Aurubis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Aurubis Bundle
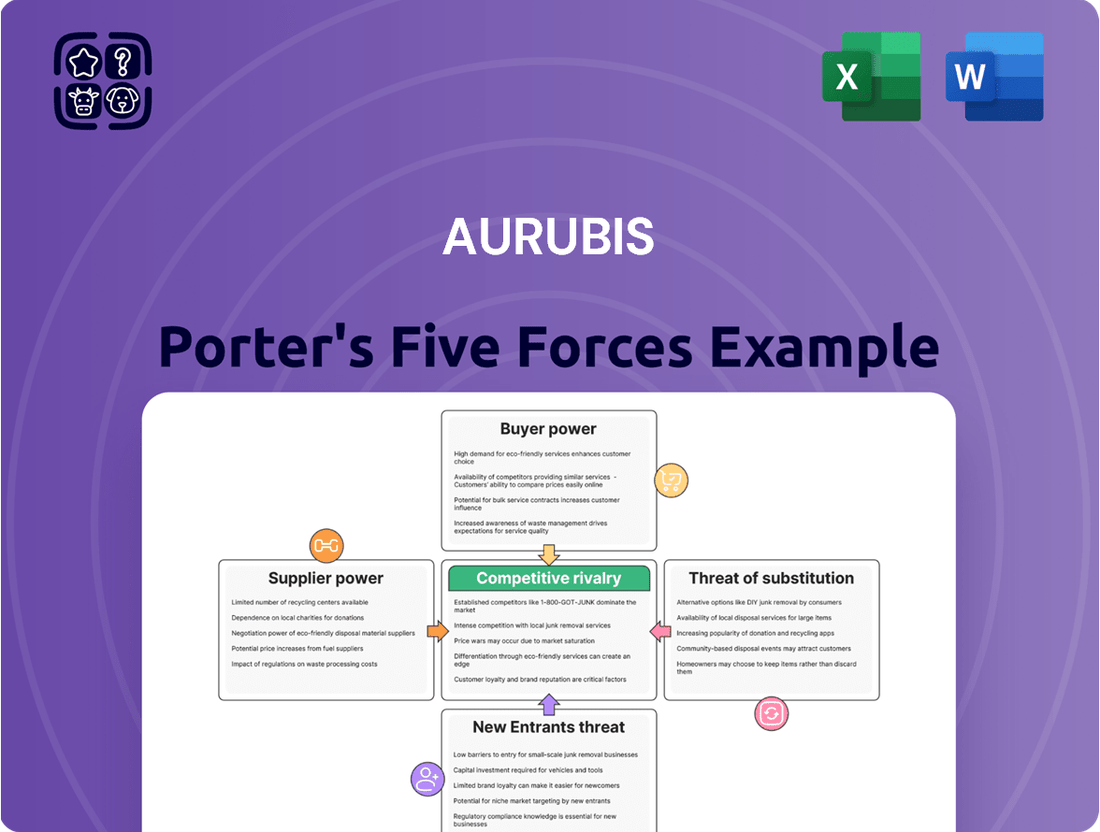
Aurubis faces significant competitive pressures, particularly from the bargaining power of buyers and the intense rivalry within the copper and metals market. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the industry effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Aurubis’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Aurubis is significantly influenced by the concentration of raw material sources. For instance, high-quality copper concentrates and specific grades of metal scrap, crucial for Aurubis's smelting and refining operations, are often sourced from a limited number of global suppliers. This scarcity can grant these suppliers considerable leverage.
In 2024, the global copper concentrate market, a key input for Aurubis, continued to see supply concentrated among a few major mining regions and companies. For example, Chile remains the world's largest copper producer, and a significant portion of global concentrate supply originates from a handful of large-scale mining operations. This concentration means that disruptions or shifts in supply from these few key players can directly impact Aurubis's input costs and availability, thereby strengthening supplier bargaining power.
