Amkor Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Amkor Technology Bundle
Amkor Technology navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the significant bargaining power of its major customers in the semiconductor packaging industry. Understanding these forces is crucial for any player in this dynamic market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Amkor Technology’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Amkor Technology's reliance on a select group of specialized suppliers for critical materials such as substrates, molding compounds, and bonding wires grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. This is particularly true for advanced packaging solutions where high-tech components are essential. For instance, in 2023, the semiconductor packaging industry experienced significant demand for advanced materials, potentially increasing the leverage of key suppliers.
The semiconductor assembly and test sector demands substantial capital for specialized machinery. For instance, advanced packaging equipment can cost millions of dollars per unit, making initial investments considerable for companies like Amkor Technology.
When Amkor needs to replace or upgrade this specialized equipment, the costs associated with new machinery, retooling existing lines, and retraining staff are substantial. This creates a significant barrier to switching vendors, effectively locking in existing relationships.
Consequently, the high switching costs empower existing equipment suppliers. Amkor is therefore more inclined to foster long-term partnerships with its current equipment providers to avoid these disruptive and expensive transitions, giving those suppliers leverage in negotiations.
The semiconductor packaging and testing industry, where Amkor Technology operates, requires a workforce with highly specialized skills. This includes engineers and technicians proficient in advanced manufacturing processes and materials science. A scarcity of this specialized talent in crucial production hubs can elevate labor expenses and bolster the negotiation leverage of individual workers or organized labor groups.
For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor industry continued to grapple with talent shortages, particularly in areas like advanced packaging. Reports indicated that certain specialized engineering roles faced competitive hiring environments, with salary increases reflecting the demand. Amkor's global operational footprint allows for some diversification in talent sourcing, yet the ongoing challenge of attracting and retaining top-tier skilled personnel remains a significant factor influencing labor costs and supplier power.
Technology-Driven Supplier Innovation
Suppliers of advanced packaging materials and specialized equipment are significant drivers of innovation in the semiconductor industry. These suppliers frequently channel substantial resources into research and development, aiming to pioneer novel solutions that can enhance performance or reduce costs. For instance, companies specializing in advanced lithography or novel substrate materials are constantly pushing boundaries.
When these supplier-led innovations become essential for Amkor Technology to maintain its competitive edge in offering cutting-edge semiconductor packaging services, the suppliers' bargaining power naturally increases. This leverage allows them to potentially dictate terms or pricing for their proprietary technologies.
Amkor's strategy necessitates close collaboration with these key technology providers. This ensures access to the latest advancements, but it can also lead to situations where Amkor faces higher costs or more restrictive licensing agreements for these critical components and equipment.
- Supplier R&D Investment: Companies like ASML, a key player in advanced lithography equipment, reported significant R&D spending, a portion of which directly benefits semiconductor packaging technology.
- Critical Technology Dependence: Amkor's ability to offer advanced packaging solutions, such as fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP), relies heavily on specialized materials and equipment from a limited number of innovative suppliers.
- Cost Implications: The integration of these advanced technologies can contribute to higher manufacturing costs, which Amkor must then balance against market demand and competitive pricing.
Impact of Geopolitical Factors on Supply Chains
Geopolitical tensions and evolving trade regulations directly influence the global supply chain for critical semiconductor materials and manufacturing equipment. For Amkor Technology, heightened tensions can lead to disruptions in raw material availability and increased costs.
Restrictions or tariffs imposed on components sourced from specific geopolitical regions can significantly narrow Amkor's supplier options. This limitation effectively amplifies the bargaining power of the remaining, unrestricted suppliers, potentially driving up prices for essential inputs.
To counter these risks, Amkor must maintain a robustly diversified supply chain strategy. This diversification is crucial for mitigating the impact of geopolitical instability and ensuring consistent operational stability and access to necessary resources.
- Geopolitical Influence: In 2024, ongoing geopolitical events, such as the US-China trade relations and regional conflicts, continued to create volatility in global supply chains, impacting the cost and availability of semiconductor materials.
- Tariff Impact: Tariffs on electronic components, which saw various adjustments throughout 2023 and into early 2024, directly affected the landed cost of goods for companies like Amkor, potentially increasing their input expenses.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Companies are increasingly investing in diversifying their supplier base and exploring nearshoring or reshoring options to reduce reliance on single-source or politically sensitive regions, a trend expected to accelerate through 2025.
