Ashapura Minechem Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ashapura Minechem Bundle
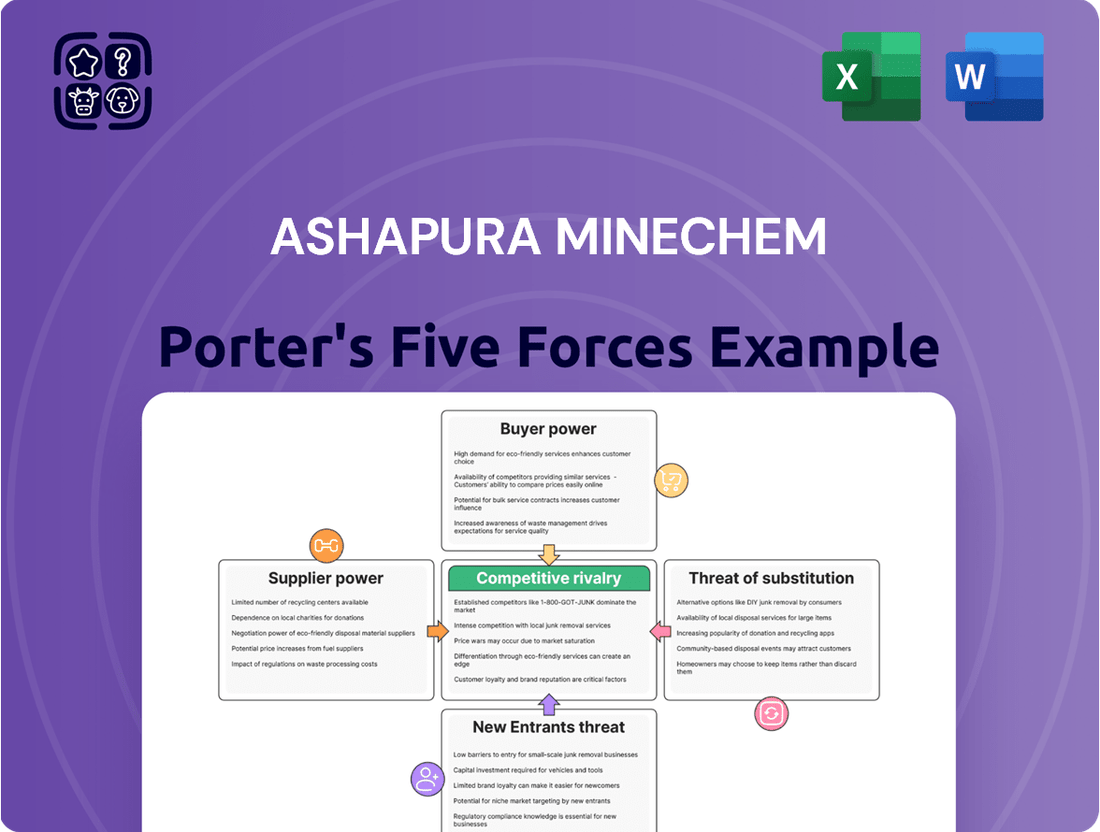
Ashapura Minechem faces significant competitive forces, including the bargaining power of its buyers who can demand lower prices and the threat of substitute products that offer similar functionalities. The intensity of rivalry within the mining sector is also a key consideration, with numerous players vying for market share.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder. The influence of suppliers, particularly for essential raw materials, can impact Ashapura Minechem's cost structure and operational efficiency.
Furthermore, the threat of new entrants, while potentially mitigated by high capital requirements, remains a factor that could disrupt the market landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ashapura Minechem’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ashapura Minechem's direct control over its key mineral resources, including bentonite, bauxite, and kaolin, through its own mining operations significantly mitigates the bargaining power of external suppliers. This vertical integration means the company is less reliant on third-party sourcing for its primary inputs, thereby securing a more stable and predictable supply chain.
The company's strategic advantage stems from owning its mines, which offers considerable control over cost stability and ensures supply security. For instance, Ashapura Minechem reported a revenue of INR 3,970 crore for the fiscal year ending March 2024, showcasing its operational scale and the benefits of its integrated model in maintaining profitability.
