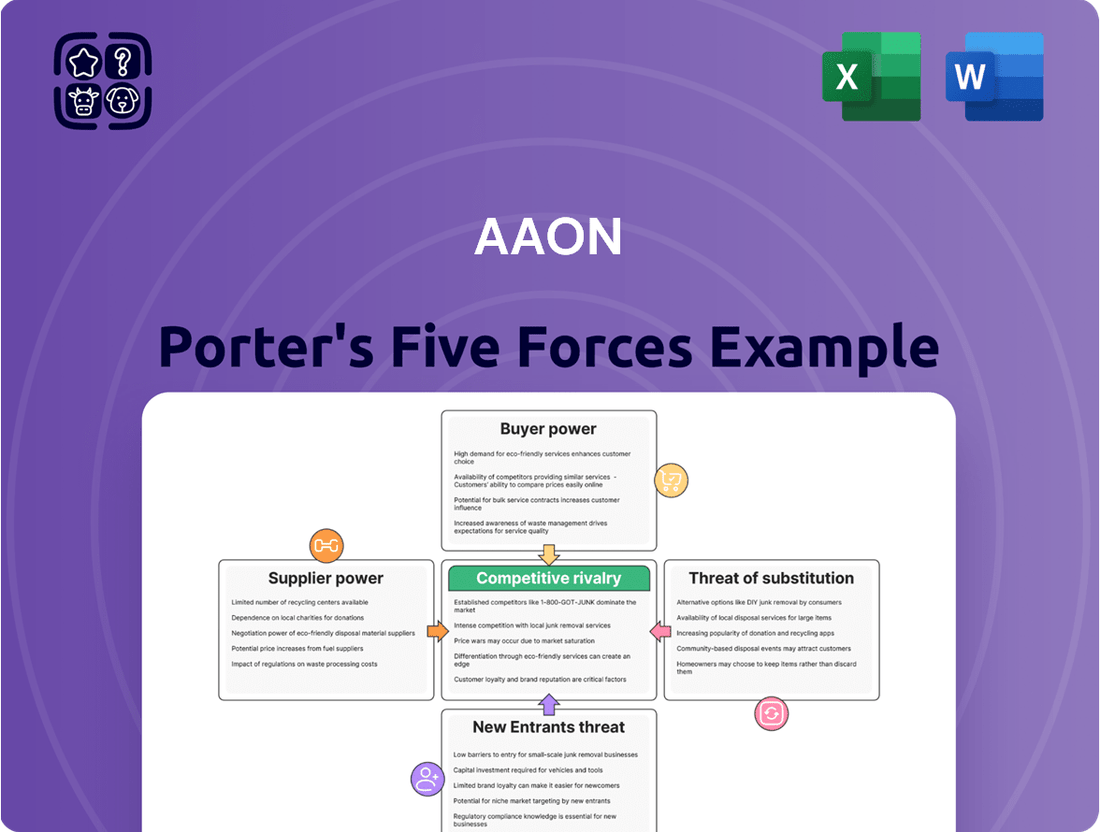
AAON Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AAON Bundle
AAON's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers and suppliers to the threat of new entrants and substitutes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone looking to grasp AAON's market position and future prospects.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping AAON’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The HVAC industry, including specialized manufacturers like AAON, depends on a variety of components. These include essential materials like semiconductors, copper, aluminum, and steel. The availability and pricing of these raw materials are significantly influenced by the concentration of their suppliers.
For AAON, the geographic concentration of key suppliers, such as China for semiconductors and aluminum, can create a situation where suppliers hold considerable sway. This concentration means fewer alternatives for AAON, potentially increasing supplier bargaining power.
In 2025, the HVAC/R sector continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions and rising costs. This environment suggests that suppliers for critical components likely possess moderate to high bargaining power, directly affecting manufacturers like AAON.