The bargaining power of Amkor Technology's suppliers is significant due to the highly specialized nature of the materials and equipment required in semiconductor packaging. Key suppliers of advanced substrates, molding compounds, and specialized manufacturing equipment hold considerable leverage, especially for cutting-edge solutions. For example, in 2024, the demand for advanced semiconductor packaging materials remained robust, potentially strengthening the negotiating position of these critical suppliers.
High switching costs further bolster supplier power. The substantial investment in specialized machinery, often costing millions of dollars per unit, makes it difficult and expensive for Amkor to change vendors. This financial commitment to existing equipment providers, coupled with the need for retooling and retraining, encourages long-term partnerships and gives these suppliers considerable influence in pricing and terms.
Innovation driven by suppliers also plays a crucial role. Companies investing heavily in R&D for new materials and equipment, such as those in advanced lithography or novel substrate development, can dictate terms when their technologies become essential for Amkor to maintain its competitive edge in advanced packaging services. This dependence on proprietary innovations can lead to higher costs for Amkor.
Geopolitical factors and trade regulations also concentrate power among suppliers. Restrictions or tariffs on materials from certain regions can limit Amkor's options, thereby increasing the leverage of remaining suppliers. This necessitates a diversified supply chain strategy to mitigate risks and ensure access to critical resources, a trend actively pursued by the industry through 2024 and projected to continue.
| Factor | Impact on Amkor Technology | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Materials & Equipment | High dependence on a limited number of advanced material and equipment providers | Strong |
| Switching Costs | Significant capital investment in specialized machinery, retooling, and training | High |
| Supplier Innovation | Reliance on supplier R&D for competitive advanced packaging solutions | Moderate to High |
| Geopolitical & Trade Factors | Potential supply chain disruptions and limited supplier options due to regulations | Moderate to High |
What is included in the product
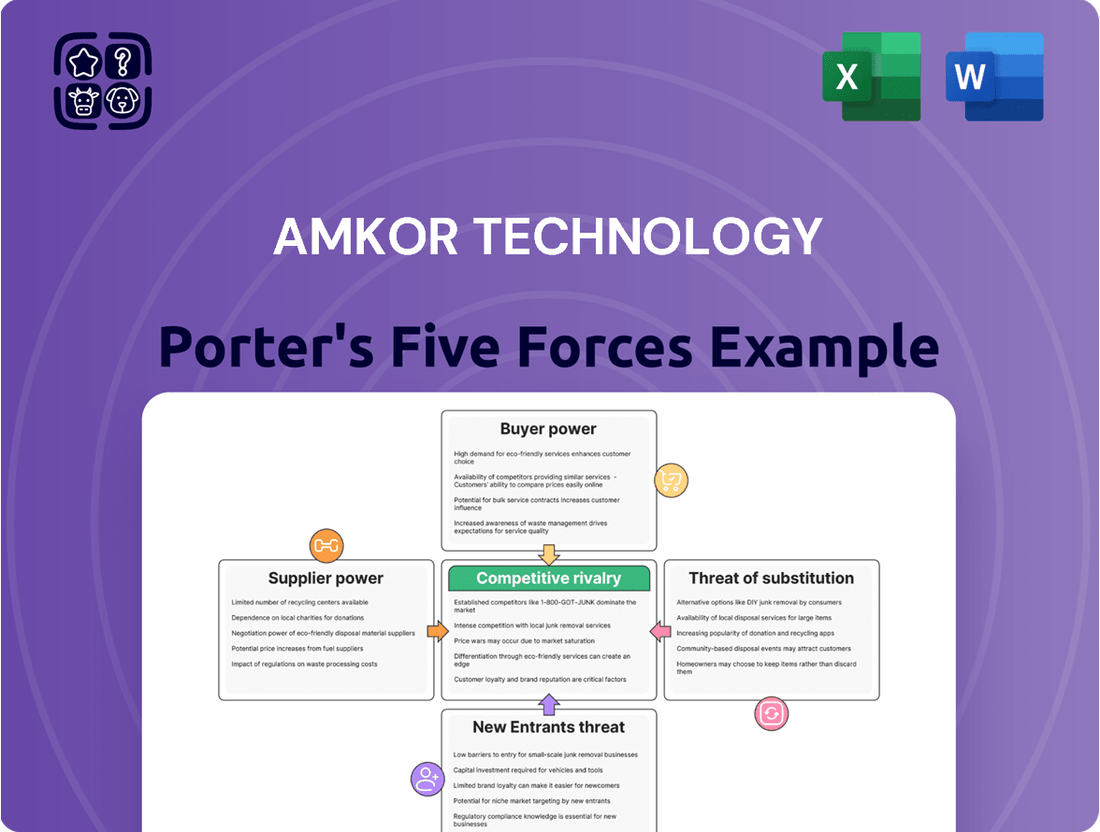
This analysis reveals how Amkor Technology navigates intense competition, buyer power, and the threat of new entrants within the semiconductor packaging industry, highlighting key strategic considerations.
