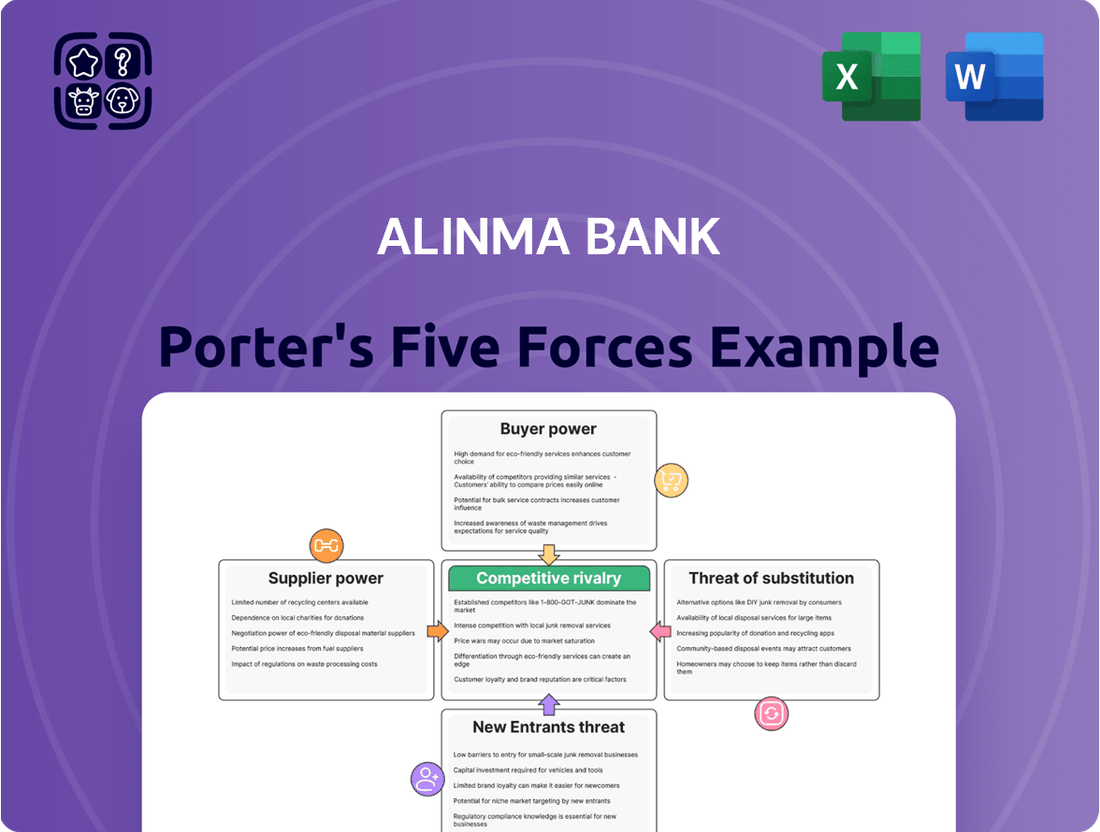
Alinma Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Alinma Bank Bundle
Alinma Bank navigates a competitive landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and the looming threat of new entrants, while supplier power remains relatively low. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Alinma Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Alinma Bank's access to funding sources, a key determinant of supplier bargaining power, is multifaceted. The bank primarily draws funds from customer deposits, interbank markets, and capital markets, including sukuk issuances. In 2024, the Saudi banking sector experienced a notable trend where lending growth outpaced deposit growth, a dynamic that can amplify the bargaining power of entities providing these crucial external funds.
While retail deposits offer a stable base, larger institutional depositors and the ability to tap into international capital markets, such as through sukuk, can significantly influence supplier leverage. The cost and accessibility of these external funds are directly tied to broader global economic conditions and prevailing investor sentiment, impacting Alinma Bank's operational flexibility.