Ashapura Minechem's long-term supply contracts for bauxite and iron ore significantly reduce the bargaining power of its suppliers. These agreements, often spanning multiple years, lock in prices and ensure a consistent flow of critical raw materials, thereby shielding the company from market fluctuations. For instance, securing such contracts for bauxite, a key ingredient in alumina production, provides a crucial advantage in a market that can experience price volatility. This stability in procurement directly translates to more predictable cost structures and operational continuity.
Ashapura Minechem's diversified sourcing strategy for non-core inputs like chemicals and machinery significantly curbs supplier bargaining power. By engaging with a wide array of suppliers, the company avoids over-reliance on any single entity, fostering a competitive environment for procurement.
This broad supplier network ensures that Ashapura Minechem can secure essential materials at favorable prices and maintain consistent availability, crucial for uninterrupted operations. For instance, in 2024, the global chemical market experienced price volatility, but Ashapura's multiple sourcing channels helped mitigate the impact of any single supplier's price hikes.
Governmental Initiatives for Domestic Sourcing
India's growing emphasis on exploring and producing critical minerals domestically is a significant factor influencing supplier power. This national strategy aims to lessen the country's dependence on imported resources. By promoting local extraction and processing, the government is fostering a more resilient domestic supply chain.
This increased focus on domestic sourcing could lead to a larger number of local suppliers for minerals. When there are more suppliers available, their individual bargaining power tends to diminish. Companies like Ashapura Minechem might find themselves with more options, leading to potentially more favorable terms.
- Reduced Import Reliance: India's policy aims to cut down on foreign mineral dependency.
- Strengthened Local Supply Chains: Initiatives support the growth of domestic mineral producers.
- Increased Supplier Competition: A larger pool of local suppliers can emerge.
- Potential for Lowered Bargaining Power: More suppliers generally mean less individual leverage over buyers.
High Switching Costs for Specialized Inputs
For highly specialized inputs, Ashapura Minechem might face suppliers with considerable bargaining power if switching costs are high. This could involve significant expenses for new equipment or research and development for alternative processing chemicals. For instance, if a key supplier provides a unique mineral processing agent crucial for Ashapura's specific ore types, the cost and time to qualify a new supplier could be substantial, giving the existing supplier leverage.
However, Ashapura Minechem's substantial scale and extensive global operations likely equip it with strategies to manage these risks. Developing long-term partnerships with key suppliers can secure favorable terms and ensure continuity of supply. Furthermore, investing in in-house research and development to create or adapt alternative processing methods can reduce reliance on any single niche supplier, thereby diminishing their bargaining power over time.
- High Switching Costs: Specialized inputs, like proprietary processing chemicals or custom-engineered mining equipment, can lead to significant costs if Ashapura Minechem needs to change suppliers.
- Supplier Leverage: Niche suppliers of these specialized inputs may temporarily gain increased bargaining power due to the high costs associated with switching.
- Mitigation Strategies: Ashapura Minechem's global scale and operational expertise likely enable it to mitigate these risks through long-term supplier relationships and investment in in-house capabilities.
- Example Scenario: If a supplier provides a unique chemical essential for processing bentonite, Ashapura's ability to find and integrate an equally effective alternative quickly determines the supplier's leverage.
Ashapura Minechem's significant vertical integration, owning its mineral resources, substantially reduces its reliance on external suppliers, thereby weakening their bargaining power. This control over key inputs like bentonite and bauxite ensures supply stability and cost predictability, crucial for its operations. The company's reported revenue of INR 3,970 crore for FY2024 underscores the benefits of this integrated model in maintaining strong financial performance.
Long-term supply contracts for raw materials like bauxite further solidify Ashapura's position by locking in prices and guaranteeing consistent material flow, insulating it from market volatility. This strategic approach to procurement, especially in volatile commodity markets, directly contributes to more stable cost structures and operational continuity.