AAON's focus on custom-engineered HVAC solutions often necessitates specialized components, potentially creating strong ties with specific suppliers. If these relationships involve unique designs or materials, the cost and effort for AAON to switch to a different supplier for those components could be substantial. This could involve significant expenses related to redesigning products, retooling manufacturing processes, or undergoing lengthy requalification periods for new parts, thereby increasing the bargaining power of those key suppliers.
However, AAON actively works to manage this potential supplier leverage. The company's strategic planning includes efforts to diversify its supplier base. This diversification aims to reduce reliance on any single supplier and mitigate the impact of switching costs. For instance, in 2023, AAON reported an increase in its cost of goods sold by 10.5% year-over-year, partly due to material costs and supply chain dynamics, highlighting the ongoing importance of supplier management.
The availability of substitutes for the raw materials and components AAON uses significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. If there are many readily available alternatives for critical parts, suppliers have less leverage. However, for AAON's specialized, high-efficiency HVAC systems, reliance on specific, advanced components can limit substitute options, thereby increasing supplier power.
The ongoing transition in the HVAC industry towards refrigerants with lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) is a prime example. Suppliers of these new, environmentally friendly refrigerants are likely to command greater power due to limited initial availability and specialized production processes. This dynamic could affect AAON's cost structure and sourcing strategies as they adapt to evolving environmental regulations and market demands.
Uniqueness of Supplier's Products/Services
When suppliers offer highly specialized or proprietary components, their bargaining power increases significantly. This is particularly true for AAON, whose advanced and custom HVAC systems rely on unique elements like specific compressor technologies or sophisticated control systems. For instance, a supplier of a novel, patented refrigerant management system for commercial HVAC units would hold considerable sway.
AAON's commitment to innovation naturally leads them to seek out unique components. This pursuit can foster a greater dependence on particular suppliers, thereby amplifying those suppliers' leverage. In 2023, the HVAC industry saw continued investment in R&D, with companies like AAON pushing for more energy-efficient and technologically advanced solutions, often requiring specialized inputs.
- Supplier Specialization: Suppliers providing unique, patented, or difficult-to-replicate components for AAON's custom HVAC solutions possess higher bargaining power.
- Technological Dependence: AAON's reliance on specific advanced technologies, such as proprietary compressor designs or integrated smart controls, strengthens the position of their suppliers.
- Innovation Drive: The company's focus on cutting-edge product development means it may need to secure exclusive access to novel materials or manufacturing processes from suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into AAON's core HVAC manufacturing business would significantly bolster their bargaining power. This scenario is more plausible for suppliers of highly specialized, critical components rather than basic raw materials.
While there's no concrete evidence indicating a strong current threat of forward integration from AAON's typical suppliers, it remains a potential, albeit theoretical, factor that could shift the power dynamic.
- Supplier Forward Integration: If suppliers can credibly threaten to enter the HVAC manufacturing market themselves, their leverage over AAON increases.
- Component Specialization: This threat is more pronounced for suppliers of unique or technologically advanced sub-components essential to HVAC system performance.
- AAON's Context: Currently, there is no direct indication that AAON's suppliers pose a significant threat of forward integration, though it's a factor to monitor.
Suppliers of specialized components for AAON's custom HVAC systems hold significant bargaining power due to limited alternatives and the high cost of switching. This is exacerbated by geographic concentration of certain raw material suppliers, as seen with semiconductors and aluminum, often sourced from regions like China. The ongoing industry shift towards lower GWP refrigerants further empowers suppliers of these new technologies.
AAON's innovation drive necessitates unique components, increasing dependence on specific suppliers and their leverage. For example, in 2023, AAON reported a 10.5% increase in cost of goods sold, partly attributed to material costs and supply chain dynamics, underscoring the impact of supplier power.
| Factor | Impact on AAON | Example/Data Point (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Geographic) | Moderate to High | Reliance on China for semiconductors and aluminum |
| Component Specialization | High | Proprietary compressor designs, advanced control systems |
| Switching Costs | High | Redesign, retooling, requalification for specialized parts |
| Industry Trends (e.g., Low GWP Refrigerants) | Potentially High | Suppliers of new refrigerants gain leverage due to limited availability |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for AAON dissects the industry's competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing a strategic roadmap for AAON's market positioning.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model, allowing for rapid identification of strategic advantages and threats.