Alinma Bank's push into advanced technologies like AI and open banking means a growing reliance on specialized tech vendors. These providers, offering crucial cybersecurity and digital infrastructure, possess significant bargaining power due to their unique skills and proprietary systems. This dependency requires Alinma to cultivate strong vendor relationships and manage them carefully to avoid price hikes or service interruptions.
The availability of skilled labor significantly impacts the bargaining power of suppliers, especially in specialized sectors like banking. In Saudi Arabia's dynamic financial landscape, demand is high for expertise in digital banking, Sharia-compliant finance, risk management, and cybersecurity. A scarcity of these specialized skills can elevate labor costs and complicate hiring, granting skilled professionals greater leverage.
Alinma Bank recognizes this challenge, actively pursuing strategies to be a premier employer within the Saudi banking sector. This focus on talent attraction and retention underscores the critical role skilled employees play, potentially influencing their bargaining power with the bank.
Regulatory Compliance Services
Suppliers of regulatory compliance services, including legal counsel and auditing firms specializing in Saudi Arabian banking laws and Sharia principles, wield considerable bargaining power over Alinma Bank. These services are essential for the bank's operational integrity and adherence to Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) directives, making them non-negotiable inputs. The specialized knowledge and critical nature of their offerings can significantly enhance their leverage.
The demand for specialized regulatory expertise is high, and the pool of providers with proven track records in the Saudi financial sector is relatively limited. This scarcity, coupled with the stringent regulatory environment, allows these suppliers to command premium pricing and favorable contract terms. For instance, the Saudi Central Bank's ongoing focus on enhancing financial sector resilience and combating financial crime in 2024 has likely increased the demand for advanced compliance solutions.
- High switching costs: Alinma Bank faces substantial costs and potential disruption when changing compliance service providers due to the need for knowledge transfer and re-establishment of trust and regulatory approvals.
- Concentration of suppliers: The market for highly specialized regulatory and Sharia compliance services in Saudi Arabia is not overly fragmented, meaning a few key players can exert significant influence.
- Importance of reputation and expertise: Suppliers with a strong reputation and deep understanding of the specific regulatory landscape are highly valued, reducing the bank's ability to negotiate aggressively on price alone.
- Essential nature of services: Compliance services are not discretionary; they are fundamental to Alinma Bank's license to operate, giving suppliers considerable leverage.
Infrastructure and Utilities
Essential infrastructure and utility providers, such as telecommunication and power companies, hold moderate bargaining power over Alinma Bank. These services are critical for Alinma's digital banking platforms and its extensive branch network. For instance, in 2024, the Saudi telecom market saw continued competition, which can temper price hikes from providers, though the essential nature of their services means Alinma cannot easily switch suppliers for core functions.
Disruptions or significant cost increases from these suppliers can directly affect Alinma's operational efficiency and overall expenses, impacting profitability. However, the regulated nature of many utility services in Saudi Arabia helps to somewhat limit the suppliers' ability to exert excessive power through pricing or service terms. For example, the Communications and Information Technology Commission (CITC) in Saudi Arabia often oversees pricing and service quality, providing a degree of stability for Alinma as a major consumer.
- Critical Dependence: Alinma Bank relies heavily on telecommunication and utility services for its digital channels and physical branches.
- Operational Impact: Price increases or service disruptions from these suppliers can negatively affect Alinma's efficiency and costs.
- Regulatory Influence: The regulated nature of these services in Saudi Arabia generally moderates supplier bargaining power.
- Market Dynamics: While competition exists in sectors like telecommunications, the essential nature of utilities provides some leverage to suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Alinma Bank is influenced by several factors, including the concentration of specialized service providers and the essential nature of their offerings. For instance, in 2024, the demand for advanced cybersecurity and Sharia-compliant financial advisory services remained high in Saudi Arabia, granting these niche suppliers considerable leverage due to limited competition and critical expertise.
Technology vendors providing specialized software and AI solutions also exhibit significant bargaining power. Alinma's increasing reliance on digital transformation means these suppliers' unique capabilities and proprietary systems can lead to higher costs and potential dependency. The bank must manage these relationships strategically to mitigate risks associated with price increases or service interruptions.