A diversified sourcing strategy for non-critical inputs and India's push for domestic mineral production also serve to dilute supplier leverage by fostering competition and increasing the availability of alternative sources. While specialized inputs can pose a challenge, Ashapura's scale and R&D investments help manage supplier power.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Ashapura Minechem's Mitigation Strategy | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Integration (Owned Mines) | Lowers | Direct control over primary mineral supply | Secured bauxite supply for alumina production |
| Long-Term Supply Contracts | Lowers | Price and volume guarantees for key inputs | Bauxite and iron ore contracts ensuring stable costs |
| Diversified Sourcing | Lowers | Engaging multiple suppliers for non-core items | Mitigating chemical price hikes through multiple vendors |
| Domestic Sourcing Initiatives (India) | Potentially Lowers | Increased local supplier competition | More options for industrial chemicals and equipment |
| High Switching Costs (Specialized Inputs) | Potentially Raises | Developing long-term partnerships, in-house R&D | Managing reliance on unique mineral processing agents |
What is included in the product
This analysis dives into the specific competitive forces impacting Ashapura Minechem, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industrial minerals sector.
Understand and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the impact of each Porter's Five Forces on Ashapura Minechem's profitability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ashapura Minechem's diverse customer base significantly dilutes the bargaining power of individual customers. By serving a wide array of industries such as oil drilling, construction, and ceramics, the company avoids dependence on any single sector.
This broad industry reach, coupled with a global operational footprint spanning regions like the North Sea, Middle East, South Asia, and Africa, further fragments its customer base. Such geographical and industrial diversification means no single customer or industry segment holds substantial sway.
For instance, Ashapura Minechem's Bentonite sales, a key product, are distributed across numerous applications, preventing any one buyer from dictating terms. This scattered demand structure inherently limits the collective bargaining power that customers might otherwise wield.
The company's strategy of not relying on a few large buyers is a crucial factor in maintaining its pricing power and reducing customer leverage. This approach ensures that the loss or dissatisfaction of one customer does not disproportionately impact overall business.
Ashapura Minechem’s ability to provide customized mineral solutions, rather than just raw materials, significantly curtails customer bargaining power. These tailored offerings require specific integration into a client's manufacturing processes, making a switch to a competitor a complex and costly undertaking. For instance, a customer relying on a precisely formulated mineral blend for their ceramic production would face substantial expenses in re-calibrating their kilns and testing new material compositions if they were to change suppliers.
The high switching costs associated with these customized solutions are a critical factor in dampening customer leverage. These costs aren't just financial; they can also include the time and effort required for process validation, quality assurance adjustments, and potential disruptions to ongoing production. This investment in Ashapura Minechem’s specific solutions creates a sticky customer base, reducing their inclination to seek alternative, potentially less integrated, suppliers.
The industrial minerals sector, where Ashapura Minechem operates, is currently witnessing robust and sustained demand. This strength is primarily fueled by significant investments in infrastructure projects globally, a burgeoning manufacturing base, and the expanding energy sector, all of which rely heavily on these essential materials.
This high demand environment naturally bolsters the bargaining power of suppliers like Ashapura. When customers face a competitive landscape for securing consistent supply, they are more willing to accept prevailing pricing and terms, thus reducing their leverage.
For instance, the global industrial minerals market was valued at approximately $300 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of over 4% through 2028, indicating a strong seller's market. This market expansion directly enhances Ashapura's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
Consequently, the bargaining power of customers in this segment is relatively weak. Their need to ensure uninterrupted operations and access to critical raw materials outweighs their ability to dictate terms, especially when alternative suppliers are limited or capacity is strained.
Product Differentiation and Quality
Ashapura Minechem's strategy of emphasizing high-quality raw materials and specialized products, like enriched drilling mud and advanced refractory materials, directly counters customer bargaining power. This focus on superior quality and tailored solutions makes their offerings distinct from more commoditized alternatives. When customers perceive significant value in these differentiated products, their ability to negotiate lower prices diminishes.
This product differentiation is crucial. For instance, in the oil and gas sector, the specific performance characteristics of drilling muds can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost. Ashapura's ability to provide these specialized, high-performing materials means customers are less likely to switch to a cheaper, lower-quality substitute, thus reducing their leverage.