Amkor's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, actionable framework to navigate competitive pressures, offering a visual roadmap for strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration risk is a significant factor in Amkor Technology's bargaining power of customers. While Amkor serves many clients, a few major ones drive a large chunk of its business. This reliance on a small group of key customers means they hold considerable sway.
In 2024, Amkor's top ten customers represented a substantial 72% of its net sales. This high dependency highlights how much power these large clients possess. If even one of these major customers decides to reduce their orders or take their business elsewhere, it could seriously hurt Amkor's revenue and overall profitability.
The outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) industry is fiercely competitive, with many global companies vying for business. This intense rivalry means Amkor's customers have significant leverage to negotiate favorable pricing and terms because they can easily turn to other OSAT providers. For instance, in 2024, the OSAT market continued to see intense price competition as companies like ASE Technology Holding and JCET Group also focused on expanding their capacity and service offerings.
Amkor's largest customers, especially major Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) such as Intel and TSMC, hold significant sway due to their capacity for backward integration. These giants possess the technical expertise and financial muscle to bring semiconductor packaging and testing capabilities in-house, directly challenging Amkor's market position. For instance, Intel has historically maintained substantial in-house packaging operations, and TSMC is also expanding its advanced packaging services, directly competing with outsourced providers like Amkor.
Volume of Purchases and Long-Term Contracts
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the volume of their purchases and the nature of their contracts. Large semiconductor companies, for instance, represent substantial clients for OSAT (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test) providers like Amkor Technology. The sheer scale of these orders grants these customers considerable leverage in negotiations.
These major players frequently lock in long-term contracts, which often come with advantageous terms. These terms can include significant pricing discounts and guaranteed access to dedicated manufacturing capacity, reflecting the value of their consistent business.
For Amkor, managing these large volume contracts is a delicate balancing act. While securing such agreements is crucial for maintaining high factory utilization rates, the company must also ensure these deals remain profitable. A substantial loss of this high-volume business could indeed have a severe impact on Amkor's operational efficiency and financial performance.
- Significant Customer Leverage: Large semiconductor firms' substantial order volumes give them considerable negotiation power with OSAT providers.
- Favorable Contract Terms: Long-term agreements often include pricing discounts and dedicated capacity, benefiting these major customers.
- Amkor's Margin Challenge: Amkor must balance securing high-volume contracts with maintaining healthy profit margins to avoid impacting utilization rates.
Customer Sophistication and Customization Demands
Amkor Technology's customers are highly sophisticated semiconductor manufacturers, frequently demanding bespoke packaging solutions tailored to their advanced integrated circuits. These clients, often leaders in their respective fields, require cutting-edge technologies and specialized services that push the boundaries of semiconductor packaging. This deep customization, coupled with the proprietary nature of the intellectual property involved, significantly elevates customer bargaining power.
The need for Amkor to invest heavily in R&D for these tailored solutions, while potentially increasing customer stickiness, also means Amkor faces substantial upfront costs. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry saw continued investment in advanced packaging technologies, with companies like Amkor focusing on heterogeneous integration and advanced materials to meet these evolving demands. This investment dynamic inherently empowers customers who can leverage Amkor's specialized capabilities.
- Sophisticated Clientele: Amkor serves leading semiconductor companies with complex technical requirements.
- Customization is Key: Customers demand highly specific, often proprietary, packaging solutions.
- R&D Investment: Amkor must invest in tailored technologies, increasing customer leverage.
- Intellectual Property: The specialized nature of the solutions further strengthens customer negotiating positions.
