing an 11.21% year-on-year growth, this segment consistently generates reliable earnings.
The bank's established corporate and wholesale banking divisions, along with its Foreign Exchange and Trade Finance services, are key revenue generators. These mature segments leverage long-standing relationships and expertise to produce consistent, high-margin income with minimal additional investment, contributing significantly to the bank's overall profitability.
Furthermore, Bank of India's diverse loan portfolio, including infrastructure and select corporate lending, acts as a steady cash generator. The net interest income of ₹36,612 crore in FY2023 underscores the predictable earnings from these stable, albeit slower-growing, segments.
The bank's extensive traditional branch network, exceeding 5,300 domestic locations, supports core banking services that yield consistent fee income and foster customer loyalty. This operational stability is reflected in the ₹2,587 crore net profit for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024.
| Business Segment | BCG Category | Key Characteristics | FY24 Data/Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deposits (CASA) | Cash Cow | Low-cost, stable funding, consistent revenue | ₹7 lakh crore domestic deposits (11.21% YoY growth) |
| Corporate & Wholesale Banking | Cash Cow | Established relationships, stable market presence, reliable income | Significant contributor to business volume & loan portfolio |
| Foreign Exchange & Trade Finance | Cash Cow | High-margin, stable income, minimal investment needs | Crucial for international trade, consistent profitability |
| Infrastructure & Select Corporate Loans | Cash Cow | Predictable interest income, stable asset base | ₹36,612 crore net interest income (FY2023) |
| Traditional Branch Network & Services | Cash Cow | Consistent fee income, customer loyalty, stable revenue | 5,300+ branches, ₹2,587 crore net profit (FY24) |
What You’re Viewing Is Included
Bank of India BCG Matrix
The Bank of India BCG Matrix preview you are viewing is the identical, fully-formatted document you will receive immediately after purchase. This means the strategic insights and visual representation of Bank of India's business units are exactly as presented, ready for your immediate analysis and decision-making without any alterations or watermarks. You can confidently assess the Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs as depicted, knowing this is the complete, professional-grade report you're investing in.
Dogs
Underperforming non-core assets within the Bank of India's BCG Matrix would represent investments that are not yielding satisfactory returns or possess a low market share in stagnant or declining sectors. These often include legacy holdings or ventures deemed non-strategic, which consume capital without contributing significantly to the bank's overall profitability or growth objectives.
Despite Bank of India's overall progress in reducing Non-Performing Assets (NPAs), certain credit segments continue to present challenges. For example, some government-backed lending schemes have experienced an increase in their absolute NPA figures, signaling areas where loan performance is lagging.
These underperforming segments, akin to 'dogs' in a BCG matrix, not only represent a drag on the bank's profitability but also tie up valuable capital and management attention. As of the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, while the bank's gross NPA ratio improved to 4.14%, specific portfolios within this might still exhibit higher stress, requiring focused resolution strategies.
Outdated technology platforms, often referred to as legacy systems, can become significant liabilities for banks. These systems can be incredibly costly to maintain, consuming a substantial portion of IT budgets without delivering commensurate value. For instance, in 2023, the global banking sector spent an estimated $1.5 trillion on IT, with a significant chunk allocated to maintaining legacy infrastructure.
These older platforms are typically inefficient, hindering the bank's ability to offer modern digital services that customers expect. They can also be inflexible, making it difficult and expensive to integrate new technologies or adapt to evolving market demands. Banks of India, like many globally, are navigating this challenge as they push for digital transformation, with older, un-migrated systems representing a clear 'dog' in their strategic portfolio.
Unprofitable International Operations (if any)
Bank of India's international operations, while extensive, may include certain branches or units that are not performing well. These could be in markets where the bank has a small market share or faces high operating expenses, especially in established or shrinking economies. For instance, if a particular overseas branch in a mature European market consistently reports negative net interest margins due to intense competition and regulatory burdens, it would be considered a dog.
Such underperforming international segments require careful assessment. The bank might consider strategies like divesting these units to free up capital or implementing significant restructuring to improve profitability. For example, if Bank of India's operations in a specific Southeast Asian country are struggling with low customer acquisition rates and high overheads, it might fall into this category. As of the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Bank of India reported a net profit of ₹2,615 crore, with its international operations contributing a significant portion to its overall business, but specific underperforming segments would be identified through detailed segment-wise profitability analysis.
