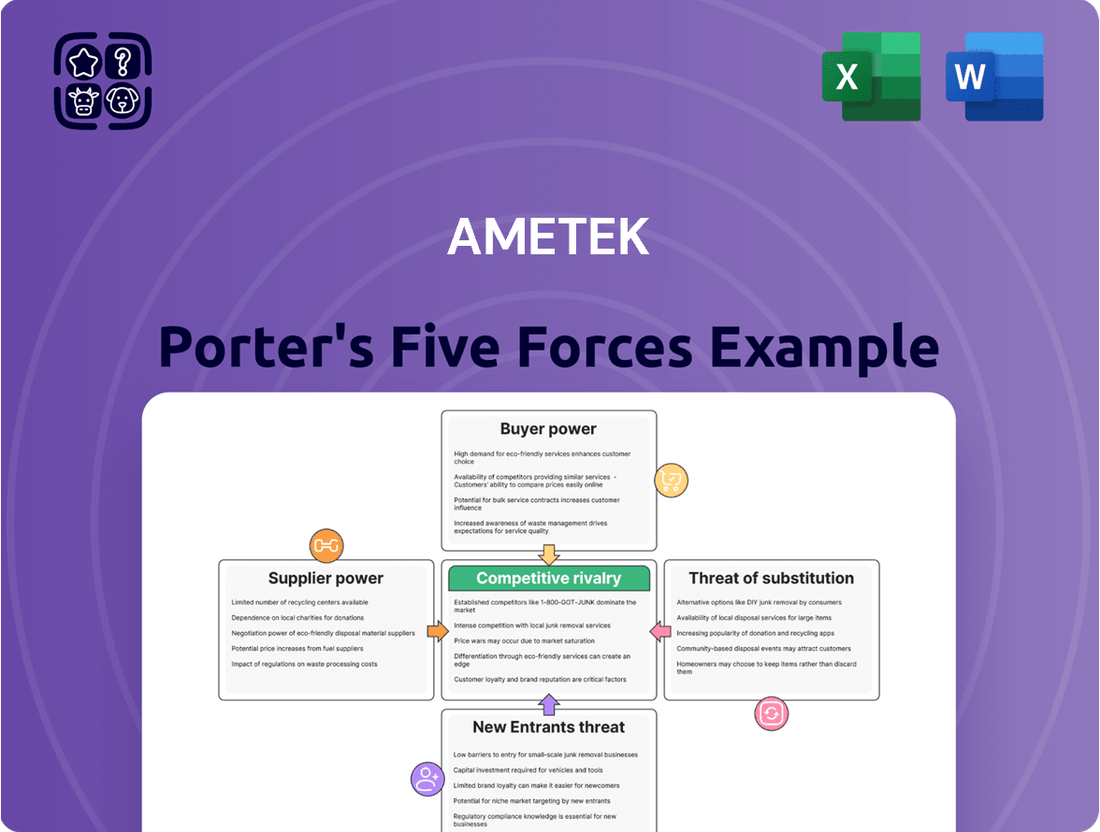
Ametek Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ametek Bundle
Our Ametek Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals how supplier power, buyer bargaining, and the threat of substitutes are shaping its competitive landscape. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating Ametek's market. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Ametek’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
AMETEK's reliance on highly specialized electronic components and sophisticated materials for its advanced instruments and devices is a key factor in supplier bargaining power. The unique or proprietary nature of these critical parts can give suppliers considerable leverage. For instance, if there are few or no viable alternatives for essential components, suppliers are in a strong position to influence pricing and delivery terms, potentially impacting AMETEK's production costs and timelines.
The number and concentration of suppliers significantly shape AMETEK's bargaining power. When a few suppliers dominate specific technology niches or raw material markets crucial for AMETEK's operations, their leverage increases. For instance, if AMETEK heavily relies on a handful of specialized component manufacturers, these suppliers can command higher prices or dictate terms, impacting AMETEK's cost structure and production flow. In 2023, AMETEK's supply chain for its advanced materials segment saw a notable concentration in certain rare earth elements, with a few global suppliers controlling a substantial portion of the market.