Customers Bargaining Power
AAON's customer base spans various sectors including education, healthcare, and retail, indicating a diversified rather than concentrated group of buyers. This broad reach typically dilutes the power of any single customer to dictate terms.
While AAON serves many, large-scale commercial or industrial projects represent significant purchase volumes. For instance, in 2024, major HVAC system upgrades in large educational facilities or healthcare campuses could involve substantial orders, granting those specific clients greater bargaining leverage.
For commercial and industrial clients, the decision to switch HVAC equipment providers often comes with significant financial and operational hurdles. These can include the expense of new installation, the complexities of integrating new systems with existing building management infrastructure, and the potential for costly business disruptions during the transition period. These factors collectively raise the bargaining power of customers.
AAON's strategic focus on delivering custom-engineered HVAC solutions amplifies these switching costs. Because their systems are meticulously designed to meet the unique specifications and operational requirements of each client, moving to a more standardized, off-the-shelf competitor becomes considerably more challenging and less economical. This specialization inherently locks in customers to a greater degree.
Customer price sensitivity remains a significant factor for AAON, even with its focus on energy efficiency and custom solutions. Commercial and industrial clients carefully weigh the initial capital outlay against projected long-term operating expenses when purchasing HVAC systems.
The current economic climate, marked by increasing regulatory compliance costs and persistent supply chain disruptions, has driven up the prices of new HVAC equipment. This trend is likely to heighten customer price sensitivity, compelling AAON to strategically balance its premium product offerings with competitive pricing strategies to maintain market share.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
Customers have a wide array of choices for their heating and cooling needs. This includes traditional HVAC systems from numerous competitors, as well as emerging alternatives like geothermal and solar-powered systems. The growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency further broadens these options.
This availability of substitutes can significantly enhance customer bargaining power. If AAON's products are not perceived as uniquely differentiated or competitively priced, customers can more easily switch to other providers. For instance, the market for energy-efficient HVAC solutions is projected to grow, with some reports indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% in the coming years, suggesting a dynamic competitive landscape.
- Broad Market Choices: Customers can select from traditional HVAC, geothermal, and solar-powered solutions.
- Sustainability Trend: Increased demand for eco-friendly options empowers customer decision-making.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: The availability of alternatives can force manufacturers like AAON to maintain competitive pricing.
- Differentiation is Key: AAON's ability to stand out through unique features or cost-effectiveness directly impacts customer loyalty and bargaining power.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by AAON's customers, meaning customers producing their own HVAC equipment, is generally low. This is primarily because AAON serves commercial and industrial clients who typically lack the intricate manufacturing processes, advanced research and development, and established supply chain networks essential for creating sophisticated HVAC systems. For instance, a large manufacturing plant might have the capacity to build some components, but replicating AAON's entire product line, from design to assembly and testing, would be prohibitively complex and costly.
Customers generally do not possess the specialized technical expertise or the capital investment necessary to develop and manufacture HVAC units that meet the rigorous performance and efficiency standards required in commercial and industrial applications. This lack of inherent capability significantly limits their ability to exert bargaining power through the threat of producing their own equipment. In 2024, the HVAC industry continued to see high barriers to entry, reinforcing this dynamic.
- Limited Technical Expertise: Customers typically lack the specialized engineering and manufacturing know-how for complex HVAC systems.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing HVAC manufacturing facilities requires substantial upfront costs for machinery, R&D, and skilled labor.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Replicating AAON's established global supply chain for specialized components is a significant hurdle.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Most industrial customers prioritize their primary business operations rather than venturing into HVAC manufacturing.
