AGBA Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AGBA Bundle
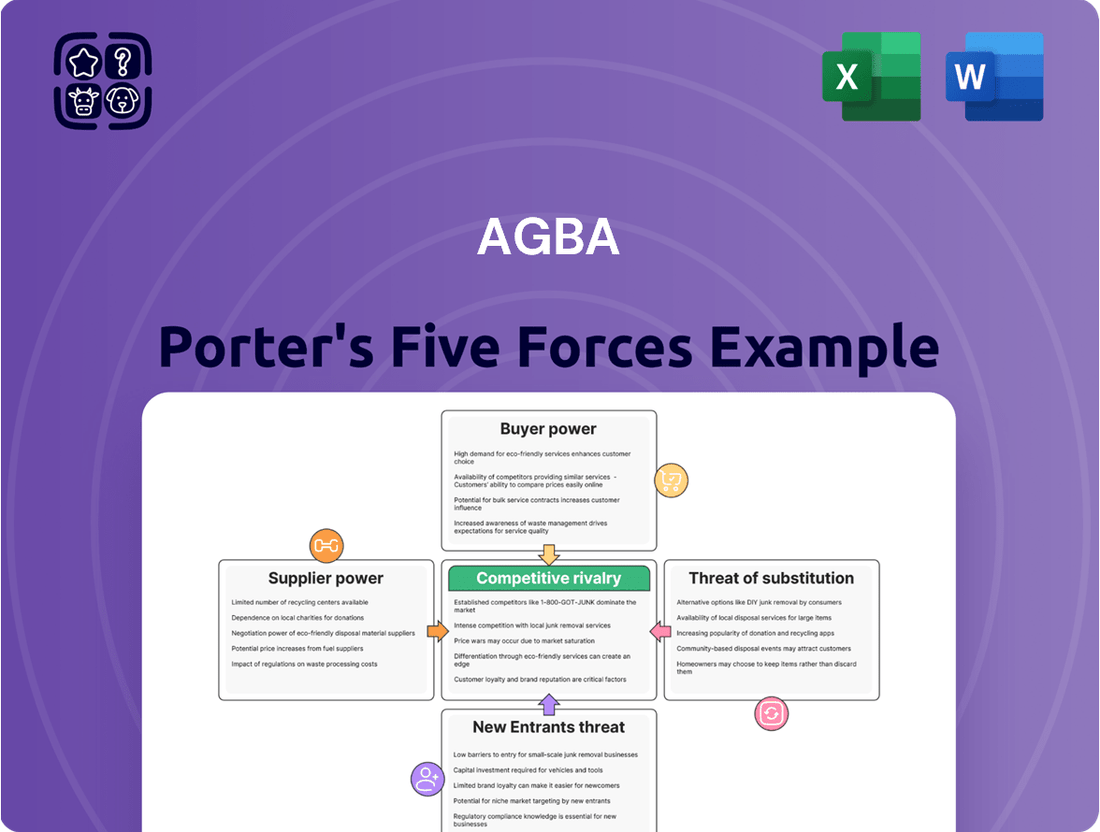
AGBA operates within a dynamic market shaped by several key competitive forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors is crucial for strategic planning. Furthermore, the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers significantly influences AGBA's profitability and operational flexibility. The threat of new entrants and the availability of substitute products also present significant challenges that AGBA must navigate effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore AGBA’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of specialized financial technology, particularly those offering unique AI-driven analytics or advanced cybersecurity for fintech platforms, can exert significant power. AGBA's reliance on cutting-edge technology for its 'financial supermarket' model means that providers of such niche solutions may have higher leverage due to high switching costs or a lack of readily available alternatives. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at over $11 trillion in 2023, with a significant portion driven by specialized technology providers.
The availability of skilled talent, particularly in specialized financial roles, significantly influences supplier bargaining power. In Hong Kong, a competitive market for experienced financial advisors, asset managers, and fintech developers means that a scarcity of these professionals can empower them. If AGBA faces difficulty in attracting and retaining such talent due to high demand or superior offers from competitors, the costs associated with human capital suppliers will likely rise, impacting operational expenses.
