Asahi Kasei Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Asahi Kasei Bundle
Asahi Kasei operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its complex market position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Asahi Kasei’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Asahi Kasei's diverse operations mean supplier concentration varies. For specialized materials in its high-performance chemicals or medical device segments, a single dominant supplier could wield significant power. For instance, if a unique polymer essential for a cutting-edge medical implant is sourced from a sole provider, Asahi Kasei's ability to negotiate pricing or terms would be limited.
However, in sectors like construction materials or basic chemicals, where numerous suppliers exist, the bargaining power of any single supplier is considerably weaker. This is evident in the broader chemical industry where commodity chemicals often face intense competition among producers, driving down supplier leverage. Asahi Kasei's 2023 annual report highlights its broad sourcing strategies, aiming to mitigate risks associated with supplier concentration across its varied business units.
The cost and complexity Asahi Kasei faces when switching suppliers significantly impact supplier bargaining power. In areas demanding specialized expertise, such as high-performance polymers or critical electronic components, these switching costs can be considerable.
These substantial costs often stem from the need for extensive re-qualification processes, integration of new technologies, and the potential disruption to production lines. For instance, if a supplier provides a unique chemical compound integral to Asahi Kasei's advanced materials, finding an equivalent that meets stringent performance and regulatory standards could involve lengthy and expensive R&D and testing phases.
In 2024, Asahi Kasei's reliance on proprietary technologies and long-term supply agreements for key raw materials in its performance chemicals segment, which generated ¥1.2 trillion in revenue in fiscal year 2023, suggests that suppliers in these niche markets hold considerable leverage. This leverage is further amplified if alternative suppliers are scarce or require significant investment from Asahi Kasei to onboard.
When suppliers offer products or services that are highly specialized, proprietary, or critical with no close substitutes, their bargaining power over Asahi Kasei increases significantly. This is especially true in sectors like healthcare, where unique medical materials or patented technologies are involved, or in advanced materials where specific performance characteristics are paramount.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Asahi Kasei's business operations significantly amplifies their bargaining power. If suppliers possess the capability and intention to begin manufacturing the very chemicals or components Asahi Kasei currently sources, they can exert greater pressure on pricing and terms.
This particular threat is more pronounced in industries demanding substantial capital investment, as it creates a higher barrier to entry for potential new suppliers looking to integrate forward. For Asahi Kasei, a credible threat of forward integration by its key suppliers means those suppliers could potentially capture a larger portion of the value chain.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers must have the technical expertise and financial resources to establish production facilities comparable to Asahi Kasei's own.
- Market Conditions: Favorable market demand and profitability in Asahi Kasei's industry would incentivize suppliers to consider forward integration.
- Asahi Kasei's Dependence: High reliance on specific suppliers for critical materials increases the supplier's leverage and the feasibility of their forward integration.
Importance of Asahi Kasei to the Supplier
The bargaining power of suppliers for Asahi Kasei is influenced by how critical Asahi Kasei is to a supplier's overall revenue. If Asahi Kasei constitutes a substantial percentage of a supplier's sales, that supplier may possess less leverage, as their business is heavily reliant on Asahi Kasei. Conversely, for large, diversified suppliers, Asahi Kasei is merely one customer among many, which significantly reduces Asahi Kasei's ability to exert pressure.
For instance, in the chemical industry, where Asahi Kasei operates, suppliers of specialized raw materials might have more power if those materials are unique and difficult to source elsewhere. However, if Asahi Kasei has the ability to switch to alternative suppliers or develop in-house production capabilities, this diminishes the supplier's leverage.
- Supplier Dependence: If Asahi Kasei accounts for a large share of a supplier's income, the supplier's bargaining power is weakened.
- Supplier Diversification: For suppliers with many clients, Asahi Kasei's importance is diluted, lessening its leverage.
- Availability of Alternatives: The existence of substitute materials or other suppliers directly impacts the supplier's power.
- Switching Costs: High costs for Asahi Kasei to change suppliers further strengthen the supplier's position.
The bargaining power of Asahi Kasei's suppliers is a mixed bag, heavily dependent on the specific industry segment and the uniqueness of the materials provided. In specialized areas like high-performance chemicals or medical devices, where suppliers offer proprietary or critical components with few substitutes, their leverage is considerably higher. For example, if a single supplier provides a unique polymer essential for a cutting-edge medical implant, Asahi Kasei's negotiation power is limited.
