Apogee Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Apogee Bundle
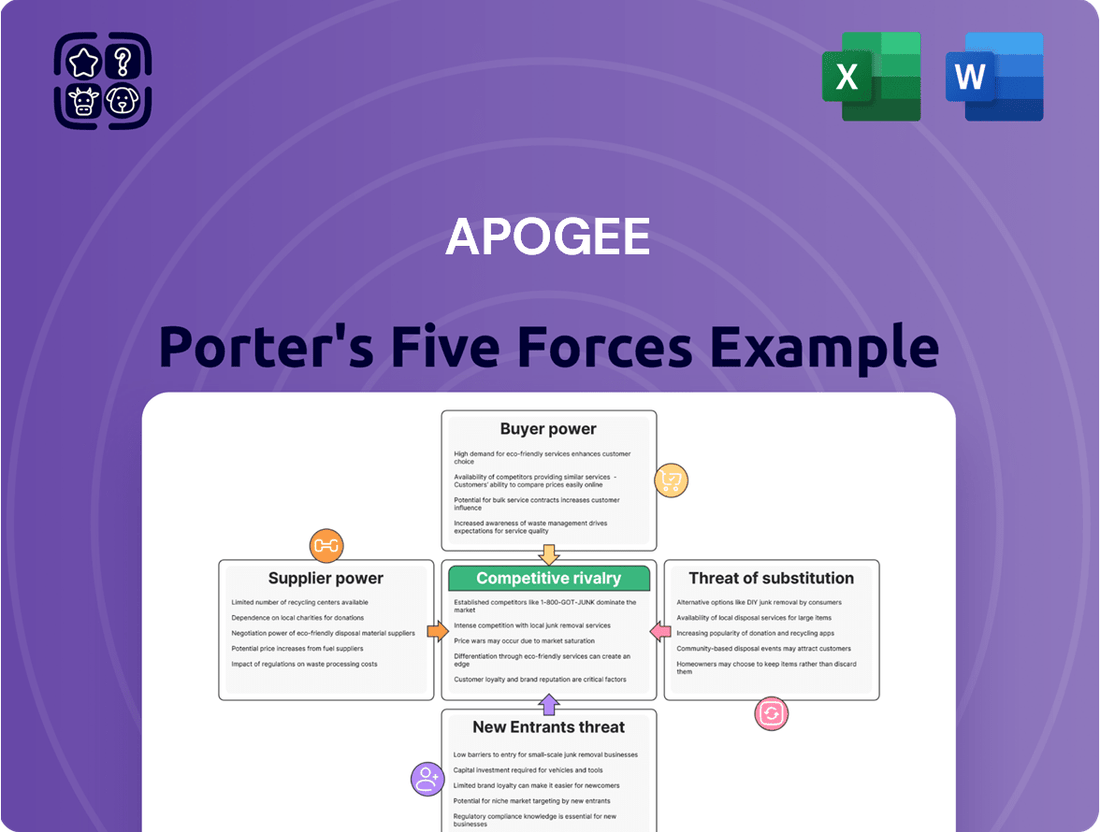
Apogee's competitive landscape is shaped by five key forces: the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any business operating within or looking to enter Apogee's market. This brief overview highlights the foundational elements of this critical analysis.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Apogee delves into the specific factors that influence each of these forces, providing a nuanced understanding of the competitive intensity. It uncovers the underlying pressures that affect profitability and strategic positioning within Apogee's industry. This detailed examination goes beyond surface-level observations to offer actionable strategic intelligence.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Apogee’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers significantly impacts Apogee Enterprises' bargaining power. For instance, if the market for specialized architectural glass, a key input, is dominated by a handful of manufacturers, these suppliers can command higher prices. In 2024, the global flat glass market, which includes architectural glass, saw continued consolidation, with a few major players holding substantial market share, thereby increasing their leverage over downstream consumers like Apogee.
Apogee's reliance on unique inputs significantly influences supplier bargaining power. For instance, if Apogee depends on specific, proprietary glass coatings or advanced framing system technologies that are not readily available from multiple vendors, suppliers of these specialized components can exert considerable leverage. This uniqueness means Apogee has fewer alternatives, potentially allowing suppliers to dictate terms and pricing, impacting Apogee's cost structure and profitability.