Amkor's customers, particularly large integrated device manufacturers (IDMs), wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and the availability of alternative OSAT providers. This competitive landscape allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. In 2024, Amkor's top ten customers accounted for 72% of its net sales, underscoring the leverage these major clients possess.
| Customer Segment | Impact on Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Major IDMs | High | Top 10 customers = 72% of net sales |
| OSAT Market Competition | High | Intense price competition from ASE, JCET |
| Backward Integration Potential | High | Intel and TSMC possess in-house capabilities |
| Customization Demands | High | Need for bespoke, advanced packaging solutions |
Same Document Delivered
Amkor Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the exact Amkor Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive upon purchase, offering a detailed examination of competitive rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. You're looking at the actual document, providing a comprehensive understanding of Amkor's competitive landscape. Once your purchase is complete, you’ll gain instant access to this fully formatted and ready-to-use analysis, ensuring no surprises and immediate utility.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The OSAT market is highly concentrated, with a few dominant players setting the pace. ASE Technology Holding and Amkor Technology are the leading forces, controlling a substantial portion of the market. This means competition is fierce among these giants.
In 2024, ASE Technology Holding solidified its leadership, holding a commanding 44.6% market share in the OSAT sector. Amkor Technology followed as the second-largest player, capturing 15.2% of the market. This significant market share concentration underscores the intense rivalry as these few companies vie for dominance.
The semiconductor packaging industry is inherently capital-intensive, demanding massive investments in state-of-the-art facilities, sophisticated machinery, and continuous research and development. For instance, building a new advanced packaging facility can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
This substantial barrier to entry means that existing players, like Amkor Technology, must maintain high production volumes to spread these fixed costs. Consequently, companies often engage in aggressive pricing tactics to ensure their production lines are running at optimal capacity, intensifying competitive rivalry.
The semiconductor packaging sector, where Amkor operates, is defined by relentless technological evolution, particularly in sophisticated techniques like 3D stacking, fan-out wafer-level packaging, and System-in-Package (SiP) integration. Staying at the forefront requires substantial and ongoing investment in research and development to deliver cutting-edge solutions.
This continuous innovation fosters an intensely competitive environment. Companies are constantly striving for technological supremacy and unique market positioning, making it challenging to maintain a competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor market saw significant R&D spending, with major players allocating billions to develop next-generation technologies, directly impacting the pressure on companies like Amkor to innovate at a similar pace.
Global Presence and Regional Competition
Amkor Technology maintains a significant global manufacturing presence, with facilities strategically located across Asia, Europe, and North America. This broad reach allows for operational efficiencies and proximity to key customer markets. However, this global footprint also places Amkor directly against both established multinational competitors and a growing number of regional players, especially those emerging from China.
The competitive landscape is intensifying as Chinese Original Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) vendors continue to gain market share and technological capabilities. These regional competitors often benefit from local government support and a focus on cost-competitiveness, presenting a significant challenge to established players like Amkor. For instance, the Chinese OSAT market is projected to grow substantially, with domestic players increasingly capturing a larger portion of this expansion.
- Global Reach vs. Regional Challengers: Amkor's worldwide manufacturing network is a strength, but it directly confronts intense competition from both large global OSAT providers and increasingly capable regional manufacturers, particularly in China.
- Rise of Chinese OSAT Vendors: Chinese OSAT companies are rapidly advancing in technology and market penetration, posing a growing competitive threat by offering competitive pricing and localized solutions.
- Navigating Diverse Market Dynamics: Operating globally requires Amkor to adapt to varying regulatory frameworks, economic conditions, and customer demands across different regions, adding complexity to competitive strategy.
- Market Share Shifts: While Amkor holds a strong position, the market share dynamics are constantly evolving, with regional players making inroads and challenging established leaders in specific segments and geographies.
Cyclical Nature of the Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor industry's inherent cyclicality fuels fierce rivalry. Periods of high demand often lead to overinvestment, creating excess capacity that intensifies competition when demand inevitably softens. This dynamic forces companies like Amkor to navigate fluctuating order volumes and pricing pressures.
During downturns, the scramble for market share can become particularly brutal. For instance, the semiconductor market experienced a significant slowdown in late 2022 and into 2023, with many segments seeing reduced demand. This environment typically translates to aggressive pricing strategies from competitors vying for the remaining business, directly impacting Amkor's revenue and profit margins.