Aurubis's reliance on specialized metal concentrates and recycling materials, some demanding unique processing, grants suppliers significant leverage. The company handles complex inputs, including those requiring proprietary technologies, making it difficult to substitute sources.
The costs associated with switching suppliers for these specialized inputs are substantial. This includes expenses for retooling production lines, adapting existing processes, and the rigorous qualification of new material streams, all of which bolster supplier bargaining power.
Suppliers of primary metal concentrates or large-scale scrap collectors could integrate forward into refining and processing, directly competing with Aurubis. This threat strengthens their negotiating position, as Aurubis must consider the possibility of losing its own processing business.
For instance, a major copper concentrate supplier in 2024, facing volatile metal prices, might explore building its own smelter. If such a supplier, like Glencore or Antofagasta Minerals, were to credibly threaten to enter Aurubis's downstream refining markets, it would diminish Aurubis's perceived value in the supply chain, thereby increasing the supplier's bargaining power.
Importance of Supplier Inputs to Aurubis's Product Quality
The quality of Aurubis's high-purity copper cathodes and other metals is directly tied to the inputs they receive. Suppliers of critical raw materials, especially those that significantly influence the final product's performance and market desirability, hold considerable sway. This dependence means that disruptions or quality issues from these key suppliers can directly impact Aurubis's reputation and profitability.
For instance, the purity of the copper concentrate purchased by Aurubis is a foundational element for their premium cathode products. Suppliers who can consistently deliver high-grade, impurity-free concentrates are in a strong position. In 2023, Aurubis processed approximately 1.5 million tonnes of copper in total, highlighting the sheer volume of raw materials required and the importance of reliable sourcing.
- Dependence on Input Purity: Aurubis's premium copper cathodes require exceptionally pure raw materials, making suppliers of high-quality concentrates crucial.
- Impact on Final Product: The performance and market value of Aurubis's metals are directly influenced by the consistency and quality of the inputs they receive.
- Supplier Leverage: Suppliers of essential, high-purity raw materials possess increased bargaining power due to their critical role in Aurubis's value chain.
- Volume Significance: With Aurubis processing around 1.5 million tonnes of copper annually (as of 2023), the scale of raw material procurement amplifies the importance of supplier relationships.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs can influence Aurubis's bargaining power with its suppliers. While Aurubis is a significant player in copper recycling, the existence of alternative raw materials, like various grades of copper scrap or concentrates, can lessen the leverage of any single supplier. For instance, in 2023, the global copper concentrate market saw diverse sourcing options emerge, potentially diluting the power of individual mine suppliers.
However, the strength of this mitigating factor depends on the specific input. If Aurubis requires highly specialized or unique inputs for which viable substitutes are scarce, then those suppliers will naturally hold more power. This leverage translates into greater ability to dictate pricing and contractual terms. The limited availability of certain high-purity recycled copper streams, for example, could grant suppliers of these specific materials enhanced bargaining leverage.
- Scrap Grade Variety: A wider array of copper scrap grades can be processed, offering flexibility in sourcing.
- Concentrate Sourcing: Global copper concentrate markets provide multiple supply origins, reducing reliance on any one source.
- Specialized Input Scarcity: Limited availability of unique or high-purity inputs strengthens supplier bargaining power.
- 2023 Market Dynamics: Fluctuations in concentrate prices and availability in 2023 highlighted the impact of substitute options on supplier leverage.
Aurubis faces considerable bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly for specialized copper concentrates and high-purity metal scrap. This is due to the concentrated nature of raw material sources and the significant costs associated with switching suppliers, which can include retooling and rigorous material qualification. The potential for suppliers to integrate forward into refining also enhances their negotiating leverage.