Switching costs for Apogee Enterprises are a significant factor influencing the bargaining power of its suppliers. If Apogee faces high costs when changing suppliers, such as expenses related to retooling manufacturing equipment, re-qualifying new materials to meet quality standards, or the administrative burden of renegotiating contracts, this dependency inherently strengthens the leverage of its current suppliers. For instance, in the architectural and construction materials sector, where Apogee operates, custom-designed components or specialized manufacturing processes can create substantial switching barriers. These high switching costs mean suppliers can often dictate terms and pricing more effectively, as Apogee may find it prohibitively expensive or time-consuming to seek alternatives.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant concern for Apogee. If suppliers were to begin manufacturing finished architectural glass or framing systems themselves, they would directly enter Apogee's market, thereby gaining substantial leverage. This move would allow them to capture more of the value chain and potentially compete with Apogee on its own turf.
This risk is amplified if these suppliers possess sophisticated manufacturing technologies or have already cultivated strong ties with Apogee's end customers. For instance, a major glass manufacturer with advanced coating capabilities could decide to produce ready-to-install window units, bypassing Apogee's fabrication processes.
Consider the situation where a key supplier of specialized coatings, critical for Apogee's high-performance glass products, has invested heavily in new, automated fabrication lines.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers with advanced manufacturing, such as automated glass cutting and assembly, are better positioned for forward integration.
- Customer Relationships: Suppliers with direct access and strong existing relationships with construction firms or developers can more easily transition to offering finished products.
- Market Dynamics: A shift in market demand towards integrated solutions could incentivize suppliers to vertically integrate to meet these needs directly.
- Financial Strength: Suppliers with robust financial backing are more capable of absorbing the investment required for forward integration.
Importance of Apogee to Suppliers
Apogee Enterprises' significance as a customer directly influences its bargaining power with suppliers. If Apogee constitutes a substantial percentage of a supplier's overall revenue, that supplier is likely to be more accommodating with pricing and terms to secure Apogee's continued business. For instance, if a key glass manufacturer derives 20% of its annual sales from Apogee, they have a strong incentive to offer competitive pricing to retain this significant client.
Conversely, when Apogee represents a minor portion of a supplier's income, the supplier holds more leverage. In such scenarios, suppliers may be less inclined to negotiate favorable terms, knowing that losing Apogee’s business would have a negligible impact on their financial performance. This dynamic is crucial in understanding the supplier's willingness to bend on pricing or delivery schedules.
- Supplier Dependence: A supplier heavily reliant on Apogee's orders will offer better terms.
- Customer Size Impact: Larger orders from Apogee can command more favorable supplier pricing.
- Market Concentration: If Apogee is a dominant buyer in a niche market, its importance to suppliers increases.
- Supplier Negotiation Leverage: A supplier with many other clients has greater power over Apogee.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Apogee Enterprises is influenced by several factors, including the concentration of suppliers, the uniqueness of inputs, and switching costs. If a few suppliers dominate the market for essential materials, like specialized architectural glass, they can exert significant pricing power. In 2024, the global flat glass market, a key sector for Apogee, continued to show consolidation, with major players holding substantial market share, indicating increased supplier leverage.
High switching costs for Apogee, such as those incurred when retooling equipment or re-qualifying materials, inherently strengthen supplier leverage. This is particularly relevant in the architectural materials sector, where custom components can create significant barriers to changing suppliers, allowing existing vendors to dictate terms more effectively.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Apogee's market, by manufacturing finished products themselves, also increases their bargaining power. This is more likely if suppliers possess advanced technology or strong customer relationships within the construction industry, enabling them to capture more of the value chain.