Conversely, in more commoditized sectors such as basic chemicals or construction materials, the presence of numerous suppliers dilutes individual supplier power. Asahi Kasei's 2023 fiscal year revenue of ¥2.4 trillion underscores its significant purchasing volume, which can be leveraged in negotiations with less specialized suppliers. However, high switching costs for specialized inputs, coupled with the threat of supplier forward integration, can significantly shift power towards suppliers in niche markets.
In 2024, Asahi Kasei's reliance on long-term agreements for key raw materials in its performance chemicals segment, which contributed ¥1.2 trillion to its 2023 revenue, highlights supplier strength in these areas. The availability of alternatives and the cost for Asahi Kasei to switch suppliers are critical determinants of this power dynamic.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Asahi Kasei Relevance (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High for specialized materials, Low for commodities | Varies by segment; critical for high-performance chemicals |
| Switching Costs | High for specialized inputs, Low for commodities | Significant for proprietary components in medical and advanced materials segments |
| Supplier Forward Integration Threat | Increases power, especially in capital-intensive industries | Potential risk for suppliers of critical chemicals and components |
| Asahi Kasei's Importance to Supplier | Low if Asahi Kasei is a small part of supplier revenue, High otherwise | Asahi Kasei's scale can reduce power for diversified suppliers |
What is included in the product
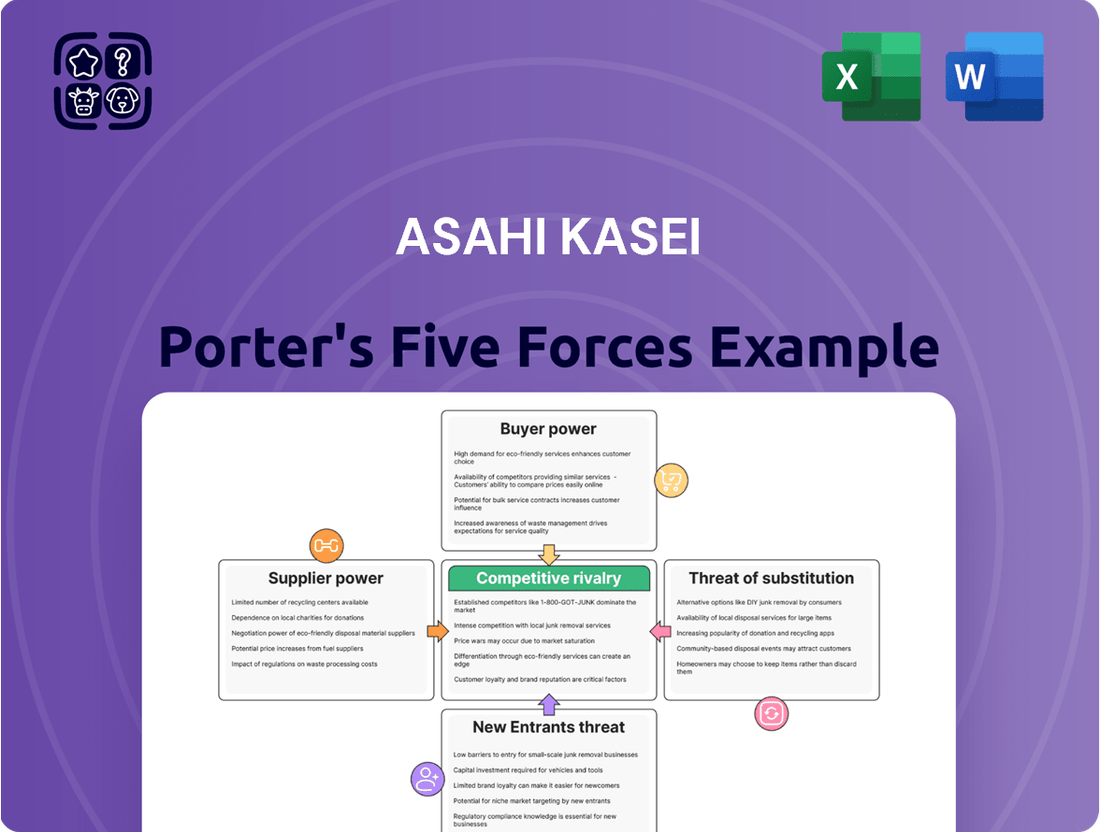
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for Asahi Kasei, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Easily identify and address competitive threats by visualizing Asahi Kasei's Porter's Five Forces, pinpointing areas of high pressure for strategic intervention.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration significantly impacts Asahi Kasei's bargaining power. If a few major clients represent a large chunk of sales within a specific business unit, those customers gain considerable leverage. For instance, if a single automotive manufacturer accounts for 15% of Asahi Kasei's performance polymers revenue, that customer can negotiate harder on price or demand tailored specifications.
