Ayala Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ayala Bundle
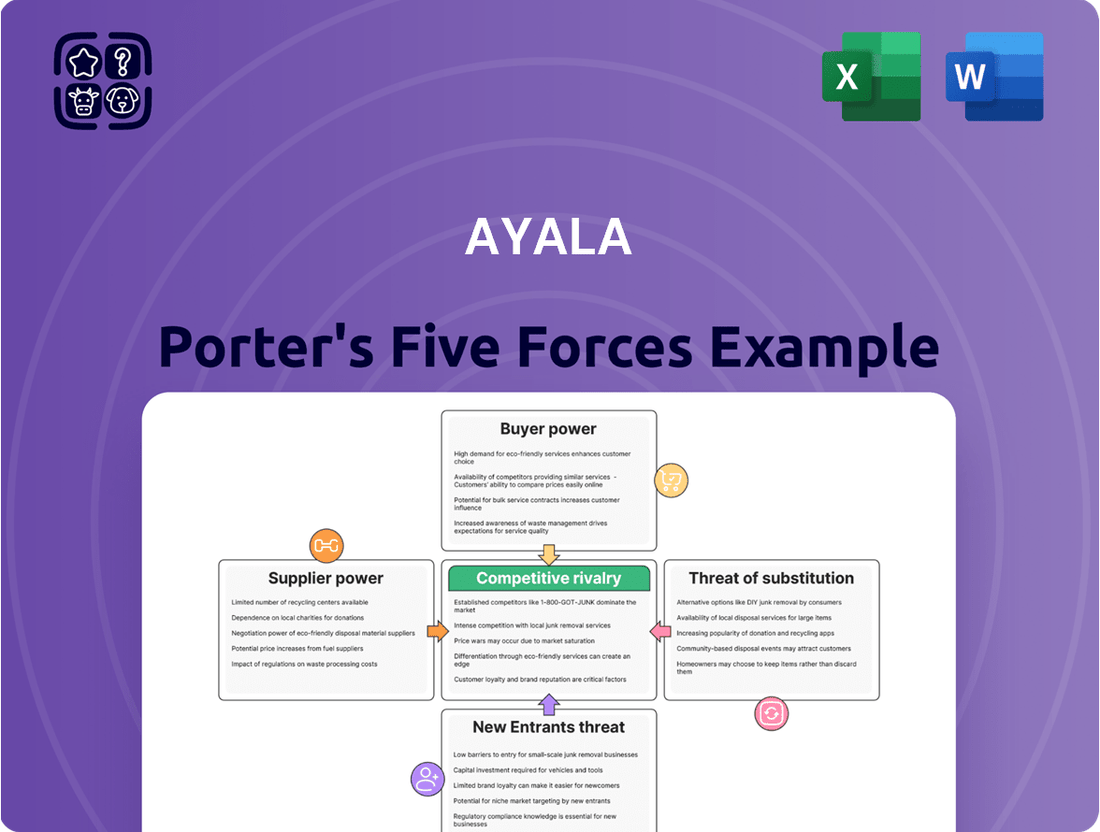
Ayala's Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intricate web of competitive forces shaping its operating landscape. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of substitutes and new entrants is crucial for strategic success.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Ayala’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ayala Corporation's exposure to supplier bargaining power is a complex interplay of its diverse business units. For instance, Globe Telecom's need for specialized telecommunications infrastructure from a limited number of global manufacturers grants those suppliers considerable leverage. Similarly, ACEN's reliance on advanced components for its renewable energy projects, where only a few firms possess the necessary technology, amplifies supplier influence.
In contrast, Ayala Land's real estate development ventures often utilize more commoditized materials like cement and steel. The presence of numerous suppliers for these basic inputs means Ayala Land faces less supplier power in these segments. This disparity highlights how the uniqueness and concentration of suppliers directly shape the bargaining power within different Ayala Corporation sectors.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ayala Corporation is significantly influenced by switching costs, which vary considerably across its diverse business segments. For its financial services arm, BPI, and telecommunications unit, Globe, the cost and complexity of switching key suppliers, such as core banking software or network infrastructure, can be substantial. This often involves significant financial investment, extensive retraining, and potential operational disruptions, thereby granting these critical suppliers greater leverage.
Conversely, Ayala Land, which operates in the property development sector, faces lower switching costs for many of its suppliers, particularly for common construction materials. The availability of multiple vendors for items like cement or steel means that changing suppliers is generally a straightforward process with minimal disruption, thus reducing the bargaining power of these particular suppliers.
