Gallagher Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Gallagher Bundle
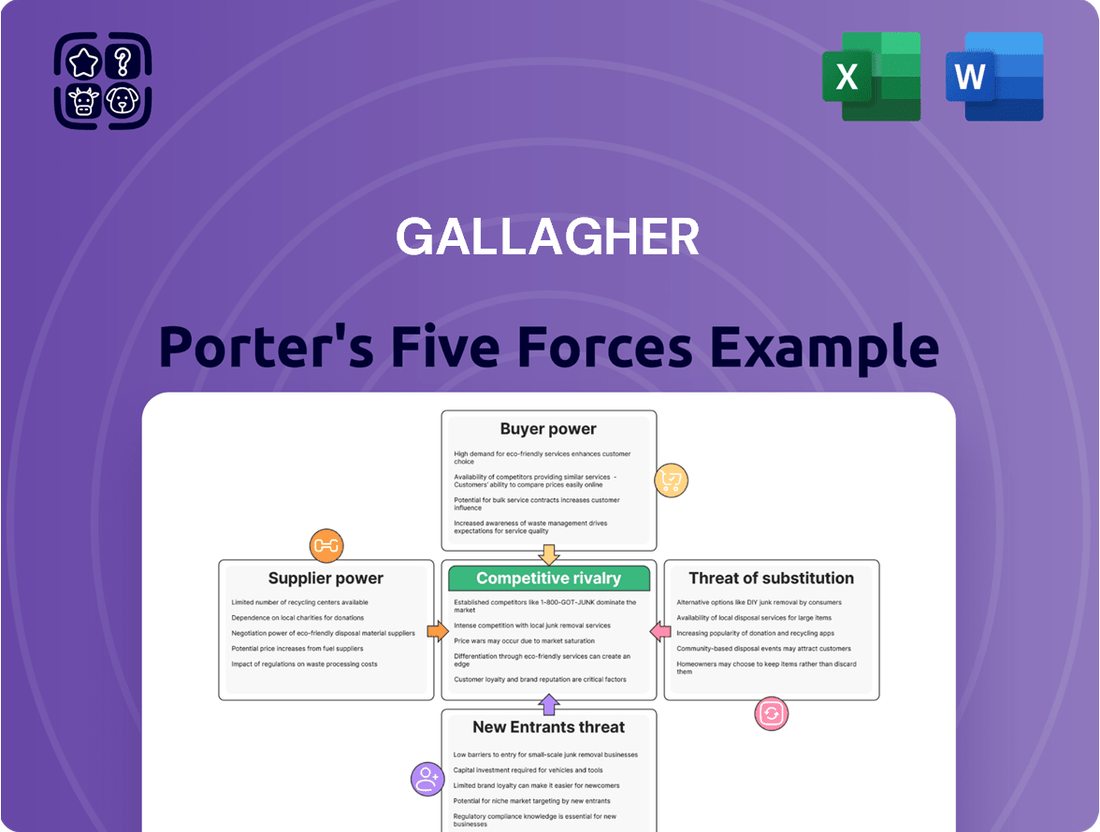
Gallagher's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces: the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these forces is crucial for any business aiming to thrive in their market.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Gallagher’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, empowering you to make informed decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The insurance industry's structure, with a limited number of large, global carriers dominating the market, significantly impacts supplier power. These major players underwrite the bulk of commercial insurance policies, meaning they hold substantial sway over the products and capacity available.
For brokers like Gallagher, this concentration means these carriers possess considerable leverage. They control the essential underwriting capacity that Gallagher requires to serve its wide array of clients, giving them a strong negotiating position.
In 2024, the top 10 global insurance carriers, by gross written premiums, controlled a significant portion of the market, demonstrating this concentration. For example, companies like UnitedHealth Group, Ping An Insurance, and AXA consistently rank among the largest, highlighting the limited number of dominant suppliers in the insurance landscape.
For highly specialized or unique risks, the number of insurance carriers possessing the necessary underwriting expertise and capacity is significantly restricted. This scarcity naturally elevates the bargaining power of these niche carriers. Gallagher relies on these specialized providers to craft tailored solutions for complex client needs across diverse sectors.