Suppliers of critical inputs, especially those influencing the purity and performance of Aurubis's final products like high-purity copper cathodes, hold substantial sway. In 2023, Aurubis processed approximately 1.5 million tonnes of copper, underscoring the scale and importance of these supplier relationships. While a variety of copper scrap grades and global concentrate markets offer some substitution possibilities, the scarcity of unique or high-purity inputs remains a key driver of supplier power.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Aurubis |
| Supplier Concentration | Limited number of global suppliers for key raw materials. | Increases supplier leverage and potential price volatility. |
| Switching Costs | High expenses for retooling, process adaptation, and new material qualification. | Reduces Aurubis's flexibility and strengthens supplier pricing power. |
| Input Purity Dependence | Critical need for high-purity materials for premium products. | Empowers suppliers of high-quality concentrates and scrap. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers potentially entering Aurubis's refining business. | Diminishes Aurubis's value proposition in the supply chain. |
What is included in the product
Aurubis's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity within the copper and precious metals industry, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces chart, simplifying complex market dynamics for Aurubis.
Customers Bargaining Power
Aurubis's customer base spans electronics, automotive, construction, and renewable energy, suggesting a broad market. However, the bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by concentration; if a few major industrial clients represent a substantial percentage of Aurubis's revenue, these large-volume buyers gain considerable leverage to negotiate lower prices or better contract conditions.
The standardization of copper cathodes and continuous cast rods significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Because these products are essentially commodities, meaning they are largely identical regardless of the producer, buyers can easily compare prices and switch suppliers. For instance, in 2024, global copper prices experienced significant volatility, with LME copper futures trading in a range that often saw differences of less than 1% between major producers for similar grades, making price the primary differentiator for customers.
Customers' switching costs are a crucial factor in assessing their bargaining power. For industrial buyers of essential materials like copper, the expense and effort involved in changing suppliers can be substantial. These costs often include rigorous requalification of new materials, potential disruptions to established production lines, and the need to reconfigure supply chains. For instance, a significant change in copper sourcing might require extensive testing to ensure compatibility and consistent quality, a process that can take months and incur considerable expense.
However, the nature of the product itself plays a vital role. In a commodity market, where products are largely standardized and interchangeable, switching costs for customers tend to be lower. This is because the perceived differences between suppliers are minimal, making it easier for customers to move from one provider to another without significant operational impact or added expense. This low switching cost environment can increase customer bargaining power, as they have more readily available alternatives.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large customers, especially those with substantial metal processing requirements, could explore backward integration into primary metal production or recycling if it becomes financially attractive. This potential shift significantly bolsters their leverage against Aurubis.
The credible threat of customers developing their own copper or other metal production capabilities directly enhances their bargaining power. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer, a significant consumer of copper, might assess the cost-effectiveness of establishing its own smelting or recycling operations. If the economics align, this capability would allow them to negotiate more aggressively on price and supply terms with Aurubis, potentially demanding lower prices or more favorable delivery schedules.
- Customer Integration Potential: The possibility of customers integrating backward into metal production or recycling serves as a potent check on Aurubis's pricing power.
- Economic Viability Threshold: The decision for customers to integrate hinges on the economic feasibility, considering capital investment, operational costs, and market price volatility for raw materials and finished metals.
- Impact on Aurubis's Margins: A successful backward integration by key customers could lead to reduced demand for Aurubis's primary products and put downward pressure on their profit margins.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers in sectors where copper represents a substantial portion of their production expenses, and whose own goods face fierce market competition, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This dynamic compels Aurubis to engage in aggressive pricing strategies, directly amplifying the leverage these cost-focused buyers hold.
For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry, a major consumer of copper, grappled with rising material costs and intense competition, particularly from electric vehicle manufacturers. This environment makes automotive clients highly attuned to copper price fluctuations, impacting Aurubis's pricing flexibility.
- High Price Sensitivity: Industries where copper is a major cost component and face intense end-product price competition lead to heightened customer price sensitivity.
- Competitive Pressure: This sensitivity forces Aurubis into price-based competition, increasing customer bargaining power.