In 2024, the digital transformation initiatives across BPI and Globe, aimed at enhancing efficiency and customer experience, likely increased the dependency on specialized technology providers. This trend could further elevate the bargaining power of suppliers in these segments due to the intricate integration and specialized nature of the services provided.
Suppliers might threaten Ayala by moving into its business areas, effectively becoming direct rivals. This risk is lower for suppliers of highly specialized parts to a large, diversified company like Ayala. However, it's a possibility for raw material providers or tech firms that could decide to offer their own end-user services.
Ayala's substantial size and strong position in its markets generally help to lessen this particular threat. For instance, Ayala Land's extensive property development projects rely on a diverse range of suppliers, making it difficult for any single supplier to gain enough leverage to integrate forward effectively.
Importance of Ayala as a Customer to Suppliers
Ayala Corporation's immense scale, demonstrated by its P230 billion capital expenditure plan for 2025 across its diverse portfolio, positions it as a critical customer for numerous suppliers. This substantial purchasing power allows Ayala to negotiate favorable terms, pricing, and delivery schedules, thereby diminishing the bargaining leverage of its suppliers.
For instance, ACEN's significant P70 billion capex allocation for 2025, intended to fuel its extensive project pipeline, underscores the considerable volume of business Ayala directs towards its supply chain partners. This financial commitment translates into a strong negotiating position for Ayala.
- Significant Purchasing Volume: Ayala's substantial capital expenditures, such as the P230 billion planned for 2025, make it a key client for many suppliers.
- Negotiating Leverage: This large purchasing volume grants Ayala considerable power to influence prices, terms, and delivery schedules with its suppliers.
- Reduced Supplier Power: Consequently, the bargaining power of Ayala's suppliers is inherently reduced due to Ayala's importance as a customer.
- Example: ACEN's Capex: ACEN's P70 billion capex for 2025 highlights the scale of Ayala's business and its impact on supplier relationships.
Availability of Substitutes for Supplier Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly shapes supplier bargaining power. In rapidly advancing sectors like renewable energy, the emergence of new technologies and alternative solutions can diminish the leverage of established equipment providers. For instance, the solar industry saw a significant drop in polysilicon prices in early 2024 due to increased production capacity and the development of alternative manufacturing processes, thereby reducing the bargaining power of existing polysilicon suppliers.
Conversely, when inputs are proprietary or subject to stringent regulations, substitutes are often scarce. This scarcity grants suppliers greater pricing power and influence. Consider the semiconductor industry, where access to advanced chip manufacturing equipment, like those produced by ASML, is highly concentrated. The lack of viable substitutes for their extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines gives ASML considerable bargaining power, a situation that continued to be evident through 2024.
- Limited Substitutes Increase Supplier Power: Industries reliant on specialized or patented components, such as advanced materials for aerospace or specific software platforms for enterprise resource planning, often face suppliers with strong bargaining power due to the lack of readily available alternatives.
- Technological Advancements Create Substitutes: In sectors like electric vehicles, the rapid development of battery technologies and charging infrastructure is creating new substitute inputs, potentially weakening the position of incumbent battery manufacturers and charging station providers as more options become viable.
- Regulatory Hurdles Limit Substitutability: For inputs requiring strict compliance with industry-specific regulations, such as pharmaceutical ingredients or specialized medical devices, the ability to switch to substitutes is often constrained, empowering existing suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ayala Corporation is a critical factor, varying significantly across its diverse business segments. For highly specialized inputs, such as advanced telecommunications equipment for Globe or proprietary components for ACEN's renewable energy projects, suppliers often hold substantial leverage due to limited alternatives and high switching costs. This was particularly evident in 2024, with ongoing supply chain complexities for critical technology components.
Conversely, segments like Ayala Land's property development often deal with more commoditized materials like cement and steel, where a wider array of suppliers and lower switching costs mean less supplier power. Ayala's immense scale, exemplified by its P230 billion capital expenditure plan for 2025, provides a strong counter-balance, allowing it to negotiate favorable terms and reduce supplier influence across its operations.
| Ayala Business Segment | Key Inputs | Supplier Bargaining Power Factors | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Globe Telecom | Telecommunications Infrastructure | Limited specialized suppliers, high switching costs | Continued demand for 5G deployment |
| ACEN | Renewable Energy Components | Proprietary technology, R&D intensity | P70 billion capex for 2025 projects |
| Ayala Land | Construction Materials | Numerous suppliers, lower switching costs | Large-scale property development |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously examines the five competitive forces impacting Ayala, offering insights into industry attractiveness and strategic positioning.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual, easy-to-understand breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ayala Corporation's customer base is incredibly broad, encompassing millions of individual consumers across its telecommunications and banking sectors, alongside numerous corporate clients and property buyers. This sheer diversity means that while individual customers generally possess minimal bargaining power due to their small transaction sizes, larger institutional clients or those making bulk purchases in areas like real estate or energy can exert more significant influence.
