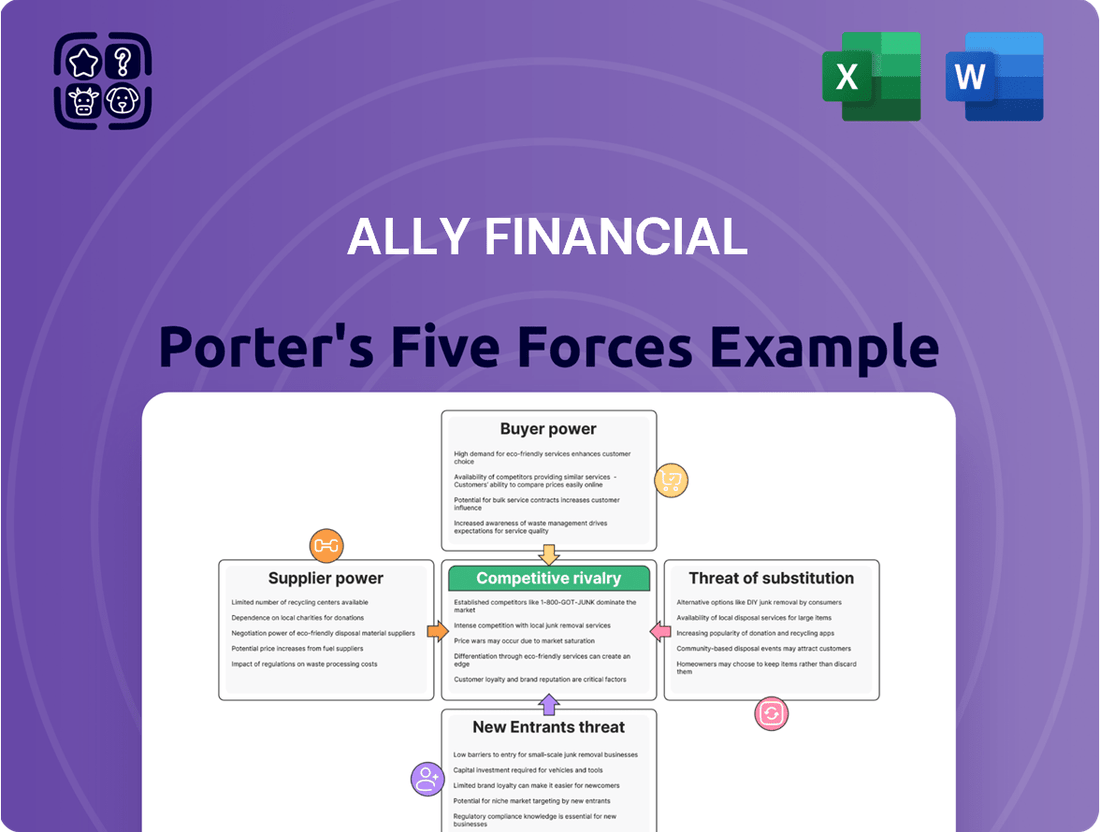
Ally Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ally Financial Bundle
Ally Financial navigates a dynamic landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving customer expectations. Understanding the underlying forces is crucial for strategic advantage.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ally Financial’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ally Financial's reliance on capital providers means these entities wield considerable influence. For instance, in early 2024, the Federal Reserve's interest rate policies directly affected the cost of borrowing for financial institutions like Ally, demonstrating the power of central banks as de facto capital providers and influencers.
Technology and software vendors hold significant bargaining power over Ally Financial due to the company's deep reliance on specialized fintech solutions, cloud infrastructure, and advanced data analytics. The critical nature of these services means Ally cannot easily switch providers without incurring substantial costs and operational disruptions.
In 2024, the demand for sophisticated cybersecurity and cloud services, essential for financial institutions like Ally, remained exceptionally high, strengthening the position of key suppliers. Companies offering proprietary platforms or unique technological innovations, which are increasingly vital for maintaining a competitive edge in digital banking, can command higher prices and more favorable terms.