Apogee's importance as a customer also plays a role; if Apogee represents a significant portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier is more likely to offer favorable terms. Conversely, if Apogee is a small client, the supplier has greater negotiation power.
| Factor | Impact on Apogee | 2024 Context/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier power | Consolidation in the flat glass market in 2024 bolstered leverage of key players. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Increases supplier power | Reliance on proprietary coatings or framing systems limits Apogee's alternatives. |
| Switching Costs | Increases supplier power | High costs for retooling or material re-qualification make changing suppliers difficult. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Increases supplier power | Suppliers with advanced tech or direct customer ties could bypass Apogee. |
| Apogee's Customer Significance | Decreases supplier power (if high) | If Apogee is a large client, suppliers are more accommodating. |
What is included in the product
Provides a comprehensive understanding of Apogee's competitive environment by analyzing the intensity of rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes. This framework helps identify strategic opportunities and challenges within Apogee's industry.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic dashboard that highlights key threats and opportunities, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Apogee's primary customers, commercial building developers and contractors, frequently place substantial orders for major construction projects. This high volume purchasing power allows them to negotiate favorable terms, including price reductions and extended payment schedules, significantly impacting Apogee's profitability. For instance, in 2024, large-scale contracts often accounted for over 60% of revenue from key accounts, giving these clients considerable leverage.
The concentration of these major customers within particular geographic areas or market niches further amplifies their influence. When a few large clients represent a significant portion of Apogee's business, their ability to switch suppliers or withhold future business becomes a potent bargaining tool. Analysis from late 2024 indicated that the top ten commercial developers represented nearly 45% of Apogee's annual sales volume, underscoring this customer concentration risk.
Switching costs for Apogee's customers are generally substantial. This is due to the highly integrated nature of their architectural glass and framing systems within large-scale construction projects. For instance, if a building project has already specified and begun installing a particular Apogee system, altering the supplier mid-project would incur significant financial penalties and project delays, thereby limiting the customer's leverage.
However, this bargaining power shifts for customers during the initial specification phase of new projects. Before any commitment is made, potential clients can more readily compare offerings and negotiate terms, as the financial and logistical hurdles of switching are minimal at this early stage.
Commercial building projects are frequently very sensitive to cost, meaning customers pay close attention to the prices of architectural elements like those Apogee provides. This heightened awareness comes from competitive bidding and the significant overall expense of construction projects, which pushes Apogee to keep its pricing competitive.
For instance, in 2024, the average cost for commercial construction projects in the U.S. continued to be a major factor, with many clients actively seeking the most cost-effective solutions. This environment directly impacts Apogee's ability to command premium pricing if competitors can offer comparable products at lower price points.
Availability of Substitutes for Customers
The availability of substitutes significantly influences customer bargaining power. If customers can easily find alternative materials or construction methods that deliver similar results at a lower price, their leverage increases. For instance, while Apogee's high-performance glass and framing systems offer distinct advantages, the broader construction market presents various building envelope solutions that can reduce a customer's reliance on Apogee's specific offerings.
Consider the architectural glass market. While Apogee is a key player, other manufacturers provide comparable glass products. In 2023, the global architectural glass market was valued at approximately USD 95 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.5% through 2030, indicating a competitive landscape with multiple suppliers and product types.
- Substitutability in Building Envelopes: Customers can opt for alternative facade systems, such as precast concrete panels, metal cladding, or even advanced composite materials, which might offer competitive pricing or different aesthetic appeals.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis for Customers: When evaluating building envelope solutions, clients weigh performance against cost. If a substitute offers 80% of Apogee's performance at 60% of the price, it becomes a powerful bargaining chip.
- Market Dynamics and Innovation: The continuous innovation in construction materials means new substitutes are always emerging, potentially eroding the unique selling proposition of specialized products like Apogee's, thereby enhancing customer power.
- Impact on Pricing: The presence of viable substitutes directly pressures Apogee's pricing strategies, as customers can threaten to switch to a less expensive alternative if prices are not competitive.
Customer's Threat of Backward Integration
The threat of customers like construction companies integrating backward into manufacturing their own glass or framing components for Apogee's products is generally low. This is primarily because the production of specialized architectural glass and related components demands significant capital investment and highly specific technical expertise, which most customers lack.
However, for exceptionally large construction firms, particularly those undertaking massive, standardized projects, the calculus might shift. If these firms identify substantial cost savings or gain a significant competitive edge by producing certain basic components in-house, they might explore backward integration. For instance, a major developer with a consistent need for standard window units could potentially find it economical to set up their own assembly lines.
- Low Integration Threat: Apogee's customers typically lack the specialized capital and expertise for backward integration into glass manufacturing.