The ease or difficulty for Asahi Kasei's customers to switch to alternative suppliers significantly influences their bargaining power. When Asahi Kasei's materials are deeply embedded in a customer's manufacturing or product design, requiring substantial investment in new equipment or processes, switching becomes costly. This high switching cost effectively diminishes the customer's leverage to demand lower prices or more favorable terms.
Customer price sensitivity directly influences their bargaining power. When customers can easily switch to competitors or when the product is a significant portion of their costs, they tend to be more sensitive to price changes. This heightened sensitivity grants them greater leverage in negotiations.
In the commodity chemical sector, where products are largely undifferentiated, customers often exhibit high price sensitivity. For instance, in 2024, the global commodity chemicals market experienced price fluctuations driven by energy costs and supply chain disruptions, allowing buyers to exert considerable pressure on suppliers like Asahi Kasei to offer competitive pricing.
Conversely, Asahi Kasei's involvement in specialized markets, such as advanced materials for electronics or innovative medical devices, often sees customers with lower price sensitivity. These customers prioritize performance, reliability, and unique functionalities, making them less inclined to switch based solely on minor price differences, thereby reducing their bargaining power.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers significantly enhances their bargaining power. If Asahi Kasei's major clients possess the financial resources and technical know-how to manufacture the components or materials they currently purchase, they can credibly threaten to do so. This leverage allows them to negotiate for lower prices or more favorable terms.
This is particularly relevant for large industrial customers who might have the scale and expertise to bring production in-house. For example, a major automotive manufacturer purchasing specialized plastics from Asahi Kasei could explore setting up its own compounding facilities if the cost savings and supply chain control are deemed sufficient. In 2024, the automotive sector, a key market for many chemical companies, continued to focus on supply chain resilience and cost optimization, making backward integration a more tangible consideration for large players.
- Increased Customer Leverage: Customers capable of backward integration can demand better pricing and terms from suppliers like Asahi Kasei.
- Strategic Consideration for Asahi Kasei: Asahi Kasei must monitor the capabilities and intentions of its key customers regarding in-house production.
- Market Dynamics: The prevalence of backward integration threats can influence Asahi Kasei's pricing strategies and investment in R&D to maintain a competitive edge.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute products significantly weakens Asahi Kasei's bargaining power with its customers. When customers have readily accessible alternatives, they are less reliant on Asahi Kasei's specific offerings, giving them more leverage to negotiate prices and terms. This is particularly true if these substitutes can fulfill the same core need, even if they are made from different materials or employ different technologies.
For instance, in the advanced materials sector where Asahi Kasei operates, the landscape is dynamic. Consider the automotive industry's shift towards lighter materials. While Asahi Kasei might offer advanced plastics and composites, the increasing adoption of aluminum or even innovative steel alloys by competitors can present viable substitutes. In 2024, the global automotive lightweight materials market was valued at approximately $170 billion, with significant growth driven by the pursuit of fuel efficiency and electric vehicle range, highlighting the competitive pressure from alternative material solutions.
- Increased Customer Options: A wide array of substitute products means customers can easily switch if Asahi Kasei's pricing or product features are not competitive.
- Price Sensitivity: The presence of substitutes often makes customers more price-sensitive, forcing Asahi Kasei to maintain competitive pricing to retain market share.
- Innovation Pressure: Asahi Kasei faces constant pressure to innovate and differentiate its products to counter the threat of substitutes, which can involve R&D investment and faster product development cycles.
- Market Share Erosion: If substitutes offer comparable performance at a lower cost or with added benefits, Asahi Kasei risks losing market share to these alternatives.
The bargaining power of Asahi Kasei's customers is influenced by several factors, including customer concentration, switching costs, price sensitivity, and the threat of backward integration. In 2024, the global chemical market saw continued emphasis on supply chain resilience and cost optimization, particularly in sectors like automotive, making these factors even more critical.
