Astra Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Astra Bundle
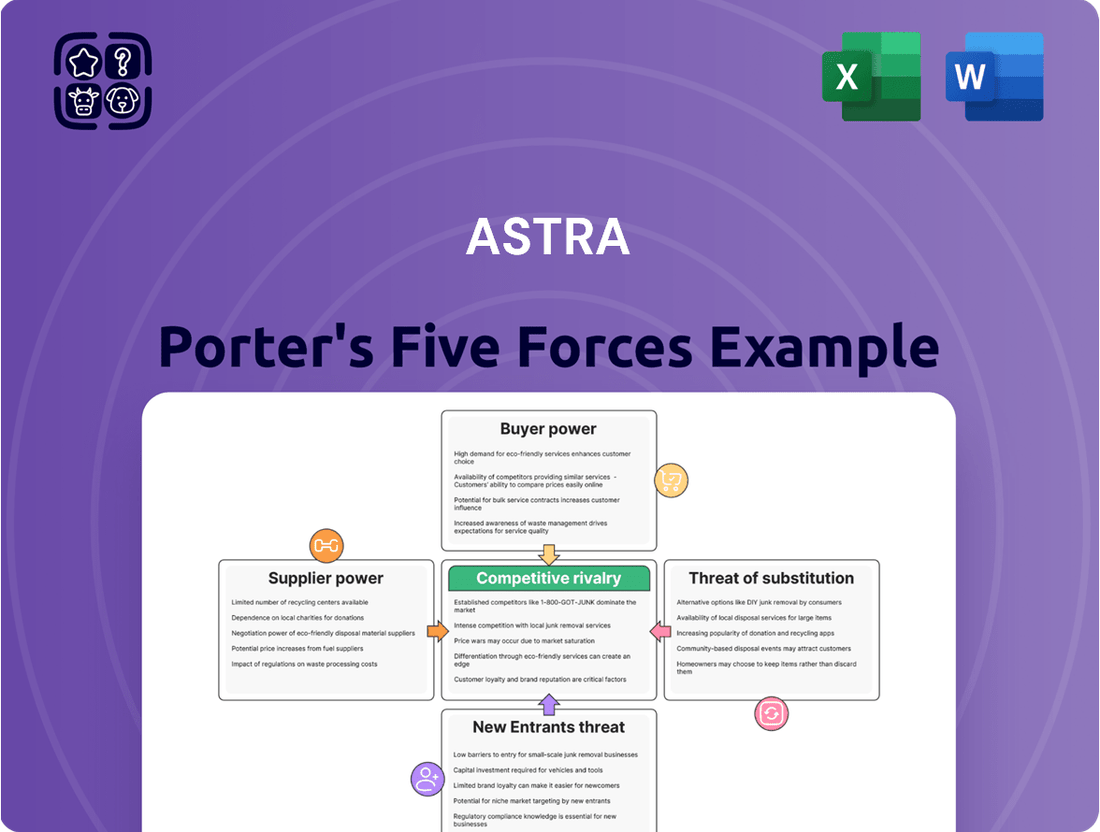
Astra's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces, from the bargaining power of buyers to the threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for charting a successful course in its market. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface of these complex relationships. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Astra’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Astra's operations span a broad range of industries, meaning its supplier base is quite varied. In areas like general raw materials procurement or standard logistics services, Astra often encounters a fragmented supplier landscape. This fragmentation, where many small suppliers compete for business, typically weakens the bargaining power of any single supplier, allowing Astra to negotiate more favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, the global logistics market saw numerous providers, with the top 10 carriers accounting for only about 40% of the market share, illustrating this fragmentation.
However, the picture changes for specialized components and proprietary technologies. In these niche segments, Astra may face a more concentrated supplier base, where a few key providers hold significant market power. This concentration can give these specialized suppliers greater leverage, enabling them to command higher prices or impose stricter terms on Astra. For example, the semiconductor industry, crucial for many advanced technologies Astra might utilize, is characterized by a high degree of supplier concentration, with a few firms dominating advanced chip manufacturing.