- Potential for Large Firms: Very large construction firms may consider integrating for standard components if cost advantages are significant.
- Example: A large developer with consistent demand for standard window units might explore in-house assembly.
The bargaining power of Apogee's customers is moderate, influenced by factors like order volume, customer concentration, and price sensitivity. While switching costs are high once a system is specified, the initial selection phase offers significant leverage to buyers. The availability of substitutes and the overall cost consciousness in the construction sector further temper Apogee's pricing flexibility.
For instance, in 2024, the average construction project budget in the US saw increased scrutiny on material costs, with clients actively seeking value. Apogee's ability to maintain strong margins is therefore dependent on its unique product offerings and the perceived value it delivers compared to alternatives.
The table below illustrates key aspects influencing customer bargaining power for Apogee:
| Factor | Apogee's Situation | Impact on Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Top 10 clients represented ~45% of sales in late 2024. | Increases leverage for these major clients. |
| Order Volume | Large commercial projects often exceed 60% of revenue from key accounts in 2024. | High volume allows negotiation for better terms. |
| Switching Costs | High once integrated into projects; low during specification. | Limits leverage mid-project, empowers during selection. |
| Price Sensitivity | Construction projects are cost-sensitive; substitutes exist. | Pressures Apogee to remain competitive on price. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Apogee Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Apogee Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive instantly after completing your purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can trust that this professionally formatted analysis is ready for immediate use and application to your strategic planning needs. This detailed breakdown will equip you with actionable insights derived directly from the content presented in this preview.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The architectural glass and framing industry is quite crowded, featuring big names like Cardinal Glass Industries, Jeld-Wen, and PPG Industries, all competing fiercely. Alongside these giants, there are many smaller, regional companies and specialists, creating a very diverse competitive environment. This means companies constantly fight for a bigger piece of the market, whether it's for large commercial projects or smaller, custom framing jobs.
The building materials sector, where Apogee operates, is generally on an upward trajectory, fueled by global urbanization and a growing emphasis on sustainable building practices. However, the pace of growth isn't uniform across all segments.
For instance, while the broader market might see robust expansion, specific niches Apogee serves, like certain traditional picture framing segments, may encounter slower growth. This disparity can heighten competitive pressures as companies vie for a larger share of the limited expansion in mature markets.
In 2024, the global construction market was projected to grow by 3.1%, according to GlobalData, but this masks varied performance within segments. Areas with less innovation or demand might see intensified rivalry as firms battle for market share among existing customers.
Apogee Enterprises distinguishes itself through high-performance, energy-efficient, and visually appealing glass and framing systems, creating a degree of product differentiation. This focus allows them to command premium pricing in certain segments of the architectural and automotive markets.
However, the competitive landscape is intense, with rivals like Saint-Gobain and NSG Group also investing heavily in innovation. These competitors are pushing boundaries in smart glass technology, developing advanced coatings for improved performance, and prioritizing sustainable building solutions, fueling an ongoing race for market advantage and product differentiation.
Exit Barriers
High fixed costs, particularly for manufacturing facilities and specialized equipment in the glass and framing sector, act as significant exit barriers for companies like Apogee. These substantial investments mean that shutting down operations can incur massive losses, forcing businesses to persist even when market conditions are unfavorable. This persistence intensifies competition as firms strive to cover their overheads, leading to more aggressive pricing strategies and a heightened level of rivalry among existing players.
The financial commitment to specialized machinery and large-scale production plants creates a situation where companies are reluctant to exit the market. For instance, the capital expenditure for a new glass tempering line can easily run into millions of dollars. This means that even during periods of reduced demand, these assets must continue to operate to avoid being written off entirely, thus contributing to overcapacity and driving down prices.
- Significant Capital Investment: The glass and framing industry requires substantial upfront investment in specialized machinery, such as automated cutting, tempering, and coating equipment, often costing millions.
- Asset Specificity: Much of this equipment is highly specialized and cannot be easily repurposed or sold for alternative uses, making divestment difficult and costly.
- Labor Commitments: Historically, the industry has relied on a skilled workforce, and severance packages or retraining obligations can add to exit costs.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term supply agreements or leases on facilities can also create financial penalties for early termination, further increasing exit barriers.