AAON's customers, while diverse, gain leverage from significant switching costs and the availability of substitutes. The complexity and expense of integrating new HVAC systems, coupled with AAON's custom-engineered solutions, make it difficult for clients to switch providers. This reliance on specialized, tailored equipment inherently strengthens AAON's position, as the cost and disruption of changing vendors are substantial.
Price sensitivity remains a key factor, especially with rising equipment costs in 2024 due to supply chain issues and regulatory compliance. Customers are carefully evaluating initial investment against long-term operational savings. The growing market for energy-efficient and sustainable alternatives, such as geothermal and solar-powered systems, further empowers customers by offering viable choices outside of traditional HVAC, potentially increasing pressure on AAON to maintain competitive pricing and unique value propositions.
| Factor | Impact on AAON | Customer Bargaining Power |
| Switching Costs | High due to custom solutions and integration complexity | High |
| Availability of Substitutes | Growing with energy-efficient and alternative technologies | Moderate to High |
| Customer Price Sensitivity | Elevated by current economic conditions and rising equipment costs | High |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Very Low due to technical expertise and capital requirements | Low |
Full Version Awaits
AAON Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive AAON Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the HVAC manufacturing industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, containing in-depth insights into buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry. Rest assured, there are no placeholders or samples; what you preview is precisely what you'll download, ready for your strategic use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The commercial HVAC market is quite crowded, with many companies vying for business. AAON faces off against some really big names in the industry. Think of giants like Lennox International, Trane, York (which is part of Johnson Controls Inc.), Carrier, and Daikin Applied. These companies generally have a much larger pool of resources at their disposal compared to AAON.
While AAON holds a smaller slice of the overall market, estimated at around 0.23% as of the first quarter of 2025, its focus on custom-engineered, energy-efficient solutions sets it apart. This specialization allows AAON to compete effectively by offering tailored products that differ from the more standardized offerings of its larger rivals.
The global commercial HVAC market is on a strong upward trajectory, with projections indicating a substantial increase of USD 28.8 billion between 2024 and 2029. This growth, occurring at a compound annual growth rate of 4.7%, is expected to push the market value to $120.6 billion by 2029.
This robust expansion is fueled by several key factors, including a heightened demand for energy-efficient HVAC solutions, the integration of smart technologies for better control and performance, and the booming construction of data centers. These drivers create a more favorable environment for industry players, potentially easing some of the intensity of competitive rivalry.
AAON stands out by focusing on energy efficiency and custom-engineered HVAC solutions, a stark contrast to competitors often relying on standardized offerings. This dedication to tailored products allows AAON to command a premium and build strong customer loyalty.
The company's ongoing innovation, particularly in advanced areas like liquid cooling for data centers and cutting-edge heat pump technologies, further solidifies its unique market position. These developments enable AAON to offer solutions with superior performance and value, moving beyond simple price competition.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, such as significant fixed assets, specialized manufacturing facilities, and long-term contracts, can intensify competitive rivalry. Companies facing these barriers are often compelled to remain in the market even during economic downturns, leading to increased pressure on pricing and market share.
The HVAC manufacturing industry, including companies like AAON, typically involves substantial capital investment in specialized machinery and facilities. This suggests moderately high exit barriers for firms in this sector.
- High Capital Investment: The HVAC sector requires significant upfront investment in manufacturing plants, specialized equipment, and research and development, making it costly for companies to exit. For instance, the capital expenditures for HVAC manufacturers can run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Specialized Assets: Many assets in HVAC manufacturing are highly specialized and have limited alternative uses, reducing their resale value and increasing the cost of exiting the market.
- Long-Term Contracts: Companies may be bound by long-term supply agreements or customer contracts, which can further deter a swift exit and keep them engaged in the market.
Diversity of Competitors
The HVAC market is characterized by a wide array of competitors, each employing distinct strategies. Some focus on high-volume production of standard units, while others, like AAON, concentrate on customized, high-efficiency systems. This diversity fuels varied competitive tactics, including price wars, innovation sprints, and service-based differentiation.