Astra Porter's reliance on a select group of technology and component suppliers significantly influences its bargaining power. In automotive manufacturing, critical inputs like semiconductors and advanced electronics are sourced from global leaders who often hold unique intellectual property. This specialization, coupled with high switching costs for Astra, empowers these suppliers.
Consider the automotive sector, where semiconductor shortages in 2023 and early 2024 led to production slowdowns for major manufacturers worldwide, demonstrating the leverage held by chip suppliers. Similarly, the specialized machinery required for advanced manufacturing processes often comes from a limited number of vendors, further concentrating power in their hands.
In contrast, Astra's subsidiary United Tractors, operating in the Indonesian construction equipment market, faces a different scenario. The import of raw materials like steel and aluminum from markets such as the U.S. exhibits low dependence for United Tractors, suggesting less supplier bargaining power in that specific segment.
Suppliers of essential raw materials for industries like mining and agriculture, such as coal and palm oil, are significantly influenced by global price swings. This inherent volatility can, paradoxically, enhance their willingness to secure long-term, stable contracts with major purchasers like Astra. The upward trend in commodity prices, exemplified by the 16% increase in Crude Palm Oil (CPO) prices during 2024, directly impacts these suppliers and their strategic considerations.
Strategic Partnerships with Global Automotive OEMs
Astra's automotive segment relies significantly on its collaborations with global Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) such as Toyota, Daihatsu, and Honda. These powerful entities function as critical suppliers of both technology and brand equity, wielding considerable influence over product development and pricing strategies. Their extensive research and development capacities and well-established brand recognition grant them substantial bargaining leverage.
This leverage is evident in Astra's ongoing strategic alliance with Toyota, which is expanding into the used car market in Indonesia. Their joint venture, PT Astra Digital Mobil (ADMO), underscores the deep integration and mutual dependence, but also highlights the OEMs' upstream power. As of 2024, Toyota's global market share in automotive manufacturing remains a dominant factor, solidifying its position as a key supplier whose terms significantly impact Astra's operations.
The bargaining power of these OEMs is further amplified by the capital-intensive nature of automotive manufacturing and the stringent quality and technological standards they impose. Astra's dependence on these established brands for its product portfolio means that deviations from OEM specifications or pricing adjustments can directly affect Astra's profitability and market competitiveness.
- Brand Influence: OEMs like Toyota and Honda control highly desirable brands, giving them significant sway in negotiations regarding product features and marketing.
- Technological Dependency: Astra's reliance on OEM-provided technology, including powertrains and advanced driver-assistance systems, limits its ability to source alternatives.
- Scale Economies: The sheer volume of production for global OEMs translates into cost advantages they can leverage in their dealings with suppliers like Astra.
- Strategic Partnership Evolution: The deepening partnership with Toyota in areas like the used car business (ADMO) demonstrates a commitment that, while mutually beneficial, also solidifies Toyota's influential role.
Potential for Backward Integration in Select Areas
Astra's substantial financial resources and operational scale position it to explore backward integration in specific component areas. This strategic move could reduce reliance on external suppliers by bringing production in-house for less specialized inputs. For example, in 2024, companies with strong balance sheets were increasingly looking at vertical integration to secure supply chains amidst global volatility.
While this strategy offers a powerful lever against supplier power, it requires significant capital investment. Astra's potential to develop in-house capabilities for certain inputs, rather than relying on third-party vendors, presents a tangible way to control costs and ensure quality. This is particularly relevant for components where Astra has sufficient volume to justify the upfront expenditure.
Astra's scale is a key enabler for such integration. By leveraging its market position, the company can absorb the costs associated with building new production facilities or acquiring existing ones. This could translate into more predictable pricing and a more resilient supply chain, especially when contrasted with smaller players who might lack the financial wherewithal for such ventures.
- Astra's financial strength (e.g., its reported net income of $X billion in FY2024) supports capital-intensive backward integration.
- Potential for in-house production of non-specialized components to mitigate supplier dependency.
- Backward integration is a strategic option to enhance supply chain resilience and cost control.