When customers are concentrated, meaning a few large clients represent a significant portion of sales, they gain substantial leverage to negotiate prices and terms. Similarly, high switching costs, where customers face significant expenses or operational disruptions to change suppliers, reduce their bargaining power. Conversely, customers who are highly price-sensitive or can easily find substitutes will exert more pressure on Asahi Kasei.
The potential for customers to integrate backward, meaning they could produce the materials themselves, also strengthens their negotiating position. Asahi Kasei must strategically manage these dynamics, balancing competitive pricing with the value of its specialized offerings and R&D investments to maintain its market standing.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Relevance for Asahi Kasei (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High if few customers dominate sales volume | A major automotive OEM accounting for 15% of performance polymers revenue can negotiate harder. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers power if switching is costly (e.g., material integration) | Specialized materials for medical devices have high switching costs, reducing customer leverage. |
| Price Sensitivity | High if substitutes are readily available or product is a large cost component | Commodity chemicals market in 2024 saw price sensitivity due to energy costs, increasing buyer power. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Increases power if customers can produce in-house | Automotive manufacturers in 2024 considered supply chain control, potentially threatening backward integration. |
What You See Is What You Get
Asahi Kasei Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Asahi Kasei Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within its industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate usability for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Asahi Kasei faces a highly competitive landscape across its core sectors. In chemicals, the market is populated by global giants and specialized regional players, all striving for dominance. For instance, the global specialty chemicals market, where Asahi Kasei has a strong presence, was valued at approximately $675 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating intense competition for market share.
The housing sector, particularly in Japan, is also characterized by numerous domestic and international construction and materials companies. This diversity in scale and approach means that competition isn't just about price but also innovation in building materials and sustainable solutions. Similarly, the healthcare sector, encompassing pharmaceuticals and medical devices, features a vast array of companies, from large multinational corporations to agile biotech startups, each vying for breakthroughs and market penetration.
This broad spectrum of competitors, varying in size, strategic focus, and product offerings, amplifies the rivalry. Companies like Asahi Kasei must constantly innovate and adapt to maintain their position against rivals who may have different strengths, whether it's cost leadership, technological specialization, or geographic focus.
The chemical industry often sees fierce competition, especially in mature markets where growth is slow. Companies fight harder for market share when the overall pie isn't expanding. For instance, in 2023, the global chemical industry experienced a modest growth rate, with some segments facing significant price pressures due to overcapacity in certain regions.
However, Asahi Kasei is strategically positioning itself in high-growth sectors. Their investment in hydrogen solutions and cutting-edge materials, which are projected to see double-digit annual growth through 2028, could mean less intense rivalry in these specific areas. This focus allows them to tap into emerging demand rather than solely battling for existing, slower-moving markets.
Asahi Kasei's capacity to distinguish its offerings through innovation, superior quality, and niche applications significantly dampens competitive rivalry. In markets for basic chemicals, where differentiation is inherently challenging, price wars often dominate.
However, in sectors such as cutting-edge medical equipment or advanced materials for specialized industries, robust product differentiation directly curtails head-to-head competition. For instance, Asahi Kasei's proprietary materials used in automotive lightweighting or its advanced sensor technologies for healthcare applications create unique value propositions that competitors find difficult to replicate, thereby lessening direct price-based rivalry in these segments.
Exit Barriers
Asahi Kasei operates in industries with significant exit barriers, a factor that can intensify competitive rivalry. These barriers include highly specialized assets and substantial investments in plant and equipment, common in its chemicals and materials segments. For instance, the chemical industry often requires long-term commitments and specialized manufacturing facilities that are difficult and costly to repurpose or sell, effectively trapping capital and discouraging firms from exiting even when unprofitable.
The presence of these high exit barriers means that even companies struggling financially may remain in the market, continuing to compete and potentially driving down prices or margins. This is especially true in capital-intensive sectors where the cost of decommissioning or selling specialized plants is prohibitive. Asahi Kasei's diversified operations, including performance polymers and specialty chemicals, are prime examples where such exit barriers are prevalent.
- Specialized Assets: Chemical plants and advanced materials manufacturing facilities represent significant, often industry-specific, capital investments that are difficult to redeploy.
- Long-term Contracts: Commitments to supply key customers or secure raw materials can create obligations that extend beyond a company's immediate profitability, hindering exit.
- Social Considerations: The impact on employees and local communities when closing down large industrial operations can also act as a de facto exit barrier, adding a layer of complexity to divestment decisions.