AMETEK faces significant supplier power due to high switching costs. For instance, re-tooling manufacturing processes or re-qualifying critical components to integrate a new supplier's offerings can be exceptionally time-consuming and expensive. This inertia means AMETEK might be hesitant to switch even if presented with slightly better pricing, as the disruption and potential impact on product performance and reliability are substantial deterrents.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If suppliers can credibly threaten to move into AMETEK's industry, they gain significant bargaining power. This means a supplier might start producing the instruments or devices AMETEK sells, becoming a direct competitor. For instance, a key component manufacturer could launch its own finished product line.
This potential for forward integration forces AMETEK to carefully manage its supplier relationships. To mitigate this threat, AMETEK might need to offer more favorable contract terms or engage in long-term partnerships to discourage suppliers from pursuing direct competition. The risk of a supplier becoming a rival can significantly impact pricing and negotiation leverage.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers could start manufacturing AMETEK's products, directly competing and increasing their bargaining power.
- Impact on AMETEK: This threat compels AMETEK to maintain strong supplier relationships and potentially accept less favorable terms to avoid direct competition.
- Strategic Consideration: AMETEK must assess the likelihood of suppliers integrating forward and factor this into its supply chain strategy and negotiation tactics.
Importance of AMETEK to Suppliers
AMETEK's significance to its suppliers directly impacts their bargaining power. If AMETEK constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier is likely to offer more favorable pricing and terms to retain AMETEK's business. Conversely, if AMETEK is a minor customer, its influence over supplier terms is considerably reduced.
In 2024, AMETEK's robust purchasing volume across its diverse segments, including Electromechanical Group and Electronic Instruments Group, likely positions it as a key customer for many of its component and raw material providers. This scale can translate into greater leverage for AMETEK in negotiating prices and supply conditions.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which suppliers rely on AMETEK for their revenue is a critical factor. High dependence grants AMETEK more bargaining power.
- AMETEK's Purchasing Power: AMETEK's ability to consolidate purchases and its overall market presence can amplify its influence over suppliers.
- Supplier Concentration: If a particular component or material is sourced from a limited number of suppliers, AMETEK's bargaining power might be somewhat constrained in those specific instances.
- Long-Term Contracts: The existence and terms of long-term supply agreements can also shape the bargaining dynamic between AMETEK and its suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for AMETEK is influenced by the availability of substitute inputs. If there are readily available alternatives for critical components or materials, AMETEK can more easily switch suppliers, reducing the leverage of any single supplier. However, for highly specialized or proprietary inputs, substitutes may be scarce, increasing supplier power.
AMETEK's supplier landscape in 2024 features a mix of concentrated and diversified supply chains. For instance, while certain advanced materials used in its aerospace and defense segment might come from a limited number of specialized providers, the broader electronic components market offers more alternatives. This variability means supplier power isn't uniform across all of AMETEK's operations.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into AMETEK's business, becoming direct competitors, is a significant factor. This potential competition amplifies supplier leverage, as they could capture more of the value chain. AMETEK's strategy often involves building strong, collaborative relationships to mitigate this risk.
AMETEK's substantial purchasing volume across its various segments, such as the Electromechanical Group and Electronic Instruments Group, generally provides it with considerable negotiation leverage. In 2024, this scale allows AMETEK to secure more favorable pricing and terms from many of its suppliers, especially those who rely heavily on AMETEK's business.
| Factor | Impact on AMETEK | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | Low availability increases supplier power. | High for specialized components; moderate for standard electronics. |
| Supplier Concentration | Few dominant suppliers increase leverage. | Notable in niche markets like rare earth elements. |
| Switching Costs | High costs reduce AMETEK's flexibility. | Significant for re-tooling and component re-qualification. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers becoming competitors increases their power. | A constant strategic consideration for AMETEK. |
| Supplier Dependence on AMETEK | High dependence reduces supplier power. | AMETEK's scale in 2024 makes it a key customer for many. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for Ametek by examining the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Pinpoint and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, making strategic adjustments straightforward.