- Low Profitability: International branches or operations consistently generating minimal profits or incurring losses.
- Market Position: Operations in mature or declining foreign markets with limited market share.
- Cost Structure: High operational costs relative to revenue in specific international locations.
- Strategic Review: Potential need for divestiture or substantial restructuring of these underperforming units.
Low-Engagement, High-Cost Customer Segments
Customer segments that are expensive to serve but bring in very little income, or don't interact much with the bank's money-making services, can be seen as dogs in the Bank of India's BCG Matrix. These are often the accounts that are either too small to be profitable or are simply not being used much, yet they still tie up the bank's resources.
For instance, consider customer segments with a high number of very small, inactive savings accounts. These accounts, while numerous, might contribute minimally to the bank's overall revenue. In 2023, the Bank of India reported a significant portion of its customer base held accounts with balances below ₹5,000, which, if inactive, represent a cost center rather than a profit driver.
- Low Revenue Generation: These segments may have a low average revenue per user (ARPU), making their servicing costs disproportionately high.
- High Operational Costs: Maintaining these accounts, even if small, incurs costs related to IT infrastructure, customer support, and regulatory compliance.
- Limited Product Adoption: Customers in these segments often show low uptake of higher-margin products like loans or investment services.
- Resource Drain: They can consume valuable branch and digital channel resources that could otherwise be allocated to more profitable customer groups.
In the Bank of India's BCG Matrix, 'dogs' represent business units or assets that have low market share and operate in low-growth industries. These are typically underperforming investments that consume resources without generating significant returns. Identifying and managing these 'dogs' is crucial for optimizing the bank's overall portfolio and capital allocation.
Specific examples within Bank of India might include certain legacy IT systems that are costly to maintain and hinder digital transformation efforts. Additionally, some international operations in mature or declining markets with a small customer base and high operating expenses could also be classified as dogs. Even certain customer segments that are expensive to serve due to low account balances and inactivity can fall into this category, tying up valuable resources.
The bank's strategy for these 'dogs' often involves either divestment to free up capital or a significant restructuring to improve their performance. For instance, a review of overseas branches might reveal units in markets with intense competition and regulatory hurdles, leading to minimal profitability. As of March 31, 2024, while Bank of India's gross NPA ratio stood at 4.14%, specific underperforming portfolios, akin to dogs, would require focused resolution.
| Category | Description | Bank of India Example | Market Share | Market Growth |
| Dogs | Low market share, low market growth | Legacy IT systems, underperforming international branches, inactive low-balance customer segments | Low | Low |
Question Marks
Bank of India is strategically investing in new digital offerings like the 'Star Diggbis' credit assessment tool and virtual account payment solutions for businesses. These innovations are positioned within the fast-expanding digital banking sector, aiming to capture future market share.
While these digital products represent a significant growth opportunity, their market penetration and customer adoption are still in early stages. This positions them as question marks, requiring further investment and development to solidify their market standing and future profitability.
Bank of India's proposed wealth management business, slated for launch by March 2026, targets India's burgeoning high net-worth individual (HNI) segment. This initiative positions the bank to potentially develop a 'Star' in the BCG matrix, given the high-growth nature of this market. However, achieving this status will necessitate substantial investment and a robust strategy to capture market share from established players.
Bank of India is actively pursuing fintech collaborations and cybersecurity hackathons, signaling a strategic move to tap into high-growth financial technology areas. These initiatives are designed to foster innovation and accelerate the development of new banking prototypes. For instance, in 2024, the bank participated in several industry-wide hackathons, showcasing a commitment to exploring cutting-edge solutions.
While these collaborations offer significant potential for market share gains and technological advancement, their direct impact and ROI remain to be fully realized. The bank’s investment in these innovation hubs, though promising, represents a strategic bet on future growth rather than a guaranteed immediate return. The ultimate success will hinge on the effective integration and market adoption of the developed prototypes.
Specific Niche Lending Products
Bank of India's specific niche lending products, such as specialized financing for renewable energy projects or bespoke solutions for the burgeoning startup ecosystem, would likely fall into the question mark category within a BCG Matrix analysis. These offerings target segments with high growth potential but may currently have limited market share or brand recognition for these particular products.