- Capital Intensity: The sheer scale of investment required in sectors like petrochemicals means that exiting the market involves substantial write-offs and unrecouped capital.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic importance of a market significantly fuels competitive rivalry. When a market is crucial for a competitor's long-term vision or global footprint, they're inclined to engage in fierce competition, potentially prioritizing market share over immediate profits. Asahi Kasei's commitment to sustainability and targeted growth sectors like hydrogen and life sciences demonstrates high strategic stakes, intensifying the competitive landscape in these areas.
For instance, the global hydrogen market, projected to reach approximately $300 billion by 2030, is a key battleground for chemical giants. Asahi Kasei's investments in hydrogen production technologies and infrastructure position it directly against major players like Air Liquide and Linde, who also view hydrogen as central to their future energy strategies. This shared strategic imperative means intense competition for market share and technological leadership.
- Strategic Focus: Asahi Kasei's emphasis on sustainability and growth areas like hydrogen and life sciences raises the stakes for all involved.
- Market Importance: Competitors with similar strategic priorities will likely compete aggressively, even if it impacts short-term profitability.
- Industry Outlook: The projected growth in the hydrogen sector, expected to reach around $300 billion by 2030, highlights the significant strategic value and thus, the heightened rivalry.
Asahi Kasei faces intense rivalry across its diverse business segments, from specialty chemicals to housing and healthcare. The sheer number of global and regional players, each with varying strengths, necessitates constant innovation and differentiation. For example, the global specialty chemicals market, a key area for Asahi Kasei, was valued at approximately $675 billion in 2023, underscoring the scale of competition for market share.
While some segments, like basic chemicals, experience price-driven competition, Asahi Kasei's focus on high-growth areas such as hydrogen solutions and advanced materials offers a strategic advantage. These emerging markets, projected for significant growth through 2028, may see less entrenched rivalry. However, the strategic importance of these sectors, like the hydrogen market projected to reach $300 billion by 2030, attracts significant investment from major players, ensuring continued competitive pressure.
The presence of high exit barriers, such as specialized assets and capital intensity in its chemical and materials businesses, can further intensify rivalry by keeping less profitable firms in the market. This dynamic means Asahi Kasei must not only compete on innovation and quality but also navigate a landscape where competitors may remain active due to the difficulty and cost of exiting.
| Segment | Key Competitors | Market Dynamics | Asahi Kasei's Position |
| Specialty Chemicals | BASF, Dow, DuPont, regional players | High growth, innovation-driven, price sensitivity in some areas | Strong differentiation through proprietary materials |
| Housing & Construction Materials | Sekisui House, Lixil, local builders | Fragmented market, focus on sustainability and design | Integrated solutions, advanced materials |
| Healthcare | Johnson & Johnson, Roche, Medtronic, biotech startups | Rapid innovation, regulatory hurdles, M&A activity | Advanced medical devices, pharmaceuticals |
| Hydrogen Solutions | Air Liquide, Linde, Mitsubishi Chemical | Emerging market, strategic importance, technological race | Investment in production and infrastructure |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Asahi Kasei is influenced by the price-performance balance offered by alternatives. For instance, in the construction sector, engineered wood or advanced composites might substitute for Asahi Kasei's concrete admixtures or insulation materials, depending on cost-effectiveness and performance gains.
In healthcare, alternative diagnostic tools or less invasive treatment methods could displace Asahi Kasei's medical devices. The chemical division faces substitutes from different production processes or bio-based alternatives that offer similar functionalities at a competitive cost.
For example, the global market for construction chemicals, a segment where Asahi Kasei operates, was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a strong demand but also a fertile ground for substitute innovations.
Customer propensity to substitute for Asahi Kasei's products is shaped by brand loyalty, perceived risk, and how easy it is to switch. For instance, in the materials sector, if a competitor offers a slightly cheaper or more readily available alternative, customers might switch, especially if the performance difference isn't significant. In 2023, the global specialty chemicals market, a key area for Asahi Kasei, saw growth driven by innovation, but also faced pressure from emerging players offering cost-effective solutions.
The relative price of substitute products poses a significant threat to Asahi Kasei, especially in its materials segment. If alternative materials offer comparable functionality at a lower cost, customers may switch, impacting Asahi Kasei's market share and profitability. For instance, in the competitive plastics market, the price difference between Asahi Kasei's specialty polymers and more commoditized alternatives can be a deciding factor for many buyers.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitutes
Ongoing technological advancements are a significant driver in the creation of new and potentially more effective substitutes for Asahi Kasei's product offerings. For instance, breakthroughs in materials science could yield novel alternatives to their established plastics and fibers. Similarly, innovative medical technologies might emerge that offer superior performance or cost-effectiveness compared to current devices in the healthcare sector.