Customers Bargaining Power
AMETEK's customer base is varied, but in certain sectors such as aerospace and defense, a few major clients, including government agencies, can account for substantial order volumes. This concentration means these large buyers hold significant sway over pricing and contract conditions, leveraging their purchasing might and the strategic importance of their business.
AMETEK's focus on advanced analytical, monitoring, and motion control solutions often means its products are highly specialized and technologically advanced. This inherent differentiation can significantly reduce the bargaining power of customers because finding equally capable alternatives can be challenging. For instance, if AMETEK's instruments offer unique performance metrics or proprietary software, customers have fewer options, thereby limiting their ability to negotiate lower prices or demand more favorable terms.
Switching costs for AMETEK's customers are often substantial, especially in demanding sectors like aerospace and specialized industrial manufacturing. These high costs stem from the deep integration of AMETEK's highly reliable and precise components into critical systems, along with the rigorous certification processes required for such applications. For instance, in aerospace, re-qualifying a new supplier's components can take years and involve millions in testing and validation, making customers hesitant to switch.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers significantly impacts AMETEK's bargaining power. If major clients, particularly those in sectors like aerospace or industrial manufacturing, possess the technical expertise and financial resources to produce their own electronic instruments or electromechanical components, they gain leverage. This capability pressures AMETEK to maintain competitive pricing and enhance its value proposition to retain these crucial relationships.
For instance, a large aerospace manufacturer might consider developing proprietary testing equipment if AMETEK’s pricing becomes too high or if they perceive a strategic advantage in controlling their supply chain for critical components. This potential for in-house production acts as a constant check on AMETEK's pricing power and necessitates continuous innovation and service differentiation.
- Customer Leverage: Large customers with the capacity for backward integration can exert considerable pressure on AMETEK, potentially leading to price concessions or demands for enhanced service offerings.
- Strategic Response: AMETEK must proactively address this threat by offering superior product quality, customized solutions, and robust after-sales support to deter customers from pursuing in-house manufacturing.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, sectors like advanced manufacturing and defense, which are key markets for AMETEK, are increasingly exploring vertical integration to secure supply chains and manage costs, amplifying this particular threat.
Availability of Substitute Products/Services for Customers
The ease with which customers can find alternative products or services directly influences their bargaining power with AMETEK. When numerous substitutes exist, customers can easily switch, forcing AMETEK to offer more competitive pricing and terms.
Even if alternatives aren't perfect one-to-one replacements, if customers can achieve their desired outcomes through different technological paths or simpler solutions, their leverage against AMETEK grows. This is particularly relevant in diversified markets where AMETEK operates.
- Customer Switching Costs: Low switching costs for customers to move to a competitor or substitute product enhance their bargaining power.
- Availability of Substitutes: A wide array of substitute products or services in AMETEK's served markets allows customers to readily compare and choose alternatives.
- Technological Alternatives: The emergence of new technologies that offer similar functionalities, even if less sophisticated, can empower customers by providing them with more choices.
- Price Sensitivity: High price sensitivity among customer segments means they are more likely to explore and adopt substitutes if AMETEK's pricing is not perceived as competitive.
The bargaining power of AMETEK's customers is moderated by the specialized nature of its offerings and high switching costs, particularly in sectors like aerospace where re-qualification is extensive. However, significant customer concentration in certain segments and the potential for backward integration by large clients in 2024's supply-chain-conscious environment present notable challenges. The availability of substitutes, while often less sophisticated, also provides customers with leverage, especially if AMETEK's pricing is not perceived as competitive.