- Product Specialization: Ashapura Minechem provides specialized products such as enriched drilling mud and advanced refractory materials, setting them apart from basic commodities.
- Quality Perception: The emphasis on high quality and performance enhances the perceived value of Ashapura's offerings.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: Higher perceived value translates to lower customer price sensitivity and reduced bargaining power.
Customer Price Sensitivity
While Ashapura Minechem's broad customer base and tailored product offerings typically limit customer bargaining power, certain segments, particularly within highly competitive industries like construction or basic manufacturing, can exhibit significant price sensitivity. This sensitivity can lead to downward pressure on pricing, especially for standardized mineral products. For instance, in 2024, the global construction industry faced fluctuating material costs, with some sub-sectors reporting increased price negotiations for bulk minerals.
This price sensitivity is directly linked to the competitive landscape of Ashapura's customers. When their end markets are saturated or experiencing margin erosion, they are more likely to seek cost reductions from their suppliers. The extent to which Ashapura can differentiate its offerings through customization and value-added services becomes crucial in mitigating this pressure. For example, a construction firm using basic aggregates might be more price-focused than a specialty ceramics manufacturer requiring precisely graded minerals.
- Price Sensitivity in Construction: In 2024, regions with high infrastructure spending often saw price competition for basic construction minerals, impacting margins for suppliers.
- Impact of Commoditization: Highly commoditized mineral grades, less reliant on specific technical specifications, are more susceptible to price-based purchasing decisions.
- Balancing Act: Ashapura's ability to balance sales of specialized, higher-margin products with more commoditized offerings is key to managing overall customer price sensitivity.
- Market Dynamics: The bargaining power of customers can fluctuate based on overall economic conditions and the supply-demand balance for specific mineral types in any given year.
Ashapura Minechem's diverse customer base and global reach significantly dilute the bargaining power of individual customers, as no single buyer or industry segment holds substantial sway. The company's strategy of avoiding reliance on a few large buyers further limits customer leverage, ensuring that the loss of one client does not disproportionately impact the business.
The company's ability to provide customized mineral solutions, requiring specific integration into client manufacturing processes, creates high switching costs. This makes it difficult and expensive for customers to change suppliers, thereby dampening their bargaining power. The strong demand in the industrial minerals sector, driven by infrastructure and manufacturing growth, further bolsters Ashapura's negotiating position.
While specialized products reduce price sensitivity, certain segments like basic construction materials can exhibit price sensitivity, especially in 2024 due to fluctuating input costs. This means Ashapura must balance sales of high-margin specialized products with more commoditized offerings to manage customer price pressures effectively.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Key Drivers |
| Customer Diversification | Low | Serving multiple industries (oil, construction, ceramics) and global regions. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Customized mineral solutions, integration into client processes, technical specifications. |
| Industry Demand | Low | Robust demand from infrastructure, manufacturing, and energy sectors. Global industrial minerals market projected to grow over 4% annually. |
| Product Differentiation | Low | High-quality, specialized products (e.g., enriched drilling mud) with performance advantages. |
| Price Sensitivity (Commoditized Products) | Moderate | Fluctuating material costs in sectors like construction; price-based purchasing decisions for basic minerals. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Ashapura Minechem Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Ashapura Minechem's position within the mining and mineral processing industry by thoroughly examining the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of new market entrants, the availability of substitute products, and the bargaining power of buyers. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis provides actionable insights into the strategic landscape Ashapura Minechem operates within, enabling informed decision-making for stakeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial minerals sector, where Ashapura Minechem is active, is notably fragmented. This means there are many companies vying for market share, ranging from large global entities to smaller regional specialists in minerals like bentonite, bauxite, and kaolin.
Ashapura Minechem faces competition from a diverse array of mining and mineral processing firms. This includes other companies that also produce a variety of minerals, intensifying the competitive landscape.
The sheer number of competitors, including those with broad product portfolios, underscores the fragmented nature of the market. This fragmentation suggests that no single player holds a dominant market position, leading to a more dynamic and competitive environment.
For instance, in the global bentonite market, while a few major players exist, there are also numerous smaller, specialized suppliers. This dynamic was evident in 2024, with ongoing efforts by companies to secure raw material access and optimize processing costs amidst fluctuating demand for end-use industries.