Strategic Commitments and Acquisitions
Apogee Enterprises' strategic acquisition of UW Solutions in 2024, aimed at bolstering its Performance Surfaces segment, highlights the intense competitive rivalry. This move, part of Apogee's broader strategy to expand its reach and capabilities, signals a market where companies are actively pursuing growth through consolidation and diversification to enhance their competitive standing.
Competitors are compelled to react to such strategic maneuvers, often by initiating their own acquisitions, joint ventures, or significant R&D investments to maintain or improve their market share and profitability. For instance, the architectural glass and aluminum sector, a key area for Apogee, has seen ongoing consolidation as players seek economies of scale and broader product portfolios to serve diverse construction needs. The acquisition of UW Solutions, which provides specialized glass fabrication and installation services, directly addresses market demands for integrated solutions.
- Apogee's 2024 acquisition of UW Solutions expanded its Performance Surfaces segment, demonstrating a commitment to growth and market penetration.
- This strategic move intensifies rivalry as competitors are pushed to make similar investments or develop alternative strategies to remain competitive.
- The trend of acquisitions in sectors like architectural glass reflects a broader industry push for scale and diversified offerings, directly impacting competitive dynamics.
- Companies are strategically investing to either capture greater market share or defend existing positions against aggressive expansion by rivals.
The competitive rivalry within Apogee's operating environment is substantial, driven by a crowded market with both large, established players and numerous smaller, specialized firms. This intense competition forces companies to constantly innovate and fight for market share across various segments of the architectural and automotive glass industries.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Apogee's architectural glass and framing systems is significant, primarily stemming from alternative building envelope materials. These include advanced composite panels and opaque cladding systems, which can offer comparable insulation and structural performance. For instance, while glass provides excellent daylighting, materials like high-performance insulated metal panels can achieve similar thermal resistance (R-values) and often at a more competitive cost for certain applications. In 2024, the market for building envelope solutions continues to see innovation, with manufacturers developing lighter, stronger, and more energy-efficient alternatives that directly challenge the dominance of traditional glass and metal systems.
The rise of smart window technologies, like electrochromic or dynamic glazing, from non-traditional manufacturers poses a significant threat of substitution. These innovative solutions can alter their transparency and energy efficiency on demand, potentially lessening the demand for conventional, fixed-performance architectural glass.
For instance, companies not previously involved in glass manufacturing are now entering the smart glass market, attracted by its growth potential. In 2024, the global smart glass market was valued at approximately $5.8 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of around 9.5% through 2030, suggesting a substantial shift away from traditional solutions.
Digital picture frames and electronic displays are emerging as significant substitutes for traditional picture framing services. These devices allow for the dynamic rotation of artwork and photographs, offering a level of versatility that static frames cannot match. As the cost of these technologies continues to fall, their appeal to consumers looking for modern and adaptable display solutions grows.
The market for digital photo frames saw considerable growth, with global sales reaching an estimated $1.2 billion in 2023. This trend is projected to continue, driven by increasing consumer adoption of smart home technology and a desire for more interactive ways to showcase personal memories and art. The convenience and ability to update displayed content without physically changing items present a compelling alternative to traditional framing.
Innovation in Insulation and Shading Solutions
Improvements in building insulation and external shading systems present a significant threat of substitution for Apogee's high-performance glass. If alternative solutions like advanced insulation materials or smart shading devices can deliver comparable energy savings and comfort, the unique selling proposition of Apogee's specialized glass might be diluted.
For instance, advancements in vacuum-insulated glass or aerogels could offer thermal performance rivaling some of Apogee's offerings without relying solely on specialized glass coatings. Likewise, sophisticated external shading systems that dynamically adjust to sunlight can reduce solar heat gain, potentially diminishing the demand for glass with integrated solar control properties.
The market for energy-efficient building materials is dynamic, with ongoing research and development. By 2024, the global building insulation market was valued at approximately $68.5 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. This suggests a robust environment for substitute technologies to emerge and gain traction.
- Innovation in Insulation: New materials like vacuum-insulated glazing (VIG) and advanced aerogels offer enhanced thermal resistance, potentially competing with high-performance glass on energy efficiency.