- Cyclical Demand: The semiconductor market is known for its boom-and-bust cycles, driven by factors like consumer electronics trends and enterprise spending.
- Capacity Overhang: Periods of strong demand can lead to increased manufacturing capacity, which then becomes a burden during downturns, exacerbating price competition.
- Pricing Pressure: Excess capacity and reduced demand force companies to lower prices to secure orders, squeezing profitability for all players in the industry.
- Amkor's Exposure: As a provider of outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) services, Amkor is directly exposed to these industry cycles and the resulting competitive pressures.
Competitive rivalry is intense in the OSAT market, with market leaders like ASE Technology Holding and Amkor Technology vying for dominance. In 2024, ASE held a significant 44.6% market share, with Amkor at 15.2%, highlighting the concentrated nature of the competition. This rivalry is further fueled by the capital-intensive nature of the industry, requiring substantial investments in advanced facilities and continuous R&D, which acts as a barrier to new entrants but intensifies competition among established players.
| Competitor | 2024 Market Share (OSAT) | Key Competitive Factors |
|---|---|---|
| ASE Technology Holding | 44.6% | Market leadership, broad service portfolio, extensive global presence |
| Amkor Technology | 15.2% | Advanced packaging technologies, global manufacturing footprint, strong customer relationships |
| JCET Group | ~8.0% (estimated) | Growing Chinese player, government support, cost competitiveness |
| SPIL | ~7.0% (estimated) | Significant player with advanced packaging capabilities |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) and major foundries often possess their own advanced packaging and testing facilities, presenting a direct substitute for Amkor's outsourced services. For instance, Intel has historically maintained significant in-house packaging capabilities, particularly for its flagship products. This internal capacity allows them to control critical aspects of production and reduces their need for external OSAT providers.
Leading wafer foundries are increasingly offering advanced backend services, directly competing with traditional Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) providers. This expansion blurs the lines, allowing foundries to control more of the value chain from silicon to final package.
For instance, TSMC, a dominant player, has been investing heavily in advanced packaging technologies like CoWoS and InFO, aiming to provide integrated solutions. This move presents a significant threat as these foundries can offer a compelling alternative to specialized OSATs, potentially reducing the need for external packaging partners for many customers.
The growing trend towards chiplet and heterogeneous integration presents a subtle but significant threat of substitutes for traditional monolithic chip packaging. This approach allows for the assembly of smaller, specialized dies into a single package, offering greater flexibility and cost-efficiency compared to large, single-die designs. For instance, advancements in 3D stacking and advanced packaging technologies, areas where Amkor excels, are enabling this shift.
While established OSATs are integral to realizing these new designs, the underlying philosophy of modularity could foster the emergence of entirely new integration methods or specialized providers. This could offer alternative pathways for chip assembly that bypass or reduce reliance on current OSAT capabilities, potentially impacting market share for companies like Amkor if they cannot adapt quickly enough to these evolving integration strategies.
New Materials and Packaging Technologies
The emergence of new materials and innovative packaging technologies poses a significant threat of substitutes for Amkor Technology. Breakthroughs in materials science or novel chip interconnection methods could render current OSAT solutions less competitive by offering enhanced performance or reduced costs.
For instance, advancements in wafer-level packaging (WLP) or advanced substrate technologies could provide alternative pathways for chip integration, potentially bypassing traditional outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) services for certain applications. Amkor's commitment to research and development, including significant investments in next-generation packaging solutions, is crucial to staying ahead of these disruptive trends.
- Emerging Materials: Innovations in materials like advanced composites or novel conductive polymers could offer superior thermal management or electrical performance, creating substitute solutions.
- New Packaging Technologies: Developments such as advanced 3D stacking or heterogeneous integration might provide alternative methods for assembling and testing semiconductor devices, potentially reducing reliance on traditional OSAT models.
- Cost and Performance Advantages: A substitute technology that significantly outperforms current offerings or achieves a lower cost structure could rapidly gain market share, impacting Amkor's revenue streams.
- Amkor's Mitigation Strategy: Amkor actively invests in R&D, aiming to be a leader in developing and adopting these new materials and technologies, thereby transforming the threat into an opportunity.