While utility and telecommunication providers have moderate power, their essential services are critical for Alinma's operations. However, regulatory oversight in Saudi Arabia, such as by the CITC for telecom, helps to temper excessive price hikes, offering some balance. The overall supplier landscape for Alinma Bank presents a mixed picture, with specialized service providers holding more sway than general infrastructure providers.
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Alinma Bank dissects the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitutes within the Saudi Arabian banking sector.
A dynamic, interactive model that allows Alinma Bank to simulate the impact of competitive shifts on profitability, thereby alleviating concerns about future revenue streams.
Customers Bargaining Power
Alinma Bank faces significant customer bargaining power due to the highly competitive Saudi Arabian banking landscape, featuring numerous local and international institutions. This intense competition, including that from other major Islamic banks, provides customers with ample options to compare services and pricing.
With a substantial customer base of 5.8 million as of March 2025, Alinma Bank must actively work to retain these clients. The ease with which customers can switch to a competitor offering better terms or services means Alinma needs to consistently deliver superior value and differentiated products to maintain its market position.
The ongoing digital transformation in the Saudi financial sector, particularly with the push towards open banking, is making it easier and cheaper for customers to switch banks. This means customers can move their money and services to a new provider with less hassle.
As digital platforms become more interconnected, customers can effortlessly transfer funds and manage their accounts across different institutions. For instance, by mid-2024, several Saudi banks reported significant increases in digital account openings, indicating a growing comfort with online banking and a potential for higher customer mobility.
This ease of switching directly empowers customers, as they face fewer barriers to leaving their current bank. This trend is a key factor in the increasing bargaining power of customers within the Saudi banking landscape.
Saudi customers, especially the younger, digitally adept population, are increasingly informed about banking options. They can easily find details on products, rates, and service quality online, often through comparison platforms. This access to information empowers them to demand better deals and digital services from financial institutions like Alinma Bank.
Diverse Customer Segments with Specific Needs
Alinma Bank caters to a broad spectrum of clients, encompassing retail, corporate, and investment customers, all operating within Sharia-compliant frameworks. This diversity means each group has unique financial requirements and service expectations, necessitating specialized offerings. For instance, by the end of Q1 2024, Alinma Bank reported total customer deposits of SAR 127.8 billion, reflecting the substantial financial activity across these segments.
The bargaining power of customers within Alinma Bank's diverse segments can be significant, particularly among larger entities. Corporate and institutional clients, due to their substantial transaction volumes and financial expertise, often wield considerable influence. They can negotiate bespoke terms, preferential rates, and customized financial solutions, directly impacting the bank's pricing and service delivery models. In 2023, Alinma Bank's net special commission income reached SAR 9.5 billion, a figure influenced by the negotiated terms with its corporate clients.
- Retail Segment: Individual customers generally have lower individual bargaining power, but collective action through switching banks can exert pressure.
- Corporate Segment: Large corporations and businesses possess significant bargaining power due to their transaction volumes and the potential for substantial revenue generation for the bank.
- Investment Segment: Institutional investors and asset managers often negotiate terms based on the size of assets under management and expected returns.
- Sharia Compliance: The adherence to Sharia principles creates a specific niche, potentially limiting alternative providers but also creating a concentrated customer base with shared expectations.
Impact of Fintech Innovations
The growing influence of fintech innovations significantly impacts the bargaining power of Alinma Bank's customers. The proliferation of specialized financial solutions, like digital payment platforms and Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services, provides consumers with readily available alternatives to traditional banking. For instance, the global BNPL market was projected to reach over $3.6 trillion by 2024, showcasing the substantial shift in consumer payment preferences.
These fintech offerings not only serve as substitutes but also elevate customer expectations regarding convenience and efficiency. Customers now anticipate seamless digital experiences, pushing Alinma Bank to continuously innovate its services to meet these evolving demands and maintain its competitive edge in the market.