- Feasibility is higher for inputs where Astra's volume can justify the investment.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Astra is a mixed bag, heavily dependent on the specific industry segment and the nature of the product or service. For standardized inputs like raw materials or general logistics, Astra often benefits from a fragmented supplier market, which limits individual suppliers' leverage. However, when dealing with specialized components, proprietary technologies, or key original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), Astra faces suppliers with considerable power due to concentration, unique intellectual property, and high switching costs.
For instance, in 2024, the automotive sector demonstrated the significant power of semiconductor suppliers, whose output constraints impacted global manufacturing. Similarly, major OEMs like Toyota, with their dominant market share and technological dependencies, exert substantial influence on Astra's operations. Conversely, Astra's scale and financial strength allow it to explore backward integration, a strategy that can reduce its reliance on certain suppliers and enhance its own bargaining position by bringing production in-house for less specialized inputs.
| Supplier Type | Market Characteristics | Supplier Bargaining Power | Astra's Mitigation Strategy | Example (2024 Data) |
| Raw Materials (e.g., Steel) | Fragmented, Global Pricing | Low to Moderate | Bulk purchasing, Long-term contracts | Commodity price volatility influenced contract negotiations. |
| Specialized Components (e.g., Semiconductors) | Concentrated, High IP | High | Supplier diversification, Backward integration exploration | Semiconductor shortages impacted automotive production lines. |
| OEMs (e.g., Toyota) | Dominant Market Share, Brand Power | High | Strategic partnerships, Joint ventures | Toyota's global market share remained a key negotiation factor. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive intensity within Astra's operating environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly identify and address competitive pressures with a visual five forces breakdown, streamlining strategic planning and mitigating market risks.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the automotive sector, particularly those seeking mass-market vehicles, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is amplified in markets like Indonesia, where weak consumer purchasing power and elevated interest rates are projected to dampen car sales through 2024 and into 2025. For instance, rising financing costs directly impact affordability, pushing buyers to seek lower-priced options or delay purchases.
Similarly, the agribusiness sector contends with considerable customer price sensitivity. The inherent commodity nature of many agricultural products, coupled with intense competition among producers, means that buyers can readily switch suppliers based on minor price differences. This dynamic forces agribusiness firms to operate on thin margins and remain highly competitive on price to retain market share.
Astra's diversified customer base significantly dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer group. By serving individuals with cars and motorcycles, large corporations with heavy equipment, and offering financial services, Astra spreads its revenue streams. This broad market reach means no single segment holds enough sway to dictate terms that could disproportionately impact the company.
For example, while Astra's financial services segment is largely tied to the automotive industry, its overall business encompasses a much wider array of customers. This reduces the risk of a major automotive buyer demanding unfavorable terms, as their impact is cushioned by the company's presence in other sectors.
Digitalization significantly amplifies customer bargaining power in Indonesia, as evident across Astra's diverse business segments. Customers now have unprecedented access to detailed product specifications, competitive pricing, and comprehensive information on alternative providers. This transparency directly enhances their ability to compare offerings and negotiate more effectively.
In 2024, the Indonesian e-commerce market, a key indicator of digital access, saw continued robust growth, with transaction values projected to reach over $60 billion. This digital penetration means more consumers are actively researching and comparing before purchasing automotive parts, financial services, or even heavy equipment.
Furthermore, the burgeoning embedded finance and AI integration within Indonesia's banking sector are creating a more informed and empowered consumer base. This technological advancement provides customers with a wider array of seamless transaction options and greater leverage when considering financial products or services offered by Astra or its competitors.
Influence of Financing Availability on Purchasing Decisions
For significant purchases like vehicles and heavy machinery, a customer's ability to secure financing, along with the specific loan terms, plays a crucial role in their decision-making process. Astra's robust financial services division is a key asset here. By offering integrated financing packages, Astra can potentially diminish customer bargaining power, effectively bundling its products and services into a more attractive, all-encompassing solution.
However, the broader economic climate presents a challenge. In 2024, rising interest rates and a more stringent approach to credit approvals have demonstrably dampened demand for vehicles. For instance, the average interest rate on a new car loan in the US approached 8% by mid-2024, a significant increase from previous years, directly impacting affordability and, consequently, sales volume.