AGBA's reliance on data and information providers for its financial services means these suppliers hold significant bargaining power. Real-time market data, financial news feeds, and customer analytics are crucial for AGBA's advisory and asset management operations. For instance, Bloomberg, a major financial data provider, reported revenues of $11.1 billion in 2023, underscoring the market's valuation of such essential information.
Providers with exclusive or highly aggregated datasets can leverage this position to negotiate higher prices or impose stringent terms. This is particularly true for specialized data that is difficult or impossible for AGBA to replicate internally, directly impacting the cost of doing business and the quality of insights AGBA can offer its clients.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Services
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly those providing regulatory compliance and legal services in Hong Kong, is significant for AGBA. These specialized service providers possess unique expertise that AGBA cannot easily replicate, essential for navigating the complex financial and healthcare regulations. For instance, in 2023, Hong Kong's financial sector saw increased scrutiny, with the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) issuing new guidelines on virtual assets, requiring significant adaptation and specialized legal counsel.
Suppliers of regulatory compliance software and legal advisory firms in this region wield substantial influence due to the non-negotiable nature of adherence to stringent rules. AGBA's operations are directly dependent on their ability to meet these legal and compliance requirements. The cost of non-compliance can lead to substantial fines, reputational damage, and operational disruptions, thereby amplifying the suppliers' leverage.
- Specialized Expertise: Suppliers of regulatory compliance software and legal advisory services in Hong Kong possess niche knowledge crucial for AGBA's adherence to financial and healthcare sector rules.
- High Switching Costs: The effort and potential disruption involved in changing providers for critical compliance functions mean AGBA faces high costs if it seeks alternative suppliers.
- Regulatory Dependence: AGBA’s operational continuity is directly tied to meeting Hong Kong’s strict regulatory framework, making compliant suppliers indispensable.
- Sector-Specific Demand: The demand for these specialized services is driven by Hong Kong’s robust financial and healthcare sectors, ensuring a consistent need for expert suppliers.
Cloud Infrastructure and Cybersecurity Vendors
AGBA's reliance on cloud infrastructure and cybersecurity means suppliers in these sectors hold significant bargaining power. The critical nature of these services, coupled with the high costs and complexities of switching providers, creates a strong dependency. For instance, major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the market, making it difficult for AGBA to negotiate substantial concessions without risking service disruption or incurring prohibitive migration expenses. In 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at over $600 billion, highlighting the scale and influence of these providers.
Cybersecurity vendors also wield considerable power, especially given the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. AGBA's need for cutting-edge security solutions to protect sensitive financial data means it must often adopt the offerings of established players. The specialized nature of cybersecurity expertise and the constant evolution of threats limit the availability of viable alternatives, thereby strengthening supplier leverage. The cybersecurity market continued its robust growth in 2024, with spending projected to exceed $270 billion globally.
- High switching costs: Migrating cloud infrastructure and integrated cybersecurity solutions can be extremely expensive and time-consuming for AGBA.
- Concentration of providers: A few dominant players in both cloud services and advanced cybersecurity limit AGBA's options.
- Critical service dependence: AGBA's core operations are directly tied to the reliability and security provided by these vendors.
- Specialized expertise: The unique skills and proprietary technology of cybersecurity firms create barriers to entry for AGBA seeking in-house solutions or alternative vendors.