While insurance carriers hold significant sway, their reliance on global brokers like Gallagher for reaching clients, especially in specialized insurance sectors, is substantial. Gallagher's vast network and established client connections can diminish a single carrier's individual leverage, as losing access to this distribution channel would directly affect their premium volumes.
Technology and Data Providers
Technology and data providers are becoming increasingly crucial for Gallagher's operations and client service. Companies offering advanced platforms, sophisticated analytics, and risk modeling software hold significant sway if their solutions are proprietary or deeply integrated with few alternatives, potentially impacting Gallagher's digital transformation investments.
The reliance on specialized technology means suppliers with unique, hard-to-replicate offerings can exert considerable influence. For instance, in 2024, the global market for big data and business analytics software was projected to reach over $300 billion, highlighting the intense demand and value placed on such tools.
- High Switching Costs: Implementing new technology platforms often involves substantial costs and operational disruption, making it difficult for Gallagher to switch providers.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers with unique, patented software or algorithms have a distinct advantage, as these cannot be easily replicated by competitors.
- Limited Number of Suppliers: In niche areas of advanced analytics or specialized risk modeling, the pool of qualified providers might be small, concentrating power among a few key players.
- Impact on Innovation: Gallagher's ability to innovate and maintain a competitive edge is directly tied to the capabilities of its technology partners, giving these suppliers leverage.
Human Capital and Talent
Highly skilled insurance professionals, such as expert brokers, risk consultants, and claims specialists, are crucial suppliers of intellectual capital and expertise to Gallagher. The intense competition for top talent, particularly those possessing deep industry knowledge and strong client relationships, significantly bolsters their bargaining power. This dynamic necessitates competitive compensation packages and robust career development programs to attract and retain these vital individuals.
The talent market in the insurance sector is particularly tight. For instance, as of early 2024, the demand for experienced insurance underwriters outpaced supply by a considerable margin, leading to salary increases of up to 15% for specialized roles. This scarcity directly translates to increased bargaining power for these professionals, as companies like Gallagher must offer more attractive terms to secure their services.
- Talent Scarcity: Shortages in specialized insurance roles empower professionals.
- Industry Expertise: Deep knowledge and client relationships are key bargaining chips.
- Compensation Demands: Competitive pay and benefits are essential to attract and retain talent.
- Career Development: Opportunities for growth and advancement are critical in retaining skilled professionals.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the insurance industry is significantly influenced by the concentration of large, global carriers who control underwriting capacity. For brokers like Gallagher, this means these dominant carriers have considerable leverage in negotiations. The limited number of specialized carriers for unique risks further amplifies their power, as Gallagher relies on them for tailored solutions.
Technology and data providers are also key suppliers, with proprietary or deeply integrated solutions giving them leverage. The high switching costs associated with new technology platforms and the scarcity of specialized talent in the insurance sector, with demand outstripping supply for roles like underwriters, further empower these suppliers. For example, in early 2024, experienced underwriter salaries saw increases of up to 15% due to this talent shortage.
| Supplier Type | Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Gallagher |
|---|---|---|
| Insurance Carriers | Market concentration, underwriting capacity control, specialization | Limited options for capacity, negotiation leverage for terms |
| Technology Providers | Proprietary solutions, high switching costs, integration dependency | Influence on digital transformation, potential cost increases |
| Skilled Professionals | Talent scarcity, specialized expertise, client relationships | Increased compensation demands, retention challenges |
What is included in the product
This analysis examines the five competitive forces shaping Gallagher's industry, providing insights into rivalry, new entrants, buyer power, supplier power, and substitute products.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual representation of all five forces, streamlining strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative brokers. Arthur J. Gallagher & Co. operates in a market where clients have access to a vast array of global, national, and niche insurance brokers. This abundance of choices allows clients to readily compare offerings, leading to increased price sensitivity and a demand for better service and coverage. For instance, in 2024, the insurance brokerage market continued to be highly competitive, with numerous independent and network-affiliated firms vying for market share, putting pressure on established players like Gallagher to offer competitive terms.
For many standardized insurance products and basic brokerage services, the financial and operational hurdles for clients to switch providers are quite minimal. This ease of movement means customers can readily shop around for better deals. For instance, in the U.S. personal lines insurance market, direct-to-consumer channels have seen significant growth, indicating a customer willingness to switch for price advantages, with online quote comparison tools readily available.