This varied competitive landscape means that companies must be adept at navigating different types of rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the market saw continued emphasis on energy efficiency, driving innovation in heat pump technology and smart building controls, areas where specialized players often excel.
- Diverse Strategies: Competitors range from mass producers of standardized HVAC units to niche specialists in custom, high-efficiency solutions.
- Varied Competitive Tactics: This diversity leads to competition based on price, innovation, and service differentiation.
- Market Dynamics: The presence of both large, diversified corporations and smaller, specialized firms creates a complex and dynamic market environment.
- 2024 Trends: A significant focus in 2024 was on energy efficiency, pushing innovation in areas like advanced heat pumps and integrated smart building controls.
Competitive rivalry in the commercial HVAC sector is intense, with AAON facing formidable opponents like Lennox, Trane, Carrier, and Daikin. These larger players often possess greater financial resources, though AAON differentiates itself through custom-engineered, energy-efficient solutions. The overall market is projected to grow significantly, reaching $120.6 billion by 2029, driven by demand for energy efficiency and smart technologies, which can create opportunities for specialized companies like AAON.
AAON's strategic focus on custom solutions and energy efficiency allows it to carve out a niche against larger, more standardized competitors. This specialization, coupled with ongoing innovation in areas like data center liquid cooling, positions AAON to compete on value rather than solely on price. The industry's high capital investment and specialized assets create moderately high exit barriers, which can contribute to sustained competitive pressure.
| Competitor | Market Share (Approximate, Q1 2025) | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Lennox International | Larger than AAON | Broad product portfolio, strong distribution |
| Trane (Ingersoll Rand) | Larger than AAON | Integrated building solutions, energy services |
| Carrier Global | Larger than AAON | Diverse HVAC offerings, global presence |
| Daikin Applied | Larger than AAON | Advanced technology, energy efficiency |
| AAON | 0.23% | Custom-engineered, energy-efficient solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Alternative heating and cooling solutions present a compelling price-performance trade-off for AAON's products. Geothermal heat pumps, for instance, can have higher upfront installation costs but offer significant long-term operational savings, potentially appealing to cost-conscious consumers or businesses focused on total cost of ownership.
Solar-powered HVAC systems and advanced natural ventilation strategies also represent viable substitutes. While initial investments in solar technology can be substantial, declining solar panel prices and government incentives, such as the 30% federal solar tax credit in the US, make them increasingly competitive. These options directly address growing consumer and regulatory demand for sustainability.
The attractiveness of these substitutes is amplified by increasing global emphasis on environmental impact and stricter energy efficiency regulations. For example, by 2025, many regions are expected to implement even more stringent building codes mandating higher energy performance, which could shift demand towards these greener alternatives, impacting AAON's market share if its offerings are not perceived as equally or more sustainable and cost-effective over their lifecycle.
Customer propensity to substitute for AAON's HVAC products is influenced by awareness of other brands, the perceived advantages of alternatives like lower operating costs or better environmental performance, and how easy it is to switch. As environmental concerns and energy efficiency standards become more important, commercial clients are increasingly looking at substitute technologies that promise greater sustainability or long-term savings.
The relative price of substitute solutions compared to AAON's custom-engineered HVAC systems is a critical consideration. If the upfront cost of AAON's highly efficient and tailored systems is substantially higher than readily available, less specialized alternatives, customers might opt for the cheaper option, especially if the long-term energy savings are not immediately apparent or valued.
For instance, while AAON focuses on high-performance, integrated solutions, the market for modular or packaged HVAC units from competitors could present a significant threat if their pricing becomes more aggressive. In 2024, the average cost of commercial HVAC installation can range widely, but a significant price gap favoring substitutes would naturally draw demand away from AAON's premium offerings, particularly for budget-conscious projects.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Rapid technological progress in heating and cooling alternatives presents a significant threat. Innovations like highly efficient heat pumps, sophisticated passive cooling strategies, and novel energy recovery systems can make substitutes more attractive and effective. For instance, advancements in Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems, which offer zoned climate control and energy efficiency, directly compete with traditional HVAC solutions.