Suppliers of specialized financial technology and data providers can hold significant sway over AGBA, especially when their offerings are unique or difficult to replicate. This leverage is amplified by the substantial global fintech market, which exceeded $11 trillion in 2023, indicating the high value placed on specialized technology. Similarly, providers of critical data, like Bloomberg with its $11.1 billion in 2023 revenue, demonstrate the indispensable nature of their services, making switching costly for AGBA.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on AGBA |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech Technology Providers | Uniqueness of solutions, high switching costs, limited alternatives | Increased costs for cutting-edge AI and cybersecurity; potential operational reliance |
| Data & Information Providers | Exclusive or aggregated datasets, critical real-time information | Higher data acquisition costs, dependence on provider quality for insights |
| Skilled Financial Talent Suppliers | Scarcity of specialized roles (e.g., fintech developers, advisors) | Increased human capital costs, potential retention challenges |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored specifically to AGBA's unique operating environment.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visually intuitive breakdown of all five forces.
Gain actionable insights into market dynamics, enabling proactive strategies to reduce competitive pressure.
Customers Bargaining Power
The digital age has dramatically amplified customer power, especially concerning information availability and price transparency. AGBA's clients, both individuals and businesses, now have instant access to a wealth of data on financial products, services, and competitor pricing. This empowers them to meticulously compare AGBA's wealth management, healthcare, and fintech solutions against those offered by numerous other providers.
This heightened transparency directly translates into increased bargaining power for AGBA's customers. They can readily identify the most competitive pricing and favorable terms available in the market. For instance, in 2024, online comparison platforms for financial services saw a significant surge in user engagement, with many reporting over a 20% year-over-year increase in traffic as consumers actively sought the best deals.
Consequently, AGBA faces pressure to maintain highly competitive pricing and offer superior value propositions to retain its client base. Customers are less likely to tolerate premium pricing without clear justification, demanding better service, innovative features, or more attractive financial returns. This dynamic necessitates AGBA's continuous focus on operational efficiency and product differentiation to mitigate the impact of this strong customer bargaining power.
Low switching costs for certain services significantly amplify customer bargaining power. For instance, in the fintech sector, a client unhappy with AGBA's platform fees or investment options can often transition to a competitor with minimal hassle. This ease of movement means customers can readily seek better terms or services elsewhere.
Consider that in 2024, the average time for a retail investor to switch brokerage accounts has decreased, with many platforms offering streamlined onboarding processes. This agility directly translates to greater leverage for customers, as they face fewer penalties or complexities in moving their financial assets away from AGBA, should they deem it necessary.
The diverse range of competitors in Hong Kong's financial market significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. AGBA's customers can readily compare offerings from traditional banks, independent financial advisors, numerous fintech platforms, and specialized healthcare providers. This abundance of alternatives forces AGBA to remain highly competitive on pricing, service quality, and product innovation to retain its customer base.
Demand for Personalized and Integrated Solutions
Customers, both individuals and businesses, are increasingly demanding financial and healthcare solutions that are tailored precisely to their unique circumstances. This trend intensifies the bargaining power of customers.
While AGBA aims to be a comprehensive 'one-stop financial supermarket,' its ability to deliver truly personalized and seamlessly integrated experiences is crucial. If AGBA falls short in offering highly customized services or a unified platform, customers possess the leverage to seek out specialized providers or assemble their own tailored packages from various sources.
Consider the growing demand for personalized wealth management. According to a 2024 report, over 65% of affluent individuals surveyed expressed a preference for financial advisors who offer bespoke strategies rather than standardized portfolios. This indicates a clear customer inclination towards customization, which directly impacts AGBA's ability to retain clients if its offerings are perceived as generic.
- Personalization in Financial Services: A 2024 survey revealed that 70% of millennials and Gen Z prioritize personalized financial advice, influencing their choice of providers.
- Integrated Healthcare and Finance: As healthcare costs rise, consumers seek integrated solutions that combine financial planning with health insurance and wellness programs, placing pressure on providers to offer holistic packages.
- Customer Churn due to Lack of Customization: In 2023, an estimated 20% of customer churn in the fintech sector was attributed to a failure to meet personalized service expectations.
- Provider Switching Behavior: Data from 2024 suggests that customers are willing to switch financial institutions if they find better-tailored product bundles or more responsive personalized service elsewhere.