For example, Bank of the Philippine Islands (BPI), a key Ayala subsidiary, reported serving 16 million customers in 2024, a substantial doubling since 2021. This highlights a highly fragmented individual customer segment, which inherently limits the collective bargaining power of the average consumer.
Customer price sensitivity significantly influences Ayala's bargaining power. In highly competitive sectors such as telecommunications and retail banking, where numerous providers exist, customers exhibit a strong inclination to switch based on price. This heightened sensitivity directly translates into greater bargaining power for these customers, compelling Ayala to maintain competitive pricing and potentially impacting profit margins.
Conversely, Ayala Land's premium real estate developments, targeting the affluent segment, often experience lower price sensitivity. For these discerning buyers, factors like location, quality, and brand reputation can outweigh minor price differences. This allows Ayala Land more leeway in pricing its premium offerings, thereby enhancing its pricing power and potentially leading to higher profitability for these specific ventures.
Customers wield significant bargaining power when a wide array of substitute products or services exists. This abundance of choices empowers them to switch providers readily if they find better value or are dissatisfied with current offerings.
In the Philippine market, this is clearly visible across sectors like banking, telecommunications, and real estate, where consumers can easily compare and transition between different providers. For instance, in 2024, Globe Telecom, while reporting strong financial performance, operates within a competitive landscape where consumers have readily available alternatives from other mobile networks and emerging digital communication platforms.
Switching Costs for Customers
The ease with which customers can switch from Ayala's offerings to a competitor's directly impacts their bargaining power. While switching providers in sectors like telecommunications or banking might involve some inconvenience or minor fees, these are typically not significant enough to deter a customer seeking better value or service.
Ayala actively works to mitigate this by implementing strategies that increase customer loyalty and reduce the likelihood of them switching. This includes robust loyalty programs, offering bundled services that create a more integrated experience, and in the case of Ayala Land, fostering a sense of community within its developments, which enhances customer stickiness.
- Customer Switching Costs: Ayala's efforts to increase switching costs are crucial in managing customer bargaining power.
- Loyalty Programs and Bundling: These initiatives aim to make it less attractive for customers to leave by offering added value and convenience.
- Integrated Offerings: For instance, Ayala Land's focus on integrated community living creates a holistic experience that discourages customers from seeking individual components elsewhere.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: By raising switching costs, Ayala can effectively reduce the leverage customers have in demanding lower prices or better terms.
Customer Information and Differentiation
Customers who are well-informed and have access to readily available information can significantly increase their bargaining power, particularly in markets where products or services are not easily distinguished from competitors. In 2024, this trend is amplified by digital platforms that offer price comparisons and product reviews, making it harder for companies to maintain pricing power if differentiation is weak.
Ayala, as a diversified conglomerate, actively works to counter this by differentiating its offerings. This is achieved through a strong brand reputation built over decades, a consistent focus on quality across its various businesses, and the development of integrated service ecosystems that create unique value. For instance, Ayala Land’s strategy of developing large-scale, master-planned communities offers a comprehensive living experience, distinguishing it from standalone property developments.
- Informed Customers: Increased access to information in 2024 empowers customers, especially in low-differentiation sectors.
- Ayala's Differentiation Strategy: Focus on brand, quality, and integrated ecosystems to enhance customer loyalty and reduce price sensitivity.
- Integrated Communities: Ayala Land's approach to creating self-sustaining communities provides a unique value proposition beyond just real estate.
The bargaining power of customers for Ayala Corporation is influenced by several factors, including the availability of substitutes and the cost for customers to switch. In sectors like telecommunications, where alternatives are plentiful and switching costs are relatively low, customers can exert considerable pressure on pricing and service terms. For example, Globe Telecom, an Ayala subsidiary, operates in a highly competitive Philippine market in 2024, where consumers can easily compare and switch between mobile providers.