The industrial minerals market is experiencing a healthy expansion. Projections indicate the overall mineral market will grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2024 to 2025. This growth trajectory is expected to continue, with an anticipated CAGR of 4.7% through 2029. Such robust growth can ease competitive pressures by allowing more companies to expand their operations without intense price competition. A steadily growing demand environment typically fosters a more collaborative competitive landscape rather than aggressive rivalry.
Ashapura Minechem, like many in the industrial minerals sector, operates with substantial upfront investments in mining equipment, processing plants, and land acquisition. These high fixed costs create a strong imperative for companies to maximize their operational capacity. For instance, in 2023, the global mining industry saw capital expenditures exceeding $100 billion, underscoring the capital-intensive nature of the business.
This drive for high capacity utilization intensifies competitive rivalry. Companies are often compelled to compete on price to secure sales volumes and cover their fixed overheads, especially when market demand softens. This can lead to aggressive pricing strategies, as demonstrated by price wars observed in certain mineral segments during periods of economic slowdown.
Product Differentiation and Customization
Ashapura Minechem actively combats competitive rivalry by moving beyond treating minerals as simple commodities. The company focuses on providing tailored solutions and specialized products designed for specific industrial needs. For example, their advanced refractory materials and solutions for hydrocarbon exploration represent significant product differentiation.
This strategy helps Ashapura Minechem sidestep intense price wars for these niche offerings. By delivering unique value propositions, they create a buffer against direct price-based competition in these specialized segments. This approach is crucial in an industry where many products are otherwise viewed as interchangeable.
- Customized Solutions: Ashapura Minechem offers tailored mineral products for diverse industrial applications, such as advanced refractory materials and hydrocarbon exploration solutions.
- Reduced Price Competition: This product differentiation lessens direct price-based rivalry for their specialized offerings.
- Commodity Price Sensitivity: For standard mineral grades, however, Ashapura Minechem still faces significant price competition from rivals.
In 2024, the global industrial minerals market experienced varied demand, with specialized products showing greater resilience to price fluctuations than bulk commodities. Ashapura Minechem's focus on value-added solutions positions it to navigate this landscape effectively.
Regulatory and ESG Compliance Challenges
The Indian mining sector operates under a demanding regulatory environment, with increasing emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) compliance. This complexity directly impacts competitive rivalry by raising the bar for operational standards and increasing the cost of doing business for all participants.
Companies that successfully navigate these stringent rules, such as those adhering to the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change guidelines or the Securities and Exchange Board of India's ESG disclosure requirements, can gain a significant competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, the focus on sustainable mining practices has intensified, with many firms reporting increased investment in environmental impact assessments and community engagement programs. Ashapura Minechem, as a key player, faces these same challenges.
- Increased Compliance Costs: Meeting ESG standards often requires substantial investment in technology, training, and reporting, which can disproportionately affect smaller players.
- Operational Efficiencies: Effective management of regulatory requirements can lead to more streamlined operations and reduced risk, creating an advantage.
- Barriers to Entry: The complexity and cost of compliance can act as a deterrent for new entrants, consolidating the market among established firms.
- Competitive Differentiation: Companies demonstrating strong ESG performance can attract investors and customers, setting them apart from competitors.
Competitive rivalry within the industrial minerals sector, where Ashapura Minechem operates, is characterized by fragmentation and a diverse range of competitors, from global giants to specialized regional firms. This dynamic is amplified by high fixed costs associated with mining and processing, pushing companies towards maximizing capacity utilization and, at times, engaging in price competition, particularly for commodity-grade minerals.
Ashapura Minechem strategically mitigates this by focusing on value-added, customized solutions, thereby reducing direct price-based rivalry in its specialized product segments. However, the overall market remains subject to intense competition, with companies vying for market share and raw material access, a trend observed throughout 2024.