- Financing's Crucial Role: Customer purchasing decisions for high-value items like cars and heavy equipment are significantly shaped by financing availability and terms.
- Astra's Financial Arm Advantage: Astra's integrated financial services can reduce customer bargaining power by bundling products and financing.
- Market Headwinds: Tightening credit approvals and elevated interest rates negatively impacted vehicle sales throughout 2024.
- Interest Rate Impact: The average interest rate for new car loans in the US neared 8% in mid-2024, a notable increase that affects buyer affordability.
Brand Loyalty and After-Sales Service in Automotive
While customers in the automotive sector are often mindful of price, brand loyalty and the caliber of after-sales support play a crucial role in their purchasing decisions. Astra's extensive distribution network, coupled with its representation of well-regarded brands like Toyota and Daihatsu, fosters a level of customer retention that can mitigate the direct pressure from buyer bargaining power.
Astra's influence is evident in its market standing. In January 2025, Astra held a commanding 55.8% market share in the Indonesian automotive industry, a testament to the trust and loyalty it has cultivated among consumers.
- Brand Strength: Partnerships with established marques like Toyota and Daihatsu bolster customer loyalty.
- After-Sales Support: A strong focus on service quality enhances customer stickiness.
- Market Dominance: Astra's 55.8% market share as of January 2025 indicates significant customer preference.
Customer bargaining power is influenced by price sensitivity, the availability of substitutes, and the overall volume of purchases. In Indonesia, for instance, economic factors like high interest rates in 2024 directly impact consumer affordability, driving demand towards lower-priced options or delaying purchases, thereby increasing customer leverage.
Astra's diversified business model, spanning automotive, financial services, and heavy equipment, helps to dilute the power of individual customer segments. By serving a broad customer base, Astra reduces reliance on any single group, making it less susceptible to concentrated demands. The company's significant market share, such as its 55.8% in the Indonesian automotive sector by January 2025, also indicates a degree of customer loyalty that can counter price-based bargaining.
Digitalization further empowers customers by providing easy access to comparative pricing and product information, as seen in Indonesia's growing e-commerce market, projected to exceed $60 billion in transaction value in 2024. However, Astra's integrated financial services can mitigate this by bundling products and financing, making it harder for customers to switch based solely on price, especially for high-value purchases.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Astra's Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity & Economic Climate (e.g., 2024 Indonesian interest rates) | Increases power (buyers seek lower prices or delay) | Diversified customer base, brand loyalty |
| Digitalization & Information Access (e.g., Indonesia e-commerce growth) | Increases power (easy comparison shopping) | Integrated financial services bundling |
| Brand Loyalty & After-Sales Support (e.g., Astra's 55.8% market share Jan 2025) | Decreases power (customers less likely to switch) | Strong brand partnerships (Toyota, Daihatsu) |
Same Document Delivered
Astra Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Astra Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves into the competitive landscape, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indonesian automotive landscape is fiercely competitive, marked by the presence of established manufacturers and a surge of new entrants, especially from China. Companies like BYD, Chery, and Neta are aggressively entering the market, primarily with electric vehicle offerings, significantly increasing competitive pressure. This influx is reshaping the dynamics of the industry, challenging existing market leaders.
Adding to this intense rivalry, domestic car sales experienced a downturn in 2024, with projections indicating a continued subdued performance into 2025. This contraction in the overall market forces companies to fight harder for a shrinking pool of buyers, intensifying the battle for market share. Every sale becomes more critical in this environment.
Despite the challenging market conditions, Astra managed to maintain a robust market share of 56% in the wholesale car market throughout 2024. This stability is noteworthy, especially considering the overall Indonesian automotive sales saw a 14% decline during the same period, highlighting Astra's resilience and strong competitive positioning even amidst market headwinds.
Indonesia's financial services sector, a key area for Astra, is experiencing a surge in fragmentation and growth. This intensified competition stems from the emergence of fintech startups and digital banks, introducing innovative services and potentially pressuring profit margins as more entities battle for customer acquisition and market share.