For large clients in property and casualty insurance or employee benefits, price sensitivity is a significant factor. These substantial buyers can use their considerable premium volumes to negotiate more competitive rates and better terms, directly impacting Gallagher's commission and service fee structures.
Client Size and Sophistication
Large corporate clients, particularly those with intricate risk exposures, often maintain dedicated, expert risk management departments. These sophisticated buyers possess significant leverage, frequently engaging in direct negotiations with insurers and demanding customized solutions and competitive pricing from brokers like Gallagher. This heightened expertise and direct engagement amplify their bargaining power.
For instance, in 2024, large enterprises continued to consolidate their insurance purchasing, seeking fewer, more strategic broker relationships. This trend means that a smaller number of very large clients can exert disproportionate influence over broker commission structures and service level agreements.
- Client Sophistication: Clients with in-house risk management teams are more informed about market conditions and pricing, enabling them to negotiate more effectively.
- Negotiating Leverage: Large clients can leverage their premium volume and complexity to demand tailored policies and concessions from brokers.
- Direct Engagement: The ability of major clients to bypass intermediaries and negotiate directly with carriers further strengthens their position.
Importance of Value-Added Services
Value-added services significantly bolster Gallagher's bargaining power with customers. While core insurance brokerage might become commoditized, Gallagher’s expertise in specialized risk management consulting, alongside advanced data analytics and streamlined third-party claims administration, creates a sticky client relationship. This comprehensive offering makes clients less likely to switch providers, thereby reducing their bargaining power.
For instance, Gallagher's investment in digital platforms and data analytics, as seen in their 2024 initiatives to enhance client insights, directly addresses evolving client needs. By providing services that go beyond basic insurance placement, Gallagher deepens client reliance.
- Specialized Risk Management: Gallagher offers tailored risk consulting, reducing client vulnerability and increasing dependence on their expertise.
- Advanced Analytics: Data-driven insights provided by Gallagher help clients optimize their risk exposure and insurance spend, making switching costly.
- Third-Party Claims Administration: Efficient and expert claims handling by Gallagher ensures client satisfaction and loyalty, diminishing their leverage.
The bargaining power of customers in the insurance brokerage sector, particularly for a firm like Arthur J. Gallagher & Co., is a critical factor in profitability. When customers have many choices or can easily switch, their ability to negotiate lower prices or demand better terms increases significantly. This is especially true for standardized products where differentiation is minimal.
In 2024, the insurance market continued to see a rise in direct-to-consumer models and online comparison tools, empowering individual and small business clients. For larger corporate clients, their substantial premium volumes provide considerable leverage. For example, a large client placing hundreds of millions in premiums can negotiate lower commission rates, directly impacting a broker's revenue.
Gallagher's ability to offer specialized, value-added services, such as sophisticated risk management consulting and data analytics, helps to mitigate this customer power. By embedding its expertise deeply into a client's operations, Gallagher can create stickiness and reduce the client's incentive or ability to switch, thereby strengthening its own negotiating position.
| Factor Influencing Customer Bargaining Power | Impact on Gallagher | 2024 Market Trend Example |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | High; increases price sensitivity and demand for better terms. | Continued growth of independent brokers and InsurTech platforms offering competitive pricing. |
| Switching Costs | Low for basic services; higher for integrated, value-added solutions. | Clients seeking integrated risk management solutions showed lower willingness to switch. |
| Client Sophistication & Size | High for large clients with in-house expertise; can leverage volume. | Large enterprises continued to consolidate broker relationships for better terms. |
| Value-Added Services | Lowers bargaining power by increasing client dependence and reducing perceived alternatives. | Gallagher's investment in data analytics and specialized consulting enhanced client retention. |
Full Version Awaits
Gallagher Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Gallagher Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive forces within an industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing sections. You're looking at the actual deliverable, ready for your immediate use and strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Gallagher, like many in the insurance brokerage and risk management sector, faces significant competitive pressure from global giants such as Marsh & McLennan, Aon, and Willis Towers Watson. These established players command substantial market share and possess extensive resources and global reach, making the competitive landscape particularly intense.
In 2024, the industry continues to see these large competitors leverage their scale and integrated service offerings to vie for market dominance. For instance, Marsh McLennan reported revenues exceeding $20 billion in 2023, highlighting the financial muscle available to these global leaders in their pursuit of new business and client retention.
