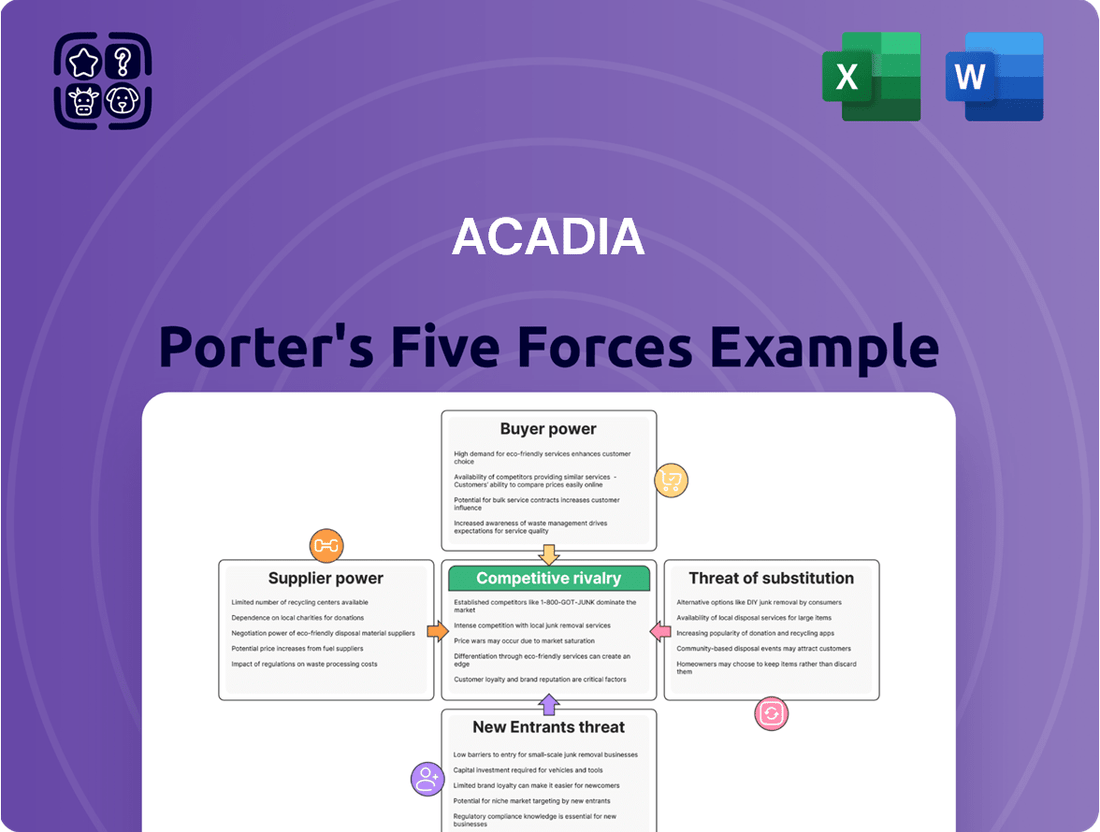
Acadia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Acadia Bundle
Acadia's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Acadia’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Acadia Realty Trust strategically targets prime retail spaces in urban and suburban areas characterized by high barriers to entry and limited supply. This scarcity of desirable locations inherently weakens the bargaining power of suppliers, as viable alternatives for retailers are scarce.
The ongoing constraint on new retail construction, a situation exacerbated by elevated construction costs and interest rates in 2024, further bolsters the negotiating position of property owners like Acadia. This lack of new supply means existing prime locations are even more valuable and sought after.
Suppliers of construction materials and labor hold moderate bargaining power, largely due to escalating costs. Construction expenses are projected to see a moderate increase of 5-7% in 2025. This rise is primarily fueled by the increasing prices of key materials such as steel and lumber, alongside growing labor expenses.