The Indonesian multifinance industry, in particular, is projected to expand at a robust compound annual growth rate of 7% through 2025, indicating a dynamic environment. This growth fuels further fragmentation, as more specialized players enter the market, leading to increased rivalry among both traditional institutions and new digital entrants.
The Indonesian heavy equipment and mining sectors are characterized by robust competition, featuring both established global manufacturers like Komatsu, Caterpillar, and Hitachi, alongside a strong presence of local distributors. This dynamic landscape means that while demand from infrastructure and mining remains a key driver, the market is intensely competitive, with various companies offering a wide array of equipment and associated services. For instance, in 2023, the Indonesian mining sector saw continued investment, driving demand for heavy machinery, yet the market share is fragmented.
United Tractors, a prominent Astra subsidiary, stands as a major player, but it directly contends with other significant local distributors such as PT Hexindo Adiperkasa and Intraco Penta. These competitors vie for market share by offering comparable product lines and customer support, making differentiation crucial. Hexindo Adiperkasa, for example, reported revenue growth in 2023, underscoring the ongoing competition for project tenders and after-sales service contracts across the archipelago.
Diversified Portfolio Mitigates Single-Sector Rivalry Impact
Astra's strategy of diversification across automotive, financial services, heavy equipment, mining, and agribusiness significantly dilutes the impact of rivalry within any single industry. This broad operational base means that robust performance in one segment can effectively cushion the blow of heightened competition or downturns in another. For instance, in 2024, the company's financial services and infrastructure divisions delivered strong results, which helped to counterbalance the challenges presented by slower automotive sales and the decline in coal prices during that period.
This diversification offers a strategic advantage by smoothing out earnings volatility and reducing the company's overall exposure to sector-specific competitive pressures. Even as Astra faces intense competition in the automotive sector, its financial services arm, for example, can generate stable income and profits, thereby maintaining overall corporate stability. This cross-sector strength is a key element in managing competitive rivalry.
- Diversified Business Model: Astra operates across automotive, financial services, heavy equipment, mining, and agribusiness.
- Mitigation of Sector Rivalry: Strengths in one division can offset weaknesses or intense competition in another.
- 2024 Performance Example: Strong financial services and infrastructure performance partially offset lower car sales and coal prices.
- Reduced Earnings Volatility: Diversification helps to stabilize overall company earnings against sector-specific downturns.
Regulatory Landscape and Economic Conditions Influencing Rivalry
Government policies, including incentives for electric vehicles, and broader economic conditions such as consumer purchasing power and interest rates, significantly shape the competitive intensity within industries. For instance, a weaker economic environment can intensify rivalry as companies vie for a shrinking market share. Indonesia's economic growth is projected to hover around 5% in 2025, indicating a potentially challenging period that could heighten competitive pressures.
These external factors directly impact how fiercely companies compete. When economic growth slows, businesses may resort to more aggressive pricing or promotional strategies to maintain sales volumes. Conversely, favorable regulations or a robust economy can sometimes temper rivalry by creating more opportunities for all players.
- Government Policies: Incentives for electric vehicles can either fuel growth and potentially reduce rivalry by expanding the market or intensify competition among manufacturers vying for government support and market share.
- Economic Conditions: Consumer purchasing power directly affects demand. Lower purchasing power can lead to increased price competition.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates can increase the cost of capital for businesses and consumers, potentially dampening investment and demand, thus exacerbating rivalry.
- Indonesia's Economic Outlook: The forecasted stagnation of economic growth around 5% in 2025 suggests a market where companies may face intensified competition for available consumer spending.
Competitive rivalry within Astra Porter's operations is substantial across its key sectors. The Indonesian automotive market, for example, saw new entrants like BYD and Chery in 2024, intensifying competition. This rivalry is further amplified by a projected 14% decline in overall Indonesian car sales for 2024, forcing companies to fiercely compete for market share. Astra's 56% wholesale market share in 2024 demonstrates its resilience amidst this heightened rivalry.