Data and information providers, such as credit bureaus and financial data aggregators, wield significant bargaining power over Ally Financial. Ally's ability to manage risk, tailor marketing campaigns, and develop new products hinges on access to robust and timely data, including credit scores and market analytics. The specialized nature and essentiality of this information create a dependency, impacting Ally's operational efficiency and competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, the demand for granular consumer behavior insights continued to rise, further solidifying the leverage of these data suppliers.
Marketing and Advertising Agencies
Marketing and advertising agencies can exert significant bargaining power over Ally Financial, especially those specializing in digital financial services. Given Ally's wholly online model, these agencies are crucial for customer acquisition and retention, making their ability to reach specific demographics and craft effective brand narratives highly valuable. In 2024, the digital advertising market saw continued growth, with spending on online ads projected to reach over $600 billion globally, highlighting the importance of agencies that can navigate this complex landscape efficiently.
The power of these agencies stems from their specialized knowledge and their capacity to deliver measurable results in a crowded digital space. Agencies proficient in data analytics and performance marketing can demonstrate a direct impact on Ally's customer acquisition cost and overall growth. For instance, a successful digital campaign managed by a top-tier agency could significantly boost Ally's online presence and customer base, thereby justifying higher fees.
- Specialized Expertise: Agencies with deep understanding of financial services marketing and digital channels hold more sway.
- Performance Metrics: Proven ability to drive customer acquisition and engagement through data-driven campaigns enhances agency leverage.
- Market Competition: The competitive nature of digital advertising means agencies with unique strategies or access to prime ad inventory can command better terms.
- Brand Impact: Agencies capable of building strong brand resonance for Ally in the digital realm are indispensable.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Services
The financial services sector, including Ally Financial, faces a landscape of stringent regulations that necessitate ongoing legal and compliance oversight. Suppliers offering specialized legal counsel, regulatory consulting, and compliance technology are positioned to wield significant influence. This power stems from the critical nature of their services, as failure to adhere to regulations can result in substantial financial penalties and reputational damage.
For instance, the U.S. financial services industry saw regulatory fines total billions in 2023, underscoring the cost of non-compliance. Ally Financial, like its peers, relies on external legal and compliance experts to navigate these complex rules, including those from bodies like the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
- Specialized Expertise: Suppliers possess niche knowledge of financial laws and regulations, which is difficult and costly for Ally to replicate internally.
- High Switching Costs: Transitioning to new legal or compliance service providers can be time-consuming and disruptive due to the need for knowledge transfer and system integration.
- Risk Mitigation: The severe consequences of regulatory breaches empower suppliers whose services are essential for risk management and legal adherence.
- Industry Scrutiny: Increased regulatory focus on areas like data privacy and fair lending in 2024 amplifies the importance of expert compliance support.
Suppliers of critical technology, data, and specialized services possess substantial bargaining power over Ally Financial. This leverage is amplified by the high switching costs and the essential nature of these inputs for Ally's operations and competitive positioning.
In 2024, the demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions and robust data analytics platforms remained exceptionally strong, allowing key vendors to dictate terms. For example, the global cybersecurity market was projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024, reflecting intense demand and supplier strength.
Ally's dependence on these specialized providers, from cloud infrastructure to regulatory compliance software, means that supplier pricing and service level agreements significantly impact operational costs and strategic flexibility.
The bargaining power of capital providers also remains a key consideration, as demonstrated by central bank policies influencing borrowing costs for financial institutions throughout 2024.
| Supplier Category | Key Dependencies for Ally | Evidence of Bargaining Power (2024) | Impact on Ally |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology & Software Vendors | Fintech solutions, cloud infrastructure, data analytics | High demand for proprietary platforms; significant switching costs | Increased costs for essential services; potential operational disruption if dissatisfied |
| Data & Information Providers | Credit bureaus, market analytics, consumer behavior data | Rising demand for granular insights; critical for risk management and marketing | Higher data acquisition costs; reliance on data quality for decision-making |
| Legal & Compliance Services | Regulatory consulting, specialized legal counsel | Stringent regulatory environment; severe penalties for non-compliance | Significant expenditure on compliance; reliance on external expertise to avoid fines |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the intensity of rivalry, threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes impacting Ally Financial's profitability.