Software-Based Solutions for System Optimization
While Amkor Technology's core business is physical semiconductor packaging, software-based solutions can act as a subtle substitute. Innovations in system-level design and software optimization can sometimes mitigate the need for the most cutting-edge, and therefore most expensive, packaging technologies. For instance, advancements in software-defined hardware or highly integrated System-on-Chip (SoC) designs might lessen the demand for specialized packaging that addresses performance bottlenecks.
This trend suggests that OSAT providers like Amkor must continuously prove the tangible value of their physical integration capabilities. The market is increasingly looking at holistic solutions, and if software can deliver a significant portion of performance gains, it could indirectly reduce the reliance on premium packaging. For example, in 2024, the semiconductor industry saw continued investment in AI-driven design tools that optimize chip layouts and power management, potentially reducing the need for advanced packaging to overcome thermal or signal integrity issues.
- Software optimization can reduce reliance on advanced packaging.
- Highly integrated SoCs offer an alternative to specialized packaging solutions.
- OSAT providers must highlight the unique value of physical integration.
- AI in chip design can impact demand for certain packaging services.
The threat of substitutes for Amkor Technology stems from various sources, including in-house capabilities of major players, advancements by foundries, and evolving integration strategies like chiplets. New materials and packaging technologies also present potential alternatives, while software optimization can sometimes reduce the need for advanced physical packaging.
For instance, TSMC's investment in advanced packaging like CoWoS and InFO offers integrated solutions, directly competing with OSAT services. Similarly, the trend towards chiplets and heterogeneous integration allows for modular assembly, potentially bypassing traditional OSAT models if new integration methods emerge. In 2024, the semiconductor industry's focus on AI-driven design tools also highlighted how software optimization could lessen demand for certain high-end packaging solutions.
| Threat of Substitutes | Description | Example | Impact on Amkor | Mitigation Strategy |
| In-house Capabilities | IDMs and major foundries possess their own advanced packaging facilities. | Intel's historical in-house packaging for flagship products. | Reduces reliance on external OSAT providers. | Focus on specialized, high-complexity packaging services. |
| Foundry Expansion | Leading foundries offer advanced backend services, blurring lines. | TSMC's investment in CoWoS and InFO technologies. | Direct competition, offering integrated solutions. | Continuous innovation in advanced packaging technologies. |
| Chiplet/Heterogeneous Integration | Modular assembly methods can bypass traditional OSAT. | Advancements in 3D stacking and modular die assembly. | Potential for new integration pathways reducing OSAT reliance. | Leadership in enabling and executing complex heterogeneous integration. |
| New Materials/Technologies | Breakthroughs in materials or interconnection methods. | Advanced composites, novel conductive polymers, advanced WLP. | Could offer superior performance or lower costs, impacting competitiveness. | Significant R&D investment in next-generation packaging. |
| Software Optimization | Software can mitigate the need for advanced packaging. | AI in chip design optimizing layouts and power management. | Indirectly reduces demand for premium packaging addressing performance bottlenecks. | Demonstrate tangible value of physical integration capabilities. |
Entrants Threaten
The OSAT industry demands massive upfront investments in advanced manufacturing, cleanrooms, and specialized machinery, making it incredibly capital-intensive. This high cost of entry acts as a significant deterrent for potential new competitors. For example, Amkor Technology's new Arizona facility is slated for an estimated $850 million in capital expenditures for 2025, highlighting the substantial financial commitment required to establish a presence.
Success in the semiconductor packaging and test industry hinges on advanced technological expertise and a relentless commitment to research and development. Amkor Technology, a key player, demonstrated this by investing $42 million in R&D during the second quarter of 2025, highlighting the significant capital required for innovation.
New companies entering this market face a formidable challenge in acquiring or developing the highly specialized intellectual property and attracting the elite engineering talent necessary to compete. This substantial barrier effectively deters many potential entrants, reinforcing the established players' positions.
Amkor Technology's deep-rooted customer relationships represent a significant barrier to new entrants. The company serves over 250 customers, including major semiconductor firms, foundries, and electronics OEMs, built on years of collaboration and demonstrated reliability.
These long-standing partnerships, often spanning decades, are characterized by a high degree of trust and a proven track record in delivering mission-critical semiconductor packaging solutions.
New competitors would face considerable difficulty in replicating this level of established trust and access to key players in the semiconductor ecosystem, making market penetration a substantial hurdle.