| Factor | Impact on AMETEK | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High for key clients, granting them significant leverage. | In 2024, AMETEK's largest customers, often in aerospace and defense, continue to represent a substantial portion of revenue, potentially exceeding 10% for individual clients. |
| Product Differentiation & Switching Costs | Lowers customer power due to specialized, integrated solutions. | AMETEK's advanced instruments often require extensive integration and certification, with switching costs in aerospace potentially running into millions of dollars and taking years to complete. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Presents a risk if customers have technical and financial capacity. | Key industrial and aerospace clients in 2024 are increasingly exploring vertical integration to secure critical components, putting pressure on AMETEK's pricing. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate, as direct substitutes are often less advanced or specialized. | While direct, high-performance substitutes are limited, customers can sometimes opt for less sophisticated alternative technologies, especially if price is a primary driver. |
What You See Is What You Get
Ametek Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Ametek Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within its industry. You're viewing the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning. This professionally formatted analysis is designed for immediate use, providing actionable insights into Ametek's market landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The electronic instruments and electromechanical devices sectors are notably fragmented, featuring a wide array of global and regional competitors. This crowded landscape includes everything from massive, diversified corporations to highly specialized niche players, all actively competing for a share of AMETEK's various end markets.
The growth rate of the diverse industries AMETEK operates in, such as aerospace, defense, power, and industrial sectors, directly impacts how fierce the competition is. When these markets are expanding rapidly, companies can often grow by simply increasing their output to meet demand, which can temper aggressive rivalry. For example, the aerospace sector experienced robust growth leading up to 2024, driven by increased air travel demand post-pandemic, allowing companies to expand without directly taking share from competitors.
AMETEK's competitive rivalry is significantly influenced by the degree of product differentiation within its diverse markets. While the company emphasizes advanced solutions, the extent to which competitors offer truly unique and sustainable product features impacts pricing power and market share. For instance, in sectors where products are more commoditized, rivalry often intensifies on price, pressuring margins.
Continuous innovation and the development of proprietary technology serve as key levers for AMETEK to mitigate this rivalry. By creating distinct value propositions through patented technologies or superior performance, AMETEK can carve out niche markets and command premium pricing. This strategy is evident in their focus on specialized instruments and automation solutions, where unique capabilities often outweigh direct price comparisons.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Ametek operates in sectors with substantial fixed costs, such as advanced manufacturing and R&D, creating a pressure to maintain high capacity utilization. This can lead to intensified competition as firms strive to spread these costs over a larger output, potentially driving down prices.
Significant exit barriers, like specialized machinery or long-term customer commitments, also contribute to fierce rivalry. Companies may feel compelled to stay in the market and compete aggressively rather than incur substantial losses from exiting. For instance, in the aerospace components sector, where Ametek has a presence, specialized tooling and certifications represent considerable sunk costs.
- High Capital Investment: Industries with significant upfront investment in plant, property, and equipment necessitate continuous operation to achieve profitability.
- Specialized Assets: Assets that have limited alternative uses create higher exit barriers, trapping companies in existing markets.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: Firms with high fixed costs are incentivized to operate at or near full capacity, often leading to price wars to capture market share.
- Industry Examples: Sectors like semiconductor manufacturing or heavy industrial equipment production, where Ametek has exposure, are characterized by these dynamics.
Strategic Stakes and Acquisitions
The strategic importance of the electronic instruments and electromechanical sectors often attracts large, diversified companies. These players may aggressively pursue market dominance or technological leadership, significantly fueling competitive rivalry. This drive for leadership can manifest in frequent mergers and acquisitions, constantly reshaping the competitive landscape and intensifying the struggle for market position.
For instance, in 2024, the industrial technology sector, which encompasses many of Ametek's markets, saw significant M&A activity. Companies like Fortive, a diversified industrial technology company, continued to make strategic acquisitions to bolster their offerings in areas like sensing and instrumentation. These moves indicate a broader trend where established players are consolidating to gain scale and technological advantage, directly impacting the competitive intensity for companies like Ametek.
- Strategic Importance Fuels Rivalry: Diversified companies view electronic instruments and electromechanical sectors as key growth areas, leading to aggressive competition.
- M&A Activity Reshapes Landscape: Frequent mergers and acquisitions alter market structures and intensify the fight for market share.
- 2024 M&A Trends: The industrial technology sector, relevant to Ametek, demonstrated robust M&A activity in 2024, with companies like Fortive actively acquiring businesses to enhance their market position.