These elevated costs directly influence Acadia Realty Trust's redevelopment initiatives and potential new property acquisitions. Consequently, suppliers gain a degree of leverage, enabling them to command higher prices for their services and essential materials, impacting Acadia's project budgets.
Acadia's reliance on specialized services for mixed-use and urban retail redevelopment grants significant leverage to suppliers possessing niche expertise. Firms with proven track records in historical preservation or complex urban planning, for instance, can dictate terms due to the scarcity of comparable capabilities. This was evident in 2024, where projects requiring advanced sustainable building certifications saw specialized engineering firms command up to 15% higher fees than general contractors.
Access to Capital and Financing
Suppliers of capital, like banks and institutional lenders, wield considerable influence. While REITs, including Acadia, were actively raising funds through debt and equity in 2024 and the first half of 2025, the cost of borrowing has climbed. For instance, average yields on unsecured debt offerings hovered around 5.5% to 5.8% in early 2025.
This increased cost of capital directly impacts Acadia's capacity to fund new acquisitions and redevelopment projects. Consequently, securing favorable financing terms becomes a critical factor in the company's strategic growth and operational capabilities.
- Increased Borrowing Costs: Average yields on unsecured debt for REITs reached 5.5-5.8% in H1 2025.
- Impact on Acquisitions: Higher financing costs can limit Acadia's ability to pursue new property purchases.
- Financing Terms are Key: Favorable loan agreements are essential for Acadia's development plans.
Land Owners in Desirable Locations
Landowners in desirable locations wield significant bargaining power over Acadia. Their properties are unique and essential for Acadia's strategy of acquiring and redeveloping prime retail spaces. This scarcity allows them to command premium prices, a trend evident in Acadia's recent transactions in high-demand urban centers.
For instance, in 2024, the average price per square foot for prime retail space in Manhattan, a key market for Acadia, continued to reflect this strong landowner leverage. Acquisitions in such areas often involve bidding wars, further solidifying the sellers' negotiating position. This dynamic directly impacts Acadia's acquisition costs and overall profitability.
- Scarcity of Prime Locations: Unique, irreplaceable assets drive up demand and price.
- Premium Pricing: Landowners can dictate higher acquisition costs due to location desirability.
- Impact on Acadia: Directly influences Acadia's capital expenditure and return on investment for new projects.
Acadia's strategic focus on prime, supply-constrained retail locations inherently limits the bargaining power of most suppliers, as alternative options are scarce. However, suppliers of specialized construction services and capital can exert significant influence due to niche expertise and rising borrowing costs.
For example, specialized engineering firms for sustainable building certifications commanded up to 15% higher fees in 2024. Furthermore, average yields on unsecured REIT debt reached 5.5-5.8% in H1 2025, increasing Acadia's cost of capital and empowering lenders.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power | Key Factors (2024-2025) | Impact on Acadia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landowners (Prime Locations) | High | Scarcity of desirable urban/suburban retail spaces; bidding wars in high-demand areas. | Increased acquisition costs, impacting project profitability. |
| Specialized Construction Services | High | Niche expertise (e.g., historical preservation, sustainability certifications); scarcity of comparable capabilities. | Higher fees for redevelopment projects, impacting budgets. |
| Capital Providers (Lenders) | Moderate to High | Rising interest rates; average unsecured REIT debt yields at 5.5-5.8% (H1 2025). | Increased cost of financing for acquisitions and developments. |
| General Construction Materials/Labor | Moderate | Projected 5-7% increase in construction expenses in 2025 due to material and labor costs. | Elevated costs for redevelopment and potential new acquisitions. |
What is included in the product
Acadia's Porter's Five Forces analysis examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing a comprehensive view of its competitive environment.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive overview of all five forces, streamlining strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Acadia Realty Trust's diverse tenant base, spanning national brands to local shops across various property types like street retail and mixed-use developments, helps mitigate individual customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, Acadia's portfolio included a wide array of retailers, ensuring that the departure of any single tenant wouldn't critically impact overall rental income.