- Fintech Growth: The digital payments sector alone saw significant expansion, with transaction volumes globally expected to exceed $10 trillion in 2024.
- Customer Expectations: Increased access to user-friendly fintech apps has raised the bar for digital banking interfaces and service speed.
- Competitive Pressure: Alinma Bank faces pressure to enhance its digital offerings, potentially through partnerships or in-house development, to retain customers attracted by fintech alternatives.
Alinma Bank's customers possess considerable bargaining power, amplified by a competitive banking sector and the ease of switching providers. This is particularly true for corporate clients who can negotiate terms due to their transaction volumes, influencing the bank's revenue streams. For example, Alinma Bank's net special commission income in 2023 was SAR 9.5 billion, partly shaped by such negotiations.
The rise of fintech solutions further empowers consumers, raising expectations for digital convenience and efficiency. This trend is evident globally, with the Buy Now, Pay Later market projected to exceed $3.6 trillion by 2024, indicating a significant shift in payment preferences and a challenge for traditional banks to keep pace.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Alinma Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | Low individual power, but collective switching pressure | Requires competitive pricing and service to retain |
| Corporate | High due to transaction volumes and negotiation leverage | Influences pricing, service customization, and revenue |
| Investment | Negotiation based on assets under management | Affects fee structures and product offerings |
What You See Is What You Get
Alinma Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Alinma Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape through the lens of threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You are looking at the actual document; once your purchase is complete, you'll receive instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Saudi Arabian banking landscape is fiercely competitive, featuring a substantial number of both domestic powerhouses and internationally licensed institutions. Prominent entities such as Saudi National Bank and Al Rajhi Bank, alongside Alinma Bank, actively compete for customer acquisition and market dominance across a wide array of financial products and services. This vigorous competition directly impacts pricing and service offerings.
Banks are locked in an intense digital transformation race, pouring significant capital into areas like artificial intelligence, open banking, and advanced mobile platforms. This competition is fueled by the growing demand from a digitally-savvy customer base and the imperative to boost both customer satisfaction and internal efficiency. For instance, by the end of 2023, many major banks reported substantial increases in their IT budgets, with some allocating over 15% of their operating expenses to digital initiatives, reflecting the high stakes involved in this ongoing innovation battle.
Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 is a powerful engine for growth, driving substantial infrastructure and economic diversification projects. This creates a fertile ground for banks like Alinma to expand their corporate lending and project financing portfolios, a key opportunity for revenue generation.
However, this very growth intensifies competitive rivalry. Banks are vying fiercely for these large-scale financing deals, which often involve complex structures and substantial capital commitments. For instance, the Public Investment Fund (PIF) alone managed assets worth over $700 billion as of early 2024, highlighting the scale of projects available and the competition to finance them.
Focus on Sharia-Compliant Offerings
Alinma Bank operates within a competitive landscape where its focus on Sharia-compliant offerings places it directly against other fully Islamic banks and conventional banks with Islamic windows. This segment is particularly dynamic as institutions vie to attract a growing customer base seeking Halal financial solutions. The Saudi Arabian Islamic finance market is projected for substantial growth, intensifying this rivalry.
The competitive rivalry within the Sharia-compliant banking sector is robust. Alinma Bank must differentiate itself by offering superior products and services that meet the stringent requirements of Islamic finance. The drive to capture market share in this expanding niche means constant innovation and customer-centric strategies are essential for sustained success.
- Market Share Dynamics: While specific market share data for exclusively Sharia-compliant banks versus Islamic windows can fluctuate, the overall Islamic banking sector in Saudi Arabia is a significant and growing portion of the financial industry.
- Asset Growth: Reports indicate a strong upward trend in Islamic finance assets globally and within Saudi Arabia, suggesting a fertile ground for competition but also highlighting the increasing number of players entering or expanding their Sharia-compliant services. For instance, the Islamic finance industry globally was valued in the trillions of dollars and continues its expansion trajectory.