Conversely, in segments like premium real estate developed by Ayala Land, customer price sensitivity is lower, with factors like location and brand reputation playing a more significant role. This allows Ayala more pricing flexibility in such ventures. The company actively works to mitigate customer bargaining power through loyalty programs and integrated service offerings, aiming to increase customer stickiness and reduce their incentive to switch.
| Ayala Subsidiary | Sector | Customer Bargaining Power Factor | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Globe Telecom | Telecommunications | High availability of substitutes, low switching costs | Operates in a competitive market with numerous alternatives; strong focus on customer retention. |
| Bank of the Philippine Islands (BPI) | Banking | Fragmented individual customer base, but institutional clients have influence | Served 16 million customers in 2024, indicating broad reach but limited individual power. |
| Ayala Land | Real Estate | Lower price sensitivity for premium developments, high brand loyalty | Premium developments benefit from strong brand reputation and integrated community concepts, reducing customer price leverage. |
Full Version Awaits
Ayala Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Ayala Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a detailed examination of the competitive landscape, offering actionable insights into industry profitability and strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Ayala Corporation faces significant competitive rivalry across its diverse business segments. In banking, its subsidiary BPI contends with formidable local institutions such as BDO Unibank, which reported total assets of PHP 4.1 trillion as of December 31, 2023, and Metrobank. The telecommunications landscape is equally intense, with Globe Telecom, another Ayala unit, battling against PLDT/Smart and the emerging DITO Telecommunity, which has been actively expanding its subscriber base and network coverage.
The real estate sector also presents a crowded field, where Ayala Land Inc. competes with other major property developers in the Philippines, all vying for market share in a dynamic and growing economy. This robust competition necessitates continuous innovation and strategic maneuvering to maintain and grow market position.
The growth rate of the industries Ayala Corporation operates in plays a crucial role in shaping competitive rivalry. In more mature or slower-growing sectors, companies often intensify their efforts to capture existing market share, leading to heightened competition.
Conversely, high-growth industries present different dynamics. For instance, ACEN, a key Ayala subsidiary, has been actively expanding in the renewable energy sector. This area, projected for robust growth through 2025, offers significant opportunities for expansion. As demand in such sectors is anticipated to outpace supply, it can temper the intensity of direct competition, allowing companies like ACEN to focus on scaling their operations and market penetration.
Ayala Corporation strives for product differentiation, especially in its property and industrial segments, by emphasizing quality and integrated service offerings. However, in sectors like banking and telecommunications, core services can become highly commoditized, intensifying price-based competition. For instance, Globe Telecom, a key Ayala subsidiary, faces a dynamic telecom market where service features often become standard, pushing competition towards pricing strategies.
To counter this, Ayala actively works on building brand loyalty and fostering customer ecosystems. A prime example is GCash, Globe's mobile wallet, which aims to create sticky customer relationships by offering a wide range of financial services beyond basic communication. This strategy is crucial for reducing customer churn and mitigating the impact of intense rivalry, as customers integrated into these ecosystems face higher switching costs.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Industries such as telecommunications and power generation demand substantial upfront investment in infrastructure. For example, building a new cellular network or a power plant involves billions of dollars in fixed costs. Companies in these sectors aim for high utilization rates to amortize these significant expenditures, making them reluctant to scale back operations even when demand softens.
These high fixed costs and the specialized nature of assets create formidable exit barriers. Once a company has invested heavily, it's difficult and costly to divest or repurpose those assets. Consequently, firms tend to persist in the market, intensifying competition rather than withdrawing, which can lead to prolonged price wars or aggressive market share battles.
Ayala Corporation's strategic investments reflect this dynamic. For instance, its significant stakes in Globe Telecom and ACEN (power generation) represent substantial fixed capital outlays. In 2023, Globe Telecom reported capital expenditures of PHP 50.1 billion, primarily for network expansion and upgrades, highlighting the ongoing need to maintain and enhance infrastructure to remain competitive.
- High Fixed Costs: Industries like telecom and power require massive initial investments in infrastructure, making it crucial for companies to maximize capacity utilization.
- Exit Barriers: The specialized and costly nature of these assets makes it difficult and expensive for companies to leave the market, leading to continued competition.
- Ayala's Investments: Ayala's portfolio, including Globe Telecom and ACEN, demonstrates a commitment to capital-intensive sectors where high fixed costs and exit barriers are inherent.