Ally Financial's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making and understanding competitive pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
For Ally Financial's deposit accounts and personal loans, customers face low switching costs. This ease of movement is amplified by the digital nature of banking, allowing consumers to readily open or close accounts with various institutions. In 2024, the continued growth of digital-only banks and enhanced online platforms from traditional banks means customers can easily find comparable or better offerings elsewhere, directly impacting Ally's customer retention.
The internet and financial comparison websites have dramatically increased customer access to information. Customers can now easily compare interest rates, fees, and product features across numerous financial institutions, especially in areas like auto finance and mortgages. This price transparency gives them significant leverage to find the best deals.
For Ally Financial, its digital-only model means its customer base is inherently comfortable with online research and comparison. This digital savviness means customers are well-equipped to leverage available information to their advantage, seeking out the most competitive offerings in areas like auto loans and savings accounts.
The standardization of core financial products, such as basic savings accounts and auto loans, significantly amplifies the bargaining power of Ally Financial's customers. When products are largely the same across different institutions, switching becomes a simple matter of comparing interest rates or fees, rather than evaluating unique product features. This commoditization means customers can easily move their business elsewhere, forcing Ally to compete aggressively on price.
In 2024, the average interest rate for a new car loan hovered around 7.35%, according to data from Bankrate. This figure highlights how sensitive customers are to rate differentials, especially for larger financial commitments like auto financing. Ally's ability to retain customers in such a standardized market hinges on offering not just competitive rates, but also superior customer service and digital experiences that add value beyond the basic product itself.
Large Customer Base and Segment Heterogeneity
Ally Financial benefits from a vast and diverse customer base, encompassing individual consumers needing auto loans and mortgages, as well as commercial entities. While individual customers typically wield limited power, the sheer volume of Ally's clientele creates a significant collective bargaining force. This broad reach means Ally must constantly adapt its products and services to cater to the distinct needs and price sensitivities of various customer segments, thereby managing a complex web of varied bargaining pressures.
The heterogeneity within Ally's customer base is a key factor in understanding customer bargaining power. For instance, in the auto finance sector, while individual consumers might not negotiate terms, the aggregate demand for specific vehicle types or loan products can influence Ally's pricing and product development strategies. In 2023, Ally's auto finance originations reached approximately $47.5 billion, highlighting the scale of its consumer interaction and the potential for collective influence.
- Diverse Customer Segments: Ally serves individuals and businesses, each with unique financial needs and expectations.
- Collective Influence: A large customer base, though individually weak, can exert significant collective bargaining power.
- Segmented Price Sensitivity: Different customer groups react differently to pricing and service offerings, requiring tailored strategies.
- Market Responsiveness: Ally's ability to segment and respond to diverse customer demands impacts its competitive positioning.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Demand
The bargaining power of customers within the financial services sector, particularly for a company like Ally Financial, is significantly influenced by prevailing economic conditions. During economic downturns, when demand for major financial products like auto loans and mortgages typically shrinks, customers gain leverage. For instance, in late 2023 and early 2024, as interest rate hikes impacted affordability, consumers had more room to negotiate terms or seek out the most competitive rates from various lenders, including Ally.
This increased customer power during weaker economic periods forces companies like Ally to be more aggressive with pricing and product offerings. They might need to lower interest rates, extend loan terms, or offer other incentives to secure business. For example, if the Federal Reserve maintains higher interest rates through much of 2024, Ally may continue to face pressure to offer attractive financing options to maintain market share in its auto finance segment.
Conversely, when the economy is robust and demand for financial products is high, customer bargaining power tends to recede. In a strong economic environment, more individuals and businesses are actively seeking credit, which naturally shifts the advantage towards lenders. This was observed in periods prior to 2022 when economic growth was strong, and lenders had more flexibility in setting terms and rates due to high consumer and business confidence.
- Economic Downturns Amplify Customer Power: Periods of reduced economic activity, such as those seen with rising inflation and interest rates in 2023-2024, give consumers more leverage to negotiate favorable terms on loans and financial products.
- Ally's Response to Weak Demand: To counter decreased demand during economic slowdowns, Ally may be compelled to offer more competitive interest rates and flexible loan conditions to attract and retain customers.
- Economic Booms Diminish Customer Power: In times of economic prosperity and increased demand for credit, the bargaining power of customers typically lessens, allowing financial institutions to operate with greater pricing flexibility.