- Product Innovation: Competition often centers on the breadth and attractiveness of Sharia-compliant products, including financing, investments, and wealth management solutions, pushing banks like Alinma to continually refine their offerings.
Pressure on Profit Margins and Service Differentiation
The banking sector, including Alinma Bank, faces intense pressure on profit margins. This is driven by the need to remain competitive through pricing strategies and the continuous introduction of new products and services. For instance, in 2024, Saudi banks generally saw net interest margins (NIMs) fluctuate due to changes in benchmark interest rates, requiring careful management to sustain profitability.
To counter this, Alinma Bank, like its peers, must focus on differentiating its services and enhancing the customer experience. This involves not just offering competitive rates but also investing in digital transformation, personalized banking solutions, and superior customer support. Banks that excel in these areas can command better pricing power and foster customer loyalty, thereby mitigating margin compression.
- Margin Pressure: Intense competition forces banks to offer competitive pricing, squeezing profit margins.
- Revenue Diversification: Banks are compelled to explore new revenue streams beyond traditional lending.
- Service Differentiation: Offering unique customer experiences and innovative products is crucial for customer retention.
- Efficiency Gains: Operational efficiency becomes paramount to maintain profitability in a competitive landscape.
Alinma Bank faces significant competitive rivalry from both large domestic banks like Saudi National Bank and Al Rajhi Bank, as well as international players. This competition is particularly fierce in the digital transformation space, with banks investing heavily in AI and mobile platforms to attract a growing digitally-savvy customer base. The Saudi banking sector saw a notable increase in digital service adoption throughout 2023, with many banks reporting over 15% of their operating expenses allocated to these initiatives.
The drive to finance Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 projects, with entities like the Public Investment Fund managing over $700 billion in assets as of early 2024, intensifies rivalry for lucrative corporate lending opportunities. Alinma Bank also competes within the dynamic Sharia-compliant banking sector against both fully Islamic banks and conventional banks with Islamic windows, pushing for product innovation and superior customer experience to capture market share in this expanding niche.
Intense competition inevitably puts pressure on profit margins, forcing banks like Alinma to focus on service differentiation and operational efficiency to maintain profitability. For instance, Saudi banks generally experienced fluctuating net interest margins in 2024 due to evolving benchmark interest rates, underscoring the need for strategic pricing and customer retention efforts.
| Competitor | Key Competitive Factor | Digital Investment (Est. % of OpEx) | Sharia-Compliant Offerings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi National Bank | Market Share, Digital Services | 15%+ | Yes (Islamic Window) |
| Al Rajhi Bank | Dominant Islamic Bank | 15%+ | Primary Focus |
| Other International Banks | Global Expertise, Niche Products | Varies | Varies |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of fintech payment solutions presents a substantial threat to Alinma Bank's traditional payment services. Digital wallets, mobile payment apps, and online platforms from fintech firms offer streamlined, often cheaper alternatives to established methods like bank transfers and card payments. This shift can erode Alinma's transaction volumes and fee-based revenue streams.
The rise of non-bank financial institutions, including those offering Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) and debt-based crowdfunding, presents a significant threat of substitution for Alinma Bank. These entities often cater to specific market segments with tailored, digitally-native products, directly competing with traditional lending and credit offerings.
In 2024, the global BNPL market was projected to reach over $3.5 trillion by 2030, indicating a substantial shift in consumer credit preferences. This growth means more customers may opt for these alternative financing methods rather than conventional bank loans, directly impacting Alinma Bank's market share in consumer and small business lending.
Direct investment and crowdfunding platforms present a significant threat by offering alternative channels for capital raising and wealth management. These digital avenues allow businesses to bypass traditional banking services for financing and individuals to manage their investments without relying solely on Alinma Bank's offerings. For instance, the global crowdfunding market was projected to reach over $200 billion by 2024, indicating a substantial shift in how capital is accessed and deployed.