Sensitivity to Performance and Fees
Customers in wealth and asset management services are particularly sensitive to both investment performance and the fees they incur. If AGBA's investment outcomes fall short of expectations or its fee structure is seen as uncompetitive, clients possess significant leverage. This can manifest as direct withdrawal of assets or a shift to rival firms offering better value propositions.
For instance, in 2024, the average expense ratio for actively managed equity mutual funds in the U.S. hovered around 0.67%, while passively managed funds averaged significantly lower at 0.05%. This stark difference highlights customer sensitivity to fees; a client paying notably higher than these benchmarks for comparable AGBA services would feel empowered to seek alternatives.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by their ability to easily switch providers. This is further influenced by transparency in performance reporting and fee disclosures. Clients can readily compare AGBA's track record and cost structure against a wide array of competitors, making informed decisions about where to allocate their capital.
- Performance Scrutiny: Client satisfaction is intrinsically linked to investment returns, with underperformance directly increasing the likelihood of fund outflows.
- Fee Sensitivity: High or uncompetitive fees erode client loyalty and provide a strong impetus for seeking alternative wealth management solutions.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of numerous competing firms with transparent pricing and performance data empowers clients to exert downward pressure on fees and demand better service.
- Data-Driven Decisions: As of mid-2024, investor surveys consistently show that fees and demonstrable performance are the top two factors influencing client retention and acquisition in the asset management sector.
Customers wield significant power due to increased information transparency and readily available comparisons in the financial services sector. In 2024, online financial comparison platforms saw a marked increase in user engagement, with many reporting over a 20% year-over-year growth in traffic as consumers actively sought the best deals.
Low switching costs further empower clients, allowing them to easily move assets to competitors offering better terms or services. For instance, the average time for a retail investor to switch brokerage accounts decreased in 2024, with streamlined onboarding processes facilitating quicker transitions.
The sheer volume of competitors in markets like Hong Kong amplifies customer bargaining power, forcing providers like AGBA to compete intensely on price, service quality, and innovation to retain clients.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Information Transparency | High - Customers can easily compare offerings. | Significant increase in user traffic on financial comparison sites. |
| Switching Costs | High - Minimal barriers to changing providers. | Reduced average time for retail investors to switch brokerage accounts. |
| Competitive Landscape | High - Numerous alternatives available. | Diverse range of fintech, banking, and advisory services in key markets. |
Preview Before You Purchase
AGBA Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete AGBA Porter's Five Forces Analysis, identical to the document you will receive instantly after purchase. You're not seeing a sample; this is the actual, professionally formatted analysis ready for your immediate use. Understand the competitive landscape of AGBA with this comprehensive breakdown of industry rivalry, threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. Invest in this detailed report to gain strategic insights into AGBA's market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Hong Kong's financial landscape is dominated by large, traditional institutions such as HSBC and Standard Chartered. These established banks boast significant capital reserves, extensive physical presences across the city, and deeply ingrained customer trust built over decades. Their comprehensive offerings, from banking to investment products, create a formidable competitive barrier for newer entrants like AGBA.
These traditional giants directly challenge AGBA in the wealth management and financial advisory sectors. They often leverage existing client relationships, offering integrated financial solutions that are hard for specialized firms to replicate. For instance, a customer already holding a mortgage with a major bank might be more inclined to use that same bank for their investment advice, a testament to the power of existing ties.
The competitive rivalry is further intensified by the sheer scale and resources these large banks possess. They can invest heavily in technology, marketing, and talent, allowing them to adapt quickly to market changes and customer demands. This deep pool of resources means they can often afford to offer more competitive pricing or more attractive benefits, putting pressure on AGBA to differentiate itself effectively.
The fintech sector in Hong Kong is buzzing with activity, and many agile startups are shaking things up. These companies are focused on digital solutions, whether it's automated investment advice, online trading platforms, or innovative payment methods. For AGBA, this means facing competition from players who can adapt quickly and cater to specific customer needs.