Customers possess significant bargaining power due to low switching costs and easy access to information, especially in the digital banking landscape. This power is amplified by the standardization of core financial products, forcing institutions like Ally Financial to compete fiercely on price and service to retain clients.
The average interest rate for new car loans in 2024 was around 7.35%, underscoring customer sensitivity to rate differences, particularly for larger financial commitments. Ally's broad customer base, while individually limited in power, creates a collective force that necessitates catering to diverse needs and price sensitivities across different segments.
Economic conditions directly influence customer leverage; during downturns in 2023-2024, consumers gained power to negotiate better terms due to reduced demand and higher interest rates. This dynamic pressures Ally to offer more competitive rates and incentives to maintain market share.
Full Version Awaits
Ally Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Ally Financial, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the financial services industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering no surprises and full utility.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Ally Financial contends with formidable competition from large traditional banks. These established players, like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America, possess vast financial resources and deeply entrenched customer relationships. For instance, as of Q1 2024, JPMorgan Chase reported total assets exceeding $3.9 trillion, dwarfing Ally's nearly $170 billion in total assets. This scale allows them to absorb market fluctuations and invest heavily in technology, directly challenging Ally across its core offerings.
These traditional banks are rapidly enhancing their digital platforms, mirroring Ally's online-first strategy. They are actively competing in key Ally segments such as auto finance, mortgages, and credit cards. Many of these institutions also boast strong brand loyalty built over decades, making it harder for digital-native banks like Ally to capture market share, especially among less digitally inclined customer segments.
The rise of digital-first banks and nimble fintechs significantly heats up competition for Ally Financial. These newer players, often focusing on specific market segments, can provide attractive interest rates and slick digital interfaces. For instance, by mid-2024, several fintechs were offering savings account APYs exceeding 5%, directly challenging Ally's deposit-gathering strategies.
These fintechs, with their leaner operational structures, can innovate and adapt much faster than traditional institutions. This agility allows them to introduce new features and services quickly, often at lower costs. Their ability to offer specialized products, like targeted lending or niche investment platforms, directly competes with Ally's broader banking services, intensifying the pressure on pricing and customer retention.
Ally Financial operates in auto finance and mortgage sectors that are notably fragmented. This means the company faces a broad range of competitors, from large national institutions to smaller, specialized lenders like credit unions and captive finance companies. For instance, the U.S. auto finance market includes major players like Ford Motor Credit and GM Financial, alongside a multitude of regional banks and independent finance firms, creating intense competition.
This high degree of fragmentation intensifies rivalry, pushing companies like Ally to constantly offer competitive rates and streamline their services to attract and retain customers. The sheer volume of lenders means market share gains can be challenging, and pricing pressure is a constant factor. In 2024, the competitive landscape remains robust, with lenders actively seeking differentiation through technology and customer experience.
Product Overlap and Ease of Comparison
Ally Financial faces intense competition due to significant product overlap. Many of its core offerings, including savings accounts, auto loans, and mortgages, are standard across the banking sector. This makes it easy for consumers to compare options and prices online, driving a focus on competitive rates.
The digital landscape further amplifies this rivalry. Customers can readily access comparison tools and financial aggregators, allowing them to quickly identify the best deals. For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate on a new car loan hovered around 7.9%, with significant variation across lenders, highlighting the importance of rate competitiveness for auto financing, a key Ally product.
- Product Homogeneity: Savings accounts, auto loans, and mortgages are common offerings across numerous financial institutions.
- Online Comparison: Digital platforms enable customers to easily compare rates and terms, increasing price sensitivity.
- Rate Competition: In 2024, average new auto loan rates were approximately 7.9%, underscoring the pressure on pricing.
- Differentiation Imperative: Ally must innovate and excel in customer service to stand out beyond mere price advantages.
Marketing and Brand Building Intensity
In the intensely competitive digital financial services landscape, marketing and brand building are paramount for attracting and keeping customers. Competitors are heavily investing in advertising, offering enticing promotions, and employing sophisticated digital engagement tactics.
Ally Financial, like its peers, faces significant pressure to maintain a strong brand presence and customer appeal. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. banking industry saw substantial marketing expenditures, with major players allocating billions towards advertising and digital outreach to capture market share.