The industrial minerals market is projected to grow robustly, with an estimated CAGR of 6.2% from 2024 to 2025, which could temper aggressive competition by expanding the available market for all players. Furthermore, stringent regulatory environments, particularly concerning ESG compliance, are raising operational standards and costs, potentially creating a competitive advantage for firms adept at navigating these complexities.
| Factor | Impact on Ashapura Minechem | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Market Fragmentation | Intense competition from numerous players | High fragmentation across bentonite, bauxite, kaolin markets |
| Capital Intensity | Pressure for high capacity utilization, potential price wars | Global mining capex exceeded $100 billion in 2023 |
| Product Differentiation | Reduces price competition for specialized offerings | Focus on advanced refractory materials, hydrocarbon exploration solutions |
| Market Growth | Potential to ease competitive pressures | Projected CAGR of 6.2% from 2024-2025 |
| Regulatory Environment (ESG) | Increased compliance costs, potential for competitive edge | Intensified focus on sustainable practices and ESG reporting in 2024 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
In sectors like oil drilling and construction, polymer slurries are increasingly being explored as substitutes for traditional bentonite-based drilling muds. These advanced slurries often boast superior environmental profiles, including biodegradability, which is a significant draw for environmentally conscious operations.
Beyond their ecological advantages, polymer slurries can offer enhanced operational efficiency. They may require smaller volumes for equivalent performance and can reduce mixing times, translating to potential cost savings in labor and equipment usage. For instance, while the upfront cost of some polymers might be higher, the reduced consumption and faster deployment can offset this. The global drilling fluids market, where bentonite is a key component, was valued at approximately USD 4.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, but the rise of efficient polymer alternatives could capture a notable share of this market.
This growing adoption of polymer slurries, driven by both environmental regulations and efficiency demands, presents a tangible threat to the established demand for bentonite in specific, high-value applications. As the technology matures and economies of scale improve, the competitive pressure on bentonite is likely to intensify.
Bauxite residue, a significant byproduct of alumina refining, is emerging as a potent threat of substitutes in the construction sector. Researchers are actively exploring its use as a replacement for fine aggregate in concrete, a common and cost-intensive component. For instance, studies published in 2024 highlight successful trials incorporating bauxite residue into cement and concrete formulations, demonstrating comparable performance characteristics to traditional materials.
The potential for bauxite residue to be converted into manufactured soil further broadens its substitutive appeal, offering an avenue for land reclamation and green infrastructure projects. This valorization of an industrial waste stream presents a compelling cost advantage over virgin bauxite extraction, a factor keenly watched by construction material suppliers. The environmental benefits, reducing landfill burden and the need for new mining, also bolster its position as an attractive alternative.
In the ceramics sector, calcined kaolin serves as a viable substitute for raw kaolin, enabling manufacturers to achieve specific characteristics such as lower shrinkage and enhanced performance in both glazes and clay bodies. This substitution directly influences the demand for traditional kaolin by offering an alternative that can meet functional requirements.
Moreover, the exploration of nanostructured additives, including titanium dioxide nanofibers and silicon dioxide nanoparticles, presents another layer of substitution. These advanced materials are being researched for their potential to significantly boost the mechanical and thermal resilience of kaolin-based ceramics. Such innovations can lead to improved product quality or a reduction in the overall amount of kaolin needed, thereby posing a threat to the market share of conventional kaolin products.
Recycling and Circular Economy Initiatives
The growing emphasis on circular economy principles and material recycling poses a threat of substitutes for companies like Ashapura Minechem. As the world shifts towards greater resource efficiency, particularly for critical minerals, the demand for newly extracted raw materials may decline over the long term.
While the recycling dynamics for industrial minerals such as bentonite, bauxite, and kaolin differ from those of metals, the overarching trend towards sustainability can spur the development of alternative materials or processes. These recycling initiatives are designed to lessen the dependence on virgin mineral extraction, thereby creating potential substitutes.
- Global Recycling Efforts: In 2023, the Ellen MacArthur Foundation reported that the global recycling rate for plastics, a common indicator for material circularity, remained low, but efforts are intensifying across various sectors.
- Resource Efficiency Investments: Venture capital funding for circular economy startups in 2024 saw significant growth, indicating a strong investor appetite for solutions that reduce reliance on virgin resources.