These smaller, nimble fintech startups often lead the charge in innovation. They introduce new business models and cutting-edge technologies, directly challenging AGBA’s existing fintech services. For instance, by mid-2024, Hong Kong saw a significant increase in digital-only banks and payment providers, many of which are startups that gained traction by offering lower fees and more user-friendly interfaces.
Beyond major banking institutions, AGBA contends with a vibrant landscape of independent wealth management firms and family offices. These entities often differentiate themselves by providing highly personalized client experiences and deep specialization in particular asset classes or investment strategies, directly appealing to high-net-worth individuals seeking tailored solutions.
The competitive edge for these independent players frequently lies in their ability to foster strong client relationships and craft bespoke investment plans, often focusing on niche markets where AGBA’s broader, more generalized approach might be less impactful. This focus on personalized service and specialized expertise presents a distinct challenge to AGBA’s model.
For instance, in 2024, the global independent wealth management sector continued its robust growth, with assets under management (AUM) for independent advisors showing a notable increase. Many of these firms are also increasingly leveraging technology to enhance client engagement and operational efficiency, further intensifying the competitive pressure on larger, more traditional players like AGBA.
Regulatory Environment and Market Maturity
Hong Kong's financial market, characterized by its maturity, fosters intense competitive rivalry. The regulatory environment is stringent, creating a framework within which established firms battle for dominance.
While these regulations act as a barrier for new entrants, they also ensure a level playing field for existing players. This leads to aggressive competition for market share, skilled professionals, and new clients within the established parameters.
- Market Maturity: Hong Kong's financial sector is highly developed, meaning growth opportunities are often incremental rather than transformative, intensifying the fight for existing business.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Strict oversight by bodies like the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) limits disruptive innovation but also standardizes operations, making price and service key differentiators.
- Talent Wars: With a concentrated pool of expertise, competition for top financial talent is fierce, driving up compensation and retention challenges for firms.
- Customer Acquisition: In a saturated market, acquiring and retaining customers requires significant investment in marketing, technology, and customer service, further fueling rivalry.
Differentiation and Technology Adoption
The intensity of competition within the financial services sector, particularly for companies like AGBA, is significantly shaped by how well competitors can differentiate themselves, especially through technology. AGBA's strategic emphasis on technology means its competitive battle isn't just about the range of products offered, but also the seamlessness, innovation, and user-friendliness of its digital interfaces.
This technological arms race compels all market participants to consistently pour resources into upgrades and new digital solutions to maintain their edge. For instance, in 2024, the global fintech market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion, underscoring the massive investment and innovation occurring in this space. Companies are differentiating through AI-powered advisory services, blockchain-based transaction efficiencies, and personalized digital banking experiences.
- Technological Differentiation: Competitors are vying to offer superior digital platforms, enhancing user experience and operational efficiency.
- Investment in Innovation: The need to stay ahead drives continuous investment in R&D for new digital financial tools and services.
- User Experience as a Key Factor: The ease of use and intuitiveness of digital interfaces are becoming critical differentiators in customer acquisition and retention.
- Market Growth: The expanding fintech market, valued in the trillions as of 2024, highlights the significant competitive activity and technological advancement.
Competitive rivalry in Hong Kong's financial sector is fierce, with established giants like HSBC and Standard Chartered leveraging deep customer trust and extensive resources. These incumbents directly challenge AGBA in wealth management, often using existing client relationships to offer integrated solutions that are difficult for specialized firms to match. Their scale allows for significant investments in technology and marketing, enabling them to compete aggressively on price and benefits.