- Aggressive Digital Advertising: Competitors are leveraging targeted online ads and social media campaigns to reach potential customers.
- Promotional Offers: High-yield savings accounts and competitive loan rates are frequently used as acquisition tools.
- Customer Engagement: Brands are focusing on personalized digital experiences and responsive customer service to foster loyalty.
- Brand Visibility: Continuous investment in marketing is essential for Ally to cut through the noise and remain a top-of-mind choice for consumers.
Ally Financial faces intense competition from established banking giants with significantly larger asset bases, such as JPMorgan Chase, which reported over $3.9 trillion in assets in Q1 2024 compared to Ally's nearly $170 billion. These large banks are rapidly enhancing their digital offerings, directly challenging Ally's online-first strategy in auto finance, mortgages, and credit cards.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by nimble fintech companies and digital-first banks that often offer more attractive interest rates, with some savings accounts exceeding 5% APY by mid-2024. Ally also contends with a fragmented auto finance market, facing numerous competitors from large captive lenders like Ford Motor Credit to smaller regional banks and credit unions, all vying for market share.
Product homogeneity, particularly in savings accounts and auto loans, forces Ally to compete heavily on price, with average new auto loan rates around 7.9% in 2024. This necessitates continuous innovation in customer service and digital experience to differentiate beyond mere pricing strategies, as competitors aggressively invest in marketing and digital engagement to capture customer attention.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | Impact on Ally | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Traditional Banks | Vast resources, established customer base, brand loyalty | Significant competitive pressure across all product lines | JPMorgan Chase: ~$3.9T+ in assets (Q1 2024) |
| Fintechs & Digital Banks | Agility, innovation, attractive rates, lean operations | Disrupts traditional models, challenges deposit gathering | Savings APYs >5% (mid-2024) |
| Auto Finance Specialists | Niche focus, captive financing, specialized products | Intense rivalry in a key Ally segment | Ford Motor Credit, GM Financial |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Direct-to-consumer lending from auto manufacturers, like Ford Credit and GM Financial, presents a significant threat of substitutes for Ally Financial in the auto finance sector. These captive finance companies offer integrated financing solutions directly at the dealership, often bundling attractive incentives and special rates that can sway customers away from independent lenders. For instance, in 2023, GM Financial reported a net revenue of $12.9 billion, demonstrating the substantial scale and market presence these direct lenders command.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for Ally Financial, particularly in the personal loan and small business financing segments. These platforms bypass traditional banking intermediaries, directly connecting borrowers with investors, often leading to more competitive rates and flexible terms than those offered by established institutions.
For instance, in 2024, the P2P lending market continued its growth trajectory, with platforms like LendingClub and Prosper facilitating billions in loans. This trend indicates a growing consumer preference for alternative lending channels, directly impacting Ally's market share in personal loans, a key revenue driver.
Consumers often bypass traditional loans by tapping into personal savings or leveraging existing assets. For instance, in 2024, the average credit card interest rate hovered around 20%, making it a potentially more expensive substitute than a personal loan for some. Home equity lines of credit (HELOCs) also offer a way to finance purchases, with average HELOC rates in early 2024 around 8-10%, presenting a lower-cost alternative for those with sufficient home equity.
Alternative Investment Vehicles for Savings
For Ally Bank's deposit account customers, alternative investment vehicles such as mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or direct stock investments can act as substitutes for traditional savings accounts. These options, while carrying different risk profiles, often present the potential for higher returns, particularly when deposit interest rates are low. For instance, in early 2024, the average savings account yield hovered around 4.5%, while the S&P 500 saw significant gains, demonstrating the return differential that can incentivize shifts.
Customers may choose to move their funds if their primary goal is capital growth rather than immediate liquidity and absolute safety. This trend is amplified when market conditions favor equities or other growth-oriented assets. The accessibility of these alternatives through online platforms and robo-advisors further lowers the barrier to entry for savers looking beyond basic deposit products.
- Higher Potential Returns: Alternatives like ETFs and mutual funds can offer yields significantly exceeding those of traditional savings accounts, especially in favorable market conditions.