The inclusion of necessity and discount/value retailers within Acadia's tenant mix further strengthens its position. This diversification means that a significant portion of its revenue comes from businesses less sensitive to economic downturns, reducing the leverage any one tenant might have to negotiate lower rents based on their own performance alone.
The retail real estate landscape, particularly in sought-after areas, has experienced remarkably low vacancy rates. For instance, in 2024, prime retail spaces across major urban centers often saw occupancy rates exceeding 95%, with many locations reporting near-zero availability. This scarcity means that when a space does become open, it's typically re-leased very quickly, often at substantial rent increases compared to previous leases.
This tight market dynamic significantly curtails the bargaining power of both current and potential retail tenants. With limited options available, tenants are less able to demand favorable lease terms or resist rent hikes. Landlords, like Acadia, are therefore in a stronger position to negotiate more advantageous lease agreements, securing higher rental income and more favorable conditions due to the intense demand for their limited prime real estate inventory.
Acadia's focus on redeveloping properties significantly enhances their value proposition for tenants. By investing in improved infrastructure and creating dynamic mixed-use environments in strategically chosen locations, Acadia attracts substantial foot traffic. This creates a compelling reason for tenants to choose Acadia's spaces, thereby diminishing their leverage.
For instance, in 2024, Acadia reported a 95% occupancy rate across its portfolio, a testament to the desirability of its redeveloped properties. Tenants are willing to commit to higher lease rates when Acadia's properties offer a clear competitive advantage and robust consumer engagement, directly impacting the bargaining power of these customers.
Shifting Consumer Preferences towards Physical Retail
Despite the continued growth of e-commerce, there's a notable resurgence in physical retail, especially among younger demographics like Gen Z. This shift is driven by a desire for experiential shopping and convenient access, which in turn bolsters demand for prime retail locations.
This renewed emphasis on brick-and-mortar experiences directly impacts the bargaining power of retail tenants. As well-located, engaging physical spaces become more sought after, tenants have less leverage to negotiate favorable lease terms.
For instance, a 2024 report by the National Retail Federation indicated that foot traffic in physical stores saw a significant increase compared to the previous year, particularly in sectors offering unique in-store experiences. This growing consumer preference for tangible retail environments directly reduces the bargaining power of retail tenants who might otherwise have more leverage in lease negotiations.
- Renewed Consumer Preference: Younger generations are increasingly favoring in-store shopping for its experiential value.
- Increased Demand for Physical Spaces: This trend strengthens the desirability of well-situated retail locations.
- Reduced Tenant Leverage: The heightened demand for physical retail spaces diminishes the bargaining power of retail tenants.
- Impact on Lease Negotiations: Tenants find it harder to negotiate favorable terms when landlords have multiple interested parties.
Tenant Improvement Costs
While landlords typically hold significant sway, the substantial expenses involved in tenant improvements can become a key negotiation point for lessees. Retailers frequently demand specific build-outs or modifications tailored to their unique brand identity and operational requirements.
The financial burden of these improvements can grant larger or anchor tenants a degree of leverage during lease discussions with property owners like Acadia.
- Tenant Improvement (TI) allowances can represent a significant portion of a landlord's capital expenditure per lease.
- For example, in 2024, TI allowances in prime retail markets could range from $50 to $150 per square foot, depending on the location and tenant's needs.
- Anchor tenants, due to their drawing power and longer lease commitments, often negotiate for higher TI allowances, directly impacting the landlord's profitability on that specific lease.
- This bargaining power shifts some of the risk and cost of property adaptation from the landlord to the tenant, influencing the overall return on investment for Acadia.
Acadia's diverse tenant mix, including necessity and discount retailers, along with a high occupancy rate of 95% in 2024 across its prime locations, significantly limits customer bargaining power. The scarcity of desirable retail spaces, with vacancy rates often below 5% in urban centers during 2024, means tenants have fewer alternatives and less leverage to negotiate favorable lease terms.