- Material Innovation: Research into bio-based and recycled composite materials continues to advance, offering potential alternatives for applications traditionally reliant on mined minerals.
Performance-Price Trade-offs of Substitutes
The attractiveness of substitute products hinges directly on their performance-to-price ratio. For instance, while some bio-based industrial fillers might boast superior environmental credentials, their initial cost can be significantly higher, potentially deterring widespread adoption in 2024. This means that companies like Ashapura Minechem must focus on showcasing the value proposition of their established mineral products, highlighting cost-effectiveness and proven performance, especially as new materials enter the market.
The decision to switch to a substitute is a complex equation balancing cost, performance, and increasingly, environmental impact. In 2024, industries are increasingly scrutinizing the total cost of ownership, including any necessary upgrades or training associated with new materials. Ashapura Minechem's strategy should therefore emphasize not just the price point of its bentonite and bauxite products, but also their reliability and ease of integration into existing manufacturing processes. For example, a slightly higher-priced substitute might be considered if it offers substantial energy savings in the long run, a factor becoming more prominent in industrial purchasing decisions.
- Performance-Price Balance: The adoption rate of substitutes is directly correlated with their performance relative to their cost.
- Environmental Trade-offs: Alternatives offering environmental benefits often come with higher initial costs or require significant process modifications.
- Competitive Pricing: Ashapura Minechem's ability to maintain competitive pricing for its traditional minerals is key to countering emerging substitutes.
- Tailored Solutions: Offering customized solutions that highlight the established advantages of existing minerals can mitigate the threat of substitution.
- Decision Drivers: The ultimate choice between traditional products and substitutes is driven by a holistic evaluation of cost, performance, and environmental considerations.
The threat of substitutes for Ashapura Minechem's products is significant, driven by advancements in material science and a global push for sustainability. Polymer slurries are increasingly replacing bentonite in drilling, offering better environmental profiles and potential cost savings through reduced usage, even if initial costs are higher. Similarly, bauxite residue is being explored as a substitute for fine aggregate in concrete, a development supported by successful trials in 2024 that demonstrated comparable performance.
The ceramics industry is also seeing shifts, with calcined kaolin offering advantages like lower shrinkage over raw kaolin. Furthermore, nanostructured additives are being researched to enhance the properties of kaolin-based ceramics, potentially reducing the overall amount of kaolin needed.
The growing emphasis on circular economy principles and material recycling presents a long-term challenge, as it can decrease the demand for newly extracted raw materials. While recycling rates for industrial minerals are still developing, investments in circular economy startups saw substantial growth in 2024, indicating a strong market trend towards resource efficiency.
| Substitute Material | Original Material | Key Advantage | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer Slurries | Bentonite Drilling Muds | Environmental profile, Efficiency | Reduced demand for bentonite in drilling |
| Bauxite Residue | Fine Aggregate in Concrete | Cost-effectiveness, Waste utilization | Competition in construction materials |
| Calcined Kaolin | Raw Kaolin | Lower shrinkage, Enhanced performance | Shift in ceramics sector |
| Nanostructured Additives | Kaolin | Improved mechanical/thermal resilience | Reduced kaolin usage in ceramics |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the industrial mineral mining and processing industry, particularly for materials like bentonite, bauxite, and kaolin, demands significant capital. This involves substantial investment in exploration, establishing mining infrastructure, building processing plants, and setting up logistics networks.
These considerable upfront expenditures serve as a major hurdle for any new companies looking to enter the market. For instance, establishing a new bauxite mine and processing facility could easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a figure that deters many potential competitors.
Furthermore, achieving economies of scale, which are crucial for profitability in this sector, necessitates large-scale operations. This requirement for significant initial investment further elevates the financial barrier to entry for new players.
India's mining sector operates under a labyrinth of regulations, encompassing environmental impact assessments, land rights, and a multitude of permits. For instance, obtaining mining leases often involves multiple government departments and can take years, significantly increasing upfront costs and delaying operations for newcomers. This intricate web of compliance acts as a substantial deterrent, making it difficult for new companies to enter the market and compete effectively.