- Risk Tolerance: The attractiveness of substitutes depends on a customer's willingness to accept greater volatility for the possibility of higher returns.
- Market Conditions: Periods of low interest rates on deposits, common in recent years, push savers to explore alternatives for better yield.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Services
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services pose a significant threat to Ally Financial by offering an alternative to traditional credit products. These services are increasingly popular for financing smaller purchases, directly competing with Ally's credit card and personal loan offerings. For instance, by mid-2024, BNPL transactions were projected to reach hundreds of billions globally, demonstrating a rapid shift in consumer payment preferences.
BNPL platforms appeal to a broad consumer base, including those who may not qualify for or prefer to avoid traditional credit. They offer a streamlined, often interest-free installment payment option, which can be more attractive than credit card interest rates or personal loan fees for many consumers. This accessibility and perceived cost-effectiveness directly siphon potential customers away from Ally's core lending business.
- Growing Market Share: BNPL services have seen explosive growth, capturing a significant portion of the point-of-sale financing market.
- Consumer Preference Shift: A growing number of consumers, particularly younger demographics, favor BNPL for its convenience and transparency.
- Impact on Traditional Lending: The rise of BNPL could lead to a decline in credit card usage and demand for small personal loans, directly affecting Ally's revenue streams.
Ally Financial faces competition from direct-to-consumer lending arms of auto manufacturers, such as Ford Credit and GM Financial. These entities offer integrated financing, often with attractive incentives that can pull customers away from independent lenders. For example, GM Financial reported substantial net revenue in 2023, highlighting their significant market presence.
Peer-to-peer lending platforms also serve as substitutes, particularly for personal and small business loans. These platforms connect borrowers directly with investors, potentially offering more competitive rates than traditional banks. The continued growth of P2P lending in 2024, with platforms facilitating billions in loans, indicates a consumer shift towards alternative financing channels.
Consumers may also opt to use personal savings or home equity lines of credit (HELOCs) instead of traditional loans. With average credit card interest rates around 20% in 2024 and HELOC rates near 8-10%, these alternatives can be more cost-effective for certain borrowers, impacting demand for Ally's loan products.
For deposit customers, investment vehicles like ETFs and mutual funds present alternatives to savings accounts, especially when deposit rates are low. In early 2024, savings account yields around 4.5% contrasted with significant S&P 500 gains, incentivizing a move towards higher-growth assets.
| Substitute Type | Key Features for Consumers | Impact on Ally Financial | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto Manufacturer Finance Arms | Integrated financing, special rates, incentives | Direct competition in auto loans | GM Financial's 2023 revenue indicates scale |
| P2P Lending Platforms | Direct borrower-investor connection, competitive rates | Competition in personal and small business loans | Billions facilitated in 2024, growing consumer preference |
| Personal Savings/HELOCs | Lower interest costs than credit cards, access to equity | Reduced demand for personal loans and credit cards | Credit card rates ~20%, HELOCs ~8-10% in early 2024 |
| Investment Vehicles (ETFs, Mutual Funds) | Potential for higher returns, capital growth | Competition for deposit balances | Savings yields ~4.5% vs. S&P 500 gains in early 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The financial services sector, including institutions like Ally Financial, faces formidable regulatory hurdles. New players must navigate a labyrinth of licensing requirements, stringent capital reserve mandates, and complex compliance frameworks such as the Dodd-Frank Act and various consumer protection laws.
Establishing a new, fully compliant financial institution demands significant upfront investment in legal expertise and operational infrastructure. For instance, the cost of adhering to cybersecurity regulations alone can be substantial, deterring many potential entrants.
These regulatory barriers, coupled with the continuous and substantial costs associated with ongoing compliance, effectively limit the threat of new entrants, protecting established players like Ally.
Entering the lending and banking sector, akin to Ally Financial, requires immense capital. Think billions for establishing lending portfolios, robust operational infrastructure, and meeting stringent regulatory capital adequacy ratios. For instance, in 2024, major banks often maintain Tier 1 capital ratios well above 12%, necessitating significant upfront investment for any new player seeking to compete.
This substantial capital demand acts as a major deterrent for potential new entrants. Raising such considerable funds is a significant hurdle, making it difficult for smaller or less-established entities to even consider entering the market at a competitive scale.