Agile fintech startups also intensify this rivalry by focusing on digital innovation, offering automated advice, online trading, and streamlined payment methods. By mid-2024, the rise of digital-only banks and payment providers, many with lower fees and user-friendly interfaces, demonstrated their ability to quickly gain traction. Furthermore, independent wealth management firms and family offices differentiate through highly personalized service and niche specialization, appealing to high-net-worth individuals and presenting a distinct challenge to AGBA’s broader approach.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | Impact on AGBA |
|---|---|---|
| Large Traditional Banks | Capital reserves, customer trust, extensive offerings | Formidable barrier, direct competition in wealth management |
| Fintech Startups | Agility, digital innovation, user-friendly interfaces | Disruptive, challenge existing services, focus on specific needs |
| Independent Wealth Managers | Personalized service, niche specialization, client relationships | Appeal to HNWIs, tailored solutions, focus on specific asset classes |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers increasingly turn to direct investment platforms and robo-advisors as viable alternatives to traditional wealth management. These digital solutions, often boasting lower expense ratios, attract investors seeking cost-efficiency and a hands-on approach. For instance, the global robo-advisory market was valued at approximately $2.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong shift in consumer preference.
The appeal of these substitutes lies in their accessibility, user-friendly interfaces, and the promise of greater control over investment portfolios. Many tech-savvy individuals find the self-directed nature or algorithm-based guidance of robo-advisors more aligned with their investment styles. This trend presents a direct challenge to firms like AGBA, as it offers a compelling alternative for wealth accumulation and management.
For individuals prioritizing basic financial security, traditional banking products like savings accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs) act as a significant substitute for more complex wealth management services. These options are often perceived as safer and easier to understand, particularly for those new to investing.
In 2024, the appeal of these traditional products remains strong, especially in environments with rising interest rates. For instance, the average interest rate on savings accounts saw an increase throughout the year, making simple deposit accounts more competitive against riskier investments. This accessibility and perceived lower risk can deter individuals from seeking out alternative, potentially higher-yield, wealth management solutions.
Customers might choose self-managed healthcare, bypassing integrated solutions like AGBA's, by utilizing public health services or visiting private clinics directly. This unbundling of services presents a significant threat. For instance, in 2024, many individuals prioritize cost-effectiveness, potentially opting for direct payment for specific medical needs rather than a comprehensive package.
Purchasing standalone health insurance policies from specialized providers also acts as a substitute. These providers might offer more competitive pricing for specific coverage areas, drawing customers away from AGBA's broader healthcare offerings. The global health insurance market, valued significantly in 2024, demonstrates this trend of specialized product demand.
Peer-to-Peer Lending and Crowdfunding Platforms
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional financial advisory and asset management services. These platforms offer alternative avenues for both capital raising and investment, often with different fee structures and accessibility compared to established financial institutions.
For businesses, P2P lending can provide faster access to capital than traditional bank loans, bypassing some of the more rigorous vetting processes. Similarly, crowdfunding allows businesses to tap into a broad base of individual investors, diversifying funding sources. This directly competes with the advisory and capital-raising functions typically performed by financial advisors and asset managers.
For individual investors, P2P lending platforms and crowdfunding opportunities offer direct investment in businesses or projects, often with potentially higher returns than traditional savings accounts or bonds. This access to alternative investment classes can divert capital that might otherwise be managed by traditional asset managers. For instance, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $120 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a substantial shift in capital allocation away from traditional channels.
- Alternative Capital Access: P2P lending platforms provide businesses with an alternative to traditional bank financing, often with quicker approval times.
- Diversified Funding Sources: Crowdfunding enables businesses to raise capital from a wide network of individual investors, reducing reliance on single institutional sources.
- Investor Diversification: Individual investors can access direct investments in various projects and businesses through P2P and crowdfunding, potentially seeking higher yields than traditional savings.
- Market Growth Indicators: The P2P lending market's significant growth, projected to reach over $300 billion by 2029, highlights its increasing role as a substitute for traditional financial services.
Specialized Professional Services
Customers increasingly opt for specialized professionals over integrated financial services. This means clients might engage separate tax consultants, estate planners, or niche investment managers instead of a single firm for all their needs. This unbundling allows them to select best-in-class providers for each specific requirement, directly substituting a comprehensive offering like AGBA's.