Alternative Lending and Peer-to-Peer Models
Alternative lending platforms, including peer-to-peer (P2P) models, present a growing threat to traditional banks like Alinma Bank. These platforms offer a direct substitute for conventional bank loans, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and individuals needing faster access to capital. For instance, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a shift in borrowing preferences.
These alternative financing channels are gaining momentum, potentially diminishing the dependence on established banking institutions for credit. By leveraging technology, P2P platforms can often provide more streamlined application processes and quicker fund disbursement compared to traditional banks. This can be particularly attractive in fast-paced business environments.
- Market Growth: The P2P lending market's substantial growth signifies increasing consumer and business acceptance of non-traditional financing.
- Efficiency Advantage: Alternative lenders often boast faster approval times and more flexible terms, appealing to borrowers seeking immediate solutions.
- Diversification of Funding: The rise of these platforms diversifies funding sources, offering businesses more options beyond traditional bank loans.
- Technological Disruption: Fintech innovations in alternative lending challenge established banking models by offering user-friendly digital experiences.
Potential for Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
The potential introduction of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) represents a significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services. While Saudi Arabia is still in the exploratory stages, the eventual rollout of a CBDC could offer an alternative to bank deposits and payment processing. SAMA's involvement in projects like mBridge highlights a forward-looking approach to digital currencies, indicating a possible future where CBDCs directly compete with commercial bank offerings.
This shift could impact Alinma Bank by potentially drawing deposits away from commercial banks and altering transaction flows. For instance, if a CBDC offers greater efficiency or lower transaction costs for certain payments, it could disintermediate traditional banking channels.
- CBDC Development: Saudi Arabia is actively exploring CBDC possibilities, with SAMA participating in international initiatives like the mBridge project, which focuses on wholesale CBDCs for cross-border payments.
- Potential Impact on Deposits: A retail CBDC could offer consumers a direct alternative to holding funds in commercial bank accounts, potentially affecting deposit bases.
- Payment System Disruption: CBDCs could streamline payment processes, potentially bypassing traditional bank infrastructure and reducing reliance on existing payment networks.
The increasing adoption of digital payment solutions by non-bank entities presents a clear substitute threat to Alinma Bank's core payment services. Fintech companies are rapidly innovating in areas like mobile wallets and online payment gateways, offering convenience and often lower transaction fees. This directly challenges Alinma's revenue from traditional payment processing.
Alternative lending platforms, including peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services, are also significant substitutes. These platforms cater to specific borrower needs with speed and flexibility that traditional banking can sometimes struggle to match. For example, the global BNPL market was projected to exceed $3.5 trillion by 2030, highlighting a substantial shift in consumer credit preferences away from traditional bank loans.
| Substitute Type | Description | Market Indicator (2024/Projected) | Impact on Alinma Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Payment Solutions | Digital wallets, mobile payment apps | Rapid growth in digital transaction volumes | Erosion of transaction fees, reduced payment processing revenue |
| Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) | Point-of-sale installment credit | Global market projected > $3.5 trillion by 2030 | Loss of market share in consumer and SME lending |
| Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending | Direct lending between individuals/businesses | Global market valued ~$50 billion in 2023, with significant growth | Reduced demand for traditional bank loans, especially for SMEs |
| Crowdfunding Platforms | Online capital raising for businesses and projects | Global market projected > $200 billion in 2024 | Bypassing traditional bank financing for businesses, alternative investment channels for individuals |
Entrants Threaten
The Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) imposes stringent regulatory requirements and licensing procedures, creating a substantial hurdle for any new bank aiming to enter the market. This robust framework is designed to safeguard financial stability and protect consumers, making it considerably difficult for emerging players to establish themselves.
The ongoing development and proposed new Banking Law underscore SAMA's commitment to maintaining a stable and growing financial sector, further reinforcing these entry barriers. For instance, in 2024, SAMA continued its proactive approach to financial sector oversight, issuing updated guidelines for digital banking services, which new entrants would need to meticulously adhere to, adding to the compliance burden.