AMETEK faces intense competition due to the fragmented nature of its markets, where numerous global and regional players vie for market share. This rivalry is amplified by the strategic importance of the electronic instruments and electromechanical sectors, attracting large, diversified companies actively pursuing market dominance through innovation and acquisitions.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by the degree of product differentiation; commoditized segments lead to price-based competition, while AMETEK's focus on advanced, proprietary technologies helps mitigate this. High fixed costs and significant exit barriers in many of AMETEK's operational areas also contribute to sustained, aggressive rivalry as firms aim to maintain capacity utilization and recover sunk costs.
The industrial technology sector, a key area for AMETEK, experienced significant merger and acquisition activity in 2024. For example, Fortive's strategic acquisitions aimed to bolster its sensing and instrumentation offerings, reflecting a broader trend of consolidation to gain scale and technological advantages, thereby intensifying competition.
| Competitive Factor | Impact on AMETEK | Evidence/Example (2024 Focus) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | Intensified rivalry from numerous global and niche players. | Wide array of competitors across electronic instruments and electromechanical devices. |
| Product Differentiation | Pressure on pricing in commoditized segments; premium pricing potential for unique offerings. | AMETEK's focus on advanced solutions and proprietary technology in specialized instruments. |
| Industry Growth Rate | Tempered rivalry during rapid expansion; increased competition during slower growth. | Robust growth in aerospace sector post-pandemic supported company expansion. |
| Strategic Importance & M&A | Aggressive pursuit of market share by diversified players; landscape reshaped by acquisitions. | Fortive's 2024 acquisitions in industrial technology to enhance market position. |
| Exit Barriers & Fixed Costs | Sustained competition due to high sunk costs and capacity utilization pressure. | Specialized machinery in aerospace components and R&D costs in manufacturing. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for AMETEK's offerings is significant, stemming from alternative technologies that can perform similar measurement and control functions. For instance, advancements in software-driven analytics and cloud-based monitoring platforms can sometimes replace the need for specialized hardware. In 2023, the global industrial automation market, which includes measurement and control systems, was valued at approximately $220 billion, with software and services representing a growing portion of this, indicating a shift that could impact traditional hardware sales.
Customers often weigh the price-performance trade-off when considering alternatives to AMETEK's offerings. If a substitute can deliver comparable functionality at a lower cost, or even better performance for a similar price, it presents a significant challenge. For instance, in the industrial automation sector where AMETEK operates, advancements in open-source software and more affordable hardware components from emerging market players can offer compelling alternatives, potentially impacting demand for AMETEK's specialized solutions.
The ease and cost for customers to switch from AMETEK's offerings to alternative solutions directly influence the threat of substitutes. If switching is straightforward, inexpensive, and requires little effort to integrate, this threat becomes more significant.
Conversely, substantial costs associated with re-tooling manufacturing processes, undergoing new certification procedures, or investing in extensive employee training can significantly diminish the appeal of substitutes. For instance, in the aerospace sector where AMETEK has a strong presence, the rigorous qualification processes for new components can create high switching costs, acting as a barrier for customers considering alternatives.
Evolution of Customer Needs
The evolution of customer needs presents a significant threat of substitutes for AMETEK. As industries shift, for example, towards greater automation and data-driven insights, customers may seek integrated solutions that offer more than AMETEK's specialized components. A move towards cloud-based monitoring systems or entirely new operational models could render traditional hardware less relevant, pushing clients towards providers offering end-to-end digital platforms.
This evolving demand landscape means that even if AMETEK excels in its current product categories, a fundamental change in how customers want to achieve their operational goals can introduce potent substitutes. For instance, the growing emphasis on predictive maintenance and IoT integration means that customers might opt for comprehensive service packages rather than individual pieces of equipment.
- Shifting Industry Paradigms: A move towards fully integrated, software-driven solutions in sectors like industrial automation and aerospace could bypass AMETEK's traditional component-based offerings.
- Demand for Miniaturization and Efficiency: As technology advances, customers increasingly demand smaller, more power-efficient components, which could be met by emerging players with novel material science or design capabilities.