This trend is supported by the growing accessibility of independent advice. For example, in 2024, the market for financial planning services saw continued growth, with many independent advisors building strong client bases by focusing on specific areas like retirement planning or sustainable investing. This fragmentation of the market presents a significant threat, as clients can cherry-pick services, potentially bypassing integrated solutions.
The threat of substitutes in this segment is amplified by several factors:
- Client Demand for Expertise: Many consumers now seek deep, specialized knowledge in areas like tax law or complex investment strategies, which they believe niche providers offer more effectively.
- Technological Enablement: Digital platforms and specialized software have made it easier for independent professionals to operate and for clients to find and engage them for specific tasks.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For certain needs, engaging a specialist for a single service can be more cost-effective than paying for a broad suite of services from an integrated provider.
- Regulatory Landscape: Evolving regulations can sometimes favor specialized advice, making it easier for niche players to comply and offer targeted services.
The threat of substitutes for AGBA's offerings is substantial, stemming from readily available digital alternatives and specialized service providers. Customers can bypass traditional financial advisory and wealth management by utilizing robo-advisors and direct investment platforms, which often come with lower fees and greater user control. For instance, the global robo-advisory market's projected significant growth in the coming years highlights this shift.
Furthermore, individuals seeking financial security may opt for simpler, traditional banking products like savings accounts and Certificates of Deposit (CDs), especially when interest rates are favorable, as they were throughout 2024. This preference for perceived safety and ease of understanding diverts potential clients from more complex wealth management solutions.
The rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding platforms also poses a significant threat. These platforms offer alternative avenues for both capital raising for businesses and direct investment for individuals, often with different fee structures and accessibility compared to established financial institutions. The substantial growth in the P2P lending market, with projections indicating continued expansion, underscores its increasing role as a substitute for traditional financial services.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on AGBA | Market Trend/Data |
| Digital Investment Platforms & Robo-Advisors | Lower fees, user control, accessibility | Customer diversion from traditional wealth management | Global robo-advisory market valued at ~$2.7B in 2023, with significant projected growth. |
| Traditional Banking Products (Savings, CDs) | Perceived safety, ease of understanding, interest rate sensitivity | Deters individuals from seeking higher-yield wealth management | Average savings account interest rates increased in 2024, making deposits more competitive. |
| P2P Lending & Crowdfunding | Alternative capital access, diversified funding/investment, potentially higher yields | Attracts capital and businesses away from traditional advisory and asset management | Global P2P lending market projected to exceed $300B by 2029; valued at ~$120B in 2023. |
| Specialized Professionals (Tax Consultants, Niche Advisors) | Deep expertise in specific areas, cost-effectiveness for single services | Unbundling of services; clients cherry-pick best-in-class providers | Continued growth in financial planning services, with independent advisors gaining traction in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
The financial and healthcare sectors in Hong Kong present formidable barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory oversight. New companies must secure extensive licensing, adhere to rigorous compliance standards, and maintain significant capital adequacy, as mandated by authorities like the Hong Kong Monetary Authority and the Food and Health Bureau. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain a financial services license in Hong Kong can range from six months to over a year, involving substantial application fees and detailed operational plans.
The threat of new entrants into the financial services sector, particularly for entities aiming to replicate AGBA's comprehensive model, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements. Establishing a digital financial ecosystem akin to a 'one-stop financial supermarket' necessitates substantial investment in cutting-edge technology, including advanced data analytics, robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive client information, and scalable cloud infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a fintech startup to develop a secure and compliant digital banking platform could easily run into tens of millions of dollars, a barrier that deters many smaller players.
In the financial services sector, brand recognition and customer trust are incredibly important. Established firms like AGBA have cultivated strong reputations and loyal customer bases over many years. For new entrants, gaining this trust is a significant hurdle.
New companies must invest heavily in marketing and often resort to aggressive pricing to even begin chipping away at customer loyalty. For example, in 2024, the cost of acquiring a new customer in the digital banking space saw an average increase of 15% compared to the previous year, highlighting the expense involved in building a customer base against established brands.