Furthermore, the imperative for a strong balance sheet to absorb potential loan losses and economic downturns further elevates this barrier. A new entrant must demonstrate financial resilience from day one, which is a tall order without a proven track record and deep pockets.
Established players like Ally Financial have cultivated strong brand recognition and deep customer trust over many years, which is essential for handling financial matters. Newcomers, especially online-only banks, must overcome the hurdle of earning this trust from the ground up in an industry where security and reliability are paramount. For example, Ally Financial reported over $230 billion in total deposits as of the first quarter of 2024, a testament to the trust they've built.
Technological Infrastructure and Cybersecurity Needs
The threat of new entrants in the digital banking space, particularly concerning technological infrastructure and cybersecurity, is significantly mitigated by the substantial upfront investment and ongoing expertise required. New players must establish robust, scalable, and highly secure IT systems from the outset to compete with established online financial institutions like Ally. This includes advanced data analytics capabilities and comprehensive cybersecurity protocols to protect customer data and ensure operational integrity.
For instance, the global cybersecurity market was projected to reach over $300 billion in 2024, highlighting the immense cost associated with building and maintaining adequate defenses. New entrants face the challenge of not only replicating Ally's existing technological sophistication but also staying ahead of evolving cyber threats.
- High Capital Expenditure: Building a secure and scalable digital banking platform demands significant investment in hardware, software, and cloud infrastructure.
- Specialized Expertise: Accessing and retaining talent with deep expertise in IT, data science, and cybersecurity is crucial and can be costly.
- Regulatory Compliance: New entrants must also navigate complex regulatory requirements related to data privacy and financial security, adding to the operational burden and cost.
Access to Funding Sources and Distribution Channels
New entrants in the financial services sector face significant hurdles in accessing capital. Established institutions like Ally Financial benefit from deep-rooted relationships with capital markets, enabling them to secure funding at more favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, Ally successfully issued various debt securities, demonstrating consistent access to diverse funding pools.
Building robust distribution channels is another substantial barrier. Ally's established partnerships, particularly within the auto industry, provide a significant advantage in customer acquisition. Newcomers must invest heavily in developing similar networks, which can be both time-consuming and expensive to replicate.
- Funding Access: Established players like Ally have proven track records, facilitating easier and cheaper access to capital markets compared to nascent firms.
- Distribution Networks: Replicating Ally's extensive dealer relationships in auto finance requires substantial upfront investment and time.
- Cost of Acquisition: New entrants often face higher customer acquisition costs due to the need to build brand recognition and trust from scratch.
The threat of new entrants for Ally Financial is considerably low due to immense capital requirements and stringent regulatory landscapes. Potential newcomers must secure billions to establish operations, meet capital adequacy ratios, and navigate complex compliance, making market entry exceptionally difficult. For example, in 2024, major banks maintained Tier 1 capital ratios above 12%, a significant barrier for any new player.
Building brand trust and robust technological infrastructure also presents a substantial hurdle. Ally's established reputation and advanced cybersecurity, costing billions globally in 2024, are difficult and expensive for new entrants to replicate. Furthermore, securing favorable capital market access and replicating extensive distribution networks, like Ally's auto finance partnerships, demands significant time and investment.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Billions needed for operations and regulatory compliance (e.g., Tier 1 capital ratios >12% in 2024). | Very High - Deters most potential entrants. |
| Regulation & Compliance | Navigating licensing, capital reserves, and laws like Dodd-Frank. | Very High - Requires extensive legal and operational investment. |
| Brand Trust & Reputation | Building customer confidence in financial security. | High - Takes years to cultivate, unlike Ally's $230B+ deposits (Q1 2024). |
| Technology & Cybersecurity | Investing in advanced, secure IT systems (global cybersecurity market >$300B in 2024). | High - Requires substantial upfront and ongoing expenditure. |
| Distribution & Capital Access | Establishing networks and securing favorable funding. | High - Ally's proven track record and partnerships are difficult to match. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ally Financial is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Ally's annual and quarterly financial reports, SEC filings, and investor presentations. We supplement this with insights from reputable financial news outlets, industry-specific research reports, and macroeconomic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