The resurgence of experiential physical retail, particularly favored by younger demographics, further strengthens Acadia's position. This renewed demand for well-located brick-and-mortar stores reduces tenant leverage, as landlords can command higher rents and more favorable conditions due to intense competition for these spaces.
However, tenant improvement allowances can shift bargaining power. In 2024, these allowances in prime markets ranged from $50 to $150 per square foot, with anchor tenants often negotiating higher amounts, impacting landlord profitability.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Tenant Diversification | Lowers individual tenant leverage | Acadia's portfolio includes national brands and local shops across various property types. |
| Retailer Type Mix | Reduces impact of economic downturns on tenant leverage | Inclusion of necessity and discount retailers. |
| Market Vacancy Rates | Significantly reduces tenant leverage | Prime retail spaces saw occupancy >95% in major urban centers in 2024. |
| Experiential Retail Demand | Diminishes tenant leverage | Increased foot traffic in physical stores, especially in experiential sectors. |
| Tenant Improvement Allowances | Can increase leverage for certain tenants | Allowances ranged from $50-$150/sq ft in prime markets in 2024; anchor tenants negotiate higher. |
What You See Is What You Get
Acadia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Acadia Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing information. You can confidently expect to download and utilize this detailed analysis without any further customization or setup.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Acadia Realty Trust operates in a highly competitive retail Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) market. Its rivals include significant publicly traded entities such as Regency Centers, Brixmor Property Group, Federal Realty Investment Trust, and Kimco Realty, all vying for prime retail assets and tenant relationships.
Despite the presence of these major players, the retail REIT landscape remains notably fragmented. This fragmentation stems from the existence of numerous regional and niche REITs that focus on specific geographic areas or property types, creating a diverse competitive environment for Acadia.
Acadia Realty Trust (AKR) actively cultivates competitive advantage by concentrating on superior, distinct real estate assets. This strategic focus on high-quality street retail, dynamic mixed-use properties, and desirable urban and suburban locales sets it apart from competitors.
By specializing in these niche segments, Acadia effectively sidesteps direct confrontation with Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) that predominantly invest in conventional enclosed malls or power centers. This differentiation is crucial in a market where broad-based retail REITs might face oversupply or slower growth.
Acadia's proven capacity to identify, secure, and enhance prime real estate in highly sought-after retail corridors provides a significant competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, Acadia continued to execute its strategy, reporting strong leasing activity and rent growth across its portfolio of differentiated assets, demonstrating the resilience and appeal of its chosen market segments.
Acadia Realty Trust's leasing and occupancy performance highlights its competitive edge. As of December 31, 2024, the company achieved a robust 95.8% leased rate across its portfolio. This strong leasing momentum, particularly within its street retail segment, directly reflects Acadia's ability to outcompete rivals for prime tenants and maintain high property utilization.
Access to Capital and Investment Management Platform
Acadia's ability to secure substantial funding, exemplified by its approximately $740 million equity raise in 2024, significantly strengthens its competitive standing. This financial muscle directly fuels its acquisition strategy, allowing it to act decisively in a capital-intensive real estate market.
Furthermore, Acadia's sophisticated investment management platform enables strategic, opportunistic investments. This dual capability—access to capital and skilled management of those funds—positions Acadia to outmaneuver competitors by pursuing accretive acquisitions and redevelopment projects more effectively.
- Capital Access: Raised ~$740 million in equity during 2024.
- Strategic Funding: Capital earmarked for acquisitions and redevelopments.
- Competitive Advantage: Financial flexibility to pursue growth opportunities.
- Platform Strength: Investment management enhances opportunistic deployment.
Market Conditions and Economic Headwinds
Competitive rivalry can intensify during periods of economic uncertainty or shifts in consumer spending. While the retail sector has shown resilience, with overall retail revenue projected to increase by approximately 3.5% in 2024, macroeconomic uncertainties could impact consumer spending and growth. This potential slowdown may lead to increased competition among landlords for desirable tenants, as vacancy rates could rise.