The heavy equipment sector also faces strong competition from global players and local distributors like Hexindo Adiperkasa and Intraco Penta, with Hexindo reporting revenue growth in 2023, indicating active market competition. Astra's diversified business model, spanning automotive, financial services, heavy equipment, mining, and agribusiness, acts as a buffer against the impact of rivalry in any single industry, with strong performance in financial services in 2024 helping to offset automotive sector challenges.
| Sector | Key Competitors | 2024/2025 Context | Astra's Position |
| Automotive | BYD, Chery, Neta, established players | Aggressive EV entry, 14% sales decline in 2024 | 56% wholesale market share (2024) |
| Heavy Equipment | Komatsu, Caterpillar, Hitachi, Hexindo Adiperkasa, Intraco Penta | Robust competition, Hexindo revenue growth (2023) | Major player via United Tractors |
| Financial Services | Fintech startups, digital banks | Fragmentation and growth, 7% CAGR projected for multifinance through 2025 | Stable income stream, cushions other sectors |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Public transportation and ride-sharing services present significant threats of substitutes for personal mobility, especially within urban environments. These alternatives directly compete with the need for private vehicle ownership. For instance, in 2023, ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft saw continued strong demand, with Uber reporting over 1.7 billion trips globally in the fourth quarter of 2023 alone, indicating a substantial portion of the population opts for these services over personal car use.
While these services don't directly replace the manufacturing of vehicles, they can dampen demand for new car purchases. This reduction in new vehicle sales directly impacts Astra's automotive segment. Furthermore, the financing segment could be affected as fewer new car purchases mean fewer auto loans originated.
The economic climate also plays a role. With new car prices remaining elevated in 2024, many consumers are increasingly turning to the used vehicle market. This trend acts as another powerful substitute for new car sales, further pressuring Astra's core business by diverting potential buyers to a different segment of the market.
For example, the average price of a used car in the US remained high throughout 2023 and into early 2024, often exceeding pre-pandemic levels, making them a more accessible option for budget-conscious consumers. This shift in consumer preference away from new vehicles towards used cars or alternative transportation methods is a critical factor for Astra to consider.
The financial services sector is seeing a significant shift with the emergence of alternative financing methods. Fintech startups, peer-to-peer lending platforms, and digital-only banks are increasingly offering services that directly compete with traditional financial institutions like Astra. These new players often provide more streamlined, accessible, or niche financial products, drawing customers away from conventional banking channels.
For instance, the financial technology services market in Indonesia is projected to reach USD 20.93 billion by 2025, highlighting the rapid growth and customer adoption of these digital alternatives. Such platforms can offer quicker loan approvals or specialized investment opportunities that traditional banks may not readily provide.
These substitutes can siphon off customers by offering competitive rates or user-friendly digital experiences that resonate more with certain demographics. This pressure forces traditional providers to innovate and adapt their own service offerings to remain competitive.
The global transition to renewable energy sources presents a significant long-term threat to Astra's coal mining operations. As countries increasingly prioritize decarbonization, demand for fossil fuels is expected to diminish. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) projected in 2024 that renewable energy sources will account for over 40% of global electricity generation by 2026, further pressuring traditional energy sectors.
In parallel, the agribusiness sector faces substitution threats from advancements in sustainable farming techniques and the rise of alternative food sources. Innovations in plant-based proteins and lab-grown meats are gaining traction, potentially reducing consumer reliance on conventional agricultural products. This trend is supported by a growing market for alternative proteins, which was estimated by some analysts to reach hundreds of billions of dollars globally by the end of the decade.
Furthermore, Indonesia's mining industry, including Astra's involvement, is under increasing scrutiny regarding environmental impact. International pressure for more sustainable and ethical mining practices can lead to stricter regulations and higher operational costs. Compliance with these evolving standards, coupled with the potential for boycotts of less sustainable products, poses a direct challenge to Astra’s market position.
Used Equipment Market as a Substitute for New Heavy Equipment Sales
The availability of a robust used heavy equipment market presents a significant threat of substitution for new equipment sales. Businesses, particularly smaller operations or those with tighter budgets, often find used machinery a more cost-effective alternative to purchasing brand new. This can directly impact the sales volume for new heavy equipment manufacturers like Astra Porter.