The threat of substitutes is amplified as these technological leaps become more accessible and economically viable. Consider the rapid evolution in battery technology, which could offer alternatives to certain chemical products Asahi Kasei manufactures for the automotive sector. In 2024, the global battery market was valued at over $100 billion, showcasing the immense potential for disruptive innovation in related material supply chains.
- Materials Science: Innovations in areas like advanced composites or bio-based materials could substitute for traditional plastics and synthetic fibers.
- Medical Technology: Novel diagnostic tools or minimally invasive treatment methods might replace existing medical devices.
- Energy Storage: Advancements in battery chemistries and designs present a growing substitute threat to materials used in traditional energy applications.
Regulatory or Environmental Shifts Favoring Substitutes
Changes in regulations or growing environmental consciousness can significantly boost the appeal of substitute products. For Asahi Kasei, a move towards bio-based or recycled materials could directly challenge its established petrochemical-based product lines if the company fails to pivot effectively.
For example, if governments implement stricter carbon emission standards, as seen in various European Union directives aiming for a circular economy, products derived from less carbon-intensive processes would gain a competitive edge. This regulatory pressure could make Asahi Kasei's traditional offerings less attractive to customers seeking sustainable solutions.
- Regulatory Pressure: Stricter environmental regulations, such as those targeting plastic waste or carbon footprints, can make substitute materials more economically viable and appealing.
- Consumer Demand: Increased consumer awareness regarding sustainability drives demand for eco-friendly alternatives, potentially impacting Asahi Kasei's market share in conventional materials.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in biodegradable plastics or advanced recycling techniques can lower the cost and improve the performance of substitutes, amplifying their threat.
- Policy Incentives: Government subsidies or tax breaks for using recycled or bio-based materials can further tilt the playing field in favor of substitutes over traditional petrochemical products.
The threat of substitutes for Asahi Kasei is moderate but growing, particularly due to advancements in materials science and increasing environmental consciousness. For instance, in the construction sector, engineered wood and advanced composites offer competitive alternatives to traditional concrete admixtures and insulation. In 2024, the global market for advanced composites was projected to exceed $20 billion, highlighting the increasing adoption of these substitute materials.
The chemical division faces substitutes from bio-based alternatives and novel production processes. For example, the market for biodegradable plastics, a direct substitute for conventional plastics, is expanding rapidly. The global bioplastics market was estimated to be around $12 billion in 2023 and is expected to see significant growth in the coming years.
In healthcare, alternative diagnostic tools and less invasive treatment methods are emerging as substitutes for established medical devices. The increasing focus on preventative care and personalized medicine further fuels the development of these alternatives.
Customer willingness to switch is influenced by factors like price, performance, and ease of adoption. While Asahi Kasei benefits from brand loyalty and established relationships, the availability of cost-effective and high-performing substitutes can sway purchasing decisions, especially in price-sensitive markets like specialty chemicals where innovation is constant.
| Sector | Asahi Kasei Product Area | Potential Substitutes | Market Context (2023-2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Concrete Admixtures, Insulation | Engineered Wood, Advanced Composites | Global Construction Chemicals Market: ~$50 billion (2023), growing demand. |
| Chemicals | Specialty Polymers, Fibers | Bio-based Materials, Recycled Plastics | Global Specialty Chemicals Market: Growing, with pressure from cost-effective alternatives. |
| Healthcare | Medical Devices | Novel Diagnostic Tools, Minimally Invasive Treatments | Advancements driven by preventative care and personalized medicine trends. |
| Automotive | Battery Materials | Alternative Battery Chemistries | Global Battery Market: Over $100 billion (2024), high potential for disruptive innovation. |
Entrants Threaten
The chemical, housing, and healthcare sectors, where Asahi Kasei operates, typically demand significant upfront capital. Establishing advanced research and development labs, state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and extensive distribution channels requires billions of dollars in investment. For instance, building a new, large-scale petrochemical facility can easily cost upwards of $1 billion, presenting a formidable hurdle for any new player aiming to compete.