The bank would need to invest heavily in marketing, product development, and building expertise to capture these emerging markets. For example, in 2024, the Indian government's push towards green finance and the continued dynamism of the startup sector present significant opportunities.
- Renewable Energy Financing: Products tailored for solar, wind, and other green energy projects, potentially offering concessional rates or longer repayment periods.
- Startup Ecosystem Loans: Specialized credit lines for early-stage startups, venture debt, or funding for specific growth phases, acknowledging the high failure rate but also the potential for exponential returns.
- Agri-Tech Lending: Financing for innovative agricultural technology adoption, targeting a sector ripe for modernization and efficiency gains.
Expansion into New Geographies/Rural Markets (with new offerings)
Bank of India's expansion into new geographies, particularly underserved rural markets, with innovative product offerings positions these ventures as question marks in its BCG Matrix. While the bank is actively increasing its branch presence in semi-urban areas, the true success of these new initiatives, especially those focused on financial inclusion and novel product adoption, is still being determined. The overall market in these regions shows growth potential, but the bank's specific market share and profitability in these nascent ventures are not yet solidified. For instance, in 2024, the bank aimed to increase its financial inclusion efforts, targeting 100 new villages with specialized digital banking solutions. The uptake and revenue generation from these specific programs are key indicators for their future classification.
These question mark areas represent opportunities for significant future growth, but also carry higher risk due to unproven market acceptance and the costs associated with establishing a new presence. The bank's strategy here involves testing new service models and products, such as micro-loans or specialized savings accounts for agricultural communities. Success in these areas could lead to a significant market share gain, but initial investment and operational expenses are high. For example, a pilot program launched in rural Maharashtra in late 2023, offering tailored agricultural insurance products, reported a customer acquisition cost of INR 500 per customer, with a projected return on investment over three years.
- Market Potential: Rural and semi-urban markets represent a growing segment, with increasing disposable incomes and a greater need for formal financial services.
- Penetration & Profitability: While expansion is underway, the bank's current market penetration and profitability in these specific new geographic ventures are still in the early stages of development.
- Product Innovation: The success of new, targeted product offerings and financial inclusion initiatives in these areas is crucial for determining their future standing.
- Risk vs. Reward: These ventures carry higher risk due to unproven market acceptance but offer substantial reward if successful, potentially transforming them into stars.
Bank of India's digital transformation initiatives, like its 'Star Diggbis' credit assessment tool and virtual account payment solutions, are prime examples of question marks. These are investments in high-growth areas, but their market penetration and customer adoption are still developing. The bank's foray into wealth management, targeting the HNI segment, also falls into this category; it has significant potential but requires substantial investment to gain traction against established players.
Furthermore, the bank's strategic collaborations with fintech firms and participation in cybersecurity hackathons in 2024 represent bets on future technological advancements. While these ventures aim to foster innovation and develop new banking prototypes, their ultimate return on investment and market impact are yet to be fully realized, making them classic question marks needing careful nurturing.
Bank of India's specialized lending products, such as those for renewable energy projects and the startup ecosystem, are also question marks. These target high-potential segments, but the bank's current market share and brand recognition in these niches are limited. Success hinges on significant investment in marketing and product development, especially given the government's focus on green finance and the dynamic startup landscape in 2024.
| Initiative | BCG Category | Market Potential | Current Status | Strategic Focus |
| Digital Offerings (e.g., Star Diggbis) | Question Mark | High (Digital Banking Sector) | Early Stage Adoption | Investment in Market Penetration |
| Wealth Management Business | Question Mark | High (HNI Segment) | Pre-Launch (Target March 2026) | Substantial Investment & Strategy Development |
| Fintech Collaborations & Hackathons | Question Mark | High (Fintech Innovation) | Ongoing Development & Prototyping | Fostering Innovation, Exploring New Solutions |
| Niche Lending (Renewable Energy, Startups) | Question Mark | High (Emerging Sectors) | Limited Market Share/Recognition | Marketing, Product Development, Expertise Building |
BCG Matrix Data Sources
Our Bank of India BCG Matrix leverages official annual reports, Reserve Bank of India data, and comprehensive market research to provide a robust strategic overview.