The threat of new entrants for Alinma Bank is significantly mitigated by the high capital investment and infrastructure costs required to establish a full-fledged banking operation. Even a digital-first bank needs substantial funding for advanced technology, robust security measures, and regulatory compliance, creating a considerable barrier.
Established banks like Alinma Bank benefit from significant brand loyalty and deep-seated customer trust, cultivated over years of operation. For instance, Alinma Bank serves a substantial customer base of 5.8 million individuals, a testament to its established presence and reliability in the Saudi Arabian financial landscape. New entrants must overcome the considerable challenge of replicating this trust and loyalty, which is paramount for success in the banking industry.
SAMA's Support for Digital-Only Banks
The Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) has been instrumental in encouraging new digital-only banks, like D360 Bank, to enter the market. This initiative aims to boost innovation and competition within the banking sector. These new entrants, while currently limited in number, pose a significant threat to incumbent institutions by offering modern, mobile-centric banking services.
These digital challengers can attract customers with lower fees and more user-friendly interfaces. For instance, the increasing adoption of digital banking services in Saudi Arabia, with mobile banking penetration reaching over 70% by early 2024, underscores the appeal of these new models. Established banks like Alinma must adapt to maintain their market share against these agile competitors.
- Regulatory Facilitation: SAMA's proactive stance supports new digital banks, lowering entry barriers.
- Agile Competitors: Digital-only banks offer streamlined, mobile-first experiences, challenging traditional models.
- Market Impact: Increased digital banking adoption (over 70% mobile penetration in KSA by early 2024) highlights the threat.
- Strategic Imperative: Incumbents need to innovate to retain customers against these leaner, tech-focused rivals.
Fintech Companies Evolving into Banks
Fintech companies, once content with specialized services, are increasingly obtaining banking licenses, transforming into formidable new entrants. This evolution allows them to offer a full suite of financial products, directly challenging established institutions like Alinma Bank.
Saudi Arabia's Monetary Authority (SAMA) has actively fostered this shift through its regulatory sandbox. By licensing numerous fintech firms, SAMA has paved the way for these innovators to become direct competitors, blurring the lines between technology providers and traditional banks.
- Growing Fintech Landscape: As of early 2024, SAMA has granted licenses to over 30 fintech companies, covering various segments like payments, lending, and digital banking.
- Expansion of Services: Many licensed fintechs are moving beyond their initial niche to offer services traditionally dominated by banks, such as account management and credit facilities.
- Competitive Pressure: This trend intensifies competition, potentially impacting Alinma Bank's market share and profitability as customers adopt these new, often more agile, digital banking alternatives.
The threat of new entrants for Alinma Bank is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and stringent regulatory oversight by the Saudi Central Bank (SAMA). While SAMA's initiatives encourage digital banking innovation, established trust and brand loyalty, evidenced by Alinma Bank's 5.8 million individual customers, act as significant deterrents for newcomers. However, the increasing number of licensed fintech companies, over 30 as of early 2024, evolving into full-service banks, presents a growing challenge.
| Factor | Impact on Alinma Bank | Supporting Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High Barrier | Establishing a full-service bank requires substantial investment in technology, infrastructure, and compliance. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | High Barrier | SAMA's licensing procedures and ongoing updates, like digital banking guidelines in 2024, create complexity for new entrants. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Mitigating Factor | Alinma Bank serves 5.8 million individual customers, indicating strong existing customer relationships. |
| Fintech Evolution | Emerging Threat | Over 30 fintechs licensed by SAMA as of early 2024 are expanding services, directly competing with traditional banks. |
| Digital Adoption | Competitive Landscape | Over 70% mobile banking penetration in KSA by early 2024 highlights the appeal and potential reach of digital-first competitors. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Alinma Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of verified data, including Alinma Bank's annual reports, publicly available financial statements, and industry-specific publications from reputable financial news outlets and research firms. We also incorporate data from Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) regulatory filings and relevant economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