- 2024 Market Context: The automotive sector, a key copper consumer, experienced significant cost pressures and market competition in 2024, underscoring this sensitivity.
The bargaining power of Aurubis's customers is substantial, particularly due to the commoditized nature of copper and the potential for backward integration. Customers in price-sensitive industries, like automotive, have significant leverage, as demonstrated by the tight price differentials observed in 2024 for similar copper grades.
The threat of customers developing their own production capabilities, such as recycling operations, further strengthens their negotiating position. This is especially true for large industrial buyers who can absorb the costs and complexities of vertical integration, putting downward pressure on Aurubis's pricing power and potentially impacting profit margins.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Aurubis |
|---|---|---|
| Product Standardization | Copper cathodes and rods are largely identical across producers. | Increases customer ability to switch based on price. |
| Customer Concentration | A few large industrial clients represent significant revenue. | These clients gain considerable negotiation leverage. |
| Switching Costs | Low for commodity copper, involving requalification and supply chain adjustments. | Facilitates easier customer transitions, enhancing bargaining power. |
| Backward Integration Potential | Customers may develop their own metal production or recycling. | Acts as a credible threat, limiting Aurubis's pricing flexibility. |
| Price Sensitivity | High in sectors where copper is a major cost and competition is fierce. | Forces Aurubis into price-based competition, amplifying customer leverage. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Aurubis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Aurubis's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the copper and precious metals industry. This comprehensive analysis is ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global non-ferrous metals and copper recycling landscape is populated by a significant number of competitors, including several large, established entities that directly challenge Aurubis. This crowded field, encompassing both primary metal producers and recycling specialists, fuels intense rivalry. Companies actively compete for crucial market share, vital raw material supplies, and a loyal customer base, creating a dynamic and demanding environment.
In mature industries, a slower growth rate often fuels more aggressive competition as companies vie for market share. While the overall demand for copper is on an upward trajectory, driven by electrification and infrastructure projects, the specific market segments Aurubis participates in may exhibit more modest growth, intensifying rivalry.
Aurubis's core products, such as copper cathodes, rods, and shapes, are largely seen as commodities. This means there's not much to make one company's copper stand out from another's in terms of inherent features.
Because these products are so similar, competition often boils down to who can offer the best price, provide superior customer service, or manage their supply chain most effectively. This can lead to intense price wars among competitors in the copper market.
In 2023, the average price for copper cathodes hovered around $8,000 to $9,000 per metric ton, illustrating the price-sensitive nature of this market where even small price differences can significantly impact sales volume and profitability for companies like Aurubis.
Exit Barriers
The non-ferrous metals industry, especially primary smelting and refining, requires massive capital outlays for plants and specialized machinery. This significant investment in fixed assets and infrastructure creates substantial exit barriers. Companies find it extremely difficult and costly to divest or shut down operations, forcing them to remain active in the market even when facing challenging economic conditions, thereby fueling intense competition.
These high sunk costs mean that firms are reluctant to leave the industry, even if profitability declines. This persistence leads to a crowded competitive landscape where existing players continue to vie for market share. For instance, Aurubis, a major player, operates complex smelters with lifespans measured in decades, representing billions in invested capital that cannot be easily recouped.
- High Capital Investment: The construction of a primary copper smelter can cost upwards of $1 billion, making it a significant hurdle for new entrants and a powerful disincentive for existing firms to exit.
- Specialized Assets: The equipment used in smelting and refining is highly specialized and has limited alternative uses, increasing the financial risk associated with exiting the market.
- Operational Lock-in: Once operations begin, there are ongoing costs and commitments, such as labor contracts and environmental compliance, that further bind companies to their existing facilities.
- Industry Consolidation: The high exit barriers contribute to industry consolidation, as fewer companies can afford to absorb the losses associated with exiting, leading to a more concentrated market structure with fewer, larger players.