- 2023 Capex: Globe Telecom's PHP 50.1 billion capital expenditure in 2023 exemplifies the continuous investment needed to sustain operations and competitiveness in these high-cost industries.
Strategic Stakes and Diversity of Competitors
The Philippine market is a strategic battleground, drawing both local conglomerates and international players, which naturally heightens competitive rivalry. This diverse set of actors, each with distinct goals—some prioritizing rapid market share acquisition and others focusing on sustained profitability—can result in unpredictable and aggressive competitive maneuvers. For instance, in 2024, the telecommunications sector saw intense competition as players like Globe Telecom and PLDT Inc. invested heavily in 5G infrastructure, aiming to capture a larger subscriber base.
Ayala Corporation, with its broad portfolio, navigates these varied competitive landscapes. While its diversified structure enables the exploitation of internal synergies, it also means confronting unique competitive pressures across different industries. For example, in the real estate sector, Ayala Land faces competition not only from domestic developers but also from international firms seeking opportunities in the growing Philippine economy, a trend that continued through early 2025.
- Strategic Importance: The Philippines remains a key growth market, attracting significant investment from global firms, thereby increasing the intensity of competition.
- Diverse Objectives: Competitors range from those focused on market share dominance, like budget airlines in the travel sector, to those prioritizing profit margins, influencing their strategic decisions.
- Ayala's Position: Ayala's diversified business model means it encounters different competitive dynamics in each of its operating segments, from banking to infrastructure.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic for Ayala Corporation's diverse business interests. In banking, BPI competes fiercely with BDO Unibank, which held PHP 4.1 trillion in total assets as of December 31, 2023, and Metrobank. The telecom sector sees Globe Telecom in direct competition with PLDT/Smart and the expanding DITO Telecommunity. Ayala Land Inc. also faces intense rivalry from numerous local and international property developers in the Philippines, a market dynamic that persisted into early 2025.
| Ayala Subsidiary | Primary Competitors | Key Competitive Factor | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPI (Banking) | BDO Unibank, Metrobank | Asset size, service offerings, digital banking | BDO total assets: PHP 4.1 trillion (Dec 31, 2023) |
| Globe Telecom (Telecommunications) | PLDT/Smart, DITO Telecommunity | Network coverage, data speeds, pricing, 5G deployment | Globe Telecom Capex: PHP 50.1 billion (2023) for network expansion |
| Ayala Land Inc. (Real Estate) | Other major Philippine developers, international firms | Project portfolio, location, pricing, amenities | Continued influx of international developers in 2024 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes is elevated when alternative offerings present a compelling price-performance advantage. Consider the financial sector where fintech innovations and digital banking platforms are increasingly providing convenient and cost-effective alternatives to traditional brick-and-mortar banks. In 2024, the digital banking sector continued its rapid expansion, with reports indicating a significant increase in customer adoption of online-only financial services, driven by lower fees and enhanced user experience.
This dynamic is also evident in the real estate market. For specific demographics, particularly younger generations or those prioritizing flexibility, renting or engaging in co-living arrangements can serve as a viable substitute for outright property ownership. This trend is supported by data from 2024 showing a sustained demand for rental properties, with rental yields remaining competitive in many urban centers, making ownership less immediately attractive for some.
Customer willingness to switch to substitutes is a key consideration. Factors like convenience, how aware customers are of alternatives, and shifts in their lifestyles all play a role in this. For instance, in 2024, the Philippines saw continued growth in e-wallets, indicating a growing comfort with digital transactions.
The Philippines' increasing digital literacy directly impacts this. As more Filipinos become comfortable with technology, they are more likely to explore and adopt digital substitutes for traditional services. This trend is evident in the expanding user base of various fintech applications, offering alternatives to traditional banking services.
The rapid pace of technological change constantly introduces new substitutes that can challenge existing business models. For instance, in the energy sector where ACEN operates, advancements in distributed solar power and increasingly efficient battery storage systems are making localized energy generation a more viable alternative to traditional, centralized grid power. This shift directly impacts the demand for ACEN's core offerings.
Ayala Corporation's diversified portfolio, spanning industrial technologies, healthcare, and education, is also susceptible to this threat. New technology-driven substitutes can emerge quickly, offering more convenient, cost-effective, or superior solutions. For example, in healthcare, advancements in telemedicine and wearable diagnostic devices could reduce the need for traditional in-person consultations and diagnostics, impacting the healthcare services segment.