The retail property market, in particular, faces pressure as e-commerce continues to gain market share. This dynamic forces physical retailers to innovate and differentiate, impacting their demand for prime retail space. Consequently, landlords must offer more attractive lease terms and amenities to secure and retain tenants, heightening the competitive landscape for leasing occupancy.
- Economic Uncertainty Impact: Macroeconomic uncertainties in 2024 could dampen consumer spending, intensifying competition among retail property landlords for tenants.
- Retail Sector Resilience: Despite headwinds, the retail sector is expected to see revenue growth in 2024, indicating underlying demand but also potential for increased tenant competition.
- E-commerce Pressure: The ongoing shift to online retail necessitates that physical store operators adapt, influencing their leasing strategies and, by extension, landlord competition for quality tenants.
- Landlord Strategies: To counter rising competition, landlords are increasingly offering flexible lease terms and enhanced property amenities to attract and retain retailers.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for Acadia Realty Trust, operating within a fragmented retail REIT market populated by major players like Regency Centers and Kimco Realty. Acadia differentiates itself by focusing on unique street retail and mixed-use properties, often sidestepping direct competition with REITs focused on traditional malls. This niche strategy proved effective in 2024, with Acadia reporting a 95.8% leased rate across its portfolio, demonstrating its ability to attract and retain tenants in sought-after locations.
| Competitor | Focus Area | 2024 Performance Indicator (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|
| Regency Centers | Grocery-anchored shopping centers | Strong occupancy in suburban markets |
| Brixmor Property Group | High-quality, open-air centers | Consistent rent growth |
| Federal Realty Investment Trust | Mixed-use, urban and suburban infill | High tenant retention rates |
| Kimco Realty | Neighborhood and community centers | Strategic portfolio repositioning |
| Acadia Realty Trust | Street retail, mixed-use, urban/suburban | 95.8% leased rate (Dec 31, 2024) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
E-commerce stands as the primary substitute for traditional brick-and-mortar retail. While online shopping experienced rapid expansion, 2024 data indicates a deceleration in e-commerce growth, with physical stores seeing a resurgence, especially for those offering unique customer experiences.
Despite this shift, the fundamental ease with which consumers can compare prices and access a vast array of products online continues to pose a significant threat to physical retail. For instance, in early 2024, e-commerce accounted for approximately 15% of total retail sales in the US, a figure that, while substantial, showed a more modest year-over-year increase compared to previous years.
The rise of direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands presents a significant substitute threat, especially for businesses reliant on traditional retail. These companies, like Warby Parker or Casper, often use digital platforms and social media to sell directly to customers, cutting out intermediaries and potentially offering more competitive pricing or unique value propositions. For instance, in 2024, the DTC e-commerce market continued its robust growth, with many established brands exploring or expanding their DTC channels to capture a larger share of the customer relationship.
While younger generations like Gen Z might lean towards in-store shopping, the overall trend shows a significant shift towards convenience and seamless omnichannel experiences. This means consumers expect to be able to shop online, in-store, and through mobile apps, with each channel complementing the others.
Retailers struggling to integrate these channels effectively may find their physical store presence becoming less relevant, leading them to downsize or close locations. For instance, a report from Coresight Research in early 2024 indicated that over 10,000 retail stores were expected to close in the US during that year, a trend driven partly by the inability to adapt to evolving consumer shopping habits.
This reduction in physical retail footprints directly impacts the demand for real estate investment trusts (REITs) that hold retail properties. If a significant number of retailers are shrinking their physical presence due to a failure to meet omnichannel expectations, the demand for retail space, and consequently the value of retail REITs, could decrease.
Alternative Retail Formats and Pop-Up Shops
The increasing popularity of alternative retail formats, such as pop-up shops and short-term leases, presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional brick-and-mortar retail spaces like those owned by Acadia. These temporary solutions offer brands a more agile and cost-effective way to test markets or launch new products without the long-term commitment of permanent leases.