- External Shading Systems: Dynamic external shading, including automated louvers and solar screens, can effectively manage solar heat gain, reducing reliance on spectrally selective glass coatings.
- HVAC Advancements: More efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems can compensate for less advanced building envelopes, indirectly reducing the perceived need for highly specialized glazing.
- Cost-Effectiveness: As substitute technologies mature, their cost-effectiveness could improve, making them more attractive alternatives to premium glass solutions.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The cost-effectiveness of substitute products is a major driver of their threat. When alternatives provide significant cost savings, especially over the long term, customers are more likely to consider switching. This includes evaluating not just the initial purchase price but also ongoing operational expenses and maintenance.
For instance, in the optical technology sector, while high-end custom lens solutions from companies like Apogee offer superior performance, more affordable off-the-shelf lenses or even advanced digital imaging software can serve as viable substitutes for certain applications. In 2024, the average cost savings for businesses adopting cloud-based data storage versus on-premises solutions could range from 15-30%, making it a compelling substitute for traditional IT infrastructure.
- Cost Savings: Substitutes offering substantial savings (e.g., 20% or more) on total cost of ownership pose a higher threat.
- Performance Trade-offs: If substitutes meet 80% or more of critical performance needs at a lower cost, switching is more likely.
- Operational Efficiency: Alternatives that reduce operating expenses or labor costs (e.g., automation software replacing manual processes) are strong substitutes.
- Market Data: Reports from late 2024 indicate that the market for renewable energy components is seeing increased adoption of lower-cost materials, impacting traditional manufacturers.
The threat of substitutes for Apogee's offerings, particularly in architectural glass, is amplified by advancements in alternative building materials and technologies. For instance, innovative composite panels and opaque cladding systems can offer comparable thermal performance and structural integrity, often at a more competitive price point. By 2024, the building envelope market continued to see a surge in lighter, more energy-efficient materials challenging traditional glass and metal systems.
The emergence of smart glass technologies, such as electrochromic or dynamic glazing from non-traditional manufacturers, presents a significant substitution threat. These advanced solutions can actively manage transparency and energy efficiency, potentially reducing the demand for conventional architectural glass. The global smart glass market, valued at approximately $5.8 billion in 2024, is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 9.5% through 2030, indicating a clear trend towards these innovative alternatives.
| Substitute Category | Key Features | Potential Impact on Apogee | Market Data (2024 Estimates) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Cladding Systems | High insulation, structural strength, cost-effectiveness | Direct competition for building envelope applications | Global building insulation market valued at ~$68.5 billion |
| Smart Glass Technologies | Dynamic transparency, energy efficiency control | Disruption of conventional glass market share | Global smart glass market valued at ~$5.8 billion |
| High-Performance Insulation | Superior thermal resistance (e.g., VIG, aerogels) | Reduces need for specialized glass coatings | Growing market for advanced building materials |
Entrants Threaten
The architectural glass and framing sector, especially for sophisticated, high-performance products, demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, specialized equipment, and robust research and development to stay competitive. For instance, setting up a modern glass fabrication facility can easily run into tens of millions of dollars.
These substantial financial hurdles act as a powerful deterrent for many aspiring new players. The sheer scale of investment required to build and equip operations capable of producing high-quality architectural glass and framing systems makes entry exceptionally challenging. This capital intensity effectively raises the barrier, protecting established firms from immediate competitive threats.
Established players like Apogee enjoy significant cost advantages due to economies of scale in production, procurement, and distribution. This allows them to offer lower unit prices, creating a substantial hurdle for new entrants who lack the volume to achieve similar efficiencies. For instance, in 2024, Apogee's large-scale manufacturing operations likely resulted in a lower cost per unit compared to a hypothetical new entrant starting with limited capacity.
Furthermore, the experience curve plays a crucial role. Apogee's years of navigating complex projects, optimizing processes, and building expertise translate into greater operational efficiency and fewer costly mistakes. This accumulated knowledge, often intangible and hard to replicate quickly, serves as a formidable barrier, making it challenging for newcomers to match the established players' cost-effectiveness and project execution capabilities.