Indirect Substitutes and Lifestyle Changes
Beyond direct product replacements, evolving lifestyle choices can significantly act as substitutes, impacting industries like real estate and telecommunications. For instance, the widespread adoption of remote work arrangements, accelerated by events in 2020 and continuing through 2024, has demonstrably reduced the demand for traditional office spaces, a key sector for many real estate developers. This shift represents a powerful indirect substitute for conventional office leasing.
In the telecommunications sector, the proliferation of Over-The-Top (OTT) messaging and calling applications has dramatically substituted the demand for traditional SMS and voice services. By mid-2024, platforms like WhatsApp and Telegram continue to dominate communication, forcing telcos to adapt. Globe, for example, has strategically shifted its revenue model to capitalize on data consumption, a direct response to this substitute threat.
- Remote Work Impact: In 2024, a significant percentage of the global workforce continued to operate remotely, impacting commercial real estate valuations and demand for office leases.
- OTT Service Dominance: By the end of 2023, global mobile data traffic had surged, largely driven by OTT communication apps, illustrating their substitution effect on traditional voice and SMS revenue for telecom operators.
- Globe's Data Monetization: Globe's strategy to focus on data services in response to OTT substitutes has shown success, with data revenue contributing a substantial portion of their overall earnings in recent financial reports.
Regulatory and Policy Landscape for Substitutes
Government regulations and policies play a crucial role in shaping the competitive landscape for substitutes. Favorable policies can significantly accelerate the adoption of alternatives, thereby increasing competitive pressure on established players like Ayala. For instance, in 2024, many governments continued to implement incentives for renewable energy adoption, which directly impacts the demand for traditional energy sources and related infrastructure services.
Policies that support the growth of digital financial services, such as open banking initiatives and digital identity frameworks, can also empower fintech substitutes. These policies can lower barriers to entry and encourage innovation, making digital alternatives more attractive compared to traditional banking and remittance services. In 2024, the global digital payments market was projected to reach over $2.5 trillion, highlighting the significant impact of enabling policies on substitute growth.
- Regulatory Support for Renewables: Government subsidies and tax credits for solar and wind power in 2024 incentivized a shift away from fossil fuels, impacting energy infrastructure providers.
- Digital Finance Initiatives: Policies promoting digital wallets and faster payment systems in emerging markets in 2024 boosted the competitiveness of fintech alternatives against traditional remittance services.
- Environmental Standards: Stricter environmental regulations enacted in 2024 increased compliance costs for traditional industries, making cleaner substitutes more appealing.
The threat of substitutes is amplified when alternatives offer a superior price-performance ratio or cater to evolving customer preferences. For example, in 2024, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) presented a growing substitute for traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, driven by environmental concerns and improving battery technology. Similarly, the continued expansion of ride-sharing services in urban areas in 2024 provided a convenient substitute for private car ownership for many commuters.
Customer awareness and switching costs are critical factors influencing the threat of substitutes. As more consumers become aware of and comfortable with alternatives, the pressure on incumbents increases. In 2024, the widespread availability of streaming services like Netflix and Disney+ significantly reduced the demand for traditional cable television subscriptions, with many households opting for more flexible and often cheaper digital alternatives.
The threat of substitutes is also shaped by technological advancements and changing lifestyle trends. The increasing adoption of remote work, a trend that continued to solidify in 2024, has reduced the need for business travel and office space, impacting sectors like airlines and commercial real estate. Furthermore, the growing preference for experiences over material possessions, particularly among younger demographics, can shift spending away from traditional product categories towards services and leisure activities.
| Industry Segment | Substitute Offering | 2024 Trend/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Increased adoption due to environmental concerns and improving infrastructure. |
| Transportation | Ride-sharing Services | Continued growth in urban centers, impacting public transport and private car usage. |
| Media & Entertainment | Streaming Services | Dominance over traditional cable, leading to cord-cutting. |
| Real Estate | Remote Work Arrangements | Reduced demand for office space and increased demand for flexible workspaces. |
Entrants Threaten
Ayala's core businesses, including real estate, telecommunications, and power, demand enormous upfront capital. For instance, establishing a nationwide telecommunications infrastructure or developing large-scale power generation facilities requires billions of dollars, presenting a formidable hurdle for new players.
ACEN's ambitious goal of reaching 1.2 GW of renewable energy capacity by the end of 2025 underscores the substantial financial commitment needed in the energy sector. Such high capital requirements effectively deter many potential entrants, safeguarding Ayala's market position.