While these pop-ups can sometimes be tenants for Acadia, their very existence highlights a substitute for the stability and longevity that traditional leases provide. Brands might opt for this flexibility, especially in dynamic retail environments, viewing it as a less risky alternative to securing a long-term physical presence.
For instance, the global pop-up retail market has seen substantial growth, with projections indicating continued expansion. In 2023, the market was valued at approximately $20 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% through 2028, demonstrating a clear trend towards these flexible retail models.
- Flexibility as a Substitute: Pop-up shops offer brands the ability to adapt quickly to market trends and consumer demand without the burden of long-term rental agreements.
- Cost-Effectiveness: These temporary retail solutions typically involve lower overhead costs compared to traditional leases, making them an attractive alternative for businesses with tighter budgets.
- Market Testing: Pop-ups provide a low-risk avenue for brands to test new geographic locations or product lines before committing to a permanent retail footprint.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: The novelty and experiential nature of pop-up shops can also appeal to consumers seeking unique shopping experiences, further solidifying their role as a viable substitute.
Home-Based Businesses and Services
The rise of home-based businesses presents an indirect substitute threat to traditional retail, particularly impacting smaller, local establishments. These businesses, often operating with lower overheads, can siphon off demand for specific goods and services that might otherwise be sought in brick-and-mortar locations.
This shift is fueled by technological advancements and a changing consumer preference for convenience and personalized services. For instance, the gig economy, which saw significant growth leading up to 2024, enables individuals to offer specialized services from home, directly competing with established businesses.
- Home-based service providers offer specialized skills with reduced overhead compared to traditional retail.
- The growth of the gig economy facilitates individuals offering services directly from home.
- This trend can gradually decrease demand for certain types of commercial retail spaces, especially for smaller, local businesses.
- Consumer preference for convenience and personalized services further supports the viability of home-based alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for traditional retail is multifaceted, encompassing online shopping, direct-to-consumer (DTC) models, and alternative physical formats like pop-up shops. E-commerce, while seeing a growth slowdown in 2024, still represents a significant substitute due to its convenience and price comparison capabilities, capturing about 15% of US retail sales early in the year. DTC brands further challenge established retailers by bypassing intermediaries, and the pop-up market's projected growth, estimated at over 5% CAGR through 2028, highlights a shift towards flexible, lower-overhead retail solutions.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | 2024 Relevance/Data |
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce | Convenience, price comparison, vast selection | ~15% of US retail sales; decelerating growth |
| Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) | Bypasses intermediaries, unique value propositions | Continued robust growth in DTC e-commerce |
| Pop-up Shops | Flexibility, lower overhead, market testing | Global market valued ~$20 billion in 2023; 5%+ CAGR projected |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the retail Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) market, particularly for premium properties like those Acadia Realty Trust (AKR) often focuses on, demands a significant financial commitment. For instance, acquiring a single prime retail center can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars.
The sheer scale of investment needed for land acquisition, sophisticated construction or redevelopment, and ongoing property management creates a formidable barrier. Newcomers must secure substantial financing, which can be challenging without an established track record, effectively deterring many potential competitors from entering the space.
Acadia Realty Trust strategically targets 'high-barrier-to-entry, supply-constrained, densely populated metropolitan areas.' This focus inherently limits the pool of available prime locations, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate their portfolio quickly.
The scarcity of desirable land and well-situated existing retail properties in these key markets presents a significant hurdle. For instance, in 2024, major metropolitan areas like New York City and Los Angeles continued to see extremely low retail vacancy rates, often below 5%, further tightening the supply of prime spaces.
New retail ventures, especially in established urban centers, encounter significant regulatory challenges. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain building permits in major US cities often stretched to several months, with some projects facing delays exceeding a year due to complex zoning reviews and compliance checks.
These stringent building codes and zoning regulations act as a substantial barrier. They increase the upfront capital investment required for new entrants, covering architectural plans, legal consultations, and compliance fees, which can easily run into tens of thousands of dollars before construction even begins.