Diversity of Competitors
The copper market, and by extension Aurubis's competitive landscape, is characterized by a significant diversity of players. These competitors operate with varied strategic imperatives, cost bases, and ultimate goals. For instance, some entities might be state-owned enterprises focused on national resource security, while others are publicly traded companies driven by shareholder value. Similarly, the distinction between primary producers, extracting ore from the ground, and recyclers, processing scrap materials, creates further strategic divergence.
This heterogeneity in competitor profiles can translate into unpredictable market behavior. A state-owned enterprise, less beholden to short-term profit pressures, might maintain production levels even during downturns, impacting market supply dynamics differently than a private recycler facing immediate cost-benefit analyses. This complexity makes it challenging for Aurubis to accurately forecast rivals' actions and craft effective counter-strategies, intensifying the overall competitive rivalry.
- Diverse Strategies: Competitors range from state-owned entities prioritizing national resource security to private firms focused on profit maximization, impacting their operational decisions.
- Varied Cost Structures: Primary producers and recyclers possess fundamentally different cost structures, influencing their pricing power and market responsiveness.
- Unpredictable Behavior: The mix of objectives and operational models among rivals leads to less predictable competitive actions, complicating strategic planning for companies like Aurubis.
- Increased Rivalry: This inherent diversity in the competitive set heightens overall rivalry as Aurubis must contend with a broader spectrum of motivations and capabilities.
Competitive rivalry within the copper industry is fierce due to the commodity nature of products, leading to price-based competition and the need for efficient operations. High capital requirements create significant barriers to entry and exit, keeping existing players engaged even in challenging times.
The market is populated by diverse competitors, including state-owned enterprises and private firms, each with different strategic goals and cost structures, contributing to unpredictable market dynamics and intensified rivalry.
In 2023, Aurubis reported an EBITDA of €1.3 billion, reflecting the scale of operations and the competitive pressures faced. The global copper market saw prices fluctuate, with the LME cash price for copper averaging around $8,500 per metric ton for the year, underscoring the price sensitivity.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Producers | Large-scale mining and smelting operations, high capital investment, often integrated. | Significant capacity, price-setters, focus on cost efficiency. |
| Recyclers | Focus on scrap metal processing, variable feedstock quality, agile operations. | Contribute to supply, compete for scrap, often have lower overheads. |
| State-Owned Enterprises | Strategic resource management, potential for long-term investment, less profit-driven. | Can maintain production irrespective of market cycles, impacting supply stability. |
| Commodity Traders | Focus on price arbitrage and market liquidity, can influence short-term price movements. | Add volatility, can exacerbate price wars. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While copper boasts excellent electrical conductivity and durability, making it ideal for many applications, substitutes like aluminum and fiber optics pose a growing threat. Aluminum, for instance, is significantly lighter and cheaper, making it an attractive alternative in power transmission lines, a sector where copper once dominated. By 2024, the global aluminum market was valued at over $240 billion, highlighting its substantial presence.
Fiber optics are increasingly replacing copper in telecommunications, offering higher bandwidth and immunity to electromagnetic interference. This shift directly impacts copper demand in a crucial segment. The global fiber optics market was projected to reach over $15 billion in 2024, demonstrating a strong and growing alternative.
Technological advancements in material science present a significant threat of substitutes for copper. Ongoing research is focused on developing new materials with properties that can rival or even surpass copper's conductivity and durability, often at a more competitive price point. For example, ongoing development in graphene and advanced composites aims to offer lighter, stronger, and potentially more conductive alternatives for various applications, from electronics to aerospace.
Innovations in product design and manufacturing can significantly impact the demand for copper. For instance, advancements leading to miniaturization in electronics mean less copper is needed per device. This trend, evident in the shrinking size of smartphones and other gadgets, directly reduces the volume of copper required, acting as a form of substitution by material efficiency.