Ashapura Minechem benefits from its established position, holding existing mining rights and access to substantial mineral reserves. This is a significant hurdle for potential new entrants.
Securing new, economically viable mineral deposits is a fiercely contested process, often demanding costly and extensive geological assessments. New players must also successfully navigate government auctions for concessions, further increasing the entry barrier.
For instance, in 2024, the Indian government continued its push for transparent mineral block allocation through auctions, with successful bids reflecting the high value placed on proven reserves. This competitive landscape, coupled with the inherent costs of exploration and acquisition, naturally restricts the threat of new entrants in the mineral sector where Ashapura Minechem operates.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Established players like Ashapura Minechem leverage significant economies of scale in mining, processing, and logistics. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs, making it difficult for new entrants to match their pricing and profitability. For instance, in the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Ashapura Minechem reported a revenue of INR 2,101.4 crore, indicating a substantial operational footprint that generates cost efficiencies.
The experience curve also presents a formidable barrier. Ashapura Minechem’s decades of operational expertise translate into optimized processes, reduced waste, and superior technical know-how. This accumulated knowledge fosters greater efficiency and productivity, which new entrants would need considerable time and investment to develop, if at all possible.
- Economies of Scale: Lower per-unit production costs for established firms.
- Experience Curve: Improved efficiency and reduced costs through accumulated knowledge.
- Capital Requirements: Significant upfront investment needed for new entrants to achieve comparable scale.
- Technological Expertise: Established firms possess advanced mining and processing technologies, creating a knowledge gap.
Established Distribution Networks and Customer Relationships
Ashapura Minechem's established distribution networks, both domestically and globally, present a formidable barrier to new entrants. These networks have been cultivated over years, fostering deep relationships with a diverse customer base across various industries. For instance, the company's reach in sectors like ceramics, construction, and animal feed requires extensive logistical capabilities and market penetration, which new players would find exceptionally challenging and costly to replicate.
The significant investment and time required to build comparable distribution channels and secure customer trust are substantial deterrents. Newcomers would face the arduous task of not only establishing supply chains but also proving reliability and quality to a market accustomed to Ashapura Minechem's long-standing presence and proven track record. This existing strong client base and sophisticated logistical infrastructure effectively create a high barrier to entry, limiting the threat from potential new competitors.
- Significant capital outlay required for distribution infrastructure development.
- Long-term customer relationships built on trust and consistent supply are difficult to displace.
- Established logistical capabilities provide cost and efficiency advantages over new entrants.
- Diversified customer base across multiple industries reduces reliance on any single sector, enhancing stability.
The threat of new entrants for Ashapura Minechem is significantly mitigated by the high capital requirements for establishing mining and processing operations. For example, acquiring exploration rights and setting up infrastructure can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a substantial barrier. Additionally, navigating India's complex regulatory landscape, which involves numerous permits and lengthy approval processes, further deters new players.
Existing players like Ashapura Minechem benefit from established economies of scale and a strong experience curve, leading to lower per-unit costs. In the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Ashapura Minechem reported revenues of INR 2,101.4 crore, underscoring its significant operational scale and cost efficiencies, which new entrants would struggle to match.
Securing viable mineral deposits through competitive auctions, as seen in 2024, and developing extensive, trusted distribution networks also present considerable hurdles. These factors, combined with Ashapura Minechem's long-standing market presence, create a robust defense against new competition.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Ashapura Minechem's Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for exploration, infrastructure, and processing plants. | Deters new companies due to substantial financial risk. | Established financial capacity and operational history reduce perceived risk. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and time-consuming permitting and land acquisition processes. | Increases costs and delays market entry significantly. | Experience in navigating regulations and existing licenses. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs achieved through large-scale operations. | New entrants struggle to achieve competitive pricing and profitability. | Significant operational footprint leads to cost efficiencies, as evidenced by INR 2,101.4 crore revenue in FY24. |
| Distribution Networks | Established logistics and customer relationships built over years. | Difficult and costly for new players to replicate market access and trust. | Extensive domestic and global networks with a diversified customer base. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Ashapura Minechem Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of meticulously researched data, including the company's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld, and relevant regulatory filings. This approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