Operating in a mature market, like many segments of the insurance brokerage industry, presents a significant hurdle for organic growth. This maturity means that most potential clients are already served, forcing companies to intensely battle for existing customer loyalty and to capture new business from rivals. In 2024, this dynamic is particularly evident as firms invest heavily in digital transformation and specialized expertise to differentiate themselves and secure a larger share of a relatively stable market.
While core brokerage services might seem alike, companies actively differentiate themselves. This is achieved through deep expertise in specific industries, cutting-edge digital tools, exceptional client support, and robust risk advisory. For instance, in 2024, many insurance brokers invested heavily in AI-powered analytics to offer more personalized risk assessments, a key differentiator.
The capacity to present a distinct and customized value proposition is vital for drawing in and keeping clients within a highly competitive arena. Firms that successfully highlight their unique strengths, like specialized underwriting capabilities or advanced claims management technology, often see stronger client retention rates.
Acquisition as a Growth Strategy
The insurance brokerage industry is marked by significant consolidation, with established firms like Gallagher frequently engaging in mergers and acquisitions. This strategy is a key growth lever, enabling companies to broaden their market presence and service offerings.
This ongoing M&A activity directly fuels competitive rivalry. As larger entities absorb smaller ones, the market becomes more concentrated, and the remaining independent or smaller firms face increased pressure to compete or become acquisition targets themselves. For instance, Gallagher's own acquisition history demonstrates this trend, with numerous deals completed annually to bolster its market position.
- Gallagher's M&A Activity: Gallagher has consistently been a top acquirer in the insurance brokerage space, with a reported 40+ acquisitions in 2023 alone, demonstrating its aggressive pursuit of growth through consolidation.
- Industry Consolidation Trend: The broader insurance brokerage market saw significant M&A volume in 2023, with deal values reaching billions, indicating a strong industry-wide push towards consolidation.
- Impact on Competition: Increased M&A activity intensifies rivalry by creating larger, more dominant players, forcing smaller competitors to innovate or seek strategic partnerships to remain competitive.
Talent Competition and Client Relationships
The competition for skilled professionals is intense, as clients often form strong bonds with specific brokers and consultants. This means that a firm's success is heavily reliant on the expertise and client relationships of its people. Companies actively seek out experienced individuals who bring established client portfolios and specialized knowledge, using competitive compensation and career advancement to attract this vital human capital.
This talent war directly impacts client retention and acquisition. For instance, in the insurance brokerage sector, a significant portion of client loyalty is built on trust in individual advisors. When a top performer moves, they often take a substantial book of business with them. Gallagher, a major player, has historically focused on acquiring smaller, specialized firms to gain both talent and client bases. In 2024, the industry continued to see high demand for professionals with expertise in areas like cyber insurance and employee benefits, driving up recruitment costs.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: Firms are investing heavily in recruitment, with signing bonuses and relocation packages becoming commonplace for experienced brokers.
- Client Churn Risk: The departure of key personnel can lead to significant client attrition, impacting revenue streams.
- Industry Specialization: Demand for niche expertise, such as in complex risk management or specific industry verticals, intensifies competition for specialized talent.
Competitive rivalry within the insurance brokerage sector is fierce, driven by large global players like Marsh McLennan and Aon, who wield significant market share and resources. In 2024, this intensity is amplified as companies battle for existing clients and new business in a mature market, often through digital innovation and specialized expertise.
Differentiation is key, with firms emphasizing industry-specific knowledge, advanced technology, and superior client service to stand out. Gallagher's own strategy includes aggressive merger and acquisition activity, acquiring over 40 firms in 2023 alone, which consolidates the market and heightens competition for remaining independent entities.
The competition for top talent is also a critical factor, as client relationships are often built on individual broker expertise. The departure of key personnel can lead to substantial client loss, making talent acquisition and retention a strategic imperative, especially for specialized skills in areas like cyber insurance.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Competitive Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Marsh McLennan | $20+ billion | Scale, integrated services, global reach |
| Aon | $12+ billion | Risk capital and human capital expertise, digital solutions |
| Willis Towers Watson | $9+ billion | Specialized advisory, data analytics, global network |
| Arthur J. Gallagher & Co. | $8+ billion | Acquisitions, niche specialization, client relationship focus |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Clients, especially larger businesses, might bypass brokers and buy insurance directly from carriers for simpler or standardized policies. This trend is fueled by the growing digitalization of insurance, making it easier for clients to engage directly with providers.