Recycling as a Substitute for Primary Production
While Aurubis is a leading player in copper recycling, for primary copper producers, recycled copper functions as a significant substitute. The growing efficiency and expanding scale of global copper recycling operations can diminish the demand for newly mined copper, thereby influencing market dynamics for primary producers.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by the increasing economic viability of recycling. For instance, in 2023, the global copper recycling market was valued at approximately $100 billion and is projected to grow, indicating a substantial alternative to primary extraction.
- Growing Recycling Capacity: Global copper recycling capacity continues to expand, offering a readily available alternative source.
- Cost Competitiveness: Recycling often presents a more cost-effective option compared to primary mining, especially when considering environmental compliance costs.
- Material Availability: The sheer volume of existing copper in circulation and available for recycling provides a consistent and substantial substitute supply.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in recycling technologies are making it possible to recover copper more efficiently from a wider range of sources.
Cost-Performance Trade-offs of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Aurubis's copper products hinges on the price-performance ratio of alternative materials. If substitutes like aluminum or advanced plastics can deliver comparable functionality at a lower price point, or enhanced performance at a similar cost, the pressure on Aurubis intensifies. For instance, in electrical wiring, aluminum has historically been a substitute for copper, offering a lower cost but often requiring larger conductor sizes for equivalent conductivity.
The cost-performance trade-offs are critical. For example, while copper boasts superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, its price volatility, influenced by global commodity markets, can make alternatives more attractive in certain applications. In 2024, LME copper prices have seen fluctuations, impacting the economic viability of using copper versus substitutes.
- Aluminum's lower cost per pound compared to copper makes it a persistent substitute in applications where weight and conductivity are not paramount.
- Advanced polymers and composites are emerging as substitutes, offering benefits like lighter weight and insulation properties, though often at a higher initial cost.
- The energy efficiency gains from using copper's superior conductivity can offset its higher material cost in some long-term applications, influencing the substitution decision.
- Technological advancements in material science continually shift the balance, potentially making new substitutes more competitive against copper.
The threat of substitutes for copper is significant, driven by materials like aluminum and fiber optics that offer competitive advantages in cost and performance. Aluminum, being lighter and cheaper, has gained traction in power transmission, with the global aluminum market exceeding $240 billion in 2024. Fiber optics are increasingly replacing copper in telecommunications due to higher bandwidth and immunity to interference, with the fiber optics market projected to reach over $15 billion in 2024.
Technological advancements also introduce new substitutes. Graphene and advanced composites are under development, aiming to rival copper's conductivity and durability at potentially lower costs. Furthermore, innovations in product design, such as miniaturization in electronics, reduce the amount of copper needed per device, acting as a form of substitution through material efficiency.
| Substitute Material | Key Advantages | Market Relevance (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lighter weight, lower cost | Global market > $240 billion |
| Fiber Optics | Higher bandwidth, EMI immunity | Global market projected > $15 billion |
| Advanced Composites/Graphene | Potential for lighter weight, higher conductivity, lower cost | Emerging, R&D intensive |
Entrants Threaten
The sheer scale of investment needed to establish a modern non-ferrous metal production and recycling facility presents a formidable hurdle for newcomers. Aurubis, for instance, operates complex smelters and refineries, and their recent investments highlight this. In 2023, the company announced a significant investment of around €100 million in its Bulgarian copper smelter, Sofia, to upgrade environmental technology, demonstrating the ongoing capital intensity of the sector.
Existing players like Aurubis enjoy substantial economies of scale, particularly in raw material procurement and global distribution. For instance, Aurubis's 2023 revenue of €14.9 billion demonstrates its significant operational volume, allowing for cost advantages in purchasing and logistics that new entrants would find hard to match.
Newcomers would face immense challenges in replicating these cost efficiencies. Without the massive production volumes that drive down per-unit costs, any new entrant would likely operate at a higher cost base, making it difficult to compete on price against established giants like Aurubis.