Access to Distribution Channels and Talent Pool
New entrants in the financial services sector face significant hurdles in securing access to critical distribution channels. These channels, whether they be established banking networks, robust online platforms, or extensive physical branch systems, are often controlled by incumbent players. For example, a new fintech firm might find it difficult to integrate with existing payment rails or gain visibility on popular investment comparison sites without substantial investment or strategic alliances.
Attracting and retaining a skilled talent pool is another formidable barrier. The financial industry demands expertise in areas like asset management, financial advisory, and cutting-edge fintech development. Established firms, with their strong brand recognition and competitive compensation packages, typically have an advantage in drawing top talent. In 2024, the demand for specialized financial professionals, particularly those with AI and data analytics skills, remained exceptionally high, making recruitment a costly endeavor for newcomers.
The challenge of competing for talent is amplified by the need for specialized knowledge. Consider the cybersecurity talent gap, a critical area for financial institutions. Reports from late 2023 and early 2024 indicated a shortage of cybersecurity professionals, driving up salaries and making it harder for new entrants to build a secure operational foundation. This scarcity means new firms must invest heavily or offer significantly more attractive terms to compete with established entities that already possess experienced teams.
- Distribution Channel Barriers: New entrants struggle to access established networks, requiring significant investment or strategic partnerships to gain market reach.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: High demand for skilled financial professionals, especially in fintech and data analytics, increases recruitment expenses for new firms.
- Competition for Expertise: Established firms leverage their reputation and resources to attract and retain top talent, creating a disadvantage for newcomers.
- Regulatory Compliance Talent: The need for specialized compliance officers and legal experts adds another layer of difficulty and cost for new financial service providers.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Existing players like AGBA leverage significant economies of scale and scope, offering a wide array of financial services. This integration allows AGBA to achieve cost efficiencies through greater operational capacity and to capitalize on cross-selling opportunities, strengthening its market position.
New entrants often face a substantial hurdle in matching these cost advantages. Without the established infrastructure and customer base, they may find it difficult to compete on price or to offer the same breadth of integrated solutions that AGBA provides.
- Economies of Scale: AGBA’s operational scale allows for lower per-unit costs in areas like technology investment and compliance management.
- Economies of Scope: Offering diverse financial products, from insurance to wealth management, enables AGBA to spread fixed costs across multiple service lines.
- Cost Disadvantage for Entrants: Newcomers must invest heavily to build comparable scale and scope, which is often prohibitively expensive.
- Competitive Barrier: This cost disparity makes it challenging for new entrants to undercut established players like AGBA on price or match their service comprehensiveness.
The threat of new entrants into the financial services sector, particularly for firms aiming to replicate AGBA's integrated model, is significantly constrained by high capital requirements and rigorous regulatory frameworks in Hong Kong. Obtaining necessary licenses and establishing robust technological infrastructure, including advanced cybersecurity, can cost tens of millions of dollars in 2024, presenting a substantial financial barrier.
Furthermore, established players like AGBA benefit from significant economies of scale and scope, allowing them to operate at lower costs and offer a wider array of services. Newcomers face a considerable cost disadvantage when trying to match this operational efficiency and the breadth of offerings, making it difficult to compete on price or service comprehensiveness.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated 2024 Impact/Cost |
| Capital Requirements | Establishing technology, compliance, and operational infrastructure. | Tens of millions of USD for a digital banking platform. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Securing licenses, adhering to standards, capital adequacy. | 6-12+ months for financial services license, substantial fees. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Cost efficiencies from large operations and diverse service offerings. | Lower per-unit costs for technology, compliance, and customer acquisition. |
| Brand Trust & Customer Loyalty | Building reputation and retaining customers against established firms. | 15% increase in customer acquisition costs in digital banking. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our AGBA Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of comprehensive data, including publicly available financial reports, market research from leading firms, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific trade publications and economic databases to ensure a robust assessment of competitive dynamics.