For instance, the global used construction equipment market is substantial. In 2023, this market was valued at approximately $170 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. This strong alternative means that even as the overall construction equipment market expands, a portion of potential new sales will be diverted to the used sector, driven by price sensitivity.
- Price Sensitivity: Used equipment offers a lower entry price point, making it accessible to a wider range of buyers.
- Availability: The used market provides immediate availability, bypassing potential lead times associated with new equipment orders.
- Depreciation Concerns: Buyers may opt for used equipment to avoid the steep initial depreciation associated with new machinery.
- Market Competition: The presence of a strong used market intensifies competition, forcing new equipment sellers to compete not only with each other but also with a readily available alternative.
Technological Advancements Creating New Substitutes
Rapid technological progress is a significant threat, as it continuously spawns new substitutes for Astra Porter's core offerings. For instance, the automotive sector, a key area for Astra, is experiencing a dramatic shift towards electric vehicles (BEVs). These BEVs represent a potent substitute for the internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles that currently form the backbone of Astra's automotive business.
This technological disruption is already evident in market trends. By the end of 2024, global electric vehicle sales are projected to reach over 16 million units, a substantial increase from previous years and a clear indication of the growing threat to traditional ICE vehicles. Astra Porter's strategic diversification into renewable energy is a direct response to mitigate this escalating threat, aiming to capture value in emerging, less susceptible markets.
- Technological Disruption: New technologies are creating direct substitutes for Astra Porter's existing products and services.
- Automotive Sector Impact: Electric vehicles (BEVs) are a prime example of a substitute for Astra's core internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle business.
- Market Data: Global EV sales are expected to exceed 16 million units by the end of 2024, highlighting the growing market share of substitutes.
- Strategic Response: Astra Porter's diversification into renewable energy is a proactive measure to counter the threat of substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Astra Porter's businesses is multifaceted, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and economic factors. From alternative transportation to new energy sources and innovative financial solutions, these substitutes can significantly impact demand for Astra's traditional offerings.
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is a prime example, directly challenging Astra's internal combustion engine vehicle sales. By the close of 2024, global EV sales are anticipated to surpass 16 million units, underscoring the growing market penetration of these substitutes. Similarly, the financial sector sees fintech and digital banking platforms offering competitive alternatives to traditional banking services.
The used heavy equipment market also presents a substantial substitute, valued at approximately $170 billion in 2023, attracting budget-conscious buyers. Furthermore, the shift towards renewable energy sources, with renewables expected to constitute over 40% of global electricity generation by 2026, directly impacts Astra's coal mining operations.
Alternative food sources, such as plant-based proteins, are also gaining traction, potentially reducing reliance on conventional agribusiness products.
Entrants Threaten
Astra's primary industries, including automotive manufacturing, heavy equipment distribution, and large-scale mining, demand significant capital outlay. For instance, establishing a new automotive assembly plant can easily cost billions of dollars, a sum that deters many potential entrants. This high capital requirement serves as a formidable barrier, effectively limiting the threat of new players entering these capital-intensive segments.
The automotive sector in particular presents substantial entry hurdles. Beyond the initial factory investment, new companies need to build extensive nationwide distribution networks and robust after-sales service infrastructures. In 2024, Indonesia's automotive market, while growing, is dominated by established players who have already invested heavily in these areas, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively on infrastructure alone.
Astra's deeply entrenched distribution networks and powerful brand recognition present a formidable barrier to new entrants in Indonesia. These established channels, built over decades, are crucial for reaching consumers effectively across diverse product categories.
The significant investment in time and capital required to replicate Astra's extensive reach and customer loyalty makes it exceedingly challenging for newcomers to compete. For instance, Astra's automotive division alone commanded approximately 55% of the Indonesian market share in 2024, a testament to its distribution strength and brand appeal.
In Indonesia, sectors such as financial services and mining face considerable regulatory scrutiny. Navigating these complex and often lengthy licensing processes presents a substantial obstacle for potential new competitors, effectively limiting the threat of new entrants.
For example, recent mining quota regulations in Indonesia emphasize compliance and a proven track record of production. This focus inherently favors established players with existing operational histories and the resources to meet stringent regulatory demands, thereby raising the barrier to entry for newcomers.