- Digital Transformation Imperatives: The drive for digital transformation across industries, including the adoption of AI and machine learning for operational optimization, may favor substitute solutions that offer embedded intelligence and connectivity.
Regulatory or Environmental Shifts
New regulations or environmental concerns can significantly impact the threat of substitutes for AMETEK's products. For instance, stricter emissions standards or mandates for energy efficiency could make alternative, greener technologies more appealing to customers. If AMETEK's current offerings are perceived as less environmentally friendly or energy-efficient compared to emerging substitutes, this trend could accelerate adoption of those alternatives.
Consider the automotive sector, a key market for AMETEK's electronic instruments and electromechanical devices. As governments worldwide push for decarbonization, electric vehicles (EVs) are increasingly replacing internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This shift directly impacts demand for components and systems traditionally used in ICE vehicles, creating a substitute threat from technologies powering EVs. For example, in 2024, EV sales are projected to continue their upward trajectory, with global market share expected to surpass 20% by year-end, according to various industry analyses. This growth implies a diminishing market for certain traditional automotive components that AMETEK might supply.
- Regulatory Push for Sustainability: Emerging environmental regulations, such as those focused on reducing carbon footprints or promoting circular economy principles, can elevate the threat of substitutes.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Stricter energy efficiency mandates can favor alternative products or technologies that consume less power, potentially displacing AMETEK's less efficient offerings.
- Emerging Compliance Requirements: New standards related to material sourcing, product lifecycle management, or waste reduction can create opportunities for substitutes designed to meet these specific compliance needs.
- Customer Demand for Green Solutions: Growing customer preference for sustainable products, driven by corporate social responsibility goals or consumer awareness, can make environmentally superior substitutes more attractive.
The threat of substitutes for AMETEK is heightened by the increasing availability of integrated, software-driven solutions that can perform similar functions to specialized hardware. For instance, advancements in AI-powered analytics and cloud platforms offer alternatives that may reduce reliance on traditional measurement and control devices. In 2024, the global market for industrial software and analytics is projected to reach over $30 billion, underscoring the growing appeal of these digital substitutes.
Customers' willingness to adopt substitutes is heavily influenced by the cost-benefit analysis, where lower prices or superior performance from alternatives can pose a significant challenge. Emerging players offering more affordable or feature-rich solutions can disrupt markets where AMETEK operates. The ease of switching also plays a crucial role; if integration costs and complexities are low, customers are more likely to explore substitutes.
Furthermore, shifts in customer needs, such as a growing demand for end-to-end digital platforms and predictive maintenance capabilities, can favor substitute solutions that offer embedded intelligence and connectivity over standalone components. This trend is amplified by regulatory pressures pushing for sustainability and energy efficiency, which can accelerate the adoption of greener alternative technologies.
Entrants Threaten
Launching a new venture in the electronic instruments and electromechanical devices sector, particularly for sophisticated offerings, demands significant financial outlay. This includes hefty investments in research and development, the establishment of specialized production sites, and building robust distribution channels.
These considerable capital requirements act as a substantial hurdle, effectively discouraging a large number of potential new players from entering the market. For instance, in 2024, the average R&D expenditure for companies in the electronic components industry reached approximately 8% of revenue, highlighting the ongoing need for substantial upfront investment.
AMETEK's deep investment in advanced analytical and motion control technologies means a significant reliance on its own unique, protected innovations. This proprietary technology, safeguarded by patents and specialized knowledge, is a formidable hurdle for any new company trying to enter the market. For instance, in 2023, AMETEK reported $6.5 billion in revenue, a portion of which is directly attributable to the value derived from its technological edge.
Established players like AMETEK leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement, leading to lower unit costs compared to potential newcomers. For instance, AMETEK's extensive global supply chain and high production volumes in 2023 allowed them to negotiate better terms with suppliers, a crucial advantage.