The rise of direct-to-consumer platforms by some insurers presents a viable substitute. For instance, in 2024, several major carriers expanded their digital offerings, reporting a 15% increase in direct policy sales for small to medium-sized businesses.
For companies with robust financial health and unique risk exposures, the option to self-insure or create a captive insurance entity presents a significant alternative to relying on traditional commercial insurance. This strategy offers enhanced command over how risks are financed, how claims are handled, and the potential to retain underwriting profits.
In 2024, the global captive insurance market continued its growth trajectory, with industry reports indicating a steady increase in the formation of new captives and a rise in gross written premiums. This trend reflects a growing appetite among larger corporations to manage their insurance costs and tailor coverage more precisely to their specific operational needs, thereby reducing reliance on external brokers.
Large corporations often possess extensive in-house risk management teams. These departments are capable of managing a substantial portion of risk identification, assessment, and mitigation internally, lessening the need for external expertise for many functions.
This internal capacity acts as a substitute for external risk management services. For example, a company like Berkshire Hathaway, with its vast internal resources and actuarial talent, might handle a significant amount of its risk assessment and strategy development without relying heavily on external brokers for these specific advisory roles.
Technology-Driven Risk Solutions
The rise of InsurTech and other technology platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional brokerage services. These solutions offer automated risk assessment, advanced compliance management, and direct policy placement, potentially bypassing intermediaries.
For instance, in 2024, InsurTech startups continued to attract substantial venture capital, with over $10 billion invested globally in the first half of the year, signaling a strong push towards digital-first insurance solutions. These platforms can streamline processes that previously required broker intervention.
- Automated Risk Assessment: AI-powered tools can now evaluate risks with high accuracy, reducing the need for manual underwriting support traditionally offered by brokers.
- Compliance Management Software: Digital solutions provide automated tracking and adherence to regulatory requirements, a service brokers often facilitate.
- Direct Policy Placement: Online marketplaces and platforms allow businesses and individuals to secure insurance policies directly, bypassing the advisory role of a broker for simpler needs.
- Cost Efficiency: Technology-driven solutions often operate at lower overheads, potentially offering more competitive pricing for specific insurance products.
Alternative Risk Transfer Mechanisms
Clients are increasingly looking beyond traditional insurance, exploring alternative risk transfer (ART) mechanisms. These can include finite risk solutions and catastrophe bonds, which tap into capital markets for coverage. For instance, the catastrophe bond market saw significant issuance in 2023, reaching an estimated $15 billion, demonstrating a growing appetite for these instruments as substitutes for traditional reinsurance.
These sophisticated financial tools can effectively bypass the need for conventional insurance brokers. By directly accessing capital markets, businesses can secure coverage for specific risks, potentially at a more competitive price point than what might be offered through standard insurance policies. This trend suggests a shift in how certain risks are managed and financed.
- Finite Risk Solutions: Offer long-term risk financing with a focus on risk retention and investment returns.
- Catastrophe Bonds: Transfer specific catastrophic risks to capital market investors, providing a payout if a predefined event occurs.
- Capital Market Instruments: A broad category including various securitized insurance products and derivatives used for risk transfer.
- Market Growth: The ART market continues to expand, with total capital in the ILS (Insurance-Linked Securities) market reaching approximately $100 billion by the end of 2023.
The threat of substitutes for insurance brokers is multifaceted, encompassing direct purchasing, self-insurance, and alternative risk transfer mechanisms. Digitalization and InsurTech platforms are key drivers, enabling clients to bypass traditional intermediaries for simpler needs. For instance, in 2024, InsurTech startups secured over $10 billion in global venture capital, highlighting the growing demand for digital-first insurance solutions.
Larger corporations, with robust in-house risk management teams, are increasingly opting to self-insure or form captive insurance entities. This trend is supported by the continued growth of the captive insurance market, with a steady rise in new formations and gross written premiums reported in 2024. These companies can manage risks internally, reducing their reliance on external brokerage services.