Aurubis, a leading copper producer, faces a significant threat from new entrants due to challenges in securing essential raw materials and advanced technology. Access to reliable, high-quality metal concentrates and complex recycling materials is paramount for efficient operations. For instance, in 2024, the global demand for copper concentrates remained robust, driven by the energy transition and electrification trends.
Newcomers often struggle to establish the deep-seated relationships with suppliers that Aurubis has cultivated over years, which are vital for consistent material flow. Furthermore, Aurubis's proprietary recycling technologies, particularly for intricate scrap materials, represent a substantial barrier. These specialized capabilities, developed through significant investment and expertise, are not easily replicated by new market participants, thus limiting their ability to compete on cost and quality.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Compliance
The non-ferrous metals industry faces significant entry barriers due to rigorous environmental regulations and complex permitting requirements. These stringent rules, designed to mitigate the environmental impact of mining and processing, necessitate substantial upfront investment in compliance technologies and expertise. For instance, the EU's Industrial Emissions Directive sets strict limits on pollutants, requiring advanced abatement systems that can cost millions of euros.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating the intricate web of national and international environmental laws, such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) in Europe, demands specialized legal and technical knowledge.
- Capital Investment: New entrants must allocate considerable capital towards pollution control equipment, waste management systems, and ongoing environmental monitoring to meet compliance standards.
- Permitting Delays: Obtaining the necessary environmental permits can be a lengthy and uncertain process, often taking several years, which can deter potential new players.
- Operational Costs: Maintaining compliance involves continuous investment in upgrades and adherence to evolving standards, adding to the ongoing operational expenses for any new company in the sector.
Brand Loyalty and Established Relationships
While copper is fundamentally a commodity, established producers like Aurubis benefit significantly from deep-seated brand loyalty and enduring relationships with major industrial clients. These partnerships, cultivated over years, are founded on a proven track record of delivering consistent quality and reliable supply chains. For instance, Aurubis's long-standing presence in the automotive and construction sectors means they have integrated supply agreements that are difficult for newcomers to penetrate.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in replicating this level of trust and dependability. Building these critical customer relationships requires time, substantial investment in demonstrating reliability, and often, a willingness to absorb initial lower margins. This established customer base acts as a significant barrier, making it challenging for new players to gain immediate market share.
- Established Customer Relationships: Aurubis leverages long-term contracts with key industrial buyers, often spanning multiple years.
- Brand Reputation for Reliability: Years of consistent supply and quality have built a strong brand reputation, fostering customer loyalty.
- High Switching Costs for Customers: Industrial customers may face significant logistical and operational challenges if they switch suppliers, reinforcing existing ties.
- Barriers to Trust Building: New entrants must invest heavily in demonstrating reliability and quality to gain the trust of major consumers, a process that can take considerable time and resources.
The threat of new entrants for Aurubis is moderate to low. The immense capital required for smelters and refineries, coupled with the need for established supplier relationships and advanced recycling technology, creates significant barriers. For example, the global copper concentrate market in 2024 remained tight, making consistent raw material access a challenge for any new player.
Environmental regulations and lengthy permitting processes further deter newcomers, demanding substantial investment in compliance. Aurubis's 2023 revenue of €14.9 billion highlights the economies of scale that new entrants would struggle to match, impacting their cost competitiveness.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High cost of establishing smelters/refineries. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Economies of Scale | Aurubis's €14.9 billion 2023 revenue implies cost advantages. | New entrants face higher per-unit costs. |
| Raw Material Access | Tight global concentrate market in 2024. | Difficulty securing consistent supply. |
| Technology & Expertise | Proprietary recycling tech is hard to replicate. | Limits cost and quality competition. |
| Environmental Regulations | Strict rules necessitate large compliance investments. | Increases upfront and operational costs. |
| Customer Relationships | Long-standing ties are hard for newcomers to break. | Challenges in gaining market share. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Aurubis Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Aurubis's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like CRU and Wood Mackenzie, and relevant LME (London Metal Exchange) pricing data.