Established brands like Ayala Land, BPI, and Globe Telecom boast decades of built-up recognition and customer loyalty. This makes it incredibly difficult for new players to gain traction.
New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and potentially offer aggressive pricing to even begin building trust and a customer base. For instance, in 2024, the telecommunications sector saw significant marketing spend from incumbents to retain subscribers amidst new service introductions.
Ayala Corporation's existing distribution channels present a formidable barrier to new entrants. For instance, Globe's extensive mobile network, serving millions across the Philippines, makes it incredibly difficult for a newcomer to establish a comparable reach quickly. Similarly, Ayala Land's established retail footprint and BPI's banking branches offer immediate customer access that new players would struggle to replicate.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly impact the threat of new entrants, especially in highly regulated sectors like banking and telecommunications. Stringent licensing requirements and ongoing regulatory oversight create substantial barriers to entry, demanding considerable time and financial investment to navigate successfully. For instance, obtaining a new banking license can be an arduous process, and access to essential resources like telecom spectrum is often limited and costly, effectively deterring many potential new players.
The regulatory landscape can act as a powerful deterrent. In 2024, the European Union continued to emphasize robust data protection and competition rules, impacting how new digital service providers could enter the market. Similarly, in the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) manages spectrum auctions, with license costs reaching hundreds of millions of dollars for key frequencies, illustrating the financial hurdle for new telecommunications companies.
- Banking Sector: New banking licenses are notoriously difficult and time-consuming to acquire, often requiring extensive capital reserves and adherence to strict compliance frameworks.
- Telecommunications: Access to crucial radio spectrum, essential for mobile services, is typically allocated through government auctions, with significant upfront costs acting as a major barrier. For example, in 2024, spectrum auctions in various countries saw billions of dollars exchanged.
- Energy and Utilities: These sectors often require permits for infrastructure development and operate under price controls and service quality regulations, adding layers of complexity and cost for new entrants.
- Pharmaceuticals: The lengthy and expensive process of drug approval by regulatory bodies like the FDA or EMA presents a formidable challenge for new pharmaceutical companies seeking to bring products to market.
Incumbency Advantages and Retaliation
Ayala Corporation benefits from significant incumbency advantages, including deeply entrenched supply chains, strong, long-standing customer relationships, and highly optimized operational efficiencies honed over decades. These established strengths create a formidable barrier for any potential new entrant aiming to disrupt its market positions.
Newcomers face the substantial threat of aggressive retaliation from Ayala. With its considerable financial resources and established market power across various sectors, Ayala can deploy strategies such as price wars, intensified marketing campaigns, or rapid product and service innovation to neutralize emerging competition and protect its market share.
Ayala's strategic focus on bringing its newer business ventures to profitability underscores its commitment to fortifying its diverse portfolio. This proactive approach is designed to enhance its competitive resilience and ensure it remains well-positioned to counter threats from new entrants across its various industries.
- Incumbency Advantages: Ayala's established supply chains and customer loyalty are key deterrents.
- Retaliation Risk: New entrants must anticipate aggressive responses from Ayala, including price cuts and marketing pushes.
- Portfolio Strengthening: Ayala's drive to achieve profitability in newer businesses signals a defensive strategy against market disruption.
The threat of new entrants for Ayala Corporation is generally low due to significant barriers across its core industries. High capital requirements, established brand loyalty, and extensive distribution networks make it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively. For example, in 2024, the cost of acquiring prime telecommunications spectrum licenses often ran into hundreds of millions of dollars globally, a substantial hurdle for any new player.
Government regulations and the potential for aggressive retaliation from Ayala further deter new entrants. Navigating complex licensing procedures and facing established market players with deep pockets and strong customer relationships requires immense resources and strategic foresight. Ayala's ongoing efforts to strengthen its newer ventures also signal a proactive defense against potential market disruptions.
| Industry | Key Barrier | Example (2024 Data/Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Spectrum Acquisition Costs | Spectrum auctions in various regions saw license costs in the hundreds of millions of dollars. |
| Real Estate | Land Acquisition & Development Costs | Large-scale property development requires significant upfront capital, often in the billions of pesos for major projects. |
| Banking | Regulatory Capital Requirements | New banks need to meet stringent capital adequacy ratios, often exceeding billions of pesos, as mandated by central banks. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon comprehensive data from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and government economic indicators. This blend ensures a robust understanding of competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