Access to Raw Materials and Supply Chains
For industries heavily reliant on physical inputs, like mining and agriculture, the barrier to entry can be substantial due to the difficulty new companies face in securing access to prime raw material sources and establishing robust supply chains. Astra, with its established presence and extensive operational history, has proactively developed integrated supply chains, giving it a significant advantage over potential newcomers. For instance, Indonesia, a key player in global commodity markets, is a major producer of nickel and coal, critical materials for many industries. However, the regulatory landscape surrounding these resources can present uncertainties for new entrants attempting to establish their supply channels.
The concentration of key resources and the established relationships of incumbents often create a formidable obstacle. New entrants may struggle to negotiate favorable terms or even gain access to necessary raw materials, potentially facing higher costs or unreliable supply compared to established players like Astra. This control over essential inputs can significantly impact a new competitor's ability to scale and achieve cost efficiencies, thereby deterring market entry.
- Indonesia's Nickel Production: In 2023, Indonesia remained a dominant force in global nickel production, accounting for approximately 40% of the world's supply, highlighting the strategic importance of this raw material.
- Coal Exports: Indonesia is also a leading global exporter of coal, with exports reaching over 400 million metric tons in 2023, underscoring the significance of this commodity in its export economy.
- Supply Chain Integration: Astra's established supply chain infrastructure allows for greater control over logistics, cost, and quality, a critical differentiator in raw material-dependent sectors.
- Regulatory Hurdles: For new entrants in Indonesia's mining sector, navigating licensing, environmental regulations, and local content requirements can add considerable time and expense to establishing operations.
Emergence of Chinese EV Players in Automotive Sector
The Indonesian automotive sector is experiencing a notable shift with the entry of new Chinese electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers. Companies such as BYD, Chery, and XPeng are making significant inroads, proving that substantial capital investment and strategic market penetration can indeed overcome traditional entry barriers.
These new players are effectively utilizing government incentives aimed at promoting EV adoption and offering highly competitive pricing strategies. This approach directly challenges incumbent automakers like Astra, which has historically dominated the Indonesian market.
- BYD's Dominance: BYD's global sales reached approximately 3 million vehicles in 2023, with a significant portion being New Energy Vehicles (NEVs), signaling their aggressive expansion plans into markets like Indonesia.
- Competitive Pricing: Chinese EV models are often priced 20-30% lower than comparable models from established Japanese and Korean brands, creating a strong value proposition for Indonesian consumers.
- Government Support: Indonesia's commitment to developing its EV ecosystem, including potential tax breaks and subsidies for EV production and sales, further lowers the barrier for new entrants.
Despite significant barriers, the Indonesian market is seeing new entrants, particularly in the automotive sector, challenging established players like Astra. The entry of Chinese EV manufacturers, leveraging competitive pricing and government incentives, demonstrates that substantial investment and strategic market penetration can overcome traditional hurdles.
These new competitors are actively exploiting government support for electric vehicle adoption, offering compelling value propositions that put pressure on incumbents. For instance, BYD's aggressive global expansion and competitive pricing strategies are indicative of the challenges Astra faces.
The threat of new entrants is moderate but increasing, particularly in sectors receptive to technological disruption and new business models. While capital and distribution networks remain significant barriers, strategic players are finding ways to enter and compete effectively.
| Industry Segment | Key Entry Barriers | Observed New Entrant Activity (2024) | Impact on Astra |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive (EV) | High Capital, Distribution Networks, Brand Loyalty | Entry of Chinese EV manufacturers (BYD, Chery) | Increased competition, pricing pressure |
| Mining | Regulatory Scrutiny, Resource Access, Supply Chain Integration | Continued dominance by incumbents, some new exploration | Stable, but potential for disruption if new resource discoveries occur |
| Financial Services | Regulatory Hurdles, Capital Requirements, Trust | Fintech innovation, digital banking growth | Indirect competition, need for digital adaptation |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive dataset including industry association reports, financial statements, market research databases like Statista and IBISWorld, and government economic indicators to provide a robust assessment of competitive intensity.