Apogee's extensive 75-year history has cemented a robust brand loyalty and fostered deep-seated relationships with key industry players like architects, contractors, and developers. This established trust and credibility present a significant hurdle for any new entrant aiming to break into the market, especially for securing substantial commercial projects.
New competitors would struggle to replicate Apogee's ingrained network of specifiers and customers, a crucial element for success in the architectural glass and aluminum sector. Building this level of industry penetration and client confidence requires considerable time and investment, making the threat of new entrants moderate.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certifications
The building materials sector, particularly for advanced architectural products, faces significant regulatory barriers. Stringent building codes, rigorous safety standards, and evolving environmental regulations are paramount. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Green Building Council's LEED certification continued to drive demand for sustainable materials, requiring new entrants to meet specific environmental performance criteria.
Navigating these complex regulatory landscapes and securing necessary certifications represents a substantial hurdle for potential new players. This process is not only time-consuming but also capital-intensive, demanding significant investment in research, development, and compliance testing. As of early 2025, the average cost for product certification in specialized building materials can range from tens of thousands to over a hundred thousand dollars, depending on the product type and the specific standards. This financial commitment acts as a strong deterrent.
- Stringent Building Codes: Compliance with local and national building codes, such as the International Building Code (IBC), is mandatory.
- Safety Standards: Meeting standards like those set by ASTM International for material performance and durability is essential.
- Environmental Regulations: Adherence to regulations concerning emissions, recycled content, and lifecycle assessments, influenced by frameworks like the Environmental Product Declaration (EPD).
- Product Certifications: Obtaining certifications from bodies like UL Solutions or NSF International for specific product attributes adds another layer of complexity and cost.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Newcomers face substantial challenges in securing access to established distribution channels and reliable supply chains for specialized materials. Established companies often benefit from long-standing relationships with suppliers and robust logistics networks, creating a significant barrier to entry. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, a sector heavily reliant on specialized materials and complex manufacturing processes, new entrants might struggle to gain preferential access to critical raw materials or compete with the established logistical efficiencies of giants like TSMC, which commands a significant portion of the global foundry market.
Existing players frequently possess preferred supplier agreements and deeply integrated logistics, making it difficult for new companies to match their operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. In the automotive sector, for example, major manufacturers like Toyota have cultivated decades-long partnerships with component suppliers, ensuring consistent quality and predictable delivery. A new car manufacturer entering the market would likely face higher initial costs for sourcing parts and establishing a comparable supply chain, impacting their ability to compete on price or availability.
- Distribution Channel Dominance: In 2024, major retailers in the consumer electronics market, such as Best Buy and Amazon, continue to hold significant power, often dictating terms and shelf space, making it challenging for new brands to gain widespread consumer visibility.
- Supply Chain Integration: Companies with highly integrated supply chains, like those in the pharmaceutical industry with patented manufacturing processes for active pharmaceutical ingredients, create substantial hurdles for new entrants needing to replicate or bypass these complex systems.
- Logistical Network Costs: Establishing a competitive logistics network can be prohibitively expensive; for example, the cost of building and maintaining a global cold chain for perishable goods represents a massive upfront investment for any new entrant in the food distribution sector.
- Supplier Relationships: Long-term, exclusive contracts between established manufacturers and key raw material providers, common in aerospace for specialized alloys, can effectively lock out new competitors from accessing essential inputs.
The architectural glass and framing sector presents substantial barriers to new entrants, primarily due to high capital requirements for sophisticated manufacturing and R&D. For instance, establishing a modern glass fabrication facility in 2024 can cost tens of millions of dollars.
Economies of scale enjoyed by established players like Apogee offer significant cost advantages, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price. Apogee's large-scale operations in 2024 likely resulted in lower unit costs than a new entrant with limited capacity.
Brand loyalty, established distribution networks, and deep customer relationships further deter new competition. Apogee's 75-year history has built trust, making it challenging for new companies to secure large commercial projects.
Stringent building codes, safety standards, and environmental regulations also act as significant hurdles. In 2024, meeting LEED certification requirements for sustainable materials added complexity and cost for new entrants, with product certifications potentially costing over $100,000.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Apogee leverages comprehensive data from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and expert analyst commentary.