AAON is actively addressing this threat by investing in its own technological advancements. Their focus on developing cutting-edge heat pump technology and specialized data center cooling solutions is a strategic move to maintain a competitive edge. In 2024, the HVAC industry saw continued growth in demand for energy-efficient solutions, with heat pumps leading the charge in many residential and commercial applications.
- Technological Leap in Heat Pumps: Continued improvements in heat pump efficiency, reaching Seasonal Performance Factors (SPF) exceeding 4.0 in some high-performance models, directly challenge conventional systems.
- Growth of Passive and Hybrid Systems: The market for passive cooling and hybrid HVAC designs, which leverage natural ventilation and smart controls, is expanding, offering lower operational costs.
- Data Center Cooling Innovations: New liquid cooling technologies for data centers are emerging as viable alternatives to traditional air cooling, a key market for AAON.
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Increasing government regulations and environmental mandates are significantly pushing the HVAC industry towards sustainable and low-carbon solutions. This trend directly accelerates the adoption of substitutes for traditional technologies. For instance, the global push for electrification and the mandated phase-out of high Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants, like R-410A, are driving demand for alternative cooling and heating systems that align with these evolving regulatory landscapes. This shift can bolster the threat from innovative alternative technologies that offer better environmental performance.
The regulatory environment is a key driver for substitute threats. As of early 2024, many regions are implementing stricter emissions standards and carbon pricing mechanisms. For example, the European Union's F-Gas Regulation continues to tighten the availability and increase the cost of high-GWP refrigerants, making alternative, lower-GWP options more economically viable and thus more threatening. This regulatory pressure encourages investment and market entry for companies developing and offering these greener substitutes.
- Regulatory Shift: Mandates for lower GWP refrigerants are increasing, making alternative technologies more competitive.
- Electrification Push: Government incentives and targets for electric heating and cooling systems reduce reliance on fossil fuel-based alternatives.
- Environmental Mandates: Stricter energy efficiency standards favor advanced technologies that can outperform older, less efficient systems.
The threat of substitutes for AAON's HVAC products is significant, driven by advancements in alternative heating and cooling technologies and increasing environmental awareness. Geothermal systems and solar-powered HVAC offer long-term savings, while passive cooling strategies and VRF systems present competitive alternatives, especially as regulations push for lower GWP refrigerants and higher energy efficiency.
These substitutes are becoming more attractive due to their potential for lower operational costs and improved environmental performance, directly responding to growing consumer and regulatory demand for sustainability. As of 2024, the HVAC market continues to see a strong demand for energy-efficient solutions, with heat pumps showing particular growth.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantage | 2024 Market Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Geothermal Heat Pumps | Long-term operational savings | Increasing adoption in new construction seeking energy efficiency |
| Solar-Powered HVAC | Reduced reliance on grid electricity, sustainability | Federal solar tax credit (30% in US) makes upfront costs more manageable |
| Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Systems | Zoned control, high energy efficiency | Gaining traction in commercial applications for precise climate management |
| Passive Cooling/Hybrid Systems | Lower operational costs, reduced energy consumption | Expansion driven by smart building technologies and demand for natural ventilation |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the commercial HVAC manufacturing sector demands significant upfront capital for research and development, establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, acquiring specialized machinery, and building robust distribution channels. For instance, AAON's strategic investments, such as the expansion of its coil manufacturing capacity in 2024, underscore the immense financial commitment needed, effectively deterring potential new competitors.
Established players like AAON leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing, procurement, and research and development. This allows them to produce units at substantially lower per-unit costs compared to potential newcomers. For instance, AAON's substantial production volumes in 2024 likely translated into more favorable pricing on raw materials and components, further solidifying their cost advantage.