The experience curve further solidifies this advantage; as AMETEK has refined its processes over years, its operational efficiency has increased, driving down costs. New entrants would face substantial hurdles in matching these cost efficiencies without first achieving comparable production volumes, posing a significant barrier to entry.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
Newcomers often struggle to secure reliable distribution channels and cultivate strong customer relationships, especially in industries like aerospace and defense where trust and long-term partnerships are paramount. Incumbents like Ametek have spent years building these networks, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction.
For instance, Ametek's established relationships with major players in the aerospace sector, which accounted for a significant portion of its revenue in 2023, present a formidable barrier. New companies must invest heavily in sales, marketing, and demonstrating a proven track record to even begin competing for these crucial customer accounts.
- Established Distribution Networks: Ametek's extensive global distribution network, developed over decades, provides immediate market access that new entrants lack.
- Customer Loyalty and Trust: Building the deep customer loyalty and trust necessary in sectors like aerospace and defense, where reliability is critical, is a time-consuming and expensive endeavor for new companies.
- Switching Costs: High switching costs for customers, often due to integration complexities and qualification processes in specialized industries, further entrench incumbents like Ametek.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certifications
The threat of new entrants for AMETEK is significantly mitigated by substantial regulatory hurdles and the need for rigorous certifications. Many of AMETEK's core markets, such as aerospace, defense, and medical devices, are characterized by extensive government oversight and demanding compliance standards. For instance, companies entering the medical device sector must navigate bodies like the FDA, which requires extensive testing and approval processes that can take years and cost millions.
These complex regulatory landscapes and the costly process of obtaining necessary approvals act as a formidable barrier. New companies often lack the established relationships, expertise, and financial resources to effectively manage these requirements. In 2024, the average time for FDA approval for a new medical device can range from several months to over three years, depending on the device's risk classification, presenting a significant deterrent to potential new competitors.
- Stringent Certifications: Markets like aerospace and defense require adherence to standards such as AS9100, which is costly and time-consuming to achieve.
- High Compliance Costs: Meeting regulatory requirements in sectors like healthcare, including data privacy (HIPAA) and product safety, incurs substantial ongoing expenses.
- Lengthy Approval Processes: Gaining certifications for new technologies or products in regulated industries can delay market entry for years, demanding significant upfront investment.
- Established Relationships: Existing players like AMETEK have built trust and long-term relationships with regulatory bodies, which new entrants struggle to replicate.
The threat of new entrants for AMETEK is considerably low due to high capital requirements for R&D and specialized manufacturing, estimated in the millions for advanced electronic instruments. Furthermore, AMETEK's proprietary technologies, protected by patents, create a significant barrier, as replicating such innovations requires substantial time and investment. In 2024, the electronic components industry saw R&D spending average around 8% of revenue, underscoring the continuous need for upfront capital.
Economies of scale in production and procurement, coupled with the experience curve, give AMETEK a cost advantage that new entrants find difficult to match. For instance, AMETEK's 2023 global supply chain efficiencies allowed for better supplier terms. Building established distribution networks and customer loyalty in sectors like aerospace, where trust is paramount, also presents a formidable challenge for newcomers, requiring years of effort and significant investment in sales and marketing.
Stringent regulatory hurdles and lengthy certification processes in AMETEK's key markets, such as medical devices and defense, further deter new entrants. Obtaining FDA approval, for example, can take over three years in 2024, demanding substantial financial resources and expertise that new companies often lack. Compliance costs and the need for adherence to standards like AS9100 in aerospace add to these barriers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, specialized manufacturing, and distribution. | Average R&D for electronic components: ~8% of revenue (2024). |
| Proprietary Technology | Patented innovations and specialized knowledge. | AMETEK's revenue in 2023: $6.5 billion, partly from technological edge. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower unit costs due to high production volumes and efficient supply chains. | AMETEK's global supply chain and production volumes in 2023. |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | Established customer relationships and integration complexities. | AMETEK's aerospace sector revenue (significant portion in 2023). |
| Regulatory & Certification | Complex government oversight and demanding compliance standards. | FDA approval time for medical devices: months to >3 years (2024). AS9100 certification costs. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for AMETEK is built upon a robust foundation of data, including AMETEK's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld and Statista.