Navigating these intricate permitting processes demands specialized expertise and considerable time, often deterring smaller or less experienced players. The sheer bureaucratic complexity can make market entry prohibitively difficult, thereby protecting existing retailers from immediate new competition.
Established Tenant Relationships and Market Knowledge
Established REITs, such as Acadia Realty Trust (AKR), benefit from deeply entrenched relationships with a diverse range of national and local retail tenants. This network is built over years, fostering trust and providing preferential access to prime leasing opportunities. For instance, as of Q1 2024, Acadia reported a robust occupancy rate of 96.7% across its portfolio, underscoring the strength of its tenant base.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in replicating this established tenant ecosystem. They must invest significant time and resources to cultivate similar connections and gain the trust of retailers, a process that can take years and may not yield immediate results. This existing market knowledge also allows established players to navigate leasing complexities and market fluctuations more effectively.
- Tenant Retention: Acadia's strong tenant relationships contribute to high retention rates, reducing turnover costs and ensuring consistent rental income.
- Market Intelligence: Years of operation provide invaluable insights into local market dynamics, consumer trends, and competitive landscapes, which are difficult for newcomers to acquire quickly.
- Leasing Advantages: Established REITs often secure more favorable lease terms due to their proven track record and strong tenant demand for their properties.
Economic and Construction Cost Environment
The threat of new entrants into the retail real estate sector is currently moderate, largely due to the economic and construction cost environment. While retail property has demonstrated surprising resilience, the landscape for new development is challenging.
Elevated construction costs, which saw significant increases in 2023 and are projected to remain high through 2024, coupled with higher interest rates, make embarking on large-scale development projects less appealing for newcomers. For instance, the US Producer Price Index for construction inputs experienced a notable uptick in recent years.
This economic climate favors established players who possess existing portfolios and, crucially, better access to capital. These incumbents can more readily navigate the higher financing costs and potentially absorb the increased expenses associated with new builds.
- Elevated Construction Costs: Building material prices and labor costs remain a significant barrier, impacting the feasibility of new retail developments in 2024.
- Higher Interest Rates: Increased borrowing costs directly affect the profitability and risk profile of new real estate projects, deterring potential entrants.
- Capital Access: Established developers with strong balance sheets and existing relationships with lenders are better positioned to undertake new projects compared to new entrants.
- Market Saturation: In certain sub-sectors or prime locations, existing retail supply may already be sufficient, further diminishing the attractiveness of new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Acadia Realty Trust is currently moderate. Significant capital is required to enter the retail REIT market, with prime property acquisitions often costing tens to hundreds of millions of dollars. For example, as of early 2024, acquiring a single well-located shopping center in a major metropolitan area could easily exceed $50 million.
Regulatory hurdles and zoning complexities further impede new players. In 2024, obtaining necessary building permits in major US cities could take several months, adding substantial time and cost to development projects. This environment favors established firms with existing market knowledge and relationships.
Acadia's strategic focus on high-barrier-to-entry, supply-constrained metropolitan areas, coupled with its established tenant relationships, creates a strong defense against new competition. For instance, Acadia's portfolio occupancy rate stood at 96.7% in Q1 2024, highlighting the demand for its properties and the difficulty for newcomers to secure desirable tenants.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of acquiring prime retail properties. | Acquiring a single prime retail center can cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex zoning laws and lengthy permitting processes. | Permit acquisition in major US cities averaged several months in 2024. |
| Established Tenant Relationships | Existing REITs have strong, long-standing ties with retailers. | Acadia's 96.7% occupancy rate in Q1 2024 demonstrates tenant demand and loyalty. |
| Market Saturation & Location Scarcity | Limited availability of prime retail spaces in desirable locations. | Prime metropolitan areas often have retail vacancy rates below 5%. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Acadia Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and publicly available competitor information.
We leverage insights from trade publications, economic indicators, and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape and its influencing factors.