New entrants would face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies without achieving similar production volumes. This disparity makes it challenging for them to compete effectively on price, particularly within the custom-engineered segment of the HVAC market where customization drives up per-unit costs even for established players.
AAON distinguishes itself by offering custom-engineered, energy-efficient HVAC solutions, coupled with a strong reputation for ongoing innovation. This focus on tailored products and a history of forward-thinking design creates a significant hurdle for newcomers.
Establishing a comparable level of product differentiation and cultivating robust brand loyalty is a time-consuming and capital-intensive endeavor. New entrants face considerable challenges in rapidly gaining market share or fostering deep customer allegiance against AAON's established presence.
Access to Distribution Channels
Access to distribution channels presents a significant hurdle for new entrants in the HVAC market. Established players have cultivated strong, long-standing relationships with contractors, distributors, and major commercial clients, creating a formidable barrier.
For instance, AAON, a prominent HVAC manufacturer, relies on a network of independent distributors and dealers to reach its customer base. New companies would need substantial investment and time to replicate this established infrastructure and secure comparable market penetration.
The difficulty in building these networks means new entrants struggle to gain efficient market access. This can translate into higher initial marketing and sales costs as they attempt to displace incumbents who already hold preferred supplier status.
Key challenges for new entrants regarding distribution channels include:
- Building trust and relationships with existing HVAC contractors and distributors.
- Securing shelf space or preferred vendor status with major HVAC supply houses.
- Developing a sales force capable of reaching and servicing diverse customer segments, from residential to large commercial projects.
- Overcoming the established brand loyalty and service networks of incumbent manufacturers.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance
The HVAC industry faces significant barriers to entry due to increasingly strict regulations on energy efficiency and refrigerants. For instance, the mandated phase-out of R-410A refrigerant, a common component in many HVAC systems, requires new manufacturers to invest in and develop compliant alternatives, adding substantial upfront costs and R&D expenses. Navigating these complex environmental and safety standards, such as those set by the EPA and ASHRAE, demands considerable expertise and financial resources, making it challenging for newcomers to establish a foothold.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Regulations like the Department of Energy's Minimum Energy Efficiency Standards (MEPS) are continually updated, requiring new entrants to design products meeting these evolving benchmarks.
- Refrigerant Transition: The global shift away from high-GWP refrigerants, like the phasedown of HFCs under the AIM Act in the US, necessitates significant investment in new equipment and supply chains for lower-GWP alternatives.
- Environmental Compliance: Compliance with regulations concerning emissions, waste disposal, and product lifecycle management adds operational complexity and cost for any new company entering the market.
- Safety Certifications: Obtaining necessary safety and performance certifications from bodies such as UL or ETL requires rigorous testing and adherence to specific industry standards, a process that can be lengthy and expensive.
The threat of new entrants in the commercial HVAC manufacturing sector is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements for R&D, manufacturing facilities, and distribution networks, as demonstrated by AAON's significant 2024 capacity expansions. Established players benefit from economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs, which makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price, especially in the custom-engineered segment. Furthermore, stringent regulatory requirements concerning energy efficiency and refrigerants necessitate considerable investment in compliant technologies, acting as a significant deterrent.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | AAON's Position (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Significant hurdle, requiring substantial funding. | Demonstrated through ongoing capacity expansions. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | Challenging to match pricing and cost efficiencies. | Substantial production volumes likely led to favorable material pricing. |
| Product Differentiation & Brand Loyalty | Custom-engineered, energy-efficient solutions and strong reputation. | Time-consuming and costly to replicate. | Focus on tailored products and innovation creates a strong brand. |
| Distribution Channels | Established relationships with contractors and distributors. | Difficult and expensive to build comparable networks. | Relies on a well-established network of independent distributors. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict energy efficiency and refrigerant standards. | Requires significant investment in new technologies and expertise. | Navigating evolving standards like refrigerant transitions adds complexity. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our AAON Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of verified data, including AAON's annual reports and SEC filings, along with industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld and HVAC trade publications.