Economies of Scale and Cost Efficiency
Existing leaders in the Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) market, such as Amkor Technology, enjoy substantial economies of scale. This translates to significant cost efficiencies in their manufacturing processes and procurement of raw materials. For instance, Amkor's extensive operational footprint allows for better utilization of advanced equipment and bulk purchasing power, driving down per-unit costs.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost advantages. Operating at a smaller scale, they cannot leverage the same purchasing volumes or spread fixed costs across as large a production base. This makes it exceptionally difficult for them to compete on price with established players, a critical factor in the highly competitive OSAT industry.
- Economies of Scale: Amkor's large-scale operations enable lower manufacturing costs per unit compared to smaller, newer competitors.
- Procurement Advantages: Bulk purchasing of materials by established firms like Amkor leads to more favorable pricing, a benefit not readily available to new entrants.
- Competitive Pricing: The OSAT market demands competitive pricing, which is challenging for new firms to achieve without comparable scale.
- Deterrent Effect: The cost advantage derived from scale acts as a significant barrier, discouraging new companies from entering the market.
Regulatory Hurdles and Geopolitical Support
The semiconductor sector faces significant barriers to entry due to evolving government policies and geopolitical considerations. For instance, the U.S. CHIPS and Science Act of 2022, with its approximately $52 billion in funding, aims to bolster domestic semiconductor manufacturing. While this legislation can foster growth for established companies and strategically chosen newcomers, it simultaneously erects complex regulatory frameworks that may inadvertently favor firms with existing geopolitical ties and established operational footprints.
New entities aspiring to enter this market must meticulously navigate these intricate regulatory environments. Success often hinges on securing substantial government backing and demonstrating alignment with national strategic interests. For example, companies seeking to build new fabrication plants in the United States under the CHIPS Act must meet specific criteria related to workforce development and supply chain security, adding layers of complexity beyond typical market entry challenges.
- Government Incentives: Programs like the CHIPS Act offer billions in funding, creating opportunities but also demanding compliance with specific national policies.
- Regulatory Complexity: New entrants must navigate a web of regulations that can be costly and time-consuming to satisfy.
- Geopolitical Alignment: Favorable treatment or access to incentives may be linked to a company's geopolitical positioning and its contribution to national technological sovereignty.
- Established Player Advantage: Existing companies with established relationships and understanding of these regulatory landscapes often possess a distinct advantage.
The threat of new entrants in the OSAT industry remains moderate, primarily due to the substantial capital investment required for advanced manufacturing facilities and cutting-edge technology. Amkor Technology's significant R&D spending, like the $42 million in Q2 2025, underscores the continuous innovation needed to stay competitive, presenting a high barrier for newcomers.
Existing customer relationships, built on years of trust and reliability, are another significant deterrent. Amkor's extensive client base of over 250 customers, including major semiconductor firms, highlights the difficulty new entrants face in gaining market access and establishing comparable credibility.
Economies of scale enjoyed by established players like Amkor Technology provide a crucial cost advantage, making it challenging for smaller, new companies to compete on price. Furthermore, evolving government policies, such as the U.S. CHIPS Act, while fostering growth, also introduce complex regulatory hurdles that can favor firms with established operational footprints and geopolitical alignment.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Amkor Example/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of advanced manufacturing, cleanrooms, and machinery. | Significant deterrent due to massive upfront investment. | $850 million CAPEX for Arizona facility (2025 est.). |
| Technological Expertise & IP | Need for advanced R&D and specialized intellectual property. | Challenging to acquire or develop, requiring substantial investment. | $42 million R&D spending (Q2 2025). |
| Customer Relationships | Long-standing, trust-based partnerships with key industry players. | Difficult to replicate, hindering market penetration. | Serves over 250 customers, including major semiconductor firms. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost efficiencies from large-scale operations and bulk purchasing. | Makes it hard to compete on price with established firms. | Extensive operational footprint and bulk purchasing power. |
| Regulatory & Geopolitical Factors | Navigating complex government policies and national strategic interests. | Favors established companies with existing ties and understanding. | Compliance with CHIPS Act criteria for workforce and supply chain. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Amkor Technology is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data from annual reports, investor relations disclosures, and industry-specific market research reports. This blend of internal company information and external industry analysis allows for a robust assessment of competitive dynamics.