Sophisticated financial tools like catastrophe bonds and finite risk solutions offer alternative risk transfer (ART) options. These tap into capital markets, allowing businesses to secure coverage directly, potentially at more competitive prices. The catastrophe bond market, for example, saw significant issuance in 2023, reaching an estimated $15 billion, underscoring the appeal of these capital market instruments.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2024/2023 Trend/Data | Impact on Brokers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-to-Consumer Platforms | Insurers offering policies directly online. | 15% increase in direct policy sales for SMBs (2024). | Reduces need for broker advice on standard policies. |
| Self-Insurance/Captives | Companies managing their own risk financing. | Continued growth in captive market formation and premiums (2024). | Bypasses brokers for risk management and placement. |
| Alternative Risk Transfer (ART) | Capital market instruments like catastrophe bonds. | $15 billion estimated catastrophe bond issuance (2023). | Offers direct access to risk financing, bypassing intermediaries. |
| InsurTech Solutions | Automated risk assessment, compliance, direct placement. | >$10 billion venture capital invested in InsurTech (H1 2024). | Streamlines processes previously handled by brokers. |
Entrants Threaten
High regulatory barriers significantly deter new entrants in the insurance brokerage sector. Operating legally requires extensive licensing, adherence to complex compliance frameworks, and meeting specific capital requirements. For instance, in 2024, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) continued to emphasize stringent solvency and consumer protection regulations across U.S. states, making it costly and time-consuming for newcomers to establish a compliant and competitive presence.
Establishing a global insurance brokerage and risk management firm, akin to Gallagher, requires immense capital for sophisticated technology, a widespread operational network, and a skilled workforce. For instance, in 2024, the global insurance market continues to see significant investment in digital transformation, with many firms allocating billions to upgrade their platforms and data analytics capabilities. This high capital threshold acts as a major deterrent for potential new entrants who may not possess the necessary financial resources.
In the insurance and risk management world, trust and a solid reputation are everything. Clients stick with companies they know and believe in, making it incredibly tough for newcomers to break in. Gallagher, for instance, has spent decades building relationships and proving its worth, a feat that takes years, if not generations, to replicate.
New entrants struggle to overcome the high barriers to entry related to brand reputation and client loyalty. Established firms like Gallagher benefit from long-standing trust, making it difficult for new players to attract clients who prioritize reliability and proven expertise. This deep-rooted client relationship is a significant deterrent to new competition.
Access to Carrier Relationships
Access to carrier relationships is a significant barrier for new insurance brokers. Established firms leverage decades of trust and volume to negotiate favorable terms and access niche products, which newcomers simply cannot replicate overnight. For instance, in 2024, the top 10 insurance brokers in the US collectively placed over $200 billion in premiums, demonstrating the scale of relationships that new entrants would need to build.
- Deep Carrier Ties: Established brokers have cultivated long-term partnerships with numerous insurance carriers.
- Product Access & Pricing: These relationships grant access to a wider product range and more competitive pricing.
- New Entrant Challenge: Building equivalent relationships takes considerable time and effort, hindering new entrants' ability to compete effectively.
Talent Acquisition and Expertise
The insurance brokerage sector is fundamentally a people business, where the deep knowledge, established connections, and adept problem-solving skills of seasoned brokers and consultants are paramount. Newcomers face a substantial hurdle in luring and keeping the best individuals who possess critical industry insights, existing client bases, and demonstrated success.
This reliance on human capital means that any new entrant must invest heavily in recruitment and training, a significant cost and time commitment. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to hire a skilled professional in the financial services sector, which includes insurance, continued to rise, often exceeding $5,000 per hire, reflecting the competitive landscape for talent.
- Human Capital Intensity: Gallagher Porter's success hinges on its brokers' expertise and client relationships.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: New entrants must overcome high recruitment and retention expenses for experienced professionals.
- Industry Experience Premium: The market demands proven track records, making it difficult for inexperienced firms to compete.
- Client Portfolios: Attracting brokers with established client lists is a key barrier to entry, as these relationships represent significant revenue streams.
The threat of new entrants in the insurance brokerage sector is generally low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for technology and operations, coupled with stringent regulatory compliance and licensing, make it difficult and expensive for newcomers to establish a foothold. For example, in 2024, the ongoing investment in digital transformation within the insurance industry, estimated in the billions globally, further elevates the financial hurdle for new players.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and government economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of competitive pressures.