Asahi Kasei, a global leader in materials science, leverages significant economies of scale. For instance, in 2024, its consolidated revenue reached approximately ¥2.5 trillion (around $16 billion USD), indicating a vast operational footprint. This scale allows for substantial cost advantages in raw material procurement, manufacturing processes, and research and development investments, making it challenging for new, smaller competitors to match Asahi Kasei's cost efficiencies and compete on price.
Asahi Kasei benefits from strong proprietary product differences and a well-established brand identity, which act as significant deterrents to new entrants. The company's diverse portfolio, ranging from performance polymers to specialty chemicals and even healthcare products, is built upon unique technological formulations and decades of research and development. For instance, in 2024, Asahi Kasei continued to invest heavily in R&D, with a reported 170 billion JPY allocated to innovation, aiming to further solidify its technological lead in areas like advanced battery materials and sustainable plastics.
Access to Distribution Channels
New players often struggle to secure shelf space or access established distribution networks, particularly in sectors like advanced materials or pharmaceuticals where specialized logistics and customer relationships are crucial. Asahi Kasei benefits significantly from its deep-rooted partnerships and extensive distribution infrastructure, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on this front.
Consider the complexities in the automotive sector, where Asahi Kasei supplies advanced plastics and fibers. New entrants would need to navigate supplier agreements with major car manufacturers and their tiered supply chains. In 2023, the global automotive plastics market was valued at over $35 billion, highlighting the scale of these established channels.
- Limited Access to Established Networks: New companies face significant hurdles in gaining entry into existing distribution channels, especially in industries with intricate supply chains.
- Asahi Kasei's Advantage: Asahi Kasei leverages its long-standing relationships and robust distribution networks, creating a substantial barrier for potential competitors.
- Sector-Specific Challenges: Industries like specialty chemicals and medical devices require specialized logistics and customer engagement, further complicating market entry for new entrants.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations present a substantial threat of new entrants for companies like Asahi Kasei, particularly in its chemical and healthcare segments. Stringent regulations, extensive licensing requirements, and rigorous environmental standards necessitate significant upfront investment and compliance efforts from any new player. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to strengthen its REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations, demanding extensive data submission and risk assessments for chemical substances, which can deter smaller or less capitalized entrants. Similarly, the pharmaceutical industry faces a complex web of approvals from bodies like the FDA in the United States, with the drug development and approval process often taking over a decade and costing billions of dollars, creating a formidable barrier.
Navigating these complex regulatory landscapes is not only time-consuming but also incurs considerable costs. New entrants must dedicate substantial resources to understanding and adhering to these rules, which can include conducting extensive safety testing, obtaining permits, and implementing robust quality control systems. This can significantly delay market entry and reduce the profitability of new ventures, thereby diminishing the overall threat of new entrants. For example, the cost of compliance with environmental regulations in the chemical industry alone can add a significant percentage to the capital expenditure required for establishing new production facilities.
- High Capital Requirements: Meeting regulatory standards for safety and environmental protection often demands substantial capital investment in specialized equipment and processes.
- Lengthy Approval Processes: Obtaining necessary licenses and approvals, especially in sectors like healthcare and advanced materials, can take years, delaying market entry.
- Ongoing Compliance Costs: Beyond initial setup, continuous adherence to evolving regulations, including reporting and auditing, adds to operational expenses.
The threat of new entrants for Asahi Kasei is generally low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for advanced manufacturing and R&D, estimated at over $1 billion for a single petrochemical plant, deter many potential competitors. Asahi Kasei's substantial economies of scale, evidenced by its ¥2.5 trillion consolidated revenue in 2024, provide cost advantages that are difficult for newcomers to overcome.
Proprietary product differentiation and strong brand loyalty, supported by a 2024 R&D investment of 170 billion JPY, further solidify Asahi Kasei's market position. Additionally, established distribution networks and long-standing customer relationships, crucial in sectors like automotive materials where the market was over $35 billion in 2023, present considerable challenges for new market participants seeking access.
Stringent government regulations and lengthy approval processes, particularly in chemicals and healthcare, add significant cost and time burdens for new entrants. For instance, evolving EU REACH regulations in 2024 and the multi-year, multi-billion dollar drug approval process by agencies like the FDA create formidable hurdles, limiting the overall threat from new companies.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Asahi Kasei leverages data from annual reports, industry-specific market research, and financial databases like Bloomberg and S&P Capital IQ to assess competitive intensity and strategic positioning.
